Abstract
Guidelines on the diagnosis and management of Aspergillus disease recommend a multi-test approach including CT scans, culture, fungal biomarker tests, microscopy and fungal PCR. The first-line treatment of confirmed invasive aspergillosis (IA) consists of drugs in the azole family; however, the emergence of azole-resistant isolates has negatively impacted the management of IA. Failure to detect azole-resistance dramatically increases the mortality rates of azole-treated patients. Despite drug susceptibility tests not being routinely performed currently, we suggest including resistance testing whilst diagnosing Aspergillus disease. Multiple tools, including DNA sequencing, are available to screen for drug-resistant Aspergillus in clinical samples. This is particularly beneficial as a large proportion of IA samples are culture negative, consequently impeding susceptibility testing through conventional methods. Pyrosequencing is a promising in-house DNA sequencing method that can rapidly screen for genetic hotspots associated with antifungal resistance. Pyrosequencing outperforms other susceptibility testing methods due to its fast turnaround time, accurate detection of polymorphisms within critical genes, including simultaneous detection of wild type and mutated sequences, and—most importantly—it is not limited to specific genes nor fungal species. Here we review current diagnostic methods and highlight the potential of pyrosequencing to aid in a diagnosis complete with a resistance profile to improve clinical outcomes.
1. Diagnosis of Aspergillosis
Aspergillosis is a fungal infection typically acquired via the inhalation of Aspergillus spores. It is most often caused by A. fumigatus and its various forms affect millions of people worldwide [1]. In immunocompetent hosts, these moulds cause a localized infection mainly in the lungs or paranasal sinuses. In immunocompromised individuals, the inhalation of spores can lead to a life-threatening invasive respiratory infection and dissemination to other organs. This invasive manifestation of aspergillosis (IA) is most life-threatening, with mortality rates varying between 50% when treated promptly and above 80% when the treatment is delayed [1,2,3,4,5].
When suspecting IA, the guidelines recommend a computed tomography (CT) scan to detect pulmonary infiltrates [6,7,8,9]. Nodules surrounded by a ground-glass attenuation (halo sign) and pleural effusions are classical CT findings of IA. Serum and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) samples should be sent for galactomannan (GM) testing and for PCR targeting Aspergillus-specific 18S rDNA [10,11]. Parallel testing for serum β-1-3-d-glucan (BDG) improves specific detection. When used in combination, these tests provide adequate sensitivity and specificity to guide antifungal treatment [6,8,12]. Direct microscopy of BAL or biopsy materials using fluorescent dyes can rapidly detect an invasive mould infection, but cannot provide a definitive diagnosis. Therefore, samples should also be sent for fungal culture, identification and susceptibility testing. However, culture is a slow and insensitive method, although its sensitivity can be improved by increasing the culture volume [13,14]. The EQUAL Aspergillosis Score 2018 is a stewardship tool summarising the key aspects of the ESCMID IA guidelines. [15].
A neutropenic haematology patient presenting with fever, chest pain and a cough, and suspected of IA when they are not responding to broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment, is a common clinical scenario. They typically have abnormal CT findings suggestive of IA; their serum and/or BAL is positive for one or more of the biomarkers, but the culture is reported with no fungal growth. The patient is started on first-line empiric treatment with voriconazole or isavuconazole [6,8]. With the rise of azole-resistant A. fumigatus strains, it is not rare that the patient fails to respond to the treatment due to antifungal resistance [16,17,18,19,20,21,22]. This is seen in patients who have been on azole prophylaxis (e.g., posaconazole) but increasingly also in azole-naïve patients. Annual surveys in five academic hospitals in the Netherlands showed that azole resistance in A. fumigatus has doubled from 2014 to 2018 [23,24]. Similar data have been reported worldwide [25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35], and an international resistance surveillance group has been set up by ISHAM/ECMM to capture more information on azole resistance worldwide [36,37].
Currently, the only method recommended by the guidelines to detect azole resistance in patients suspected of having an infection caused by azole-resistant A. fumigatus is susceptibility testing by culture [6,8,38,39]. However, more than half of BAL cultures are reported with no fungal growth and IA diagnosis is made based on radiology, fungal biomarker and molecular test results which do not provide information on resistance [40,41,42,43]. In these cases, failure to respond to treatment is often the only evidence of resistance to the given drugs. On the other hand, even in the case of a positive culture and access to susceptibility testing or resistance screening, the turnaround times for these culture-based methods are long, and the delivery of results in clinically useful time frame is challenging. Particularly in smaller centres, where susceptibility testing is not available on site, this timeline often exceeds one week [39,44].
The outcome of IA depends on the early initiation of effective treatment. This relies on rapid detection of antifungal resistance. Failure to detect azole resistance leads to significantly increased mortality rates in azole-treated patients [45]. Here, we describe the available methods for the detection of azole resistance in A. fumigatus, with a focus on a novel pyrosequencing-based method using the A. fumigatus cyp51A target. This method can detect any polymorphisms in critical genes, provide epidemiological data on azole resistance and also provide a quick and reliable diagnosis in culture-negative cases.
2. Azole Resistance
Mutations in genes involved in the A. fumigatus ergosterol biosynthetic pathway, including hmg1, erg6, cyp51A and cyp51B among others, are described as having a role in azole resistance [26,46,47,48,49,50,51]. The means for testing non-cyp51A-mediated mechanisms of resistance lag far behind and therefore, for the purpose of this discussion, we concentrate on cyp51A. Azole-resistant strains harbour genes with specific point mutations in combination or absence of tandem repeats in the promoter region. Aspergillus species are intrinsically resistant to fluconazole and ketoconazole due to a naturally occurring point mutation in cyp51A, encoding lanosterol 14-α-sterol demethylase [52]. Polymorphisms in cyp51A are frequently described as the main resistance mechanism arising from long-term azole use, associated with chronic aspergillosis [27,28,53]. Alternatively, the most common pan-azole resistance mechanism in A. fumigatus cyp51A was found to be a combination of a 34-bp long tandem repeat (TR) in the promoter region and a leucine-to-histidine change at codon 98, in short TR34/L98H [54,55,56,57,58,59]. The TR46/Y121F/T289A is a less widespread but emerging azole resistance mutation, which was first reported in the Netherlands in 2009 [60]. Both resistance mechanisms are regularly recovered from environmental isolates worldwide [31,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71], and therefore are likely to have developed resistance from the substantial use of environmental azole fungicides [31,55,69,72,73,74,75,76,77,78]. In 2017, the first azole-resistant A. fumigatus cyp51A TR46/Y121F/T289A mutant was isolated in the UK from a patient that had no prior history of azole antifungal use, suggesting resistance must have been acquired through the environment [79]. The global prevalence of environmental azole-resistant A. fumigatus strains is a major concern for all, but particularly susceptible patients.
Numerous single point mutations in A. fumigatus cyp51A lead to resistance, where the most common include amino acid substitutions of glycine at codon 54 (G54), proline at codon 216 (P216), phenylalanine at codon 219 (F219), methionine at codon 220 (M220), and glycine at codon 448 (G448) (Table 1) ([18,26,54,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93] and reviewed in [94]). Other resistance mechanisms are described to be a combination of point mutations or the less common TR53 [89,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102].

Table 1.
Overview of the known and emerging cyp51A-associated azole resistance mechanisms.
3. Molecular Techniques for Discerning cyp51A Resistance Polymorphisms
Molecular tests for the detection of azole-resistant cyp51A genotypes of A. fumigatus in clinical specimens have been developed over the past 20 years. Numerous in-house assays ranging from nested PCR, mixed-format and real-time PCR approaches have been developed and tested [103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110]. Other molecular approaches (reviewed in [105]) include the analysis of high resolution melt curves [111,112]. However, despite all this work, only three commercial kits are currently available (AsperGenius, PathoNostics, Maastricht, Netherlands, MycoGENIE, Ademtech, Pessac, France and Fungiplex® Aspergillus Azole-R IVD PCR, Bruker Daltonik GmbH, Bremen, Germany), attesting to the difficulty of developing robust molecular assays [113]. All three commercial real-time PCRs (RT-PCR) are designed to identify the promoter region insertion polymorphisms TR34/L98H and TR46/Y121F/T289A and specific alleles [109,114,115,116,117,118,119]. Approaches targeting polymorphisms in the cyp51A open reading frame (ORF, e.g., G54, M220, G138, G448) [120,121,122] have lagged behind.
Pyrosequencing is an alternative molecular method, which can be used to screen for all known polymorphisms [123]. This DNA sequencing technique has recently been optimised to screen clinical respiratory samples and A. fumigatus isolates for both insertion and ORF cyp51A-associated polymorphisms [124]. The efficacy of pyrosequencing to detect resistance in respiratory samples from patients with chronic pulmonary aspergillosis (CPA) was demonstrated in a recent audit of UK National Aspergillosis Centre (NAC) cases [125]. Resistance was identified in almost a quarter of culture negative samples, translating to a significant number of resistant cases that would have been missed had pyrosequencing not been used.
4. The Pyrosequencing Method
The pyrosequencing method is based on the ‘sequencing-by-synthesis’ principle and is widely used to detect epigenetic modifications in malignant cells and microbes but also to discover biomarkers [126,127]. The method relies on the detection of light that is released during nucleotide incorporation into the amplifying DNA (Figure 1). The first step in the assay for the detection of azole-resistant cyp51A genotypes of A. fumigatus, is to obtain the template DNA by PCR amplification of target gene fragments using genomic A. fumigatus DNA or patient respiratory samples. The sense strand must be labelled with 5′ biotin as biotinylated PCR products will bind to the streptavidin–sepharose beads and—since only one strand carries biotin—this promotes the generation of ssDNA template [128,129]. Once the ssDNA fragments are immobilized, the sequencing primer needs to be annealed to the template ssDNA and the pyrosequencing reaction can begin (Figure 1A). During the pyrosequencing reaction, pyrophosphate is released when a nucleotide is incorporated to the growing dsDNA product and is converted by sulfurolyase into ATP, which is then utilized by luciferase to produce light (Figure 1B). Nucleotides are added sequentially to the enzymes- and substrates mixture and, therefore, the sequence can be read as the reaction proceeds. The light peak on the pyrogram is proportional to the number of incorporated nucleotides. After every cycle, the enzyme apyrase degrades the excess nucleotides and regenerates the reaction solution for the next nucleotide [130], which can be added in a known order corresponding to the nucleotide sequence of the region or in an arbitrary, repeated order. Single point mutations can be identified by comparing the pyrogram of the synthesised DNA with that of the reference DNA. To summarise, completing one pyrosequencing run includes DNA extraction of the clinical sample, followed by PCR amplification of the four target gene fragments and ends with the pyrosequencing reactions of biotinylated PCR products (Figure 2).
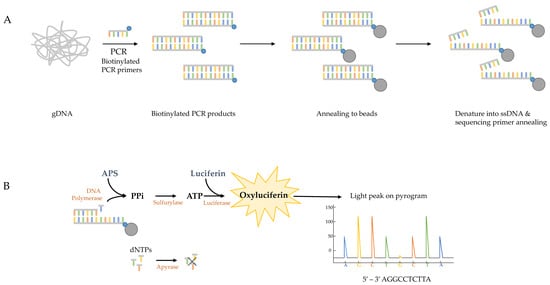
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the pyrosequencing method. (A) Genomic DNA (gDNA) of clinical samples or fungal isolates are used as template in the initial PCR with biotinylated (blue dots) primers. The biotinylated PCR products are immobilized by annealing to streptavidin-sepharose beads (grey dots). The DNA strands are then separated allowing the sequencing primer to anneal to the ssDNA templates. (B) The four enzymes (polymerase, sylfurylase, luciferase and apyrase) and two substrates (adenosine 5’ phosphosulfate (APS) and luciferin) promote the production of light after nucleotide incorporation in every cycle, resulting in light peaks on the pyrogram that are representative of the DNA sequence. The excess nucleotides are degraded after each cycle by apyrase and the reaction solution is rejuvenated for the incorporation of the next nucleotide.
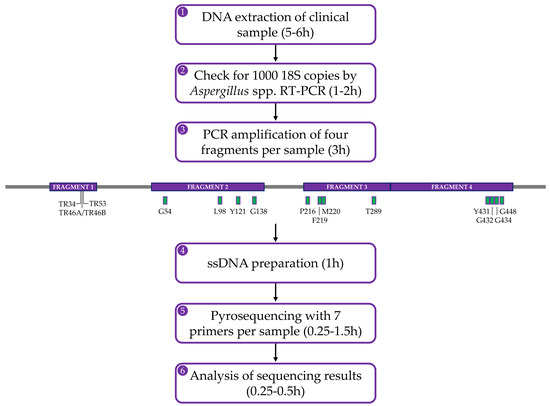
Figure 2.
Flowchart of the in-house pyrosequencing-based method showing the steps that are involved to complete one pyrosequencing experiment. The initial steps (1–3) to enable pyrosequencing require the detection of ample A. fumigatus genomic DNA. The cyp51A gene, including 550 bases upstream and 58 bases downstream of the ORF, is targeted as four fragments (from 235–427 bp in length) by endpoint PCR using biotinylated primers as shown in purple in the gene diagram (modified with SnapGene software from GSL Biotech; available at snapgene.com). TR sites are specified in fragment 1 and SNPs associated with resistance (green boxes) are indicated in fragments 2–4. Following confirmation of successful amplification, PCR products are processed (steps 4–5) using the PyroMark Q24 Advanced instrument, kit and accessories (Qiagen, GmBH, Hilden, Germany). Each fragment comprises at least two hotspots (or insertion in the case of the 5′ upstream fragment) which is sequenced individually. Pyrograms are analysed (step 6) manually against a reference A. fumigatus strain sequence.
This pyrosequencing assay generates reads of up to 150 bp per reaction and provides a large number of sequence reads in a single run, resulting in significant sampling depth. This allows the detection of not only the most numerous specific A. fumigatus cyp51A sequences, but also of the lower-abundance reads, which is especially important in processing clinical samples where there is a potential mixture of genomes from human tissue, fungal hyphae of different A. fumigatus genotypes, other fungi and other microorganisms. An advantage of this method is that PCR amplicons obtained by endpoint PCR do not need to be purified prior to setting up the pyrosequencing reactions, only checked for successful amplification by agarose gel electrophoresis. Furthermore, the limit of detection is similar to that of RT-PCR-based assays. In practice, clinical samples positive by Aspergillus spp. RT-PCR (>1000 18S copies equivalent to approximately 50 genomes) routinely yield successful pyrograms.
It is common that samples from patients with CPA on azole therapy remain negative in culture weeks after the onset of clinical deterioration later shown to be due to azole resistance. Therefore, a sensitive assay such as pyrosequencing can provide clinically useful results and have a significant impact on patient outcomes [14]. The in-house pyrosequencing-based assay is easily implemented within a molecular-based workflow and can be used to screen clinical samples directly within 11–14 h, from start (extraction) to finish (pyrogram analysis). This rapid turnaround time can help achieve a prompt diagnosis, resulting in more effective treatment and consequently reduce mortality and morbidity due to Aspergillus infections. The cyp51A screening method can also be utilised to monitor and report the local prevalence of cyp51A genotypes. In practice, we assay patients who are suspected of starting to fail therapy and follow up every time they produce a PCR-positive sample, something already shown to be important for regular monitoring of patient well-being [54].
A significant advantage of the pyrosequencing assay over RT-PCR strategies is that the method can be adapted to any gene or genomic region of interest. The current A. fumigatus PCR-based resistance assays do not reveal the less common or potential mutations involved in azole resistance. In Manchester, 43% of the azole-resistant patient isolates were reported to be non-cyp51A related [26] and numerous studies have revealed that azole resistance is most certainly due to other genes [46,47,48,49,50,51,131,132,133,134]. Besides gene mutations in the ergosterol biosynthesis pathway, other non-cyp51A-mediated resistance mechanisms involve the overexpression of drug efflux transporters such as ABC- and MFS-transporters [96,135,136,137]. Therefore, sequencing entire target genes can be more informative and can be done using the classical Sanger method or Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS). A small study of four azole-resistant A. fumigatus isolates using NGS revealed non-cyp51A polymorphisms including point mutations in SrbA, Mdr1, abcE, ERG3 and ERG24 and amino acid substitutions in HMG1, ERG3 and ERG24 [48]. Although most laboratories do not yet have the capacity to perform NGS in-house, pyrosequencing is relatively cost-effective because the approach is targeted to a specific region or ‘hot spot’ and requires less equipment (a thermal cycler for endpoint PCR and the PyroMark Q24 Advanced instrument).
Pyrosequencing is already an established technology for exploratory and testing in a broad range of disciplines, particularly those in which culture dependent methods are limited by insensitivity [138,139,140,141,142]. Moreover, in comparison to Sanger sequencing, pyrosequencing is favoured due to factors such as assay sensitivity, specificity, limit of detection, detection of rare and mixed mutations, turnaround time and costs [140,143]. Regular monitoring for resistance by pyrosequencing offers the potential for early appropriate drug therapy leading to better clinical outcomes, improved antifungal stewardship and cost savings. At the UK NAC, the annual cost of azole therapy was £2,049,900 in 2018/19 for 543 patients, a cost of approximately £3800 per patient to the UK National Health Service (NHS) [144]. A prevalence of approximately 5.3% azole resistance (indicated by Band 3 classification) indicates that, in addition to the patient benefit achieved by targeted drug therapy, a considerable cost saving could be made by avoiding unnecessary or inappropriate drug administration if samples were screened for resistance mechanisms parallel to standard diagnostic tests. One study found that the median time in which wildtype isolates develop azole resistance can be as short as 4 months in patients treated with azoles [54]. It is hoped that by screening patients with chronic forms of aspergillosis, who are on long term azole-antifungal therapy and at risk of acquiring azole resistance [145,146], we can capture drug resistance early.
5. Conclusions
In summary, the incidence of azole-resistant Aspergillus infections and the associated poor clinical outcomes make screening for resistance mechanisms crucial in the management of aspergillosis. A combination of tests is needed to assure effective treatment and allow antifungal stewardship. Commercially available PCR assays can be useful for time-pressing samples in smaller clinical laboratories, but the range of polymorphisms they are designed to detect is very limited. Pyrosequencing is a promising in-house DNA sequencing method that can be used to screen for genetic hotspots associated with antifungal resistance rapidly and is not limited to specific genes nor fungal species. The rise of antifungal resistance is ongoing, and new mutations associated with resistance might be missed without a sequence-based approach. In addition to the analysis of cyp51A, this method can easily be exploited to look at other genes that play a role in either azole resistance or resistance against other antifungal drugs. Laboratories that do not have real-time thermocyclers or the capacity for in-house sequencing should consider sending their samples for sequencing to either mycology reference centres or companies providing sequencing services. Rapid and reliable diagnosis is important for survival of IA patients and screening clinically relevant samples will provide important epidemiological data on A. fumigatus.
Author Contributions
All authors participated in literature review and writing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was co-funded by the NIHR Manchester Biomedical Research Centre and NHS England.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all members of the Mycology Reference Centre Manchester (MRCM) team and the National Aspergillosis Centre (NAC) team for their support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Brown, G.D.; Denning, D.W.; Gow, N.A.; Levitz, S.M.; Netea, M.G.; White, T.C. Hidden killers: Human fungal infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taccone, F.S.; Van den Abeele, A.M.; Bulpa, P.; Misset, B.; Meersseman, W.; Cardoso, T.; Paiva, J.A.; Blasco-Navalpotro, M.; De Laere, E.; Dimopoulos, G.; et al. Epidemiology of invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients: Clinical presentation, underlying conditions, and outcomes. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmidis, C.; Denning, D.W. The clinical spectrum of pulmonary aspergillosis. Thorax 2015, 70, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meersseman, W.; Vandecasteele, S.J.; Wilmer, A.; Verbeken, E.; Peetermans, W.E.; Van Wijngaerden, E. Invasive aspergillosis in critically ill patients without malignancy. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 170, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayr, A.; Lass-Florl, C. Epidemiology and antifungal resistance in invasive Aspergillosis according to primary disease: Review of the literature. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2011, 16, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patterson, T.F.; Thompson, G.R.; Denning, D.W.; Fishman, J.A.; Hadley, S.; Herbrecht, R.; Kontoyiannis, D.P.; Marr, K.A.; Morrison, V.A.; Nguyen, M.H.; et al. Practice Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Aspergillosis: 2016 Update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, e1–e60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinz, W.J.; Buchheidt, D.; Christopeit, M.; Von Lilienfeld-Toal, M.; Cornely, O.A.; Einsele, H.; Karthaus, M.; Link, H.; Mahlberg, R.; Neumann, S.; et al. Diagnosis and empirical treatment of fever of unknown origin (FUO) in adult neutropenic patients: Guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Working Party (AGIHO) of the German Society of Hematology and Medical Oncology (DGHO). Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 1775–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullmann, A.J.; Aguado, J.M.; Arikan-Akdagli, S.; Denning, D.W.; Groll, A.H.; Lagrou, K.; Lass-Florl, C.; Lewis, R.E.; Munoz, P.; Verweij, P.E.; et al. Diagnosis and management of Aspergillus diseases: Executive summary of the 2017 ESCMID-ECMM-ERS guideline. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, e1–e38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhnke, M.; Behre, G.; Buchheidt, D.; Christopeit, M.; Hamprecht, A.; Heinz, W.; Heussel, C.P.; Horger, M.; Kurzai, O.; Karthaus, M.; et al. Diagnosis of invasive fungal diseases in haematology and oncology: 2018 update of the recommendations of the infectious diseases working party of the German society for hematology and medical oncology (AGIHO). Mycoses 2018, 61, 796–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, P.M.; Steinmann, J. Overview of Commercially Available PCR Assays for the Detection of Aspergillus spp. DNA in Patient Samples. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruciani, M.; Mengoli, C.; Barnes, R.; Donnelly, J.P.; Loeffler, J.; Jones, B.L.; Klingspor, L.; Maertens, J.; Morton, C.O.; White, L.P. Polymerase chain reaction blood tests for the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis in immunocompromised people. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 9, CD009551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avni, T.; Levy, I.; Sprecher, H.; Yahav, D.; Leibovici, L.; Paul, M. Diagnostic accuracy of PCR alone compared to galactomannan in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid for diagnosis of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis: A systematic review. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 3652–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraczek, M.G.; Kirwan, M.B.; Moore, C.B.; Morris, J.; Denning, D.W.; Richardson, M.D. Volume dependency for culture of fungi from respiratory secretions and increased sensitivity of Aspergillus quantitative PCR. Mycoses 2014, 57, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergidis, P.; Moore, C.B.; Novak-Frazer, L.; Richardson, R.; Walker, A.; Denning, D.W.; Richardson, M.D. High-volume culture and quantitative real-time PCR for the detection of Aspergillus in sputum. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornely, O.A.; Koehler, P.; Arenz, D.S.C.M. EQUAL Aspergillosis Score 2018: An ECMM score derived from current guidelines to measure QUALity of the clinical management of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. Mycoses 2018, 61, 833–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linden, J.W.; Arendrup, M.C.; Warris, A.; Lagrou, K.; Pelloux, H.; Hauser, P.M.; Chryssanthou, E.; Mellado, E.; Kidd, S.E.; Tortorano, A.M.; et al. Prospective multicenter international surveillance of azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2015, 21, 1041–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verweij, P.E.; Chowdhary, A.; Melchers, W.J.; Meis, J.F. Azole Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus: Can We Retain the Clinical Use of Mold-Active Antifungal Azoles? Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 62, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Rubio, R.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Mellado, E. Triazole Resistance in Aspergillus Species: An Emerging Problem. Drugs 2017, 77, 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.C.; Hawkins, N.J.; Sanglard, D.; Gurr, S.J. Worldwide emergence of resistance to antifungal drugs challenges human health and food security. Science 2018, 360, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perlin, D.S.; Rautemaa-Richardson, R.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A. The global problem of antifungal resistance: Prevalence, mechanisms, and management. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2017, 17, e383–e392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buil, J.B.; Snelders, E.; Denardi, L.B.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Verweij, P.E. Trends in Azole Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus, the Netherlands, 1994–2016. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meis, J.F.; Chowdhary, A.; Rhodes, J.L.; Fisher, M.C.; Verweij, P.E. Clinical implications of globally emerging azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Greeff, S.C.; Mouton, J.W. Nethmap 2015: Consumption of Antimicrobial Agents and Antimicrobial Resistance Among Medically Important Bacteria in the Netherlands/MARAN 2015: Monitoring of Antimicrobial Resistance and Antibiotic Usage in Animals in the Netherlands in 2014; Rijksinstituut Voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu: Catharijnesingel, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- De Greeff, S.C.; Mouton, J.W.; Schoffelen, A.F.; Verduin, C.M. NethMap 2019: Consumption of Antimicrobial Agents and Antimicrobial Resistance Among Medically Important Bacteria in the Netherlands/Maran 2019: Monitoring of Antimicrobial Resistance and Antibiotic Usage in Animals in the Netherlands in 2018; Rijksinstituut Voor Volksgezondheid en Milieu: Catharijnesingel, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Abdolrasouli, A.; Petrou, M.A.; Park, H.; Rhodes, J.L.; Rawson, T.M.; Moore, L.S.P.; Donaldson, H.; Holmes, A.H.; Fisher, M.C.; Armstrong-James, D. Surveillance for Azole-Resistant Aspergillus fumigatus in a Centralized Diagnostic Mycology Service, London, United Kingdom, 1998–2017. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueid, A.; Howard, S.J.; Moore, C.B.; Richardson, M.D.; Harrison, E.; Bowyer, P.; Denning, D.W. Azole antifungal resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus: 2008 and 2009. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2010, 65, 2116–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, S.J.; Cerar, D.; Anderson, M.J.; Albarrag, A.; Fisher, M.C.; Pasqualotto, A.C.; Laverdiere, M.; Arendrup, M.C.; Perlin, D.S.; Denning, D.W. Frequency and evolution of Azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus associated with treatment failure. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denning, D.W.; Park, S.; Lass-Florl, C.; Fraczek, M.G.; Kirwan, M.; Gore, R.; Smith, J.; Bueid, A.; Moore, C.B.; Bowyer, P.; et al. High-frequency triazole resistance found in nonculturable Aspergillus fumigatus from lungs of patients with chronic fungal disease. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astvad, K.M.T.; Jensen, R.H.; Hassan, T.M.; Mathiasen, E.G.; Thomsen, G.M.; Pedersen, U.G.; Christensen, M.; Hilberg, O.; Arendrup, M.C. First detection of TR46/Y121F/T289A and TR34/L98H alterations in Aspergillus fumigatus isolates from azole-naive patients in Denmark despite negative findings in the environment. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 5096–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choukri, F.; Botterel, F.; Sitterlé, E.; Bassinet, L.; Foulet, F.; Guillot, J.; Costa, J.M.; Fauchet, N.; Dannaoui, E. Prospective evaluation of azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus clinical isolates in France. Med. Mycol. 2015, 53, 593–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rivero-Menendez, O.; Soto-Debran, J.C.; Medina, N.; Lucio, J.; Mellado, E.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A. Molecular Identification, Antifungal Susceptibility Testing, and Mechanisms of Azole Resistance in Aspergillus Species Received within a Surveillance Program on Antifungal Resistance in Spain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, e00865-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewell, T.R.; Zhu, J.; Rhodes, J.; Hagen, F.; Meis, J.F.; Fisher, M.C.; Jombart, T. Nonrandom Distribution of Azole Resistance across the Global Population of Aspergillus fumigatus. MBio 2019, 10, e00392-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermeulen, E.; Lagrou, K.; Verweij, P.E. Azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus: A growing public health concern. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 26, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiederhold, N.P.; Gil, V.G.; Gutierrez, F.; Lindner, J.R.; Albataineh, M.T.; McCarthy, D.I.; Sanders, C.; Fan, H.; Fothergill, A.W.; Sutton, D.A. First Detection of TR34 L98H and TR46 Y121F T289A Cyp51 Mutations in Aspergillus fumigatus Isolates in the United States. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2016, 54, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Feng, C.-L.; Chen, F.; He, Q.; Su, X.; Shi, Y. Triazole Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus Clinical Isolates Obtained in Nanjing, China. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2017, 130, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Resendiz Sharpe, A.; Lagrou, K.; Meis, J.F.; Chowdhary, A.; Lockhart, S.R.; Verweij, P.E. Triazole resistance surveillance in Aspergillus fumigatus. Med. Mycol. 2018, 56, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, P.E.; Lestrade, P.P.A.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Meis, J.F. Azole resistance surveillance in Aspergillus fumigatus: Beneficial or biased? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2079–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arikan-Akdagli, S.; Ghannoum, M.; Meis, J.F. Antifungal Resistance: Specific Focus on Multidrug Resistance in Candida auris and Secondary Azole Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinea, J.; Verweij, P.E.; Meletiadis, J.; Mouton, J.W.; Barchiesi, F.; Arendrup, M.C. Subcommittee on Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of the E.E.C.f.A.S.T. How to: EUCAST recommendations on the screening procedure E.Def 10.1 for the detection of azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus isolates using four-well azole-containing agar plates. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestrade, P.P.; Van der Velden, W.; Bouwman, F.; Stoop, F.J.; Blijlevens, N.M.A.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Verweij, P.E.; Donnelly, J.P. Epidemiology of invasive aspergillosis and triazole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus in patients with haematological malignancies: A single-centre retrospective cohort study. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohno, S.; Izumikawa, K.; Ogawa, K.; Kurashima, A.; Okimoto, N.; Amitani, R.; Kakeya, H.; Niki, Y.; Miyazaki, Y. Intravenous micafungin versus voriconazole for chronic pulmonary aspergillosis: A multicenter trial in Japan. J. Infect. 2010, 61, 410–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, G.M.; Van der Beek, M.T.; Von dem Borne, P.A.; Boelens, J.; Steel, E.; Kampinga, G.A.; Span, L.F.; Lagrou, K.; Maertens, J.A.; Dingemans, G.J.; et al. PCR-based detection of Aspergillus fumigatus Cyp51A mutations on bronchoalveolar lavage: A multicentre validation of the AsperGenius assay(R) in 201 patients with haematological disease suspected for invasive aspergillosis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 3528–3535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meersseman, W.; Lagrou, K.; Maertens, J.; Wilmer, A.; Hermans, G.; Vanderschueren, S.; Spriet, I.; Verbeken, E.; Van Wijngaerden, E. Galactomannan in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid: A tool for diagnosing aspergillosis in intensive care unit patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2008, 177, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L.; Alcazar-Fuoli, L.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Monzon, A.; Mellado, E.; Cuenca-Estrella, M. Time of incubation for antifungal susceptibility testing of Aspergillus fumigatus: Can MIC values be obtained at 24 h? Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 4502–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lestrade, P.P.A.; Meis, J.F.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Verweij, P.E. Triazole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus: Recent insights and challenges for patient management. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, D.; Arai, T.; Takahashi, H.; Kusuya, Y.; Watanabe, A.; Kamei, K. Non-cyp51A Azole-Resistant Aspergillus fumigatus Isolates with Mutation in HMG-CoA Reductase. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 1889–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buied, A.; Moore, C.B.; Denning, D.W.; Bowyer, P. High-level expression of cyp51B in azole-resistant clinical Aspergillus fumigatus isolates. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 512–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, C.; Nelson-Sathi, S.; Singh, A.; Radhakrishna Pillai, M.; Chowdhary, A. Genomic perspective of triazole resistance in clinical and environmental Aspergillus fumigatus isolates without cyp51A mutations. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2019, 132, 103265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, S.; Cramer, R.A. Regulation of Sterol Biosynthesis in the Human Fungal Pathogen Aspergillus fumigatus: Opportunities for Therapeutic Development. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybak, J.M.; Ge, W.; Wiederhold, N.P.; Parker, J.E.; Kelly, S.L.; Rogers, P.D.; Fortwendel, J.R. Mutations in hmg1, Challenging the Paradigm of Clinical Triazole Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. MBio 2019, 10, e00437-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahanshiri, Z.; Shams-Ghahfarokhi, M.; Asghari-Paskiabi, F.; Saghiri, R.; Razzaghi-Abyaneh, M. α-Bisabolol inhibits Aspergillus fumigatus Af239 growth via affecting microsomal ∆(24)-sterol methyltransferase as a crucial enzyme in ergosterol biosynthesis pathway. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 33, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardelli, F.; Macedo, D.; Dudiuk, C.; Cabeza, M.S.; Gamarra, S.; Garcia-Effron, G. Aspergillus fumigatus Intrinsic Fluconazole Resistance Is Due to the Naturally Occurring T301I Substitution in Cyp51Ap. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 5420–5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linden, J.W.M.; Snelders, E.; Kampinga, G.A.; Rijnders, B.J.A.; Mattsson, E.; Debets-Ossenkopp, Y.J.; Kuijper, E.J.; Van Tiel, F.H.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Verweij, P.E. Clinical implications of azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus, The Netherlands, 2007-2009. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2011, 17, 1846–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camps, S.M.; Van der Linden, J.W.; Li, Y.; Kuijper, E.J.; Van Dissel, J.T.; Verweij, P.E.; Melchers, W.J. Rapid induction of multiple resistance mechanisms in Aspergillus fumigatus during azole therapy: A case study and review of the literature. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snelders, E.; Camps, S.M.; Karawajczyk, A.; Schaftenaar, G.; Kema, G.H.; Van der Lee, H.A.; Klaassen, C.H.; Melchers, W.J.; Verweij, P.E. Triazole fungicides can induce cross-resistance to medical triazoles in Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snelders, E.; Camps, S.M.; Karawajczyk, A.; Rijs, A.J.; Zoll, J.; Verweij, P.E.; Melchers, W.J. Genotype-phenotype complexity of the TR46/Y121F/T289A cyp51A azole resistance mechanism in Aspergillus fumigatus. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2015, 82, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snelders, E.; Van der Lee, H.A.; Kuijpers, J.; Rijs, A.J.; Varga, J.; Samson, R.A.; Mellado, E.; Donders, A.R.; Melchers, W.J.; Verweij, P.E. Emergence of azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus and spread of a single resistance mechanism. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellado, E.; Garcia-Effron, G.; Alcazar-Fuoli, L.; Melchers, W.J.; Verweij, P.E.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L. A new Aspergillus fumigatus resistance mechanism conferring in vitro cross-resistance to azole antifungals involves a combination of cyp51A alterations. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2007, 51, 1897–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buil, J.B.; Hagen, F.; Chowdhary, A.; Verweij, P.E.; Meis, J.F. Itraconazole, Voriconazole, and Posaconazole CLSI MIC Distributions for Wild-Type and Azole-Resistant Aspergillus fumigatus Isolates. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Linden, J.W.; Camps, S.M.; Kampinga, G.A.; Arends, J.P.; Debets-Ossenkopp, Y.J.; Haas, P.J.; Rijnders, B.J.; Kuijper, E.J.; Van Tiel, F.H.; Varga, J.; et al. Aspergillosis due to voriconazole highly resistant Aspergillus fumigatus and recovery of genetically related resistant isolates from domiciles. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, A.; Kathuria, S.; Xu, J.; Sharma, C.; Sundar, G.; Singh, P.K.; Gaur, S.N.; Hagen, F.; Klaassen, C.H.; Meis, J.F. Clonal expansion and emergence of environmental multiple-triazole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus strains carrying the TR(3)(4)/L98H mutations in the cyp51A gene in India. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsopoulou, A.; Posso, R.; Vale, L.; Bebb, S.; Johnson, E.; White, P.L. Determination of the Prevalence of Triazole Resistance in Environmental Aspergillus fumigatus Strains Isolated in South Wales, UK. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, A.; Sharma, C.; Van den Boom, M.; Yntema, J.B.; Hagen, F.; Verweij, P.E.; Meis, J.F. Multi-azole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus in the environment in Tanzania. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 2979–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocchi, S.; Poncot, M.; Morin-Crini, N.; Laboissiere, A.; Valot, B.; Godeau, C.; Lechenault-Bergerot, C.; Reboux, G.; Crini, G.; Millon, L. Determination of azole fungal residues in soils and detection of Aspergillus fumigatus-resistant strains in market gardens of Eastern France. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 32015–32023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riat, A.; Plojoux, J.; Gindro, K.; Schrenzel, J.; Sanglard, D. Azole Resistance of Environmental and Clinical Aspergillus fumigatus Isolates from Switzerland. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e02088-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, O.; Tunnermann, J.; Dudakova, A.; Tangwattanachuleeporn, M.; Weig, M.; Gross, U. Environmental isolates of azole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus in Germany. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 4356–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, E.; Maertens, J.; Schoemans, H.; Lagrou, K. Azole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus due to TR46/Y121F/T289A mutation emerging in Belgium, July 2012. Euro Surveill. 2012, 17, 20326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chowdhary, A.; Kathuria, S.; Randhawa, H.S.; Gaur, S.N.; Klaassen, C.H.; Meis, J.F. Isolation of multiple-triazole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus strains carrying the TR/L98H mutations in the cyp51A gene in India. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhary, A.; Sharma, C.; Kathuria, S.; Hagen, F.; Meis, J.F. Azole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus with the environmental TR46/Y121F/T289A mutation in India. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 555–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lockhart, S.R.; Frade, J.P.; Etienne, K.A.; Pfaller, M.A.; Diekema, D.J.; Balajee, S.A. Azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus isolates from the ARTEMIS global surveillance study is primarily due to the TR/L98H mutation in the cyp51A gene. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 4465–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, K.L.; Mellado, E.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L.; Johansen, H.K.; Arendrup, M.C. Environmental study of azole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus and other aspergilli in Austria, Denmark, and Spain. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 4545–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowyer, P.; Denning, D.W. Environmental fungicides and triazole resistance in Aspergillus. Pest. Manag Sci. 2014, 70, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buil, J.B.; Hare, R.K.; Zwaan, B.J.; Arendrup, M.C.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Verweij, P.E. The fading boundaries between patient and environmental routes of triazole resistance selection in Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS Pathog 2019, 15, e1007858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromley, M.J.; Van Muijlwijk, G.; Fraczek, M.G.; Robson, G.; Verweij, P.E.; Denning, D.W.; Bowyer, P. Occurrence of azole-resistant species of Aspergillus in the UK environment. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2014, 2, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verweij, P.E.; Snelders, E.; Kema, G.H.J.; Mellado, E.; Melchers, W.J.G. Azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus: A side-effect of environmental fungicide use? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2009, 9, 789–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Jin, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Lin, D.; Yu, Y. Fungicides induced triazole-resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus associated with mutations of TR46/Y121F/T289A and its appearance in agricultural fields. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 326, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stensvold, C.R.; Jørgensen, L.N.; Arendrup, M.C. Azole-Resistant Invasive Aspergillosis: Relationship to Agriculture. Curr. Fungal Infect. Rep. 2012, 6, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoustra, S.E.; Debets, A.J.M.; Rijs, A.J.M.M.; Zhang, J.; Snelders, E.; Leendertse, P.C.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Rietveld, A.G.; Zwaan, B.J.; Verweij, P.E. Environmental Hotspots for Azole Resistance Selection of Aspergillus fumigatus, the Netherlands. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, C.B.; Novak-Frazer, L.; Muldoon, E.; Dunn, K.W.; Masania, R.; Richardson, M.D.; Rautemaa-Richardson, R. First isolation of the pan-azole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus cyp51A TR46/Y121F/T289A mutant in a UK patient. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2017, 49, 512–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Ferreira, M.E.; Capellaro, J.L.; Dos Reis Marques, E.; Malavazi, I.; Perlin, D.; Park, S.; Anderson, J.B.; Colombo, A.L.; Arthington-Skaggs, B.A.; Goldman, M.H.; et al. In vitro evolution of itraconazole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus involves multiple mechanisms of resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 4405–4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.E.d.S.; Colombo, A.L.; Paulsen, I.; Ren, Q.; Wortman, J.; Huang, J.; Goldman, M.H.S.; Goldman, G.H. The ergosterol biosynthesis pathway, transporter genes, and azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43, S313–S319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, P.A.; Parmegiani, R.M.; Wei, S.Q.; Mendrick, C.A.; Li, X.; Loebenberg, D.; DiDomenico, B.; Hare, R.S.; Walker, S.S.; McNicholas, P.M. Mutations in Aspergillus fumigatus resulting in reduced susceptibility to posaconazole appear to be restricted to a single amino acid in the cytochrome P450 14alpha-demethylase. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 577–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, S.E.; Goeman, E.; Meis, J.F.; Slavin, M.A.; Verweij, P.E. Multi-triazole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus infections in Australia. Mycoses 2015, 58, 350–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mellado, E.; Garcia-Effron, G.; Alcazar-Fuoli, L.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L. Substitutions at methionine 220 in the 14alpha-sterol demethylase (Cyp51A) of Aspergillus fumigatus are responsible for resistance in vitro to azole antifungal drugs. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 2747–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, O.; Weig, M.; Reichard, U.; Lugert, R.; Kuhns, M.; Christner, M.; Held, J.; Peter, S.; Schumacher, U.; Buchheidt, D.; et al. cyp51A-Based mechanisms of Aspergillus fumigatus azole drug resistance present in clinical samples from Germany. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 3513–3517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregson, L.; Goodwin, J.; Johnson, A.; McEntee, L.; Moore, C.B.; Richardson, M.; Hope, W.W.; Howard, S.J. In vitro susceptibility of Aspergillus fumigatus to isavuconazole: Correlation with itraconazole, voriconazole, and posaconazole. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5778–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan Natesan, S.; Wu, W.; Cutright, J.L.; Chandrasekar, P.H. In vitro-in vivo correlation of voriconazole resistance due to G448S mutation (cyp51A gene) in Aspergillus fumigatus. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2012, 74, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellete, B.; Raberin, H.; Morel, J.; Flori, P.; Hafid, J.; Manhsung, R.T. Acquired resistance to voriconazole and itraconazole in a patient with pulmonary aspergilloma. Med. Mycol. 2010, 48, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albarrag, A.M.; Anderson, M.J.; Howard, S.J.; Robson, G.D.; Warn, P.A.; Sanglard, D.; Denning, D.W. Interrogation of related clinical pan-azole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus strains: G138C, Y431C, and G434C single nucleotide polymorphisms in cyp51A, upregulation of cyp51A, and integration and activation of transposon Atf1 in the cyp51A promoter. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2011, 55, 5113–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alanio, A.; Sitterle, E.; Liance, M.; Farrugia, C.; Foulet, F.; Botterel, F.; Hicheri, Y.; Cordonnier, C.; Costa, J.M.; Bretagne, S. Low prevalence of resistance to azoles in Aspergillus fumigatus in a French cohort of patients treated for haematological malignancies. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Guerra, T.M.; Mellado, E.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L. A point mutation in the 14alpha-sterol demethylase gene cyp51A contributes to itraconazole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 1120–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, E.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Zoll, J.; Brown, A.J.P.; Verweij, P.E.; Warris, A. In-host microevolution of Aspergillus fumigatus: A phenotypic and genotypic analysis. Fungal Genet. Biol. FG B 2018, 113, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escribano, P.; Peláez, T.; Muñoz, P.; Bouza, E.; Guinea, J. Is azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus a problem in Spain? Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2815–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero-Menendez, O.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A.; Mellado, E.; Cuenca-Estrella, M. Triazole Resistance in Aspergillus spp.: A Worldwide Problem? J. Fungi 2016, 2, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodiamont, C.J.; Dolman, K.M.; Ten Berge, I.J.; Melchers, W.J.; Verweij, P.E.; Pajkrt, D. Multiple-azole-resistant Aspergillus fumigatus osteomyelitis in a patient with chronic granulomatous disease successfully treated with long-term oral posaconazole and surgery. Med. Mycol. 2009, 47, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Cantero, A.; Lopez-Fernandez, L.; Guarro-Artigas, J.; Capilla, J. Update and recent advances on azole resistance mechanisms in Aspergillus. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescar, J.; Meyer, I.; Akshita, K.; Srinivasaraghavan, K.; Verma, C.; Palous, M.; Mazier, D.; Datry, A.; Fekkar, A. Aspergillus fumigatus harbouring the sole Y121F mutation shows decreased susceptibility to voriconazole but maintained susceptibility to itraconazole and posaconazole. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2014, 69, 3244–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snelders, E.; Karawajczyk, A.; Schaftenaar, G.; Verweij, P.E.; Melchers, W.J.G. Azole resistance profile of amino acid changes in Aspergillus fumigatus CYP51A based on protein homology modeling. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 2425–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, S.J.; Webster, I.; Moore, C.B.; Gardiner, R.E.; Park, S.; Perlin, D.S.; Denning, D.W. Multi-azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2006, 28, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zeng, R.; Zhang, L.; Li, D.; Lv, G.; Shen, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, N.; et al. Multiple cyp51A-based mechanisms identified in azole-resistant isolates of Aspergillus fumigatus from China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2015, 59, 4321–4325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snelders, E.; Huis In t Veld, R.A.G.; Rijs, A.J.M.M.; Kema, G.H.J.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Verweij, P.E. Possible environmental origin of resistance of Aspergillus fumigatus to medical triazoles. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 4053–4057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, R.K.; Gertsen, J.B.; Astvad, K.M.T.; Degn, K.B.; Løkke, A.; Stegger, M.; Andersen, P.S.; Kristensen, L.; Arendrup, M.C. In Vivo Selection of a Unique Tandem Repeat Mediated Azole Resistance Mechanism (TR(120)) in Aspergillus fumigatus cyp51A, Denmark. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2019, 25, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, J.D.; Spiess, B.; Buchheidt, D.; Hoenigl, M. (New) Methods for Detection of Aspergillus fumigatus Resistance in Clinical Samples. Curr. Fungal Infect. Rep. 2019, 13, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buil, J.B.; Zoll, J.; Verweij, P.E.; Melchers, W.J.G. Molecular Detection of Azole-Resistant Aspergillus fumigatus in Clinical Samples. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudakova, A.; Spiess, B.; Tangwattanachuleeporn, M.; Sasse, C.; Buchheidt, D.; Weig, M.; Groß, U.; Bader, O. Molecular Tools for the Detection and Deduction of Azole Antifungal Drug Resistance Phenotypes in Aspergillus Species. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 30, 1065–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiess, B.; Seifarth, W.; Merker, N.; Howard, S.J.; Reinwald, M.; Dietz, A.; Hofmann, W.K.; Buchheidt, D. Development of novel PCR assays to detect azole resistance-mediating mutations of the Aspergillus fumigatus cyp51A gene in primary clinical samples from neutropenic patients. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 3905–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernal-Martínez, L.; Gago, S.; Buitrago, M.J.; Gomez-Lopez, A.; Rodríguez-Tudela, J.L.; Cuenca-Estrella, M. Analysis of performance of a PCR-based assay to detect DNA of Aspergillus fumigatus in whole blood and serum: A comparative study with clinical samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2011, 49, 3596–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Meije, Y.; Diaz-Pedroche, C.; Gomez-Lopez, A.; Buitrago, M.J.; Bernal-Martinez, L.; Grande, C.; Juan, R.S.; Lizasoain, M.; Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L.; et al. Value of serial quantification of fungal DNA by a real-time PCR-based technique for early diagnosis of invasive Aspergillosis in patients with febrile neutropenia. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 47, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Postina, P.; Skladny, J.; Boch, T.; Cornely, O.A.; Hamprecht, A.; Rath, P.M.; Steinmann, J.; Bader, O.; Miethke, T.; Dietz, A.; et al. Comparison of Two Molecular Assays for Detection and Characterization of Aspergillus fumigatus Triazole Resistance and Cyp51A Mutations in Clinical Isolates and Primary Clinical Samples of Immunocompromised Patients. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Garnaud, C.; Brenier-Pinchart, M.-P.; Thiébaut-Bertrand, A.; Saint-Raymond, C.; Camara, B.; Hamidfar, R.; Cognet, O.; Maubon, D.; Cornet, M.; et al. Direct Molecular Diagnosis of Aspergillosis and CYP51A Profiling from Respiratory Samples of French Patients. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal-Martinez, L.; Gil, H.; Rivero-Menendez, O.; Gago, S.; Cuenca-Estrella, M.; Mellado, E.; Alastruey-Izquierdo, A. Development and Validation of a High-Resolution Melting Assay To Detect Azole Resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, e01083-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuohy, M.J.; Reja, V.; Park, S.; Perlin, D.S.; Wnek, M.; Procop, G.W.; Yen-Lieberman, B. Use of a high-resolution melt assay to characterize codon 54 of the cyp51A gene of Aspergillus fumigatus on a Rotor-Gene 6000 instrument. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 2248–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alanio, A.; Bretagne, S. Performance evaluation of multiplex PCR including Aspergillus-not so simple! Med. Mycol. 2017, 55, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauwvlieghe, A.F.A.D.; Vonk, A.G.; Buddingh, E.P.; Hoek, R.A.S.; Dalm, V.A.; Klaassen, C.H.W.; Rijnders, B.J.A. Detection of azole-susceptible and azole-resistant Aspergillus coinfection by cyp51A PCR amplicon melting curve analysis. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2017, 72, 3047–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- White, P.L.; Posso, R.B.; Barnes, R.A. Analytical and Clinical Evaluation of the PathoNostics AsperGenius Assay for Detection of Invasive Aspergillosis and Resistance to Azole Antifungal Drugs Directly from Plasma Samples. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2356–2366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, G.L.; Van de Sande, W.W.; Dingemans, G.J.; Gaajetaan, G.R.; Vonk, A.G.; Hayette, M.P.; Van Tegelen, D.W.; Simons, G.F.; Rijnders, B.J. Validation of a new Aspergillus real-time PCR assay for direct detection of Aspergillus and azole resistance of Aspergillus fumigatus on bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montesinos, I.; Argudin, M.A.; Hites, M.; Ahajjam, F.; Dodemont, M.; Dagyaran, C.; Bakkali, M.; Etienne, I.; Jacobs, F.; Knoop, C.; et al. Culture-Based Methods and Molecular Tools for Azole-Resistant Aspergillus fumigatus Detection in a Belgian University Hospital. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dannaoui, E.; Gabriel, F.; Gaboyard, M.; Lagardere, G.; Audebert, L.; Quesne, G.; Godichaud, S.; Verweij, P.E.; Accoceberry, I.; Bougnoux, M.E. Molecular Diagnosis of Invasive Aspergillosis and Detection of Azole Resistance by a Newly Commercialized PCR Kit. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 3210–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulska, M.; Furfaro, E.; De Carolis, E.; Drago, E.; Pulzato, I.; Borghesi, M.L.; Zappulo, E.; Raiola, A.M.; Grazia, C.D.; Del Bono, V.; et al. Use of Aspergillus fumigatus real-time PCR in bronchoalveolar lavage samples (BAL) for diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis, including azole-resistant cases, in high risk haematology patients: The need for a combined use with galactomannan. Med. Mycol. 2019, 57, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balashov, S.V.; Gardiner, R.; Park, S.; Perlin, D.S. Rapid, high-throughput, multiplex, real-time PCR for identification of mutations in the cyp51A gene of Aspergillus fumigatus that confer resistance to itraconazole. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garcia-Effron, G.; Dilger, A.; Alcazar-Fuoli, L.; Park, S.; Mellado, E.; Perlin, D.S. Rapid detection of triazole antifungal resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, Y.; Stensvold, C.R.; Perlin, D.S.; Arendrup, M.C. Azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus from bronchoalveolar lavage fluid samples of patients with chronic diseases. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trama, J.P.; Mordechai, E.; Adelson, M.E. Detection of Aspergillus fumigatus and a mutation that confers reduced susceptibility to itraconazole and posaconazole by real-time PCR and pyrosequencing. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 906–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Novak-Frazer, L.H.D.; Hill, S.; Masania, R.; Denning, D.W.; Moore, C.; Rautemaa-Richardson, R.; Richardson, M. Profiling Aspergillus Fumigatus Cyp51a Polymorphisms by Pyrosequencing Reveals Triazole Resistance When Susceptibility Testing is Not Possible; ECCMID: Madrid, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, L.; Rautemaa-Richardson, R.; Novak-Frazer, L.; Hill, S.; Hassan, D.; Richardson, M.D.; Gangneux, J.-P.; Lortholary, O.; Cornely, O.A.; Pagano, L. Identification of Cyp51A-mediated triazole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus using pyrosequencing: An audit of UK National Aspergillosis Centre cases. In Proceedings of the 9th Trends in Medical Mycology, Nice, France, 11–14 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Florea, A. Pyrosequencing and Its Application in Epigenetic Clinical Diagnostics. Epigenetic Biomarkers and Diagnostics; Academic Press: Cambridge, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Wiederhold, N.P.; Grabinski, J.L.; Garcia-Effron, G.; Perlin, D.S.; Lee, S.A. Pyrosequencing to detect mutations in FKS1 that confer reduced echinocandin susceptibility in Candida albicans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 4145–4148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Royo, J.L.; Galan, J.J. Pyrosequencing for SNP genotyping. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009, 578, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronaghi, M. Pyrosequencing sheds light on DNA sequencing. Genome Res. 2001, 11, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiagen. PyroMark® Q24 Advanced and PyroMark Q24 Advanced CpG Reagents Handbook. Available online: https://www.qiagen.com/us/products/instruments-and-automation/pyrosequencing/consumables/pyromark-q24-advanced-accessories-and-reagents/#orderinginformation (accessed on 9 December 2019).
- Camps, S.M.T.; Dutilh, B.E.; Arendrup, M.C.; Rijs, A.J.M.M.; Snelders, E.; Huynen, M.A.; Verweij, P.E.; Melchers, W.J.G. Discovery of a HapE mutation that causes azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus through whole genome sequencing and sexual crossing. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballard, E.; Weber, J.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Tammireddy, S.; Whitfield, P.D.; Brakhage, A.A.; Brown, A.J.P.; Verweij, P.E.; Warris, A. Recreation of in-host acquired single nucleotide polymorphisms by CRISPR-Cas9 reveals an uncharacterised gene playing a role in Aspergillus fumigatus azole resistance via a non-cyp51A mediated resistance mechanism. Fungal Genet. Biol. FG B 2019, 130, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hortschansky, P.; Haas, H.; Huber, E.M.; Groll, M.; Brakhage, A.A. The CCAAT-binding complex (CBC) in Aspergillus species. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2017, 1860, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Chen, P.; Gao, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, A.; Liu, F.; Lu, L. Screening and Characterization of a Non-cyp51A Mutation in an Aspergillus fumigatus cox10 Strain Conferring Azole Resistance. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 61, e02101–e02116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraczek, M.G.; Bromley, M.; Buied, A.; Moore, C.B.; Rajendran, R.; Rautemaa, R.; Ramage, G.; Denning, D.W.; Bowyer, P. The cdr1B efflux transporter is associated with non-cyp51a-mediated itraconazole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 1486–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneau, I.; Coste, A.T.; Sanglard, D. Identification of Aspergillus fumigatus multidrug transporter genes and their potential involvement in antifungal resistance. Med. Mycol. 2016, 54, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Liu, J.; Zeng, M.; Sang, H. Exploring the molecular mechanism of azole resistance in Aspergillus fumigatus. J. Mycol. Med. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Damaschke, N.; Yao, T.; McCormick, J.; Wagner, J.; Jarrard, D. Pyrosequencing for accurate imprinted allele expression analysis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 116, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Castillo, F.Y.; Loera-Muro, A.; Jacques, M.; Garneau, P.; Avelar-González, F.J.; Harel, J.; Guerrero-Barrera, A.L. Waterborne pathogens: Detection methods and challenges. Pathogens 2015, 4, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siqueira, J.F., Jr.; Fouad, A.F.; Rôças, I.N. Pyrosequencing as a tool for better understanding of human microbiomes. J. Oral Microbiol. 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chikamatsu, K.; Aono, A.; Hata, H.; Igarashi, Y.; Takaki, A.; Yamada, H.; Sakashita, K.; Mitarai, S. Evaluation of PyroMark Q24 pyrosequencing as a method for the identification of mycobacteria. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 90, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, H.; Deng, Y.-M.; Xu, X.; Sessions, W.; Barr, I.G. Rapid detection of new B/Victoria-lineage haemagglutinin variants of influenza B viruses by pyrosequencing. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2019, 93, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Mehta, A.; Panigrahi, M.K.; Nath, S.; Saikia, K.K. NPM1 Mutation Analysis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Comparison of Three Techniques-Sanger Sequencing, Pyrosequencing, and Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction. Turk. J. Haematol. 2018, 35, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chronic Pulmonary Aspergillus Annual Report 2018/2019. Available online: https://aspergillosis.org/nac-reports/ (accessed on 13 December 2019).
- Chowdhary, A.; Kathuria, S.; Xu, J.; Meis, J.F. Emergence of azole-resistant aspergillus fumigatus strains due to agricultural azole use creates an increasing threat to human health. PLoS Pathog. 2013, 9, e1003633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, D.; Watanabe, A.; Kamei, K.; Goldman, G.H. Epidemiological and Genomic Landscape of Azole Resistance Mechanisms in Aspergillus Fungi. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).