Research Progress and Management Strategies for the Common Mycotoxin Contamination of Traditional Chinese Medicines
Abstract
1. Introduction
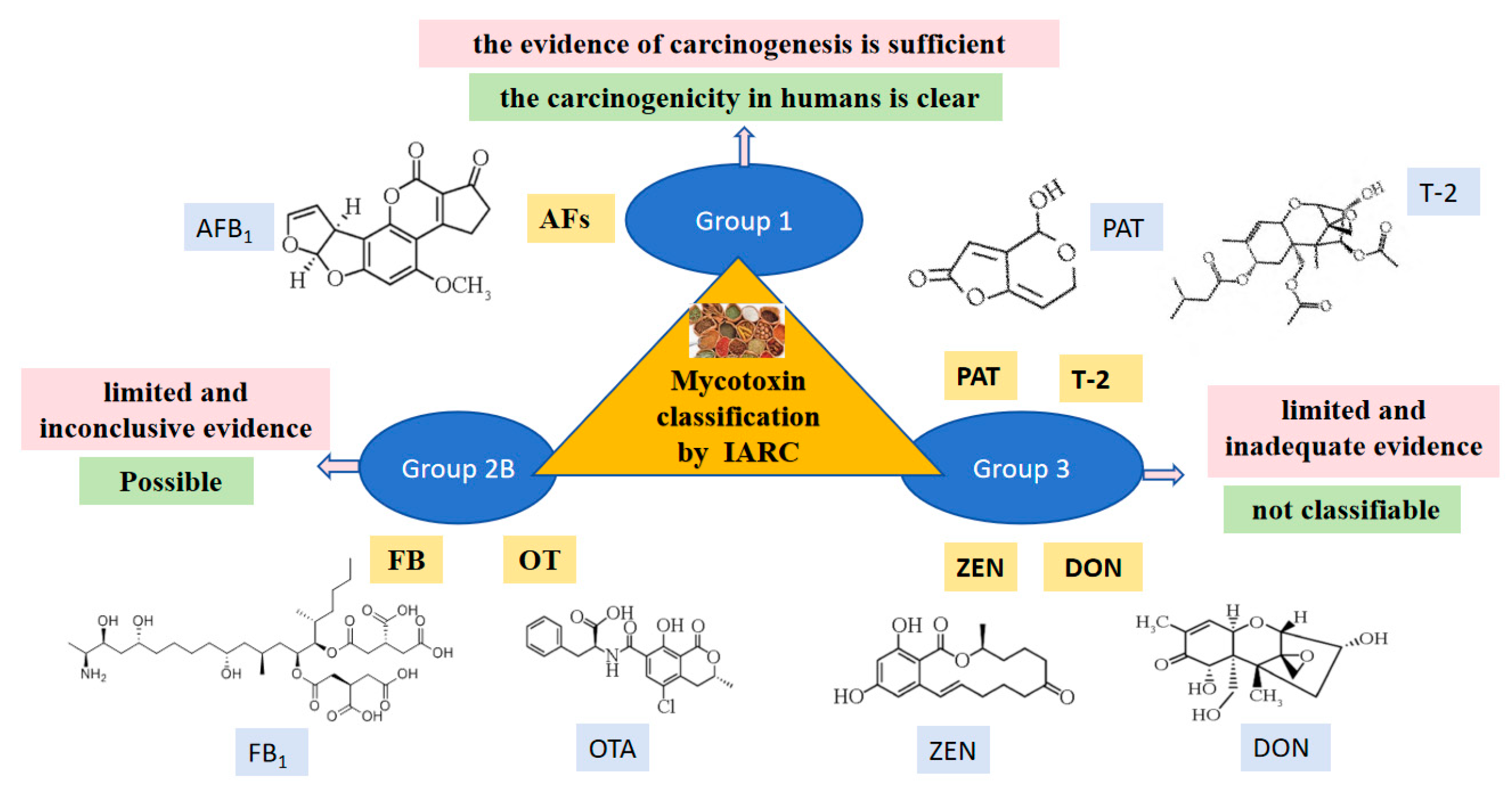
2. Mycotoxin Contamination in Traditional Chinese Medicines
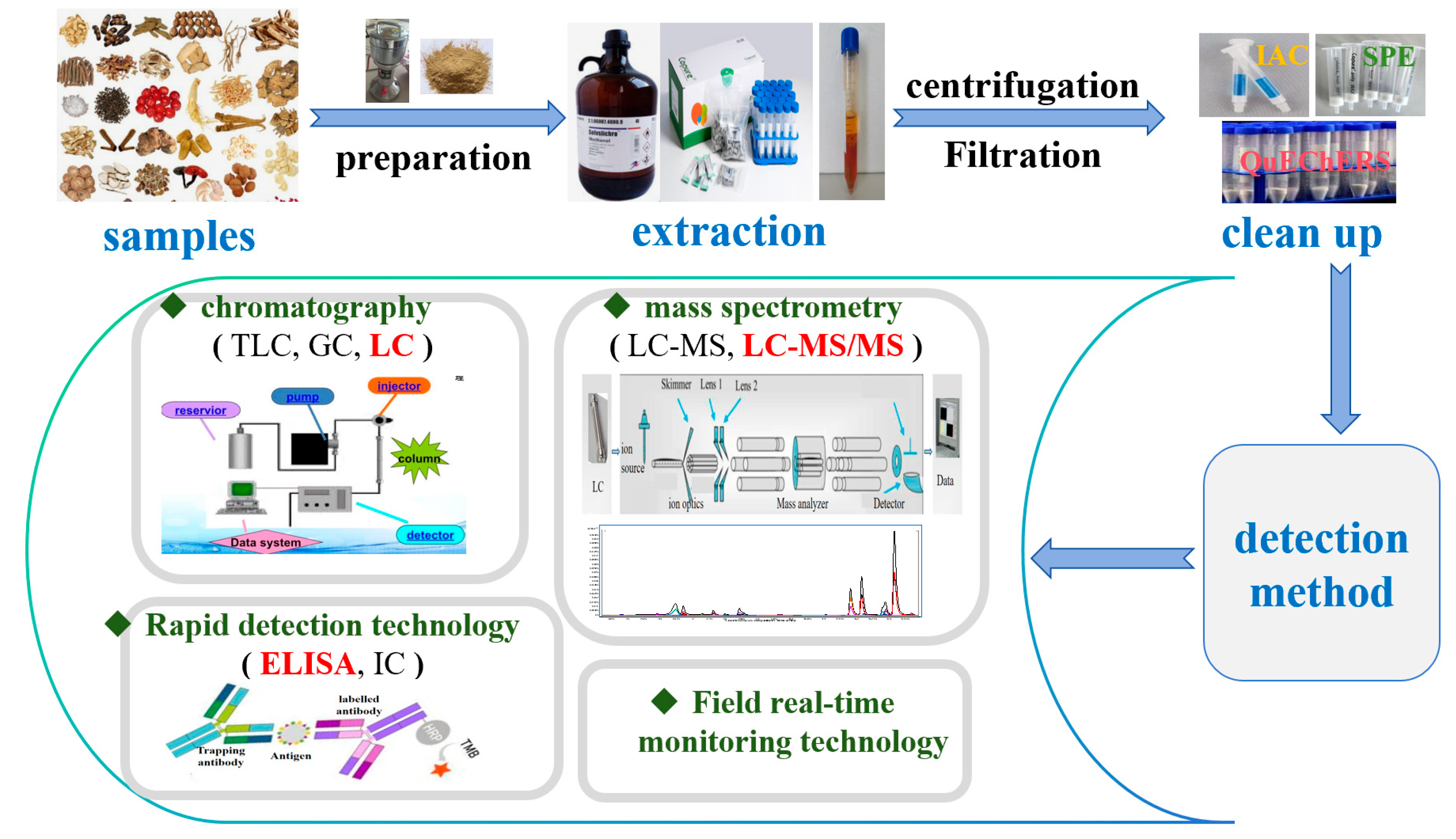
3. Detection Methods of Mycotoxins in Traditional Chinese Medicines
3.1. Detection Methods and Limited Standards of Mycotoxins in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia
3.2. The Process of Common Detection Methods for Mycotoxins
3.2.1. Liquid Chromatography
3.2.2. Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)
3.2.3. Rapid Detection Technology
3.2.4. Field Real-Time Monitoring Technology
| Detection Method | Sample | Pretreatment Technology | The Number of Toxins Detected | Toxin Species Detected | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC (including fluorescence detector with post column photochemical derivatization, or post-column iodine derivatization) | Ziziphi spinosae semen, Citri reticulatae pericarpium, Paeoniae radix alba, Angelica sinensis radix, Ophiopogonis radix, Schisandra chinensis fructus, Isatidis radix, Astragali radix, Bupleuri radix, Salviae miltiorrhizae radix et rhizoma | IAC | 4 | AFB1 | [21] |
| Sterculiae lychnophorae semen, Ziziphi spinosae semen, Jujubae fructus, Scorpio, Sojae semen praeparatum, Arctii fructus, Euphorbiae semen, Platycladi semen, Coicis semen, Persicae semen, Citri reticulatae pericarpium | IAC | 4 | AFB1, AFB2, AFG1, AFG2 | [76] | |
| Myristicae semen | Ultrasound assisted solid–liquid extraction and IAC | 5 | AFB1, AFB2, AFG1, AFG2, OTA | [24] | |
| Astragali radix, Scutellaria radix, Angelica sinensis radix, Glycyrrhizae radix et rhizoma, Morindae officinalis radix, Atractylodis rhizoma, Salviae miltiorrhizae radix et rhizoma, Panacis quinquefolii radix | IAC | 9 | OTA | [33] | |
| Corydalis rhizoma, Armeniacae semen amarum, Ephedrae herba, Platycladi semen | IAC | 4 | Total AFs | [77] | |
| Jujubae fructus, Angelica sinensis radix, Astragali radix, Bombyx batryticatus, Sterculiae lychnophorae semen, Ginseng radix et rhizoma, Notoginseng radix et rhizoma, Persicae semen, Coicis semen, Citri reticulatae pericarpium, Ziziphi spinosae semen | IAC | 4 | Total AFs | [78] | |
| Platycladi semen, Coicis semen, Cassiae semen, Codonopsis radix | IAC | 4 | AFB1, Total AFs | [79] | |
| Coicis semen | IAC | 7 | AFB1, AFB2, AFG1, AFG2, ZOL, ZEN | [80] | |
| HPLC-MS/MS | Myristicae semen | IAC | 12 | OTA, AFB1, AFB2 | [81] |
| Myristicae semen | QuEChERS | 21 | AFB1, AFB2, AFG1, AFG2, AFM1 | [82] | |
| Eupolyphaga steleophaga | QuEChERS | 9 | FB1, FB2 | [19] | |
| Angelica sinensis radix | SPE | 9 | AFB1, AFB2, AFG1 | [81] | |
| Persicae semen | QuEChERS | 10 | AFB1 | [82] | |
| Coicis semen | / | 14 | ZEN, AFB1, AFB2, DON, ST | [50] | |
| Astragali radix, Coicis semen, Eupolyphaga steleophaga | SLE-SPE, QuEChERS | 21 | AFB1, AFB2, OTA, OTB, PA | [85] | |
| Notoginseng radix et rhizoma | SPE | 26 | FB1 | [42] | |
| Quisqualis fructus | SPE | 22 | AFB1, AFB2, AFM1, OTA, OTB, ZEN | [54] | |
| Coicis semen, Polygalae radix, Eupolyphaga steleophaga, Polygalae Radix, Eupolyphaga Steleophaga | multi-IAC | 10 | AFB1–AFs, AFB1–FBs, AFB1–DON, AFB1–T-2, AFB1–OTA | [85] | |
| Coicis semen, Galli gigerii endothelium corneum, Hordei fructus germinatus, Persicae semen, Dioscoreae rhizoma, Poria | multifunction clean-up columns | 16 | AFB1, AFB2, AFG1, ZEN, DON, OTA, NIV, FB1, FB2, FB3 | [58] | |
| Polygoni multiflori radix | Modified QuEChERS | 12 | AFB1, AFG1, T-2, HT-2, OTA, OTB, FB1, FB2 | [61] | |
| Dichondra micrantha Urb. | Modified QuEChERS | 10 | AFB1, AFG1, ZEN, OTA, DON, FB1 | [86] | |
| Glehniae radix, Astragali radix, Codonopsis radix | mPFC- QuEChERS | 16 | OTA, ST, 15-ACE | [87] | |
| Polygonati rhizoma, Ophiopogonis radix | SPE | 10 | FB2, ZEN | [43] | |
| Lonicerae flos, Puerariae lobatae radix, Hippophae fructus | Accelerated solvent extraction (ASE)-QuEChERS | 16 | AFB1, AFG2, OTA, FB1 | [88] | |
| Immunochromatographic detection technique | Dendrobium candidum | ELISA | 1 | AFB1 | [91] |
| Ziziphi spinosae semen, Persicae semen, Hordei fructus germinatus, Polygalae radix, Cassiae semen, Platycladi semen | ELISA | 4 | Total AFs | [92] | |
| Ground beetle, cockroach, Silkworm, Earthworm | ELISA | 1 | AFB1 | [100] | |
| Jujubae fructus, Nelumbinis semen, Coicis semen, Poria, Lilii bulbus, Euryales semen, Sojae semen nigrum, Pseudostellariae radix, Cinnamomi cortex, Phragmitis rhizoma, Dioscoreae rhizoma, Codonopsis radix, Crataegi fructus, Vignae semen, Prunellae spica | ELISA | 4 | AFB1, Total AFs | [91] | |
| Ginseng radix et rhizoma, Astragali radix, Angelica sinensis radix | Lateral flow immunochromatography, LFIC | 3 | ZEN, AFB1, OTA | [94] | |
| Lotus seed | ELISA | 1 | AFB1 | [101] | |
| Fallopia multiflora, Codonopsis pilosula, Apricot kernel, Zingiber officinale, Wild jujube seed, Malt, Cassia obtusifolia, Red lotus seed | immunochromatographic test strip (ICS) | 6 | AFB1, ZEN, T-2 | [102] | |
| Astragali radix, Scutellariae radix, Glycyrrhizae radix et rhizoma, Atractylodis macrocephalae rhizoma, Bupleuri radix, Lonicerae japonicae flos, Phellodendri chinensis cortex, Chuanxiong rhizoma, Isatidis radix, Pinelliae rhizoma, Notoginseng radix et rhizoma, Polygonati rhizoma, polygoni multiflori radix | IAC and ELISA | 1 | OTA | [96] | |
| Field real-time monitoring technology | Coicis semen, Jujubae fructus, Cassiae semen | electrochemical biosensor | 1 | AFB1 | [98] |
| Nelumbinis semen, Panacis quinquefolii radix | electrochemical biosensor | 1 | OTA | [99] |
4. Comprehensive Prevention and Control Strategies for Mycotoxins in Traditional Chinese Medicines
5. Regulatory Recommendations for Mycotoxins Contamination in Traditional Chinese Medicines
5.1. Improve the Detection Standards
5.2. Supplement Limit Regulations
5.3. Strengthen Risk Monitoring Programs
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, R.S.; Ye, C.; Hu, Q.P.; Tong, P.Z.; Sun, D.M.; Chen, X.D.; Deng, C.Y.; Luo, W.H. Research progress on mycotoxin contamination of traditional Chinese medicine. Guangdong Chem. Ind. 2024, 51, 76–79. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, G.F.; Guo, X.T.; Liang, Y.C.; Liu, C.S.; Zhang, G.Z.; Liang, C.L.; Huang, Z.X.; Zheng, Y.Q.; Chen, S.L.; Dong, L.L. Occurrence of fungi and mycotoxins in herbal medicines and rapid detection of toxin-producing fungi. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 333, 122082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.S.; Xu, H.; Wang, W.L.; Zhan, R.T.; Chen, W.W. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxin B1, B2, G1, G2, ochratoxin A and sterigmatocystin in traditional Chinese medicines by LC-MS-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3031–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Zhao, X.S.; Liu, X.M.; Yang, M.H. Composition and toxin-producing characteristics of exogenous contaminated fungi from Codonopsis pilosula. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 34, 66–70. [Google Scholar]
- Su, C.Y.; Wei, J.C.; Hu, Y.J.; Luo, Y.; Gao, W.W. Optimization of isolation method of contamination fungi on three root medicinal herbs. Mod. Chin. Med. 2017, 19, 688–692. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.X.; Zhou, H.Y.; Guo, T.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.H.; Ma, L. Recent advances on formation, transformation, occurrence, and analytical strategy of modified mycotoxins in cereals and their products. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Chen, H.P.; Liu, Y.P. Research status of fungal and mycotoxins pollution of Chinese medicinal materials. World Sci. Technol. Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2015, 11, 2381–2388. [Google Scholar]
- Alshannaq, A.; Yu, J.H. Occurrence, toxicity, and analysis of major mycotoxins in food. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 632–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.R.; Tang, X.Q.; Jallow, A.; Qi, X.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, P.W. Development of an ultrasensitive and rapid fluorescence polarization immunoassay for ochratoxin A in rice. Toxins 2020, 12, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Ma, S.C.; Lin, R.C. A Survey of research on mycotoxins contamination of nature medicines. Chin. Pharm. Aff. 2009, 23, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Omotayo, O.P.; Omotayo, A.O.; Mwanza, M.; Babalola, O.O. Prevalence of mycotoxins and their consequences on human health. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 35, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Rocha, M.E.B.; Da Chagas Oliveira Freire, F.; Feitosa Maia, F.E.; Florindo Guedes, M.I.; Rondina, D. Mycotoxins and their effects on human and animal health. Food Control 2014, 36, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.L.; Kong, W.J.; Yang, M.H.; Han, J.P.; Chen, S.L. Safety issues and new rapid detection methods in traditional Chinese medicinal materials. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, L.; Jiang, J.Y.; Zhang, L.; Dou, X.W.; Zhen, O.Y.; Wan, L.; Yang, M.H. Occurrence and analysis of mycotoxins in domestic Chinese herbal medicines. Mycology 2020, 11, 126–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.J.; Liao, Z.Q.; Jin, G.Y. Progress in detection methods for mycotoxin. Drug Stand. China 2023, 24, 465–475. [Google Scholar]
- Nan, M.N.; Xue, H.L.; Bi, Y. Contamination, detection and control of mycotoxins in fruits and vegetables. Toxins 2022, 14, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostry, V.; Malir, F.; Toman, J.; Grosse, Y. Mycotoxins as human carcinogens-the IARC monographs classification. Mycotoxin Res. 2017, 33, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.M.; Mubatanhema, W.; Jurjevic, Z. Biology and ecology of mycotoxigenic Aspergillus species as related to economic and health concerns. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2002, 504, 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.M.; Wang, P.Y.; Zhu, K. Research progress in simultaneous detection of mycotoxins in traditional Chinese medicine. SHS Web Conf. 2023, 179, 05002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.W.; Xiong, L.Y.; Wang, R.F.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Q.S.; Lei, Y.; Wang, Q. Determination of aflatoxin G2, G1, B2, B1 in 34 batches of Chinese herbs by HPLC associated with post column photochemical derivatization. Res. Pract. Chin. Med. 2013, 27, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.Z.; Wang, Z.; Gao, W.W.; Chen, J.; Yang, M.H.; Kuang, Y.; Huang, L.F.; Chen, S.L. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A in licorice roots and fritillary bulbs by solid-phase extraction coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1048–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.J.; Jiao, X.L.; Hu, Y.J.; Lu, Z.H.; Gao, W.W. Mycobiota and mycotoxins in traditional medicinal seeds from China. Toxins 2015, 7, 3858–3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.J.; Liu, S.Y.; Qiu, F.; Xiao, X.H.; Yang, M.H. Simultaneous multi-mycotoxin determination in nutmeg by ultrasound-assisted solid-liquid extraction and immunoaffinity column clean-up coupled with liquid chromatography and on-line post-column photochemical derivatization fluorescence detection. Analyst 2013, 138, 2729–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarzadeh, S.; Hadidi, M.; Forough, M.; Nafchi, A.M.; Khaneghah, A.M. The control of fungi and mycotoxins by food active packaging: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2023, 23, 6393–6411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Ma, Y.R.; Liang, J.B.; Wei, Z.W.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, M.; He, H.; Qu, C.F.; Cai, J.Q.; et al. AHR mediates the aflatoxin B1 toxicity associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.K.; Zan, L.S. Advances in studies on hazards, detection methods and biodegradation of aflatoxins. Prog. Vet. Med. 2009, 30, 91–94. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wu, F. Global burden of aflatoxin-induced hepatocellular carcinoma: A risk assessment. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez, M.; Rodríguez, A.; Peromingo, B.; Núñez, F.; Rodríguez, M. Enterococcus faecium: A promising protective culture to control growth of ochratoxigenic moulds and mycotoxin production in dry-fermented sausages. Mycotoxin Res. 2019, 36, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabañes, F.J.; Bragulat, M.R.; Castellá, G. Ochratoxin A producing species in the genus Penicillium. Toxins 2010, 2, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malir, F.; Ostry, V.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Malir, J.; Toman, J. Ochratoxin A: 50 years of research. Toxins 2016, 8, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, J.I. Toxigenic fungi and mycotoxins. Br. Med. Bull. 2000, 56, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Wang, L.N.; Pan, J.Y.; Xiang, L.; Yang, M.H.; Logrieco, A.F. Determination of ochratoxin A in traditional Chinese medicinal plants by HPLC-FLD. Food Addit. Contam. A 2010, 27, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yang, Z.; Jin, M.N.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Y.W.; Wu, X.; Zhou, Y.H. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxin, zearalenone, and ochratoxin A in Massa Medicata Fermentata by high-performance liquid chromatography and fluorescence detection. China Med. Pharm. 2024, 14, 61–64. [Google Scholar]
- Hohler, D. Ochratoxin A in food and feed: Occurrence, legislation and mode of action. Eur. J. Nutr. 1998, 37, 2–12. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, X.; Feng, Y.C.; Suo, D.C.; Xiao, Z.M.; Wang, S.; Liang, Y.; Fan, X. Simultaneous determination of 11 mycotoxins in maize via multiple-impurity adsorption combined with liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Foods 2022, 11, 3624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, E.; Dietrich, D.R. Ochratoxin A: The continuing enigma. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2005, 35, 33–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwabulili, F.; Xie, Y.L.; Li, Q.; Sun, S.M.; Yang, Y.H.; Ma, W.B. Research progress of ochratoxin a bio-detoxification. Toxicon 2023, 222, 107005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelderblom, W.C.A.; Marasas, W.F.O. Controversies in fumonisin mycotoxicology and risk assessment. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2012, 31, 215–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rheeder, J.P.; Marasas, W.F.O.; Vismer, H.F. Production of fumonisin analogs by Fusarium species. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2002, 68, 2101–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, Y.F.; Sun, X.; Zhang, M.M.; Xie, Z.M. Simultaneous determination of nine mycotoxins in Eupolyphaga steleophaga and six kinds of Chinese medicinal preparations containing Eupolyphaga steleophaga by UHPLC-MS combined with QuEChERS. Chin. Mod. Med. 2022, 24, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.M.; Du, C.X.; Liu, X.X.; Liu, G.P.; Mao, D.; Liang, Y.F.; Huang, X.J.; Zhu, X.F.; Chen, K.; Ji, S. Simultaneous determination of 26 mycotoxins in Notoginseng Radix et Rhizoma by QuEChERS-ultra-high-performance liquid chromatograpty-tandem mass spectrometry. World Chin. Med. 2019, 14, 798–804. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, L.; Tang, Y.; Chen, T.Z.; Cui, H.M.; Luo, H. Determination of 10 mycotoxins in Polygonati rhizoma and Ophiopogonis radix as a genuine regional drug of Sichuan by solid-phase extraction coupled with LC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 43, 1369–1380. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.M.; Su, J.M.; Lei, H.Y.; Ning, L.Z.; Zhao, Z.M. Progress in fumonisin research. Prog. Vet. Med. 2014, 35, 97–100. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, D.; Yu, J.J.; Ehrlich, K.C. Toxins of filamentous fungi. Chem. Immunol. 2002, 81, 167–206. [Google Scholar]
- Adejumo, T.O.; Hettwer, U.; Karlovsky, P. Survey of maize from southwestern Nigeria for zearalenone, alpha- and beta-zearalenols, fumonisin B1 and enniatins produced by Fusarium species. Food Addit. Contam. 2007, 24, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazar, S.; Omurtag, G. Fumonisins, trichothecenes and zearalenone in cereals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 2062–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, H.B.; Seo, J.A.; Lee, Y.W. Co-occurrence of Fusarium mycotoxins in mouldy and healthy corn from Korea. Food Addit. Contam. 1999, 16, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briones-Reyes, D.; Gomez-Martinez, L.; Cueva-Rolon, R. Zearalenone contamination in corn for human consumption in the state of Tlaxcala, Mexico. Food Chem. 2007, 100, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manova, R.; Ladenova, R. Incidence of zearalenone and fumonisins in Bulgarian cereal production. Food Control. 2009, 20, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.F.; Liu, W.K.; Logrieco, A.F.; Yang, M.G.; Ou-yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Guo, Q. Determination of zearalenone in tradtional Chinese medicinal plants and related products by HPLC-FLD. Food Addit. Contam. A 2011, 28, 885–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.H.; Pan, X.J.; Yin, F.; Zhang, S.F.; Gao, T.; Feng, T.H.; Zhang, C.J.; Cai, L.T.; Liang, Z.S.; Zhang, X.D. Simultaneous Determination of Eight Fungal Toxins in Coix Seeds by QuEChERS Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Zhejiang Sci-Tech Univ. 2025, 53, 254–262. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.X.; Jiang, W.K.; Yang, C.G.; Yuan, Q.S.; Guo, L.P.; Shen, Y.W.; Wen, N.T.; Zhang, J.Q.; Zhou, T. Contamination status and exposure risk of mycotoxins in Coicis semen. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2023, 48, 1491–1497. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Huang, X.J.; Luo, X.; Dai, Q.; Wen, Y.S.; Zhao, X.Q. Simultaneous detection and risk assessment of 22 fungal toxins in Quisqualis indica L. using UHPLC-MS/MS. Lishizhen Med. Mater. Med. Res. 2021, 32, 984–987. [Google Scholar]
- Mahato, D.K.; Devi, S.; Pandhi, S.; Sharma, B.; Maurya, K.K.; Mishra, S.; Dhawan, K.; Selvakumar, R.; Kamle, M.; Mishra, A.K.; et al. Occurrence, impact on agriculture, human health, and management strategies of zearalenone in food and feed: A review. Toxins 2021, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMullen, M.; Jones, R.; Gallenberg, D. Scab of wheat and barley: A re-emerging disease of devastating impact. Plant Dis. 1997, 81, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.; Srivastava, S.; Dewangan, J.; Divakar, A.; Kumar Rath, S. Global occurrence of deoxynivalenol in food commodities and exposure 581 risk assessment in humans in the last decade: A survey. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2020, 60, 1346–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.H.; Li, Z.H.; Yang, L.; Yuan, Y.C.; Wang, S.X.; Wang, A.X.; Li, W.; Zheng, F.J. Determination and analysis of 16 mycotoxins in medicinal and edible traditional chinese medicine. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2022, 43, 268–275. [Google Scholar]
- Daenicke, S.; Keese, C.; Goyarts, T.; Döll, S. Effects of deoxynivalenol (DON) and related compounds on bovine peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) in vitro and in vivo. Mycotox. Res. 2011, 27, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.M.; Wang, H.; Wu, L.X.; Wang, L.Q.; Wang, D.; Wang, M. Research progress of deoxynivalenol in wheat. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2020, 11, 423–432. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Su, X.; Feng, W.H.; Li, R.R.; Liu, X.Q.; Li, P.Y.; Wang, Z.M. Simultaneous determination of 12 mycotoxins in Polygoni Multiflori Radix by UPLC-ESI-MS/MS combined with modified QuEChERS. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2016, 41, 1474–1479. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, D.T.; Gao, Y.J.; Zhang, W.J.; Bi, T.C.; Wang, X.; Ma, C.X.; Rong, R. Development a multi-immunoaffinity column LC-MS-MS method for comprehensive investigation of mycotoxins contamination and co-occurrence in traditional Chinese medicinal materials. J. Chromatogr. B. 2021, 1178, 122730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohnal, V.; Jezkova, A.; Jun, D.; Kuca, K. Metabolic pathways of T-2 Toxin. Curr. Drug Metab. 2008, 9, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.X.; Zhang, H.X.; Hua, R.M. Research progress in toxicological effects and mechanism of T-2 toxin. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2011, 6, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Paster, N.; Barkai-Golan, R. Mouldy fruits and vegetables as a source of mycotoxins: Part 2. World Mycotoxin J. 2008, 4, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xi, J.H.; Liu, Z.G.; Chen, M.X.; Lu, Z.H.; Xue, H.L.; Bi, Y. Isolation and identification of pathogens causing blue mold of lanzhou lily during postharvest storage and control of disease and mycotoxin accumulation by ozone treatment. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, B.R.; Yang, X.; Xue, H.L.; Nan, M.N.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Z.G.; Bi, Y.; Shang, S.Q. isolation of main pathogens causing postharvest disease in fresh Codonopsis pilosula during different storage stages and ozone control against disease and mycotoxin accumulation. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, J.H.; Yang, D.Y.; Xue, H.L.; Liu, Z.G.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Shang, S.Q. Isolation of the main pathogens causing postharvest disease in fresh Angelica sinensis during different storage stages and impacts of ozone treatment on disease development and mycotoxin production. Toxins 2023, 15, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.C.; Yang, M.H.; Xu, J. Research advance on patulin. Guizhou Agric. Sci. 2010, 38, 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, K.Q. Chemical detection methods for penicillin. Foreign Med. Hyg. Vol. 2001, 28, 29–32. [Google Scholar]
- De Sales-Neto, J.M.; Rodrigues-Mascarenhas, S. Immunosuppressive effects of the mycotoxin patulin in macrophages. Arch. Microbiol. 2024, 206, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadok, I.; Stachniuk, A.; Staniszewska, M. Developments in the monitoring of patulin in fruits using liquid chromatography: An overview. Food Anal. Methods 2018, 12, 76–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.R.; Xu, Y.X.; Xu, F.; Gao, W. High sensitive method for the detection of aflatoxins in extract from Chinese medicinal herb. J. Cap. Med. Univ. 2011, 32, 379–383. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, C.C.; Chen, D.; Ma, H.Y.; Jiang, Y. Graphene oxide adsorbent based dispersive solid phase extraction coupled with multi-pretreatment clean-up for analysis of trace aflatoxins in traditional proprietary Chinese medicines. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1044–1045, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Liu, H.L.; Chen, J.M. Immunoaffinity column cleanup with liquid chromatography using post-column bromination for aflatoxins in medicinal herbs and plant extracts. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2005, 43, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, N.N.; Zhou, L.M.; Liu, J.T.; Hu, N.H. Simultaneous determination of content of four aflatoxins in 21 kinds of traditional Chinese medicine decocting pieces by high performance liquid chromatography. Shandong J. Tradit. Chin. 2019, 38, 1067–1071. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.H.; Chen, J.M.; Zhang, X.H. Immunoaffinity column clean-up and liquid chromatography with post-column derivatization for analysis of aflatoxins in traditional Chinese medicine. Chromatographia 2005, 62, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, R.; Mao, D.; Wang, S.M.; Wang, K.; Ji, S. Determination of aflatoxin G2, G1, B2, B1 in eleven kinds of Chinese herbs by HPLC. Chin. J. Pharm. 2010, 41, 368–372. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, L.N.; Wang, Y.D.; Dou, X.W.; Duan, Y.P.; Yang, S.M.; Wang, J.H.; Yang, M.H. Comparative study on the distribution of aflatoxins contamination status in four commonly used Chinese herbal pieces. Mod. Tradit. Chin. Med. Materia-World Sci. Technol. 2020, 22, 3718–3725. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.H.; Dou, J.Y.; Xiao, Z.G. Study on the content changes of fungal toxin in YiYiRen under different storage conditions. West. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2018, 31, 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, D.; Ye, L.L.; Wang, S.M.; Liu, X.X.; Chen, K.; Ji, S. Simultaneous determination of 12 mycotoxins in Myristicae Semen by LC-MS /MS. China Pharm. 2020, 23, 1311–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.S.; Liu, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.K.; Yang, M.H. Development and optimization of a method based on QuEChERS-dSPE followed by UPLC-MS/MS for the simultaneous determination of 21 mycotoxins in nutmeg and related products. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.F.; Jiao, J.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, F.; Huang, Y.F.; Wang, Q.; Liu, L.L.; Zhang, H. Simultaneous determination of 9 mycotoxins in Angelica sinensis by ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Cold-Arid Agri. Sci. 2024, 3, 974–980. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, H.Y.; Xiao, Z.G.; Xu, Q. Determination of 10 mycotoxins in Peach kernel by high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Cold Drought Agric. Sci. 2024, 2, 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, M.; OuYang, Z.; Yang, M. A comprehensive strategy for screening and exploring multi-class mycotoxins contamination status in Astragali Radix. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, D.J.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, H.H.; Li, P.; Huang, H.L. Establishment of UPLC-MS/MS determination of 10 mycotoxins in Dichondra micrantha UIb. J. Southwest Minzu Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.). 2023, 49, 530–536. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.M.; Gu, S.Q.; Gu, L.H.; Li, J.M. Determination of 16 mycotoxins in three radix and rhizome Chinese herbal medicines by mPFC-QuEChERS with UPLC-MS/MS. J. Instrum. Anal. 2024, 43, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Z.; Qu, L.; Gu, S.Q.; Chen, R.H.; Li, Y.; Deng, X.J.; Guo, D.H.; Feng, F. Determination of 16 mycotoxins in drug and food homologous products by ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry combined with accelerated solvent extraction and QuEChERS. Chin. J Chromatogr. 2020, 38, 782–790. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, Q.; Hu, B.S.; Shen, Q.; Yang, G.; Liang, X.; Sun, X.; Liu, F.Q. Development of a sensitive ELISA for the analysis of the organophosphorous insecticide fenthion in fruit samples. Food Chem. 2008, 106, 1278–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urusov, A.E.; Zherdev, A.V.; Petrakova, A.V.; Sadykhov, E.G.; Koroleva, O.V.; Dzantiev, B.B. Rapid multiple immunoenzyme assay of mycotoxins. Toxins 2015, 7, 238–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.S.; Wang, L.L.; Ma, F.R.; Ye, Y.P.; Bi, Y.N.; Wang, L.X. Determination of aflatoxin B1 in Dendrobium candidum of Yunnan province by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay method. J. Food Saf. Qual. 2020, 11, 7052–7056. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, X.Y.; Mao, W.W.; Wang, Y.D.; Feng, H.; Zhang, D.H.; Zhang, L.L. Rapid detection of total aflatoxin in traditional herbal medicines by ELISA. Chin. Tradit. Pat. Med. 2020, 42, 2376–2381. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.Q.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, S.Q. Study on the determination of aflatoxin in traditional Chinese medicine slices with the homology of medicine and food by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Mod. Food. 2022, 28, 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, B.F.; Ma, B.; Li, J.L.; Mei, Q.; Zhou, Y.X.; Zhang, M.Z. Simultaneous and rapid detection of three mycotoxins in food and medicine homologous materials by fluorescent nanoparticle-based immunochromatography. Mod. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 40, 227–235. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, S.L.; Ma, J.J.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Wang, H.G.; Sun, J.H.; Yan, Y.X. One step rapid detection of fumonisin B1, dexyonivalenol and zearalenone in grains. Food Control 2020, 117, 107107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Z.; Zhang, X.Z.; Yuan, Y.W.; Zhang, W. Detection of ochratoxin A using immunoaffinity chromatography combined with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Food Sci. 2024, 45, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.N.; Liao, X.F.; Jia, B.Y.; Shi, L.C.; Zhang, D.K.; Wang, R.L.; Zhou, L.D.; Kong, W.J. Development of a ZnCdS@ZnS quantum dots-based label-free electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for sensitive determination of aflatoxin B1 in lotus seed. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.H.; You, J.K.; Wang, T.Y.; Yu, Y.Y.; Zhang, H.Y. Electrochemical biosensor for rapid detection of AFB1 in Chinese herbal medicine. Chin. J. Anal. Lab. 2021, 40, 130–134. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, S.; Huang, R.F.; Mao, W.W.; Zhang, H.Y. Construction of electrochemical aptamer sensor for rapid detection of OTA in Chinese herbal medicine. Chin. J. Anal. Lab. 2024, 43, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.J.; Zhang, L.; Luo, J.Y.; Qin, J.A.; Jiang, J.Y.; Qin, L.; Zhao, Z.G.; Yang, S.H.; Yang, M.H. Development of a sensitive indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for high-throughput detection and risk assessment of aflatoxin B1 in animal-derived medicines. Toxicon 2021, 197, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.F.; Dou, X.W.; Kong, W.J.; Yang, M.H.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, M.; Ou-yang, Z. Contamination level of aflatoxin B1 in Lotus seeds rapid screening by indirect competitive ELISA method. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2015, 40, 704–709. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.Y.; Li, X.J.; Xie, J.H.; Huang, Z.B. Rapid and simultaneous detection of aflatoxin B1, zearalenone, and T-2 toxin in medicinal and edible food using gold immunochromatographic test strip. Foods 2023, 12, 633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
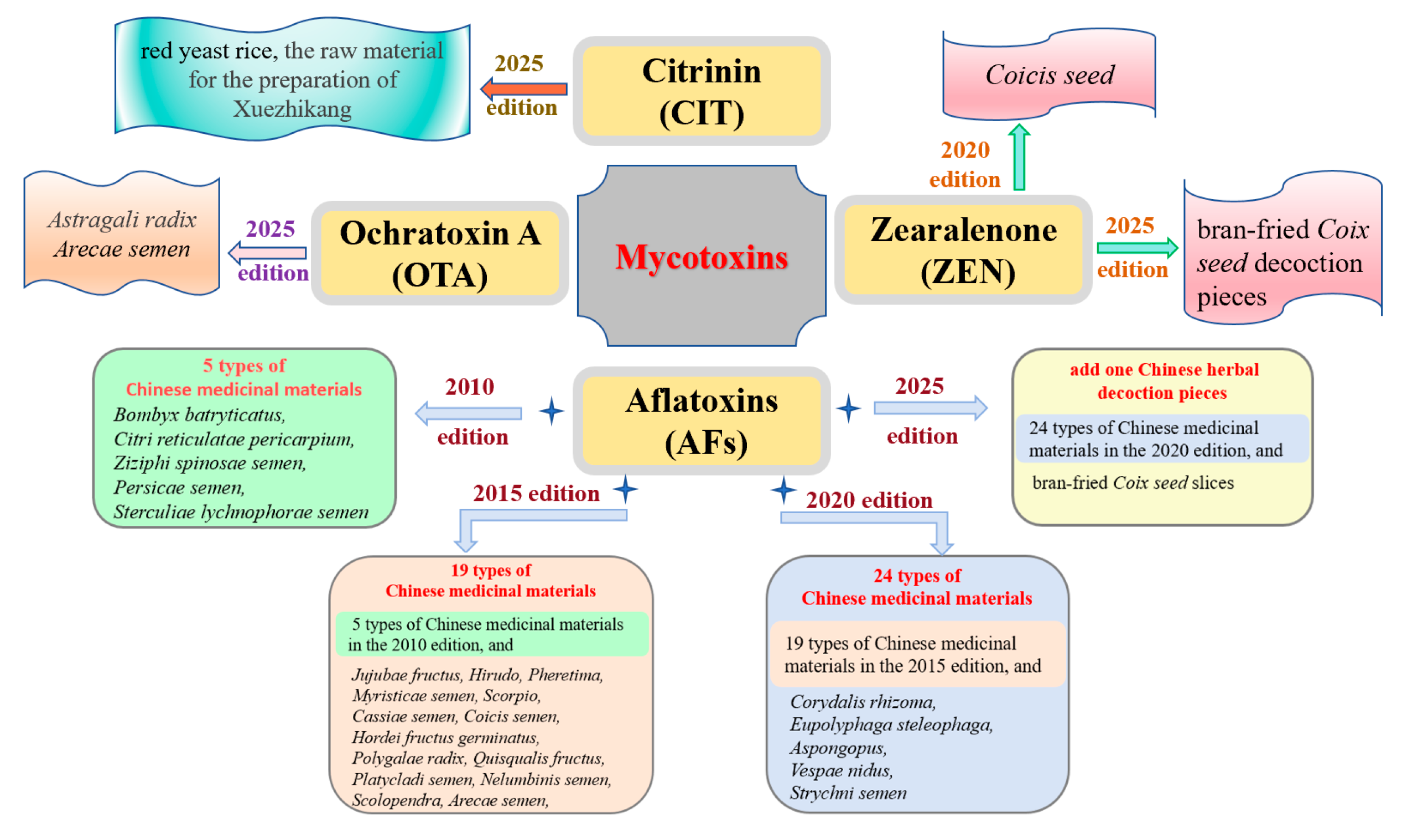
| Traditional Chinese Medicines | The Limit Value of Mycotoxins (μg/kg) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Total AFs | AFB1 | ZEN | |
| Bombyx batryticatus, Citri reticulatae pericarpium, Ziziphi spinosae semen, Persicae semen, Hirudo, Sterculiae lychnophorae semen, Jujubae fructus, Pheretima, Myristicae semen, Cassiae semen, Hordei fructus germinatus, Quisqualis fructus, Polygalae radix, Platycladi semen, Scorpio, Nelumbinis semen, Scolopendra, Arecae semen, Coicis semen, Corydalis rhizoma, Aspongopus, Eupolyphaga steleophaga, Vespae nidus, and Strychni semen. | 10 | 5 | / |
| Coicis semen | / | / | 500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Xue, H.; Han, Y.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Y. Research Progress and Management Strategies for the Common Mycotoxin Contamination of Traditional Chinese Medicines. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11060411
Yang Z, Xue H, Han Y, Ding H, Zhang Y. Research Progress and Management Strategies for the Common Mycotoxin Contamination of Traditional Chinese Medicines. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(6):411. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11060411
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhimin, Huali Xue, Ye Han, Hui Ding, and Ying Zhang. 2025. "Research Progress and Management Strategies for the Common Mycotoxin Contamination of Traditional Chinese Medicines" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 6: 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11060411
APA StyleYang, Z., Xue, H., Han, Y., Ding, H., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Research Progress and Management Strategies for the Common Mycotoxin Contamination of Traditional Chinese Medicines. Journal of Fungi, 11(6), 411. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11060411





