Differential Diagnosis of Fungal Pneumonias vs. Tuberculosis in AIDS Patients by Using Two New Molecular Methods
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Control Strains and Plasmids
2.2. Primer and Probe Design
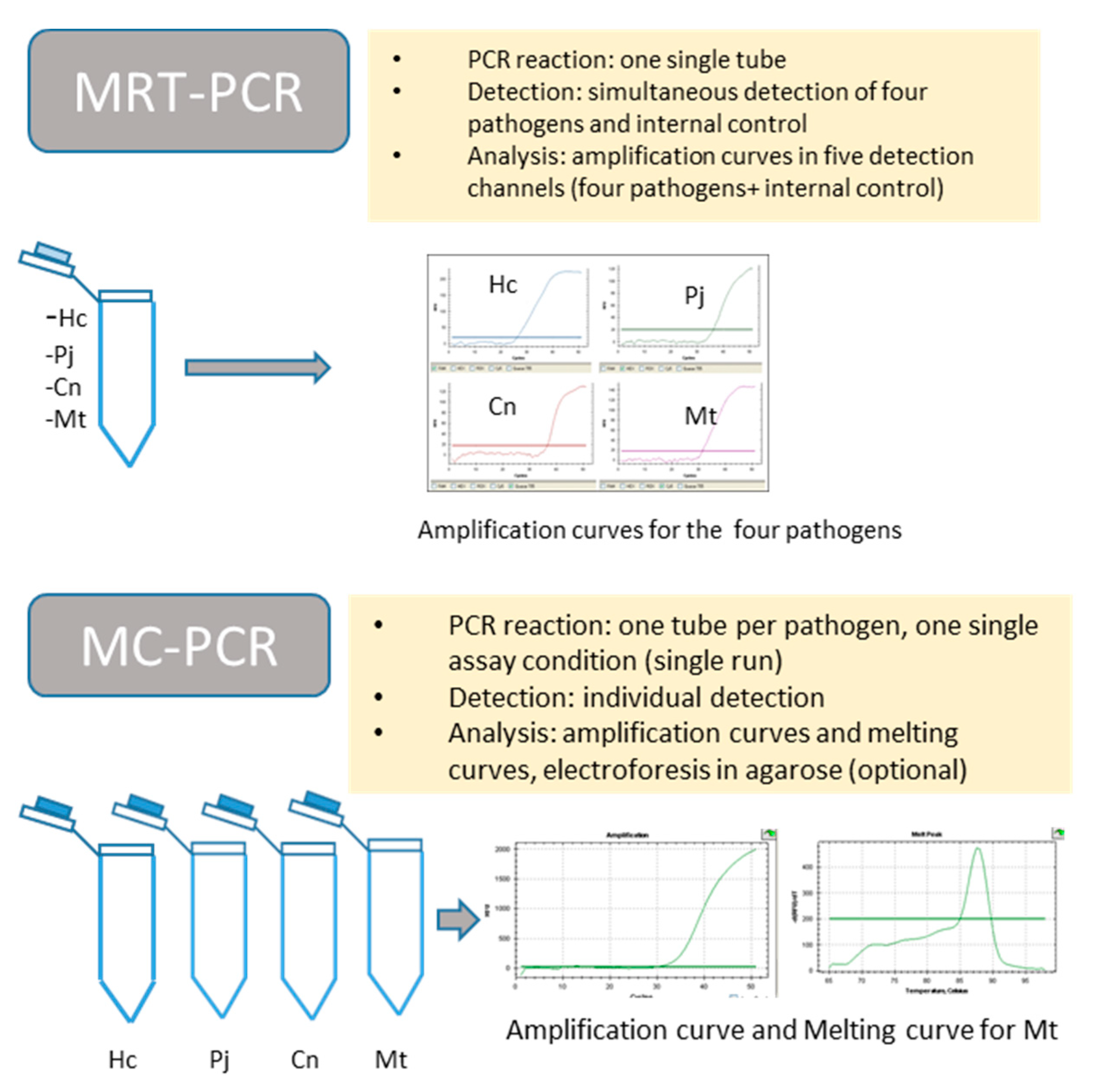
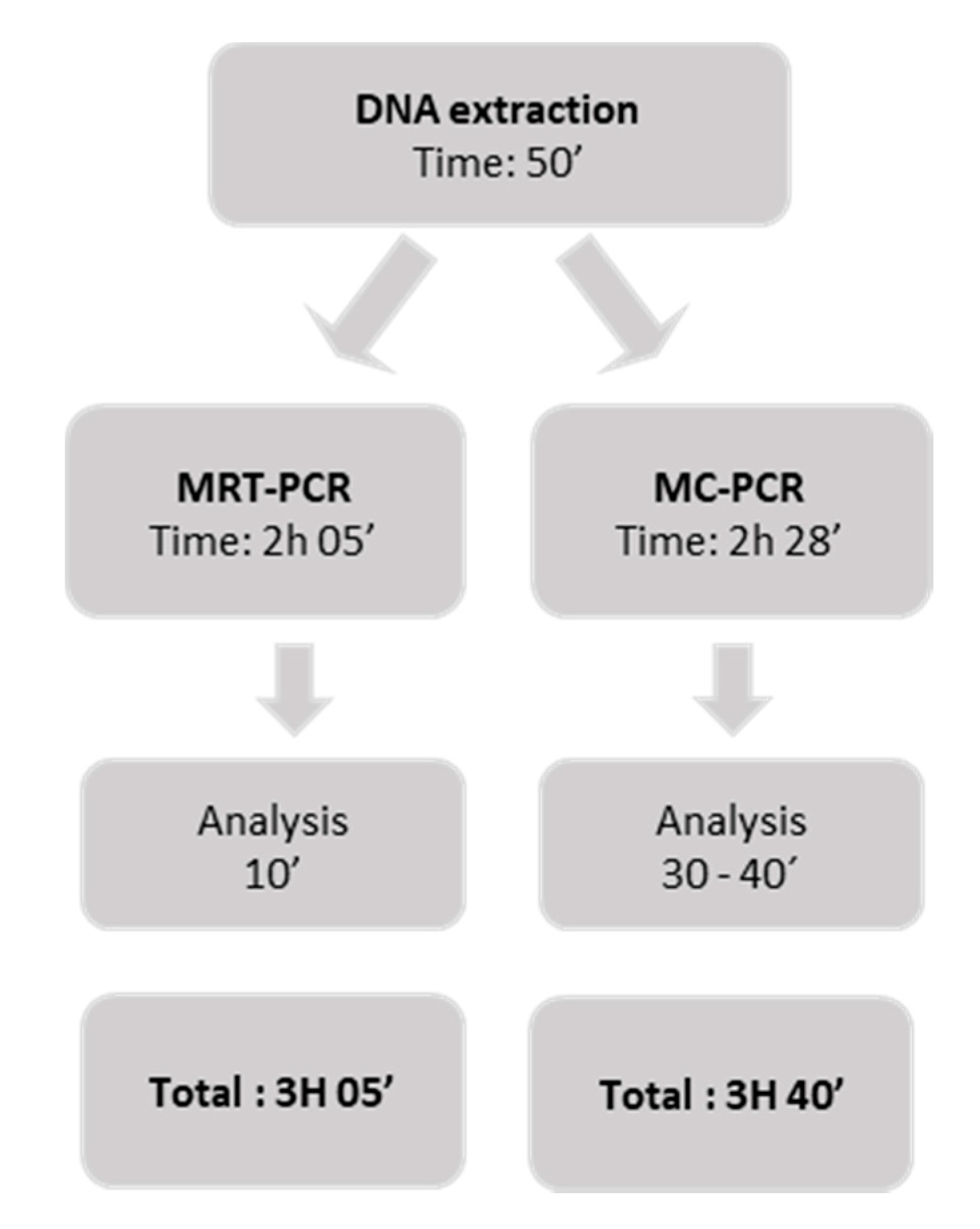
2.3. PCR Assay
2.4. Standardization of Both Techniques
2.5. DNA Extraction
2.6. Validation with Clinical Samples
3. Results
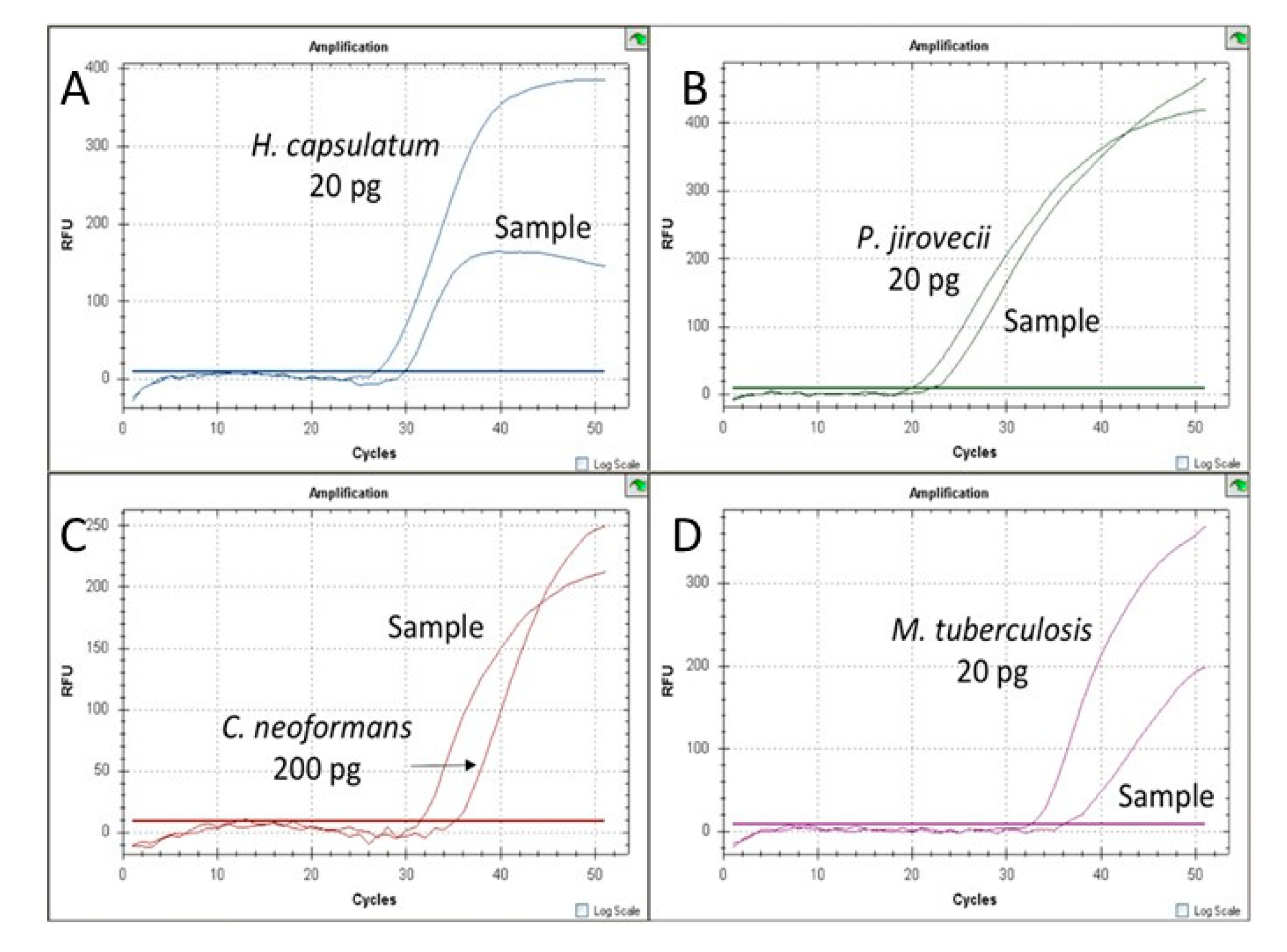
3.1. Standardization of MRT-PCR Assay
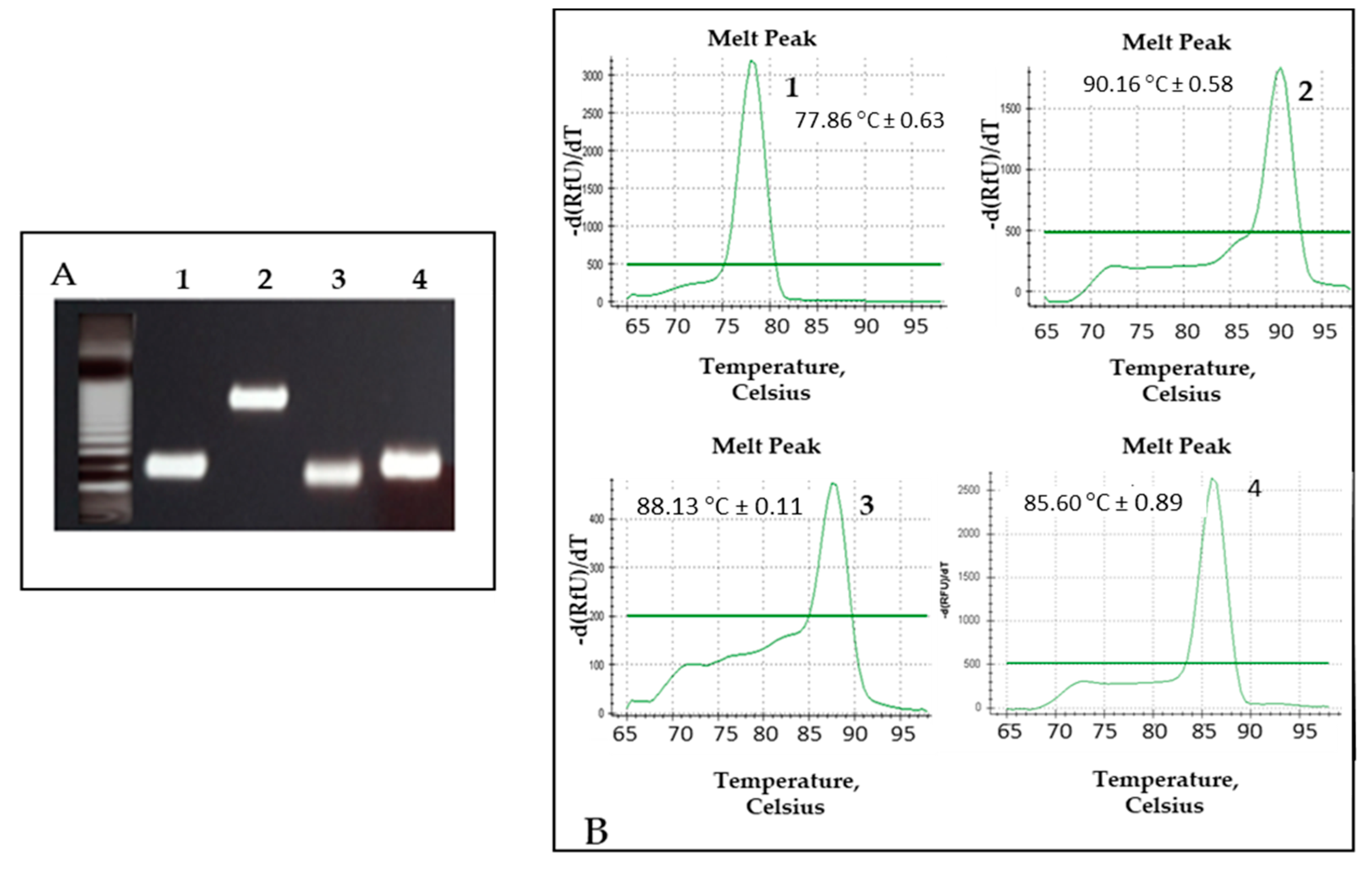
3.2. Standardization of MC-PCR Assay
3.3. Validation of MRT-PCR Assay with Clinical Samples
3.4. Validation of MC-PCR Assay with Clinical Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gingo, M.R.; Balasubramani, G.K.; Kingsley, L.; Rinaldo, C.R.; Alden, C.B.; Detels, R.; Greenblatt, R.M.; Hessol, N.A.; Holman, S.; Huang, L.; et al. The Impact of HAART on the Respiratory Complications of HIV Infection: Longitudinal Trends in the MACS and WIHS Cohorts. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adenis, A.A.; Valdes, A.; Cropet, C.; McCotter, O.Z.; Derado, G.; Couppie, P.; Chiller, T.; Nacher, M. Burden of HIV-associated histoplasmosis compared with tuberculosis in Latin America: A modelling study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong-James, D.; Meintjes, G.; Brown, G.D. A neglected epidemic: Fungal infections in HIV/AIDS. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limper, A.H.; Adenis, A.; Le, T.; Harrison, T.S. Fungal infections in HIV/AIDS. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e334–e343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, D.W. Minimizing fungal disease deaths will allow the UNAIDS target of reducing annual AIDS deaths below 500 000 by 2020 to be realized. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denis, B.; Lortholary, O. Infections fongiques pulmonaires chez les patients séropositifs pour le VIH. Rev. Mal. Respir. 2013, 30, 682–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Cerdeira, C.; Arenas, R.; Morenocoutino, G.; Vásquez, E.; Fernandez, R.D.; Chang, P. Micosis sistémicas en pacientes con virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana/sida. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas 2014, 105, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabey, D.; Peeling, R.W.; Ustianowski, A.; Perkins, M.D. Diagnostics for the developing world. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 2, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, A.K.J.; Singh, S.R.; Prem, K.; Hsu, L.Y.; Yi, S. Delayed diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis in high-burden countries: A systematic review protocol. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e029807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nacher, M.; Adenis, A.; Aznar, C.; Blanchet, D.; Vantilcke, V.; Demar, M.; Carme, B.; Couppié, P. How Many Have Died from Undiagnosed Human Immunodeficiency Virus–Associated Histoplasmosis, A Treatable Disease? Time to Act. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2014, 90, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, M.E.; Canton, A.; Sosa, N.; Puga, E.; Talavera, L. Disseminated Histoplasmosis in Patients with AIDS in Panama: A Review of 104 Cases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 1199–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samayoa, B.; Roy, M.; Cleveland, A.A.; Medina, N.; Lau-Bonilla, D.; Scheel, C.M.; Gomez, B.L.; Chiller, T.; Arathoon, E. High Mortality and Coinfection in a Prospective Cohort of Human Immuno-deficiency Virus/Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome Patients with Histoplasmosis in Guatemala. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 97, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caceres, D.H.; Valdes, A. Histoplasmosis and Tuberculosis Co-Occurrence in People with Advanced HIV. J. Fungi 2019, 5, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida-Silva, F.; Damasceno, L.S.; Serna, M.J.B.; Valero, C.; Quintella, L.P.; Almeida-Paes, R.; Muniz, M.D.M.; Zancope-Oliveira, R.M. Multiple opportunistic fungal infections in an individual with severe HIV disease: A case report. Revista Iberoamericana de Micología 2016, 33, 118–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronis, M.L.; Dos Santos, R.P.; Goldani, L.Z. Disseminated Histoplasma capsulatum and Cryptococcus neoformans Co-Infection in Patients with AIDS. Mycopathologia 2011, 172, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlovic, D.; Kularatne, R.; Ferraz, V.; Smego, R.A. Dual Pulmonary Infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Pneumocystis carinii in Patients Infected with Human Immunodeficiency Virus. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage, C.A.; Knox, K.S.; Wheat, L.J. Endemic mycoses: Overlooked causes of community acquired pneumonia. Respir. Med. 2012, 106, 769–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheat, L.J.; Azar, M.M.; Bahr, N.C.; Spec, A.; Relich, R.F.; Hage, C. Histoplasmosis. Infect. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2016, 30, 207–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babafemi, E.O.; Cherian, B.P.; Banting, L.; Mills, G.A.; Ngianga, K. Effectiveness of re-al-time polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in patholog-ical samples: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst. Rev. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, M.; Derendinger, B.; Dolby, T.; Simpson, J.; Van Helden, P.D.; Rice, J.E.; Wangh, L.J.; Theron, G.; Warren, R.M. Diagnostic Accuracy and Utility of FluoroType MTBDR, a New Molecular Assay for Multidrug-Resistant Tuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tevere, V.J.; Hewitt, P.L.; Dare, A.; Hocknell, P.; Keen, A.; Spadoro, J.P.; Young, K.K. Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by PCR amplification with pan-Mycobacterium primers and hybridization to an M. tuberculosis-specific probe. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1996, 34, 918–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolia-Diafouka, P.; Godreuil, S.; Bourdin, A.; Carrère-Kremer, S.; Kremer, L.; Van De Perre, P.; Tuaillon, E. Optimized Lysis-Extraction Method Combined With IS6110-Amplification for Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Paucibacillary Sputum Specimens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurwidya, F.; Handayani, D.; Burhan, E.; Yunus, F. Molecular Diagnosis of Tuberculosis. Chonnam Med. J. 2018, 54, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schito, M.; Migliori, G.B.; Fletcher, H.A.; McNerney, R.; Centis, R.; D’Ambrosio, L.; Bates, M.; Kibiki, G.; Kapata, N.; Corrah, T.; et al. Perspectives on Advances in Tuberculosis Diagnostics, Drugs, and Vaccines. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, S102–S118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanio, A.; Hauser, P.M.; Lagrou, K.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Helweg-Larsen, J.; Matos, O.; Cesaro, S.; Maschmeyer, G.; Einsele, H.; Donnelly, J.P.; et al. ECIL guidelines for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with haematological malignancies and stem cell transplant recipients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2386–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bialek, R.; Feucht, A.; Aepinus, C.; Just-Nübling, G.; Robertson, V.J.; Knobloch, J.; Hohle, R. Evaluation of Two Nested PCR Assays for Detection of Histoplasma capsulatum DNA in Human Tissue. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 1644–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buitrago, M.J.; Berenguer, J.; Mellado, E.; Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L.; Cuenca-Estrella, M. Detection of imported histoplasmosis in serum of HIV-infected patients using a real-time PCR-based assay. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2006, 25, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martagon-Villamil, J.; Shrestha, N.; Sholtis, M.; Isada, C.M.; Hall, G.S.; Bryne, T.; Lodge, B.A.; Reller, L.B.; Procop, G.W. Identification of Histoplasma capsulatum from culture extracts by real-time PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 1295–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tansarli, G.; Chapin, K. Diagnostic test accuracy of the BioFire® FilmArray® meningitis/encephalitis panel: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baddley, J.W.; Dismukes, W.E. Cryptococcosis. In Essentials of Clinical Mycology, 2nd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gago, S.; Esteban, C.; Valero, C.; Zaragoza, O.; Puig, d.l.B.; Buitrago, M.J. A multiplex re-al-time PCR assay for identification of Pneumocystis jirovecii, Histoplasma capsulatum, and Crypto-coccus neoformans/Cryptococcus gattii in sam-ples from AIDS patients with opportunistic pneumonia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1168–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Martínez, L.; Buitrago, M.J.; Castelli, M.V.; Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L.; Cuenca-Estrella, M. Development of a single tube multiplex real-time PCR to detect the most clinically relevant Mucormycetes species. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2013, 19, E1–E7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buitrago, M.J.; Canteros, C.E.; De León, G.F.; Gonzalez, A.; De Oliveira, M.M.-E.; Muñoz, C.O.; Ramirez, J.A.; Toranzo, A.I.; Zancope-Oliveira, R.; Cuenca-Estrella, M. Comparison of PCR protocols for detecting Histoplasma capsulatum DNA through a multicenter study. Revista Iberoamericana de Micología 2013, 30, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.M.; Cohen, J.; Krausz, T.; Van Noorden, S.; Holden, D.W. The alkaline protease of Aspergillus fumigatus is not a virulence determinant in two murine models of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 1650–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thierry, D.; Brisson-Noël, A.; Vincent-Lévy-Frébault, V.; Nguyen, S.; Guesdon, J.L.; Gicquel, B. Characterization of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis insertion sequence, IS6110, and its application in diagnosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 2668–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brisson-Noël, A.; Nguyen, S.; Aznar, C.; Chureau, C.; Garrigue, G.; Pierre, C.; Bartoli, M.; Bonete, R.; Pialoux, G.; Gicquel, B. Diagnosis of tuberculosis by DNA amplification in clinical practice evaluation. Lancet 1991, 338, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, S.; Vanhuls, P.; Delcroix, G.; Courcol, R.; Lemaitre, N. Comparison of the Xpert MTB/RIF test with an IS6110-TaqMan real-time PCR assay for direct detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in respiratory and nonrespiratory specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 1772–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Khéchine, A.; Henry, M.; Raoult, D.; Drancourt, M. Detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex organisms in the stools of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Microbiology 2009, 155, 2384–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, R.E.L.; Gascoyne-Binzi, D.M.; Gillespie, S.H.; Dickens, A.; Qamer, S.; Hawkey, P.M. Comparison of Variable Number Tandem Repeat and IS6110-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Analyses for Discrimination of High- and Low-Copy-Number IS6110 Mycobacterium tuberculosis Isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2453–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Donnelly, J.P.; Chen, S.C.; Kauffman, C.A.; Steinbach, W.J.; Baddley, J.W.; Verweij, P.E.; Clancy, C.J.; Wingard, J.R.; Lockhart, S.R.; Groll, A.H.; et al. Revision and Update of the Consensus Definitions of Invasive Fungal Disease From the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer and the Mycoses Study Group Education and Research Consortium. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitrago, M.J.; Bernal-Martínez, B.L.; Castelli, M.V.; Rodríguez-Tudela, J.L.; Cuenca-Estrella, M. Histoplasmosis and Paracoccidioidomycosis in a Non-Endemic Area: A Review of Cases and Diagnosis. J. Travel Med. 2010, 18, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Morant, D.; Sánchez-Montalvá, A.; Salvador, F.; Sao-Avilés, A.; Molina, I. Imported endemic mycoses in Spain: Evolution of hospitalized cases, clinical characteristics and correlation with migratory movements, 1997–2014. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Clinical Strains | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Species | Origin | Use in This Work |
| CNM-CM6019 | Histoplasma capsulatum | MRL (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-CM2721 | Histoplasma capsulatum | MRL (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-CM5659 | Histoplasma capsulatum | MRL (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-CM7057 | Histoplasma capsulatum | MRL (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-CL 2132 | Cryptococcus neoformans | MRL (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-CLH99 | Cryptococcus neoformans | MRL (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-CLWN99 | Cryptococcus neoformans | MRL (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-UM 405 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex | MU (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-UM 495 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex | MU (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-UM 76 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex | MU (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-UM 77 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex | MU (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-UM78 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex | MU (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-UM 81 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex | MU (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-UM 82 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex | MU (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-UM 102 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex | MU (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-UM 1596 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex | MU (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-UM 1689 | Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex | MU (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| CNM-CL 5719 | Candida albicans | MRL (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-CL 5683 | Candida parapsilosis | MRL (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-CL5742 | Candida tropicalis | MRL (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-CL3505 | Aspergillus terreus | MRL (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-CMAF237 | Aspergillus fumigatus | MRL (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-CM 3509 | Aspergillus flavus | MRL (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-CM 1627 | Scedosporium prolificans | MRL (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-CM 3035 | Fusarium solani | MRL (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-CM 3020 | Rhizopus oryzae | MRL (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-CM 4244 | Rhizopus microsporus | MRL (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-CM 2908 | Paracoccidioides brasiliensis | MRL (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-CM 2437 | Mucor spp. | MRL (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-UM 406 | Mycobacterium kansasii | MU (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-UM 407 | Mycobacterium avium | MU (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-UM 408 | Mycobacterium abscessus | MU (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-UM 409 | Mycobacterium gordonae | MU (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| CNM-UM 410 | Mycobacterium interjectum | MU (ISCIII) | Specificity |
| Plasmids | |||
| Name | Construction | Origin | Use in this work |
| pICJF * | PGEM-Easy plasmid+jellyfishderivedsequence [32] | MRL (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| pSG4 * | pGEMT-Easy plasmid+ mtLSU target region | MRL (ISCIII) | Standardization |
| Primer or Probe | Sequence |
|---|---|
| OliPJMitoc1 (f) | 5′-CAGAAGAATTGTGGTAAGTA-3′ |
| OliPJMitoc2 (r) | 5′-CGAGATATTCAGTGCTATAC-3′ |
| PJmitocMB | 5′-HEXCGCGATCCGGACTAGGATATAGCTGGTTGATCGCGBHQ1-3′ |
| Oli MTB IS6110 1 (f) | 5′-TAGTGCATTGTCATAGG-3′ |
| Oli MTB IS6110 2 (r) | 5′-GATCTCAGTACACATCGA-3′ |
| MTBIS6110MB | 5′-CY5.5CGCGATCATTACGCCGGGCTGACAGGTAATCAGATCGCG BHQ2-3′ |
| Disease (N° Samples) | Samples | MRT-PCR Positive Results | MC-PCR Positive Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Histoplasmosis (9) | Respiratory samples (3) | 2 | 3 |
| Biopsy (6) | 6 | 6 | |
| Total | 9 | 8 (88.8%) | 9 (100%) |
| Pneumocystosis (11) | BAL a (11) | 11 | 11 |
| Total | 11 | 11 (100%) | 11 (100%) |
| Cryptococcosis (5) | BAL b (1) | 1 | 1 |
| CSF c (1) | 1 | 1 | |
| Biopsy (3) | 3 | 3 | |
| Total | 5 | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) |
| Tuberculosis (17) | Respiratory samples (9) | 8 | 8 |
| Adenopathy (3) | 2 | 2 | |
| Abscess (2) | 1 | 1 | |
| FNAP d (2) | 1 | 1 | |
| Exudate (1) | 1 | 1 | |
| Total | 17 | 13 (76.4%) | 13 (76.4%) |
| TOTAL | 42 | 37 (88.1%) | 38 (90.4%) |
| Disease (Number of Samples) | Samples | MRT-PCR Results (Negatives/Total) |
|---|---|---|
| Aspergillosis (1) | BAS b (1) | 1/1 |
| Mucormycosis (2) | Biopsy (2) | 2/2 |
| Candidiasis (3) | Blood (1), CSF c (1), Biopsy (1) | 3/3 |
| Paracoccidioidomycosis (1) | Biopsy (1) | 1/1 |
| Negative a (4) | BAL d (3) BAS (1) | 4/4 |
| Total | 11 | 11/11 (100%) |
| Disease (Number of Samples) | Samples | MC-PCR Results (Negatives/Total) |
|---|---|---|
| Aspergillosis (8) | BAS b (5), BALc (1), Biopsy (2) | 6/8 |
| Mucormycosis (6) | Biopsy (5), CSF d (1) | 6/6 |
| Candidiasis (4) | Biopsy (2), CSF d (1), Blood (1) | 4/4 |
| Paracoccidioidomycosis (1) | Biopsy (1) | 1/1 |
| Negative a (14) | BAL c (9), BAS b (5) | 12/14 |
| Total | 33 | 28/33 (85%) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bernal-Martínez, L.; Herrera, L.; Valero, C.; de la Cruz, P.; Ghimpu, L.; Mesa-Arango, A.C.; Santoni, G.; Goterris, L.; Millán, R.; Buitrago, M.J. Differential Diagnosis of Fungal Pneumonias vs. Tuberculosis in AIDS Patients by Using Two New Molecular Methods. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7050336
Bernal-Martínez L, Herrera L, Valero C, de la Cruz P, Ghimpu L, Mesa-Arango AC, Santoni G, Goterris L, Millán R, Buitrago MJ. Differential Diagnosis of Fungal Pneumonias vs. Tuberculosis in AIDS Patients by Using Two New Molecular Methods. Journal of Fungi. 2021; 7(5):336. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7050336
Chicago/Turabian StyleBernal-Martínez, Leticia, Laura Herrera, Clara Valero, Paula de la Cruz, Larisa Ghimpu, Ana C. Mesa-Arango, Gabriela Santoni, Lidia Goterris, Rosario Millán, and María José Buitrago. 2021. "Differential Diagnosis of Fungal Pneumonias vs. Tuberculosis in AIDS Patients by Using Two New Molecular Methods" Journal of Fungi 7, no. 5: 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7050336
APA StyleBernal-Martínez, L., Herrera, L., Valero, C., de la Cruz, P., Ghimpu, L., Mesa-Arango, A. C., Santoni, G., Goterris, L., Millán, R., & Buitrago, M. J. (2021). Differential Diagnosis of Fungal Pneumonias vs. Tuberculosis in AIDS Patients by Using Two New Molecular Methods. Journal of Fungi, 7(5), 336. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7050336






