Frequency and Duration of, and Risk Factors for, Diagnostic Delays Associated with Histoplasmosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
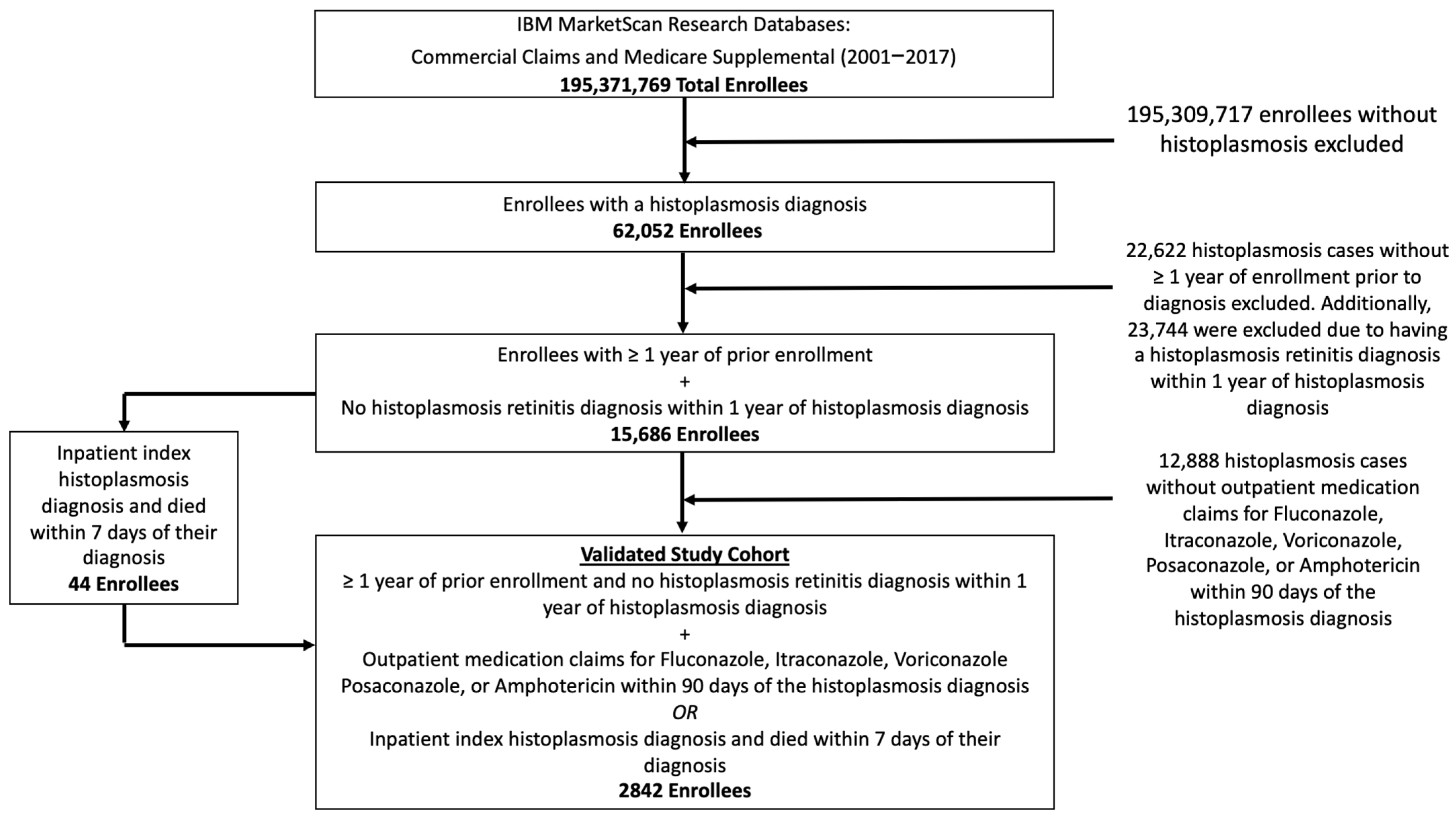
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Study Population
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Edwards, L.B.; Acquaviva, F.A.; Livesay, V.T.; Cross, F.W.; Palmer, C.E. An atlas of sensitivity to tuberculin, PPD-B, and histoplasmin in the United States. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1969, 99, 1–132. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, G.R., 3rd; Le, T.; Chindamporn, A.; Kauffman, C.A.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Ampel, N.M.; Andes, D.R.; Armstrong-James, D.; Ayanlowo, A.; Baddley, W.; et al. Global guideline for the diagnosis and management of the endemic mycoses: An initiative of the European Confederation of Medical Mycology in cooperation with the International Society for Human and Animal Mycology. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, e364–e374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skillman, D.; Riek, L.; Davis, B.; Harris, J.R.; Nett, R.J. Histoplasmosis in a state where it is not known to be endemic—Montana, 2012–2013. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 834–837. [Google Scholar]
- Azar, M.M.; Zhang, X.; Assi, R.; Hage, C.; Wheat, L.J.; Malinis, M.F. Clinical and epidemiological characterization of histoplasmosis cases in a nonendemic area, Connecticut, United States. Med. Mycol. 2018, 56, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, N.; Kubat, R.C.; Poplin, V.; Adenis, A.A.; Denning, D.W.; Wright, L.; McCotter, O.; Schwartz, I.S.; Jackson, B.R.; Chiller, T.; et al. Re-drawing the Maps for Endemic Mycoses. Mycopathologia 2020, 185, 843–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nacher, M.; Blanchet, D.; Bongomin, F.; Chakrabarti, A.; Couppié, P.; Demar, M.P.; Denning, D.W.; Djossou, F.; Epelboin, L.; Govender, N.; et al. Histoplasma capsulatum antigen detection tests as an essential diagnostic tool for patients with advanced HIV disease in low and middle income countries: A systematic review of diagnostic accuracy studies. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wheat, L.J.; Azar, M.M.; Bahr, N.C.; Spec, A.; Relich, R.F.; Hage, C. Histoplasmosis. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 30, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, J.H.; Feudtner, C.; Heydon, K.; Walsh, T.J.; Zaoutis, T.E. Hospitalizations for Endemic Mycoses: A Population-Based National Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 822–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azar, M.M.; Hage, C.A. Clinical Perspectives in the Diagnosis and Management of Histoplasmosis. Clin. Chest Med. 2017, 38, 403–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodwin, R.A.; Loyd, J.E.; Prez, R.M.D. Histoplasmosis in Normal Hosts. Medicine 1981, 60, 231–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauffman, C.A. Histoplasmosis: A Clinical and Laboratory Update. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 20, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wheat, L.J.; Slama, T.G.; Eitzen, H.E.; Kohler, R.B.; French, M.L.V.; Biesecker, J.L. A Large Urban Outbreak of Histoplasmosis: Clinical Features. Ann. Intern. Med. 1981, 94, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheat, L.J.; Slama, T.G.; Norton, J.A.; Kohler, R.B.; Eitzen, H.E.; French, M.L.V.; Sathapatayavongs, B. Risk Factors for Disseminated or Fatal Histoplasmosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 1982, 96, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheat, L.J.; Connolly-Stringfield, P.A.; Baker, R.L.; Curfman, M.F.; Eads, M.E.; Israel, K.S.; Norris, S.A.; Webb, D.H.; Zeckel, M.L. Disseminated histoplasmosis in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome: Clinical findings, diagnosis and treatment, and review of the literature. Medicine 1990, 69, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage, C.A.; Bowyer, S.; Tarvin, S.E.; Helper, D.; Kleiman, M.B.; Wheat, L.J. Recognition, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Histoplasmosis Complicating Tumor Necrosis Factor Blocker Therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Assi, M.; Martin, S.; Wheat, L.J.; Hage, C.; Freifeld, A.; Avery, R.; Baddley, J.W.; Vergidis, P.; Miller, R.; Andes, D.; et al. Histoplasmosis After Solid Organ Transplant. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 1542–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddell, J.; Wheat, L.J. Central Nervous System Infection with Histoplasma capsulatum. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pincelli, T.; Enzler, M.; Davis, M.; Tande, A.J.; Comfere, N.; Bruce, A. Oropharyngeal histoplasmosis: A report of 10 cases. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 44, e181–e188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.L.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.-J.; Wang, Y.-P.; Yang, J.-L. Intestinal histoplasmosis in immunocompetent adults. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 4027–4033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage, C.A.; Knox, K.S.; Wheat, L.J. Endemic mycoses: Overlooked causes of community acquired pneumonia. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azar, M.M.; Loyd, J.L.; Relich, R.F.; Wheat, L.J.; Hage, C.A. Current Concepts in the Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Management of Histoplasmosis Syndromes. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 41, 013–030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruegg, G.; Zimmerli, S.; Trachsel, M.; Berezowska, S.; Engelbrecht, S.; Martin, Y.; Perrig, M. Pulmonary Histoplasmosis Mimicking Metastatic Lung Cancer: A Case Report. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.; Homsi, N.; Kapila, R. Crohn’s disease or histoplasmosis? A case of severe disseminated histoplasmosis mimicking Crohn’s disease and literature review. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2020, 30, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sizemore, T.C. Rheumatologic manifestations of histoplasmosis: A review. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 2963–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, A.D.; Larson, L.; Rauseo, A.M.; Rutjanawech, S.; Hendrix, M.J.; Powderly, W.G.; Spec, A. A comparison of presentations and outcomes of histoplasmosis across patients with varying immune status. Med. Mycol. 2021, 56, 624–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.C.; Polgreen, L.; Cavanaugh, J.E.; Hornick, D.; Polgreen, P.M. Missed Opportunities to Diagnose Tuberculosis Are Common Among Hospitalized Patients and Patients Seen in Emergency Departments. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2015, 2, ofv171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.C.; Koeneman, S.H.; Arakkal, A.T.; Cavanaugh, J.E.; Polgreen, P.M. Incidence, Duration, and Risk Factors Associated With Missed Opportunities to Diagnose Herpes Simplex Encephalitis: A Population-Based Longitudinal Study. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, D.A.; Kanzaria, H.K.; Schriger, D.L. Unrecognized Cardiovascular Emergencies Among Medicare Patients. JAMA Intern. Med. 2018, 178, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liberman, A.L.; Newman-Toker, D.E. Symptom-Disease Pair Analysis of Diagnostic Error (SPADE): A conceptual framework and methodological approach for unearthing misdiagnosis-related harms using big data. BMJ Qual. Saf. 2018, 27, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsai, A.J. Occurrence of never events after total joint arthroplasty in the United States. Arch. Orthop. Trauma. Surg. 2019, 139, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunz, D.; Camboni, D.; Philipp, A.; Flörchinger, B.; Terrazas, A.; Müller, T.; Schmid, C.; Diez, C. The ‘Weekend Effect’ in adult patients who receive extracorporeal cardiopulmonary resuscitation after in- and out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Resusc. Plus 2020, 4, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauls, L.; Johnson-Paben, R.; McGready, J.; Murphy, J.; Pronovost, P.J.; Wu, C. The Weekend Effect in Hospitalized Patients: A Meta-Analysis. J. Hosp. Med. 2017, 12, 760–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, A.C.; Arakkal, A.T.; Koeneman, S.; Cavanaugh, J.E.; Gerke, A.K.; Hornick, D.B.; Polgreen, P.M. Incidence, duration and risk factors associated with delayed and missed diagnostic opportunities related to tuberculosis: A population-based longitudinal study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e045605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toscanini, M.A.; Nusblat, A.D.; Cuestas, M.L. Diagnosis of histoplasmosis: Current status and perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 1837–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, M.L.; Franklin, N.; Gordon, R. Diagnostic Error in Internal Medicine. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 1493–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassirer, J.P.; Kopelman, R.I. Cognitive errors in diagnosis: Instantiation, classification, and consequences. Am. J. Med. 1989, 86, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, G. Premature closure? Not so fast. BMJ Qual. Saf. 2017, 26, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norman, G.R.; Eva, K.W. Diagnostic error and clinical reasoning. Med. Educ. 2010, 44, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Huang, W.K.; Huang, T.S.; Kunin, C. MInappropriate use of antibiotics and the risk for delayed admission and masked diagnosis of infectious diseases: A lesson from Taiwan. Arch. Intern. Med. 2001, 161, 2366–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nishiguchi, S.; Nishino, K.; Kitagawa, I.; Tokuda, Y. Factors associated with delayed diagnosis of infective endocarditis: A retrospective cohort study in a teaching hospital in Japan. Medicine 2020, 99, e21418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartside, J.G.; Alcorn, K.; Cross, J.W.; Maloney, S.; Keijzers, G. Appropriateness of antibiotic prescribing in the Emergency Department. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2019, 74, 515–520. [Google Scholar]
- Zetts, R.M.; Stoesz, A.; Smith, B.A.; Hyun, D.Y. Outpatient Antibiotic Use and the Need for Increased Antibiotic Stewardship Efforts. Pediatrics 2018, 141, e20174124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Llor, C.; Bjerrum, L. Antibiotic prescribing for acute bronchitis. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2016, 14, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, W.; Myint, T.; LaRue, R.; Minderman, M.; Gunn, S.; Wheat, L.J.; Hage, C.A. Diagnosis of Histoplasmosis Using the MVista Histoplasma Galactomannan Antigen Qualitative Lateral Flow-Based Immunoassay: A Multicenter Study. Open Forum. Infect. Dis. 2021, 8, ofab454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
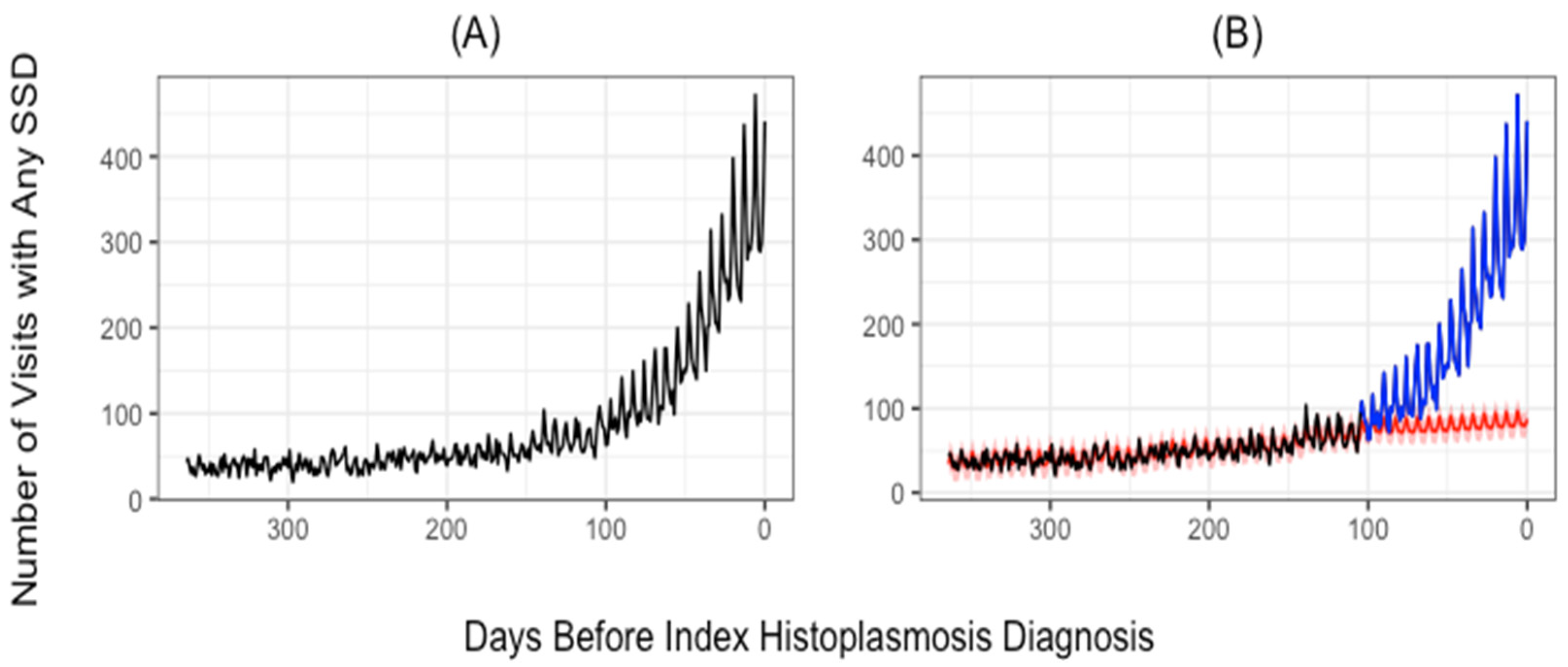
| Variable | Total Patients (% of Patients) |
|---|---|
| Age at Diagnosis | |
| <18 | 147 (5.2%) |
| 18–35 | 430 (15.1%) |
| 36–45 | 490 (17.2%) |
| 46–55 | 689 (24.2%) |
| 56–65 | 751 (26.4%) |
| >65 | 335 (11.8%) |
| Sex | |
| Male | 1418 (49.9%) |
| Female | 1424 (50.1%) |
| Enrollment time prior to index (years) | |
| Mean | 4.6 |
| Median | 3.5 |
| Range | 1.0–16.9 |
| Count ≤ 1.5 years | 348 (12.2%) |
| Count ≤ 2 years | 668 (23.5%) |
| Count ≤ 3 years | 1180 (41.5%) |
| Count > 3 years | 1662 (58.5%) |
| Region | |
| Rural | 729 (25.7%) |
| Urban | 2096 (73.8%) |
| Missing | 17 (0.6%) |
| Month of index diagnosis | |
| January | 265 (9.3%) |
| February | 266 (9.4%) |
| March | 260 (9.1%) |
| April | 241 (8.5%) |
| May | 247 (8.7%) |
| June | 231 (8.1%) |
| July | 227 (8.0%) |
| August | 219 (7.7%) |
| September | 227 (8.0%) |
| October | 214 (7.5%) |
| November | 223 (7.8%) |
| December | 222 (7.8%) |
| Metric/Category | Count (Percentage of All Patients)/Mean | 95% CI (from Bootstrapping) |
|---|---|---|
| Number of missed opportunities | ||
| 0 | 487 (17.1%) | 431–542 (15.2–19.1%) |
| >=1 | 2355 (82.9%) | 2300–2411 (80.9–84.8%) |
| >=2 | 1960 (69.0%) | 1871–2045 (65.8–72.0%) |
| >=3 | 1550 (54.5%) | 1435–1660 (50.5–58.4%) |
| >=4 | 1159 (40.8%) | 1035–1282 (36.4–45.1%) |
| >=5 | 825 (29.0%) | 705–946 (24.8–33.3%) |
| Mean—Overall | 4.03 | 3.73–4.33 |
| Mean—Outpatient | 3.48 | 3.21–3.74 |
| Mean—Inpatient | 0.20 | 0.18–0.22 |
| Mean—ED | 0.35 | 0.31–0.39 |
| Duration of delays (days) | ||
| >=0 | 2355 (100.0%) | 2300–2411 (NA) |
| >=10 | 2116 (88.9%) | 2053–2166 (87.4–90.2%) |
| >=20 | 1802 (75.7%) | 1718–1865 (73.3–77.7%) |
| >=30 | 1475 (61.9%) | 1390–1555 (59.0–65.0%) |
| >=40 | 1174 (49.7%) | 1065–1280 (45.6–53.4%) |
| >=50 | 833 (35.2%) | 713–954 (30.4–39.7%)] |
| >=60 | 477 (20.0%) | 463–492 (19.4–20.6%) |
| >=70 | 401 (17.0%) | 279–517 (11.9–21.6%) |
| >=80 | 117 (5.0%) | 61–175 (2.6–7.4%) |
| >=90 | 28 (1.2%) | 17–53 (0.7–2.3%) |
| Mean | 39.46 | 36.04–44.00 |
| Variable | Adjusted Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weekend (visits that occurred on a Saturday or Sunday) | 1.855 | 1.514, 2.273 | <0.001 |
| Female Sex | 0.984 | 0.900, 1.075 | 0.716 |
| Age | |||
| <18 | REF | REF | REF |
| 18–35 | 1.048 | 0.834, 1.316 | 0.689 |
| 36–45 | 1.142 | 0.911, 1.430 | 0.249 |
| 46–55 | 1.169 | 0.941, 1.453 | 0.159 |
| 56–65 | 1.192 | 0.959, 1.480 | 0.113 |
| >65 | 1.279 | 1.010, 1.621 | 0.041 |
| Settings visited | |||
| Outpatient only | REF | REF | REF |
| All three (inpatient, outpatient, and ED) | 0.158 | 0.102, 0.246 | <0.001 |
| ED only | 6.784 | 3.892, 11.823 | <0.001 |
| Inpatient only | 0.129 | 0.111, 0.151 | <0.001 |
| Inpatient and ED | 0.149 | 0.110, 0.202 | <0.001 |
| Inpatient and outpatient | 0.134 | 0.114, 0.158 | <0.001 |
| Outpatient and ED | 2.898 | 1.836, 4.573 | <0.001 |
| Urban vs. not urban | 1.019 | 0.920, 1.129 | 0.715 |
| Asthma prior to change point | 1.161 | 0.983, 1.371 | 0.079 |
| COPD prior to change point | 1.298 | 1.130, 1.491 | <0.001 |
| ILD prior to change point | 1.591 | 0.811, 3.122 | 0.177 |
| HIV prior to index | 0.845 | 0.670, 1.065 | 0.154 |
| Chest CT prior to change point | 1.602 | 1.457, 1.761 | <0.001 |
| Chest X-ray prior to change point | 2.363 | 2.126, 2.625 | <0.001 |
| Respiratory antibiotics between change point and 1 day prior to index | 1.285 | 1.173, 1.408 | <0.001 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miller, A.C.; Arakkal, A.T.; Koeneman, S.H.; Cavanaugh, J.E.; Thompson, G.R.; Baddley, J.W.; Polgreen, P.M. Frequency and Duration of, and Risk Factors for, Diagnostic Delays Associated with Histoplasmosis. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8050438
Miller AC, Arakkal AT, Koeneman SH, Cavanaugh JE, Thompson GR, Baddley JW, Polgreen PM. Frequency and Duration of, and Risk Factors for, Diagnostic Delays Associated with Histoplasmosis. Journal of Fungi. 2022; 8(5):438. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8050438
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiller, Aaron C., Alan T. Arakkal, Scott H. Koeneman, Joseph E. Cavanaugh, George R. Thompson, John W. Baddley, and Philip M. Polgreen. 2022. "Frequency and Duration of, and Risk Factors for, Diagnostic Delays Associated with Histoplasmosis" Journal of Fungi 8, no. 5: 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8050438
APA StyleMiller, A. C., Arakkal, A. T., Koeneman, S. H., Cavanaugh, J. E., Thompson, G. R., Baddley, J. W., & Polgreen, P. M. (2022). Frequency and Duration of, and Risk Factors for, Diagnostic Delays Associated with Histoplasmosis. Journal of Fungi, 8(5), 438. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof8050438







