Global Distribution Patterns of Dark Matter Fungi in Cold Seep: A Metagenomic Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Microbial Diversity and Function Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
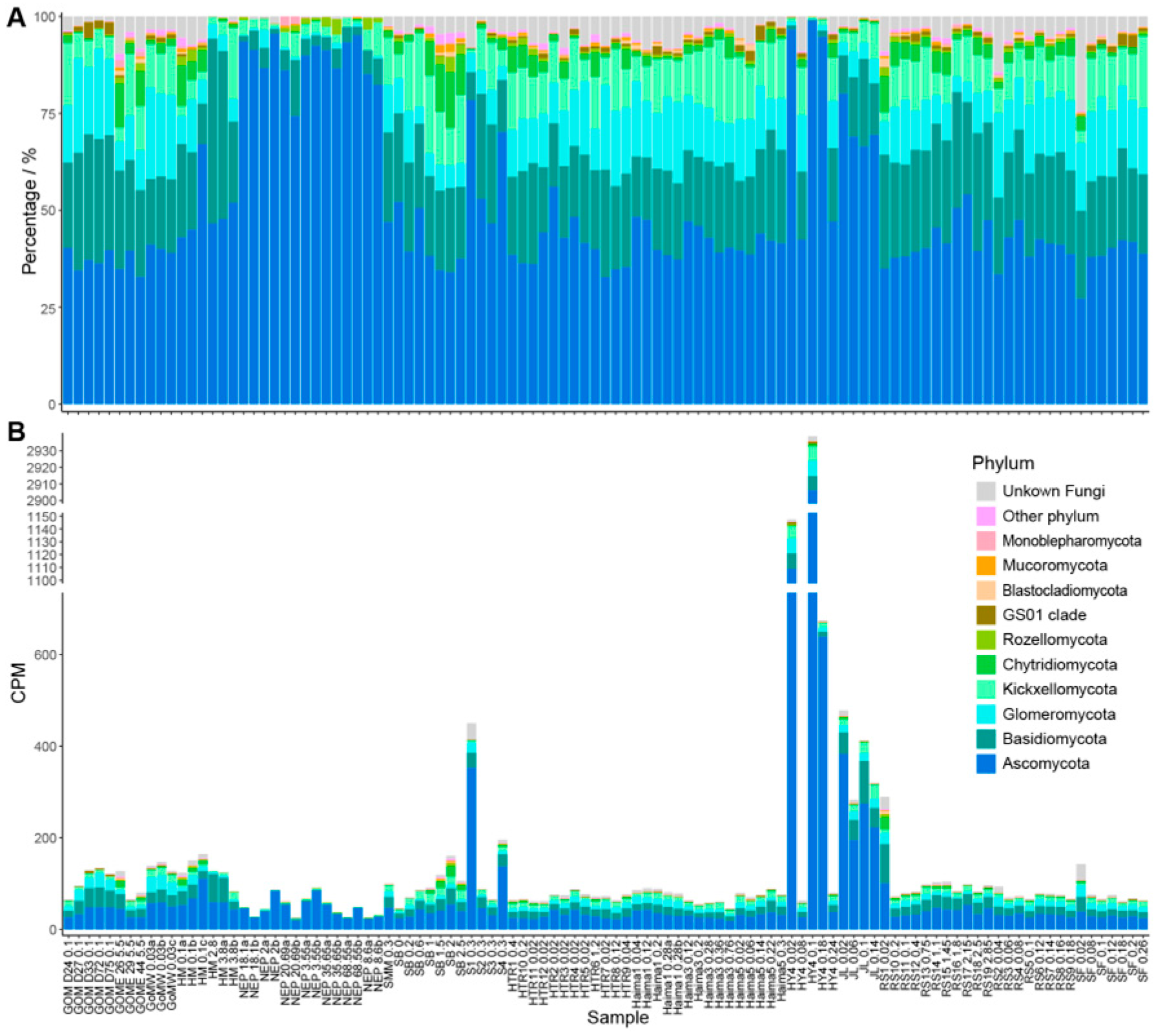
3.1. Distribution and Abundance of Fungal Taxa in Cold Seeps
3.2. Assembly Patterns of the Fungal Community in Cold Seeps
4. Discussion
4.1. Diversity and Unique Global Distribution Pattern of Cold Seep Fungal Community
4.2. Multi-Scale Assembly Model of Cold Seep Fungal Communities
4.3. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sibuet, M.; Olu, K. Biogeography, biodiversity and fluid dependence of deep-sea cold-seep communities at active and passive margins. Deep.-Sea Res. II 1998, 45, 517–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.A. Ecology of cold seep sediments: Interactions of fauna with flow, chemistry and microbes. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. Annu. Rev. 2005, 43, 1–46. [Google Scholar]
- Boetius, A.; Wenzhöfer, F. Seafloor oxygen consumption fuelled by methane from cold seeps. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olu-Le Roy, K.; Sibuet, M.; Fiala-Médioni, A.; Gofas, S.; Salas, C.; Mariotti, A.; Foucher, J.-P.; Woodside, J. Cold seep communities in the deep eastern Mediterranean Sea: Composition, symbiosis and spatial distribution on mud volcanoes. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2004, 51, 1915–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Bartlett, D.H.; Xiao, X. Current developments in marine microbiology: High-pressure biotechnology and the genetic engineering of piezophiles. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Qiu, J.-W.; Hu, Y.; Peckmann, J.; Guan, H.; Tong, H.; Chen, C.; Chen, J.; Gong, S.; Li, N.; et al. Cold seep systems in the South China Sea: An overview. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2018, 168, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, S.E.; Felden, J.; Gruber-Vodicka, H.R.; Marcon, Y.; Knittel, K.; Ramette, A.; Boetius, A. In situ development of a methanotrophic microbiome in deep-sea sediments. ISME J. 2019, 13, 197–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Åström, E.K.L.; Carroll, M.L.; Ambrose, W.G.; Sen, A.; Silyakova, A.; Carroll, J. Methane cold seeps as biological oases in the high-Arctic deep sea. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 63, S209–S231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joye, S.B. The Geology and Biogeochemistry of Hydrocarbon Seeps. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2020, 48, 205–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Ventura, G.T.; Owino, Y.; Lalk, E.J.; MacAdam, N.; Dooma, J.M.; Ono, S.; Fowler, M.; MacDonald, A.; Bennett, R.; et al. Cold seep formation from salt diapir-controlled deep biosphere oases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2316878121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Luo, Y.; Tan, X.; Zhao, D.; Bi, X.; Li, C.; Zheng, Y.; Xiang, H.; Hu, S. Global Marine Cold Seep Metagenomes Reveal Diversity of Taxonomy, Metabolic Function, and Natural Products. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2024, 22, qzad006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaeberlein, T.; Lewis, K.; Epstein, S.S. Isolating “uncultivable” microorganisms in pure culture in a simulated natural environment. Science 2002, 296, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Liu, F.; Liu, L.-R.; Li, M.; Cai, L.; Liu, S.; Mao, J. Culturing the uncultured marine fungi in the omics age: Opportunities and challenges. Fungal. Biol. Rev. 2024, 48, 100353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladfelter, A.S.; James, T.Y.; Amend, A.S. Marine fungi. Curr. Biol. 2019, 29, R191–R195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handelsman, J. Metagenomics: Application of genomics to uncultured microorganisms. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 669–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugenholtz, P.; Tyson, G.W. Metagenomics. Nature 2008, 455, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Rattray, J.E.; Campbell, D.C.; Webb, J.; Chakraborty, A.; Adebayo, O.; Matthews, S.; Li, C.; Fowler, M.; Morrison, N.M.; et al. Thermogenic hydrocarbon biodegradation by diverse depth-stratified microbial populations at a Scotian Basin cold seep. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lv, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Q.; Yang, Z.; Boon, N.; Wang, F.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y. Genomic and enzymatic evidence of acetogenesis by anaerobic methanotrophic archaea. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, A.; Ruff, S.E.; Dong, X.; Ellefson, E.D.; Li, C.; Brooks, J.M.; McBee, J.; Bernard, B.B.; Hubert, C.R.J. Hydrocarbon seepage in the deep seabed links subsurface and seafloor biospheres. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 11029–11037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Su, X.; Chen, F.; Holland, M.; Yang, S.; Liang, J.; Su, P.; Dong, H.; Hou, W. Microbial diversity of two cold seep systems in gas hydrate-bearing sediments in the South China Sea. Mar. Environ. Res. 2019, 144, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Yang, S.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, Y. Stimulated Organic Carbon Cycling and Microbial Community Shift Driven by a Simulated Cold-Seep Eruption. Mbio 2022, 13, e00087–00022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breyer, E.; Stix, C.; Kilker, S.; Roller, B.R.K.; Panagou, F.; Doebke, C.; Amano, C.; Saavedra, D.E.M.; Coll-García, G.; Steger-Mähnert, B.; et al. The contribution of pelagic fungi to ocean biomass. Cell 2025, 188, 3992–4002.e3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amend, A.; Burgaud, G.; Cunliffe, M.; Edgcomb, V.P.; Ettinger, C.L.; Gutiérrez, M.H.; Heitman, J.; Hom, E.F.Y.; Ianiri, G.; Jones, A.C.; et al. Fungi in the Marine Environment: Open Questions and Unsolved Problems. mBio 2019, 10, e01189-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, X.; Cao, L.; Tan, H.; Fang, S.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, S. Fungal communities from methane hydrate-bearing deep-sea marine sediments in South China Sea. ISME J. 2007, 1, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, Y.; Nagahama, T.; Hatada, Y.; Nunoura, T.; Takami, H.; Miyazaki, J.; Takai, K.; Horikoshi, K. Fungal diversity in deep-sea sediments—The presence of novel fungal groups. Fungal Ecol. 2010, 3, 316–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahama, T.; Takahashi, E.; Nagano, Y.; Abdel-Wahab, M.A.; Miyazaki, M. Molecular evidence that deep-branching fungi are major fungal components in deep-sea methane cold-seep sediments. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 2359–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaler, A.D.; Van Dover, C.L.; Vilgalys, R. Ascomycete phylotypes recovered from a Gulf of Mexico methane seep are identical to an uncultured deep-sea fungal clade from the Pacific. Fungal Ecol. 2012, 5, 270–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.P.; Cao, H.L.; Shek, C.S.; Tian, R.M.; Wong, Y.H.; Batang, Z.; Al-Suwailem, A.; Qian, P.Y. Diversity and distribution of eukaryotic microbes in and around a brine pool adjacent to the Thuwal cold seeps in the Red Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coelho, F.J.R.C.; Louvado, A.; Domingues, P.M.; Cleary, D.F.R.; Ferreira, M.; Almeida, A.; Cunha, M.R.; Cunha, Â.; Gomes, N.C.M. Integrated analysis of bacterial and microeukaryotic communities from differentially active mud volcanoes in the Gulf of Cadiz. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrier, V.; Svenning, M.M.; Gründger, F.; Niemann, H.; Dessandier, P.-A.; Panieri, G.; Kalenitchenko, D. The Impact of Methane on Microbial Communities at Marine Arctic Gas Hydrate Bearing Sediment. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Huang, N.; Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Jing, H. Microbial Eukaryotes Associated With Sediments in Deep-Sea Cold Seeps. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 782004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shekarriz, E.; Chen, J.; Xu, Z.; Liu, H. Disentangling the Functional Role of Fungi in Cold Seep Sediment. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e01978–01922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Shekarriz, E.; Wu, W.; Chen, B.; Liu, H. High Microeukaryotic Diversity in the Cold-Seep Sediment. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 86, 2003–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Luo, M.; Xu, Y.; Gong, S.; Chen, D. Production of Labile Protein-Like Dissolved Organic Carbon Associated With Anaerobic Methane Oxidization in the Haima Cold Seeps, South China Sea. Front. Mar. Sci. 2021, 8, 797084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sapir, A.; Dillman, A.R.; Connon, S.A.; Grupe, B.M.; Ingels, J.; Mundo-Ocampo, M.; Levin, L.A.; Baldwin, J.G.; Orphan, V.J.; Sternberg, P.W. Microsporidia-nematode associations in methane seeps reveal basal fungal parasitism in the deep sea. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghukumar, S. Fungi in Coastal and Oceanic Marine Ecosystems; Raghukumar, S., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 378. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Qian, P.Y. Microbial community changes along the active seepage site of one cold seep in the Red Sea. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarenkov, K.; Zirk, A.; Piirmann, T.; Pöhönen, R.; Ivanov, F.; Nilsson, R.H.; Kõljalg, U. Full UNITE+INSD Dataset for Eukaryotes, Version 21.04.2024; UNITE Community: London, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinform. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Liu, L.R.; Pan, Y.P.; Pan, J.; Li, M. Long-read assembled metagenomic approaches improve our understanding on metabolic potentials of microbial community in mangrove sediments. Microbiome 2023, 11, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Friendly, M.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; McGlinn, D.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package, R package version 2.6-8. 2024. Available online: https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/CRAN/web/packages/vegan/index.html (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Hernandez-Agreda, A.; Gates, R.D.; Ainsworth, T.D. Defining the Core Microbiome in Corals’ Microbial Soup. Trends Microbiol. 2017, 25, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Custer, G.F.; Gans, M.; van Diepen, L.T.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Buerkle, C.A. Comparative analysis of core microbiome assignments: Implications for ecological synthesis. mSystems 2023, 8, e0106622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glockner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.L.; Dong, X.; Lu, R.; Zhou, Y.L.; Zheng, P.F.; Feng, D.; Wang, Y. Microbial ecology of sulfur cycling near the sulfate-methane transition of deep-sea cold seep sediments. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 6844–6858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-L.; Wu, Y.-Z.; Zhou, G.-w.; Huang, H.; Wang, Y. Metabolic diversification of anaerobic methanotrophic archaea in a deep-sea cold seep. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2020, 2, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Lyu, L.; Ju, F.; Li, J.; Zhang, S. Exploring the role of organotrophic microbes in geochemical cycling of cold seep sediments. Innov. Geosci. 2025, 3, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Huang, J.E.; Phurbu, D.; Qu, Z.S.; Liu, F.; Cai, L. A deep metagenomic atlas of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau lakes reveals their microbial diversity and salinity adaptation mechanisms. Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 116483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Sato, Y.; Morishima, K. BlastKOALA and GhostKOALA: KEGG Tools for Functional Characterization of Genome and Metagenome Sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 726–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Wang, M.; Pan, H.; Burgaud, G.; Liang, S.; Guo, J.; Luo, T.; Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Cai, L. Highlighting patterns of fungal diversity and composition shaped by ocean currents using the East China Sea as a model. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 564–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tharwat, A.; Gaber, T.; Ibrahim, A.; Hassanien, A.E. Linear discriminant analysis: A detailed tutorial. AI Commun. 2017, 30, 169–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Gallagher, E.D. Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 2001, 129, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takishita, K.; Yubuki, N.; Kakizoe, N.; Inagaki, Y.; Maruyama, T. Diversity of microbial eukaryotes in sediment at a deep-sea methane cold seep: Surveys of ribosomal DNA libraries from raw sediment samples and two enrichment cultures. Extremophiles 2007, 11, 563–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takishita, K.; Tsuchiya, M.; Reimer, J.D.; Maruyama, T. Molecular evidence demonstrating the basidiomycetous fungus Cryptococcus curvatus is the dominant microbial eukaryote in sediment at the Kuroshima Knoll methane seep. Extremophiles 2005, 10, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.F.M.; Esteves, A.C.; Alves, A. Marine Fungi: Opportunities and Challenges. Encyclopedia 2022, 2, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagano, Y.; Nagahama, T. Fungal diversity in deep-sea extreme environments. Fungal Ecol. 2012, 5, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redou, V.; Navarri, M.; Meslet-Cladiere, L.; Barbier, G.; Burgaud, G. Species richness and adaptation of marine fungi from deep-subseafloor sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 81, 3571–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, M.; Selosse, M.-A.; Rexer, K.-H.; Urban, A.; Oberwinkler, F. Sebacinales: A hitherto overlooked cosm of heterobasidiomycetes with a broad mycorrhizal potential. Mycol. Res. 2004, 108, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüßler, A.; Schwarzott, D.; Walker, C. A new fungal phylum, the Glomeromycota: Phylogeny and evolution. Mycol. Res. 2001, 105, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, T.; Sabo, I.A.; Lambu, Z.N.; Danlami, D.; Shehu, A.A. Hydrocarbon Degradation Potentials of Fungi: A Review. J. Environ. Bioremediation Toxicol. 2022, 5, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozupone, C.A.; Knight, R. Global patterns in bacterial diversity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11436–11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louca, S.; Polz, M.F.; Mazel, F.; Albright, M.B.N.; Huber, J.A.; O’Connor, M.I.; Ackermann, M.; Hahn, A.S.; Srivastava, D.S.; Crowe, S.A.; et al. Function and functional redundancy in microbial systems. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2018, 2, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, B.A.; Hansen, K.; Pfister, D.H. A phylogenetic overview of the family Pyronemataceae (Ascomycota, Pezizales). Mycol. Res. 2007, 111, 549–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsen, L.; Thurmer, A.; Meinicke, P.; Buee, M.; Morin, E.; Martin, F.; Pilate, G.; Daniel, R.; Polle, A.; Reich, M. Fungal soil communities in a young transgenic poplar plantation form a rich reservoir for fungal root communities. Ecol. Evol. 2012, 2, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossart, H.-P.; Wurzbacher, C.; James, T.Y.; Kagami, M. Discovery of dark matter fungi in aquatic ecosystems demands a reappraisal of the phylogeny and ecology of zoosporic fungi. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 19, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossart, H.P.; Van den Wyngaert, S.; Kagami, M.; Wurzbacher, C.; Cunliffe, M.; Rojas-Jimenez, K. Fungi in aquatic ecosystems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, J.Y.; Liu, L.; Hua, Z.S.; Fang, B.Z.; Zhou, E.M.; Salam, N.; Hedlund, B.P.; Li, W.J. Microbial dark matter coming to light: Challenges and opportunities. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2021, 8, nwaa280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Konopka, A.E.; Fredrickson, J.K. Stochastic and deterministic assembly processes in subsurface microbial communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Ning, D. Stochastic community assembly: Does it matter in microbial ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00002–00017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.F.; Pan, J.; Pan, Y.P.; Li, M. Biogeography, Assembly Patterns, Driving Factors, and Interactions of Archaeal Community in Mangrove Sediments. mSystems 2021, 6, e0138120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Ren, K.; Isabwe, A.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Yang, J. Stochastic processes shape microeukaryotic community assembly in a subtropical river across wet and dry seasons. Microbiome 2019, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pop Ristova, P.; Wenzhofer, F.; Ramette, A.; Felden, J.; Boetius, A. Spatial scales of bacterial community diversity at cold seeps (Eastern Mediterranean Sea). ISME J. 2015, 9, 1306–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.M.; Stegen, J.C.; Kim, M.; Dong, K.; Adams, J.M.; Lee, Y.K. Soil pH mediates the balance between stochastic and deterministic assembly of bacteria. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1072–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez, P.; Salcedo, D.L.; Espinosa-Asuar, L.; Gasca-Pineda, J.; Hernandez-Monroy, A.; Soto, L.A. Fungal Diversity in Sediments From Deep-Sea Extreme Ecosystems: Insights Into Low- and High-Temperature Hydrothermal Vents, and an Oxygen Minimum Zone in the Southern Gulf of California, Mexico. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 802634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldrop, M.P.; Zak, D.R.; Blackwood, C.B.; Curtis, C.D.; Tilman, D. Resource availability controls fungal diversity across a plant diversity gradient. Ecol. Lett. 2006, 9, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novakova, A.; Hubka, V.; Valinova, S.; Kolarik, M.; Hillebrand-Voiculescu, A.M. Cultivable microscopic fungi from an underground chemosynthesis-based ecosystem: A preliminary study. Folia Microbiol. 2018, 63, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahey, C.; Parker, W.C.; Paquette, A.; Messier, C.; Antunes, P.M. Soil fungal communities contribute to the positive diversity–productivity relationship of tree communities under contrasting water availability. J. Ecol. 2023, 111, 2023–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Yan, L.; Korpelainen, H.; Niinemets, Ü.; Li, C. Plant-plant interactions and N fertilization shape soil bacterial and fungal communities. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 128, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Khan, M.I.; Kalsoom, F.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z. Role of gene regulation and inter species interaction as a key factor in gut microbiota adaptation. Arch. Microbiol. 2022, 204, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nekola, J.C.; White, P.S. The distance decay of similarity in biogeography and ecology. J. Biogeogr. 2004, 26, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soininen, J.; McDonald, R.; Hillebrand, H. The distance decay of similarity in ecological communities. Ecography 2007, 30, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinger, L.; Boetius, A.; Ramette, A. Bacterial taxa-area and distance-decay relationships in marine environments. Mol. Ecol. 2014, 23, 954–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Filker, S.; Xu, K.; Huang, P.; Zheng, S. Microeukaryote communities exhibit phyla-specific distance-decay patterns and an intimate link between seawater and sediment habitats in the Western Pacific Ocean. Deep. Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2020, 160, 103279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, H.; Yang, S.; Dai, X. Stochastic and deterministic assembly processes in seamount microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 87, e0070123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Variables | All Samples | Arctic | Western Atlantic | Gulf of Mexico | Northeast Pacific | South China Sea | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | CPM | Species | CPM | Species | CPM | Species | CPM | Species | CPM | Species | CPM | ||
| Spatial | Sediment depth | −0.339 *** | −0.328 *** | −0.697 | −0.714 | 0.901 ** | 0.829 * | 0.773 ** | −0.448 | −0.418 | −0.385 | 0.074 | −0.085 |
| Water depth | 0.336 *** | 0.393 *** | - | - | - | - | 0.591 * | −0.012 | - | - | −0.235 * | 0.490 *** | |
| Biotic | Prokaryotes | −0.003 | 0.551 *** | −0.153 | 0.324 | −0.302 | 0.050 | −0.105 | 0.643 * | 0.071 | 0.537 * | 0.043 | 0.622 *** |
| ANME | −0.123 | 0.130 | −0.704 | 0.044 | −0.368 | 0.012 | −0.651 * | 0.467 | 0.776 *** | 0.393 | −0.220 * | −0.094 | |
| SRB | −0.015 | 0.263 ** | −0.091 | 0.159 | −0.336 | 0.092 | −0.306 | 0.656 * | 0.797 *** | 0.450 * | −0.412 *** | 0.027 | |
| dsr | 0.141 | 0.431 *** | −0.843 * | 0.301 | −0.819 * | −0.482 | −0.708 ** | 0.579 * | 0.748 *** | 0.535 * | −0.044 | 0.340 ** | |
| mcr | 0.153 | 0.404 *** | −0.929 ** | −0.481 | −0.472 | −0.073 | −0.742 ** | 0.655 * | 0.684 ** | 0.518 * | −0.096 | 0.262 * | |
| Carbon fix | 0.143 | 0.320 *** | −0.883 ** | −0.217 | −0.489 | −0.069 | −0.807 ** | 0.537 * | 0.542 * | 0.553 * | 0.109 | 0.066 | |
| Physicochemical | CH4 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −0.810 * | −0.934 ** |
| TC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.424 | 0.507 * | - | - | |
| TN | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −0.202 | −0.351 | −0.305 * | 0.063 | |
| TS | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | −0.145 | 0.189 | - | - | |
| TIC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.071 | 0.361 | - | - | |
| TOC | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.318 | 0.192 | −0.297 | −0.361 * | |
| C/N | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.586 * | 0.628 * | - | - | |
| CaCO3 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | 0.076 | 0.363 | - | - | |
| SO42- | - | - | 0.542 | −0.680 | −0.747 | −0.822 * | - | - | - | - | 0.823 * | 0.959 *** | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.-F.; Jiang, Y.; Mao, J. Global Distribution Patterns of Dark Matter Fungi in Cold Seep: A Metagenomic Meta-Analysis. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120878
Zhang Z-F, Jiang Y, Mao J. Global Distribution Patterns of Dark Matter Fungi in Cold Seep: A Metagenomic Meta-Analysis. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(12):878. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120878
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Zhi-Feng, Yi Jiang, and Jian Mao. 2025. "Global Distribution Patterns of Dark Matter Fungi in Cold Seep: A Metagenomic Meta-Analysis" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 12: 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120878
APA StyleZhang, Z.-F., Jiang, Y., & Mao, J. (2025). Global Distribution Patterns of Dark Matter Fungi in Cold Seep: A Metagenomic Meta-Analysis. Journal of Fungi, 11(12), 878. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120878





