Identification of a Novel Pathogen of Peanut Root Rot, Ceratobasidium sp. AG-A, and the Potential of Selected Bacterial Biocontrol Agents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material and Test Strains
2.2. Isolations of Ceratobasidium sp.
2.3. Identification of Ceratobasidium sp. AG-A Isolate RC-103
2.4. Pathogenicity Tests
2.5. Antagonistic Activity of Biocontrol Strains
2.6. Effects of Biocontrol Bacteria on the Growth and Disease Level of Peanut
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
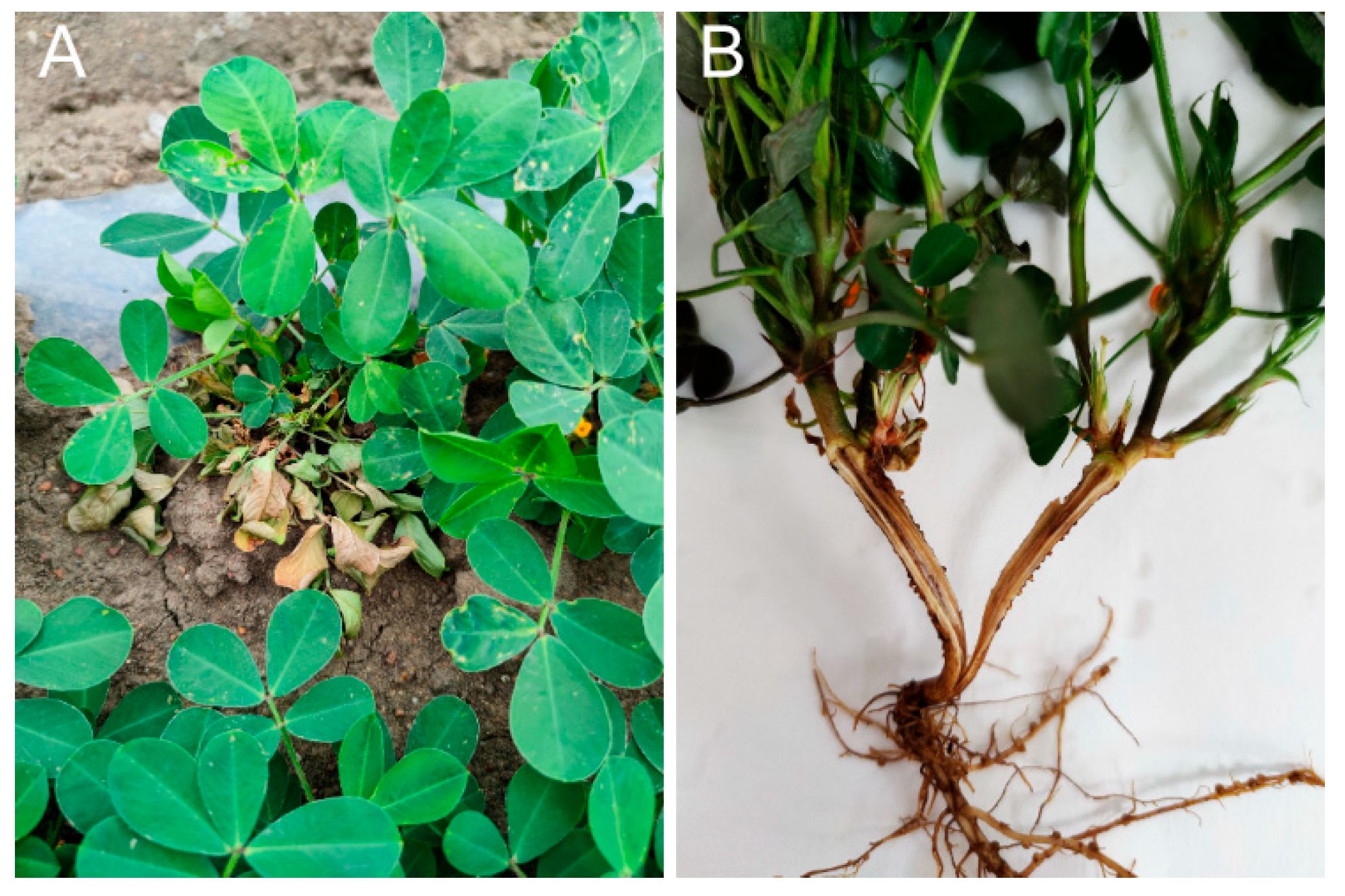
3.1. Disease Assessment
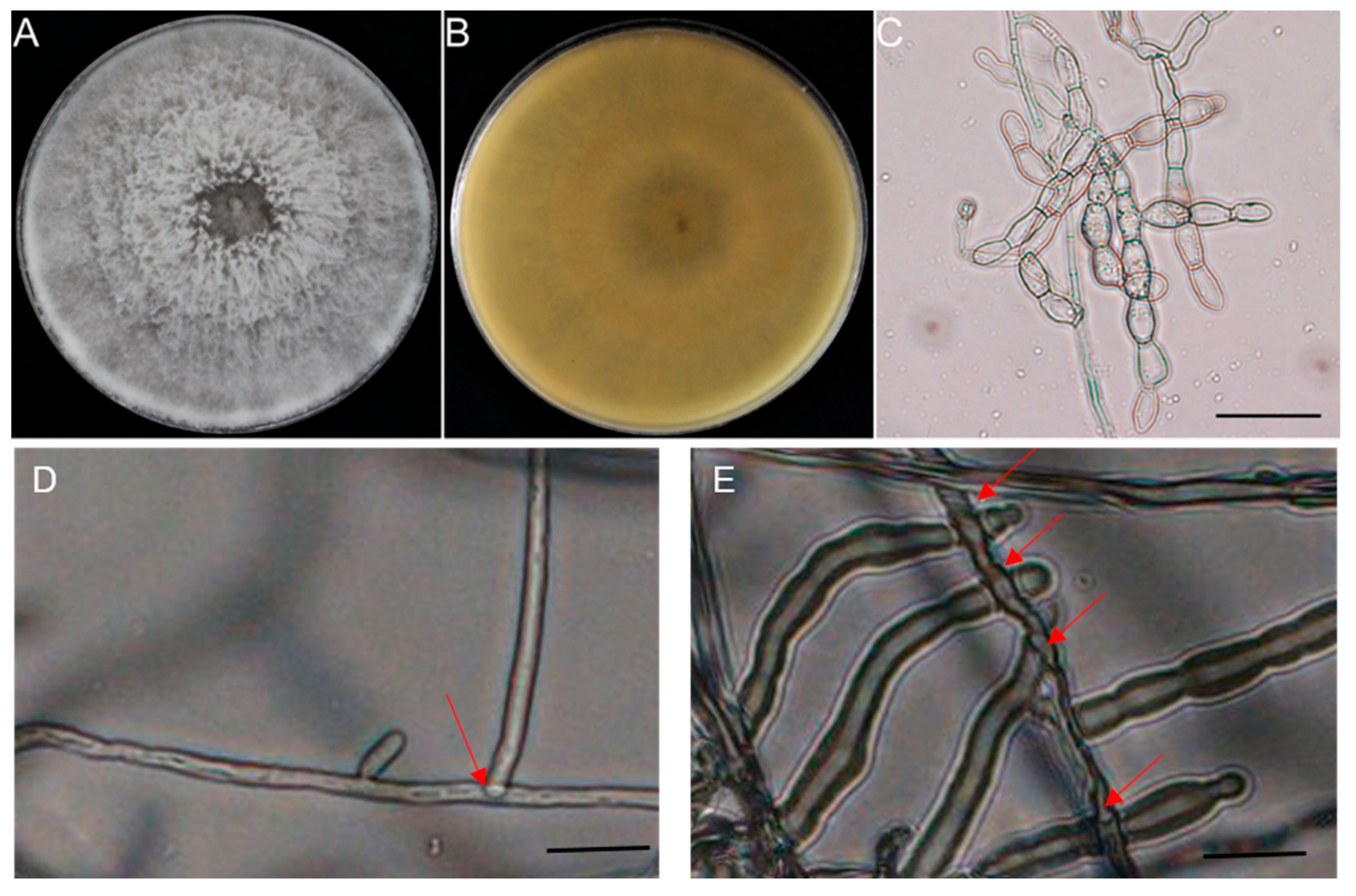
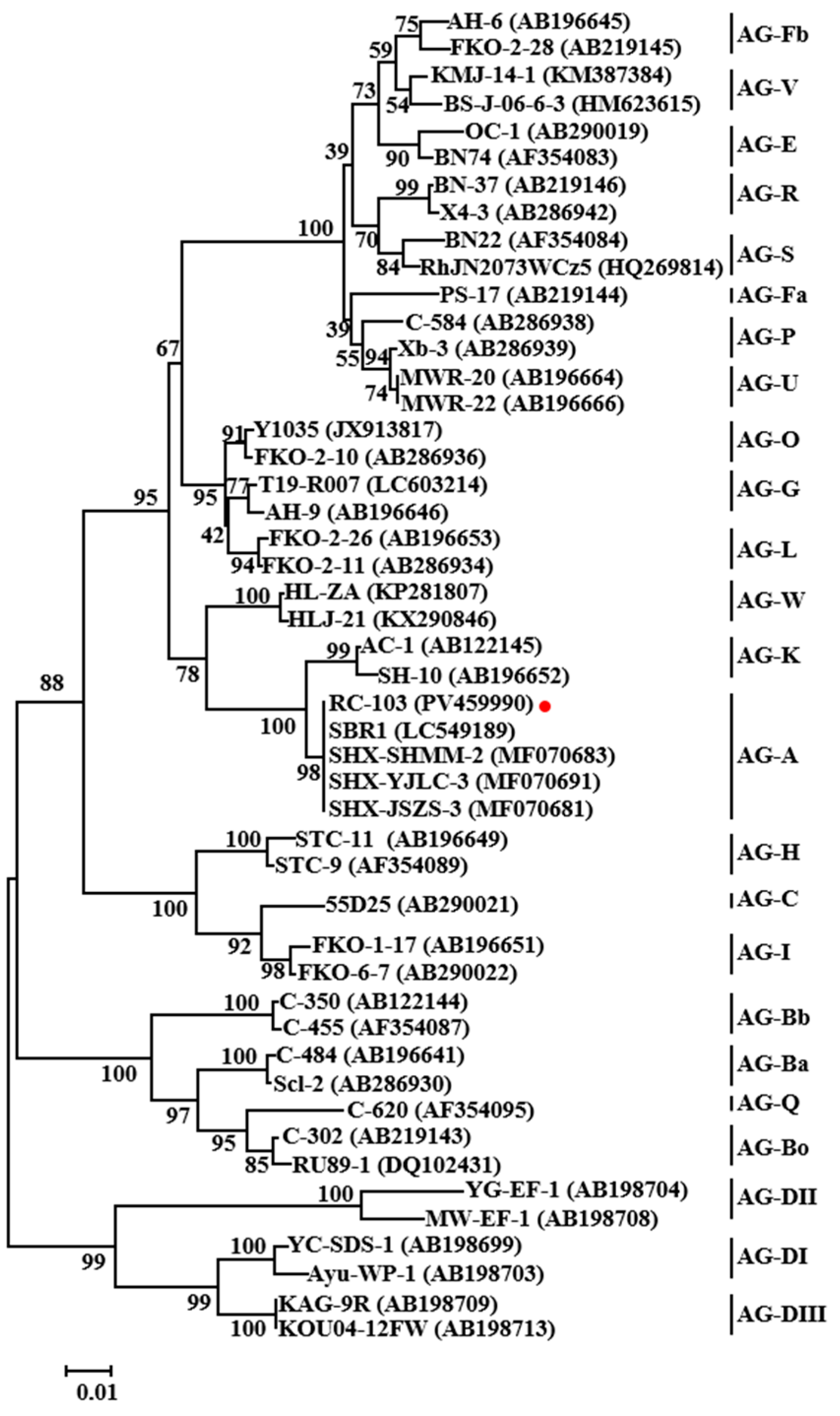
3.2. Isolations and Identification of Ceratobasidium sp. AG-A
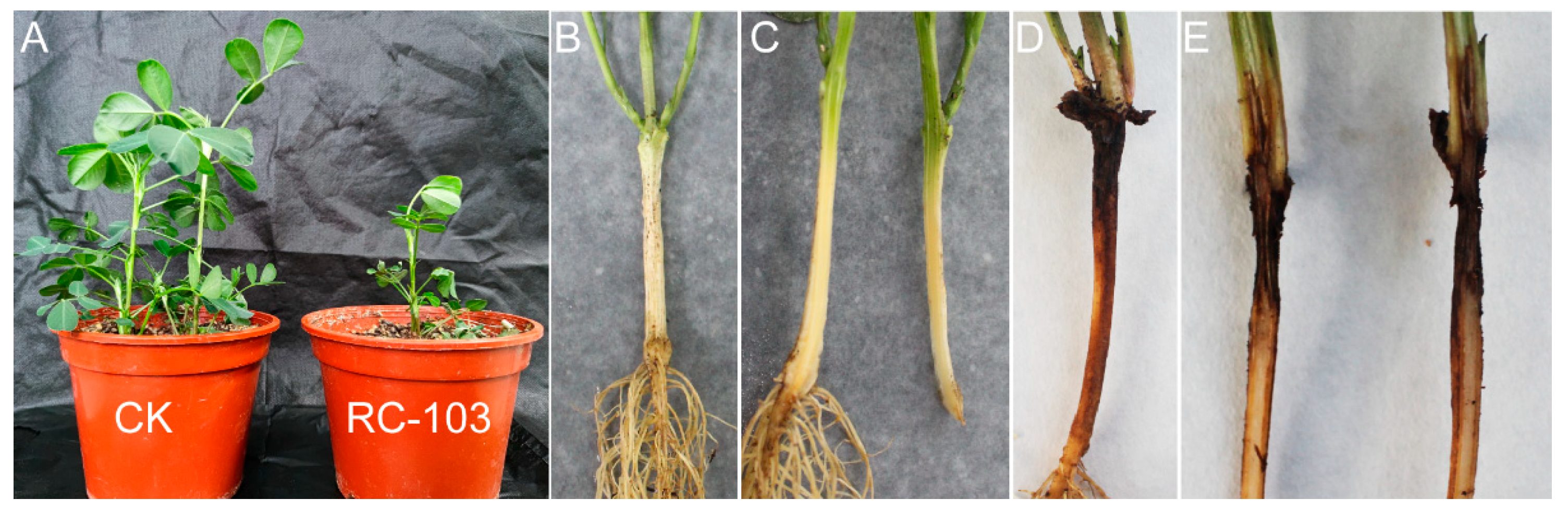
3.3. Pathogenicity
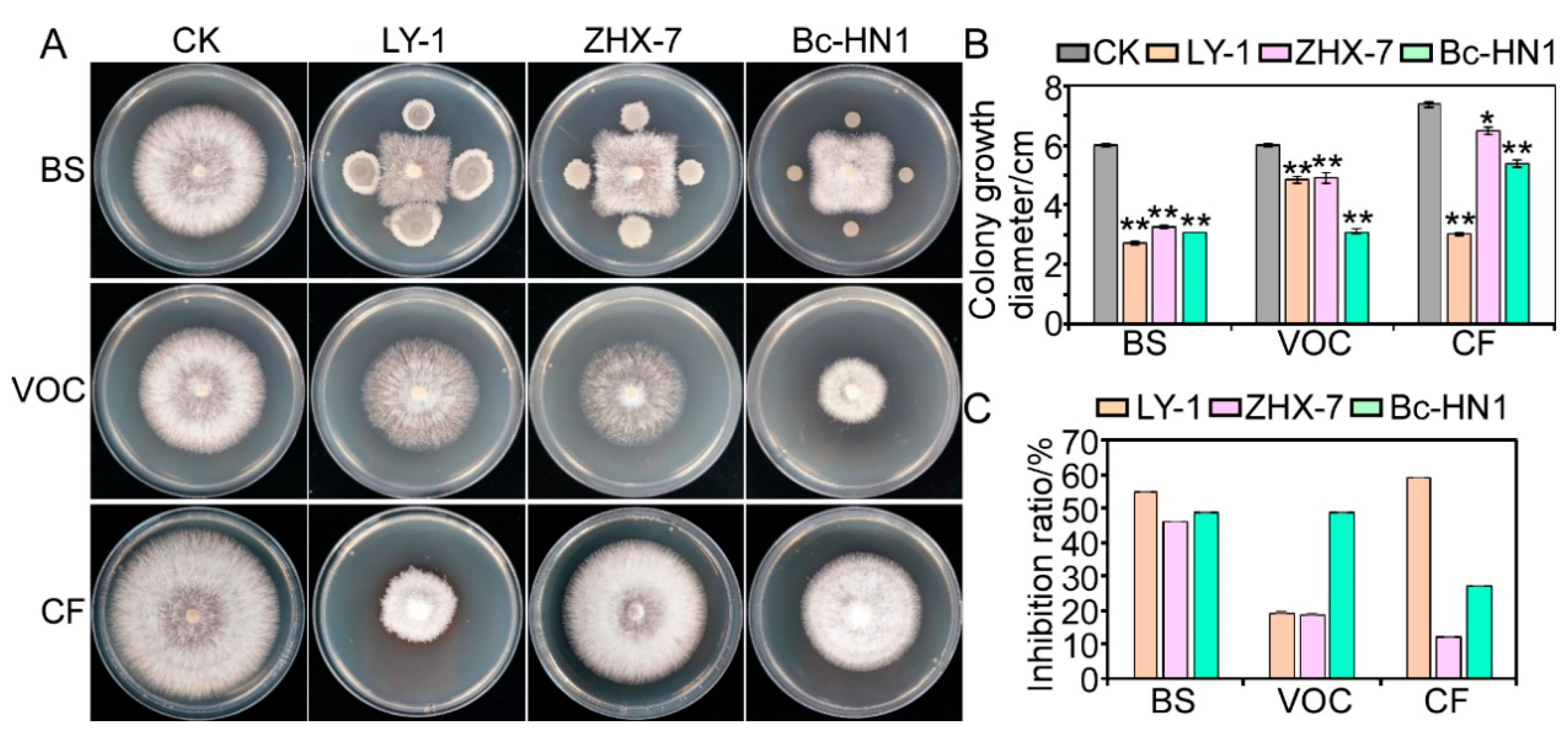
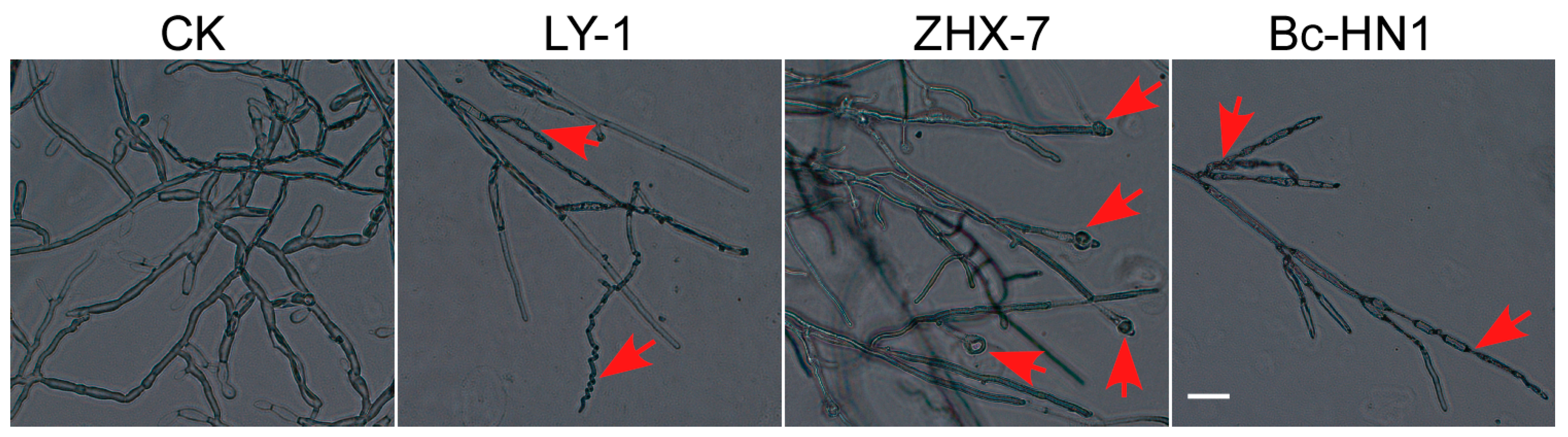
3.4. Antagonistic Activity of Biocontrol Bacteria Against Isolate RC-103
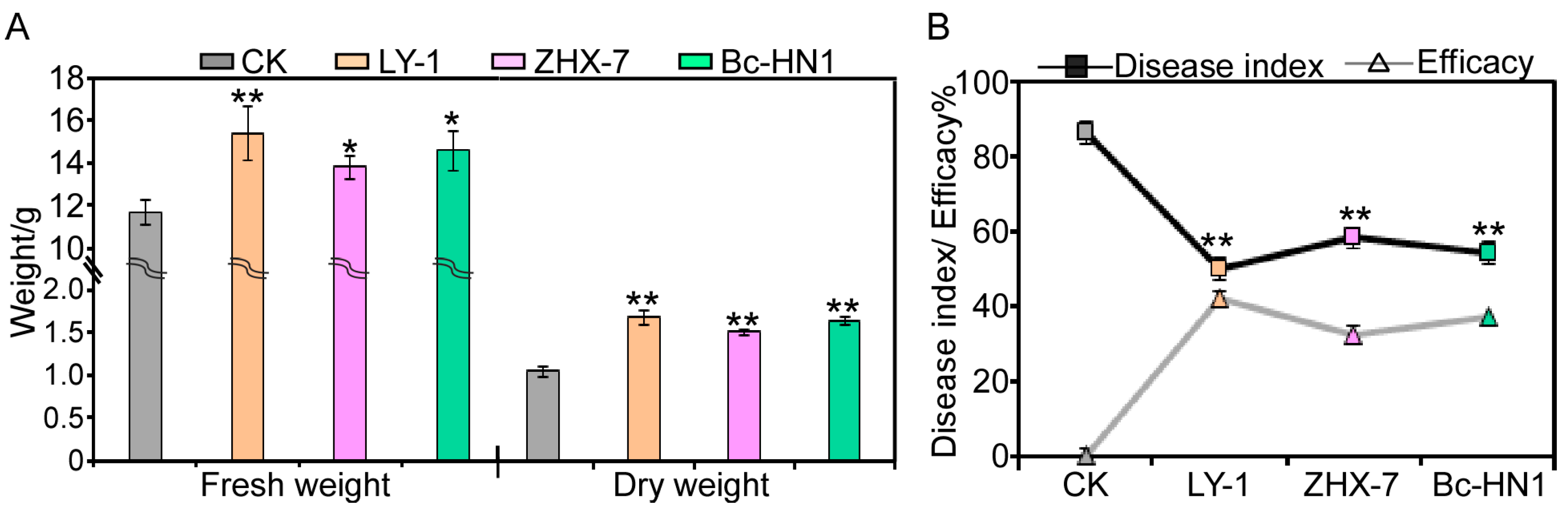
3.5. Biological Efficacy Against Peanut Root Rot
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AGs | Anastomosis groups |
| UNR | Uninucleate Rhizoctonia |
| BNR | Binucleate Rhizoctonia |
| MNR | Multinucleate Rhizoctonia |
| NaClO | Sodium hypochlorite |
| PDA | Potato dextrose agar |
| ITS | Internal transcribed spacer |
| RPB2 | The second largest subunit of RNA polymerase II |
| LB | Luria-Bertani |
| SPSS | Statistical Product and Service Solutions |
| BS | Bacterial suspension |
| VOCs | Volatile organic compounds |
| CF | Cell-free culture filtrate |
| PGPB | Plant growth-promoting bacterium |
References
- Bishi, S.K.; Lokesh, K.; Mahatma, M.K.; Khatediya, N.; Chauhan, S.M.; Misra, J.B. Quality traits of Indian peanut cultivars and their utility as nutritional and functional food. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FAOSTAT. Statistical Database FAOSTAT; FAOSTAT: Rome, Italy, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Yu, J.; Guo, Z.; Song, X.; Xu, M.; He, K.; Zhang, X.; Chi, Y. First report of peanut root rot caused by Fusarium acuminatum in Shandong Province, China. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 2882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Yang, J.; Wu, J.; Chi, Y.; Xie, L. First report of Aspergillus niger causing root rot of peanut in China. Plant Dis. 2015, 99, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, Y.; He, K.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J.; Xu, M.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, C.; Chi, Y. First report of root rot caused by Macrophomina phaseolina in peanut Shandong Province, China. Plant Dis. 2023, 107, 4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharon, M.; Sneh, B.; Kuninaga, S.; Hyakumachi, M. The advancing identification and classification of Rhizoctonia spp. using molecular and biotechnological methods compared with the classical anastomosis grouping. Mycoscience 2006, 47, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Li, Y.; Duan, C.; Li, X.; Naito, S.; Conner, R.L.; Yang, G.; Li, C. Identification of AG-V, a new anastomosis group of binucleate Rhizoctonia spp. from taro and ginger in Yunnan province. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 148, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cao, S.; Chen, H. Taxonomy of Rhizoctonia fungi: Status quo and problems. Microbiol. China 2022, 49, 3469–3491. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, S.; Han, C.; Wu, X. A Binucleate Rhizoctonia anastomosis group (AG-W) is the causal agent of sugar beet seedling damping-off disease in China. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 155, 53–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gónzalez, D.; Rodriguez-Carres, M.; Boekhout, T.; Stalpers, J.; Kuramae, E.E.; Nakatani, A.K.; Vilgalys, R.; Cubeta, M.A. Phylogenetic relationships of Rhizoctonia fungi within the Cantharellales. Fungal Biol. 2016, 120, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, Z.; Zhou, S.; Han, Q.; Zhang, M.; Peng, Y.; Hsiang, T.; Chen, X. Evolutionary and genomic comparisons of hybrid uninucleate and nonhybrid Rhizoctonia fungi. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misawa, T.; Kurose, D. Anastomosis group and subgroup identification of Rhizoctonia solani strains deposited in NARO Genebank, Japan. J. Gen. Plant Pathol. 2019, 85, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinehart, T.A.; Copes, W.E.; Toda, T.; Cubeta, M.A. Genetic Characterization of binucleate Rhizoctonia species causing web blight on azalea in Mississippi and Alabama. Plant Dis. 2007, 91, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saroj, A.; Kumar, A.; Saeed, S.T.; Samad, A.; Alam, M. First report of Tagetes erecta damping off caused by Ceratobasidium sp. from India. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza-Moller, A.; Rentería-Martínez, M.E.; Guerra-Camacho, M.A.; Romo-Tamayo, F.; Ochoa-Meza, A.; Moreno-Salazar, S.F. First report of root rot of watermelon caused by Ceratobasidium sp. in Sonora, Mexico. Plant Dis. 2014, 98, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.X.; Wu, Y.F.; Gong, H.H.; Lin, Y.J.; Chen, C.Y. First report of binucleate Rhizoctonia AG-L causing root and stem rot of wishbone flower (Torenia fournieri) in Taiwan. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Li, S.; Ma, Z.; Wang, W.; Gao, L.; Han, C.; Yang, A.; Wu, X. Anastomosis groups and mycovirome of Rhizoctonia isolates causing sugar beet root and crown rot and their sensitivity to flutolanil, thifluzamide; pencycuron. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabago-Zavala, K.; Valenzuela-Escoboza, F.A.; Mora-Romero, G.A.; Lizárraga-Sánchez, G.J.; Tovar-Pedraza, J.M. First report of Ceratobasidium sp. (AG-A and AG-G) causing root rot and stem canker of common bean in Mexico. Plant Dis. 2022, 107, 958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Wu, Q.; Wang, X.; Kuberan, T.; Shu, F.; Duns, G.J.; Chen, J. First report of blight caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG4-HGI on Pinellia ternata in Guizhou, China. Plant Dis. 2022, 107, 1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firmansyah, M.A.; Erfiani, E.; Jayanegara, A.; Achmad, A.; Wijayanto, N. In vitro biological control of Ceratobasidium ramicola by using tannin extracts from Acacia villosa, Myristica fragrans, Acacia mangium; Calliandra calothyrsus leaves. Braz. J. Biol. 2020, 80, 235–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubekri, K.; Soumare, A.; Mardad, I.; Lyamlouli, K.; Ouhdouch, Y.; Hafidi, M.; Kouisni, L. Multifunctional role of Actinobacteria in agricultural production sustainability: A review. Microbiol. Res. 2022, 261, 127059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Aes, J.; Hua, G.K.; De Maeyer, K.; Pannecoucque, J.; Forrez, I.; Ongena, M.; Dietrich, L.E.; Thomashow, L.S.; Mavrodi, D.V.; Höfte, M. Biological control of Rhizoctonia root rot on bean by phenazine- and cyclic lipopeptide-producing Pseudomonas CMR12a. Phytopathology 2011, 101, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, F.; Saberi-Riseh, R.; Khodaygan, P. Survivability and controlled release of alginate-microencapsulated Pseudomonas fluorescens VUPF506 and their effects on biocontrol of Rhizoctonia solani on potato. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 183, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, A.; Reza, H.A.; Hossein, A.; Naderi, Q.D.; Maryam, F.; Hervan, E.M. Biocontrol of Rhizoctonia solani damping-off of sugar beet with native Streptomyces strains under field conditions. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2009, 19, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afify, A.H.; El-Sayed, A.; Elpana, S.J.J.o.F.; Sciences, D. Biological control of Rhizoctonia solani causing sugar beet damping—off. J. Food Dairy Sci. 2018, 10, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Farhaoui, A.; El Alami, N.; Khadiri, M.; Ezrari, S.; Radouane, N.; Baala, M.; Tahiri, A.; Lahlali, R. Biological control of diseases caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG-2-2 in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) using plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria (PGPR). Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2023, 124, 101966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, C.P.; Dubey, R.C.; Kang, S.C.; Maheshwari, D.K. Antibiosis-mediated necrotrophic effect of Pseudomonas GRC2 against two fungal plant pathogens. Curr. Sci. 2001, 81, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Muthukumar, A.; Sevugapperumal, N.; Ayyadurai, E.; Sangeetha, G. In Vitro efficacy of bacterial endophytes against the chilli damping-off pathogen Pythium aphanidermatum. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2010, 49, 179–186. [Google Scholar]
- Das, J.; Kumar, R.; Yadav, S.K.; Jha, G. The alternative sigma factors, rpoN1 and rpoN2 are required for mycophagous activity of Burkholderia gladioli strain NGJ1. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 2781–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.; Sui, W.W.; Bai, X.Y.; Qiu, Z.L.; Li, X.G.; Zhu, J.Z. Characterization and biocontrol mechanism of Streptomyces olivoreticuli as a potential biocontrol agent against Rhizoctonia solani. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2023, 197, 105681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demissie, Y.T. Diagnosis of fungal and bacterial diseases based on symptom & sign. Am. J. Plant Biol. 2019, 4, 57. [Google Scholar]
- Parmeter, J.R.; Sherwood, J.R.T.; Platt, W.D. Anastomosis grouping among isolates of Thanatephorus cucumeris. Phytopathology 1969, 59, 1270–1278. [Google Scholar]
- White, T.J.; Bruns, T.; Lee, S.; Taylor, J. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR Protocols: A Guide to Methods and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1990; pp. 315–322. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.J.; Whelen, S.; Hall, B.D. Phylogenetic relationships among ascomycetes: Evidence from an RNA polymerse II subunit. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; He, K.; Song, X.; Yu, J.; Guo, Z.; Xu, M. Isolation and identification of Bacillus subtilis LY-1 and its antifungal and growth-promoting effects. Plants 2023, 12, 4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhang, B.; Liu, H.; Han, J.; Zhang, Y. Identification of endophytic Bacillus velezensis ZSY-1 strain and antifungal activity of its volatile compounds against Alternaria solani and Botrytis cinerea. Biol. Control 2017, 105, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Chen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Cai, H.; Guo, C. Bacillus subtilis HSY21 can reduce soybean root rot and inhibit the expression of genes related to the pathogenicity of Fusarium oxysporum. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 178, 104916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sneh, B.; Burpee, L.; Ogoshi, A. Identification of Rhizoctonia Species; The American Phytopathological Society: St. Paul, MN, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.H.; Zhang, R.Q.; Du, H.F.; Chi, Y.C.; Xia, S.C. Rhizoctonia solani identified as the disease causing agent of peanut leaf rot in China. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faske, T.R.; Spurlock, T.N. First report of aerial blight of peanut caused by Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IA in Arkansas. Plant Dis. 2013, 97, 1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Zaid, G.A.; Darwish, M.H.; Ghozlan, H.A.; Abdel-Gayed, M.A.; Sabry, S.A. Sustainable management of peanut damping-off and root rot diseases caused by Rhizoctonia solani using environmentally friendly bio-formulations prepared from batch fermentation broth of chitinase-producing Streptomyces cellulosae. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yan, H.; Lu, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, R.; Sun, T. Research on the tan disease of peanut shells. J. Peanut Sci. 2009, 38, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, R.; Chi, Y.; Xu, M.; Xia, S. Harm and etioloty of Rhizoctonia on peanuts. Chin. J. Oil Crop Sci. 2015, 37, 862–867. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Y.S.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, F.B.; Zhang, S.Q.; Gao, M. First report of Ceratobasidium sp. causing root rot of garlic in China. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baiswar, P.; Ngachan, S.V. First report of root and collar rot of strawberry (Fragaria×ananassa) caused by Ceratobasidium sp. AG-B(o) (binucleate Rhizoctonia) in India. Plant Dis. 2018, 102, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Yao, L.; Liu, C.; Wu, C.; Han, Y. First report of Ceratobasidium sp. AG-I (binucleate Rhizoctonia) causing root rot of Hedychium coronarium Koen in China. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 2023, 45, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, N.P.; Moreno, M.V.; Stenglein, S.; Stancanelli, S.; Wright, E.R.; Rivera, M.C. Ceratobasidium sp. AG-A, root pathogen of Calibrachoa hybrida. Chil. J. Agric. Anim. Sci. 2022, 38, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Jian, Y.; Jin, L.; Tang, S.; Li, Z. Complete genome sequence data of rare Actinomycetes strain Saccharothrix texasensis 6-C, a biological control agent for potato late blight. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2021, 34, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Han, X.; Cao, J.; Li, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Gou, J.; Zheng, Y.; Meng, C.; Zhang, C. Biocontrol potential of Bacillus velezensis EM-1 associated with suppressive rhizosphere soil microbes against tobacco bacterial wilt. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 940156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choub, V.; Won, S.-J.; Ajuna, H.B.; Moon, J.-H.; Choi, S.-I.; Lim, H.-I.; Ahn, Y.S. Antifungal activity of volatile organic compounds from Bacillus velezensis CE 100 against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeidan, R.; Ul-Hassan, Z.; Al-Thani, R.; Migheli, Q.; Jaoua, S. In-vitro application of a qatari Burkholderia cepacia strain (QBC03) in the biocontrol of mycotoxigenic fungi and in the reduction of ochratoxin a biosynthesis by Aspergillus carbonarius. Toxins 2019, 11, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, X.; He, K.; Guo, Z.; Yu, J.; Zhang, X. Isolation and identification of Bacillus velezensis ZHX-7 and its antibacterial and growth-promoting effects. J. Biothechnol. Bull. 2023, 39, 229–236. [Google Scholar]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Song, X.; Xu, M.; He, K.; Chi, Y.; Guo, Z. Identification of a Novel Pathogen of Peanut Root Rot, Ceratobasidium sp. AG-A, and the Potential of Selected Bacterial Biocontrol Agents. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070472
Li Y, Zhang X, Song X, Xu M, He K, Chi Y, Guo Z. Identification of a Novel Pathogen of Peanut Root Rot, Ceratobasidium sp. AG-A, and the Potential of Selected Bacterial Biocontrol Agents. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(7):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070472
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ying, Xia Zhang, Xinying Song, Manlin Xu, Kang He, Yucheng Chi, and Zhiqing Guo. 2025. "Identification of a Novel Pathogen of Peanut Root Rot, Ceratobasidium sp. AG-A, and the Potential of Selected Bacterial Biocontrol Agents" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 7: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070472
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhang, X., Song, X., Xu, M., He, K., Chi, Y., & Guo, Z. (2025). Identification of a Novel Pathogen of Peanut Root Rot, Ceratobasidium sp. AG-A, and the Potential of Selected Bacterial Biocontrol Agents. Journal of Fungi, 11(7), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11070472





