Functional Analysis of FoCrpA in Fusarium oxysporum Causing Rice Seedling Blight
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Strains, Rice Variety, Plasmids
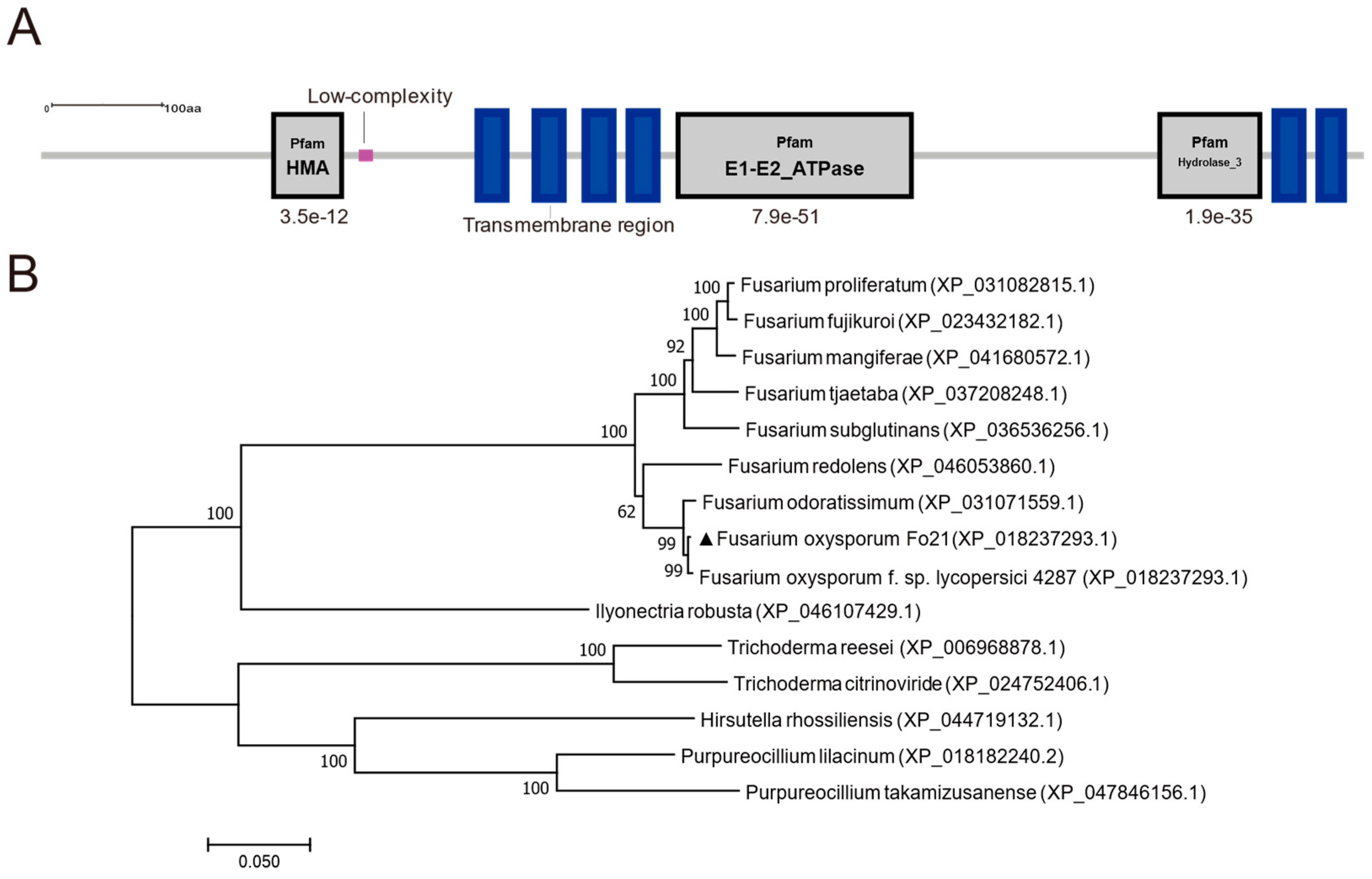
2.2. Protein Sequence Analysis and Phylogenetic Reconstruction
2.3. Targeted Gene Disruption and Complementation
2.4. Phenotype Analysis
2.5. Toxicity Assays with Culture Filtrates and Pathogenicity Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of FoCrpA from F. oxysporum
3.2. Generation of FoCrpA Deletion Mutants and Complementation Assay
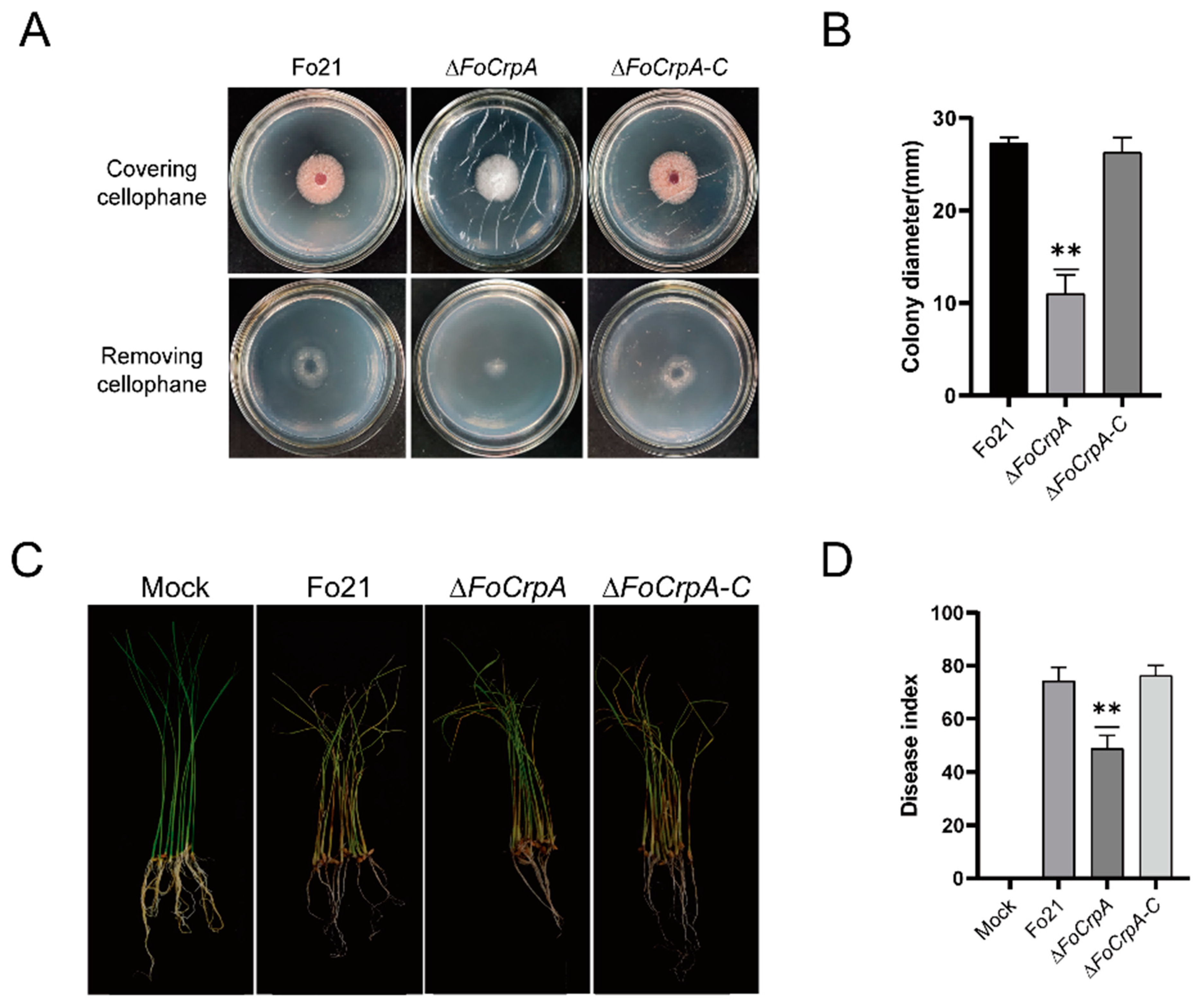
3.3. Effects of FoCrpA on Vegetative Growth and Conidiogenesis
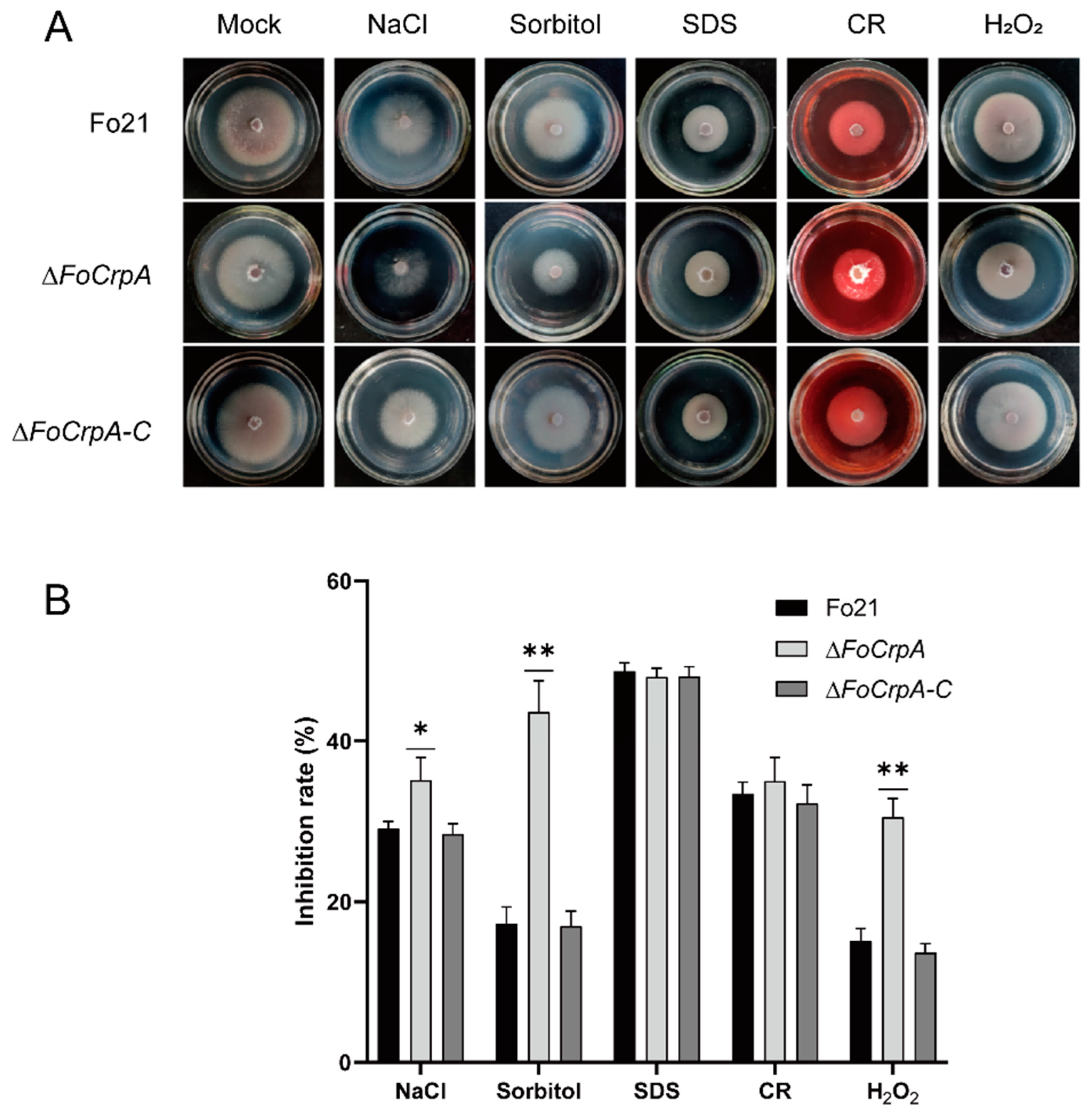
3.4. Response of FoCrpA to Stress Agents
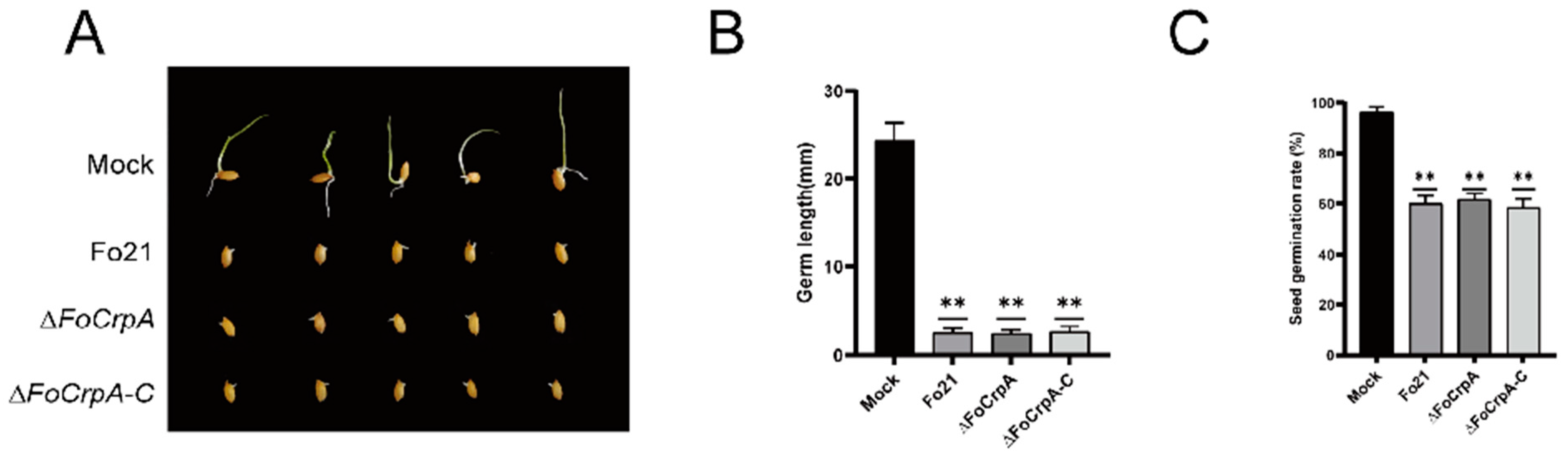
3.5. Culture Filtrates Toxicity from FoCrpA Mutants
3.6. Effect of FoCrpA Mutants on Pathogenicity
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khepar, V.; Sidhu, A.; Sharma, A.B. Nanomaterized Zinc Sulfide-Meerschaum Biomatrix Efficiently Suppressed Fusarium verticilloides with Augmented Rice Seed Quality Benefits during Storage. Pest Manag. Sci. 2023, 79, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaire, S.P.; Zhou, X.G.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, J.; Jo, Y.K. Identification and distribution of fungal pathogens associated with seedling blight of rice in the southern United States. Plant Pathol. 2023, 72, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.G.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Liu, J.X.; Ali, E.; Ji, P.; Pan, H.Y. Occurrence of seedling blight caused by Fusarium tricinctum on rice in China. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, L.; Li, W.Q.; Liu, J.X.; Li, Y.G.; Wei, D. First report of seedling blight caused by Fusarium redolens on rice in northeast China. Plant Dis. 2019, 103, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Wei, P.; Cao, M.; Zhu, L.; Lu, Y. First Report of Rice Seedling Blight Caused by Burkholderia plantarii in North and Southeast China. Plant Dis. 2016, 100, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaire, S.P.; Zhou, X.-G.; Jo, Y.-K.; Shi, J. First Report of Rhizoctonia solani AG-4 Causing Seedling Disease in Rice. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaire, S.-P.; Zhou, X.-G.; Jo, Y.-K. Sterile white basidiomycete fungus Marasmius graminum: A new pathogen causing seedling blight in rice. Plant Dis. 2021, 105, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, R.; Xu, C.; Liu, C.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, S.; Li, Y. Characterisation of Pythium aristosporum Oomycete—A novel pathogen causing rice seedling blight in China. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafey, R.A.S.; Attia, K.A.; Mostafa, F.A.; Elamawi, R.M. Incidence and molecular identification of Cochliobolus carbonum as causal organism of rice seedling blight. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.X.; Cai, Y.N.; Jiang, W.Y.; Li, Y.G.; Zhang, Q.F.; Pan, H.Y. Population structure and genetic diversity of fungi causing rice seedling blight in northeast China based on microsatellite markers. Plant Dis. 2020, 104, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Hu, J.; Tan, K.; Zhao, F.; Yuan, M.; Zhang, J.; Gai, Z. Preventive effects of fluoro-substituted benzothiadiazole derivatives and chitosan oligosaccharide against the rice seedling blight induced by Fusarium oxysporum. Plants 2019, 8, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochi, A.; Konishi, H.; Ando, S.; Sato, K.; Yokoyama, K.; Tsushima, S.; Yoshida, S.; Morikawa, T.; Kaneko, T.; Takahashi, H. Management of bakanae and bacterial seedling blight diseases in nurseries by irradiating rice seeds with atmospheric plasma. Plant Pathol. 2017, 66, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenashen, M.; Derbalah, A.; Hamza, A.; Mohamed, A.; El Safty, S. Antifungal activity of fabricated mesoporous alumina nanoparticles against root rot disease of tomato caused by Fusarium oxysporium. Pest Manag. Sci. 2017, 73, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ding, W.; Liu, C. Unraveling the metabolite signature of endophytic Bacillus velezensis strain showing defense response towards Fusarium oxysporum. Agronomy 2021, 11, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.G.; Wang, J.L.; Cai, J. Effects of Fenaminosulf on Growth of Pepper (Capsicum annuum L.), Microbial Communities and Enzymatic Activities of the Soil Infested with Fusarium oxysporum. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 83, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yruela, I. Copper in Plants: Acquisition, Transport and Interactions. Funct. Plant Biol. 2009, 36, 409–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arredondo, M.; Núñez, M.T. Iron and Copper Metabolism. Mol. Asp. Med. 2005, 26, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapiero, H.; Townsend, D.M.; Tew, K.D. Trace Elements in Human Physiology and Pathology. Copper. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2003, 57, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Shi, L.; Zhang, T.; Ren, A.; Jiang, A.; Yu, H.; Zhao, M. Cross talk between calcium and reactive oxygen species regulates hyphal branching and ganoderic acid biosynthesis in Ganoderma lucidum under copper stress. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e00438-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xiao, X.Z.; Wei, F.; Qiu, J.; Wu, M.; Gao, H.H.; Yang, W.F.; Luo, S.Q. Cloning and expression analysis of copper transporter genes in rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis Müll. Arg.). Plant Physiol. J. 2016, 52, 1389–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkhead, J.L.; Gogolin Reynolds, K.A.; Abdel-Ghany, S.E.; Cohu, C.M.; Pilon, M. Copper homeostasis. New Phytol. 2009, 182, 799–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutigny, S.; Sautron, E.; Finazzi, G.; Rivasseau, C.; Frelet-Barrand, A.; Pilon, M.; Rolland, N.; Seigneurin-Berny, D. HMA1 and PAA1, two chloroplast-envelope PIB-ATPases, play distinct roles in chloroplast copper homeostasis. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1529–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seigneurin-Berny, D.; Gravot, A.; Auroy, P.; Mazard, C.; Kraut, A.; Finazzi, G.; Grunwald, D.; Rappaport, F.; Vavasseur, A.; Joyard, J.; et al. HMA1, a new Cu-ATPase of the chloroplast envelope, is essential for growth under adverse light conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 2882–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, Y.; Izumitsu, K.; Tanaka, C. Phylogenetic analysis of heavy-metal ATPases in fungi and characterization of the copper-transporting ATPase of Cochliobolus heterostrophus. Mycol. Res. 2009, 113, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisot, D.; Dufresne, M.; Veneault, C.; Laugé, R.; Langin, T. Clap1, a gene encoding a copper-transporting ATPase involved in the process of infection by the phytopathogenic fungus Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2002, 268, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Shadkchan, Y.; Tannous, J.; Landero Figueroa, J.A.; Wiemann, P.; Osherov, N.; Wang, S.; Keller, N.P. Contribution of ATPase copper transporters in animal but not Plant virulence of the crossover pathogen Aspergillus flavus. Virulence 2018, 9, 1273–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullins, E.D.; Chen, X.; Romaine, P.; Raina, R.; Geiser, D.M.; Kang, S. Agrobacterium-Mediated transformation of Fusarium oxysporum: An efficient tool for insertional mutagenesis and gene transfer. Phytopathology 2001, 91, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.-H.; Xie, X.-L.; Lin, X.-F.; Shi, J.-X.; Ding, Z.-J.; Ling, J.-F.; Xi, P.-G.; Zhou, J.-N.; Leng, Y.; Zhong, S.; et al. Functional characterization of the gene FoOCH1 encoding a putative α-1,6-mannosyltransferase in Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. Cubense. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2014, 65, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Liu, J.; He, Y.; Payizila, A.; Li, Y. Biological control ability and antifungal activities of Bacillus velezensis Bv S3 against Fusarium oxysporum that causes rice seedling blight. Agronomy 2024, 14, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inesi, G. Molecular features of copper binding proteins involved in copper homeostasis. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antsotegi-Uskola, M.; Markina-Iñarrairaegui, A.; Ugalde, U. Copper resistance in Aspergillus nidulans relies on the P(I)-Type ATPase CrpA, regulated by the transcription factor AceA. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Probst, C.; Garcia-Santamarina, S.; Brooks, J.T.; Van Der Kloet, I.; Baars, O.; Ralle, M.; Thiele, D.J.; Alspaugh, J.A. Interactions between copper homeostasis and the fungal cell wall affect copper stress resistance. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antsotegi-Uskola, M.; Markina-Iñarrairaegui, A.; Ugalde, U. New insights into copper homeostasis in filamentous fungi. Int. Microbiol. 2020, 23, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, Y.; Ding, C. The role of copper homeostasis at the host-pathogen axis: From bacteria to fungi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Santamarina, S.; Thiele, D.J. Copper at the fungal pathogen-host axis. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 18945–18953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.R.; Isikhuemhen, O.S.; Anike, F.N. Fungal-metal interactions: A review of toxicity and homeostasis. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchamp, C.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutase:improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 44, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broxton, C.N.; Culotta, V.C. SOD enzymes and microbial pathogens: Surviving the oxidative storm of infection. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janusz, G.; Pawlik, A.; Świderska-Burek, U.; Polak, J.; Sulej, J.; Jarosz-Wilkołazka, A.; Paszczyński, A. Laccase properties, physiological functions, and evolution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Li, J.; Huang, C.; Zhang, D.; Xu, Y.; Yang, X.; Song, J.; Wang, D.; Qiu, N.; Short, D.P.G.; et al. Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase (VdSOD1) mediates reactive oxygen species detoxification and modulates virulence in Verticillium dahliae. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2021, 22, 1092–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Pu, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, K.; Liu, X. The laccase gene (LAC1) is essential for Colletotrichum gloeosporioides development and virulence on mango leaves and fruits. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 99, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, Y.; Izumitsu, K.; Morita, A.; Tanaka, C. A copper-transporting ATPase BcCCC2 is necessary for pathogenicity of Botrytis cinerea. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2010, 284, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Du, W.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, L.; Zeng, Q.; Chai, Y.; Dai, C.; Lu, L. The Aspergillus fumigatus transcription factor AceA is involved not only in Cu but also in Zn detoxification through regulating transporters CrpA and ZrcA. Cell. Microbiol. 2018, 20, e12864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; He, D.; Fang, X.; Xu, J.; Lee, Y.W.; Keller, N.P.; Shi, J. Copper tolerance mediated by FgAceA and FgCrpA in Fusarium graminearum. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primer Name | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|
| Hyg-F | TCGCCCTTCCTCCCTTTATTTCAG |
| Hyg-R | CTACACAGCCATCGGTCCAGAC |
| SuR-F | CTCTCCGTTGCTTATCCTTGCCTA |
| SuR-R | CGCCATCACTACGCCTTGTCTT |
| FoCrpA-UP-F | GATCTTCACTAGTGGGAATTCCCCGTGATGATTTGCCCAATGAAT |
| FoCrpA-UP-R | TTGGGTACCGAGCTCGAATTCCGCCATGTTGACTGCTGTGAGA |
| FoCrpA-DN-F | TGGGGATCCTCTAGAGTCGACTGGTATTGGCAGTGGTAGTGTTGG |
| FoCrpA-DN-R | CTTGCATGCCTGCAGGTCGACCCGACGGAGGATCAAGATGTAAGC |
| Hup-R | TGCTCACCGCCTGGACGACTAA |
| Hdn-F | TGGACCGATGGCTGTGTAGAAGT |
| Cup | AGGCTTGGAGGAGAATGGTTGG |
| Cdn | AAGCCTTCCTTACGCCTGATGATG |
| FoCrpA-F | TGCTCACCGCCTGGACGACTAA |
| FoCrpA-R | TGGACCGATGGCTGTGTAGAAGT |
| C-FoCrpA-F | CCGGGTACCGAGCTCGAATTCCCGTTGCTCTGCCGTATCTTGAA |
| C-FoCrpA-R | AGCTGTCAAACATGAGAATTCAAGCCTTCCTTACGCCTGATGATG |
| Actin-F | GTTGCCTGAGACTTGACGACGAT |
| Actin-R | CTCCTCCGAACCATCCGCTACA |
| Stains | Disease Index |
|---|---|
| Fo21 | 74.30 ± 5.11 a |
| ∆FoCrpA | 48.90 ± 4.85 b |
| ∆FoCrpA-C | 76.37 ± 3.65 a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Hou, L.; Liu, Q.; Ren, R.; Lv, A.; Liu, X.; Xiong, T.; Guo, P.; et al. Functional Analysis of FoCrpA in Fusarium oxysporum Causing Rice Seedling Blight. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040317
Wang C, Wang L, Zhao X, Hou L, Liu Q, Ren R, Lv A, Liu X, Xiong T, Guo P, et al. Functional Analysis of FoCrpA in Fusarium oxysporum Causing Rice Seedling Blight. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(4):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040317
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chun, Liang Wang, Xuanjie Zhao, Lei Hou, Qingran Liu, Rui Ren, Anqi Lv, Xinyang Liu, Tianliang Xiong, Peng Guo, and et al. 2025. "Functional Analysis of FoCrpA in Fusarium oxysporum Causing Rice Seedling Blight" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 4: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040317
APA StyleWang, C., Wang, L., Zhao, X., Hou, L., Liu, Q., Ren, R., Lv, A., Liu, X., Xiong, T., Guo, P., Xu, X., Ni, Z., Liu, C., & Zhang, J. (2025). Functional Analysis of FoCrpA in Fusarium oxysporum Causing Rice Seedling Blight. Journal of Fungi, 11(4), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11040317






