Combinatorial Biosynthesis of Novel Multi-Hydroxy Carotenoids in the Red Yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains and Cultivation
2.2. Plasmid Construction and Transformantion of X. dendrorhous, Combinatorial Biosynthesis of Carotenoid Standards in E. coli
2.3. Carotenoid Extraction, Purification and Chemical Derivatization
2.4. HPLC and HR-ESI-MS Analysis
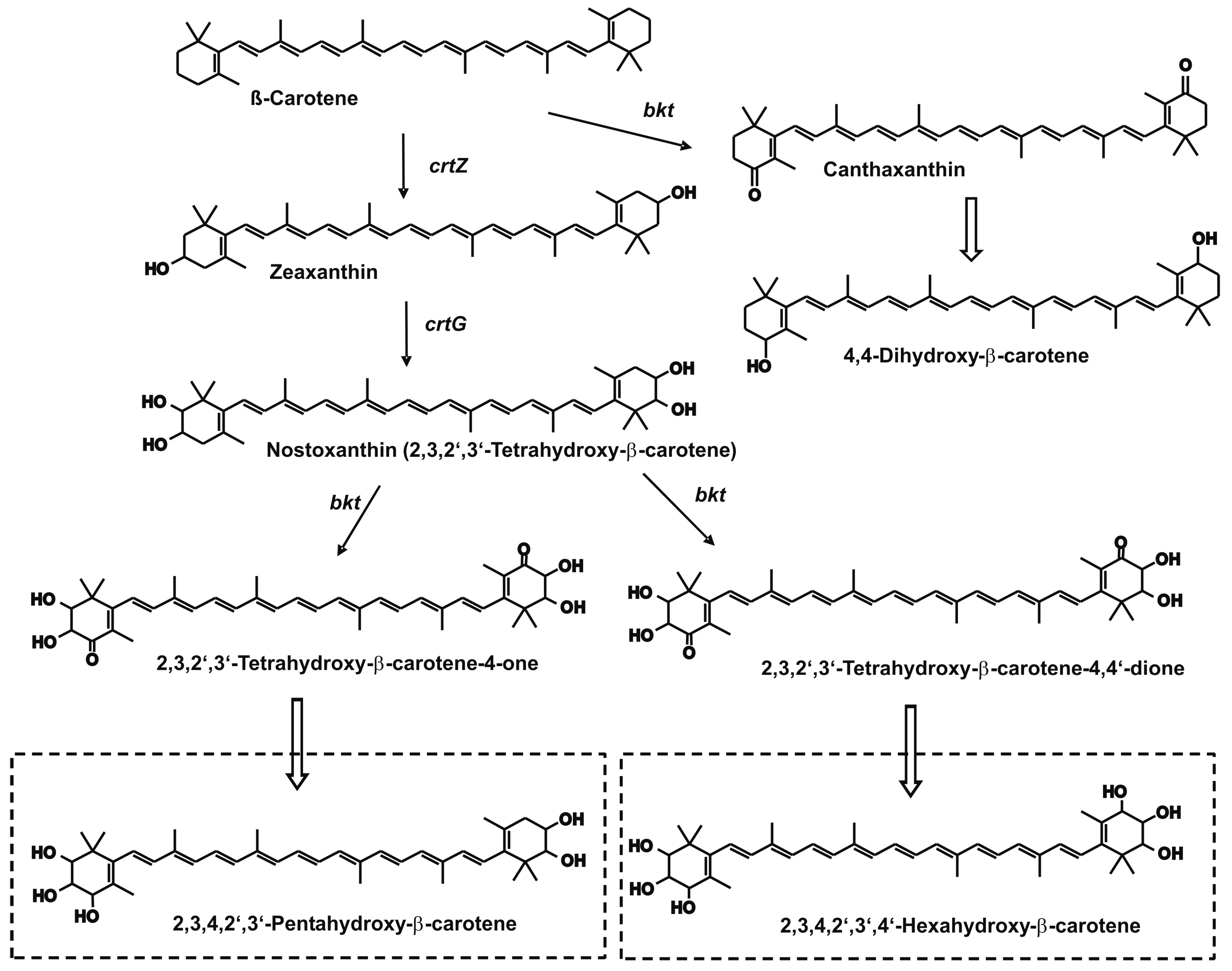
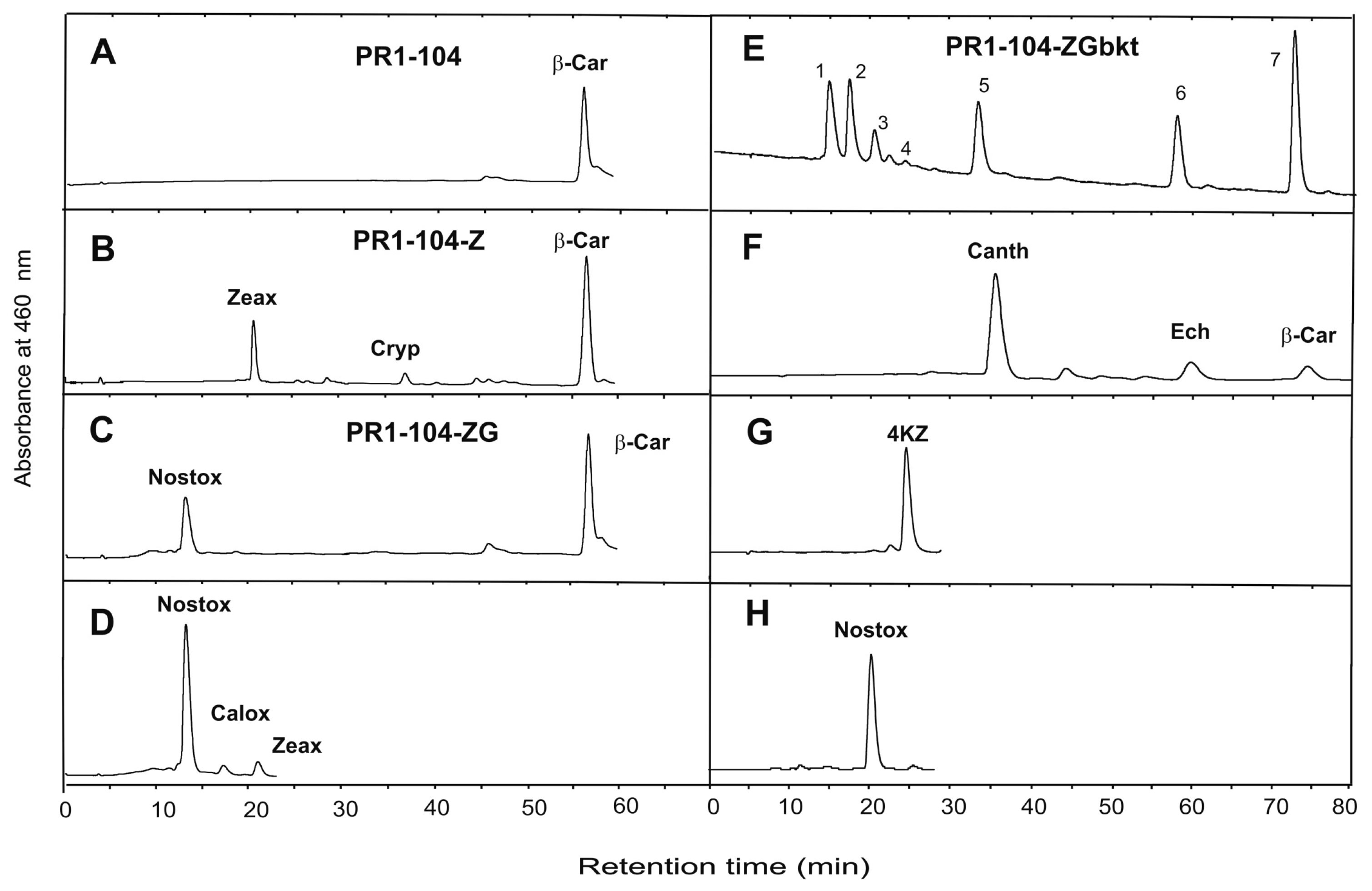
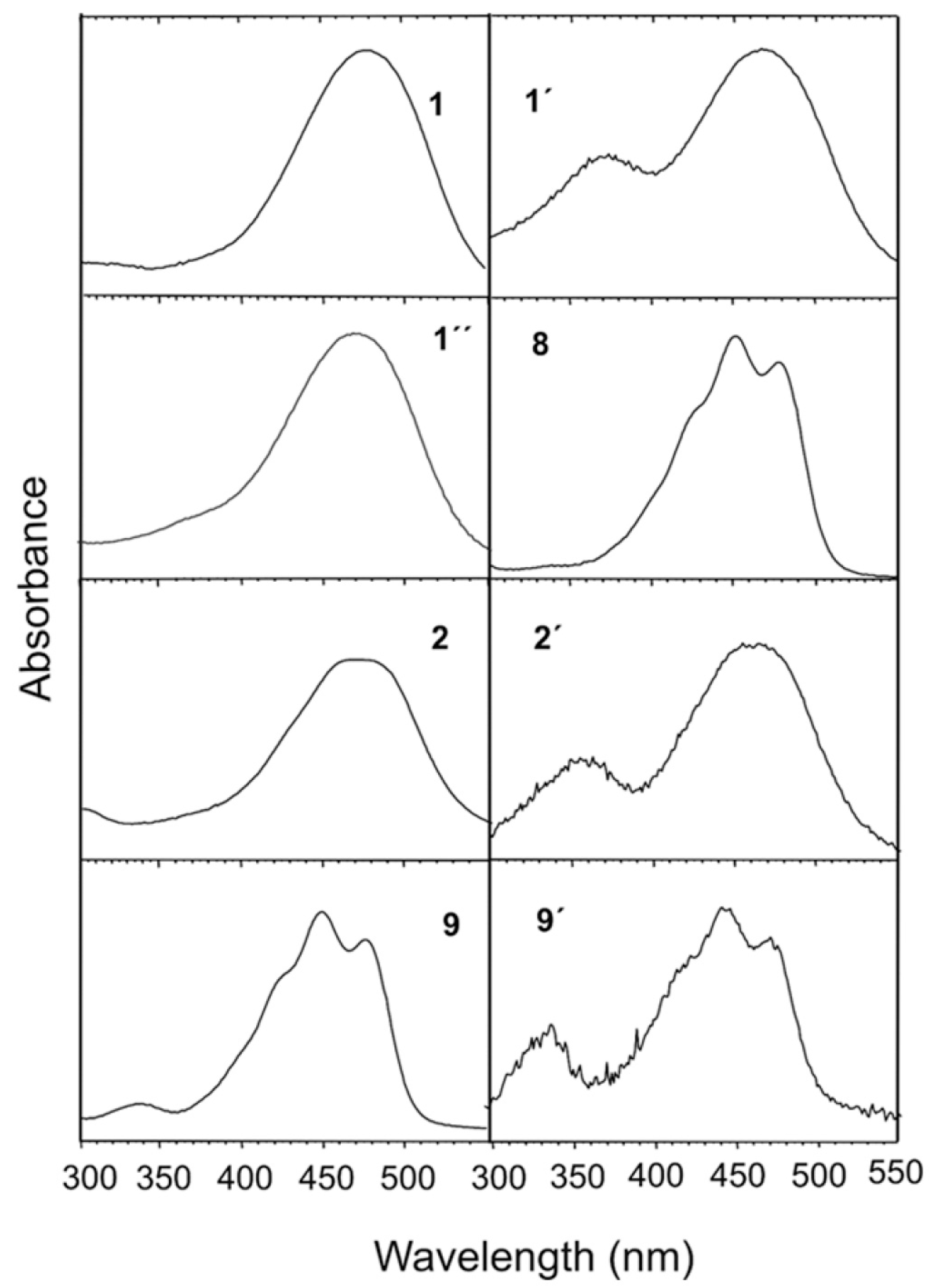
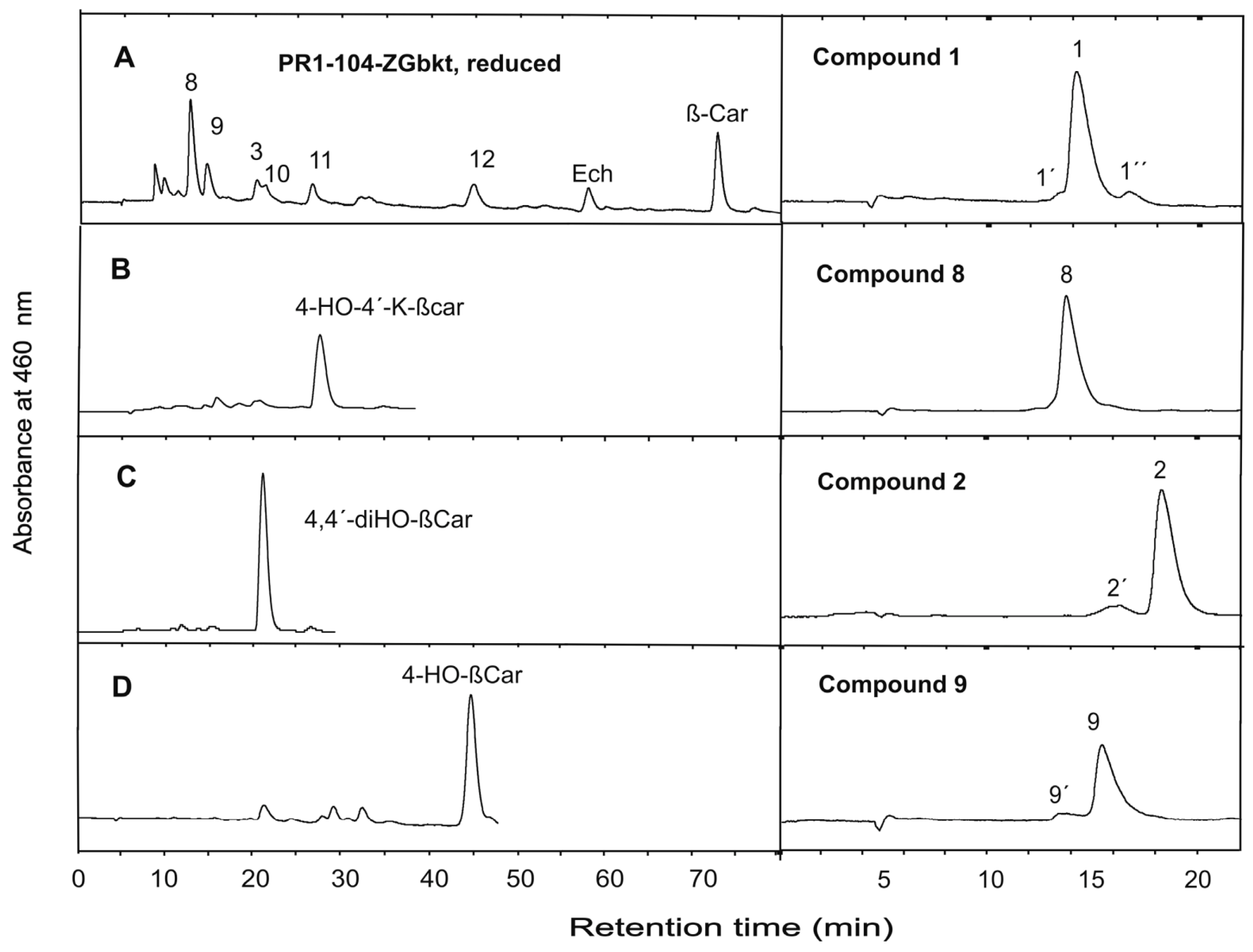
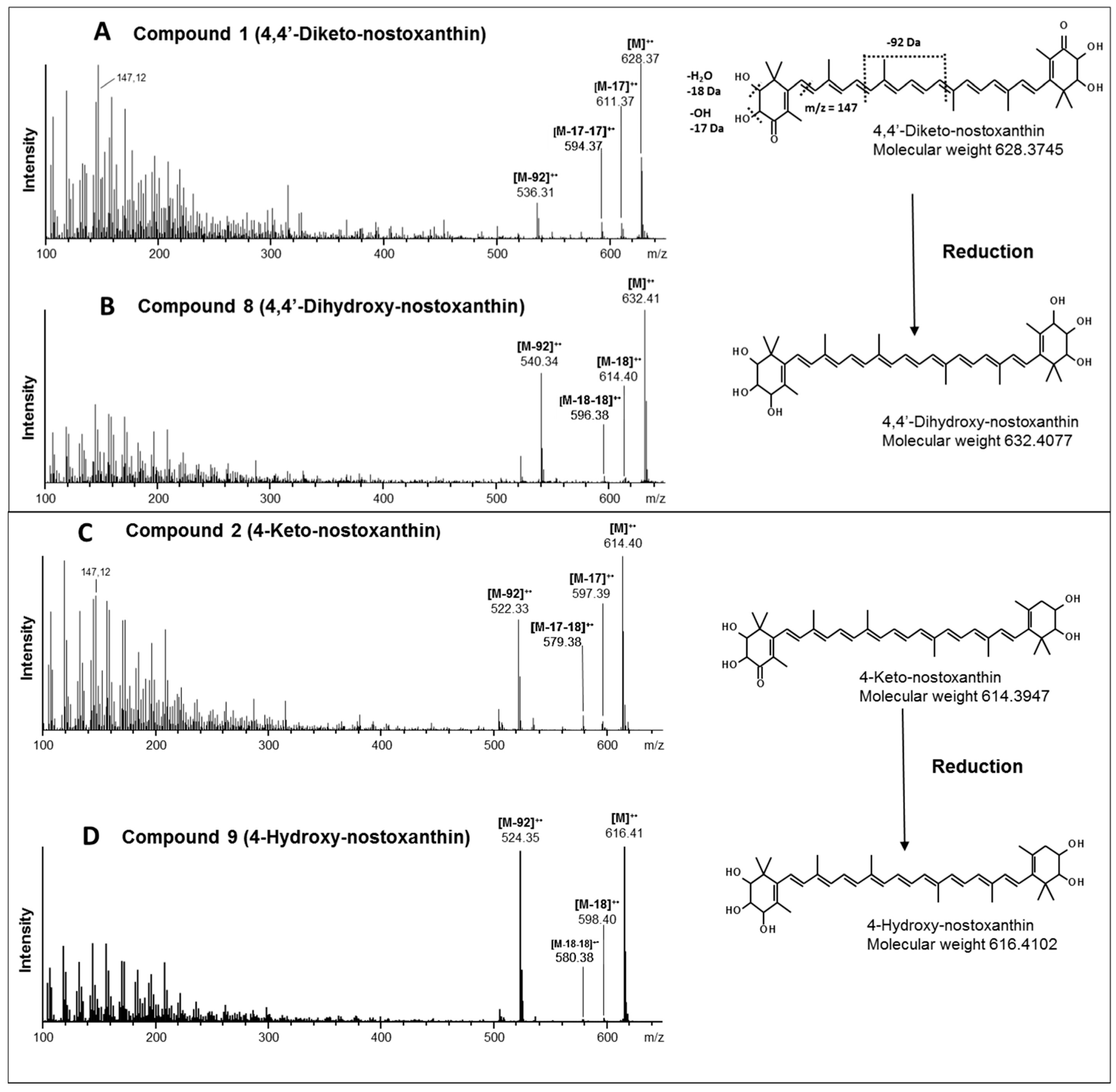
3. Results
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Andrewes, A.G.; Starr, M.P. (3R,3′R)-Astaxanthin from the yeast Phaffia rhodozyma. Phytochemistry 1976, 15, 1009–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandmann, G.; Misawa, N. Fungal carotenoids. In The Mycota X; industrial application; Osiewacz, H.D., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002; pp. 247–262. [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Saiz, M.; de la Fuente, J.L.; Barredo, J.L. Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous for the industrial production of astaxanthin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 88, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, I.; Schewe, H.; Gassel, S.; Jin, C.; Buckingham, J.; Hümbelin, M.; Sandmann, G.; Schrader, J. Biotechnological production of astaxanthin with Phaffia rhodozyma/Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 8, 555–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandmann, G. Carotenoids of biotechnological importance. In Biotechnology of Isoprenoids, Advances in Biochemical Engineering/Biotechnology; Schrader, J., Bohlmann, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 148, pp. 449–467. [Google Scholar]
- Visser, H.; Sandmann, G.; Verdoes, J.C. Xanthophylls in fungi: metabolic engineering of the astaxanthin biosynthetic pathway in Xantophyllomyces. dendrorhous. In Methods in Biotechnology: Microbial Processes and Products; Humana: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gassel, S.; Breitenbach, J.; Sandmann, G. Genetic engineering of the complete carotenoid pathway towards enhanced astaxanthin formation in Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous starting from a high-yield mutant. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, K.Y.; Morita, T.; Mochizuki, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Ogino, C.; Araki, M.; Kondo, A. Development of a multi-gene expression system in Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. Microb. Cell Factories 2014, 13, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Gassel, S.; Steiger, S.; Xia, X.; Bauer, R.; Sandmann, G.; Thines, M. The genome of the basal agaricomycete Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous provides insights into the organization of its acetyl-CoA derived pathways and the evolution of agaricomycotina. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, P.; Falconnier, B.; Bricout, J.; Vladescu, B. β-Carotene producing mutants of Phaffia rhodozyma. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1994, 41, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojima, K.; Breitenbach, J.; Visser, H.; Setoguchi, Y.; Tabata, K.; Hoshino, T.; van den Berg, J.; Sandmann, G. Cloning of the astaxanthin synthase gene from Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous (Phaffia rhodozyma) and its assignment as a β-carotene 3-hydroxylase/4-ketolase. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2006, 275, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollmann, H.; Breitenbach, J.; Sandmann, G. Engineering of the carotenoid pathway in Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous leading to the synthesis of zeaxanthin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 101, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, M.; Misawa, N.; Sandmann, G. Metabolic engineering of the terpenoid biosynthetic pathway of Escherichia coli for production of the carotenoids β-carotene and zeaxanthin. Biotechnol. Lett. 1999, 21, 791–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, A.; Harada, H.; Choi, S.-K.; Misawa, N.; Shindo, K. Production of caloxanthin-β-d-glucoside, zeaxanthin 3,3-β-d-diglucoside, and nostoxanthin in a recombinant Escherichia coli expressing system harbouring seven carotenoid biosynthesis genes, including crtX and crtG. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, M.; Takaichi, S.; Steiger, S.; Wang, Z.Y.; Sandmann, G. Novel hydroxycarotenoids with improved antioxidative properties produced by gene combination in Escherichia coli. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishida, Y.; Adachi, K.; Kasai, H.; Shizuri, Y.; Shindo, K.; Sawabe, A.; Komemushi, S.; Miki, W.; Misawa, N. Elucidation of a carotenoid biosynthesis gene cluster encoding a novel enzyme, 2,2′-β-hydroxylase, from Brevundimonas. sp. strain SD212 and combinatorial biosynthesis of new or rare xanthophylls. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 4286–4296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borovkov, A.Y.; Rivkin, M.I. XcmI-Containing vector for direct cloning of PCR products. BioTechniques 1997, 22, 812–814. [Google Scholar]
- Misawa, N.; Satomi, Y.; Kondo, K.; Yokoyama, A.; Kajiwara, S.; Saito, T.; Ohtani, T.; Miki, W. Structure and functional analysis of a marine bacterial carotenoid biosynthesis gene cluster and astaxanthin biosynthetic pathway proposed at the gene level. J. Bacteriol. 1995, 177, 6575–6584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.J.; Huang, J.C.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, Z.F.; Sandmann, G.; Chen, F. Functional characterization of various algal carotenoid ketolases reveals that ketolating zeaxanthin efficiently is essential for high production of astaxanthin in transgenic Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 3659–3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitenbach, J.; Gerjets, T.; Sandmann, G. Catalytic properties and reaction mechanism of the CrtO carotenoid ketolase from the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 529, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.K.; Matsuda, S.; Hoshino, T.; Peng, X.; Misawa, N. Characterization of bacterial β-carotene 3,3'-hydroxylases, CrtZ, and P450 in astaxanthin biosynthetic pathway and adonirubin production by gene combination in Escherichia coli. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eugster, C.H. Chemical derivatization: Microsomale tests for the presence of common functional groups in carotenoids. In Carotenoid Volume 1A Isolation and Analysis; Britton, G., Liaaen-Jensen, S., Pfander, H., Eds.; Birkhäuser Verlag: Basel, Switzerland, 1995; pp. 71–80. [Google Scholar]
- Steiger, S.; Perez-Fons, L.; Cutting, S.M.; Fraser, P.D.; Sandmann, G. Annotation and functional assignment of the genes for the C30 carotenoid pathways from the genomes of two bacteria Bacillus indicus and Bacillus firmus. Microbiology 2015, 161, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimming, O.; Fleischhacker, F.; Nollmann, F.I.; Bode, H.B. Yeast homologous recombination cloning leading to the novel peptides ambactin and xenolindicin. ChemBioChem 2014, 15, 1290–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandmann, G. Combinatorial biosynthesis of carotenoids in a heterologous host: A powerfull approach for the biosynthesis of novel structures. ChemBioChem 2002, 3, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata-Gómez, L.C.; Montañez, J.C.; Méndez-Zavala, A.; Aguilar, C.N. Biotechnological production of carotenoids by yeasts: an overview. Microb. Cell Factories 2014, 13, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchecker, R.; Liaaen-Jensen, S.; Borch, G.; Siegelman, H.W. Carotenoids of Anacystis nidulans, structures of caloxanthin and nostoxanthin. Phytochemistry 1976, 15, 1015–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, A.; Miki, W.; Zumida, H.; Shizuri, Y. New trihydroxy-keto-carotenoids Isolated from an astaxanthin-producing marine bacterium. Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 1996, 60, 200–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, P.; Kleinig, H.; Englert, G.; Meister, W.; Noaek, K. Carotenoids of Rhizobia. IV. Isolation and structure elucidation of the carotenoids of a mutant of Rhizobium lupine. Helvetica Chim. Acta 1979, 260, 2551–2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanowska, J.; Gruszecki, W.I. Heat-induced and light-induced isomerization of the xanthophyll pigment zeaxanthin. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2005, 80, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, S.M.; Christou, P.; Canela-Garayoa, R. Identification of carotenoids using mass spectrometry. Mass Spectromet. Rev. 2014, 33, 353–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledetzky, N.; Osawa, A.; Iki, K.; Pollmann, H.; Gassel, S.; Breitenbach, J.; Shindo, K.; Sandmann, G. Multiple transformation with the crtYB gene of the limiting enzyme increased carotenoid synthesis and generated novel derivatives in Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 545, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Plasmid | Primers |
|---|---|
| pPRcDNA1bkt830 | β-Carotene 4-ketolase gene bkt from Haematococcus pluvialis (D45881) |
| Primers: 5’-ATATGAATTCATGCACGTCGCATCGGCACT-3’ (forward) 5’-TATACTCGAGTCATGCCAAGGCAGGCACCAG-3’ (reverse) | |
| pPR2TNH-crtG | β-Carotene 2-hydroxylase gene crtG from Brevundimonas SD212 [16] (AB181388) |
| Primers: 5’-GGAATTCATGTTGAGGGATCTGCTCATC-3’ (forward) 5’-GCTCGAGTCACCGAAGAGGCGCTGAG-3’ (reverse) | |
| pPR2TNo-crtZo | β-Carotene 3-hydroxylase gene crtZ from Brevundimonas SD212 [21]), codon optimized (KX063854) |
| Sequences: 5’-GAATTCATGGCTTGGCTCACCTGGA-3’ (start) 5’-ATCTTCTTCTTCTGGAGCT TGAGTCGAC-3’ (end) |
| Compound | Trivial Name | Sum Formula [M]+ | Calculated m/z | Detected m/z | Mass Error [Δppm] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4,4´-Diketo-nostoxanthin | C40H52O6 | 628.3758 | 628.3745 | 1.3 |
| 2 | 4-Keto-nostoxanthin | C40H54O5 | 614.3966 | 614.3947 | 1.9 |
| 8 | 4,4´-Dihydroxy-nostoxanthin | C40H56O6 | 632.4071 | 632.4077 | 0.6 |
| 9 | 4-Hydroxy-nostoxanthin | C40H56O5 | 616.4122 | 616.4102 | 2.0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pollmann, H.; Breitenbach, J.; Wolff, H.; Bode, H.B.; Sandmann, G. Combinatorial Biosynthesis of Novel Multi-Hydroxy Carotenoids in the Red Yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof3010009
Pollmann H, Breitenbach J, Wolff H, Bode HB, Sandmann G. Combinatorial Biosynthesis of Novel Multi-Hydroxy Carotenoids in the Red Yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. Journal of Fungi. 2017; 3(1):9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof3010009
Chicago/Turabian StylePollmann, Hendrik, Jürgen Breitenbach, Hendrik Wolff, Helge B. Bode, and Gerhard Sandmann. 2017. "Combinatorial Biosynthesis of Novel Multi-Hydroxy Carotenoids in the Red Yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous" Journal of Fungi 3, no. 1: 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof3010009
APA StylePollmann, H., Breitenbach, J., Wolff, H., Bode, H. B., & Sandmann, G. (2017). Combinatorial Biosynthesis of Novel Multi-Hydroxy Carotenoids in the Red Yeast Xanthophyllomyces dendrorhous. Journal of Fungi, 3(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof3010009






