The Early Terrestrial Fungal Lineage of Conidiobolus—Transition from Saprotroph to Parasitic Lifestyle
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Phylogenetic Reconstruction
2.2. Ancestral States Reconstruction (ACR)
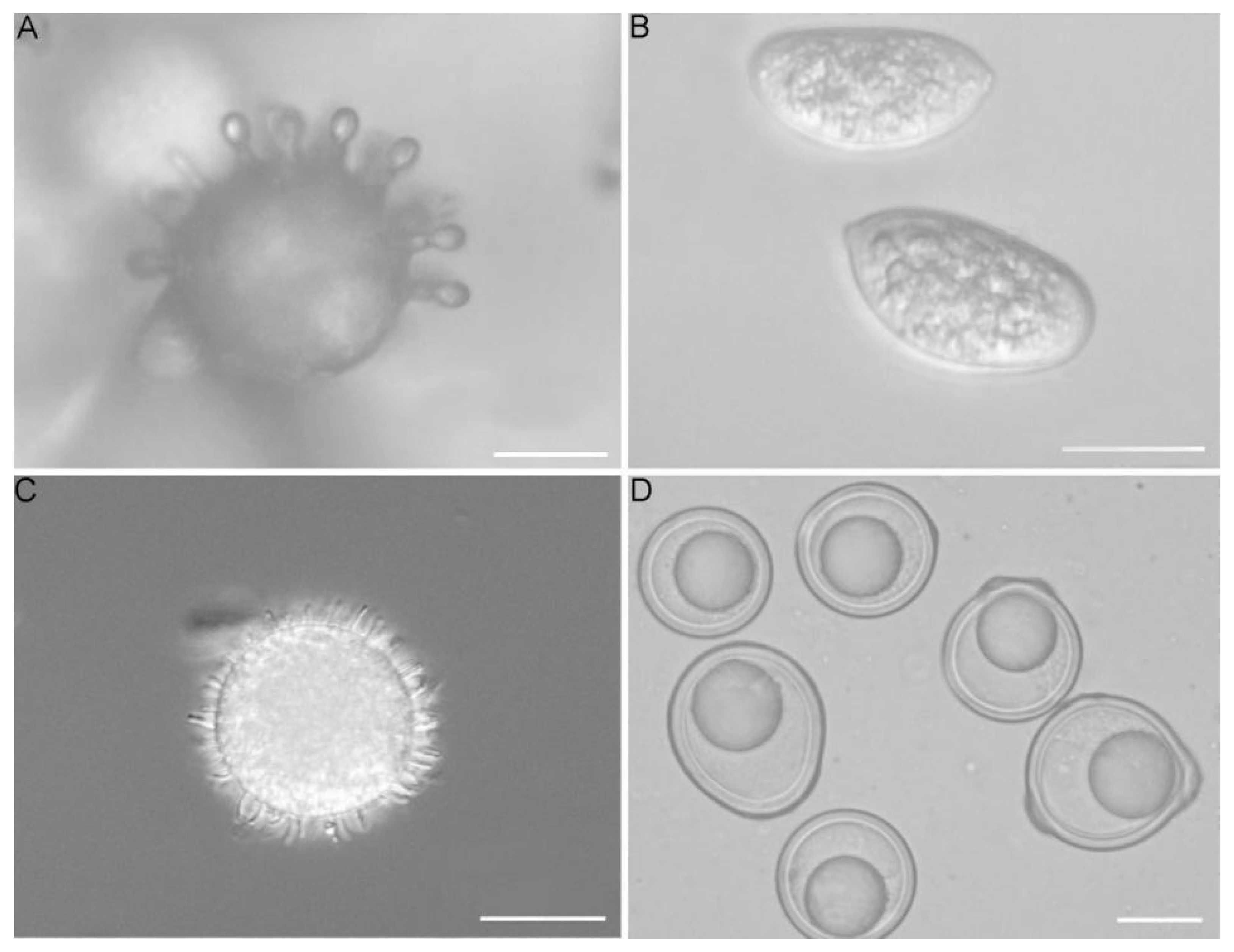
2.3. Light Microscopy
3. Results
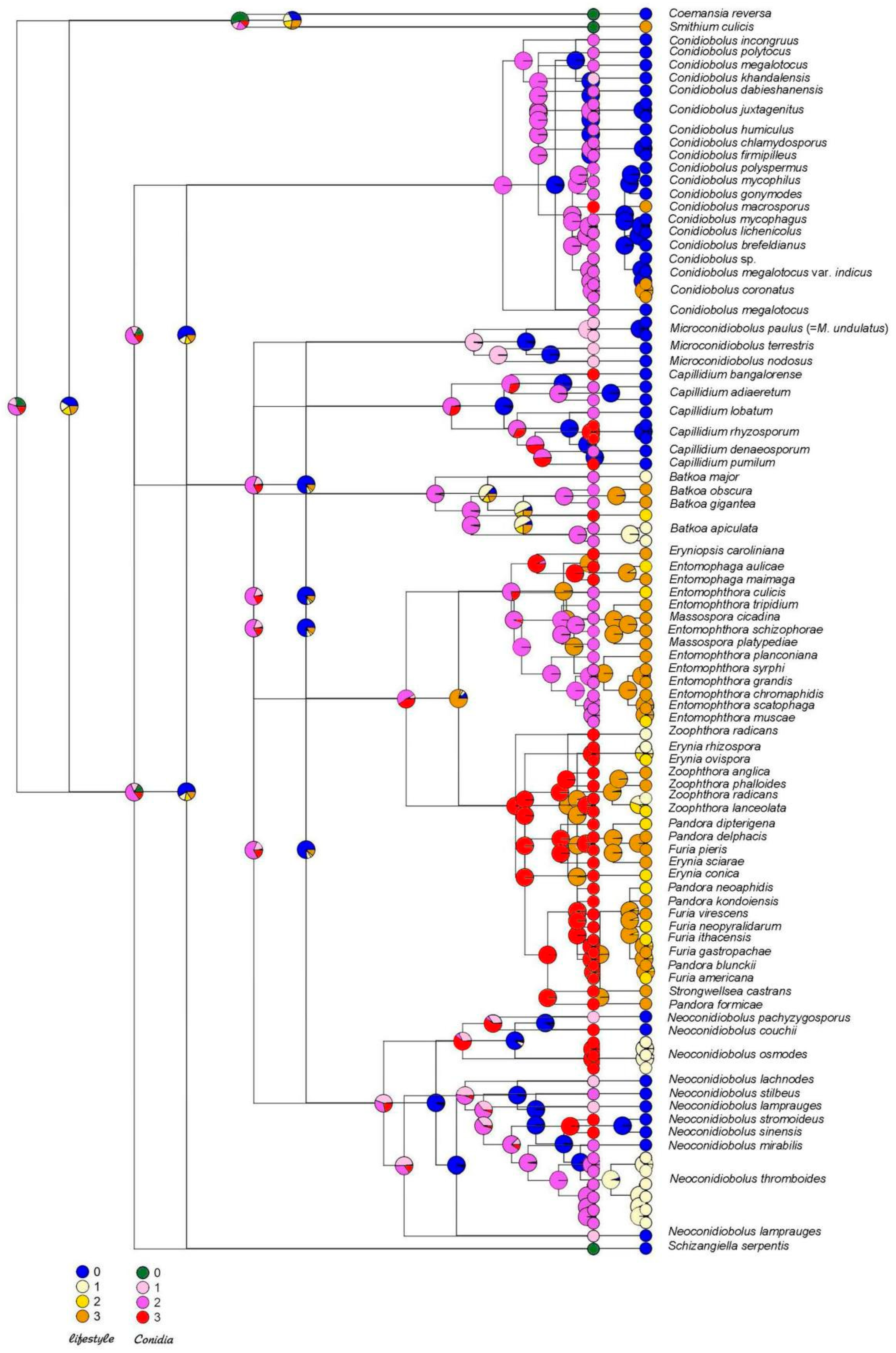
3.1. Phylogenetic Reconstruction
3.2. Taxonomy
3.2.1. Batkoaceae Gryganskyi, A.E. Hajek & Stajich, fam. nov. [MB 844345]
3.2.2. Capillidiaceae Y. Nie, Stajich & K.T. Hodge, fam. nov. [MB 844346]
3.2.3. Conidiobolaceae B. Huang, Stajich & K.T. Hodge, fam. nov. [MB 844347]
3.2.4. Neoconidiobolaceae X.Y. Liu, Stajich & K.T. Hodge, fam. nov. [MB 844348]
4. Ancestral State Reconstruction
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humber, R.A. Evolution of entomopathogenicity in rungi. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2008, 98, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möckel, L.; Meusemann, K.; Misof, B.; Schwartze, V.U.; De Fine Licht, H.H.; Voigt, K.; Stielow, B.; de Hoog, S.; Beutel, R.G.; Buellesbach, J. Phylogenetic revision and patterns of host specificity in the fungal Subphylum Entomophthoromycotina. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullens, B.A. Cross-transmission of Entomophthora muscae (Zygomycetes: Entomophthoraceae) among naturally infected muscoid fly (Diptera: Muscidae) hosts. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1989, 53, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryganskyi, A.P.; Golan, J.; Hajek, A.E. Season-long infection of diverse hosts by the entomopathogenic fungus Batkoa Major. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0261912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaronski, S.T. Chapter 11—Mass production of entomopathogenic fungi: State of the art. In Mass Production of Beneficial Organisms; Morales-Ramos, J.A., Rojas, M.G., Shapiro-Ilan, D.I., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2014; pp. 357–413. ISBN 978-0-12-391453-8. [Google Scholar]
- Humber, R.A. Synopsis of a revised classification for the Entomophthorales (Zygomycotina). Mycotaxon 1989, 34, 441–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Yu, D.S.; Wang, C.F.; Liu, X.Y.; Huang, B. A taxonomic revision of the genus Conidiobolus (Ancylistaceae, Entomophthorales): Four clades including three new genera. Mycokeys 2020, 66, 55–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cai, Y.; Nie, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Huang, B. Azygosporus gen. nov., a synapomorphic clade in the family Ancylistaceae. MycoKeys 2021, 85, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffre, D.; Jensen, A.B.; Lopez Lastra, C.C.; Humber, R.A.; Folgarait, P.J. Conidiobolus lunulus, a new entomophthoralean species isolated from leafcutter ants. Mycologia 2021, 113, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stajich, J.E. Andrii Shows How to Culture Conidiobolus from Leaf Litter; ZyGoLife: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2015; Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ea6RoU9kbvg (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Kimura, M.; Yaguchi, T.; Sutton, D.A.; Fothergill, A.W.; Thompson, E.H.; Wickes, B.L. Disseminated human conidiobolomycosis due to Conidiobolus lamprauges. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 752–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vilela, R.; Mendoza, L. Human pathogenic Entomophthorales. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2018, 31, e00014-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Huang, B. Two new species in Capillidium (Ancylistaceae, Entomophthorales) from China, with a proposal for a new combination. MycoKeys 2022, 89, 139–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoriev, I.V.; Nordberg, H.; Shabalov, I.; Aerts, A.; Cantor, M.; Goodstein, D.; Kuo, A.; Minovitsky, S.; Nikitin, R.; Ohm, R.A.; et al. The Genome Portal of the Department of Energy Joint Genome Institute. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D26–D32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirarab, S.; Reaz, R.; Bayzid, M.D.S.; Zimmermann, T.; Swenson, M.S.; Warnow, T. ASTRAL: Genome-scale coalescent-based species tree estimation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rambaut, A. Title of the Software, FigTree v1.3.1; Institute of Evolutionary Biology, University of Edinburgh: Edinburgh, UK, 2010; Available online: http://tree.bio.ed.ac.uk/software/figtree/ (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2021. Available online: http://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Revell, L.J. Phytools: An R package for phylogenetic comparative biology (and other things). Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madisson, W.P.; Madisson, D.R. Mesquite: A Modular System for Evolutionary Analysis. Version 3.04. 2011. Available online: https://www.mesquiteproject.org/ (accessed on 25 July 2022).
- Brefeld, O. Conidiobolus utriculosus and minor. Unters. Gesammtgebiete Mykol. 1884, 6, 35–78. [Google Scholar]
- Gryganskyi, A.P.; Humber, R.A.; Smith, M.E.; Miadlikowska, J.; Wu, S.; Voigt, K.; Walther, G.; Anishchenko, I.M.; Vilgalys, R. Molecular phylogeny of the Entomophthoromycota. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 65, 682–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryganskyi, A.P.; Humber, R.A.; Smith, M.E.; Hodge, K.; Huang, B.; Voigt, K.; Vilgalys, R. Phylogenetic lineages in Entomophthoromycota. Persoonia 2013, 30, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nie, Y.; Wang, L.; Cai, Y.; Tao, W.; Zhang, Y.J.; Huang, B. Mitochondrial genome of the entomophthoroid fungus Conidiobolus heterosporus provides insights into evolution of basal fungi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 103, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Huang, B. The gene rearrangement, loss, transfer and deep intronic variation in mitochondrial genomes of Conidiobolus. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 765733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryganskyi, A.P.; Golan, J.; Muszewska, A.; Idnurm, A.; Dolatabadi, S.; Kutovenko, V.B.; Kutovenko, V.O.; Gajdeczka, M.T.; Anishchenko, I.M.; Pawlowska, J. Sequencing the genomes of the terrestrial fungal lineages, What Have We Learned? Microorganisms 2022, unpublished. [Google Scholar]
- Elya, C.; De Fine Licht, H.H. The genus Entomophthora: Bringing the insect destroyers into the twenty-first century. IMA Fungus 2021, 12, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gryganskyi, A.P.; Nie, Y.; Hajek, A.E.; Hodge, K.T.; Liu, X.-Y.; Aadland, K.; Voigt, K.; Anishchenko, I.M.; Kutovenko, V.B.; Kava, L.; et al. The Early Terrestrial Fungal Lineage of Conidiobolus—Transition from Saprotroph to Parasitic Lifestyle. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8080789
Gryganskyi AP, Nie Y, Hajek AE, Hodge KT, Liu X-Y, Aadland K, Voigt K, Anishchenko IM, Kutovenko VB, Kava L, et al. The Early Terrestrial Fungal Lineage of Conidiobolus—Transition from Saprotroph to Parasitic Lifestyle. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(8):789. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8080789
Chicago/Turabian StyleGryganskyi, Andrii P., Yong Nie, Ann E. Hajek, Kathie T. Hodge, Xiao-Yong Liu, Kelsey Aadland, Kerstin Voigt, Iryna M. Anishchenko, Vira B. Kutovenko, Liudmyla Kava, and et al. 2022. "The Early Terrestrial Fungal Lineage of Conidiobolus—Transition from Saprotroph to Parasitic Lifestyle" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 8: 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8080789
APA StyleGryganskyi, A. P., Nie, Y., Hajek, A. E., Hodge, K. T., Liu, X.-Y., Aadland, K., Voigt, K., Anishchenko, I. M., Kutovenko, V. B., Kava, L., Vuek, A., Vilgalys, R., Huang, B., & Stajich, J. E. (2022). The Early Terrestrial Fungal Lineage of Conidiobolus—Transition from Saprotroph to Parasitic Lifestyle. Journal of Fungi, 8(8), 789. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8080789






