Understanding Pathogenesis and Care Challenges of Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in Fungal Infections
Abstract
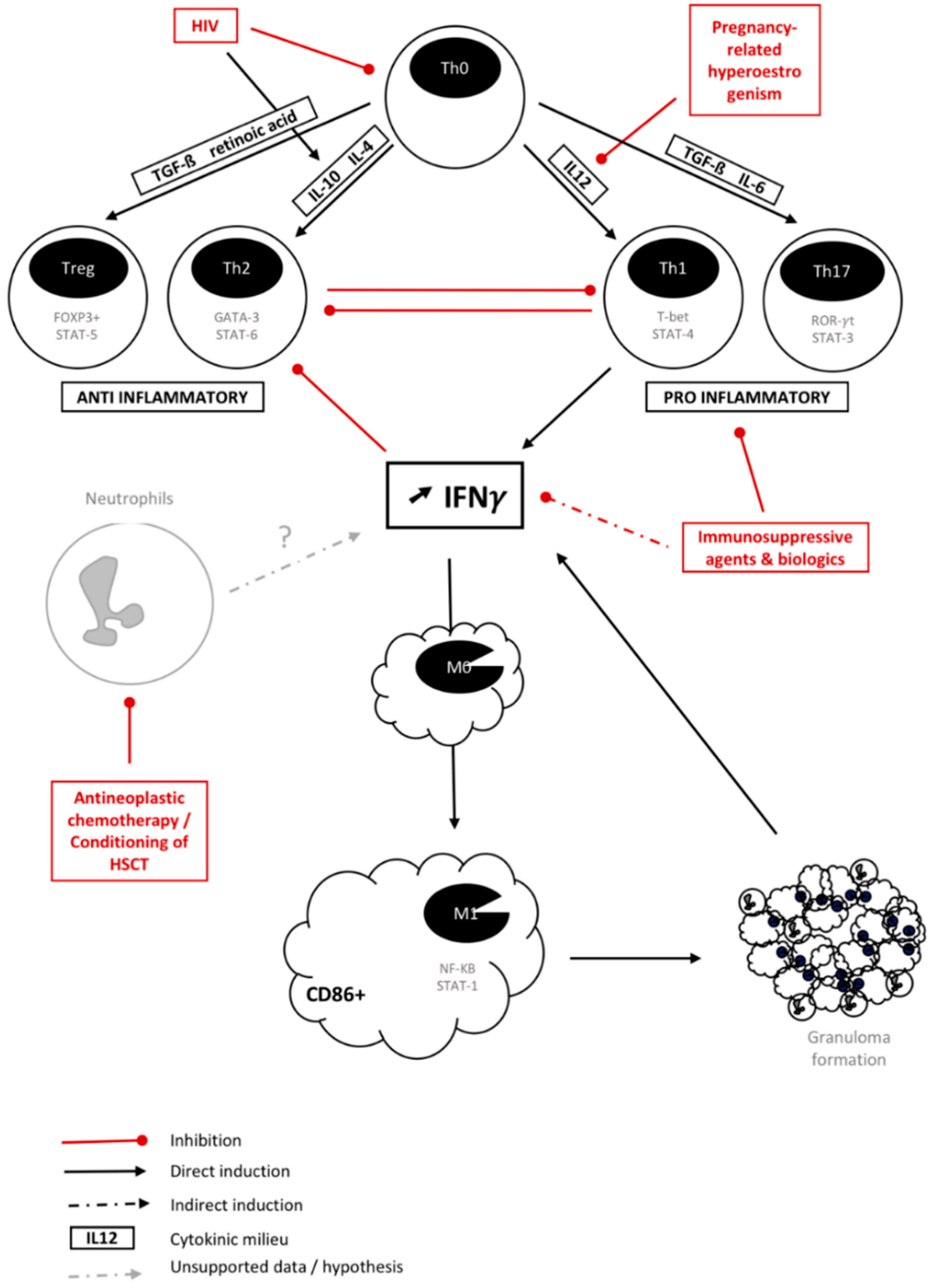
:1. Introduction
2. Fungal-Pathogen-Associated IRIS Characteristics
2.1. Cryptococcus
2.2. Candida
2.3. Aspergillus
2.4. Histoplasma
2.5. Pneumocystis jiroveci
2.6. Other Fungi
3. Is There a Common Background for Fungal IRIS?
4. A Limited Therapeutic Arsenal Against IRIS
5. Predict and Prevent: The Cornerstone of IRIS Management Today
5.1. Prediction with Diagnostic Markers
5.2. Prevention by Delaying and/or Tapering Immune Restoration
6. Conclusions/Perspective
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Enoch, D.A.; Yang, H.; Aliyu, S.H.; Micallef, C. The changing epidemiology of invasive fungal infections. Meth. Mol. Biol. 2017, 1508, 17–65. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, N.; Lortholary, O.; Alexander, B.D.; Gupta, K.L.; John, G.T.; Pursell, K.; Muñoz, P.; Klintmalm, G.B.; Stosor, V.; del Busto, R.; et al. An immune reconstitution syndrome-like illness associated with Cryptococcus neoformans infection in organ transplant recipients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 1756–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.Y.; Singh, N. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in non-HIV immunocompromised patients. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 22, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Perfect, J.R. Immune reconstitution syndrome and exacerbation of infections after pregnancy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, M.A. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: A reappraisal. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddow, L.J.; Colebunders, R.; Meintjes, G.; Lawn, S.D.; Elliott, J.H.; Manabe, Y.C.; Bohjanen, P.R.; Sungkanuparph, S.; Easterbrook, P.J.; French, M.A.; et al. Cryptococcal immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in HIV-1-infected individuals: Proposed clinical case definitions. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfect, J.R.; Dismukes, W.E.; Dromer, F.; Goldman, D.L.; Graybill, J.R.; Hamill, R.J.; Harrison, T.S.; Larsen, R.A.; Lortholary, O.; Nguyen, M.H.; et al. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of cryptococcal disease: 2010 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 291–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beardsley, J.; Wolbers, M.; Kibengo, F.M.; Ggayi, A.-B.M.; Kamali, A.; Cuc, N.T.K.; Binh, T.Q.; Chau, N.V.V.; Farrar, J.; Merson, L.; et al. Adjunctive Dexamethasone in HIV-Associated Cryptococcal Meningitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 542–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Legris, T.; Massad, M.; Purgus, R.; Vacher-Coponat, H.; Ranque, S.; Girard, N.; Berland, Y.; Moal, V. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome mimicking relapsing cryptococcal meningitis in a renal transplant recipient. Transplant Infect. Dis. 2010, 13, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Sifri, C.D.; Silveira, F.P.; Miller, R.; Gregg, K.S.; Huprikar, S.; Lease, E.D.; Zimmer, A.; Dummer, J.S.; Spak, C.W.; et al. Cryptococcosis in patients with cirrhosis of the liver and posttransplant outcomes. Transplantation 2015, 99, 2132–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.Y.; Alexander, B.D.; Huprikar, S.; Forrest, G.N.; Bruno, D.; Lyon, G.M.; Wray, D.; Johnson, L.B.; Sifri, C.D.; Razonable, R.R.; et al. Predictors of immune reconstitution syndrome in organ transplant recipients with cryptococcosis: Implications for the management of immunosuppression. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 60, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Lortholary, O.; Alexander, B.D.; Gupta, K.L.; John, G.T.; Pursell, K.; Muñoz, P.; Klintmalm, G.B.; Stosor, V.; Limaye, A.P.; et al. Allograft loss in renal transplant recipients with Cryptococcus neoformans associated immune reconstitution syndrome. Transplantation 2005, 80, 1131–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanternier, F.; Chandesris, M.O.; Poiree, S.; Bougnoux, M.E.; Mechai, F.; Mamzer-Bruneel, M.F.; Viard, J.P.; Galmiche-Rolland, L.; Lecuit, M.; Lortholary, O. Cellulitis revealing a Cryptococcosis-related immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in a renal allograft recipient. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 2826–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhein, J.; Bahr, N.C.; Morawski, B.M.; Schutz, C.; Zhang, Y.; Finkelman, M.; Meya, D.B.; Meintjes, G.; Boulware, D.R. Detection of high cerebrospinal fluid levels of (1→3)-β-d-Glucan in cryptococcal meningitis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2014, 1, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhein, J.; Bahr, N.C.; Hemmert, A.C.; Cloud, J.L.; Bellamkonda, S.; Oswald, C.; Lo, E.; Nabeta, H.; Kiggundu, R.; Akampurira, A.; et al. Diagnostic performance of a multiplex PCR assay for meningitis in an HIV-infected population in Uganda. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 84, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ecevit, I.Z.; Clancy, C.J.; Schmalfuss, I.M.; Nguyen, M.H. The poor prognosis of central nervous system cryptococcosis among nonimmunosuppressed patients: A call for better disease recognition and evaluation of adjuncts to antifungal therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2006, 42, 1443–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somerville, L.K.; Henderson, A.P.; Chen, S.C.A.; Kok, J. Successful treatment of Cryptococcus neoformans immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in an immunocompetent host using thalidomide. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2015, 7, 12–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.C.A.; Meyer, W.; Sorrell, T.C. Cryptococcus gattii infections. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 980–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rammaert, B.; Desjardins, A.; Lortholary, O. New insights into hepatosplenic candidosis, a manifestation of chronic disseminated candidosis. Mycoses 2012, 55, e74–e84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttila, V.J.; Lamminen, A.E.; Bondestam, S.; Korhola, O.; Färkkilä, M.; Sivonen, A.; Ruutu, T.; Ruutu, P. Magnetic resonance imaging is superior to computed tomography and ultrasonography in imaging infectious liver foci in acute leukaemia. Eur. J. Haematol. 1996, 56, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hot, A.; Maunoury, C.; Poiree, S.; Lanternier, F.; Viard, J.P.; Loulergue, P.; Coignard, H.; Bougnoux, M.E.; Suarez, F.; Rubio, M.T.; et al. Diagnostic contribution of positron emission tomography with [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose for invasive fungal infections. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rammaert, B.; Candon, S.; Maunoury, C.; Bougnoux, M.-E.; Jouvion, G.; Braun, T.; Correas, J.-M.; Lortholary, O. Thalidomide for steroid-dependent chronic disseminated candidiasis after stem cell transplantation: A case report. Transplant Infect. Dis. 2016, 19, e12637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, N.; Mazoyer, E.; Porcher, R.; Raffoux, E.; Suarez, F.; Ribaud, P.; Lortholary, O.; Molina, J.M. Hepatosplenic candidiasis in the era of new antifungal drugs: A study in Paris 2000-2007. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, E185–E187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, M.; Al-Ramadi, B.; Bernsen, R.; Kristensen, J.; Alizadeh, H.; Hedstrom, U. Prospective evaluation of mannan and anti-mannan antibodies for diagnosis of invasive Candida infections in patients with neutropenic fever. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todeschini, G.; Murari, C.; Bonesi, R.; Pizzolo, G.; Verlato, G.; Tecchio, C.; Meneghini, V.; Franchini, M.; Giuffrida, C.; Perona, G.; Bellavite, P. Invasive aspergillosis in neutropenic patients: Rapid neutrophil recovery is a risk factor for severe pulmonary complications. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 29, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miceli, M.H.; Maertens, J.; Buvé, K.; Grazziutti, M.; Woods, G.; Rahman, M.; Barlogie, B.; Anaissie, E.J. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in cancer patients with pulmonary aspergillosis recovering from neutropenia: Proof of principle, description, and clinical and research implications. Cancer 2007, 110, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, N.; Suarez, J.F.; Avery, R.; Lass-Flörl, C.; Geltner, C.; Pasqualotto, A.C.; Lyon, G.M.; Barron, M.; Husain, S.; Wagener, M.M.; Montoya, J.G. Immune reconstitution syndrome-like entity in lung transplant recipients with invasive aspergillosis. Transplant Immunol. 2013, 29, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.; Hong, H.-L.; Lee, S.-O.; Choi, S.-H.; Kim, Y.S.; Woo, J.H.; Kim, S.-H. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in neutropenic patients with invasive pulmonary aspergillosis. J. Infect. 2015, 70, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiprono, S.K.; Masenga, J.E. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: Cutaneous and bone histoplasmosis mimicking leprosy after treatment. J. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 03, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiggundu, R.; Nabeta, H.W.; Okia, R.; Rhein, J.; Lukande, R. Unmasking histoplasmosis immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in a patient recently started on antiretroviral therapy. ACR 2016, 6, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passos, L.; Talhari, C.; Santos, M.; Ribeiro-Rodrigues, R.; Ferreira, L.C.D.L.; Talhari, S. Histoplasmosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. An Bras. Dermatol. 2011, 86, S168–S172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jazwinski, A.; Naggie, S.; Perfect, J. Immune reconstitution syndrome in a patient with disseminated histoplasmosis and steroid taper: Maintaining the perfect balance. Mycoses 2011, 54, 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergidis, P.; Avery, R.K.; Wheat, L.J.; Dotson, J.L.; Assi, M.A.; Antoun, S.A.; Hamoud, K.A.; Burdette, S.D.; Freifeld, A.G.; McKinsey, D.S.; et al. Histoplasmosis complicating tumor necrosis factor–α blocker therapy: A retrospective analysis of 98 cases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breton, G.; Adle-Biassette, H.; Therby, A.; Ramanoelina, J.; Choudat, L.; Bissuel, F.; Huerre, M.; Dromer, F.; Dupont, B.; Lortholary, O. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in HIV-infected patients with disseminated histoplasmosis. AIDS 2006, 20, 119–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edman, J.C.; Kovacs, J.A.; Masur, H.; Santi, D.V.; Elwood, H.J.; Sogin, M.L. Ribosomal RNA sequence shows Pneumocystis carinii to be a member of the fungi. Nature 1988, 334, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.F.; Limper, A.H. Current insights into the biology and pathogenesis of Pneumocystis pneumonia. Nat. Rev. Micro. 2007, 5, 298–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-W.; Heo, J.Y.; Lee, Y.-M.; Kim, S.J.; Jeong, H.W. Unmasking granulomatous Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia with nodular opacity in an HIV-infected patient after initiation of antiretroviral therapy. Yonsei Med. J. 2016, 57, 1042–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barry, S.M.; Lipman, M.C.I.; Deery, A.R.; Johnson, M.A.; Janossy, G. Immune reconstitution pneumonitis following Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in HIV-infected subjects. HIV Med. 2002, 3, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.K.; Cheng, V.C.; Tang, B.S.; Hung, I.F.; Lee, R.A.; Hui, D.S.; Yuen, K.Y. The unmasking of Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia during reversal of immunosuppression: Case reports and literature review. BMC Infect. Dis. 2004, 4, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, H.P.; Hart, E.; Venkatesan, P. Early development of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome related to Pneumocystis pneumonia after antiretroviral therapy. Int J STD AIDS 2014, 25, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, M.C.B.; Silva, C.I.S.; Ellis, J.; Phillips, P.; Müller, N.L. Organizing pneumonia as a manifestation of Pneumocystis jiroveci immune reconstitution syndrome in HIV-positive patients: Report of 2 cases. J. Thorac. Imaging 2008, 23, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wislez, M.; Bergot, E.; Antoine, M.; Parrot, A.; Carette, M.; Mayaud, C.; Cadranel, J. Acute Respiratory Failure Following HAART Introduction in Patients Treated for Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2001, 164, 847–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanio, A.; Hauser, P.M.; Lagrou, K.; Melchers, W.J.G.; Helweg-Larsen, J.; Matos, O.; Cesaro, S.; Maschmeyer, G.; Einsele, H.; Donnelly, J.P.; et al. ECIL guidelines for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in patients with haematological malignancies and stem cell transplant recipients. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2016, 71, 2386–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, S.; Polatino, S.; Estrada-Y-Martin, R.M. Pneumocystis-associated organizing pneumonia as a manifestation of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in an HIV-infected individual with a normal CD4+ T-cell count following antiretroviral therapy. Int. J. STD AIDS 2009, 20, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleindienst, R.; Fend, F.; Prior, C.; Margreiter, R.; Vogel, W. Bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia associated with Pneumocystis carinii infection in a liver transplant patient receiving tacrolimus. Clin. Transplant. 1999, 13, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, N.; Soans, B. Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia associated with Pneumocystis carinii infection and sirolimus therapy in a renal transplant patient. Australas. Radiol. 2006, 50, 68–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, C.; Hajjawi, R.; Barlow, G.; Thaker, H.; Adams, K.; Moss, P. Penicillium marneffei presenting as an immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) in a patient with advanced HIV. BMJ Case Rep. 2013, 2013, bcr2012007555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudjaritruk, T.; Sirisanthana, T.; Sirisanthana, V. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome from Penicillium marneffei in an HIV-infected child: A case report and review of literature. BMC Infect. Dis. 2012, 12, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, L.; Nath, R.; Hazarika, D.; Mahanta, J. Atypical cutaneous lesions of Penicillium marneffei infection as a manifestation of the immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome after highly active antiretroviral therapy. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2010, 76, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, A.; Shankland, G.S.; Seaton, R.A. Penicillium marneffei infection presenting as an immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in an HIV patient. Int. J. STD AIDS 2010, 21, 780–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, N.T.; Vinh, L.D.; Liem, N.T.; Shikuma, C.; Day, J.N.; Thwaites, G.; Le, T. Clinical features of three patients with paradoxical immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome associated with Talaromyces marneffei infection. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2018, 19, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortimer, R.B.; Libke, R.; Eghbalieh, B.; Bilello, J.F. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome presenting as superior vena cava syndrome secondary to Coccidioides lymphadenopathy in an HIV-infected patient. J. Int. Assoc. Physicians AIDS Care 2008, 7, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, S.M.; Roza, T.H. HIV Immune Recovery Inflammatory Syndrome and Central Nervous System Paracoccidioidomycosis. Mycopathologia 2016, 182, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galhardo, M.C.G.; Silva, M.T.T.; Lima, M.A.; Nunes, E.P.; Schettini, L.E.C.; de Freitas, R.F.; de Almeida Paes, R.; de Sousa Neves, E.; do Valle, A.C.F. Sporothrix schenckii meningitis in AIDS during immune reconstitution syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2010, 81, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dony, A.; Perpoint, T.; Ducastelle, S.; Ferry, T. Disseminated fusariosis with immune reconstitution syndrome and cracking mycotic aortic aneurysm in a 55-year-old patient with acute myeloid leukaemia. BMJ Case Rep. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crombie, K.; Spengane, Z.; Locketz, M.; Dlamini, S.; Lehloenya, R.; Wasserman, S.; Maphanga, T.G.; Govender, N.P.; Kenyon, C.; Schwartz, I.S. Paradoxical worsening of Emergomyces africanus infection in an HIV-infected male on itraconazole and antiretroviral therapy. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, F.; Lecuit, M.; Dupont, B.; Bellaton, E.; Huerre, M.; Rohrlich, P.S.; Lortholary, O. Adjuvant corticosteroid therapy for chronic disseminated candidiasis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 46, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lortholary, O.; Fontanet, A.; Mémain, N.; Martin, A.; Sitbon, K.; Dromer, F.; French Cryptococcosis Study Group. Incidence and risk factors of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome complicating HIV-associated cryptococcosis in France. AIDS 2005, 19, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bettelli, E.; Korn, T.; Oukka, M.; Kuchroo, V.K. Induction and effector functions of TH17 cells. Nature 2008, 453, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, C.T.; Hatton, R.D. Interplay between the TH17 and TReg cell lineages: A (co-)evolutionary perspective. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 883–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, C.T.; Hatton, R.D.; Mangan, P.R.; Harrington, L.E. IL-17 Family Cytokines and the Expanding Diversity of Effector T Cell Lineages. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 25, 821–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, F.O.; Gordon, S. The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: Time for reassessment. F1000Prime Rep 2014, 6, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shearer, G.M. HIV-Induced immunopathogenesis. Immunity 1998, 9, 587–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, Y. The changes in the T helper 1 (Th1) and T helper 2 (Th2) cytokine balance during HIV-1 infection are indicative of an allergic response to viral proteins that may be reversed by Th2 cytokine inhibitors and immune response modifiers-a review and hypothesis. Virus Genes 2004, 28, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; He, M.; Wang, Y.; Liao, A.-H. Modulators of the Balance between M1 and M2 Macrophages during Pregnancy. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiodras, S.; Samonis, G.; Boumpas, D.T.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Fungal Infections Complicating Tumor Necrosis Factor α Blockade Therapy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 181–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasunami, Y.; Kojo, S.; Kitamura, H.; Toyofuku, A.; Satoh, M.; Nakano, M.; Nabeyama, K.; Nakamura, Y.; Matsuoka, N.; Ikeda, S.; et al. Vα14 NK T cell–triggered IFN-γ production by Gr-1 +CD11b +cells mediates early graft loss of syngeneic transplanted islets. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, J.L.; Chan, J.; Lin, P.L. Macrophages and control of granulomatous inflammation in tuberculosis. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Das, P.; Rampal, R.; Udinia, S.; Kumar, T.; Pilli, S.; Wari, N.; Ahmed, I.K.; Kedia, S.; Gupta, S.D.; Kumar, D.; et al. Selective M1 macrophage polarization in granuloma-positive and granuloma-negative Crohn’s disease, in comparison to intestinal tuberculosis. Intest. Res. 2018, 16, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Blondel, G.; Mars, L.T.; Liblau, R.S. Pathogenesis of the immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in HIV-infected patients. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 25, 312–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, J.; Boasso, A.; Velilla, P.A.; Zhang, R.; Vaccari, M.; Franchini, G.; Shearer, G.M.; Andersson, J.; Chougnet, C. HIV-1-driven regulatory T-cell accumulation in lymphoid tissues is associated with disease progression in HIV/AIDS. Blood 2006, 108, 3808–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montes, M.; Sanchez, C.; Lewis, D.E.; Graviss, E.A.; Seas, C.; Gotuzzo, E.; White, A.C. Jr. Normalization of FoxP3+ Regulatory T Cells in Response to Effective Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 203, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seddiki, N.; Sasson, S.C.; Santner-Nanan, B.; Munier, M.; van Bockel, D.; Ip, S.; Marriott, D.; Pett, S.; Nanan, R.; Cooper, D.A.; et al. Proliferation of weakly suppressive regulatory CD4+ T cells is associated with over-active CD4+ T-cell responses in HIV-positive patients with mycobacterial immune restoration disease. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ingram, P.R.; Howman, R.; Leahy, M.F.; Dyer, J.R. Cryptococcal Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome following Alemtuzumab Therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 44, e115–e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otahbachi, M.; Nugent, K. Granulomatous Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia in a patient with chronic lymphocytic leukemia: A literature review and hypothesis on pathogenesis. Phytochemistry. 2007, 333, 131–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Huang, L.; Sung, S.-S.J.; Lobo, P.I.; Brown, M.G.; Gregg, R.K.; Engelhard, V.H.; Okusa, M.D. NKT cell activation mediates neutrophil IFN-gamma production and renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 5899–5911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Cassatella, M.A.; Costantini, C.; Jaillon, S. Neutrophils in the activation and regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, M.; Maggi, L.; Micheletti, A.; Lazzeri, E.; Tamassia, N.; Costantini, C.; Cosmi, L.; Lunardi, C.; Annunziato, F.; Romagnani, S.; et al. Evidence for a cross-talk between human neutrophils and Th17 cells. Blood 2010, 115, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elenkov, I.J.; Wilder, R.L.; Bakalov, V.K.; Link, A.A.; Dimitrov, M.A.; Fisher, S.; Crane, M.; Kanik, K.S.; Chrousos, G.P. IL-12, TNF-alpha, and hormonal changes during late pregnancy and early postpartum: Implications for autoimmune disease activity during these times. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4933–4938. [Google Scholar]
- Bellocchio, S.; Gaziano, R.; Bozza, S.; Rossi, G.; Montagnoli, C.; Perruccio, K.; Calvitti, M.; Pitzurra, L.; Romani, L. Liposomal amphotericin B activates antifungal resistance with reduced toxicity by diverting Toll-like receptor signalling from TLR-2 to TLR-4. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2005, 55, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben-Ami, R.; Lewis, R.E.; Kontoyiannis, D.P. Immunocompromised Hosts: Immunopharmacology of Modern Antifungals. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gil-Lamaignere, C.; Roilides, E.; Maloukou, A.; Georgopoulou, I.; Petrikkos, G.; Walsh, T.J. Amphotericin B lipid complex exerts additive antifungal activity in combination with polymorphonuclear leucocytes against Scedosporium prolificans and Scedosporium apiospermum. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2002, 50, 1027–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roilides, E.; Lyman, C.A.; Filioti, J.; Akpogheneta, O.; Sein, T.; Lamaignere, C.G.; Petraitiene, R.; Walsh, T.J. Amphotericin B Formulations Exert Additive Antifungal Activity in Combination with Pulmonary Alveolar Macrophages and Polymorphonuclear Leukocytes against Aspergillus fumigatus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 1974–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simitsopoulou, M.; Roilides, E.; Maloukou, A.; Gil-Lamaignere, C.; Walsh, T.J. Interaction of amphotericin B lipid formulations and triazoles with human polymorphonuclear leucocytes for antifungal activity against Zygomycetes. Mycoses 2008, 51, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voelz, K.; May, R.C. Cryptococcal Interactions with the Host Immune System. Eukaryotic Cell 2010, 9, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wiesner, D.L.; Moskalenko, O.; Corcoran, J.M.; McDonald, T.; Rolfes, M.A.; Meya, D.B.; Kajumbula, H.; Kambugu, A.; Bohjanen, P.R.; Knight, J.F.; et al. Cryptococcal genotype influences immunologic response and human clinical outcome after meningitis. mBio 2012, 3, e00196-12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desnos-Ollivier, M.; Patel, S.; Spaulding, A.R.; Charlier, C.; Garcia-Hermoso, D.; Nielsen, K.; Dromer, F. Mixed infections and in vivo evolution in the human fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans. mBio 2010, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanio, A.; Gits-Muselli, M.; Mercier-Delarue, S.; Dromer, F.; Bretagne, S. Diversity of Pneumocystis jirovecii during infection revealed by ultra-deep pyrosequencing. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, P.; Morahan, G.; Huang, D.; Stone, E.; Cheong, K.Y.M.; Castley, A.; Rodgers, M.; McIntyre, M.Q.; Abraham, L.J.; French, M.A. Polymorphisms in cytokine genes define subpopulations of HIV-1 patients who experienced immune restoration diseases. AIDS 2002, 16, 2043–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogola, G.O.; Ouma, C.; Jura, W.G.; Muok, E.O.; Colebunders, R.; Mwinzi, P.N. A non-synonymous polymorphism in IL-23R Gene (rs1884444) is associated with reduced risk to schistosomiasis-associated Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in a Kenyan population. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 14, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.H.; Foster, C.B.; Taylor, J.G.; Erichsen, H.C.; Chen, R.A.; Walsh, T.J.; Anttila, V.-J.; Ruutu, T.; Palotie, A.; Chanock, S.J. Association between chronic disseminated candidiasis in adult acute leukemia and common IL4 promoter haplotypes. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 187, 1153–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narendran, G.; Kavitha, D.; Karunaianantham, R.; Gil-Santana, L.; Almeida-Junior, J.L.; Reddy, S.D.; Kumar, M.M.; Hemalatha, H.; Jayanthi, N.N.; Ravichandran, N.; et al. Role of LTA4H Polymorphism in Tuberculosis-Associated Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome Occurrence and Clinical Severity in Patients Infected with HIV. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meintjes, G.; Scriven, J.; Marais, S. Management of the Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep 2012, 9, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhen, T.; Cidlowski, J.A. Anti-inflammatory action of glucocorticoids—New mechanisms for old drugs. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 1711–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahid, P.; Dorman, S.E.; Alipanah, N.; Barry, P.M.; Brozek, J.L.; Cattamanchi, A.; Chaisson, L.H.; Chaisson, R.E.; Daley, C.L.; Grzemska, M.; et al. Official American Thoracic Society/Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/Infectious Diseases Society of America Clinical Practice Guidelines: Treatment of Drug-Susceptible Tuberculosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, e147–e195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meintjes, G.; Wilkinson, R.J.; Morroni, C.; Pepper, D.J.; Rebe, K.; Rangaka, M.X.; Oni, T.; Maartens, G. Randomized placebo-controlled trial of prednisone for paradoxical tuberculosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. AIDS 2010, 24, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caillot, D.; Couaillier, J.F.; Bernard, A.; Casasnovas, O.; Denning, D.W.; Mannone, L.; Lopez, J.; Couillault, G.; Piard, F.; Vagner, O.; et al. Increasing volume and changing characteristics of invasive pulmonary aspergillosis on sequential thoracic computed tomography scans in patients with neutropenia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 19, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, G.; Cervera, C.; Michelena, J.; Marco, F.; Moreno, A.; Navasa, M. Immune reconstitution syndrome after voriconazole treatment for cryptococcal meningitis in a liver transplant recipient. Liver Transplant. 2008, 14, 1671–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Montaner, J.S.G. Corticosteroids Prevent Early Deterioration in Patients with Moderately Severe Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia and the Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). Ann. Intern. Med. 1990, 113, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabria, S.; Barakat, L.; Ogbuagu, O. Steroid-exacerbated HIV-associated cutaneous Kaposi’s sarcoma immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: “Where a good intention turns bad”. Int. J. STD AIDS 2016, 27, 1026–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Sánchez, M.; Iglesias, M.C.; Ablanedo-Terrazas, Y.; Ormsby, C.E.; Alvarado-De La Barrera, C.; Reyes-Terán, G. Steroids are a risk factor for Kaposi’s sarcoma-immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome and mortality in HIV infection. AIDS 2016, 30, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackmore, T.K.; Manning, L.; Taylor, W.J.; Wallis, R.S. Therapeutic Use of Infliximab in Tuberculosis to Control Severe Paradoxical Reaction of the Brain and Lymph Nodes. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2008, 47, e83–e85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, D.C.; Faldetta, K.F.; Pei, L.; Sheikh, V.; Utay, N.S.; Roby, G.; Rupert, A.; Fauci, A.S.; Sereti, I. A paradoxical treatment for a paradoxical condition: Infliximab use in three cases of mycobacterial IRIS. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 62, 258–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lwin, N.; Boyle, M.; Davis, J.S. Adalimumab for Corticosteroid and Infliximab-Resistant Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in the Setting of TB/HIV Coinfection. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2018, 5, ofy027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaube, G.; De Castro, N.; Gueguen, A.; Lascoux, C.; Zagdanski, A.M.; Alanio, A.; Molina, J.M. Treatment with adalimumab for severe immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in an HIV-infected patient presenting with cryptococcal meningitis. Medecine et Maladies Infectieuses 2016, 46, 154–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sitapati, A.M.; Kao, C.L.; Cachay, E.R.; Masoumi, H.; Wallis, R.S.; Mathews, W.C. Treatment of HIV-Related Inflammatory Cerebral Cryptococcoma with Adalimumab. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, e7–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunel, A.-S.; Reynes, J.; Tuaillon, E.; Rubbo, P.-A.; Lortholary, O.; Montes, B.; Le Moing, V.; Makinson, A. Thalidomide for steroid-dependent immune reconstitution inflammatory syndromes during AIDS. AIDS 2012, 26, 2110–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaplan, J.E.; Benson, C.; Holmes, K.K.; Brooks, J.T.; Pau, A.; Masur, H. Guidelines for prevention and treatment of opportunistic infections in HIV-infected adults and adolescents: Recommendations from CDC, the National Institutes of Health, and the HIV Medicine Association of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. MMR Recomm. Rep. 2009, 58, 1–207. [Google Scholar]
- Bergman, P.W.; Björkhem-Bergman, L. Is there a role for statins in fungal infections? Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2014, 11, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; Singh, N. Potential role of statins for the management of immune reconstitution syndrome. Med. Hypotheses 2011, 76, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tleyjeh, I.M.; Kashour, T.; Hakim, F.A.; Zimmerman, V.A.; Erwin, P.J.; Sutton, A.J.; Ibrahim, T. Statins for the prevention and treatment of infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 1658–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorzou, M.P.; Chini, M.; Lioni, A.; Tsekes, G.; Nitsotolis, T.; Tierris, I.; Panagiotou, N.; Rontogianni, D.; Harhalakis, N.; Lazanas, M. Successful treatment of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome-related hemophagocytic syndrome in an HIV patient with primary effusion lymphoma. Hematol. Rep. 2016, 8, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calic, Z.; Cappelen-Smith, C.; Hodgkinson, S.J.; McDougall, A.; Cuganesan, R.; Brew, B.J. Treatment of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome with intravenous immunoglobulin in a patient with multiple sclerosis treated with fingolimod after discontinuation of natalizumab. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 598–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.; Wandel, S.; Colebunders, R.; Attia, S.; Furrer, H.; Egger, M. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in patients starting antiretroviral therapy for HIV infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2010, 10, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manabe, Y.C.; Campbell, J.D.; Sydnor, E.; Moore, R.D. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome: Risk factors and treatment implications. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2007, 46, 456–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Lim, A.; Omarjee, S.; Levitz, S.M.; Gosnell, B.I.; Spelman, T.; Elliott, J.H.; Carr, W.H.; Moosa, M.-Y.S.; Ndung’u, T.; et al. Cryptococcosis-IRIS is associated with lower Cryptococcus-specific IFN-γ responses before antiretroviral therapy but not higher T-cell responses during therapy. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 898–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Dorasamy, A.A.; Gosnell, B.I.; Elliott, J.H.; Spelman, T.; Omarjee, S.; Naranbhai, V.; Coovadia, Y.; Ndung’u, T.; Moosa, M.-Y.S.; et al. Clinical and mycological predictors of cryptococcosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. AIDS 2013, 27, 2089–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, H.A.; Nakouzi, A.; Chang, C.C.; Kuniholm, M.H.; Carreño, L.J.; Wang, T.; Ndung’u, T.; Lewin, S.R.; French, M.A.; Pirofski, L.-A. Association between plasma antibody responses and risk for Cryptococcus-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 17, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulware, D.R.; Meya, D.B.; Bergemann, T.L.; Wiesner, D.L.; Rhein, J.; Musubire, A.; Lee, S.J.; Kambugu, A.; Janoff, E.N.; Bohjanen, P.R. Clinical features and serum biomarkers in HIV immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome after cryptococcal meningitis: A prospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 2010, 7, e1000384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulware, D.R.; Bonham, S.C.; Meya, D.B.; Wiesner, D.L.; Park, G.S.; Kambugu, A.; Janoff, E.N.; Bohjanen, P.R. Paucity of initial cerebrospinal fluid inflammation in cryptococcal meningitis is associated with subsequent immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.C.; Omarjee, S.; Lim, A.; Spelman, T.; Gosnell, B.I.; Carr, W.H.; Elliott, J.H.; Moosa, M.-Y.S.; Ndung’u, T.; French, M.A.; Lewin, S.R. Chemokine levels and chemokine receptor expression in the blood and the cerebrospinal fluid of HIV-infected patients with cryptococcal meningitis and cryptococcosis-associated immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 2013, 208, 1604–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, R.J.; Walker, N.F.; Scriven, J.; Meintjes, G. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in HIV-infected patients. HIV 2015, 7, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bicanic, T.; Meintjes, G.; Rebe, K.; Williams, A.; Loyse, A.; Wood, R.; Hayes, M.; Jaffar, S.; Harrison, T. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in HIV-associated cryptococcal meningitis: A prospective study. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2009, 51, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shelburne, S.A.; Darcourt, J.; White, A.C.; Greenberg, S.B.; Hamill, R.J.; Atmar, R.L.; Visnegarwala, F. The role of immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in AIDS-related Cryptococcus neoformans disease in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 40, 1049–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitoria, M.; Ford, N.; Clayden, P.; Pozniak, A.L.; Hill, A.M. When could new antiretrovirals be recommended for national treatment programmes in low-income and middle-income countries. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2017, 12, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psichogiou, M.; Basoulis, D.; Tsikala-Vafea, M.; Vlachos, S.; Kapelios, C.J.; Daikos, G.L. Integrase Strand Transfer inhibitors and the emergence of Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS). CHR 2018, 15, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutertre, M.; Cuzin, L.; Demonchy, E.; Puglièse, P.; Joly, V.; Valantin, M.-A.; Cotte, L.; Huleux, T.; Delobel, P.; Martin-Blondel, G. Initiation of antiretroviral therapy containing integrase inhibitors increases the risk of IRIS requiring hospitalization. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2017, 76, e23–e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandesris, M.-O.; Kelaidi, C.; Méchaï, F.; Bougnoux, M.-E.; Brousse, N.; Viard, J.-P.; Poirée, S.; Lecuit, M.; Hermine, O.; Lortholary, O. Granulocyte Colony Stimulating Factor-induced exacerbation of fungus-related Immune Restoration Inflammatory Syndrome: A case of chronic disseminated candidiasis exacerbation. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2010, 43, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanc, F.-X.; Sok, T.; Laureillard, D.; Borand, L.; Rekacewicz, C.; Nerrienet, E.; Madec, Y.; Marcy, O.; Chan, S.; Prak, N.; et al. Earlier versus later start of antiretroviral therapy in HIV-infected adults with tuberculosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torok, M.E.; Yen, N.T.B.; Chau, T.T.H.; Mai, N.T.H.; Phu, N.H.; Mai, P.P.; Dung, N.T.; Chau, N.V.V.; Bang, N.D.; Tien, N.A.; et al. Timing of Initiation of antiretroviral therapy in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-associated tuberculous meningitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, 1374–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zolopa, A.R.; Andersen, J.; Komarow, L.; Sanne, I.; Sanchez, A.; Hogg, E.; Suckow, C.; Powderly, W. Early antiretroviral therapy reduces AIDS progression/death in individuals with acute opportunistic infections: A multicenter randomized strategy trial. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e5575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makadzange, A.T.; Ndhlovu, C.E.; Takarinda, K.; Reid, M.; Kurangwa, M.; Gona, P.; Hakim, J.G. Early versus delayed initiation of antiretroviral therapy for concurrent HIV infection and cryptococcal meningitis in sub-saharan Africa. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 50, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisson, G.P.; Molefi, M.; Bellamy, S.; Thakur, R.; Steenhoff, A.; Tamuhla, N.; Rantleru, T.; Tsimako, I.; Gluckman, S.; Ravimohan, S.; et al. Early versus delayed antiretroviral therapy and cerebrospinal fluid fungal clearance in adults with HIV and cryptococcal meningitis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 56, 1165–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulware, D.R.; Meya, D.B.; Muzoora, C.; Rolfes, M.A.; Huppler Hullsiek, K.; Musubire, A.; Taseera, K.; Nabeta, H.W.; Schutz, C.; Williams, D.A.; et al. Timing of antiretroviral therapy after diagnosis of cryptococcal meningitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2487–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scriven, J.E.; Graham, L.M.; Schutz, C.; Scriba, T.J.; Wilkinson, K.A.; Wilkinson, R.J.; Boulware, D.R.; Urban, B.C.; Meintjes, G.; Lalloo, D.G. The CSF Immune Response in HIV-1-Associated Cryptococcal Meningitis: Macrophage Activation, Correlates of Disease Severity, and Effect of Antiretroviral Therapy. J. Acquir. Imm. Defic. Syndr. 2017, 75, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southern African HIV Clinicians Society, T. Guideline for the prevention, diagnosis and management of cryptococcal meningitis among HIV-infected persons: 2013 update. S. Afr. J. HIV Med. 2013, 14, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abassi, M.; Boulware, D.R.; Rhein, J. Cryptococcal Meningitis: Diagnosis and Management Update. Curr. Trop. Med. Rep. 2015, 2, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, N. Hypercalcemia Related to Immune Reconstitution in Organ Transplant Recipients with Granulomatous Opportunistic Infections. Transplantation 2006, 82, 986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Pathogen | Patient Background | Symptoms | Diagnostic Test | Histopathology | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryptococcus species | HIV SOT Pregnancy | Headaches, seizures, neurological deficits Lymphadenopathy, pneumonitis, chorioretinitis, skin and soft tissues lesions | Diagnosis of exclusion * No consensual diagnostic test Sterile CSF culture BDG- CSF PCR- | Granulomatous lesions | [7,14,15] |
| Candida species | Neutropenia (acute leukemia, lymphoma, stem cell transplant) | Fever, abdominal pain, liver and spleen enlargement MRI: mm-sized abscesses in liver, spleen, kidney, and/or lungs | Diagnosis of exclusion * ⍐ liver enzymes ⍐ BDG Mannan/anti-mannan antibody detection | Epithelioid granuloma, necrosis with minimal inflammatory reaction, micro-abscesses with major inflammatory reaction | [19,22,24] |
| Aspergillus species | Neutropenia (Stem cell transplant and acute leukemia) | Hypoxia, chest pain, dyspnea, hemoptysis CT scan: ⍐ pulmonary infiltrates | Diagnosis of exclusion * ⍗ galactomannan | Insufficiently studied | [25,26,28] |
| Histoplasma capsulatum | HIV SOT TNF-α receptor inhibitors | Hemoptysis, dyspnea, lymphadenopathy, skin nodules CT scan: pulmonary bilateral nodules and ground-glass opacities | Diagnosis of exclusion * ⍗ Histoplasma serum antigen Sterile culture | Well-formed granulomatous inflammation | [29,30,31,32,33] |
| Pneumocystis jiroveci | HIV Corticosteroid-treated patients | Fever, cough, dyspnea, night sweat | Diagnosis of exclusion * | Organizing pneumonia: organizing granulation tissue | [39,40,41,42,44] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dellière, S.; Guery, R.; Candon, S.; Rammaert, B.; Aguilar, C.; Lanternier, F.; Chatenoud, L.; Lortholary, O. Understanding Pathogenesis and Care Challenges of Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in Fungal Infections. J. Fungi 2018, 4, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4040139
Dellière S, Guery R, Candon S, Rammaert B, Aguilar C, Lanternier F, Chatenoud L, Lortholary O. Understanding Pathogenesis and Care Challenges of Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in Fungal Infections. Journal of Fungi. 2018; 4(4):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4040139
Chicago/Turabian StyleDellière, Sarah, Romain Guery, Sophie Candon, Blandine Rammaert, Claire Aguilar, Fanny Lanternier, Lucienne Chatenoud, and Olivier Lortholary. 2018. "Understanding Pathogenesis and Care Challenges of Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in Fungal Infections" Journal of Fungi 4, no. 4: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4040139
APA StyleDellière, S., Guery, R., Candon, S., Rammaert, B., Aguilar, C., Lanternier, F., Chatenoud, L., & Lortholary, O. (2018). Understanding Pathogenesis and Care Challenges of Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome in Fungal Infections. Journal of Fungi, 4(4), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof4040139







