Genome-Wide SSR Markers Reveal Genetic Diversity and Establish a Core Collection for Commercial Hypsizygus marmoreus Germplasm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Strains
2.2. Genomic DNA Extraction
2.3. Primer Development
2.4. SSR Analysis
2.5. Agronomic Trait Measurement of H. marmoreus
2.6. Establishment of Molecular Identification Codes for H. marmoreus Germplasm
3. Results
3.1. Simple Sequence Repeat Markers and Genetic Structural Analysis of H. marmoreus
3.2. Genetic Diversity Analysis Using SSR Markers
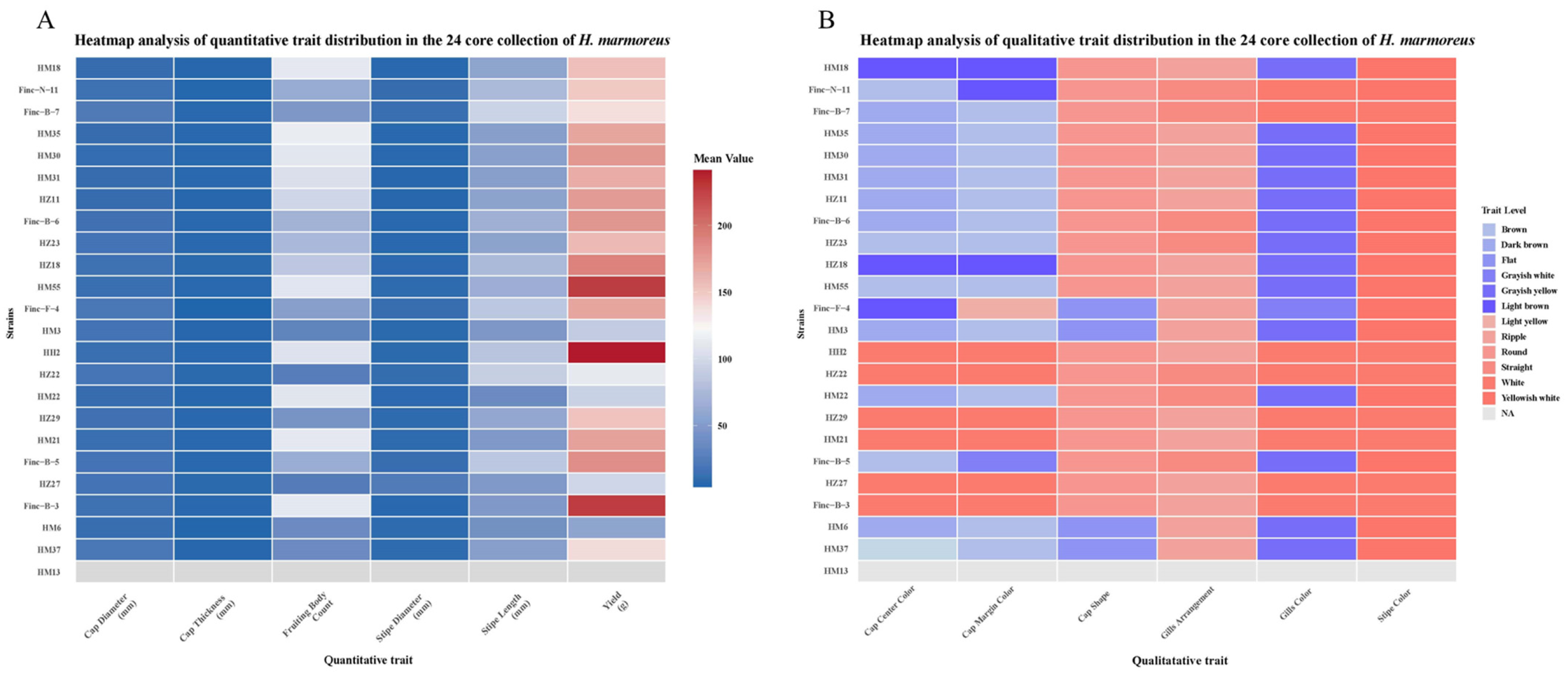
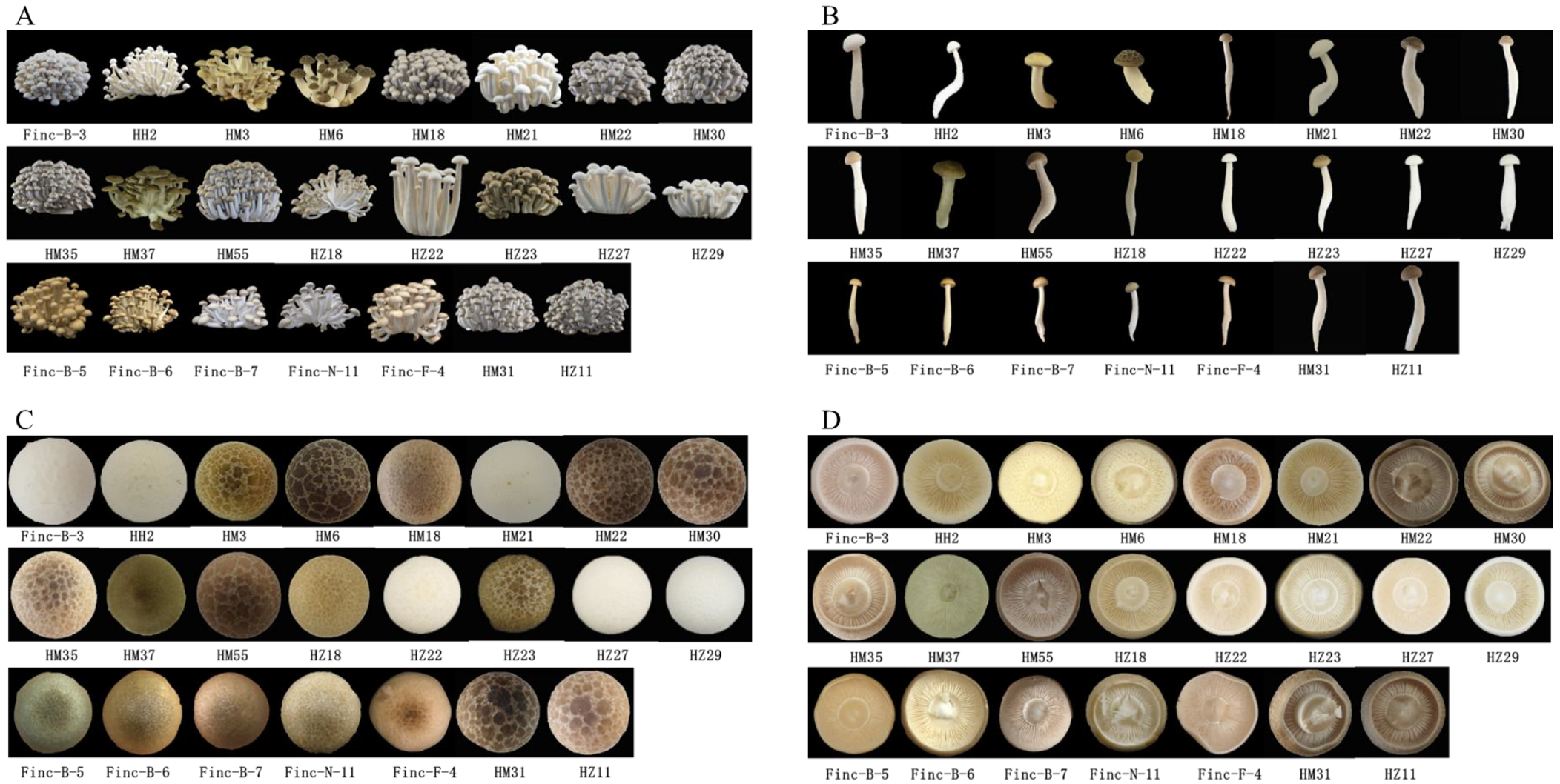
3.3. Agronomic Traits of Core Collection Cultivation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kirk, P.M.; Cannon, P.F.; David, J.C.; Stalpers, J.A. Ainsworth and Bisby’s Dictionary of the Fungi, 9th ed.; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Galić, M.; Stajić, M.; Ćilerdžić, J. Hypsizygus marmoreus—A novel potent degrader of lignocellulose residues. Cellul. Chem. Technol. 2020, 54, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.S.; Yan, W.J.; Deng, W.Q.; Song, B.; Li, T.H. Genetic Diversity Analysis of Hypsizygus marmoreus with Target Region Amplification Polymorphism. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 619746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lin, J.; Yan, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, T.; Gan, B. Evaluation of the nutritional value, umami taste, and volatile organic compounds of Hypsizygus marmoreus by simulated salivary digestion in vitro. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 7, 100591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, X.H.; Wang, Z.H.; Liu, N.W.; Song, L.; Yan, B.Q.; Xing, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, K.F.; Zhao, Y.L.; Chen, X.; et al. Fingerprinting 146 Chinese chestnut (Castanea mollissima Blume) accessions and selecting a core collection using SSR markers. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.; Yan, Z.F.; Kook, M.C.; Li, C.T.; Yi, T.H. Genetic and Chemical Diversity of Edible Mushroom Pleurotus Species. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 6068185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, B.; Liu, D.; Miao, Y. Genome Resequencing and Transcriptome Analysis Reveal the Genetic Diversity of Wolfiporia cocos Germplasm and Genes Related to High Yield. J. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajeev, K.V.; Pallavi, S.; Vikas, K.S.; Arvind, K.; Qifa, Z.; Jeffrey, L.B. 5Gs for crop genetic improvement. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2020, 56, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarei, A.; Zamani, Z.; Sarkhosh, A. Biodiversity, Germplasm Resources and Breeding Methods. In The Pomegranate: Botany, Production and Uses; CAB International: Wallingford, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari, K.K.; Singh, A.; Pattnaik, S.; Sandhu, M.; Kaur, S.; Jain, S.; Tiwari, S.; Mehrotra, S.; Anumalla, M.; Samal, R.J.P.B. Identification of a diverse mini—Core panel of Indian rice germplasm based on genotyping using microsatellite markers. Plant Breed. 2015, 134, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankel, O.H.; Brown, A.H.D. Plant Genetic Resources Today: A Critical Appraisal; George Allan and Unwin: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.M.; Arif, M.; Zi, Y.; Sze, S.H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.B. Molecular and genetic dissection of the USDA rice mini-core collection using high-density SNP markers. Plant Sci. 2021, 308, 110910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porta, B.; Condón, F.; Franco, J.; Iriarte, W.; Bonnecarrère, V.; Guimaraens-Moreira, M.; Vidal, R.; Galván, G.A. Genetic Structure, Core Collection, and Regeneration Quality in White Dent Corn Landraces. Crop Sci. 2018, 58, 1644–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, N.; Kim, K.S.; Jeong, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, S.K.; Lee, J.S.; Jeong, S.C.; Kang, S.T.; Ha, B.K.; Kim, D.Y.; et al. Korean soybean core collection: Genotypic and phenotypic diversity population structure and genome-wide association study. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beier, S.; Thiel, T.; Münch, T.; Scholz, U.; Mascher, M. MISA-web: A web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 2583–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, J.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y.; Aluko, O.O.; Wu, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G. MG2C: A user-friendly online tool for drawing genetic maps. Mol. Hortic. 2021, 1, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, F.C.; Boyle, T.J.B. Population genetic analysis of codominant and dominant markers and quantitative traits. Belg. J. Bot 1997, 129, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Rohlf, F.J. NTSYS-pc 2.0; Numerical Taxonomy and Multivariate Analysis System; Exeter Software: Setauket, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.W.; Chung, H.K.; Cho, G.T.; Ma, K.H.; Chandrabalan, D.; Gwag, J.G.; Kim, T.S.; Cho, E.G.; Park, Y.J. PowerCore: A program applying the advanced M strategy with a heuristic search for establishing core sets. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 2155–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansen, J.; van Hintum, T. Genetic distance sampling: A novel sampling method for obtaining core collections using genetic distances with an application to cultivated lettuce. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2007, 114, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosson, P.; Decroocq, V.; Methods, F.R.J.P. Development and characterization of 96 microsatellite markers suitable for QTL mapping and accession control in an Arabidopsis core collection. Plant Methods 2014, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
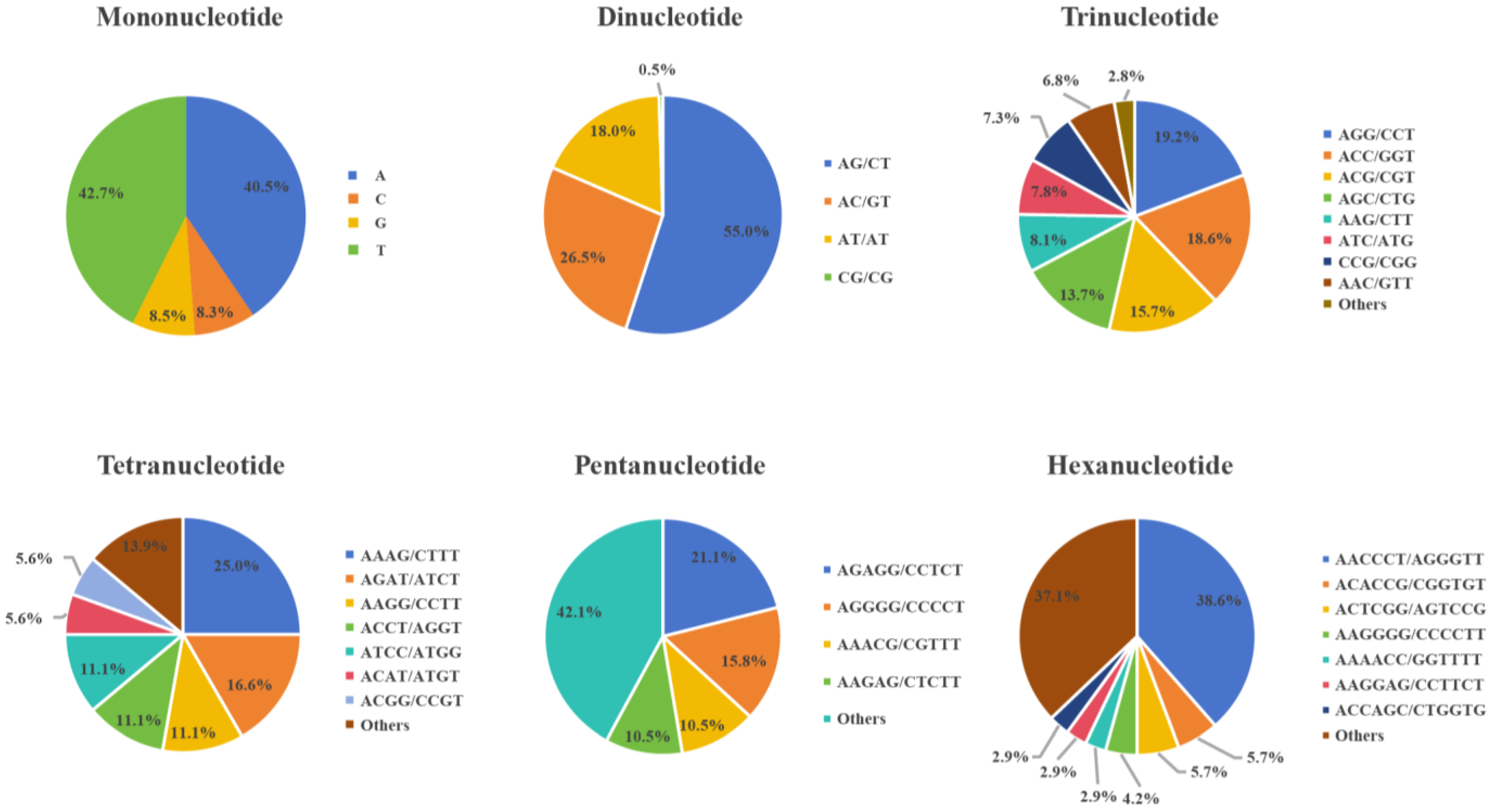
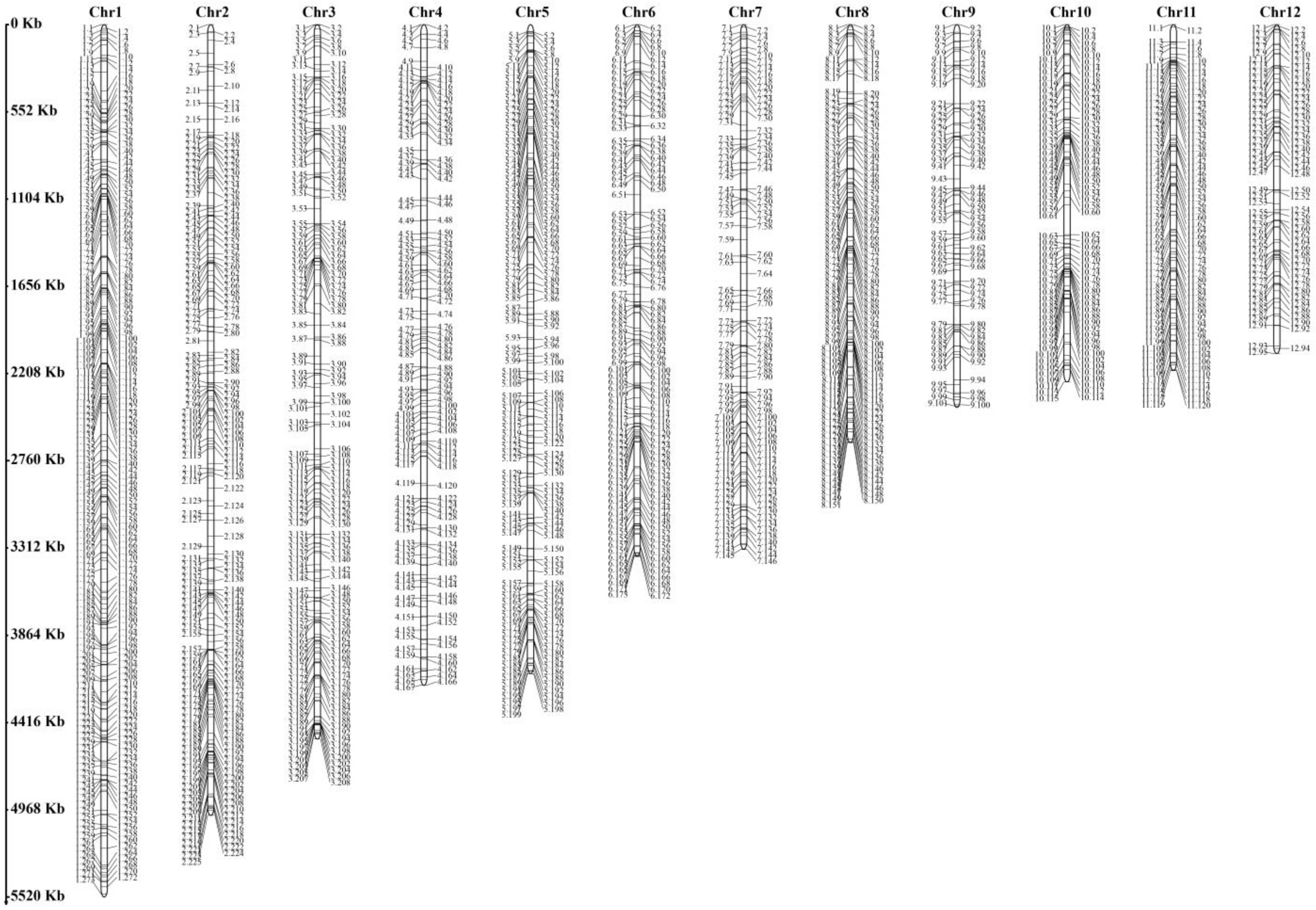
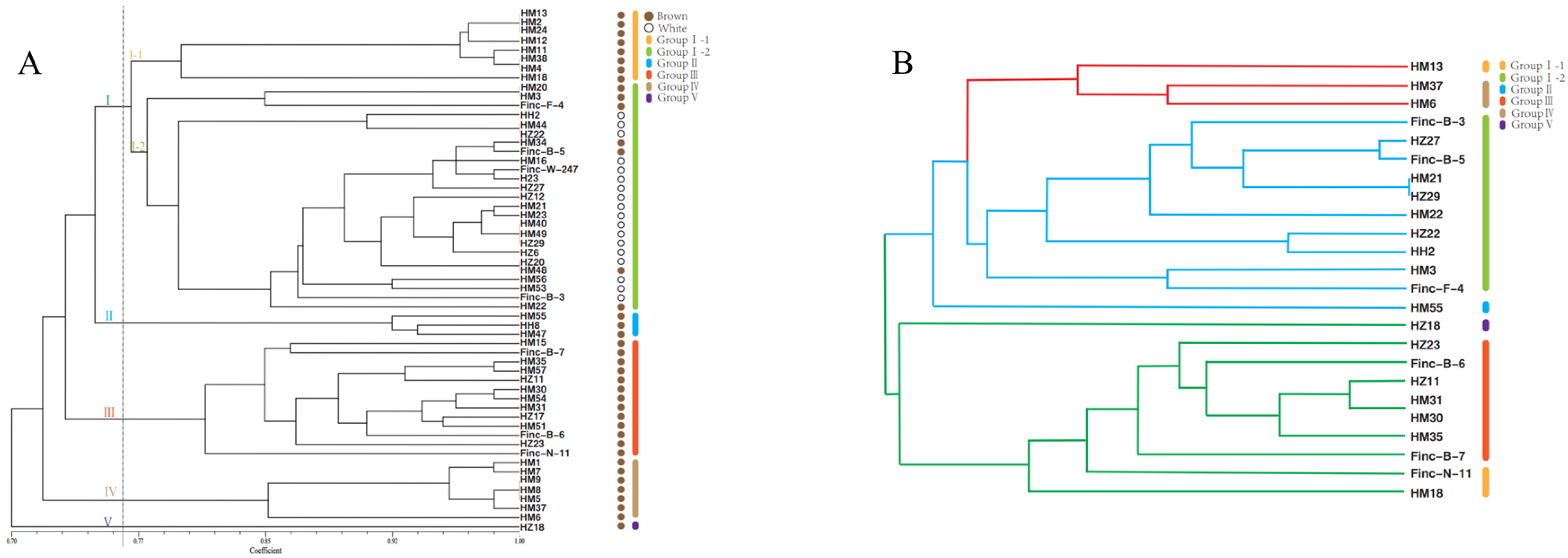
| Locus Name | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | PIC | Na | Ne | He | I |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSR3 | F:GCGAAACCATATTCATGCGT | 0.476 | 5 | 2.283 | 0.562 | 0.916 |
| R:ATTACTTGTCGTCGGCAGGA | ||||||
| SSR11 | F:GGAGTTTGAGTTGAGGCAGC | 0.725 | 9 | 4.174 | 0.760 | 1.524 |
| R:ATGAACCAGACCAAAGACCG | ||||||
| SSR12 | F:GGCACGGACATAGACCTCAT | 0.325 | 5 | 1.690 | 0.408 | 0.598 |
| R:GTGGTGGTGTGACGACGTAT | ||||||
| SSR15 | F:GATTGTTCGCTGGAACACCT | 0.436 | 6 | 2.109 | 0.526 | 0.846 |
| R:ACTCACGATGAAGGCAAACG | ||||||
| SSR18 | F:GAGGATTGAAGGGACTGTCG | 0.132 | 7 | 1.166 | 0.142 | 0.271 |
| R:CCTCATCCTCCGACTCTACG | ||||||
| SSR22 | F:TGCTGGTGAGTGAGTTGGAG | 0.374 | 4 | 1.988 | 0.497 | 0.690 |
| R:ACGGCGACATAATCTGCTCT | ||||||
| SSR26 | F:GTGATTGGGTTCGTGTCGTC | 0.339 | 9 | 1.563 | 0.360 | 0.734 |
| R:ACCTCGAGCTCAACTTCTGC | ||||||
| SSR32 | F:AACCTCCAGTCACAACCTGC | 0.171 | 8 | 1.232 | 0.188 | 0.336 |
| R:CCTTGCTTCTTGTCGGATGT | ||||||
| SSR35 | F:TCCGTGAGAGGACGGAGTAG | 0.592 | 11 | 2.840 | 0.648 | 1.185 |
| R:CTCAGCAACGACGAACAACC | ||||||
| SSR36 | F:TCTTCTTGTAGAGCGCCTCG | 0.586 | 10 | 2.658 | 0.624 | 1.241 |
| R:CTCTCGACGCGTGTTCCT | ||||||
| SSR38 | F:TCTTCTTGTTCGGCGGTATC | 0.323 | 7 | 1.590 | 0.371 | 0.639 |
| R:ATCCGGCACAGGTAAAGATG | ||||||
| SSR48 | F:GCCGTGTGACACCAAATACA | 0.523 | 9 | 2.513 | 0.602 | 0.992 |
| R:ACATCTAACCGACCCACGAC | ||||||
| SSR51 | F:CACCCCCTCATCCTACACAT | 0.582 | 17 | 2.909 | 0.656 | 1.082 |
| R:TGGTCAGAAGAAACGTCGTG | ||||||
| SSR61 | F:CTTCCTTGTCCCGACATGAT | 0.360 | 5 | 1.757 | 0.431 | 0.701 |
| R:GGCTCGGCCTTAGTGTGTAA | ||||||
| SSR65 | F:CTGCTCCTCGTTCTTTGAGC | 0.327 | 3 | 1.702 | 0.413 | 0.603 |
| R:GGTAAGGTCTGGGACGGATT | ||||||
| Total | 6.271 | 115 | 32.174 | 7.189 | 12.360 | |
| Mean | 0.418 | 7.67 | 2.145 | 0.479 | 0.824 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Shang, J.; Zhou, C.; Wan, J.; Li, J.; Li, W.; Bao, D.; Wu, Y. Genome-Wide SSR Markers Reveal Genetic Diversity and Establish a Core Collection for Commercial Hypsizygus marmoreus Germplasm. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120842
Li Y, Zhou H, Shang J, Zhou C, Wan J, Li J, Li W, Bao D, Wu Y. Genome-Wide SSR Markers Reveal Genetic Diversity and Establish a Core Collection for Commercial Hypsizygus marmoreus Germplasm. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(12):842. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120842
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yan, Heli Zhou, Junjun Shang, Chenli Zhou, Jianing Wan, Jinxin Li, Wenyun Li, Dapeng Bao, and Yingying Wu. 2025. "Genome-Wide SSR Markers Reveal Genetic Diversity and Establish a Core Collection for Commercial Hypsizygus marmoreus Germplasm" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 12: 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120842
APA StyleLi, Y., Zhou, H., Shang, J., Zhou, C., Wan, J., Li, J., Li, W., Bao, D., & Wu, Y. (2025). Genome-Wide SSR Markers Reveal Genetic Diversity and Establish a Core Collection for Commercial Hypsizygus marmoreus Germplasm. Journal of Fungi, 11(12), 842. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120842






