Deciphering the Role of Reshaped Fungal Microbiome in Cadmium Accumulation in Rice Grains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection
2.2. Soil Physicochemical Property and Grain Cd Concentration Analysis
2.3. DNA Extraction and Sequencing of Rice Rhizospheric Fungi and Seed Endophytic Fungi
2.4. Data Processing of High-Throughput Sequencing
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Key Environmental Factors Affecting Cd Accumulation in Rice Grains
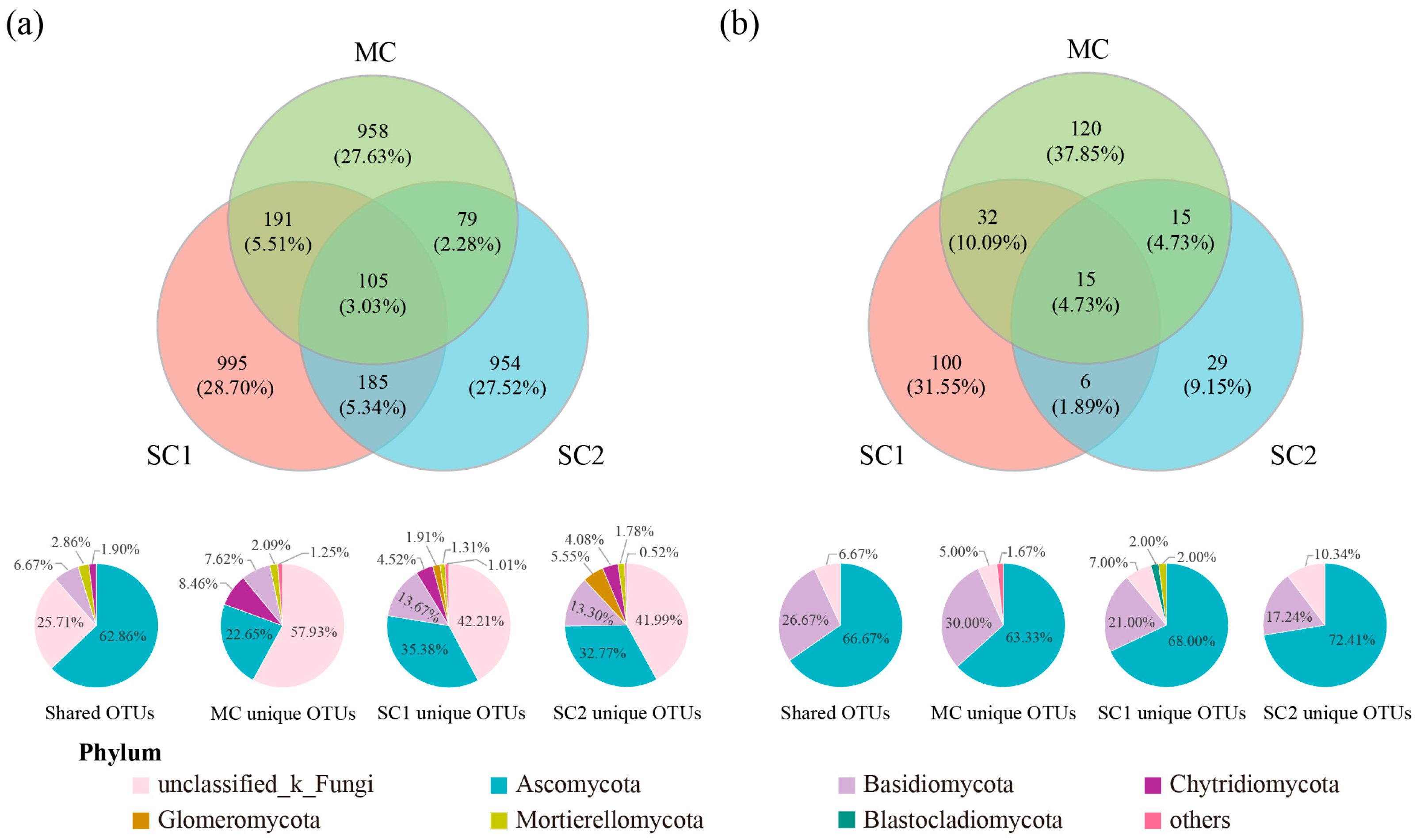
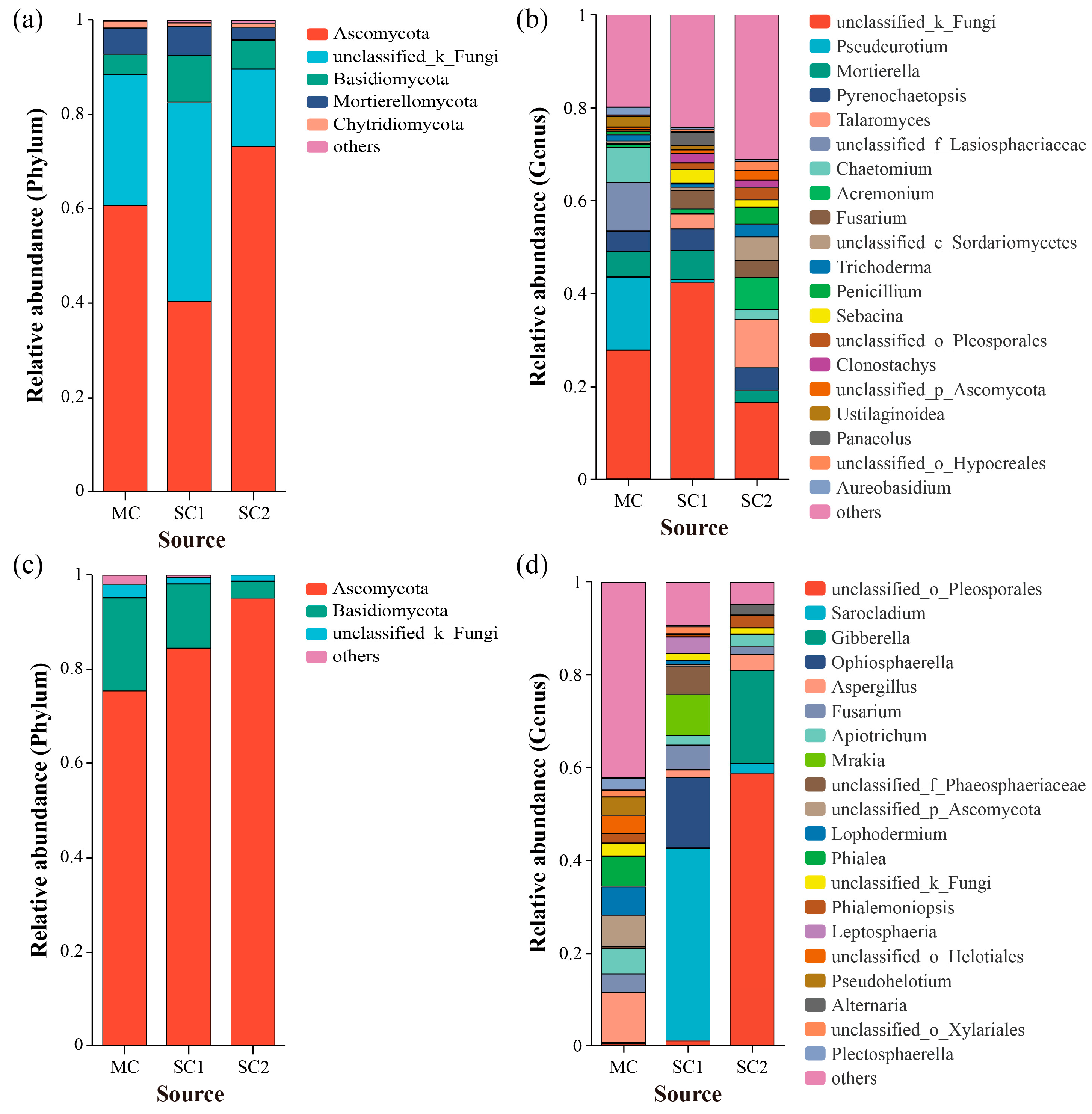
3.2. Effect of Cd Stress on Community Composition of Rice RF and SEF
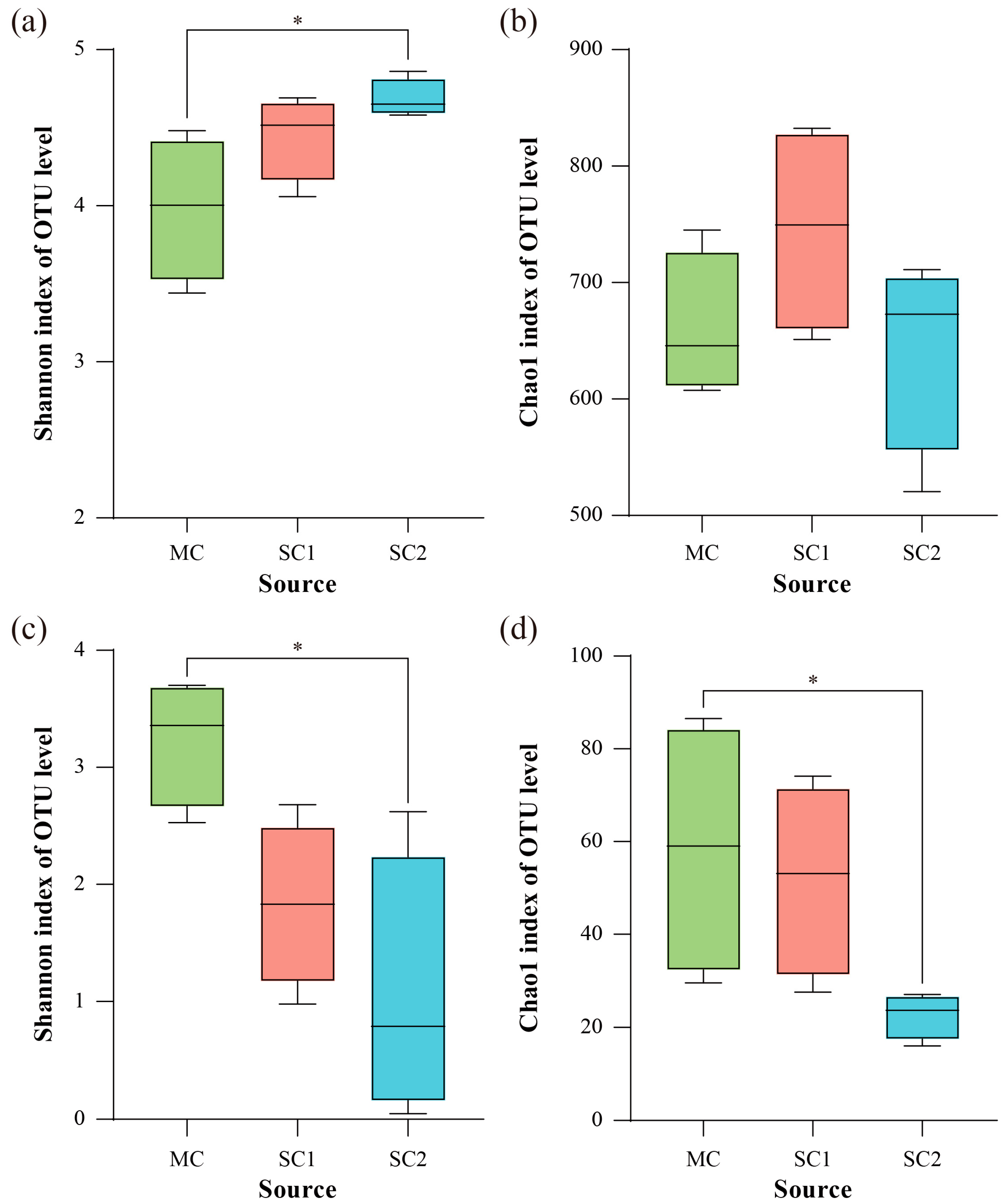
3.3. The Key Environmental Factors Affecting Diversity of Rice RF and SEF
3.4. Biomarkers of RF and SEF for Rice from Different Cd Contaminated Sites
3.5. The Correlations Between Fungal Communities and Environmental Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Impact of Soil Physiochemical Properties on Rice Grain Cd Accumulation
4.2. Impact of Soil Physiochemical Properties on Rice Rhizospheric Fungi Community and Its Potential Role in Rice Grain Cd Accumulation
4.3. Impact of Soil Factors and Grain Cd Concentration on Rice Seed Endophytic Fungi Community and Its Potential Role in Rice Grain Cd Accumulation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Azhar, U.; Ahmad, H.; Shafqat, H.; Babar, M.; Shahzad Munir, H.M.; Sagir, M.; Arif, M.; Hassan, A.; Rachmadona, N.; Rajendran, S.; et al. Remediation Techniques for Elimination of Heavy Metal Pollutants from Soil: A Review. Environ. Res. 2022, 214, 113918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, W.; Shi, W.; Cui, Y.; Chen, L.; Shao, J. Source Apportionment and Migration Characteristics of Heavy Metal(Loid)s in Soil and Groundwater of Contaminated Site. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 338, 122584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imseng, M.; Wiggenhauser, M.; Keller, A.; Müller, M.; Rehkämper, M.; Murphy, K.; Kreissig, K.; Frossard, E.; Wilcke, W.; Bigalke, M. Fate of Cd in Agricultural Soils: A Stable Isotope Approach to Anthropogenic Impact, Soil Formation, and Soil-Plant Cycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 1919–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Xue, N.; Han, Z. A Meta-Analysis of Heavy Metals Pollution in Farmland and Urban Soils in China over the Past 20 Years. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 101, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Alhag, S.K.; Al-Shahari, E.A.; Al-Fakeh, M.S.; Abou Fayssal, S.; Bachheti, R.K.; Širić, I.; Eid, E.M. Impact of Irrigation with Contaminated River Water on Growth, Yield, and Heavy Metals Accumulation in Planted Armenian Cucumber (Cucumis melo var. flexuosus (L.) Naudin.). Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2024, 236, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Fayssal, S.; Kumar, P.; Popescu, S.M.; Khanday, M.U.D.; Sardar, H.; Ahmad, R.; Gupta, D.; Kumar Gaur, S.; Alharby, H.F.; Al-Ghamdi, A.G. Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) Cultivated in Domestic Wastewater and Lake Water Irrigated Soils. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huybrechts, M.; Hendrix, S.; Kyndt, T.; Demeestere, K.; Vandamme, D.; Cuypers, A. Short-Term Effects of Cadmium on Leaf Growth and Nutrient Transport in Rice Plants. Plant Sci. 2021, 313, 111054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-L.; Li, Z.-Y.; Mao, J.-Y.; Chen, Z.-M.; Liu, H.-L.; Liang, G.-Y.; Zhang, D.-B.; Wen, P.-J.; Mo, Z.-Y.; Jiang, Y.-M. Contamination and Health Risks Brought by Arsenic, Lead and Cadmium in a Water-Soil-Plant System Nearby a Non-Ferrous Metal Mining Area. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 270, 115873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satarug, S.; Vesey, D.A.; Gobe, G.C.; Phelps, K.R. Estimation of Health Risks Associated with Dietary Cadmium Exposure. Arch. Toxicol. 2023, 97, 329–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigby, H.; Smith, S.R. The Significance of Cadmium Entering the Human Food Chain via Livestock Ingestion from the Agricultural Use of Biosolids, with Special Reference to the UK. Environ. Int. 2020, 143, 105844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, Y.-X.; Zhang, N.; Hu, B.; Jin, T.; Xu, H.; Qin, Y.; Yan, P.; Zhang, X.; Guo, X.; et al. NRT1.1B Is Associated with Root Microbiota Composition and Nitrogen Use in Field-Grown Rice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Cheng, L.; Nian, H.; Jin, J.; Lian, T. Linking Plant Functional Genes to Rhizosphere Microbes: A Review. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 902–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Xiao, X.; Wei, W.; Li, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Wang, M. Soil Rare Microorganisms Mediated the Plant Cadmium Uptake: The Central Role of Protists. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 908, 168505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altaf, M.; Ilyas, T.; Shahid, M.; Shafi, Z.; Tyagi, A.; Ali, S. Trichoderma Inoculation Alleviates Cd and Pb-Induced Toxicity and Improves Growth and Physiology of Vigna radiata (L.). ACS Omega 2024, 9, 8557–8573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Irshad, M.; Hussain, A.; Qadir, M.; Mehmood, A.; Rahman, M.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Almutairi, M.H.; Ali, S.; Hamayun, M. Phosphate Solubilizing Aspergillus Niger PH1 Ameliorates Growth and Alleviates Lead Stress in Maize through Improved Photosynthetic and Antioxidant Response. BMC Plant Biol. 2024, 24, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, C.; Wu, F.; Jin, X.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Wei, Z. Biochar Amendment Reduces Cadmium Uptake by Stimulating Cadmium-Resistant PGPR in Tomato Rhizosphere. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 136138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Q.; Yang, L.; Yang, H.; Meng, F.; Hu, W.; Zhang, P. Phanerochaete chrysosporium Reduces Heavy Metal Uptake in Rice by Affecting Rhizosphere Microbes and Root Metabolism. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 299, 118403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.; Li, T.; Huang, Y.; Liu, T.; Dong, Y. Exogenous Nano-Silicon Enhances the Ability of Intercropped Faba Bean to Alleviate Cadmium Toxicity and Resist Fusarium wilt. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2025, 23, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Yadav, G.; Tyagi, J.; Kumar, A.; Koul, M.; Joshi, N.C.; Hashem, A.; Abd Allah, E.F.; Mishra, A. Synergistic Impact of Serendipita Indica and Zhihengliuella sp. ISTPL4 on the Mitigation of Arsenic Stress in Rice. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1374303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Tang, T.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, P.; Xiong, Y.; Feng, J.; Peng, M.; Zhu, J.; Yong, X.; Jia, Y.; et al. Characterization of Endophytic Bacterial Communities in Abelmoschus Manihot under Cd Stress and Isolation of Cd-Resistant Bacteria. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 496, 139367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Xu, K.; Lu, L.; Shu, Q.; Tian, S. The Endophytic Fungus Serendipita Indica Reshapes Rhizosphere Soil Microbiota to Improve Salix suchowensis Growth and Phytoremediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 495, 138620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, A.; Leglize, P.; Lopez, S.; Sterckeman, T.; Benizri, E. Noccaea Caerulescens Seed Endosphere: A Habitat for an Endophytic Bacterial Community Preserved through Generations and Protected from Soil Influence. Plant Soil. 2022, 472, 257–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Parmar, S.; Tang, W.; Hu, H.; White, J.F.; Li, H. Effects of Fungal Seed Endophyte FXZ2 on Dysphania ambrosioides Zn/Cd Tolerance and Accumulation. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 995830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truyens, S.; Jambon, I.; Croes, S.; Janssen, J.; Weyens, N.; Mench, M.; Carleer, R.; Cuypers, A.; Vangronsveld, J. The Effect of Long-Term Cd and Ni Exposure on Seed Endophytes of Agrostis capillaris and Their Potential Application in Phytoremediation of Metal-Contaminated Soils. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2014, 16, 643–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Song, Q.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y. Mitigation Strategies for Excessive Cadmium in Rice. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 22, 3847–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.H.; Tang, S.Q.; Wei, X.J.; Shao, G.N.; Jiao, G.A.; Sheng, Z.H.; Luo, J.; Hu, P.S. The Cadmium and Lead Content of the Grain Produced by Leading Chinese Rice Cultivars. Food Chem. 2017, 217, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Carey, M.; Meharg, C.; Williams, P.N.; Signes-Pastor, A.J.; Triwardhani, E.A.; Pandiangan, F.I.; Campbell, K.; Elliott, C.; Marwa, E.M.; et al. Rice Grain Cadmium Concentrations in the Global Supply-Chain. Expo. Health 2020, 12, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, N.; Li, Y.W.; Cai, Q.Y.; Li, H.Y.; Mo, C.H.; Wong, M.H. Cadmium in Rice: Transport Mechanisms, Influencing Factors, and Minimizing Measures. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, M.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, Z.; Guo, T.; Wang, J. Cadmium Pollution of Soil-Rice Ecosystems in Rice Cultivation Dominated Regions in China: A Review. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 280, 116965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xiao, Y.; Lv, F.; Hu, L.; Wei, L.; Yuan, Z.; Lin, H. Bacterial Community Structure and Functional Potential of Rhizosphere Soils as Influenced by Nitrogen Addition and Bacterial Wilt Disease under Continuous Sesame Cropping. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 125, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, N.A.; Ravi, A.; Joseph, B.J.; Jose, A.; Jithesh, O.; Krishnankutty, R.E. Phenazine 1-Carboxylic Acid Producing Seed Harbored Endophytic Bacteria from Cultivated Rice Variety of Kerala and Its Broad Range Antagonism to Diverse Plant Pathogens. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2023, 15, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, P.; Tian, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Yi, Z.; Ao, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, J. Bacterial Seed Endophyte and Abiotic Factors Influence Cadmium Accumulation in Rice (Oryza sativa) along the Yangtze River Area. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 263, 115352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhong, Q.; Gong, G.; Wang, G.; Guo, X.; Xu, X. Effects of Soil Chemical Properties and Fractions of Pb, Cd, and Zn on Bacterial and Fungal Communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 715, 136904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmar, S.; Li, Q.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Yan, J.; Sharma, V.K.; Wei, Y.; Li, H. Endophytic Fungal Community of Dysphania ambrosioides from Two Heavy Metal-Contaminated Sites: Evaluated by Culture-Dependent and Culture-Independent Approaches. Microb. Biotechnol. 2018, 11, 1170–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Peng, D.; Liu, L.; Jiang, H.; Bai, L. Cultivar-Dependent Rhizobacteria Community and Cadmium Accumulation in Rice: Effects on Cadmium Availability in Soils and Iron-Plaque Formation. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 116, 90–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Chen, A.J.; Zong, Q.; Du, Z.; Guo, Q.; Liu, T.; Chen, W.; Gao, L. Microbiome Signature of Endophytes in Wheat Seed Response to Wheat Dwarf Bunt Caused by Tilletia Controversa Kühn. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e00390-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gao, W.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, X.; Kong, W.; Niu, S.; Gao, K.; Yang, H. Community Composition and Trophic Mode Diversity of Fungi Associated with Fruiting Body of Medicinal Sanghuangporus vaninii. BMC Microbiol. 2022, 22, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, D.; Fernandes, T.; Martins, F.; Pereira, J.A.; Tavares, R.M.; Santos, P.M.; Baptista, P.; Lino-Neto, T. Illuminating Olea europaea L. Endophyte Fungal Community. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 245, 126693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Zhao, C.; Li, B.; Wu, Y.; Wang, H.; Yan, Z. Different Techniques Reveal the Difference of Community Structure and Function of Fungi from Root and Rhizosphere of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Plant Biol. 2023, 25, 848–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; White, J.F.; Malik, K.; Chen, T.; Li, C. Inoculation of Barley (Hordeum vulgare) with the Endophyte Epichloë bromicola Affects Plant Growth, and the Microbial Community in Roots and Rhizosphere Soil. J. Fungi 2022, 8, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Zhang, H.; Lin, X.; Zhu, J.; Jia, Z. Response of Leaf Endophytic Bacterial Community to Elevated CO2 at Different Growth Stages of Rice Plant. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cestarić, D.; Škvorc, Ž.; Franjić, J.; Sever, K.; Krstonošić, D. Forest Plant Community Changes in the Spačva Lowland Area (E Croatia). Plant Biosyst. Int. J. Deal. All Asp. Plant Biol. 2017, 151, 584–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bello, A.; Li, X.; Liu, W.; Egbeagu, U.U.; Zhao, L.; Han, Y.; Cheng, L.; et al. Investigation of Underlying Links between Nitrogen Transformation and Microorganisms’ Network Modularity in the Novel Static Aerobic Composting of Dairy Manure by “Stepwise Verification Interaction Analysis”. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 883, 163674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality-Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2018.
- GB 2762-2022; National Food Safety Standard-Maximum Levels of Contaminants in Foods. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2022.
- Chen, B.; Tan, S.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, A.; Zheng, H. Soil Nutrient Heterogeneity Affects the Accumulation and Transfer of Cadmium in Bermuda Grass (Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers.). Chemosphere 2019, 221, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xiong, J.; Tao, L.; Cao, Z.; Tang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yu, X.; Fu, G.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y. Regulatory Mechanisms of Nitrogen (N) on Cadmium (Cd) Uptake and Accumulation in Plants: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, X.; Yao, H.; Cui, S.; Peng, Y.; Gao, X.; Yuan, C.; Chen, X.; Hu, Y.; Mao, X. Activated Low-Grade Phosphate Rocks for Simultaneously Reducing the Phosphorus Loss and Cadmium Uptake by Rice in Paddy Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 780, 146550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Liao, Q.; Fu, H.; Ye, Z.; Mao, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Xin, J. Effect of Potassium Intake on Cadmium Transporters and Root Cell Wall Biosynthesis in Sweet Potato. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 250, 114501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Fu, G.; Yu, Y.; Wan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, H. Effects of Different Potassium Fertilizers on Cadmium Uptake by Three Crops. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2019, 26, 27014–27022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgo, L.; Rabêlo, F.H.S.; Rossi, M.L.; dos Santos, F.H.; Nogueira, M.L.G.; Alleoni, L.R.F.; Linhares, F.S.; Vangronsveld, J.; Lavres, J. Effect of Selenium and Soil pH on Cadmium Phytoextraction by Urochloa decumbens Grown in Oxisol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 447, 130771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Peng, Y.; Jeyakumar, P.; Lin, L.; Zhang, D.; Yang, M.; Zhu, J.; Ki Lin, C.S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; et al. Soil pH Restricts the Ability of Biochar to Passivate Cadmium: A Meta-Analysis. Environ. Res. 2023, 219, 115110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Li, W.; Pang, X.; Liu, Q.; Yin, C. Soil Properties and Root Traits Are Important Factors Driving Rhizosphere Soil Bacterial and Fungal Community Variations in Alpine Rhododendron nitidulum Shrub Ecosystems along an Altitudinal Gradient. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 864, 161048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, P.; Xu, M.; Ahamad, L.; Chaudhary, A.; Kumar, G.; Adeleke, B.S.; Verma, K.K.; Hu, D.-M.; Širić, I.; Kumar, P.; et al. Application of Synthetic Consortia for Improvement of Soil Fertility, Pollution Remediation, and Agricultural Productivity: A Review. Agronomy 2023, 13, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, M.; Dai, Z.; Hussain, S.; Tariq, M.; Danish, S.; Khan, I.U.; Qi, S.; Du, D. The Soil pH and Heavy Metals Revealed Their Impact on Soil Microbial Community. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 321, 115770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, R.; He, X.; Gao, N.; Li, Q.; Qiu, Z.; Hou, Y.; Shen, W. Soil pH Amendment Alters the Abundance, Diversity, and Composition of Microbial Communities in Two Contrasting Agricultural Soils. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e04165-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Gao, M.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Su, J.; Li, H. Combined Effects of Acidification and Warming on Soil Denitrification and Microbial Community. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1572497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, R.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Yun, W.; Luo, B.; Chai, R.; Zhang, C.; Xiang, X.; Su, X. Changes in Phosphorus Mobilization and Community Assembly of Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Rice Rhizosphere under Phosphate Deficiency. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 953340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapata, D.; López, J.E.; Saldarriaga, J.F. Plant Growth-Promoting and Biocontrol Potential of Aspergillus tubingensis and Talaromyces islandicus. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 2354–2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.-E.; Yao, H. Phosphorus Input Alters the Assembly of Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Root-Associated Communities. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 79, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, T.; Xiang, P.; Bao, Z.; Tu, W.; Li, L.; Wang, Q. Phosphate Mining Activities Affect Crop Rhizosphere Fungal Communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Song, W.; Zhang, X.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L. Potential Application of Novel Cadmium-Tolerant Bacteria in Bioremediation of Cd-Contaminated Soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 255, 114766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Chenu, C.; Kappler, A.; Rillig, M.C.; Fierer, N. The Interplay between Microbial Communities and Soil Properties. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Seshadri, B.; Bolan, N.; Sarkar, B.; Ok, Y.S.; Zhang, W.; Rumpel, C.; Sparks, D.; Farrell, M.; Hall, T.; et al. Microbial Functional Diversity and Carbon Use Feedback in Soils as Affected by Heavy Metals. Environ. Int. 2019, 125, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Xiao, W.; Ye, Y.; Wu, C.; Hu, Y.; Shi, H. Adaptation of Soil Fungi to Heavy Metal Contamination in Paddy Fields-a Case Study in Eastern China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 27819–27830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yao, J.; Liu, B.; Li, M.; Liu, J.; Jiang, S.; Yu, W.; Zhao, Y.; Duran, R. Active Tailings Disturb the Surrounding Vegetation Soil Fungal Community: Diversity, Assembly Process and Co-Occurrence Patterns. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 865, 161133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ważny, R.; Jędrzejczyk, R.J.; Domka, A.; Pliszko, A.; Kosowicz, W.; Githae, D.; Rozpądek, P. How Does Metal Soil Pollution Change the Plant Mycobiome? Environ. Microbiol. 2023, 25, 2913–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Shen, Q.; Wang, L.; Qiu, G.; Shi, J.; Xu, J.; Brookes, P.C.; Liu, X. Effects of Cd, Cu, Zn and Their Combined Action on Microbial Biomass and Bacterial Community Structure. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 510–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Wu, S.; Shi, W.; Hu, H.; Lin, T.; Zhao, K.; Hou, G.; Fan, C.; Li, X.; Chen, G. Combined Effects of Cadmium and Simulated Acid Rain on Soil Microbial Communities in the Early Cultivation of Populus beijingensis Seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2024, 280, 116583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanka; Dwivedi, S.K. Fungi Mediated Detoxification of Heavy Metals: Insights on Mechanisms, Factors and Recent. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilawar, N.; Hamayun, M.; Iqbal, A.; Lee, B.; Ali, S.; Ahmad, A.; Alrefaei, A.F.; Faraj, T.K.; Kim, H.-Y.; Hussain, A. Rhizofungus Aspergillus terreus Mitigates Heavy Metal Stress-Associated Damage in Triticum aestivum L. Plants 2024, 13, 2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, E.; Babai Ahari, A.; Arzanlou, M.; Oustan, S.; Khazaei, S.H. Tolerance to Heavy Metals in Filamentous Fungi Isolated from Contaminated Mining Soils in the Zanjan Province, Iran. Chemosphere 2017, 185, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Luo, J.; Guo, X.; Qiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Vaculík, M.; Li, T. Phyllosphere Microbiome Assists the Hyperaccumulating Plant in Resisting Heavy Metal Stress. J. Environ. Sci. 2025, 154, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shadmani, L.; Jamali, S.; Fatemi, A. Isolation, Identification, and Characterization of Cadmium-Tolerant Endophytic Fungi Isolated from Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Roots and Their Role in Enhancing Phytoremediation. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2021, 52, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Dai, H.; Wei, S.; Skuza, L.; Chen, Y. Effects of Cd-Resistant Fungi on Uptake and Translocation of Cd by Soybean Seedlings. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 132908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Chen, R.; Chen, L.; Yang, B.; Jiang, L.; Fang, J. Endophytic Fungus Talaromyces sp. MR1 Promotes the Growth and Cadmium Uptake of Arabidopsis thaliana L. Under Cadmium Stress. Curr. Microbiol. 2023, 80, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, T.; Qi, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S.; Yan, J.; Qiu, H.; Yu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Wang, J.; Gong, J. An Endophytic Fungus Interacts with the Defensin-like Protein OsCAL1 to Regulate Cadmium Allocation in Rice. Mol. Plant 2024, 17, 312–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Na, M.; Wang, Y.; Ge, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, S. Cadmium Levels and Soil pH Drive Structure and Function Differentiation of Endophytic Bacterial Communities in Sedum plumbizincicola: A Field Study. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Cui, Y.; Li, H.; Kuang, A.; Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Ji, X. Rhizospheric Soil and Root Endogenous Fungal Diversity and Composition in Response to Continuous Panax notoginseng Cropping Practices. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 194, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gong, L.; Gan, D.; Li, X.; Yao, J.; Wang, L.; Qu, J.; Cong, J.; Zhang, Y. Diversity, Function and Assembly of the Trifolium repens L. Root-Associated Microbiome under Lead Stress. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 438, 129510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Peng, R.; Xie, Y.; Ji, X.; Liu, S.; Jiang, H. Cultivar-Specific Response of a Root-Associated Microbiome Assembly of Rice to Cadmium Pollution. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2025, 227, 110128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Chen, D.; Xu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Huang, J.; Gao, R.; Bai, J.; Hou, Q. Effects of Different Heavy Metal Stressors on the Endophytic Community Composition and Diversity of Symphytum officinale. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; He, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhuang, L. Comparison of Network Connectivity and Environmental Driving Factors of Root-Associated Fungal Communities of Desert Ephemeral Plants in Two Habitat Soils. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 332, 117375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, C.S.F.; Cheow, Y.L.; Ng, S.L.; Ting, A.S.Y. Discovering Metal-Tolerant Endophytic Fungi from the Phytoremediator Plant Phragmites. Water Air Soil. Pollut. 2018, 229, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.A.; Li, H.-Y.; Kowalski, K.P.; Bergen, M.; Torres, M.S.; White, J.F. Evaluation of the Functional Roles of Fungal Endophytes of Phragmites australis from High Saline and Low Saline Habitats. Biol. Invasions 2016, 18, 2689–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Zhou, J.; Feng, C.; Wang, S.; Haegeman, B.; Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhou, J.; Xu, J.; et al. Abundant Fungi Dominate the Complexity of Microbial Networks in Soil of Contaminated Site: High-Precision Community Analysis by Full-Length Sequencing. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 861, 160563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- War, A.F.; Bashir, I.; Reshi, Z.A.; Kardol, P.; Rashid, I. Insights into the Seed Microbiome and Its Ecological Significance in Plant Life. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 269, 127318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelfattah, A.; Tack, A.J.M.; Lobato, C.; Wassermann, B.; Berg, G. From Seed to Seed: The Role of Microbial Inheritance in the Assembly of the Plant Microbiome. Trends Microbiol. 2023, 31, 346–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
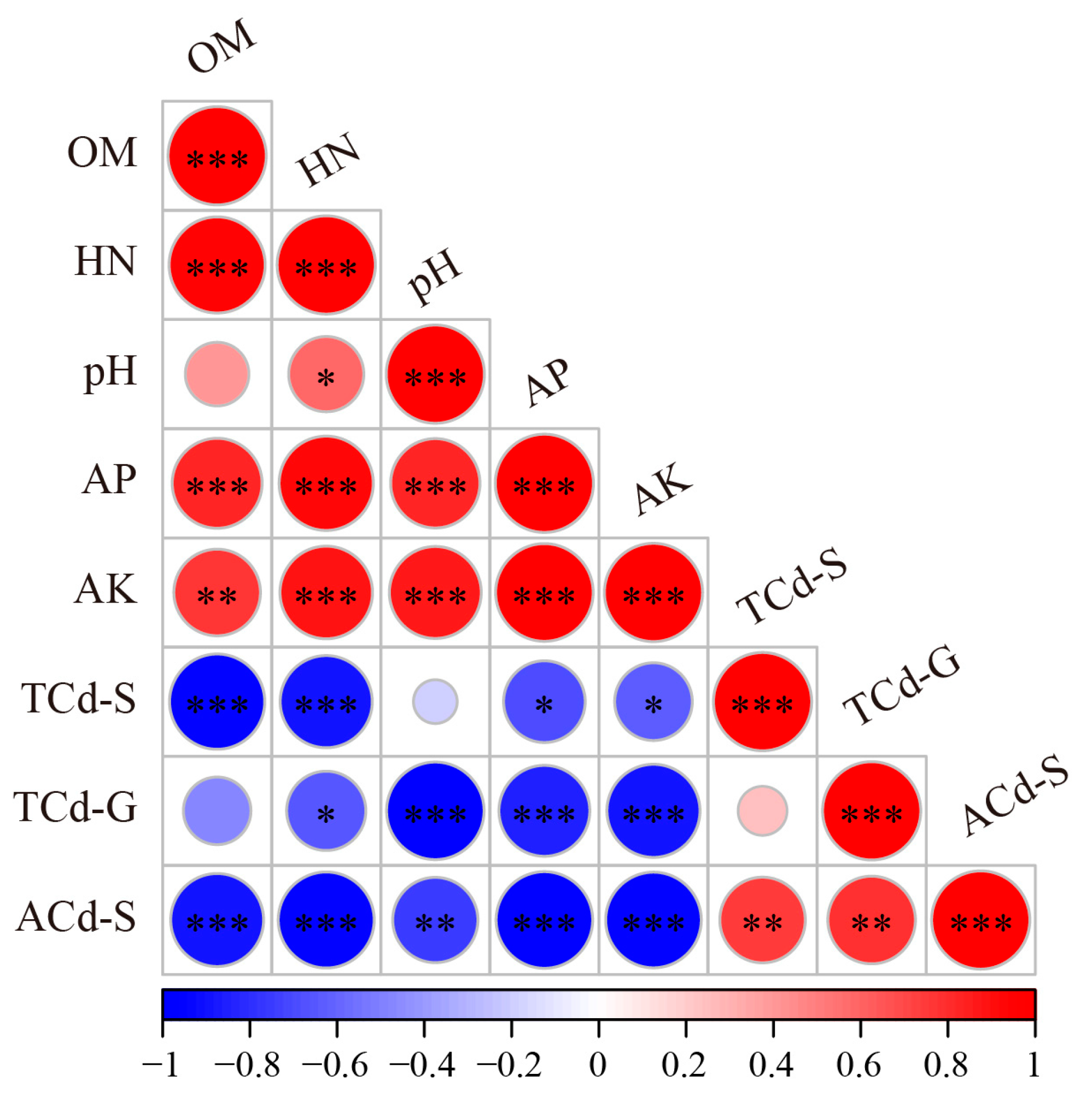
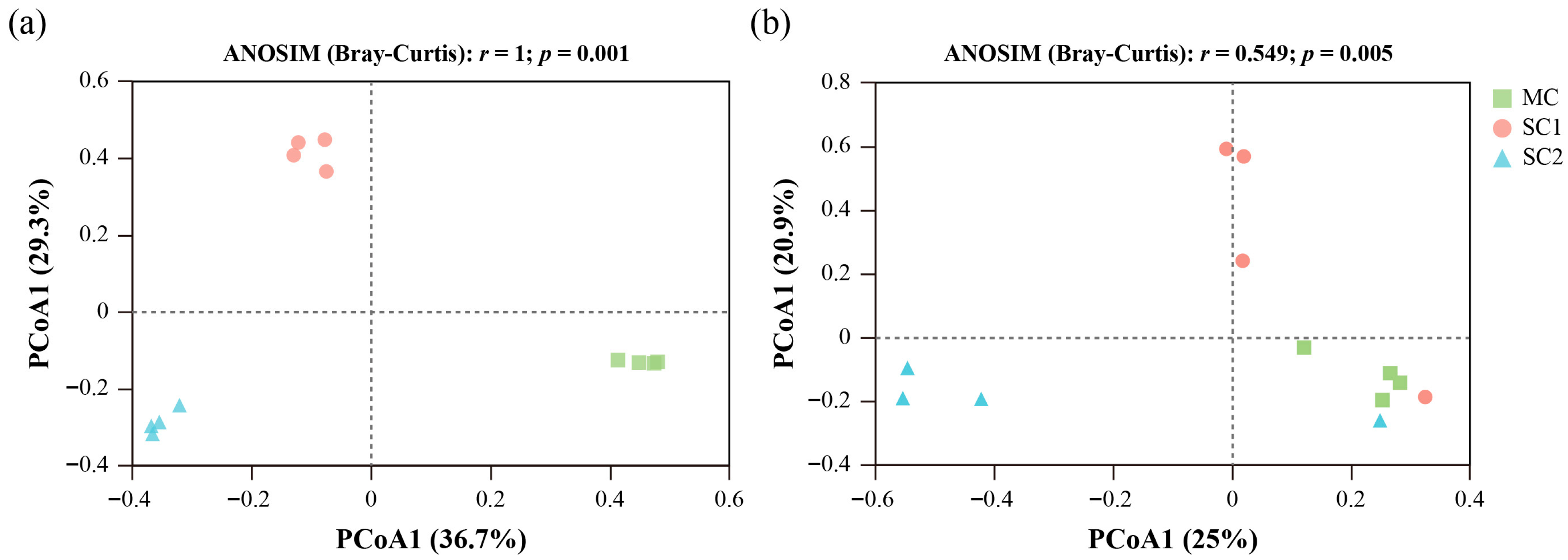
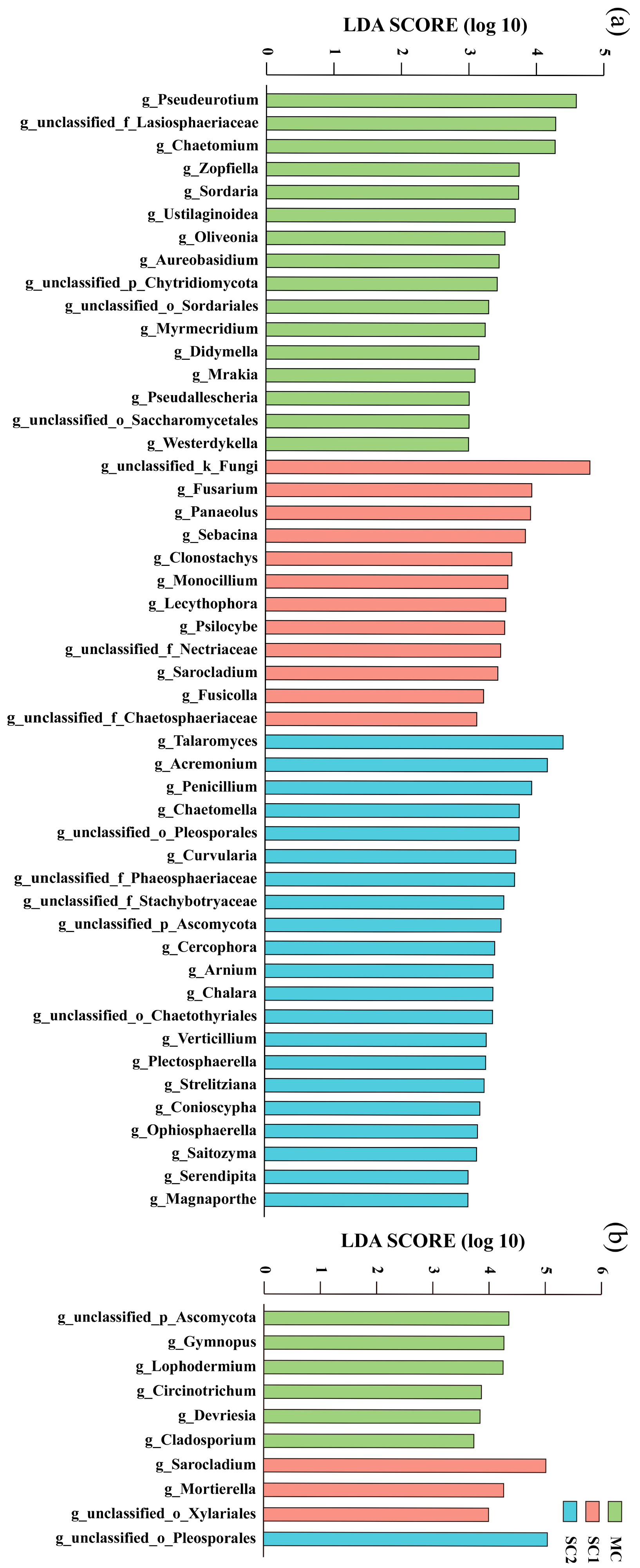
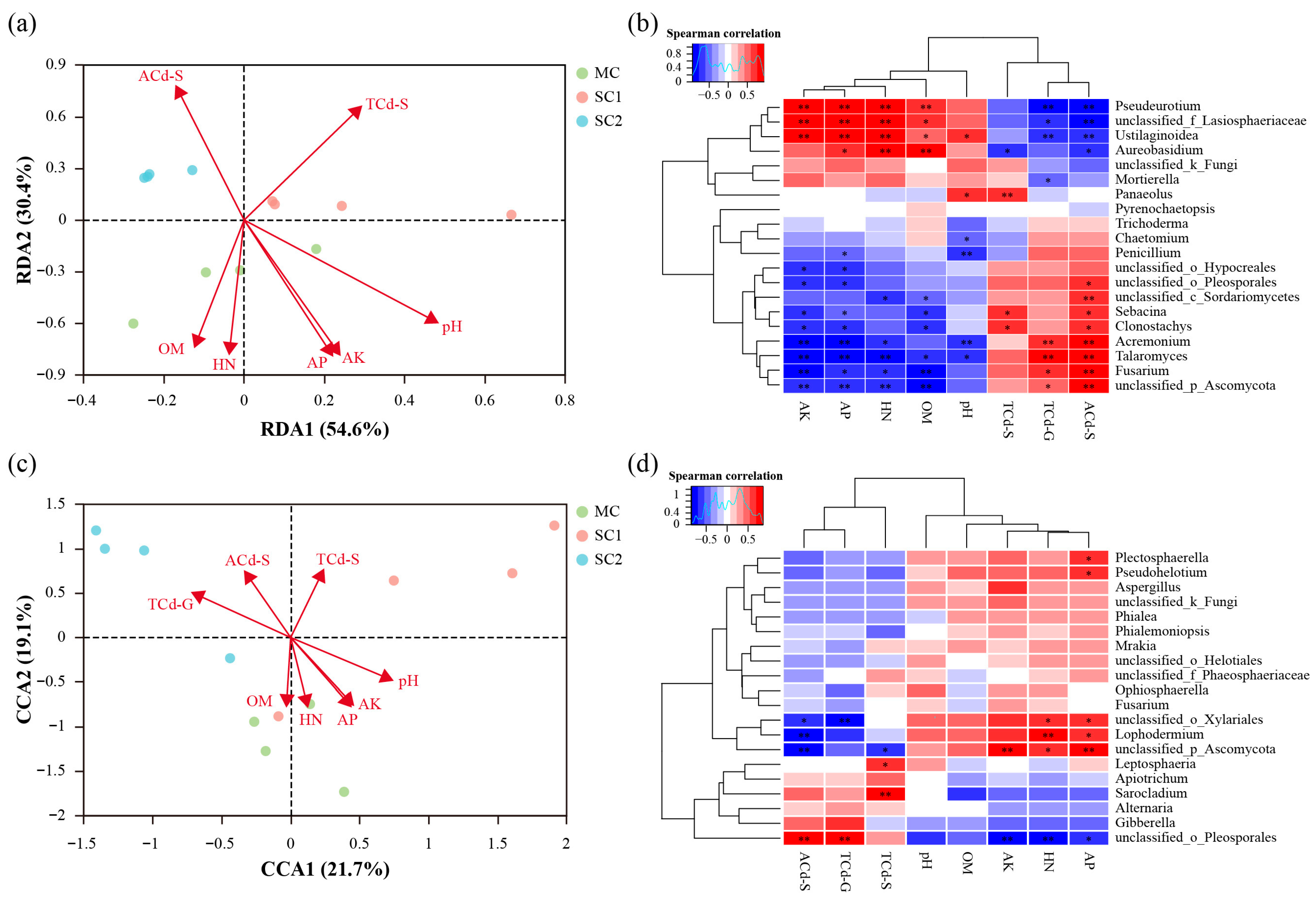
| Site | Physiochemical Properties of Soil | Cd Concentrations | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OM (g/kg) | HN (mg/kg) | AP (mg/kg) | AK (mg/kg) | pH | TCd-S (mg/kg) | ACd-S (mg/kg) | TCd-G (mg/kg) | |
| MC | 82.19 ± 4.48 a | 240.03 ± 4.14 a | 37.10 ± 0.57 a | 137.00 ± 1.83 a | 6.72 ± 0.20 a | 2.00 ± 0.10 c | 1.26 ± 0.08 c | 0.13 ± 0.03 b |
| SC1 | 43.96 ± 0.87 b | 181.10 ± 9.69 b | 20.40 ± 1.27 b | 116.50 ± 2.89 b | 6.81 ± 0.21 a | 3.29 ± 0.13 a | 2.12 ± 0.09 b | 0.16 ± 0.04 b |
| SC2 | 45.27 ± 5.34 b | 166.55 ± 6.84 c | 4.75 ± 0.84 c | 89.75 ± 2.21 c | 4.68 ± 0.03 b | 2.93 ± 0.15 b | 2.73 ± 0.22 a | 2.58 ± 0.20 a |
| Factors | Rhizospheric Fungi | Seed Endophytic Fungi | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shannon | Chao1 | Shannon | Chao1 | |||||
| r | p | r | p | r | p | r | p | |
| OM | −0.4133 | 0.037 * | 0.1189 | 0.628 | 0.6084 | 0.008 ** | 0.4126 | 0.152 |
| HN | −0.5674 | 0.021 * | 0.0699 | 0.774 | 0.6993 | 0.006 ** | 0.6923 | 0.070 |
| AP | −0.7018 | 0.009 ** | 0.0841 | 0.776 | 0.6970 | 0.003 ** | 0.8021 | 0.029 * |
| AK | −0.8932 | 0.005 ** | −0.0909 | 0.717 | 0.6643 | 0.005 ** | 0.6573 | 0.035 * |
| pH | −0.5378 | 0.044 * | 0.3579 | 0.225 | 0.3158 | 0.060 | 0.4351 | 0.058 |
| TCd-S | 0.3958 | 0.069 | 0.4336 | 0.295 | −0.5524 | 0.018 * | −0.1678 | 0.366 |
| ACd-S | 0.7391 | 0.016 * | −0.0280 | 0.920 | −0.7622 | 0.005 ** | −0.8042 | 0.027 * |
| TCd-G | NA | NA | NA | NA | −0.5149 | 0.049 * | −0.4623 | 0.024 * |
| Rhizospheric Fungi Community | Seed Endophytic Fungi Community | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RDA1 | RDA2 | r2 | p | CCA1 | CCA2 | r2 | p | |
| OM | −0.1739 | −0.9848 | 0.7506 | 0.007 ** | −0.0541 | −0.9985 | 0.5838 | 0.037 * |
| HN | −0.0497 | −0.9988 | 0.8145 | 0.003 ** | 0.1539 | −0.9881 | 0.6031 | 0.030 * |
| AP | 0.2851 | −0.9585 | 0.8989 | 0.001 *** | 0.5061 | −0.8625 | 0.7685 | 0.001 *** |
| AK | 0.3085 | −0.9512 | 0.9012 | 0.001 *** | 0.5295 | −0.8483 | 0.7606 | 0.002 ** |
| pH | 0.6516 | −0.7586 | 0.8029 | 0.003 ** | 0.8527 | −0.5225 | 0.7708 | 0.004 ** |
| TCd-S | 0.4244 | 0.9055 | 0.7030 | 0.009 ** | 0.3217 | 0.9469 | 0.6346 | 0.019 * |
| ACd-S | −0.2263 | 0.9741 | 0.8521 | 0.002 ** | −0.4183 | 0.9083 | 0.6526 | 0.013 * |
| TCd-G | NA | NA | NA | NA | −0.8321 | 0.5547 | 0.7604 | 0.004 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, W.; Chen, M.; Lai, Y.; Yang, D.; Soares, M.A.; Gond, S.K.; Li, H. Deciphering the Role of Reshaped Fungal Microbiome in Cadmium Accumulation in Rice Grains. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120837
Gong W, Chen M, Lai Y, Yang D, Soares MA, Gond SK, Li H. Deciphering the Role of Reshaped Fungal Microbiome in Cadmium Accumulation in Rice Grains. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(12):837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120837
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Weijun, Minghui Chen, Yibin Lai, Dian Yang, Marcos Antônio Soares, Surendra Kumar Gond, and Haiyan Li. 2025. "Deciphering the Role of Reshaped Fungal Microbiome in Cadmium Accumulation in Rice Grains" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 12: 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120837
APA StyleGong, W., Chen, M., Lai, Y., Yang, D., Soares, M. A., Gond, S. K., & Li, H. (2025). Deciphering the Role of Reshaped Fungal Microbiome in Cadmium Accumulation in Rice Grains. Journal of Fungi, 11(12), 837. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11120837






