Cutaneous Disseminated and Extracutaneous Sporotrichosis: Current Status of a Complex Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Brief Historical Background
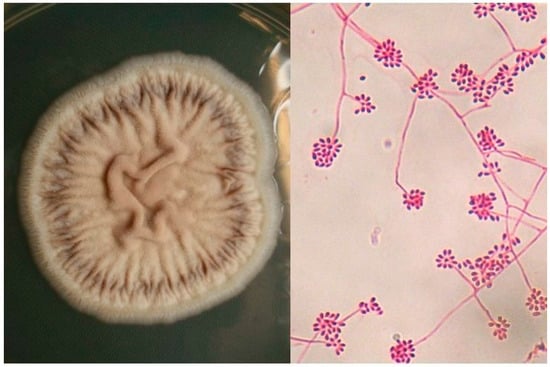
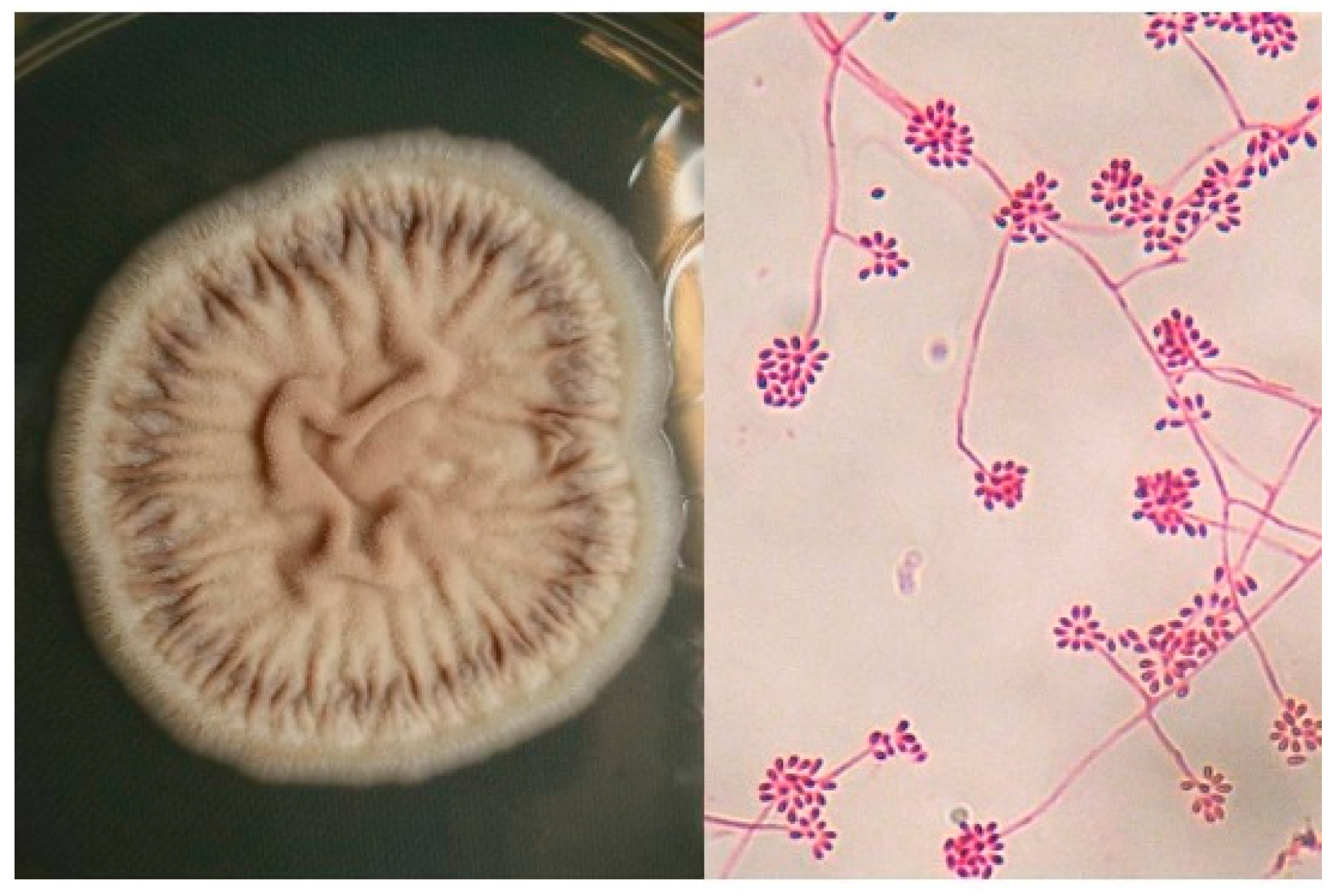
3. Etiology
4. Epidemiology
4.1. Geographical Distribution
4.2. Habitat and Ecological Conditions
4.3. Entrance and Incubation Period
4.4. Occupation, Gender and Age
5. Predisposing Factors
6. Pathogenesis
7. Clinical Features
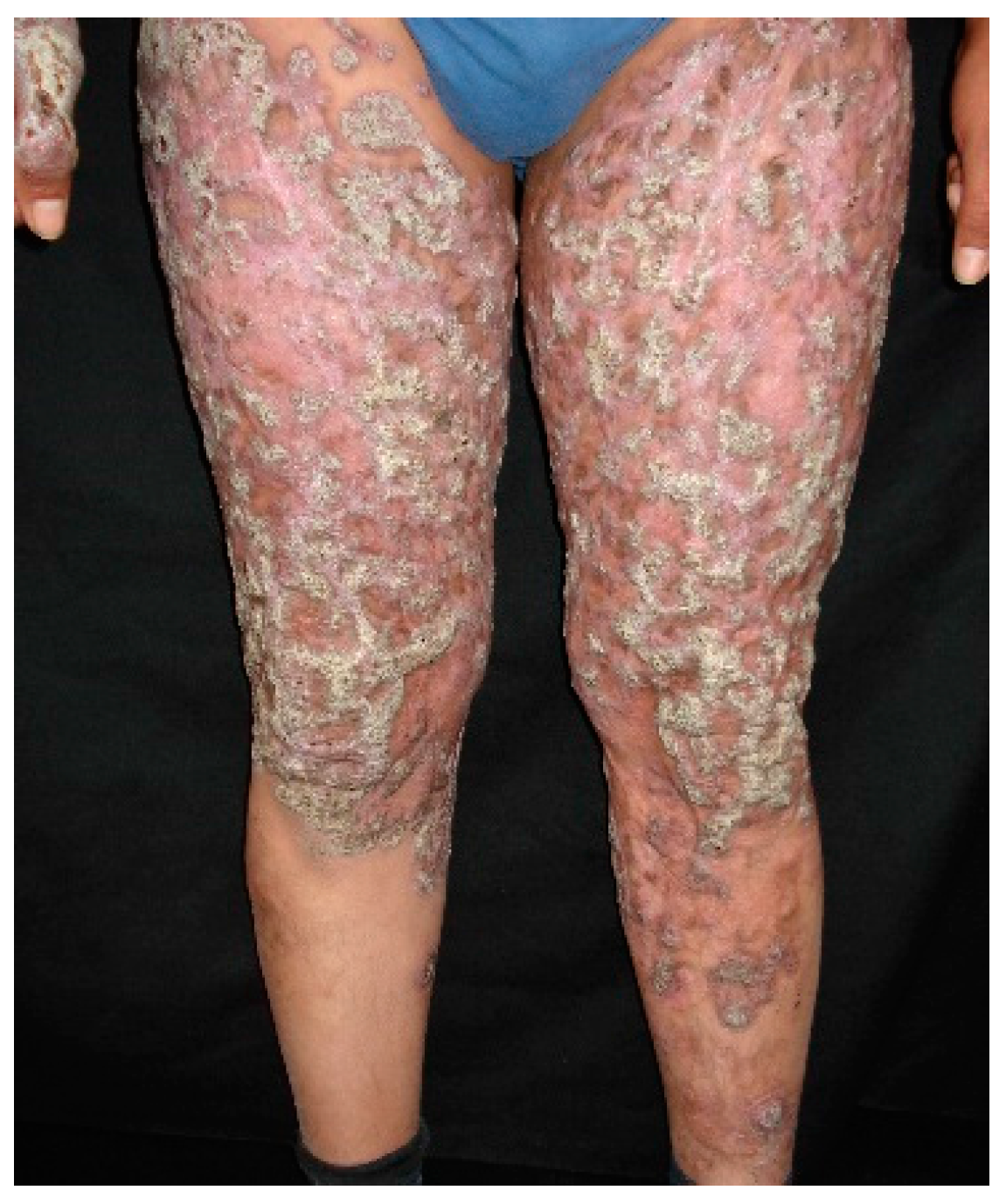
7.1. Cutaneous Sporotrichosis
7.2. Extracutaneous Sporotrichosis
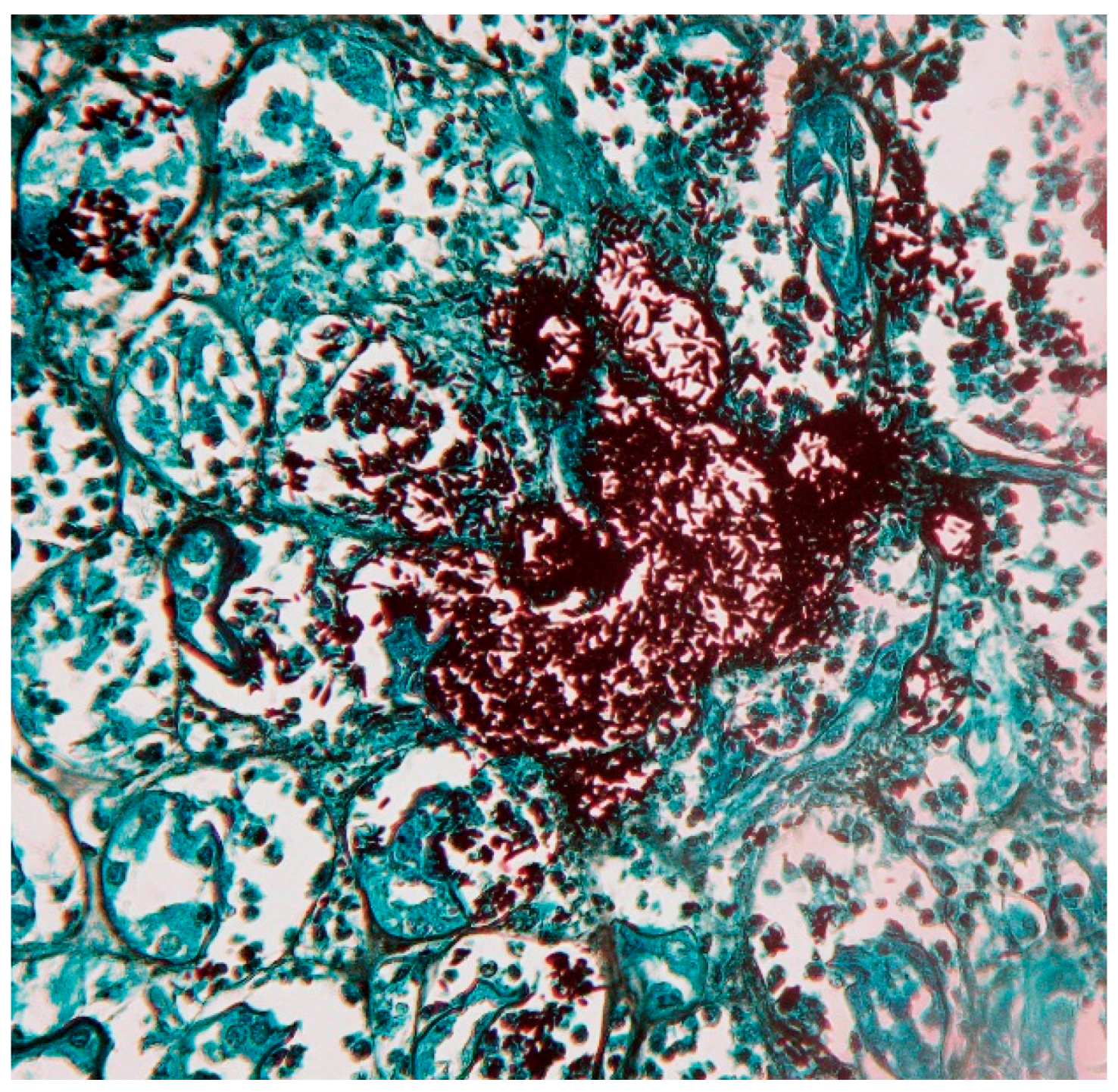
8. Laboratory Diagnosis
9. Treatment
10. Conclusions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ramos-e-Silva, M.; Vasconcelos, C.; Carneiro, S.; Cestari, T. Sporotrichosis. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schechtman, R.C. Sporotrichosis: Part I. Skinmed 2010, 8, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonifaz, A.; Vazquez-Gonzalez, D. Sporotrichosis: An update. G Ital. Dermatol. Venereol. 2010, 145, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barros, M.B.; de Almeida Paes, R.; Schubach, A.O. Sporothrix schenckii and Sporotrichosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 24, 633–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engle, J.; Desir, J.; Bernstein, J.M. A rose by any other name. Skinmed 2007, 6, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.M.; de Hoog, S.; de Camargo, Z.P. Emergence of pathogenicity in the Sporothrix schenckii complex. Med. Mycol. 2013, 51, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakrabarti, A.; Bonifaz, A.; Gutierrez-Galhardo, M.C.; Mochizuki, T.; Li, S. Global epidemiology of sporotrichosis. Med. Mycol. 2015, 53, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, S.A.; Gremião, I.D.; Kitada, A.A.; Boechat, J.S.; Viana, P.G.; Schubach, T.M. The epidemiological scenario of feline sporotrichosis in Rio de Janeiro, State of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2014, 47, 392–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, P.G.; Tellez, I.; Deep, A.E.; Nolasco, D.; Holgado, W.; Bustamante, B. Sporotrichosis in Peru: Description of an area of hyperendemicity. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2000, 30, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante, B.; Campos, P.E. Endemic sporotrichosis. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 14, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifaz, A.; Vázquez-González, D. Diagnosis and treatment of sporotrichosis lymphocutaneous: What are the options? Curr. Fungal Infect. Rev. 2013, 7, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, S.S.; Zhong, S.X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Yao, L.; Huo, S.S. Report of 457 sporotrichosis cases from Jilin province, Northeast China, a serious endemic region. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 27, 313–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takenaka, M.; Yoshizaki, A.; Utani, A.; Nishimoto, K. A survey of 165 sporotrichosis cases examined in Nagasaki prefecture from 1951 to 2012. Mycoses 2014, 57, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schenk, B.R. On refractory subcutaneous abscesses caused by a fungus possibly related to Sporotrichia. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1898, 9, 286–290. [Google Scholar]
- Hektoen, L.; Perkins, C.F. Refractory subcutaneous abscesses caused by Sporothrix schenckii. a new pathogenic fungus. J. Boston Soc. Med. Sci. 1900, 5, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aram, H. Sporotrichosis. A historical approach. Int. J. Dermatol. 1986, 25, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Beurmann, L.H.G. Les Sporotrichoses; Felix Alcan: Paris, France, 1912. [Google Scholar]
- Marimon, R.; Cano, J.; Gene, J.; Sutton, D.A.; Kawasaki, M.; Guarro, J. Sporothrix brasiliensis, S. globosa, and S. mexicana, three new Sporothrix species of clinical interest. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3198–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellez, M.D.; Batista-Duharte, A.; Portuondo, D.; Quinello, C.; Bonne-Hernandez, R.; Carlos, I.Z. Sporothrix schenckii complex biology: Environment and fungal pathogenicity. Microbiology 2014, 160, 2352–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Romero, E.; Reyes-Montes Mdel, R.; Perez-Torres, A.; Ruiz-Baca, E.; Villagomez-Castro, J.C.; Mora-Montes, H.M.; Flores-Carreon, A.; Toriello, C. Sporothrix schenckii complex and sporotrichosis, an emerging health problem. Future Microbiol. 2011, 6, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrid, H.; Cano, J.; Gene, J.; Bonifaz, A.; Toriello, C.; Guarro, J. Sporothrix globosa, a pathogenic fungus with widespread geographical distribution. Rev. Iberoam Micol. 2009, 26, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marimon, R.; Gené, J.; Cano, J.; Guarro, J. Sporothrix luriei: A rare fungus from clinical origin. Med. Mycol. 2008, 46, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.M.; de Hoog, G.S.; de Cássia-Pires, D.; Brihante, R.S.; Sidrim, J.J.; Gadelha, M.F.; Colombo, A.L.; de Camargo, Z.P. Genetic diversity and antifungal susceptibility profiles in causative agents of sporotrichosis. BMC Infect. Dis. 2014, 23, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.M.; Cruz-Choappa, R.; Fernandes, G.F.; de Hoog, G.S.; de Camargo, Z.P. Sporothrix chilensis sp. nov. (Ascomycota: Ophiostomatales), a soil-borne agent of human sporotrichosis with mild-pathogenic potential to mammals. Fungal Biol. 2016, 120, 246–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Beer, Z.W.; Duong, T.A.; Wingfield, M.J. The divorce of Sporothrix and Ophiostoma: Solution to a problematic relationship. Stud. Mycol. 2016, 83, 165–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simson, F.W. Sporotrichosis infection in mines in Witwatersrand. A symposium. Proc Transv. Mine Med. Officers Assoc. 1947, 4, 51–54. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, D.M.; Salkin, I.F.; Duncan, R.A.; Hurd, N.J.; Haines, J.H.; Kemna, M.E.; Coles, F.B. Isolation and characterization of Sporothrix schenckii from clinical and environmental sources associated with the largest U.S. epidemic of sporotrichosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ramirez Soto, M.C. Sporotrichosis: The story of an endemic region in Peru over 28 Years (1985 to 2012). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchotene, K.O.; Madrid, I.M.; Klafke, G.B.; Bergamashi, M.; Della Terra, P.P.; Rodrigues, A.M. Sporothrix brasiliensis outbreaks and the rapid emergence of feline sporotrichosis. Mycoses 2015, 58, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Aleman, M.A.; Araiza, J.; Bonifaz, A. Aislamiento y caracterización de cepas silvestres de Sporothrix schenckii e investigación de reactores a la esporotricina. Gac. Med. Mex 2004, 140, 507–512. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hagen, F.; Stielow, B.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Samerpitak, K.; Zhou, X.; Feng, P.; Yang, L.; Chen, M.; Deng, S.; et al. Phylogeography and evolutionary patterns in Sporothrix spanning more than 14,000 human and animal case reports. Persoonia 2015, 35, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, A.K.; Teh, B.M.; McGrath, C.; Thompson, P.J. Pulmonary sporotrichosis: Case series and systematic analysis of literature on clinico-radiological patterns and management outcomes. Med. Mycol. 2013, 51, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aung, A.K.; Spelman, D.W.; Thompson, P.J. Pulmonary Sporotrichosis: An evolving clinical paradigm. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 36, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, D.F.; de Siqueira Hoagland, B.; do Valle, A.C.; Fraga, B.B.; de Barros, M.B.; de Oliveira Schubach, A.; de Almeida-Paes, R.; Cuzzi, T.; Rosalino, C.M.; Zancope-Oliveira, R.M.; et al. Sporotrichosis in HIV-infected patients: Report of 21 cases of endemic sporotrichosis in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Med. Mycol. 2012, 50, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, D.F.; Valle, A.C.; da Silva, M.B.; Campos, D.P.; Lyra, M.R.; de Souza, R.V.; Veloso, V.G.; Zancope-Oliveira, R.M.; Bastos, F.I.; et al. Sporotrichosis: An emerging neglected opportunistic infection in HIV-infected patients in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, J.A.; Freitas, D.F.; Lamas, C.C. The impact of sporotrichosis in HIV-infected patients: A systematic review. Infection 2015, 43, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirado-Sánchez, A.; Bonifaz, A. Sporotrichosis in Children: An Update. Curr. Fungal Infect. Rep. 2016, 10, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrejon, O.V.; Robles, M.; Zubieta Arroyo, O.E. Fatal fungaemia due to Sporothrix schenckii. Mycoses 1995, 38, 373–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinoza-Hernandez, C.J.; Jesus-Silva, A.; Toussaint-Caire, S.; Arenas, R. Disseminated sporotrichosis with cutaneous and testicular involvement. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014, 105, 204–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassif, P.W.; Granado, I.R.; Ferraz, J.S.; Souza, R.; Nassif, A.E. Atypical presentation of cutaneous sporotrichosis in an alcoholic patient. Dermatol. Online J. 2012, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, C.A.; Pappas, P.G.; McKinsey, D.S.; Greenfield, R.A.; Perfect, J.R.; Cloud, G.A.; Thomas, C.J.; Dismukes, W.E. Treatment of lymphocutaneous and visceral sporotrichosis with fluconazole. Clin. Infect. Dis. 1996, 22, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewing, G.E.; Bosl, G.J.; Peterson, P.K. Sporothrix schenckii meningitis in a farmer with Hodgkin’s disease. Am. J. Med. 1980, 68, 455–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, D.; Gourley, W.K.; Alperin, J.B. Sporotrichosis as a presenting manifestation of hairy cell leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 1994, 46, 134–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunce, P.E.; Yang, L.; Chun, S.; Zhang, S.X.; Trinkaus, M.A.; Matukas, L.M. Disseminated sporotrichosis in a patient with hairy cell leukemia treated with amphotericin B and posaconazole. Med. Mycol. 2012, 50, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solorzano, S.; Ramirez, R.; Cabada, M.M.; Montoya, M.; Cazorla, E. Disseminated cutaneous sporotrichosis with joint involvement in a woman with type 2 diabetes. Rev. Peru Med. Exp. Salud. Publica 2015, 32, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severo, L.C.; Festugato, M.; Bernardi, C.; Londero, A.T. Widespread cutaneous lesions due to Sporothrix schenckii in a patient under a long-term steroids therapy. Rev. Inst. Med. Trop. Sao Paulo 1999, 41, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gewehr, P.; Jung, B.; Aquino, V.; Manfro, R.C.; Spuldaro, F.; Rosa, R.G.; Goldani, L.Z. Sporotrichosis in renal transplant patients. Can. J. Infect. Dis. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 24, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullberg, R.M.; Quintanilla, A.; Levin, M.L.; Williams, J.; Phair, J.P. Sporotrichosis: Recurrent cutaneous, articular, and central nervous system infection in a renal transplant recipient. Rev. Infect. Dis. 1987, 9, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, C.P.; do Valle, A.C.; Freitas, D.F.; Reis, R.; Galhardo, M.C. Pregnancy during a sporotrichosis epidemic in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Int. J. Gynaecol. Obstet. 2012, 117, 294–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yap, F.B. Disseminated cutaneous sporotrichosis in an immunocompetent individual. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 15, 727–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Cabello, R.; Bonifaz, A.; Romero-Feregrino, R.; Sanchez, C.J.; Linares, Y.; Zavala, J.T.; Romero, L.C.; Romero-Feregrino, R.; Vega, J.T. Disseminated sporotrichosis. BMJ Case Rep. 2011, 25, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, K.; Turker, T.; Zangeneh, T. Disseminated sporotrichosis in an immunocompetent patient. Case Rep. Plast Surg. Hand Surg. 2016, 3, 44–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, T.; Duan, H.; Furue, M. Immunohistochemical detection of interferon-γ-producing cells in granuloma formation of sporotrichosis. Med. Mycol. 2002, 40, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uenotsuchi, T.; Takeuchi, S.; Matsuda, T.; Urabe, K.; Koga, T.; Uchi, H.; Nakahara, T.; Fukagawa, S.; Kawasaki, M.; Kajiwara, H.; et al. Differential induction of Th1-prone immunity by human dendritic cells activated with Sporothrix schenckii of cutaneous and visceral origins to determine their different virulence. Int. Immunol. 2006, 18, 1637–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdan, F.F.; Faleiros, J.C.; Ferreira, L.S.; Monnazzi, L.G.; Maia, D.C.; Tansine, A.; Placeres, M.C.; Carlos, I.Z.; Santos-Junior, R.R. Dendritic cell are able to differentially recognize Sporothrix schenckii antigens and promote Th1/Th17 response in vitro. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- 56 Zhang, Z.; Liu, X.; Lv, X.; Lin, J. Variation in genotype and higher virulence of a strain of Sporothrix schenckii causing disseminated cutaneous sporotrichosis. Mycopathologia 2011, 172, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, D.F.; Santos, S.S.; Almeida-Paes, R.; de Oliveira, M.M.; do Valle, A.C.; Gutierrez-Galhardo, M.C.; Zancope-Oliveira, R.M.; Nosanchuk, J.D. Increase in virulence of Sporothrix brasiliensis over five years in a patient with chronic disseminated sporotrichosis. Virulence 2015, 6, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonifaz, A.; Peniche, A.; Mercadillo, P.; Saul, A. Successful treatment of AIDS-related disseminated cutaneous sporotrichosis with itraconazole. AIDS Patient Care STDs 2001, 15, 603–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, H.; Tanioka, M.; Yonezawa, M.; Arakawa, A.; Matsumura, Y.; Kore-eda, S.; Miyachi, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Mochizuki, T. A case of atypical sporotrichosis with multifocal cutaneous ulcers. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2008, 33, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stalkup, J.R.; Bell, K.; Rosen, T. Disseminated cutaneous sporotrichosis treated with itraconazole. Cutis 2002, 69, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fontes, P.C.; Kitakawa, D.; Carvalho, Y.R.; Brandao, A.A.; Cabral, L.A.; Almeida, J.D. Sporotrichosis in an HIV-positive man with oral lesions: A case report. Acta Cytol. 2007, 51, 648–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anees, A.; Ali, A.; Fordham, E.W. Abnormal bone and gallium scans in a case of multifocal systemic sporotrichosis. Clin. Nucl. Med. 1986, 11, 663–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordhan, A.; Ramdial, P.K.; Morar, N.; Moodley, S.D.; Aboobaker, J. Disseminated cutaneous sporotrichosis: A marker of osteoarticular sporotrichosis masquerading as gout. Int. J. Dermatol. 2001, 40, 717–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Carvalho Aguinaga, F.; Trope, B.M.; Fernandes, N.C.; Engel, D.C.; Ramos, E.S.M. Sporotrichosis with bone involvement: An alert to an occupational disease. Case Rep. Dermatol. 2014, 6, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lederer, H.T.; Sullivan, E.; Crum-Cianflone, N.F. Sporotrichosis as an unusual case of osteomyelitis: A case report and review of the literature. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2016, 11, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orofino-Costa, R.; Unterstell, N.; Carlos Gripp, A.; de Macedo, P.M.; Brota, A.; Dias, E.; de Melo Teixeira, M.; Felipe, M.S.; Bernardes-Engemann, A.R.; Lopes-Bezerra, L.M. Pulmonary cavitation and skin lesions mimicking tuberculosis in a HIV negative patient caused by Sporothrix brasiliensis. Med. Mycol. Case Rep. 2013, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callens, S.F.; Kitetele, F.; Lukun, P.; Lelo, P.; Van Rie, A.; Behets, F.; Colebunders, R. Pulmonary Sporothrix schenckii infection in a HIV positive child. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2006, 52, 144–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, D.F.; Lima, M.A.; de Almeida-Paes, R.; Lamas, C.C.; do Valle, A.C.; Oliveira, M.M.; Zancope-Oliveira, R.M.; Gutierrez-Galhardo, M.C. Sporotrichosis in the central nervous system caused by Sporothrix brasiliensis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 61, 663–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyra, M.R.; Nascimento, M.L.; Varon, A.G.; Pimentel, M.I.; Antonio Lde, F.; Saheki, M.N.; Bedoya-Pacheco, S.J.; Valle, A.C. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in HIV and sporotrichosis coinfection: Report of two cases and review of the literature. Rev. Soc. Bras. Med. Trop. 2014, 47, 806–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintella, L.P.; Passos, S.R.; do Vale, A.C.; Galhardo, M.C.; Barros, M.B.; Cuzzi, T.; Reis Rdos, S.; de Carvalho, M.H.; Zappa, M.B.; Schubach Ade, O. Histopathology of cutaneous sporotrichosis in Rio de Janeiro: A series of 119 consecutive cases. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2011, 38, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, M.A.; Cockerill, F.R., 3rd; Cortese, D.A.; Roberts, G.D. Disseminated sporotrichosis with Sporothrix schenckii fungemia. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1984, 2, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosinski, R.M.; Axelrod, P.; Rex, J.H.; Burday, M.; Sivaprasad, R.; Wreiole, A. Sporothrix schenckii fungemia without disseminated sporotrichosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Scott, E.N.; Kaufman, L.; Brown, A.C.; Muchmore, H.G. Serologic studies in the diagnosis and management of meningitis due to Sporothrix schenckii. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 317, 935–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardes-Engemann, A.R.; Costa, R.C.; Miguens, B.R.; Penha, C.V.; Neves, E.; Pereira, B.A.; Dias, C.M.; Mattos, M.; Gutierrez, M.C.; Schubach, A.; et al. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the serodiagnosis of several clinical forms of sporotrichosis. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes-Bezerra, L.M.; Schubach, A.; Costa, R.O. Sporothrix schenckii and sporotrichosis. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2006, 78, 293–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, G.F.; Lopes-Bezerra, L.M.; Bernardes-Engemann, A.R.; Schubach, T.M.; Dias, M.A.; Pereira, S.A.; de Camargo, Z.P. Serodiagnosis of sporotrichosis infection in cats by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using a specific antigen, SsCBF, and crude exoantigens. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 147, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, A.M.; de Hoog, G.S.; de Camargo, Z.P. Molecular diagnosis of pathogenic Sporothrix species. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0004190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marimon, R.; Serena, C.; Gene, J.; Cano, J.; Guarro, J. In vitro antifungal susceptibilities of five species of sporothrix. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 732–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahajan, V.K. Sporotrichosis: An overview and therapeutic options. Dermatol. Res. Pract. 2014, 2014, 272376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kauffman, C.A.; Bustamante, B.; Chapman, S.W.; Pappas, P.G. Clinical practice guidelines for the management of sporotrichosis: 2007 update by the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2007, 45, 1255–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolao, F.; Podzamczer, D.; Ventin, M.; Gudiol, F. Efficacy of acute phase and maintenance therapy with itraconazole in an AIDS patient with sporotrichosis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1994, 13, 609–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lima Barros, M.B.; Schubach, A.O.; de Vasconcellos Carvalhaes de Oliveira, R.; Martins, E.B.; Teixeira, J.L.; Wanke, B. Treatment of cutaneous sporotrichosis with itraconazole—Study of 645 patients. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2011, 52, e200–e206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paixao, A.G.; Galhardo, M.C.; Almeida-Paes, R.; Nunes, E.P.; Goncalves, M.L.; Chequer, G.L.; Lamas Cda, C. The difficult management of disseminated Sporothrix brasiliensis in a patient with advanced AIDS. AIDS Res. Ther. 2015, 12, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orfino-Costa, R.; Bernardes-Engemann, A.R.; Azulay-Abulafia, L.; Benvenuto, F.; Neves Mde, L.; Lopes-Bezerra, L.M. Sporotrichosis in pregnancy: Case reports of 5 patients in a zoonotic epidemic in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2011, 86, 995–998. [Google Scholar]
- Baker, J.H.; Goodpasture, H.C.; Kuhns, H.R., Jr.; Rinaldi, M.G. Fungemia caused by an amphotericin B-resistant isolate of Sporothrix schenckii. Successful treatment with itraconazole. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1989, 113, 1279–1281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Silva, F.; Capilla, J.; Mayayo, E.; Guarro, J. Efficacy of posaconazole in murine experimental sporotrichosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 2273–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez-Galhardo, M.C.; Zancopé-Oliveira, R.M.; Monzón, A.; Rodriguez-Tudela, J.L.; Cuenca-Estrella, M. Antifungal susceptibility profile in vitro of Sporothrix schenckii in two growth phases and by two methods: Microdilution and E-test. Mycoses 2010, 53, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Silva, F.; Capilla, J.; Mayayo, E.; Guarro, J. Modest efficacy of voriconazole against murine infections by Sporothrix schenckii and lack of efficacy against Sporothrix brasiliensis. Mycoses 2014, 57, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Cutaneous Lymphatic and Cutaneous Fixed Types [1,2,3,4,5,9,10,11,12,13,28,37,79,80] | Cutaneous-Disseminated, Disseminated and Pulmonary Types [1,2,3,4,5,12,13,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,79,80,81,82,83,84] |
|---|---|---|
| Main etiological agents | S. schenckii (sl) & S. brasiliensis | S. schenckii (sl) & S. brasiliensis |
| Gender proportion Male:Female | 1:1, with slight male predominance. | 8:2 Male predominance especially by association with HIV/AIDS. |
| Age group | Mainly in young adults (2/3) and children (1/3) | Mostly in adults and rare in children. |
| Predisposing factors | Primarily immunocompetent patient. | HIV/AIDS, chronic alcoholism, diabetes, hematologic cancer, steroid treatment, pregnancy and rare in immunocompetent patients. |
| Location | Mainly in upper limbs; in children on the face and limbs | The cutaneous form is present throughout the body. Extracutaneous manifestations are common (lungs, meningeal and osteoarticular) |
| Laboratory diagnosis | Yeast forms are not commonly seen (only 5%–10%). Asteroid bodies are seen. Gold standard: culture. Positive sporotrichin (100% of cases) | Yeast forms are easily seen (100%). Clusters of round and lengthened yeast forms are noted. Gold standard: culture. Sporotrichin is usually negative. |
| Treatment/time | Itraconazole Potassium iodide From 3 to 6 months. | Initial: Amphotericin B Intensive: Amphotericin B + Itraconazole. Maintenance: Itraconazole 6–12 months. |
| Outcome | Good | Bad. Average death (HIV/AIDS) 30%. |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bonifaz, A.; Tirado-Sánchez, A. Cutaneous Disseminated and Extracutaneous Sporotrichosis: Current Status of a Complex Disease. J. Fungi 2017, 3, 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof3010006
Bonifaz A, Tirado-Sánchez A. Cutaneous Disseminated and Extracutaneous Sporotrichosis: Current Status of a Complex Disease. Journal of Fungi. 2017; 3(1):6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof3010006
Chicago/Turabian StyleBonifaz, Alexandro, and Andrés Tirado-Sánchez. 2017. "Cutaneous Disseminated and Extracutaneous Sporotrichosis: Current Status of a Complex Disease" Journal of Fungi 3, no. 1: 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof3010006
APA StyleBonifaz, A., & Tirado-Sánchez, A. (2017). Cutaneous Disseminated and Extracutaneous Sporotrichosis: Current Status of a Complex Disease. Journal of Fungi, 3(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof3010006