Distribution Pattern and Assembly Process of Fungal Communities Along Altitude Gradient in Sediments of the Yellow River Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
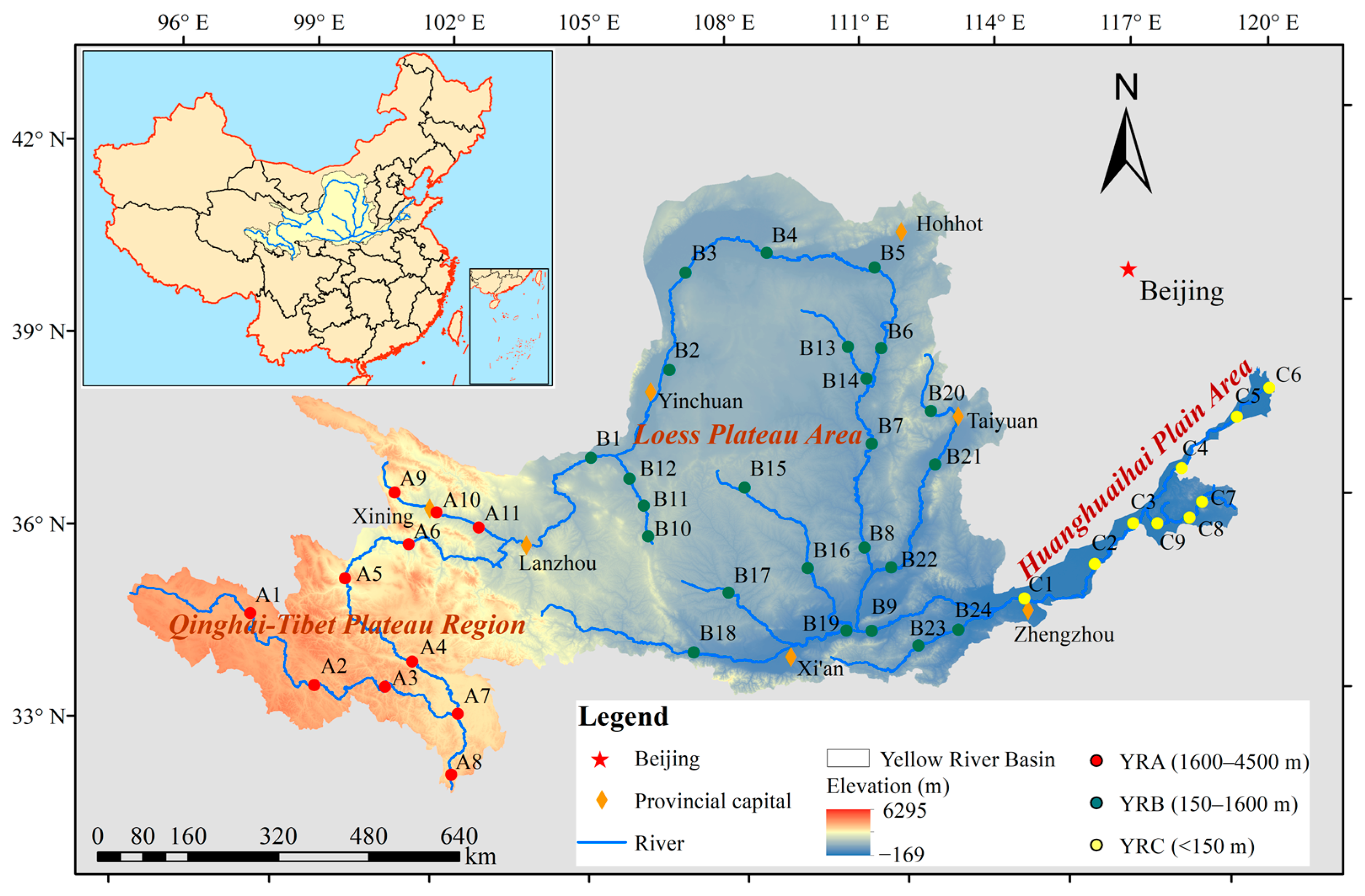
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.3. High-Throughput Sequencing
2.4. Data Statistics and Microbial Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Species Composition and Diversity of Fungal Communities
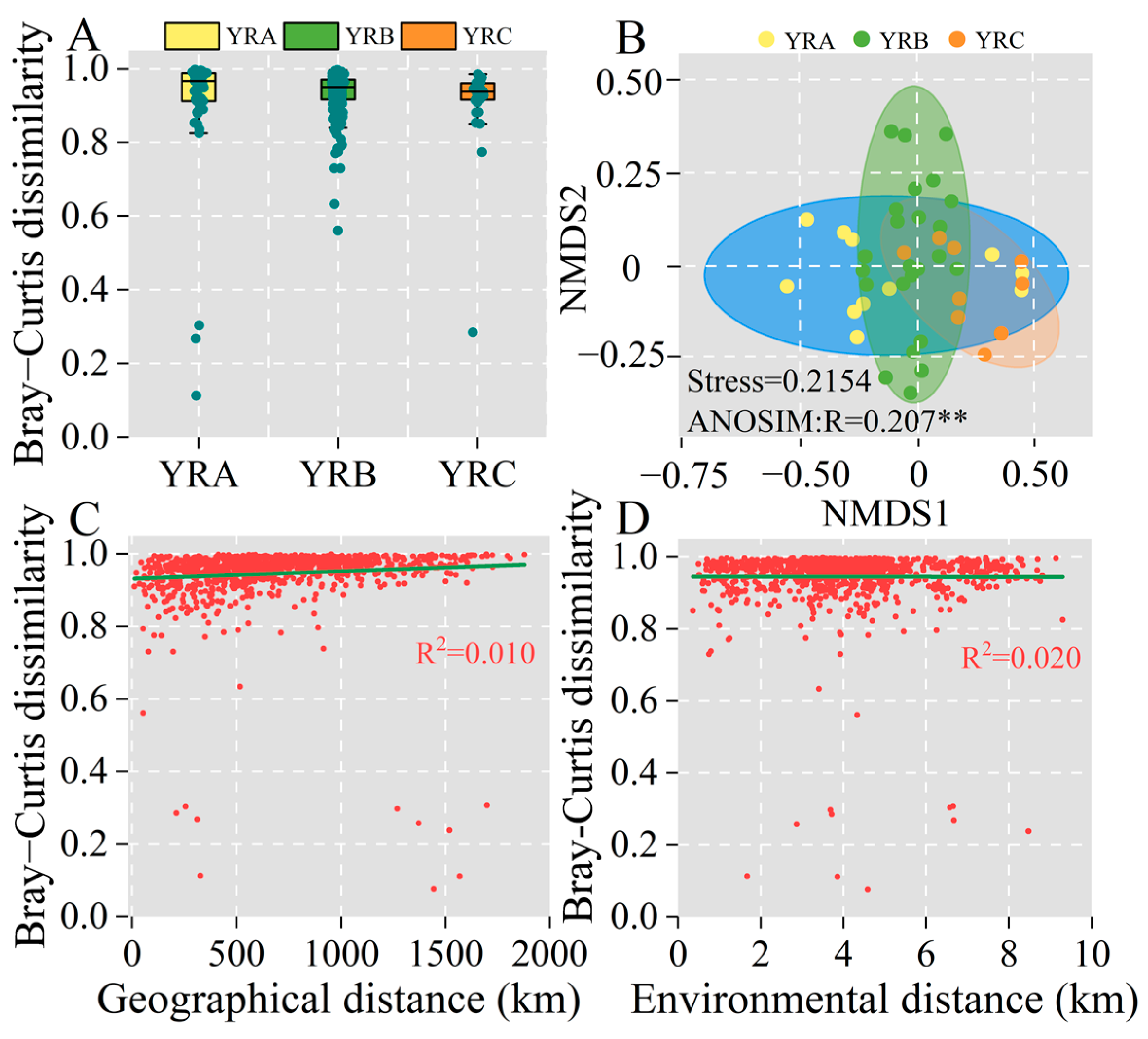
3.2. Biogeographical Analysis of Fungal Communities
3.3. Characteristics of Fungal Community Co-Occurrence Networks
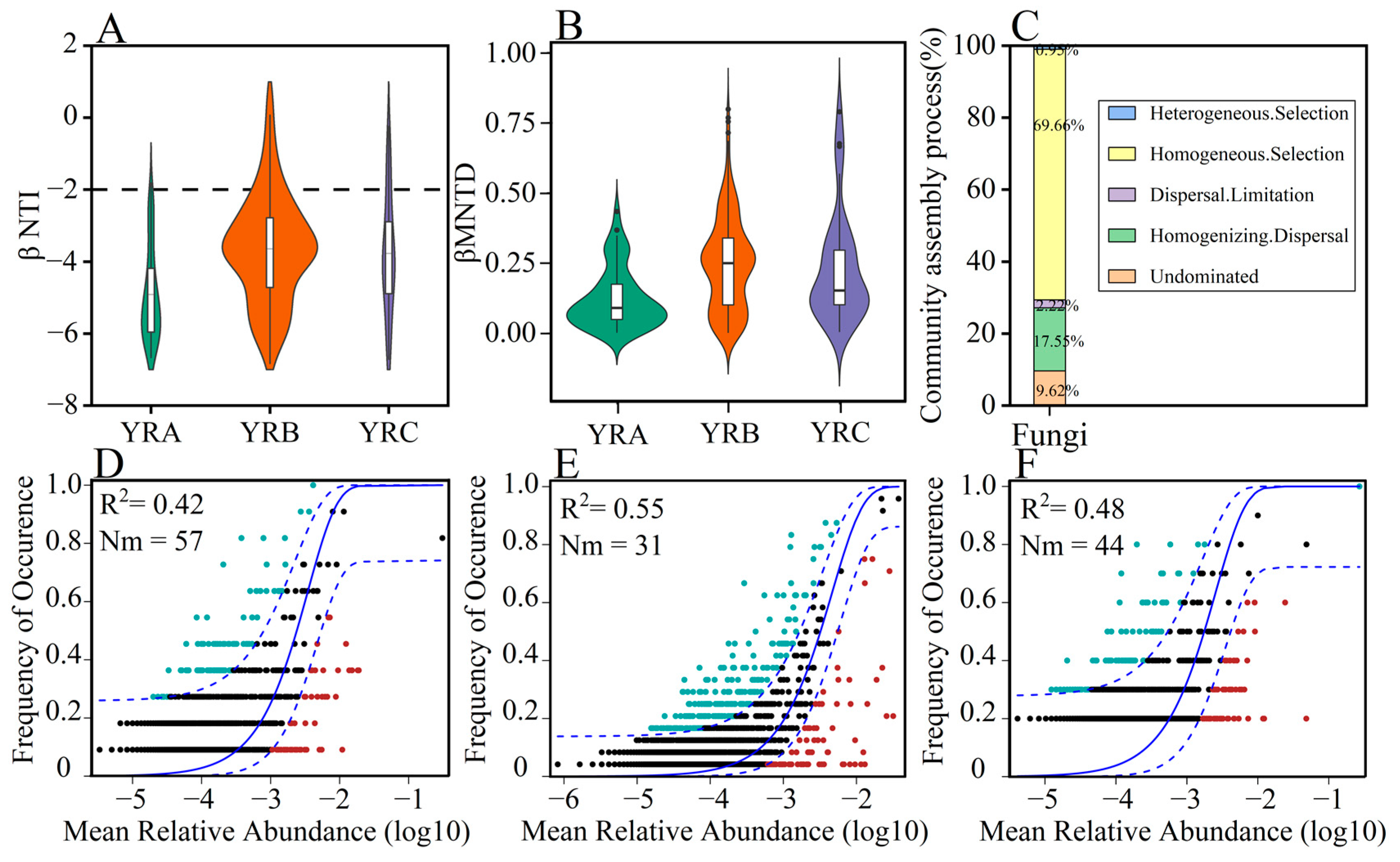
3.4. Analysis of Fungal Community Assembly Processes
3.5. Analysis of Factors Influencing Fungal Community Differences
4. Discussion
4.1. Fungal Community Structure and Diversity at Different Altitudinal Gradients
4.2. Assembly Processes of Fungal Communities in Sediments
4.3. Co-Occurrence Network Analysis of Fungal Communities
4.4. Main Factors Influencing Fungal Community Changes in Sediments of the Yellow River Basin
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.C.; Hu, S.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.L.; Li, R.W.; Hu, Y.X.; Yao, H.Y.; Wang, Z. Microbiome analysis in Asia’s largest watershed reveals inconsistent biogeographic pattern and microbial assembly mechanisms in river and lake systems. iScience 2024, 27, 110053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, S.A.; Barbosa da Costa, N.; Shapiro, B.J.; Fradette, M.; Huot, Y.; Walsh, D.A. A large-scale assessment of lakes reveals a pervasive signal of land use on bacterial communities. ISME J. 2020, 14, 3011–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.Y.; Yang, X.Y.; Chen, N.W.; Hou, L.Y.; Ma, Y.; Yu, C.P. Response of bacterial communities to environmental changes in a mesoscale subtropical watershed, Southeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 746–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.; Yen, J.Y.; Guan, Y.; Ke, D.; Liu, C. Differential responses of stream water and bed sediment microbial communities to watershed degradation. Environ. Int. 2020, 134, 105198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Li, Y.J.; Wang, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.Y.; Riaz, L.; Wang, Q.Q.; Zeng, X.P.; Qin, Z.; Irfan, M.; Yang, Q.X. Methodology comparison of environmental sediment fungal community analysis. Environ. Res. 2024, 263, 120260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lücking, R.; Aime, M.C.; Robbertse, B.; Miller, A.N.; Ariyawansa, H.A.; Aoki, T.; Cardinali, G.; Crous, P.W.; Druzhinina, I.S.; Geiser, D.M.; et al. Unambiguous identification of fungi: Where do we stand and how accurate and precise is fungal DNA barcoding? IMA Fungus 2020, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyde, K.D.; Fryar, S.; Tian, Q.; Bahkali, A.H.; Xu, J.C. Lignicolous freshwater fungi along a north–south latitudinal gradient in the Asian/Australian region; can we predict the impact of global warming on biodiversity and function? Fungal Ecol. 2016, 19, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.H.; Wang, Q.J.; Liao, K.L.L.; Jian, Z.Y.; Zhao, C.; Qu, J.H. Fungal Community as a Bioindicator to Reflect Anthropogenic Activities in a River Ecosystem. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siriarchawatana, P.; Harnpicharnchai, P.; Phithakrotchanakoon, C.; Kitikhun, S.; Mayteeworakoon, S.; Chunhametha, S.; Huong, V.T.L.; Eurwilaichitr, L.; Jiang, C.Y.; Cai, L.; et al. Fungal communities as dual indicators of river biodiversity and water quality assessment. Water Res. 2024, 253, 121252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Alizamir, M.; Seo, Y.; Heddam, S.; Chung, I.M.; Kim, Y.O.; Kisi, O.; Singh, V.P. Estimating the incubated river water quality indicator based on machine learning and deep learning paradigms: BOD5 Prediction. Math. Biosci. Eng. 2022, 19, 12744–12773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabon, M.S.; Hyde, K.D.; Jones, E.B.G.; Luo, Z.L.; Dong, W.; Hurdeal, V.G.; Gentekaki, E.; Rossi, W.; Leonardi, M.; Thiyagaraja, V.; et al. Freshwater fungal numbers. Fungal Divers. 2022, 114, 3–235. [Google Scholar]
- Warnasuriya, S.D.; Udayanga, D.; Manamgoda, D.S.; Biles, C. Fungi as environmental bioindicators. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 892, 164583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamminen, M.; Spaak, J.; Tlili, A.; Eggen, R.; Stamm, C.; Räsänen, K. Wastewater constituents impact biofilm microbial community in receiving streams. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 857, 151080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamond, J.M. Assembly of species communities. In Ecology and Evolution of Communities; Harvard University Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1975; pp. 342–444. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Li, X.D.; Yang, S.X.; Chao, X.; Liu, H.Q.; Ba, S. Distribution patterns and community assembly processes of eukaryotic microorganisms along an altitudinal gradient in the middle reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River. Water Res. 2023, 239, 120047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini-Andreote, F.; Stegen, J.C.; Van-Elsas, J.D.; Salles, J.F. Disentangling mechanisms that mediate the balance between stochastic and deterministic processes in microbial succession. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1326–E1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.Y.; Sun, F.; Deng, X.L.; Storn, N. Soil carbon fractions drive microbial community assembly processes during forest succession. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 373, 123638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.K.; De Los Reyes, F.L. Quantifying patterns of microbial community assembly processes in bioreactors using different approaches leads to variable results. Water Res. 2025, 272, 122903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, D.F.; Franzetti, A.; Gómez, I.; Huovinen, P. Functional filtering and random processes affect the assembly of microbial communities of snow algae blooms at Maritime Antarctic. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 805, 150305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Ning, D.L. Stochastic community assembly–Does it matter in microbial ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00002-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, J.X.; Wang, L.F.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.L.; Zhang, H.J.; Niu, L.H. Grain size tunes microbial community assembly and nitrogen transformation activity under frequent hyporheic exchange: A column experiment. Water Res. 2020, 182, 116040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.J.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.Y.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, X.C.; Guo, L.D. Research progress on community assembly mechanisms of fungi. Mycosystema 2023, 42, 13–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y.T.; Li, M.; Pan, B.Z.; Zhao, G.N.; Gao, L. Disentangling the drivers of phytoplankton community composition in a heavily sediment-laden transcontinental river. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 302, 113939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.A.; Tian, S.M.; Shang, F.D.; Shi, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, Y.T. Impacts of oxbow lake evolution on sediment microbial community structure in the Yellow River source region. Environ. Res. 2024, 252, 119042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.H.; Jiang, W.L.; Sun, N.; Shi, J.F.; Zhang, D.P.; Zhang, J.J.; Wang, Z.K.; Yang, J.S.; Yu, J.B.; Lv, Z.B. Responses of the structure and function of microbes in Yellow River Estuary sediments to different levels of mercury. Mar. Environ. Res. 2023, 190, 106097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.X.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Wei, K.X.; Zhang, L.X.; Wang, X.; Wang, F.Q.; Liu, J.; Cheng, S.C. Structural changes and assembly mechanisms of microbial communities during rapid sedimentation of Yellow River sediments. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 35, 103702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Liu, L.Z.; Yang, J.H.; Wu, J.J. Vegetation greening in more than 94% of the Yellow River Basin (YRB) region in China during the 21st century caused jointly by warming and anthropogenic activities. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 125, 107479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.G.; Lou, Y.; Hong, S.Z.; Zhang, X.X.; Huang, Q.Z.; Huang, G.H. Assessment of meteorological factors and human activities impact on wheat and maize water requirements in the Yellow River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 955, 177056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.Z.; Liu, N.; Li, J.F.; Wang, B.L.; Shi, X.J.; Liang, X.; Yang, M.L.; Xu, S.; Liu, C.Q. Chemodiversity of Dissolved Organic Matter Is Governed by Microbial Biogeography in Inland Waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 7753–7763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.L.; Li, L.Q.; Li, H.R.; Liu, C.; Deng, Y.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y. Spatiotemporal variations of plankton communities in different water bodies of the Yellow River: Structural characteristics, biogeographic patterns, environmental responses, and community assembly. J. Hydrol. 2024, 640, 131702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, X.; Yang, S.X.; Liu, H.Q.; Yan, B.J.; Wei, P.P.; Wu, X.J.; Ba, S. Mechanism and driving factors of phytoplankton community construction in the lower reaches of Yarlung Zangbo River. J. Lake Sci. 2025, 37, 215–229. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.; Hu, E.; Shi, Y.F.; Pan, B.Z.; Li, M. Linking microbial community coalescence to ecological diversity, community assembly and species coexistence in a typical subhumid river catchment in northern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 938, 173367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.Y.; Huang, D.; Wang, F.H.; Ye, M.; Jiang, X. Spatial dynamics of prokaryotic microbial communities in sediments of the Yellow Sea: Assembly process, co-occurrence relationships, and environmental implications. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.C.; Zhi, Z.X.; Li, Z.B.; Zhuang, J.; Guo, M.J.; Fang, K.; Yi, J.; Ren, Z.P.; Gao, H.D.; Jia, L. Attribution of sediment changes and influencing factors of microbial communities in sediment in the Wuding River basin of the Yellow River. Catena 2025, 249, 108626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jyväsjärvi, J.; Lehosmaa, K.; Aroviita, J.; Turunen, J.; Rajakallio, M.; Marttila, H.; Tolkkinen, M.; Mykrä, H.; Muotka, T. Fungal assemblages in predictive stream bioassessment: A cross-taxon comparison along multiple stressor gradients. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 121, 106986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobad-Nejhad, M.; Dima, B.; Cui, B.K.; Si, J. Basidiomycete fungi: From biosystematics and biodiversity to biotechnology. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1128319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.H.; Liu, B.H.; Li, J.M.; Deng, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, N.; Li, F.; Li, C.L.; Huang, X.H.; Hu, Z.X. Diversity and Distribution of Fungi in the Marine Sediments of Zhanjiang Bay, China. J. Fungi 2025, 10, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.H.; Nong, X.Z.; Chen, L.H.; Wei, J.H.; Li, R.H. Spatiotemporal variation characteristics and environmental relationships of sediment loadings in large rivers of China: National perspective from 2002 to 2022. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wang, P.F.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Miao, L.Z.; Liu, S.; Yuan, Q.S. Dam construction alters function community composition of diazotrophs in riparian and soils across an environmental gradient. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 132, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Mi, T.Z.; He, H.; Chen, Y.; Zhen, Y.; Yu, Z.G. Active bacterial and archaeal communities in coastal sediments: Biogeography pattern, assembly process and co-occurrence relationship. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 750, 142252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.X.; Yang, Q.; Li, X.D.; Chao, X.; Liu, H.Q.; Wei, L.R.X.; Ba, S. Deterministic processes dominate the geographic distribution pattern and community assembly of phytoplankton in typical plateau rivers. Biodivers. Sci. 2023, 31, 43–57. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.M.; Liu, J.X.; Zhao, P.Y.; Jia, T.; Li, C.; Chai, B.F. Biogeographic patterns and assembly mechanisms of bacterial communities differ between habitat generalists and specialists across elevational gradients. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Southwell, R.V.; Hilton, S.L.; Pearson, J.M.; Hand, L.H.; Bending, G.D. Inclusion of seasonal variation in river system microbial communities and phototroph activity increases environmental relevance of laboratory chemical persistence tests. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 733, 139070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishihama, S.; Haraguchi, A.; Kawano, T.; Michiki, K.; Nakazawa, K.; Suzuki, T.; Uezu, K.; Yoshizuka, K. Seasonal changes in the microbial population of the water column and sediments of the Ongagawa River, northern Kyushu, Japan. Limnology 2008, 9, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Xu, R.Z.; Shen, X.X.; Gao, P.; Xue, Z.X.; Huang, D.C.; Jin, G.Q.; Li, C.; Cao, J.S. The response of sediment microbial communities to temporal and site-specific variations of pollution in interconnected aquaculture pond and ditch systems. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahram, M.; Kohout, P.; Anslan, S.; Harend, H.; Abarenkov, K.; Tedersoo, L. Stochastic distribution of small soil eukaryotes resulting from high dispersal and drift in a local environment. ISME J. 2016, 10, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.J.; Konopka, A.E.; Fredrickson, J.K. Stochastic and deterministic assembly processes in subsurface microbial communities. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.J.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Konopka, A.E. Estimating and mapping ecological processes influencing microbial community assembly. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodelianakis, S.; Washburne, A.D.; Bourquin, M.; Pramateftaki, P.; Kohler, T.J.; Styllas, M.; Tolosano, M.; De Staercke, V.; Schön, M.; Busi, S.B.; et al. Microdiversity characterizes prevalent phylogenetic clades in the glacier-fed stream microbiome. ISME J. 2022, 16, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prussin, A.J.; Belser, J.A.; Bischoff, W.; Kelley, S.T.; Lin, K.; Lindsley, W.G.; Nshimyimana, J.P.; Schuit, M.; Wu, Z.; Bibby, K.; et al. Viruses in the Built Environment (VIBE) meeting report. Microbiome 2020, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.L.; Li, Y. Microbial community coalescence: Does it matter in the Three Gorges Reservoir? Water Res. 2021, 205, 117638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.B.; Huang, J.; Xia, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, K.; Lin, L.; Li, X.Y.; Li, B. Spatial distribution and assembly processes of bacterial communities in riverine and coastal ecosystems of a rapidly urbanizing megacity in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 934, 173298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.Y.; Zhong, M.; Guo, E.D.; Xu, H.S.; Wen, C.; Zhu, S.Q.; Li, Q.; Zhu, D.; Luo, X. Response of bacterial and fungal communities in natural biofilms to bioavailable heavy metals in a mining-affected river. Water Res. 2024, 267, 122470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konopka, A.; Lindemann, S.; Fredrickson, J. Dynamics in microbial communities: Unraveling mechanisms to identify principles. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Sun, S.H.; Wang, P.F.; Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Gao, H.; Miao, L.Z.; Liu, S.; Yuan, Q.S. Sedimentary microeukaryotes reveal more dispersal limitation and form networks with less connectivity than planktonic microeukaryotes in a highly regulated river. Freshw. Biol. 2021, 66, 826–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberán, A.; Bates, S.T.; Casamayor, E.O.; Fierer, N. Using network analysis to explore co-occurrence patterns in soil microbial communities. ISME J. 2014, 8, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, C.A.; Jiang, Y.Q.; Zeng, R.J.; Yao, M.J.; Li, X.Z. A guide for comparing microbial co-occurrence networks. IMETA 2024, 2, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.M.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Lu, Y.C.; Liu, Y.L.; An, R.; Luo, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, B. Optimization of ecological network function and structure by coupling spatial operators and biomimetic intelligent algorithm. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 465, 142794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shade, A.; Peter, H.; Allison, S.D.; Baho, D.L.; Berga, M.; Bürgmann, H.; Huber, D.H.; Langenheder, S.; Lennon, J.T.; Martiny, J.B.H.; et al. Fundamentals of microbial community resistance and resilience. Front. Microbiol. 2012, 3, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Bi, Y.L.; Cao, Y.; Peng, S.P.; Christie, P.; Ma, S.P.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xie, L.L. Shifts in composition and function of soil fungal communities and edaphic properties during the reclamation chronosequence of an open-cast coal mining dump. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Li, Y.; Yang, L.Y.; Shi, H.Q.; Li, L.H.; Bai, W.M.; Zhao, Y. Soil acidification under long-term N addition decreases the diversity of soil bacteria and fungi and changes their community composition in a semiarid grassland. Microb. Ecol. 2023, 85, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Y.; Song, Y.Y.; Song, C.C.; Wang, X.W.; Wang, N.N.; Gao, S.Q.; Cheng, X.F.; Liu, Z.D.; Gao, J.L.; Du, Y. Effect of nitrogen addition on soil microbial functional gene abundance and community diversity in Permafrost Peatland. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, F.; Zhu, L.P.; Zhang, T.; Liu, S.Y.; Jian, L.; Lu, S.C. Structure and Function of Fungal Community in Channel Sediments of Different Sections of Jialing River. Environ. Sci. 2024, 45, 4006–4013. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, L.; Huang, J.J.; Yin, Q.L.; Xie, L.; Bai, X.; Pang, Q.Q.; Zhao, J.; Yang, W.G.; Peng, F.u.Q.; Zhu, X.; et al. The effects of land use patterns on carbon and nitrogen cycling microbe in a river of the upper reaches of the Yellow River. China Environ. Sci. 2024, 44, 6846–6857. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Obi, C.C.; Adebusoye, S.A.; Ugoji, E.O.; Ilori, M.O.; Amund, O.O.; Hickey, W.J. Microbial communities in sediments of Lagos Lagoon, Nigeria: Elucidation of community structure and potential impacts of contamination by municipal and industrial wastes. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.J.; Yi, Y.J.; Yang, Y.F.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.H.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z.F. Impact of anthropogenic activities on the sediment microbial communities of Baiyangdian shallow lake. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2020, 35, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, J.N.; Gao, G.H.; Bartlam, M.G.; Wang, Y.Y. Distribution and diversity of fungi in freshwater sediments on a river catchment scale. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 329. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.J.; Zheng, J.F.; Pan, G.X.; Zhang, X.H.; Li, L.Q.; Tippkotter, R. Changes in microbial community structure and function within particle size fractions of a paddy soil under different long-term fertilization treatments from the Tai Lake region, China. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2007, 58, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhou, X.T.; Lu, X.; Xu, Y.F.; Wei, Z.P.; Ruan, A.D. Grain size distribution drives microbial communities vertically assemble in nascent lake sediments. Environ. Res. 2023, 227, 115828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogaro, G.; Datry, T.; Mermillod-Blondin, F.; Foulquier, A.; Montuelle, B. Influence of hyporheic zone characteristics on the structure and activity of microbial assemblages. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 2567–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.M.; Zhang, S.R.; Zhong, Q.M.; Gong, G.S.; Wang, G.Y.; Guo, X.; Xu, X.X. Effects of soil chemical properties and fractions of Pb, Cd, and Zn on bacterial and fungal communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Xie, Y.H.; Peng, R.; Ji, X.H.; Bai, L.Y. Heavy metals and nutrients mediate the distribution of soil microbial community in a typical contaminated farmland of South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 947, 174322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, R.K.; Devi, R. Heavy metal tolerance and adaptability assessment of indigenous filamentous fungi isolated from industrial wastewater and sludge samples. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2018, 7, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Q.L.; Jiang, J.M.; Li, X.Y.; Xie, X. Study on the Mechanism of Heavy Metal Enrichment of Macrofungi. J. Mt. Agric. Biol. 2021, 40, 36–41. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


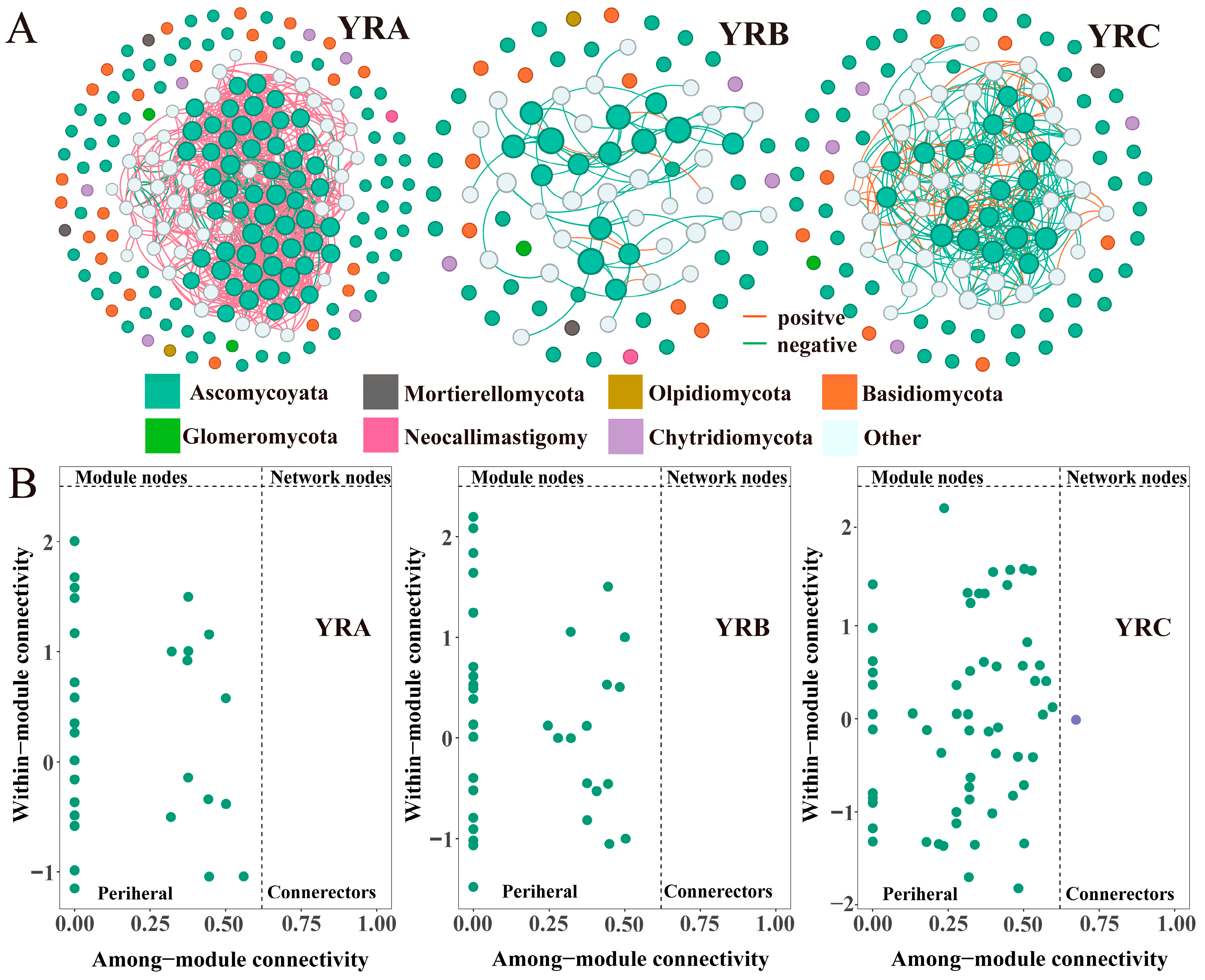
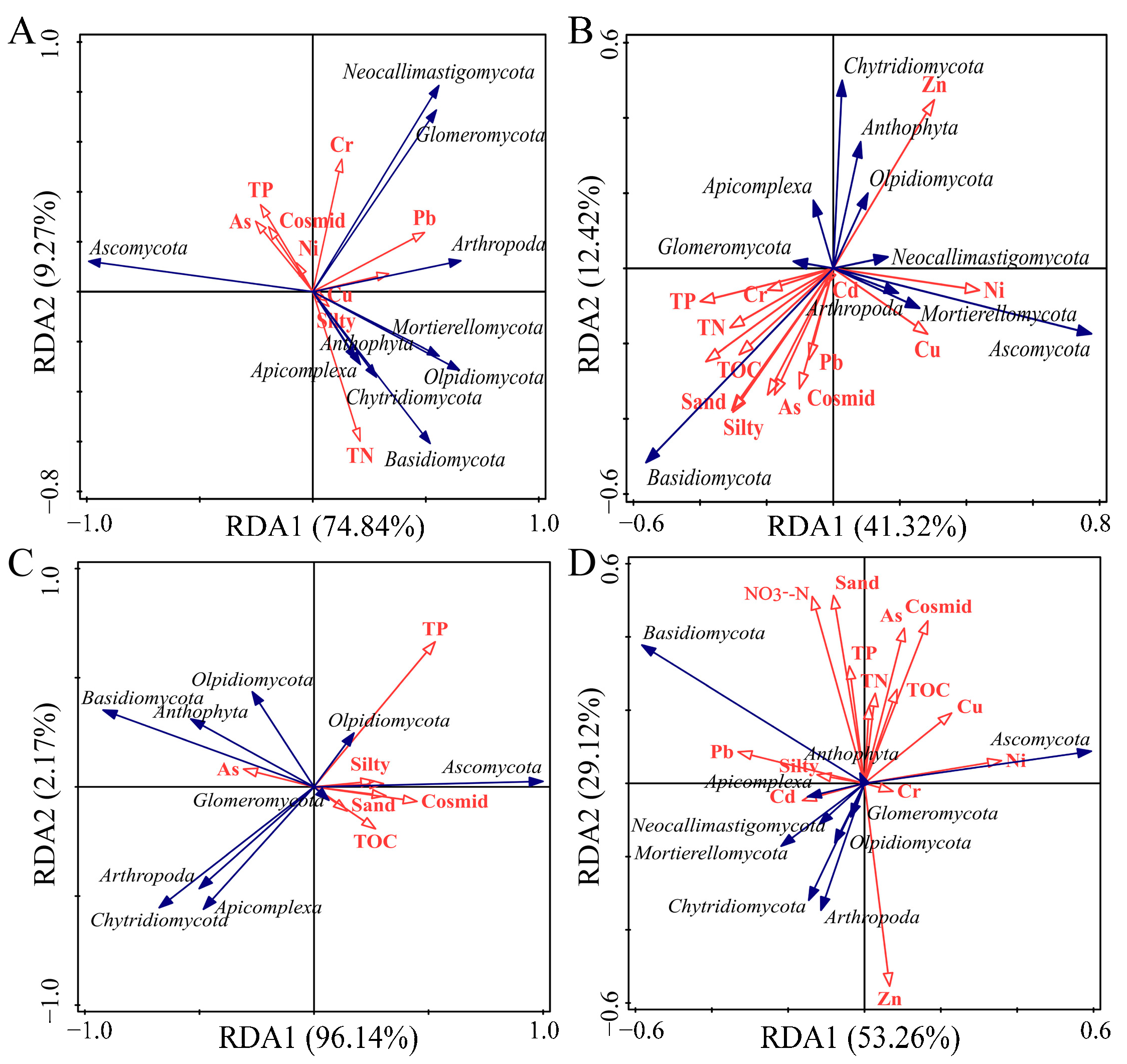

| Basin | Node | Edge | Average Degree | Average Path Length | Network Diameter | Clustering Coefficient | Density | Heterogeneity | Centralization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YRA | 61 | 328 | 10.75 | 2.27 | 3 | 0.52 | 0.18 | 0.51 | 0.24 |
| YRB | 51 | 54 | 2.12 | 3.13 | 5 | 0.21 | 0.04 | 0.68 | 0.08 |
| YRC | 45 | 66 | 2.93 | 3.61 | 5 | 0.27 | 0.07 | 0.63 | 0.09 |
| Basin | Explained Variation (%) | Explanatory Variables (Contribution %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axls 1 | Axls 2 | All Axes | ||
| YRA | 74.84 | 19.27 | 94.11 | Pb (19.4), Ni (24), TN (17.4), Silty (11.6) |
| YRB | 41.32 | 12.42 | 53.74 | Ni(13.9), Sand(14.4), TN(10.4) |
| YRC | 96.14 | 2.17 | 98.31 | TP (27.9), Consimd (24), As (12), NO3−-N (11.6) |
| Yellow River Basin | 53.26 | 29.12 | 82.38 | TOC (10.2), Pb (15.5), Silty (10.7), TN (12.3) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, K.; Xu, G.; Chen, X.; Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Cheng, Y. Distribution Pattern and Assembly Process of Fungal Communities Along Altitude Gradient in Sediments of the Yellow River Basin. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11030214
Fang K, Xu G, Chen X, Li J, Cheng Y, Cheng Y. Distribution Pattern and Assembly Process of Fungal Communities Along Altitude Gradient in Sediments of the Yellow River Basin. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(3):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11030214
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Kang, Guoce Xu, Xin Chen, Jing Li, Yuting Cheng, and Yifan Cheng. 2025. "Distribution Pattern and Assembly Process of Fungal Communities Along Altitude Gradient in Sediments of the Yellow River Basin" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 3: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11030214
APA StyleFang, K., Xu, G., Chen, X., Li, J., Cheng, Y., & Cheng, Y. (2025). Distribution Pattern and Assembly Process of Fungal Communities Along Altitude Gradient in Sediments of the Yellow River Basin. Journal of Fungi, 11(3), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11030214





