Composite Chitosan/Agarose Ferrogels for Potential Applications in Magnetic Hyperthermia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Morphological Study
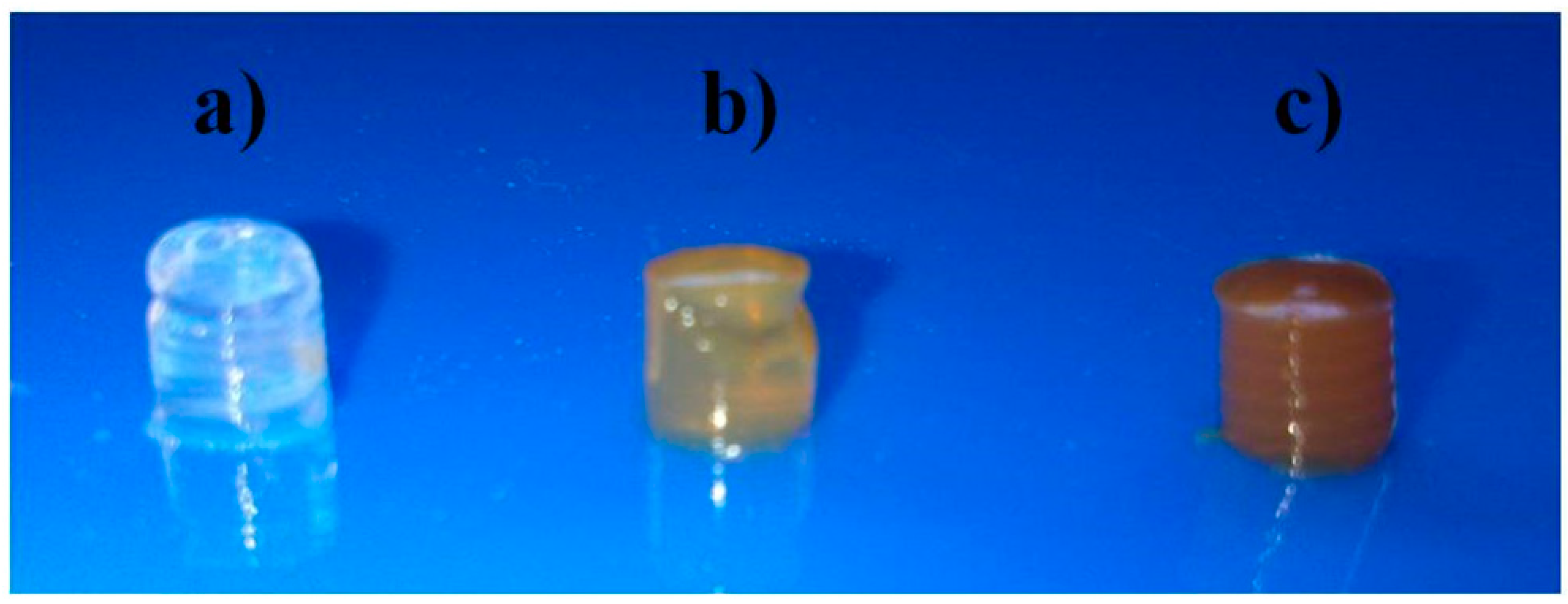
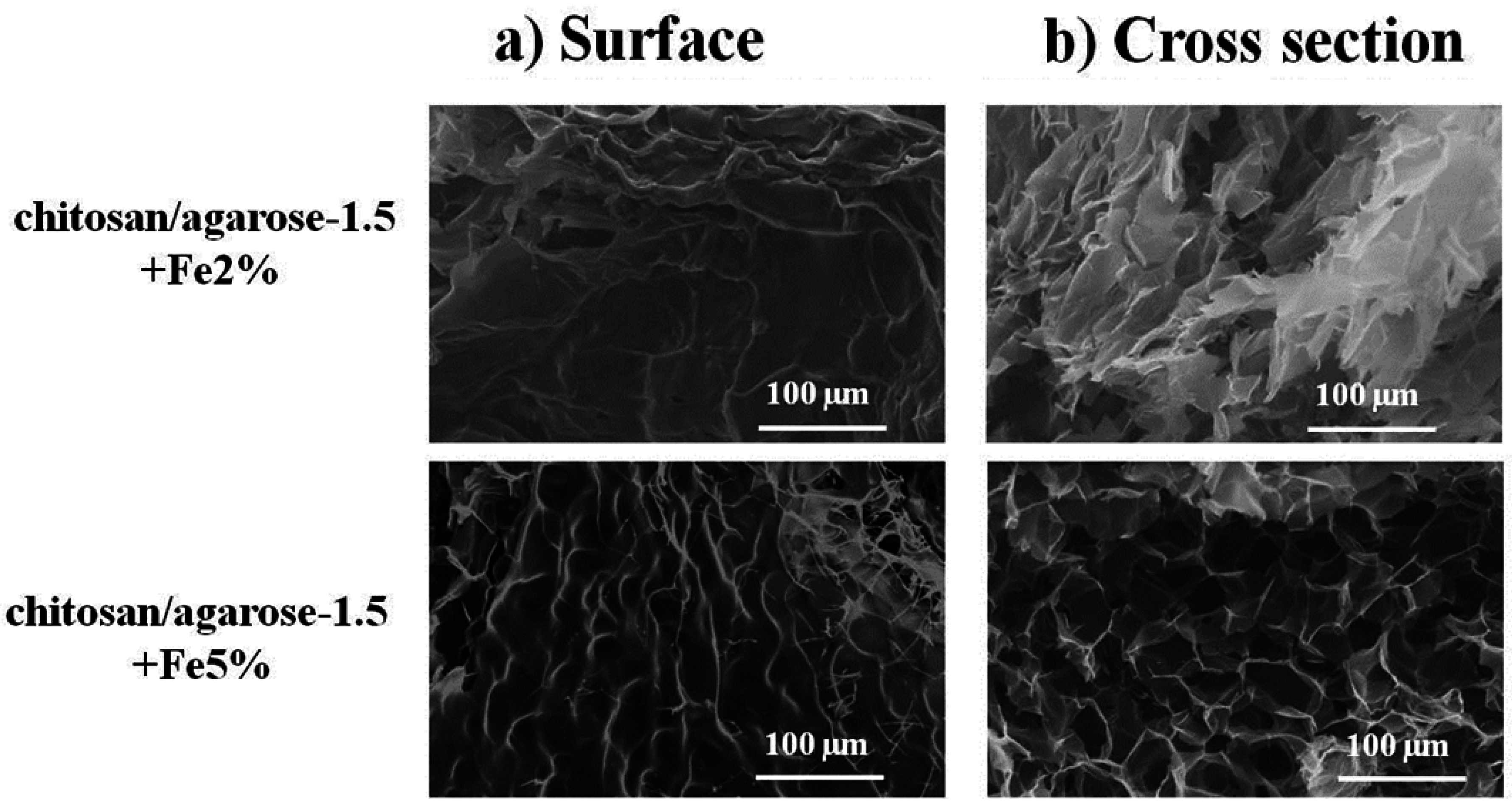
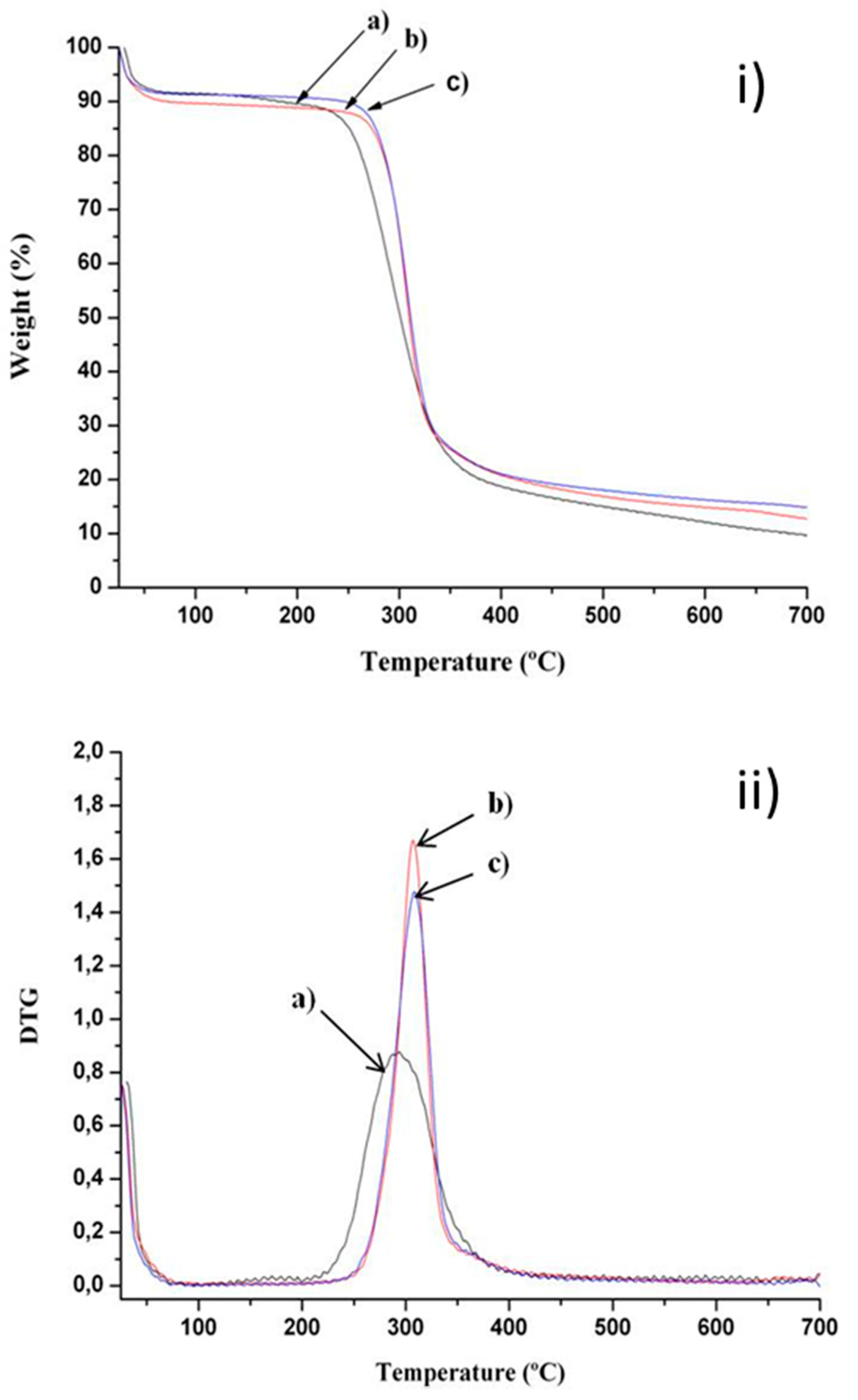
2.2. Thermal Stability
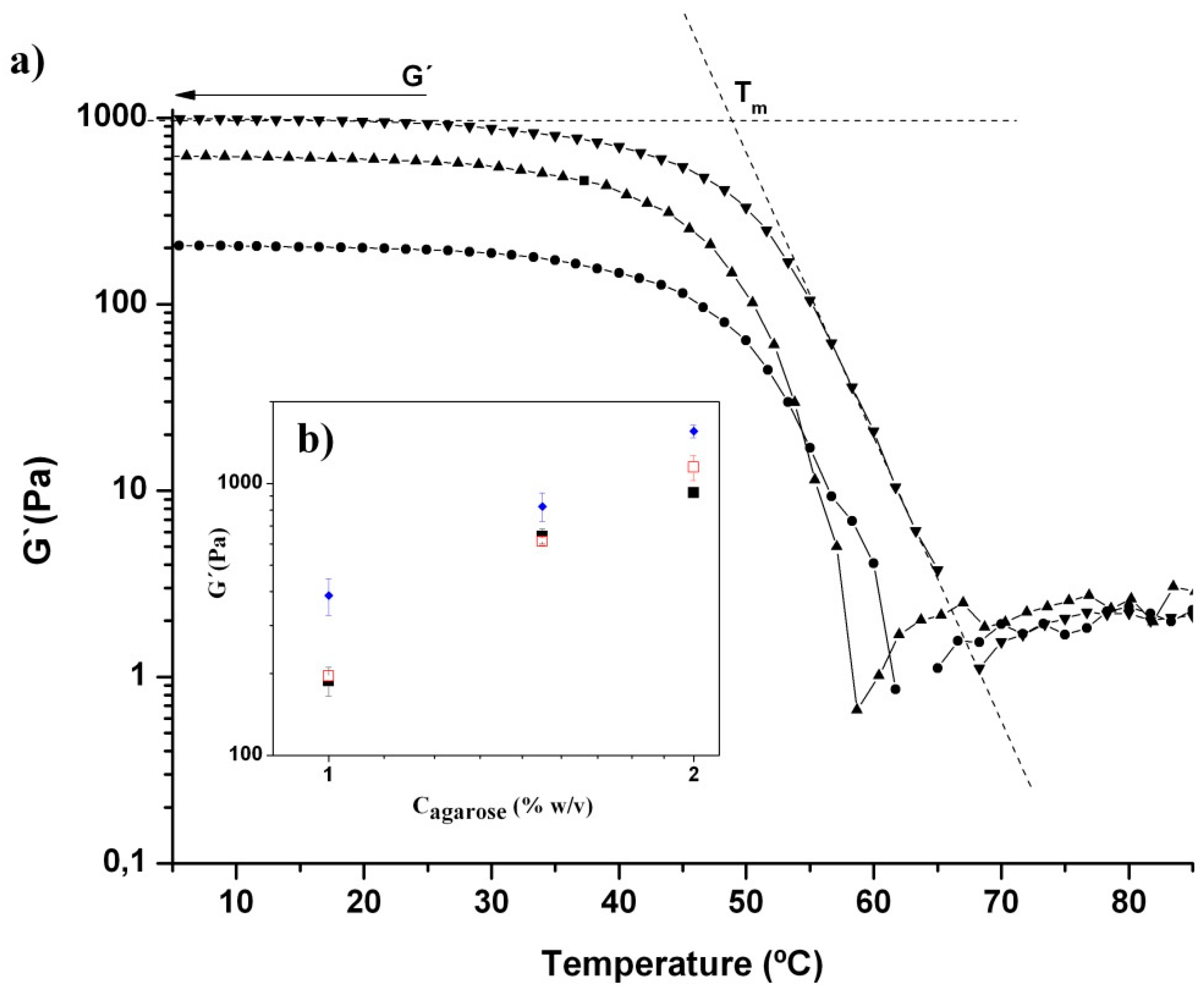
2.3. Viscoelastic Properties
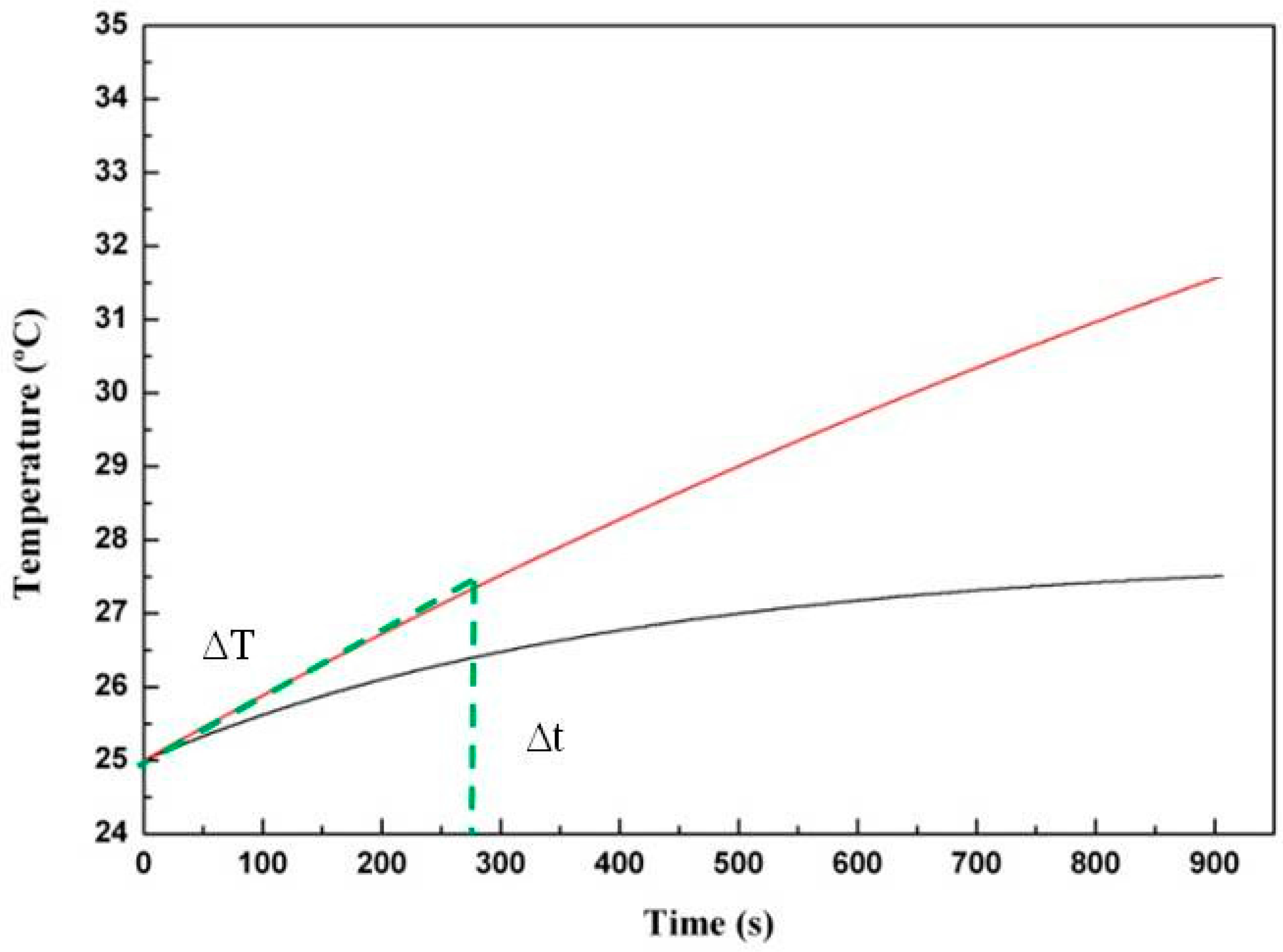
2.4. Specific Power Absorption Experiments
| Samples | ∆T/∆t (°C/s) | Water content (%) | Fe3O4 (mg/mL) * | SPA (W/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ferrofluid | 1.61 | 89.7 | 69.9 | 96 |
| Chi/Aga-1.5+ Fe2% | 0.007 | 96.8 | 0.96 | 30 |
| Chi/Aga-1.5+ Fe5% | 0.009 | 97.1 | 1.16 | 32 |
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Materials
4.2. Preparation of Composite Chi/Aga Blank Hydrogels and Chi/Aga Ferrogels
4.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
4.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis
4.5. Dynamic Oscillatory Measurements
4.6. Determination of Magnetic Remote Heating
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Buwalda, S.J.; Boere, K.W.M.; Dijkstra, P.J.; Feijen, J.; Vermonden, T.; Hennink, W.E. Hydrogels in a historical perspective: From simple networks to smart materials. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 254–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, N.; Gunn, J.; Zhang, M. Chitosan-based hydrogels for controlled, localized drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 83–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, J.M.; Leong, K.W. Natural polymers for gene delivery and tissue engineering. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2006, 58, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majedi, F.S.; Hasani-Sadrabadi, M.M.; Emami, S.H.; Taghipoor, M.; Dashtimoghadam, E.; Bertsch, A.; Moaddel, H.; Renaud, P. Microfluidic synthesis of chitosan-based nanoparticles for fuel cell applications. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 7744–7746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzzarelli, R.A.A.; Boudrant, J.; Meyer, D.; Manno, N.; DeMarchis, M.; Paoletti, M.G. Current views on fungal chitin/chitosan, human chitinases, food preservation, glucans, pectins and inulin: A tribute to Henri Braconnot, precursor of the carbohydrate polymers science, on the chitin bicentennial. Carbohyd. Polymer. 2012, 87, 995–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzzarelli, R.A.A.; Muzzarelli, C. Chitosan Chemistry: Relevance to the Biomedical Sciences. In Polysaccharides I; Heinze, T., Ed.; Springer Berlin Heidelberg: Berlin, Germany, 2005; Volume 186, pp. 151–209. [Google Scholar]
- Dash, M.; Chiellini, F.; Ottenbrite, R.M.; Chiellini, E. Chitosan—A versatile semi-synthetic polymer in biomedical applications. Prog. Polymer Sci. 2011, 36, 981–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Saravanakumar, G.; Kim, K.; Kwon, I.C. Targeted delivery of low molecular drugs using chitosan and its derivatives. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puga, A.M.; Lima, A.C.; Mano, J.F.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C. Pectin-coated chitosan microgels crosslinked on superhydrophobic surfaces for 5-fluorouracil encapsulation. Carbohyd. Polymer. 2013, 98, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Mardyani, S.; Chan, W.C.W.; Kumacheva, E. Design of biocompatible chitosan microgels for targeted pH-mediated intracellular release of cancer therapeutics. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1568–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Cai, C.; Lin, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X. Degradation controllable biomaterials constructed from lysozyme-loaded Ca-alginate microparticle/chitosan composites. Polymer 2011, 52, 5139–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, R.; Zamora-Mora, V.; Sibaja-Ballestero, M.; Vega-Baudrit, J.; López, D.; Mijangos, C. Influence of iron oxide nanoparticles on the rheological properties of hybrid chitosan ferrogels. J. Colloid Inter. Sci. 2009, 339, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hee Kim, E.; Sook Lee, H.; Kook Kwak, B.; Kim, B.-K. Synthesis of ferrofluid with magnetic nanoparticles by sonochemical method for MRI contrast agent. J. Magnetism Magnet. Mater. 2005, 289, 328–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.-Y.; Huang, K.-L.; Jiang, Y.-R.; Ding, P.; Yang, D.-L. Preparation and characterization of carboxyl functionalization of chitosan derivative magnetic nanoparticles. Biochem. Eng. J. 2008, 40, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, R.; Sacristan, J.; Nogales, A.; Fernandez, M.; Ezquerra, T.A.; Mijangos, C. Structure and viscoelastic properties of hybrid ferrogels with iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized in situ. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 3910–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Huang, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Chen, Y.; Lu, T.; Lu, T.J.; Xu, F. Magnetic hydrogels and their potential biomedical applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23(6), 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, R.; Sacristán, J.; Asín, L.; Torres, T.E.; Ibarra, M.R.; Goya, G.F.; Mijangos, C. Magnetic hydrogels derived from polysaccharides with improved specific power absorption: Potential devices for remotely triggered drug delivery. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 12002–12007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Stegemann, J.P. Thermogelling chitosan and collagen composite hydrogels initiated with β-glycerophosphate for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3976–3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farshi Azhar, F.; Olad, A.; Salehi, R. Fabrication and characterization of chitosan–gelatin/nanohydroxyapatite–polyaniline composite with potential application in tissue engineering scaffolds. Des. Monomers Polym. 2014, 17, 654–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miguel, S.P.; Ribeiro, M.P.; Brancal, H.; Coutinho, P.; Correia, I.J. Thermoresponsive chitosan–agarose hydrogel for skin regeneration. Carbohyd. Polym. 2014, 111, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Wu, X.S. Preparation and characterization of agarose hydrogel nanoparticles for protein and peptide drug delivery. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 1997, 2, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, C.T.; Thorpe, S.D.; O’Brien, F.J.; Robinson, A.J.; Kelly, D.J. The effect of concentration, thermal history and cell seeding density on the initial mechanical properties of agarose hydrogels. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2009, 2, 512–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Gilbert, R.J.; He, W. Simple Agarose−Chitosan gel composite system for enhanced neuronal growth in three dimensions. Biomacromolecules 2009, 10, 2954–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Z.-X.; Yang, G.-P.; Wang, G.-C.; Niu, J.-F.; Cao, X.-Y. Preparation of porous chitosan/agarose microsphere and its R-phycoerythrin release properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 2759–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, L. Preparation of berbamine loaded chitosan-agarose microspheres and in vitro release study. Polímeros 2012, 22(5), 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.-H.; Wang, P.; Kim, H.-E. Blend fibers of chitosan-agarose by electrospinning. Mater. Let. 2009, 63, 2510–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora-Mora, V.; Velasco, D.; Hernández, R.; Mijangos, C.; Kumacheva, E. Chitosan/agarose hydrogels: Cooperative properties and microfluidic preparation. Carbohyd. Polym. 2014, 111, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peniche-Covas, C.; Argüelles-Monal, W.; San Román, J. A kinetic study of the thermal degradation of chitosan and a mercaptan derivative of chitosan. Polym. Degrad. Stabil. 1993, 39, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.M.; Wu, C.X.; Huang, J.Y.; Peng, X.H.; Chen, P.; Tang, S.Q. Synthesis and characterization of a degradable composite agarose/HA hydrogel. Carbohyd. Polym. 2012, 88, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E., Jr.; Torres, T.E.; Rossi, L.M.; Rechenberg, H.R.; Berquo, T.S.; Ibarra, A.; Marquina, C.; Ibarra, M.R.; Goya, G.F. Size dependence of the magnetic relaxation and specific power absorption in iron oxide nanoparticles. J. Nanopart. Res. 2013, 15, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, C.S.S.R.; Mohammad, F. Magnetic nanomaterials for hyperthermia-based therapy and controlled drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 789–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadat, M.E.; Patel, R.; Sookoor, J.; Bud'ko, S.L.; Ewing, R.C.; Zhang, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Pauletti, G.M.; Mast, D.B.; Shi, D. Effect of spatial confinement on magnetic hyperthermia via dipolar interactions in Fe3O4 nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng.: C Mater. Biol Appl. 2014, 42, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zamora-Mora, V.; Soares, P.I.P.; Echeverria, C.; Hernández, R.; Mijangos, C. Composite Chitosan/Agarose Ferrogels for Potential Applications in Magnetic Hyperthermia. Gels 2015, 1, 69-80. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels1010069
Zamora-Mora V, Soares PIP, Echeverria C, Hernández R, Mijangos C. Composite Chitosan/Agarose Ferrogels for Potential Applications in Magnetic Hyperthermia. Gels. 2015; 1(1):69-80. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels1010069
Chicago/Turabian StyleZamora-Mora, Vanessa, Paula I.P. Soares, Coro Echeverria, Rebeca Hernández, and Carmen Mijangos. 2015. "Composite Chitosan/Agarose Ferrogels for Potential Applications in Magnetic Hyperthermia" Gels 1, no. 1: 69-80. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels1010069
APA StyleZamora-Mora, V., Soares, P. I. P., Echeverria, C., Hernández, R., & Mijangos, C. (2015). Composite Chitosan/Agarose Ferrogels for Potential Applications in Magnetic Hyperthermia. Gels, 1(1), 69-80. https://doi.org/10.3390/gels1010069







