New Guaiane-Type Sesquiterpenoids Biscogniauxiaols A–G with Anti-Fungal and Anti-Inflammatory Activities from the Endophytic Fungus Biscogniauxia Petrensis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General Experimental Procedures
2.2. Fungal Material
2.3. Fermentation, Extraction and Isolation
2.4. Quantum Chemical Calculation (ECD)
2.5. Specific Rotation Calculation (SRC)
2.6. Anti-Fungal Assay
2.7. Anti-Inflammatory Assay
2.8. Cytotoxicity and MDR Reversal Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structure Identification of Compounds 1–7
3.2. Results of Bioactivity Assays
3.2.1. Anti-Fungal Evaluation of Compounds
3.2.2. Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Compounds
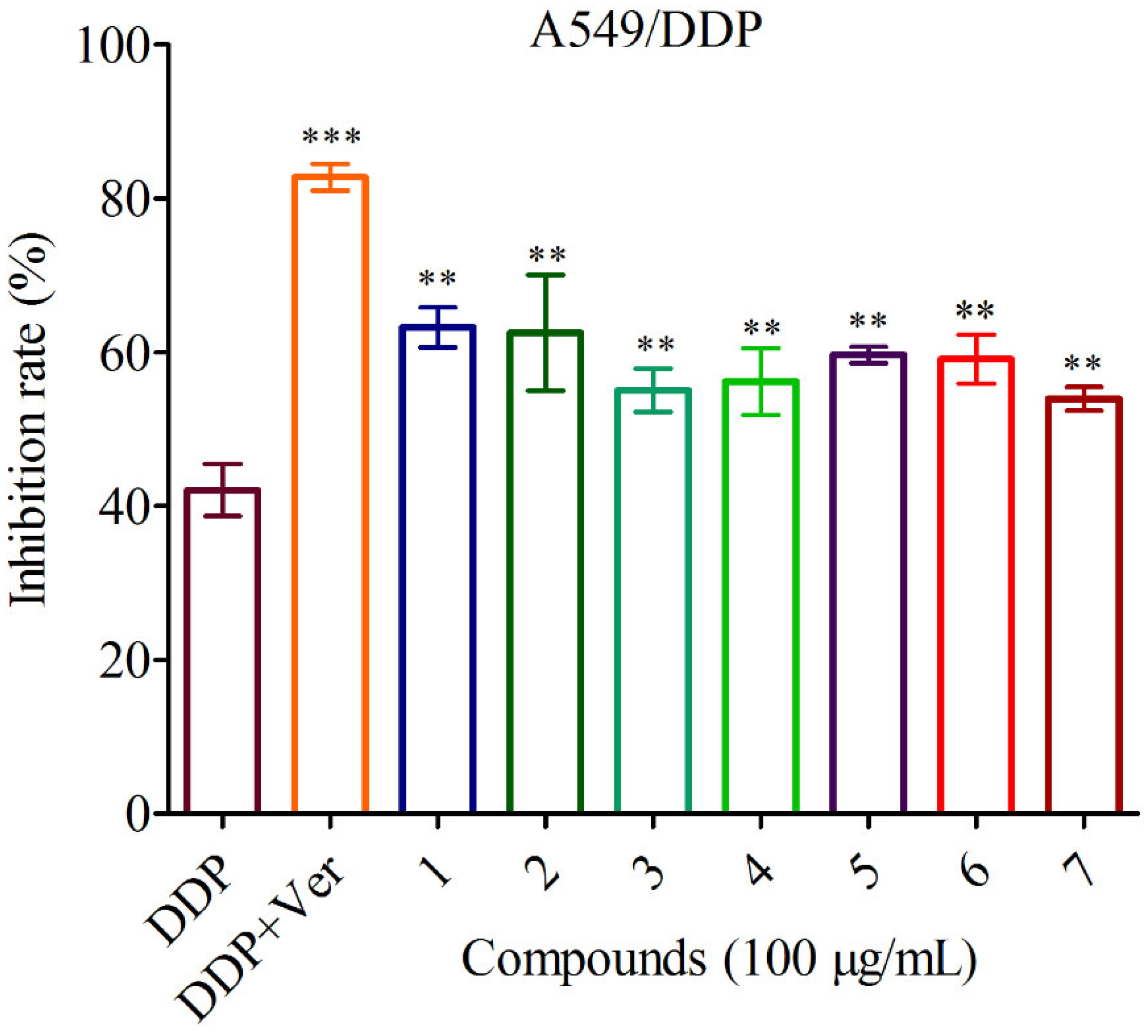
3.2.3. Anti-cancer and MDR Reversal Effects of Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, K.; Ai, H.L.; Liu, J.K. Identifcation and bioactivities of secondary metabolites derived from endophytic fungi isolated from ethnomedicinal plants of tujia in hubei province: A review. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2021, 11, 185–205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amirzakariya, B.Z.; Shakeri, A. Bioactive terpenoids derived from plant endophytic fungi: An updated review (2011–2020). Phytochemistry 2022, 197, 113130. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Li, Z.Y.; Qin, S.Y.; Xin, B.S.; Liu, Y.Y.; Lin, B.; Yao, G.D.; Huang, X.X.; Song, S.J. Three unusual sesquiterpenes with distinctive ring skeletons from Daphne penicillata uncovered by molecular networking strategies. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 15298–15306. [Google Scholar]
- Ruan, Q.F.; Jiang, S.Q.; Zheng, X.Y.; Tang, Y.Q.; Yang, B.; Yi, T.; Jin, J.; Cui, H.; Zhao, Z.X. Pseudoguaianelactones A–C: Three unusual sesquiterpenoids from Lindera glauca with anti-inflammatory activities by inhibiting the LPS-induced expression of iNOS and COX-2. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 1517. [Google Scholar]
- Su, L.H.; Geng, C.A.; Li, T.Z.; Ma, Y.B.; Huang, X.Y.; Zhang, X.M.; Chen, J.J. Artatrovirenols A and B: Two cagelike sesquiterpenoids from Artemisia atrovirens. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 13466–13471. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.H.; He, J.; Li, X.N.; Huang, R.; Song, F.; Chen, Y.W.; Miao, C.P. Guaiane sesquiterpenes and isopimarane diterpenes from an endophytic fungus Xylaria sp. Phytochemistry 2014, 105, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.M.; Fan, M.; Xue, Y.; Peng, L.Y.; Wu, X.D.; Liu, D.; Li, R.T.; Zhao, Q.S. Guaiane-type sesquiterpenoids from Alismatis Rhizoma and their anti-inflammatory activity. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 65, 403–407. [Google Scholar]
- Su, L.H.; Ma, Y.B.; Geng, C.A.; Li, T.Z.; Huang, X.Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, X.; Tang, S.; Shen, C.; Gao, Z.; et al. Artematrovirenins A-P, guaiane-type sesquiterpenoids with cytotoxicities against two hepatoma cell lines from Artemisia atrovirens. Bioorgan. Chem. 2021, 114, 105072. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.E.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, J.J. Torilin, a sesquiterpene from Torilis japonica, reverses multidrug-resistance in cancer cells. Planta. Med. 1998, 64, 333. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Q.B.; Hou, Z.L.; Shi, S.C.; Ren, H.; Yao, G.D.; Lin, B.; Huang, X.X.; Song, S.J. Discovery of guaiane-type sesquiterpenoids from the roots of Daphne genkwa with neuroprotective effects. Bioorgan. Chem. 2020, 95, 103545. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Q.M.; Chen, M.H.; Li, X.H.; Peng, C.; Lin, D.S.; Li, X.N.; He, Y.; Xiong, L. Absolute configurations and bioactivities of guaiane-type sesquiterpenoids isolated from pogostemon cablin. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1919–1927. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.G.; Zhong, X.L.; Xiao, Y.Z.; Zhu, S.L.; Muhammad, I.; Yan, S.; Jin, H.Z.; Zhang, W.D. Vieloplains A-G, seven new guaiane-type sesquiterpenoid dimers from xylopia vielana. Bioorgan. Chem. 2019, 88, 102891. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Su, J.C.; Liu, Y.H.; Deng, B.; Hu, Z.F.; Wu, J.L.; Xia, R.F.; Chen, C.; He, Q.; Chen, J.-C.; et al. Stelleranoids A-M, guaiane-type sesquiterpenoids based on [5,7] bicyclic system from Stellera chamaejasme and their cytotoxic activity. Bioorgan. Chem. 2021, 115, 105251. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, W.; Li, T.Z.; Huang, X.Y.; He, X.F.; Geng, C.A.; Zhang, X.M.; Chen, J.J. Artemzhongdianolides A1-A21, antihepatic fibrosis guaiane-type sesquiterpenoid dimers from Artemisia zhongdianensis. Bioorgan. Chem. 2022, 128, 106056. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.H.; Liu, J.W.; Wu, Y.C.; Li, Y.M.; Guo, F.J. Guaiane-type sesquiterpenes from Curcuma wenyujin. Phytochemistry 2022, 198, 113164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.Y.; Nontachaiyapoom, S.; Hyde, K.D.; Jeewon, R.; Doilom, M.K.; Chomnunti, P.; Kang, J.C. Biscogniauxia dendrobii sp. nov. and B. petrensis from Dendrobium orchids and the first report of cytotoxicity (towards A549 and K562) of B. petrensis (MFLUCC 14-0151) in vitro. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2020, 134, 382–393. [Google Scholar]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Revision C.01; Gaussian Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bannwarth, C.; Ehlert, S.; Grimme, S. GFN2-xTB—An accurate and broadly parametrized self-consistent tight-binding quantum chemical method with multipole electrostatics and density-dependent dispersion contributions. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 1652–1671. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, T. Molclus Program, Version 1.9.9.5. Available online: http://www.keinsci.com/research/molclus.html. (accessed on 3 September 2022).
- Grimme, S. Exploration of chemical compound, conformer, and reaction space with meta-dynamics simulations based on tight-binding quantum chemical calculations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 2847–2862. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grimme, S.; Bannwarth, C.; Shushkov, P. A robust and accurate tight-binding quantum chemical method for structures, vibrational frequencies, and noncovalent interactions of large molecular systems parametrized for all spd-block elements (Z = 1–86). J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2017, 13, 1989–2009. [Google Scholar]
- Neese, F. The ORCA program system. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Comput. Mol. Sci. 2012, 2, 73–78. [Google Scholar]
- Cordisco, E.; Petenatti, E.; Svetaz, L.; Sortino, M. Evaluation of the antifungal photodynamic activity of Thymophylla pentachaeta extracts against Candida albicans and its virulence factors. Phytomedicine 2021, 90, 153608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iraji, A.; Yazdanpanah, S.; Alizadeh, F.; Mirzamohammadi, S.; Ghasemi, Y.; Pakshir, K.; Yang, Y.; Zomorodian, K. Screening the antifungal activities of monoterpenes and their isomers against Candida species. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2020, 129, 1541–1551. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Niu, S.; Xie, C.L.; Xia, J.M.; Luo, Z.H.; Shao, Z.Z.; Yang, X.W. New anti-infammatory guaianes from the Atlantic hydrothermderived fungus Graphostroma sp. MCCC 3A00421. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.H.; Li, P.H.; Li, X.M.; Yang, S.Q.; Liu, K.C.; Wang, B.G.; Li, X. Chevalinulins A and B, proangiogenic alkaloids with a spiro[bicyclo[2.2.2]octane-diketopiperazine] skeleton from deep-sea cold-seep-derived fungus Aspergillus chevalieri CS-122. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 2684–2688. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Zhao, W.Y.; Shi, S.C.; Han, F.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, Q.B.; Yao, G.D.; Lin, B.; Huang, X.X.; Song, S.J. Guaiane-type sesquiterpenoids from the roots of Daphne genkwa and evaluation of their neuroprotective effects. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 1510–1517. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Xie, X.S.; Fang, X.W.; Ma, K.X.; Wu, S.H. Five new guaiane sesquiterpenes from the endophytic fungus Xylaria sp. YM 311647 of Azadirachta indica. Chem. Biodivers. 2015, 12, 1281–1286. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Chen, X.Y.; Hu, Y.Z.; Li, M.H.; Wu, Y.T.; Dai, M.H.; Huang, Z.L.; Sun, P.H.; Zheng, J.X.; Ren, Z.; et al. Sesquiterpenoids and triterpenoids with anti-inflammatory effects from Artemisia vulgaris L. Phytochemistry 2022, 204, 113428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Su, L.H.; Zhang, X.T.; Ma, Y.B.; Geng, C.G.; Huang, X.Y.; Hu, J.; Li, T.Z.; Tang, S.; Shen, C.; Gao, Z.; et al. New guaiane-type sesquiterpenoid dimers from Artemisia atrovirens and their antihepatoma activity. Acta. Pharm. Sin. B. 2021, 11, 1648–1666. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Xu, Q.Q.; Zhou, X.W.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.B.; Yang, M.H.; Luo, J.; Luo, J.G.; Kong, L.Y. Rare dimeric guaianes from Xylopia vielana and their multidrug resistance reversal activity. Phytochemistry 2019, 158, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
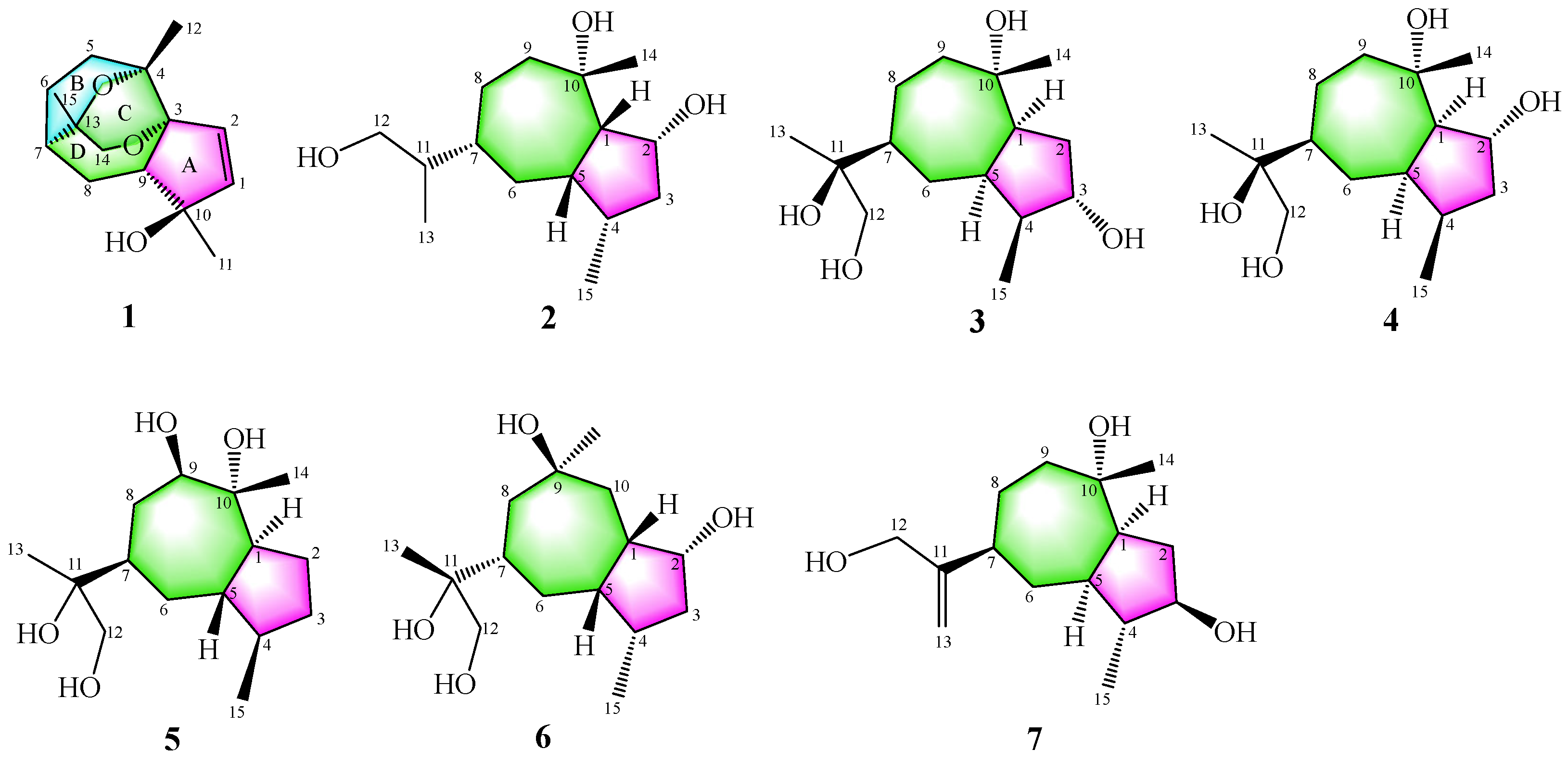






| No. | 1 (In DMSO-d6) | 2 (In CD3OD) | 3 (In CD3OD) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH | δC | δH | δC | δH | |
| 1 | 147.0, CH | 5.93 d (5.7) | 62.75, CH | 2.03 dd (9.8, 7.5) | 52.72, CH | 2.06 m |
| 2 | 130.7, CH | 5.60 d (5.8) | 75.33, CH | 4.23 q (7.0) | 37.04, CH2 | 2.09 m 1.53 m |
| 3 | 85.7, C | 43.10, CH2 | 1.66 m | 74.26, CH | 4.07 m | |
| 4 | 76.5, C | 37.15, CH | 2.18 m | 44.75, CH | 1.94 m | |
| 5 | 32.3, CH2 | 1.61 m 1.43 m | 46.50, CH | 2.27 m | 45.88, CH | 2.02 m |
| 6 | 22.5, CH2 | 1.97 m 1.54 m | 28.50, CH2 | 1.31 m 1.05 m | 27.58, CH2 | 1.57 m 1.19 m |
| 7 | 36.6, CH | 1.87 m | 41.14, CH | 1.66 m | 46.75, CH | 1.69 m |
| 8 | 26.9, CH2 | 1.83 m 1.5 m | 30.01, CH2 | 1.63 m 1.38 m | 25.44, CH2 | 1.91 m 1.34 m |
| 9 | 56.2, CH | 2.44 dd (12.2, 8.0) | 41.85, CH2 | 1.82 m | 39.24, CH2 | 1.92 m 1.52 m |
| 10 | 80.1, C | 75.72, C | 75.37, C | |||
| 11 | 23.3, CH3 | 1.16 s | 43.47, CH | 1.54 m | 76.59, C | |
| 12 | 25.7, CH3 | 1.15 s | 66.29, CH2 | 3.46 dd (10.8, 6.7) 3.33 dd (10.8, 7.1) | 68.61, CH2 | 3.44 d (7.1) |
| 13 | 72.1, C | 12.88, CH3 | 0.82 d (7.0) | 20.81, CH3 | 1.07 s | |
| 14 | 71.1, CH2 | 3.87 d (8.9) 3.27 d (8.9) | 28.25, CH3 | 1.29 s | 28.58, CH3 | 1.18 s |
| 15 | 25.0, CH3 | 1.08 s | 16.79, CH3 | 0.88 d (7.2) | 10.15, CH3 | 0.92 d (7.3) |
| 10-OH | -OH | 4.67 s | ||||
| No. | 4 (In CD3OD) | 5 (In CD3OD) | 6 (In CDCl3) | 7 (In CD3OD) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| δC | δH | δC | δH | δC | δH | δC | δH | |
| 1 | 63.06, CH | 2.01 m | 50.34, CH | 2.16 m | 53.38, CH | 2.00 m | 49.84, CH | 2.23 m |
| 2 | 75.33, CH | 4.19 m | 27.52, CH2 | 1.81 m | 73.90, CH | 4.15 m | 36.99, CH2 | 2.09 m 1.58 m |
| 3 | 43.19, CH2 | 1.64 m 1.70 m | 33.78, CH2 | 1.60 m 1.39 m | 37.14, CH2 | 2.23 m 1.48 m | 78.75, CH | 3.44 m |
| 4 | 37.28, CH | 2.19 m | 40.09, CH | 2.06 m | 43.77, CH | 1.97 m | 49.52, CH | 1.24 s |
| 5 | 47.14, CH | 2.25 m | 46.13, CH | 2.12 m | 45.87, CH | 1.95 m | 47.20, CH | 1.60 m |
| 6 | 27.45, CH2 | 0.99 m 1.55 m | 29.82, CH2 | 1.63 m 1.09 m | 24.64, CH2 | 1.77 m 1.19 m | 38.52, CH2 | 1.75 m 1.44 m |
| 7 | 46.40, CH | 1.72 m | 44.58, CH | 1.59 m | 44.92, CH | 1.75 m | 44.54, CH | 1.97 m |
| 8 | 25.53, CH2 | 1.32 m 1.91 m | 34.90, CH2 | 2.20 m 1.30 m | 23.69, CH2 | 1.77 m 1.17 m | 33.34, CH2 | 1.73 m 1.51 m |
| 9 | 40.49, CH2 | 1.61 m 1.85 m | 81.10, CH | 3.37 m | 74.62, C | 46.51, CH2 | 1.86 m 1.67 m | |
| 10 | 75.60, C | 78.17, C | 33.86, CH2 | 1.95 m 1.52 m | 75.95, C | |||
| 11 | 76.47, C | 75.90, C | 75.82, C | 157.27, C | ||||
| 12 | 68.55, CH2 | 3.43 d (3.7) | 68.77, CH2 | 3.44 m | 68.54, CH2 | 3.38 d (10.95) 3.56 d (10.95) | 65.09, CH2 | 4.01 s |
| 13 | 21.08, CH3 | 1.06 s | 20.60, CH3 | 1.06 s | 18.43, CH3 | 1.04 s | 107.51, CH2 | 4.95 m 4.82 s |
| 14 | 29.08, CH3 | 1.29 s | 18.43, CH3 | 1.14 s | 30.92, CH3 | 1.19 s | 23.70, CH3 | 1.25 s |
| 15 | 16.66, CH3 | 0.90 d (7.0) | 16.04, CH3 | 0.83 d (7.1) | 10.01, CH3 | 1.01 d (6.95) | 16.34, CH3 | 0.96 d (6.4) |
| Compounds | MIC (μM) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1.60 |
| 2 | 6.25 |
| 3 | 23.53 |
| 4 | 12.50 |
| 5 | 11.76 |
| 6 | 47.06 |
| 7 | 6.30 |
| Amphotericin B a | 0.43 |
| Fluconazole b | 2.61 |
| Compounds | IC50 (μM) | CC50 (μM) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4.60 ± 0.42 | >80 |
| 2 | 20.00 ± 1.54 | >100 |
| 3 | 60.20 ± 0.81 | >80 |
| 4 | 62.48 ± 1.23 | >100 |
| 5 | 50.76 ± 0.68 | >100 |
| 6 | 75.50 ± 0.73 | >100 |
| 7 | 18.38 ± 1.12 | >100 |
| Indomethacin a | 22.94 ± 1.42 | >100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, L.; Zheng, W.; Qian, S.-Y.; Yang, M.-F.; Lu, Y.-Z.; He, Z.-J.; Kang, J.-C. New Guaiane-Type Sesquiterpenoids Biscogniauxiaols A–G with Anti-Fungal and Anti-Inflammatory Activities from the Endophytic Fungus Biscogniauxia Petrensis. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9040393
Han L, Zheng W, Qian S-Y, Yang M-F, Lu Y-Z, He Z-J, Kang J-C. New Guaiane-Type Sesquiterpenoids Biscogniauxiaols A–G with Anti-Fungal and Anti-Inflammatory Activities from the Endophytic Fungus Biscogniauxia Petrensis. Journal of Fungi. 2023; 9(4):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9040393
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Long, Wen Zheng, Sheng-Yan Qian, Ming-Fei Yang, Yong-Zhong Lu, Zhang-Jiang He, and Ji-Chuan Kang. 2023. "New Guaiane-Type Sesquiterpenoids Biscogniauxiaols A–G with Anti-Fungal and Anti-Inflammatory Activities from the Endophytic Fungus Biscogniauxia Petrensis" Journal of Fungi 9, no. 4: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9040393
APA StyleHan, L., Zheng, W., Qian, S.-Y., Yang, M.-F., Lu, Y.-Z., He, Z.-J., & Kang, J.-C. (2023). New Guaiane-Type Sesquiterpenoids Biscogniauxiaols A–G with Anti-Fungal and Anti-Inflammatory Activities from the Endophytic Fungus Biscogniauxia Petrensis. Journal of Fungi, 9(4), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof9040393





