Edible Fungi Melanin: Recent Advances in Extraction, Characterization, Biological Activity and Applications
Abstract
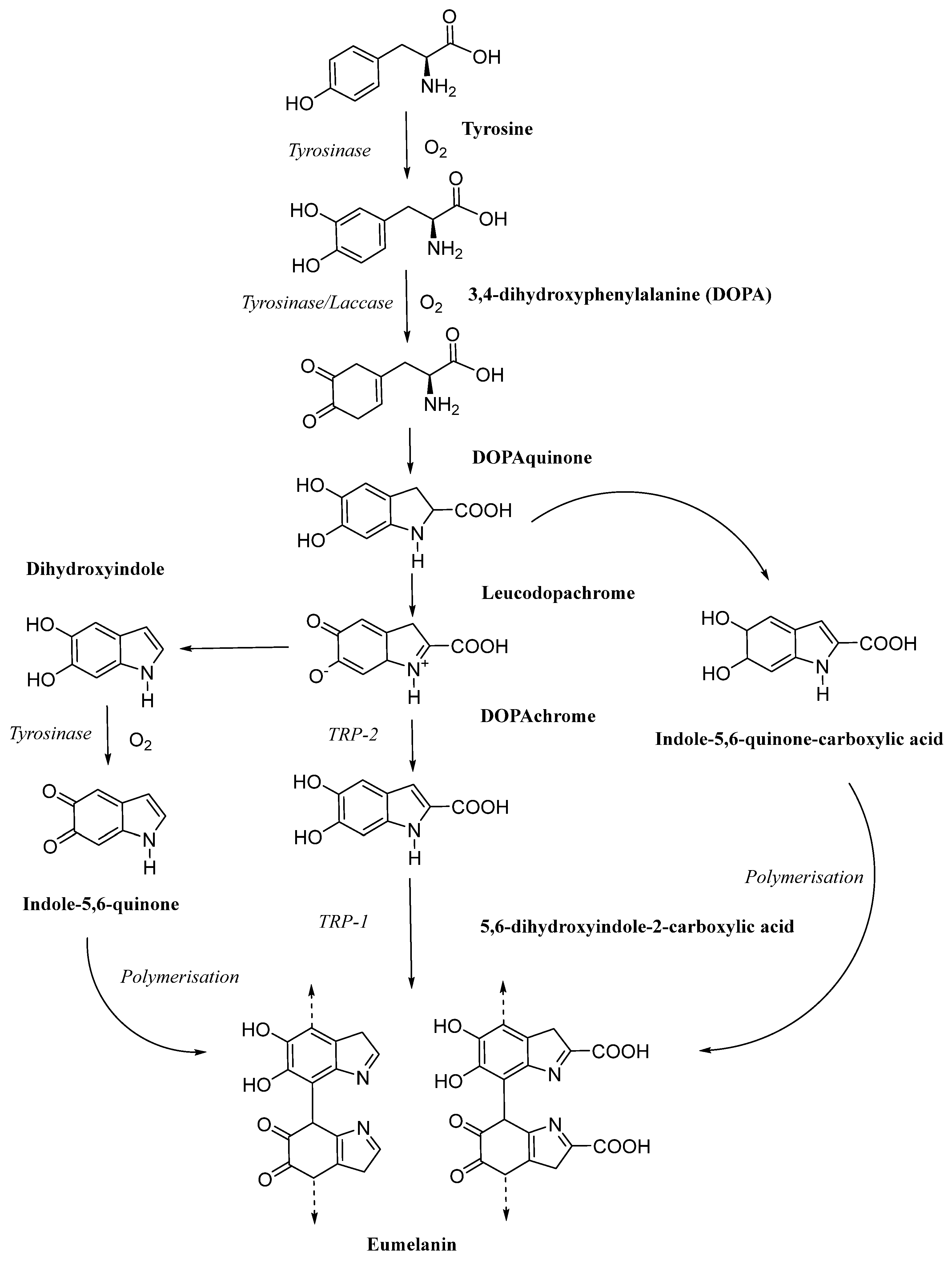
1. Introduction
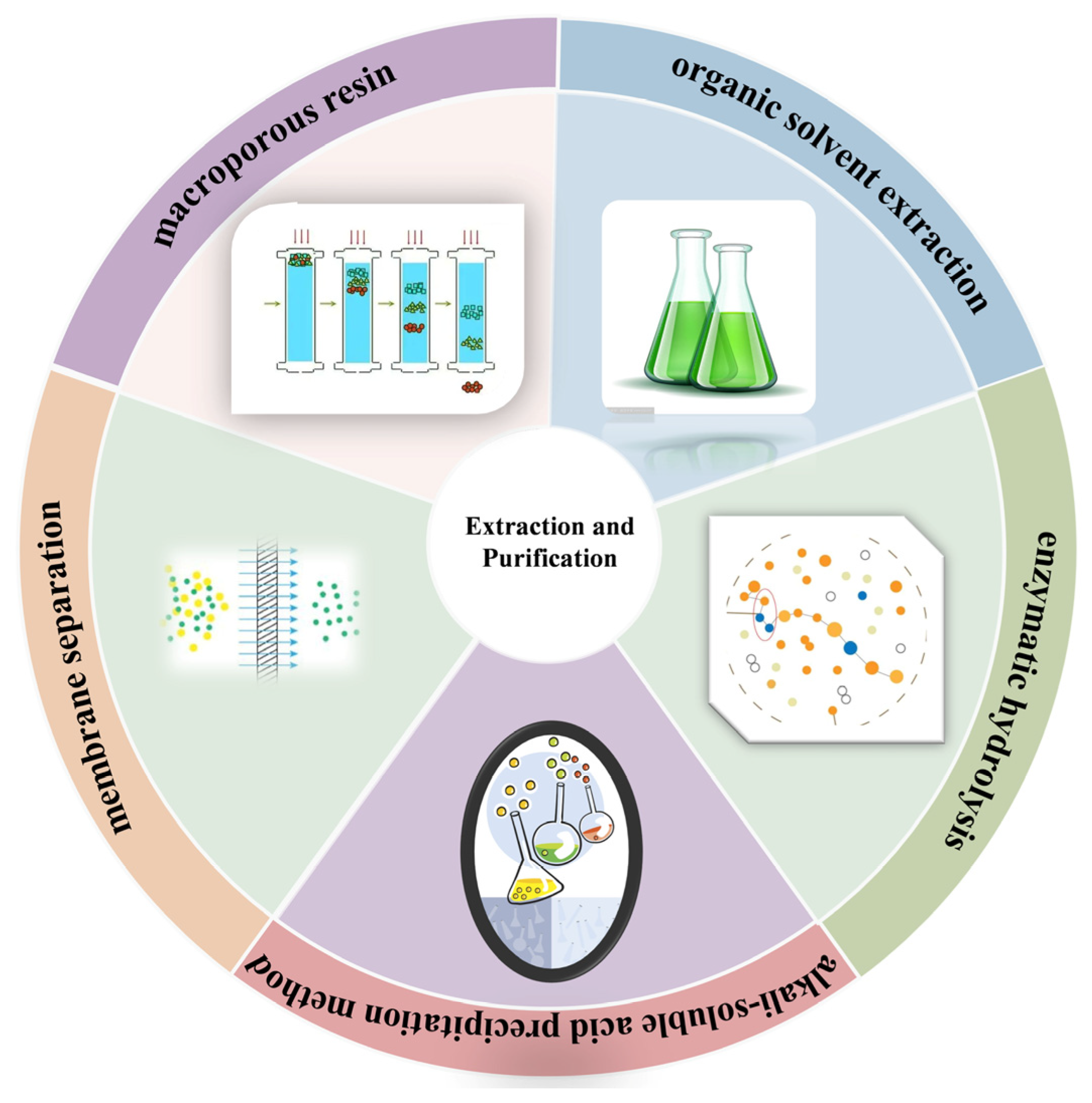
2. Extraction and Purification
2.1. Solvent Extraction Method
2.2. Alkali Extraction and Acid Precipitation Method
2.3. Enzymatic Hydrolysis Method
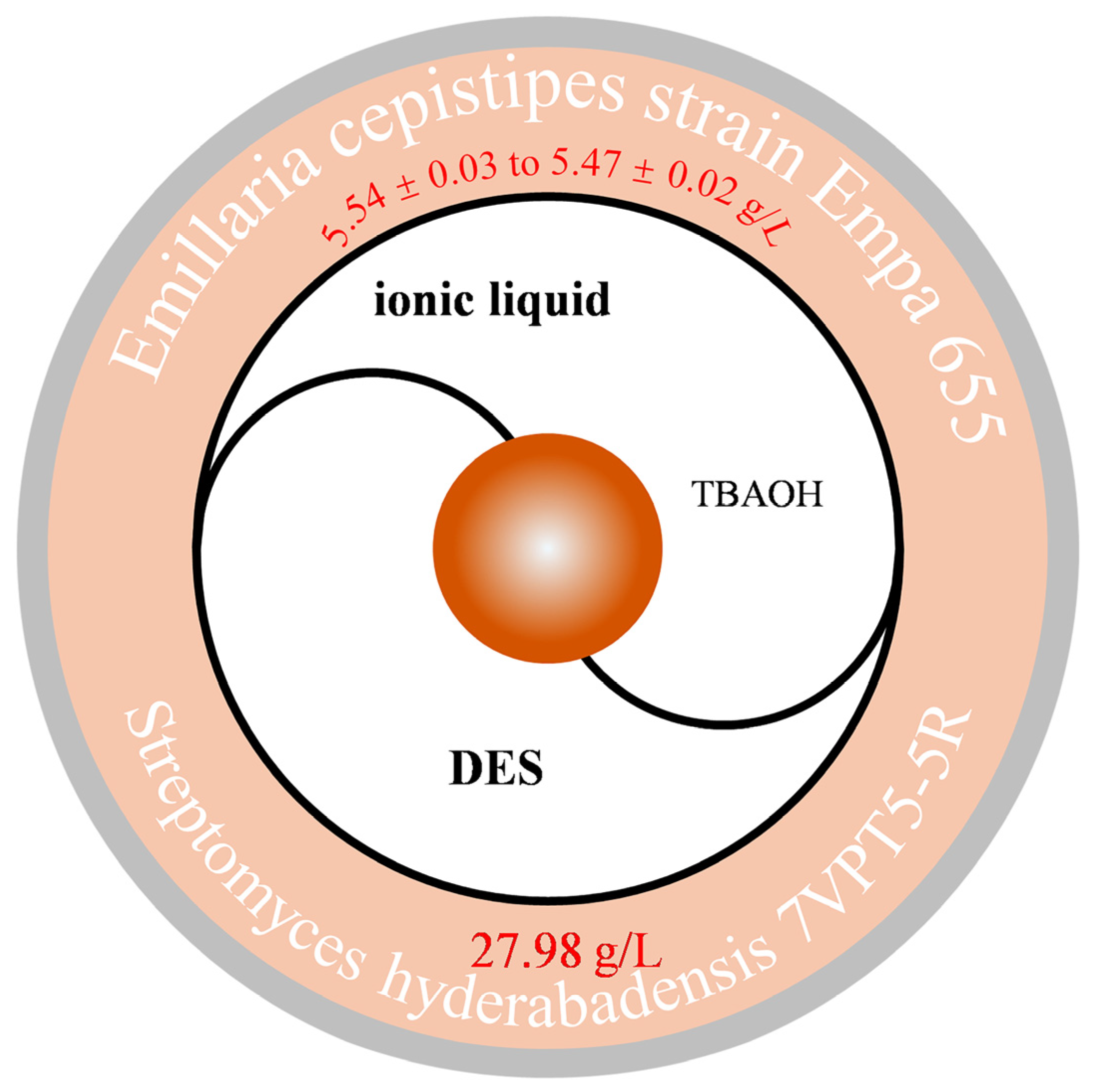
2.4. Other Auxiliary Methods
2.5. Efficient Preparation Exploration Strategy
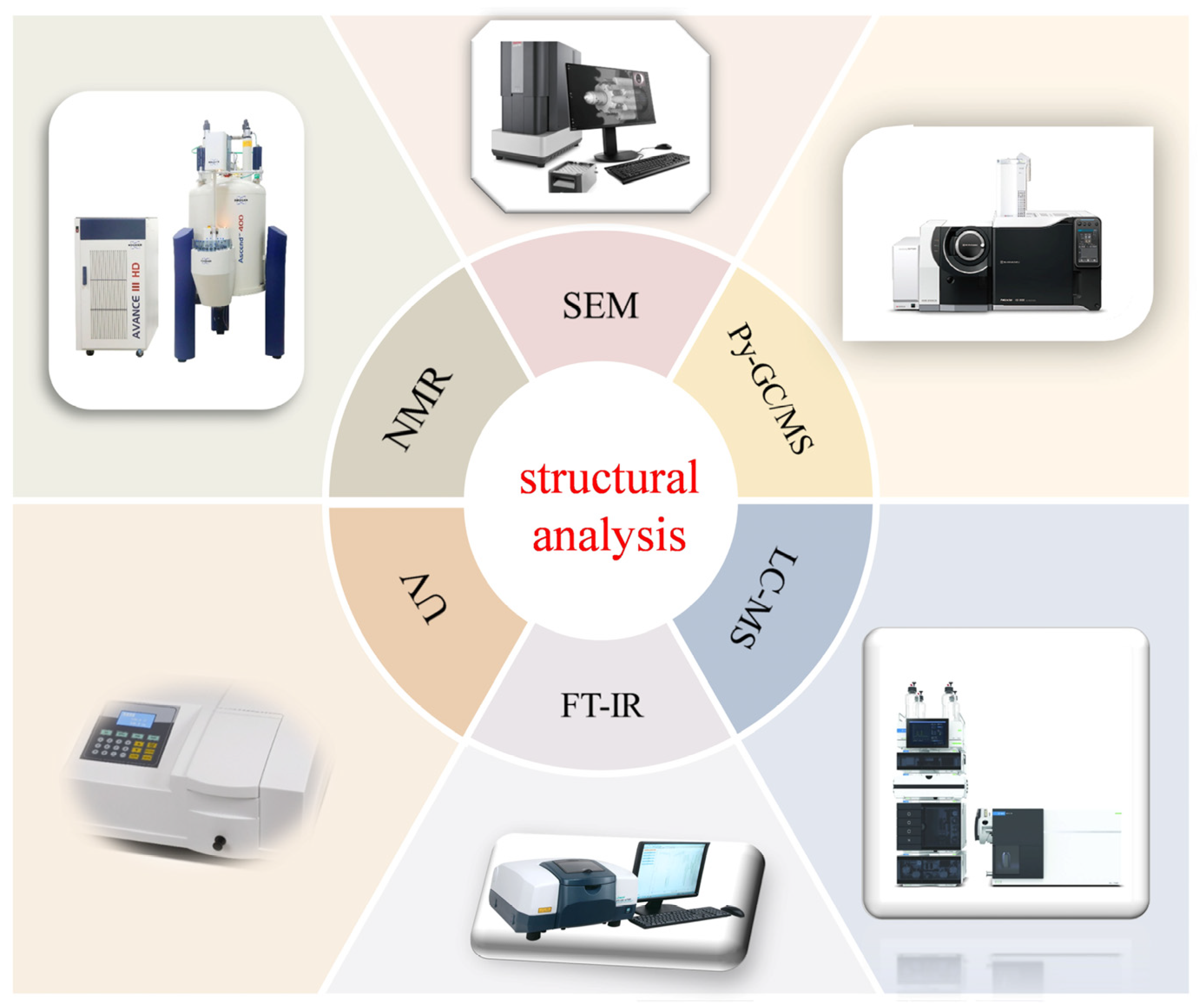
3. Characterization of Melanin
3.1. UV–Visible Spectroscopy
3.2. FT-IR
3.3. Physicochemical Properties
3.4. Pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (Py-GC/MS)
3.5. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)
3.6. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR)
3.7. Surface Morphology
3.8. Liquid Chromatograph Mass Spectromete (LC-MS)
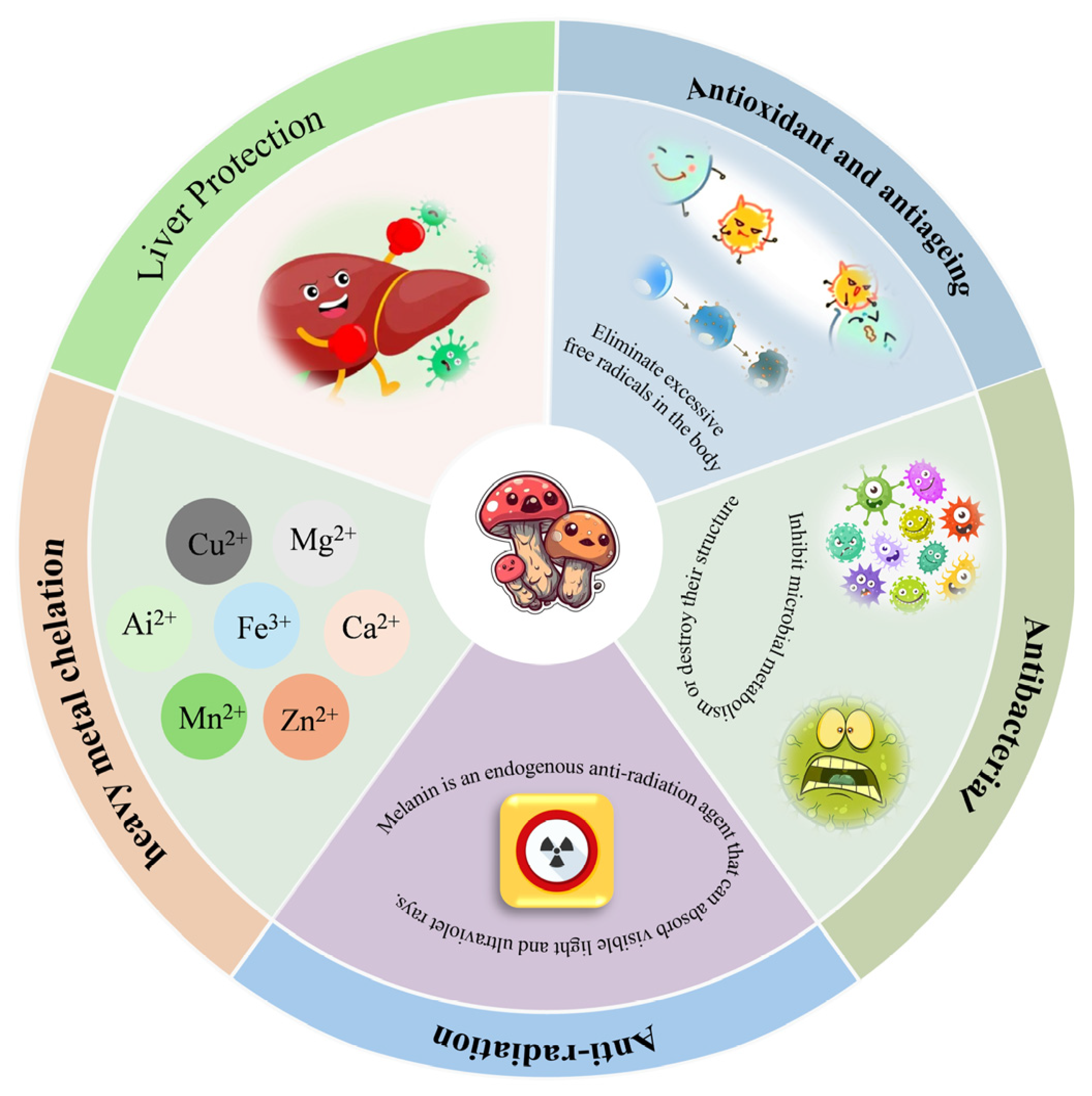
4. Biological Activity
4.1. Antioxidant and Antiageing
4.2. Antibacterial
4.3. Anti-Radiation
4.4. Metal Chelating Ability
4.5. Liver Protection
5. Applications of Melanins
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.R.; Wang, D.W.; Chen, Y.T.; Liu, T.T.; Zhang, S.S.; Fan, H.X.; Liu, H.C.; Li, Y. Healthy function and high valued utilization of edible fungi. Food Sci. Hum. Well. 2021, 10, 408–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.N.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Z.X. Efficient physical extraction of active constituents from edible fungi and their potential bioactivities: A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 105, 468–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A.; Mylarapu, A.; Krishna, K.V.; Kumar, D.S. An insight into the nutritional and medicinal value of edible mushrooms: A natural treasury for human health. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 381, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosset, G. Biotechnological production of melanins with microorganisms. In Bio-Pigmentation and Biotechnological Implementations; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Nimse, S.B.; Mathew, D.E.; Dhimmar, A.; Sahastrabudhe, H.; Gajjar, A.; Ghadge, V.A.; Kumar, P.; Shinde, P.B. Microbial melanin: Recent advances in biosynthesis, extraction, characterization, and applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2021, 53, 107773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solano, F. Melanins: Skin pigments and much more—Types, structural models, biological functions, and formation routes. New J. Sci. 2014, 2014, 498276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenman, H.C.; Casadevall, A. Synthesis and assembly of fungal melanin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 93, 931–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riley, P.A. Melanin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell B 1997, 29, 1235–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.L.; Xu, H.Y.; Gao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.B.; Shi, N.; Guo, L.X.; Liu, P.P. Application of melanin as biological functional material in composite film field. Sci. Eng. Compos. Mater. 2022, 29, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalmi, P.; Bodke, P.; Wahidullah, S.; Raghukumar, S. The fungus Gliocephalotrichum simplex as a source of abundant, extracellular melanin for biotechnological applications. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 28, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chongkae, S.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Pruksaphon, K.; Laliam, A.; Pornsuwan, S.; Youngchim, S. Production of melanin pigments in saprophytic fungi in vitro and during infection. J. Basic Microb. 2019, 59, 1092–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, H.Z. The function of melanin or six blind people examine an elephant. Bioessays 1992, 14, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, T.; Ozlu, B.; Ivanová, L.; Lee, S.; Lee, H.; Krajcovic, J.; Shim, B.S. Multifunctional natural and synthetic melanin for bioelectronic applications: A review. Biomacromolecules 2024, 25, 5489–5511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Ischia, M.; Napolitano, A.; Ball, V.; Chen, C.T.; Buehler, M.J. Polydopamine and eumelanin: From structure–property relationships to a unified tailoring strategy. Acc. Chem. Res. 2014, 47, 3541–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, X.M.; Xue, F.Z.; Cai, Q.; Zhu, X.F.; Wu, X.P.; Fu, J.S. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant and antibacterial activities of melanin from Tremella fuciformis bran. Mycosystema 2023, 42, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Yuan, Y.; Xue, F.Z.; Wu, X.P.; Fu, J.S. Optimization of fermentation conditions for extracellular melanin production from Inonotus hispidus and its antioxidant activity. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2023, 37, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.J.; Liu, S.J.; Wang, J. Antioxidant activity stability and application of melanin obtained from Phlebopus portentosus. Acta Edulis Fungi 2023, 30, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.H.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J.Z.; Gui, L.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Cai, N.; Li, H.P.; Ren, S.H.; Li, T.L.; Shu, L.L. Synthesis and structural characteristics analysis of melanin pigments induced by blue light in Morchella sextelata. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1276457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hou, R.L.; Wang, D.T.; Mai, M.X.; Wu, X.P.; Zheng, M.F.; Fu, J.S. Comprehensive utilization of edible mushroom Auricularia auricula waste residue—Extraction, physicochemical properties of melanin and its antioxidant activity. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 7, 3774–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prados-Rosales, R.; Toriola, S.; Nakouzi, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Stark, R.; Gerfen, G.; Tumpowsky, P.; Dadachova, E.; Casadevall, A. Structural characterization of melanin pigments from commercial preparations of the edible mushroom Auricularia auricula. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 7326–7332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Wu, W.Y.; Zhang, F.P.; Hu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, X.P.; Fu, J.S. Differences between water-soluble and water-insoluble melanin derived from Inonotus hispidus mushroom. Food Chem. X 2022, 16, 100498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.L.; Liu, X.; Xiang, K.K.; Chen, L.T.; Wu, X.P.; Lin, W.X.; Zheng, M.F.; Fu, J.S. Characterization of the physicochemical properties and extraction optimization of natural melanin from Inonotus hispidus mushroom. Food Chem. 2019, 277, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.J.; Zhang, X.J.; Sun, S.W.; Zhang, L.Y.; Shan, S.K.; Zhu, H. Production of natural melanin by Auricularia auricula and study on its molecular structure. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavan, M.E.; Lopez, N.I.; Pettinari, M.J. Melanin biosynthesis in bacteria, regulation and production perspectives. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 1357–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Deepshikha.; Chaturvedi, V.; Verma, P. The amazing world of biological pigments: A review on microbial melanins. Dyes Pigment. 2025, 237, 112711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.P.; Xia, Y.X. Melanin in fungi: Advances in structure, biosynthesis, regulation, and metabolic engineering. Microb. Cell Fact. 2024, 23, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.; Yang, H.Y.; Liu, S.; Yu, H.H.; Li, D.; Li, P.C.; Xing, R.G. Melanin: Insights into structure, analysis, and biological activities for future development. J. Mater. Chem. B 2023, 11, 7528–7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suthar, M.; Dufossé, L.; Singh, S.K. The enigmatic world of fungal melanin: A comprehensive review. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Rhim, J.W. New insight into melanin for food packaging and biotechnology applications. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 2022, 62, 4629–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran-Ly, A.N.; Reyes, C.; Schwarze, F.W.M.R.; Ribera, J. Microbial production of melanin and its various applications. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 36, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madkhali, N.; Alqahtani, H.R.; Al-Terary, S.; Laref, A.; Hassib, A. Control of optical absorption and fluorescence spectroscopies of natural melanin at different solution concentrations. Opt. Quant. Electron. 2019, 51, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, M.; Viveiros, R.; Correia, T.R.; Correia, I.J.; Bonifácio, V.D.; Casimiro, T.; Aguiar-Ricardo, A. Natural melanin: A potential pH-responsive drug release device. Int. J. Pharmaceut. 2014, 469, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghadge, V.; Kumar, P.; Maity, T.K.; Prasad, K.; Shinde, P.B. Facile alternative sustainable process for the selective extraction of microbial melanin. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 2681–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Avilés, M.D.R.; Montes-Avila, J.; Díaz-Camacho, S.P.; Picos-Salas, M.A.; López-Angulo, G.; Reynoso-Soto, E.A.; Osuna-Martínez, L.U.; Delgado-Vargas, F. Soluble melanins of the Randia echinocarpa fruit–Structural characteristics and toxicity. J. Food Biochem. 2019, 43, e13077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Luo, Z.M.; Men, Y.Z.; Yang, P.; Peng, H.B.; Guo, R.R.; Tian, Y.; Pang, Z.Q.; Yang, W.L. Red blood cell membrane-camouflaged melanin nanoparticles for enhanced photothermal therapy. Biomaterials 2017, 143, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Prasad, K. Multi-tasking hydrated ionic liquids as sustainable media for the processing of waste human hair: A biorefinery approach. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 3328–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjan, S.; Kulkarni, G.; Yaligara, V.; Kyoung, L.; Karegoudar, T.B. Purification and physiochemical characterization of melanin pigment from Klebsiella sp. GSK. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 1513–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, M.H.S.; Sujith, S. Filamentous fungal-mediated melanin nanoparticles for heavy metal detoxification via bioadsorption: A sustainable approach. Biodegradation 2025, 36, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Tong, L.P. Extraction, modification, and application of natural melanin. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2023, 68, 1406–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Chang, M.C.; Xu, L.J.; Meng, J.L.; Zuo, N.K.; Pan, X. Structural characterization, physicochemical properties of melanin from fruiting body, hyphae and spores of Ganoderma lucidu. Biotechnol. Bull. 2021, 37, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.M.; Yao, F.; Wu, W.; Fan, X.Z.; Chen, Z.; Ma, K.; Shi, D.F.; Gao, H. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activity of natural melanin extracted from the wild wood ear mushroom, Auricularia auricula (Agaricomycetes). Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2022, 24, 67–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medihi, N.I.; Haiyee, Z.A.; Sukor, R.; Raseetha, S. Exploring the functional properties and nutritional values of colored oyster mushrooms species (Pleurotus, Agaricomycetes): A review. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2024, 26, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.W.; Zhang, X.L.; Sun, X.R.; Luo, Y.; Du, H.X.; Meng, J.L.; Xu, L.J.; Chang, M.C. Extraction, characterisation, stability and antioxidant capacity of Agrocybe aegerita melanin. Acta Edulis Fungi 2017, 24, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.N.; Wang, R.A.; Zhang, P. Extraction and identification of melanin from Flammulina velutipes. Acta Edulis Fungi 2015, 22, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.P.; Xue, F.Z.; Xu, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wu, X.P.; Zhang, J.L.; Fu, J.S. Optimization of solid-state fermentation extraction of Inonotus hispidus fruiting body melanin. Foods 2021, 10, 2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribera, J.; Panzarasa, G.; Stobbe, A.; Osypova, A.; Rupper, P.; Klose, D.; Schwarze, F.W. Scalable biosynthesis of melanin by the basidiomycete Armillaria cepistipes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 67, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.M.; Xiao, J.J.; Liu, B.T.; Zhuang, Y.L.; Sun, L.P. Study on the preparation and chemical structure characterization of melanin from Boletus griseus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Ma, Z.H.; Wang, C.T.; Chen, W. Melanin in Auricularia auricula: Biosynthesis, production, physicochemical characterization, biological functions, and applications. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2024, 33, 1751–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuyen, H.V.; Nguyen, M.H.; Roach, P.D.; Golding, J.B.; Parks, S.E. Microwave-assisted extraction and ultrasound-assisted extraction for recovering carotenoids from Gac peel and their effects on antioxidant capacity of the extracts. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 6, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Yan, Y.H.; Wu, F.Q.; Zhang, F.P.; Huang, H.C.; Wu, X.P.; Fu, J.S. Extraction optimization of melanin from Auricularia heimuer with complex enzyme and its antioxidant activity analysis. J. Northwest A F Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 50, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Xie, C.Y.; Fan, G.J.; Gu, Z.X.; Han, Y.B. Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of melanin from Auricularia auricula fruit bodies. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2010, 11, 611–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ye, M.; Song, S.; Li, L.; Shaikh, F.; Li, J.H. Isolation, purification, and anti-aging activity of melanin from Lachnum singerianum. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 174, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.W.; Yang, Z.N.; Fan, R.H.; Chu, J.L.; Fang, C.L.; Zhang, Y.S.; Shi, W.T.; Zhang, Y.J. Isolation, characterization, and antioxidant activity of melanin from Auricularia auricula (Agaricomycetes). Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2023, 25, 55–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, E.R.V.; Melo, A.S.; Lima, A.S.; Lemos, V.A.; Oliveira, G.S.; Clethen, C.F.; Bezerra, M.A. A review of the use of central composite design in the optimization of procedures aiming at food chemical analysis. Food Chem. 2025, 480, 143849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemavathi, M.; Shekhar, S.; Varghese, E.; Jaggi, S.; Sinha, B.; Mandal, N.K. Theoretical developments in response surface designs: An informative review and further thoughts. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 2022, 51, 2009–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolmeh, M.; Jafari, S.M. Applications of response surface methodology in the food industry processes. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2017, 10, 413–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Xiao, G.N.; Thring, R.W.; Chen, W.; Zhou, H.B.; Yang, H.L. Production and characterization of melanin by submerged culture of culinary and medicinal fungi Auricularia auricula. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 176, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.P.; Bao, Y.H.; Kong, X.; Tian, J.J.; Han, B.; Zhang, J.C.; Chen, X.J.; Zhang, P.Q.; Wang, H.; Dai, X.D.; et al. Optimization of melanin extraction from the wood ear medicinal mushroom, Auricularia auricula-judae (Agaricomycetes), by response surface methodology and its antioxidant activities in vitro. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2018, 20, 1087–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, H.S.R.; Subiramanian, S.R.; Thyagarajan, D.; Mohammed, N.B.; Saravanakumar, V.K.; Govindaraj, M.; Maheswari, K.M.; Karthikeyan, N.; Kumar, C.R. Melanin biopolymers from microbial world with future perspectives—A review. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Coutinho, J.A.; Weingarten, M. Sustainable recovery of microbial-derived natural pigments using deep eutectic solvents: Advances, potential, and challenges. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 361, 131413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K.; Sequeira, R.A.; Maity, T.K.; Prasad, K. Bio-ionic liquid promoted selective coagulation of κ-carrageenan from Kappaphycus alvarezii extract. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 111, 106382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Chaudhary, J.P.; Mondal, D.; Meena, R.; Prasad, K. A green and sustainable approach to utilize bio-ionic liquids for the selective precipitation of high purity agarose from an agarophyte extract. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 2867–2873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Wang, C.M.; Huang, F.; Jia, H.H.; Wei, P. Wheat straw cellulose dissolution and isolation by tetra-n-butylammonium hydroxide. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 94, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pombeiro-Sponchiado, S.R.; Sousa, G.S.; Andrade, J.C.; Lisboa, H.F.; Gonçalves, R.C. Production of melanin pigment by fungi and its biotechnological applications. Melanin 2017, 1, 47–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Ischia, M.; Wakamatsu, K.; Napolitano, A.; Briganti, S.; Garcia-Borron, J.C.; Kovacs, D.; Meredith, P.; Pezzella, A.; Picardo, M.; Sarna, T.; et al. Melanins and melanogenesis: Methods, standards, protocols. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2013, 26, 616–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Garcia-Pichel, F. Microbial ultraviolet sunscreens. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pralea, I.-E.; Moldovan, R.-C.; Petrache, A.-M.; Ilieș, M.; Hegheș, S.-C.; Ielciu, I.; Nicoară, R.; Moldovan, M.; Ene, M.; Radu, M.; et al. From extraction to advanced analytical methods: The challenges of melanin analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gessler, N.N.; Egorova, A.S.; Belozerskaya, T.A. Melanin pigments of fungi under extreme environmental conditions. Appl. Biochem. Microbiol. 2014, 50, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.F.; Ji, C.M.; Tang, B.P. Purification, characterisation and biological activity of melanin from Streptomyces sp. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivasagan, P.; Venkatesan, J.; Senthilkumar, K.; Sivakumar, K.; Kim, S.K. Isolation and characterization of biologically active melanin from Actinoalloteichus sp. MA-32. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 58, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, A.S.; Melo, J.S. One-pot green synthesis of eumelanin: Process optimization and its characterization. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 47671–47680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.Q.; Luo, J.; Xie, C.L.; Wei, J.H.; Pan, G.Q.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Li, C.F. Characterization and biological activities of melanin from the medicinal fungi Ophiocordyceps sinensis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Vergel, G.; Figueroa-Martinez, F.; Garza-López, P.M.; García-Ortiz, N.; Loera, O. DOPA-melanin, component and tolerance factor to heat and UV-B radiation in the conidia of two species of Cordyceps. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2022, 32, 437–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Xie, M.X.; Lu, M.; Shi, L.; Shi, T.Y.; Yu, M. Characterization of the physicochemical properties, antioxidant activity, and antiproliferative activity of natural melanin from S. reiliana. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Souza, R.A.; Kamat, N.M.; Nadkarni, V.S. Purification and characterisation of a sulphur rich melanin from edible mushroom Termitomyces albuminosus Heim. Mycology 2018, 9, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonner, T.G.; Duncan, A. Infra-red spectra of some melanins. Nature 1962, 194, 1078–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.P.; Zhang, P.Q.; Dai, X.D.; Yao, X.G.; Zhou, S.Y.; Ma, Q.F.; Liu, J.N.; Tian, S.; Zhu, J.N.; Zhang, J.C.; et al. Extraction, physicochemical properties, and antioxidant activity of natural melanin from Auricularia heimuer fermentation. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1131542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierżęga-Lęcznar, A.; Chodurek, E.; Stępień, K.; Wilczok, T. Pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry of synthetic neuromelanins. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 2002, 62, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierżęga-Lęcznar, A.; Kurkiewicz, S.; Stępień, K. Detection and quantitation of a pheomelanin component in melanin pigments using pyrolysis–gas chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry system with multiple reaction monitoring mode. J. Mass Spectrom. 2012, 47, 242–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, G.; Wakamatsu, K.; Panzella, L.; Ito, S.; Napolitano, A.; D’Ischia, M. Isomeric cysteinyldopas provide a (photo) degradable bulk component and a robust structural element in red human hair pheomelanin. Pigment. Cell Melanoma Res. 2009, 22, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.M.; Xie, S.Y.; Tao, Y.X.; Wu, X.P.; Fu, J.S. Pyrolysis products of melanin from Auricularia heimuer new cultivar ‘Nonghei No. 2’ analyzed by Py-GC/MS. Mycosystema 2023, 42, 1766–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, F.Z.; Huang, H.C.; Wu, F.Q.; Li, X.M.; Wu, X.P.; Fu, J.S. Research status and industrial application of fungal melanin. Biotechnol. Bull. 2021, 37, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Chen, X.; Li, G.W.; Guo, G.Y.; Yang, L. Structural characteristics of pheomelanin-like pigment from Lachnum singerianum. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 284, 1742–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Wang, Y.; Guo, G.Y.; He, Y.L.; Lu, Y.; Ye, Y.W.; Yang, Q.H.; Yang, P.Z. Physicochemical characteristics and antioxidant activity of arginine-modified melanin from Lachnum YM-346. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2490–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, A.S.; Tripathi, A.; Melo, J.S. On-column enzymatic synthesis of melanin nanoparticles using cryogenic poly (AAM-co-AGE) monolith and its free radical scavenging and electro-catalytic properties. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 87206–87215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.Y.; Garcia-Rivera, J.; Yan, B.; Casadevall, A.; Stark, R.E. Unlocking the molecular structure of fungal melanin using 13C biosynthetic labeling and solid-state NMR. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 8105–8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.L.; Huang, C.Y.; Zhang, Z.H.; Gao, W. Isolation and identification of pigments from oyster mushrooms with black, yellow and pink caps. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulin, J.V.; Batagin-Neto, A.; Graeff, C.F. Identification of common resonant lines in the EPR spectra of melanins. J. Phys. Chem. B 2019, 123, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Zhou, X.H.; McCallum, N.C.; Hu, Z.Y.; Ni, Q.Z.; Kapoor, U.; Heil, C.M.; Cay, K.S.; Zand, T.; Mantanona, A.; et al. Unraveling the structure and function of melanin through synthesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 2622–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvakumar, P.; Rajasekar, S.; Periasamy, K.; Raaman, N. Isolation and characterization of melanin pigment from Pleurotus cystidiosus (telomorph of Antromycopsis macrocarpa). World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2008, 24, 2125–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, W.; Chen, X.H.; Jiang, M.; Dong, M.S. In vitro antibiofilm activity of the melanin from Auricularia auricula, an edible jelly mushroom. Ann. Microbiol. 2012, 62, 1523–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.Q.; Dai, D.H.; Chen, G.C.; Hu, W.L. Antioxidant activities of melanin from Gomphidius viscidus and its anti-aging, anti-stress injury effects on Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Chin. Inst. Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 24, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.J. Study on the antioxidant of the Auriculaia auricuia melanin. Food Res. Dev. 2013, 34, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Yin, D.M.; Hu, W.Z.; Jiang, A.L.; Chen, C.; Gu, Z.X. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of Auricularia auricula melanin. Sci. Technol. Food Ind. 2013, 34, 118–120+125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Yin, D.M.; Jiang, H.; Du, X.W.; Liu, C.H.; Gu, Z.X. Composition analysis and antioxidant activity of Auricularia auricula melanin. Food Sci. 2013, 34, 138–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.L.; Yuan, Y.; Xiang, K.K.; Wu, X.P.; Lin, W.X.; Zheng, M.F.; Fu, J.S. Cellulase and ultrasonic wave synergistic extraction technology of melanin from Auricularia heimuer and analysis of antioxidant activity of the melanin product. Mycosystema 2019, 38, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menichetti, A.; Mordini, D.; Montalti, M. Melanin as a photothermal agent in antimicrobial systems. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmasova, M.A.; Sysoeva, M.A. Chemical composition and biological activity of the BuOH fraction from chaga melanin. Pharm. Chem. J. 2017, 51, 292–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wang, Y.F.; Qi, X.F.; Zeng, W.M.; Zhang, Y.L.; Lei, H. The physicochemical properties and antioxidant and bacteriostatic activities of Auricularia auricula melanin modificated by Arginine. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 7443–7454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauslaa, Y.; Solhaug, K.A. Fungal melanins as a sun screen for symbiotic green algae in the lichen Lobaria pulmonaria. Oecologia 2001, 126, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Revskaya, E.; Chu, P.; Howell, R.C.; Schweitzer, A.D.; Bryan, R.A.; Harris, M.; Gerfen, G.; Jiang, Z.W.; Jandl, T.; Kim, K.; et al. Compton scattering by internal shields based on melanin-containing mushrooms provides protection of gastrointestinal tract from ionizing radiation. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2012, 27, 570–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogarty, R.V.; Tobin, J.M. Fungal melanins and their interactions with metals. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 1996, 19, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.L.; Yang, L.; Gao, L.; Wang, F.; Shi, N.; Zhao, Y.H.; Guo, L.X.; Wang, H.B. Research progress and application of melanin metal chelate. Mater. Rev. 2020, 34, 11145–11152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Hu, W.Z.; Ma, K.; Tian, M.X. Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of melanin and fractions from Auricularia auricula fruiting bodies. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2015, 24, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, B.; Gu, Z.X.; Han, Y.B. Comparison of physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of melanins from fruit-bodies and fermentation broths of Auricularia auricula. Int. J. Food Prop. 2013, 16, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, T.G.; Younger, R.; Poe, C.; Farmer, P.J.; Szpoganicz, B. Studies on synthetic and natural melanin and its affinity for Fe (III) ion. Bioinorg. Chem. Appl. 2012, 2012, 712840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattoon, E.R.; Cordero, R.J.B.; Casadevall, A. Fungal melanins and applications in healthcare, bioremediation and industry. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramachandran, A.; Jaeschke, H. Oxidative stress and acute hepatic injury. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2018, 7, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.G.; Xu, C.S. Proteomic analysis of the regenerating liver following 2/3 partial hepatectomy in rats. Biol. Res. 2014, 47, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fareed, M.M.; Khalid, H.; Khalid, S.; Shityakov, S. Deciphering molecular mechanisms of carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity: A brief systematic review. Curr. Mol. Med. 2024, 24, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Qi, Y.; Lv, H.Y.; Lin, W.X.; Wu, X.P.; Fu, J.S. The improvement of Auricularia heimuer melanin on acute liver injuried mice. Mycosystema 2018, 37, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.L.; Liu, X.; Yan, J.J.; Xiang, K.K.; Wu, X.P.; Lin, W.X.; Chen, G.S.; Zheng, M.F.; Fu, J.S. Characterization of natural melanin from Auricularia auricula and its hepatoprotective effect on acute alcohol liver injury in mice. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 1017–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.L.; Liu, X.; Wu, X.P.; Zheng, M.F.; Fu, J.S. Therapeutic effect of natural melanin from edible fungus Auricularia auricula on alcohol-induced liver damage in vitro and in vivo. Food Sci. Hum. Well. 2021, 10, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Chen, H.; Cao, Y.J.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, W.F.; Guo, W.L.; Lv, X.C.; Rao, P.F.; Ni, L.; Liu, P.H. Auricularia auricula melanin protects against alcoholic liver injury and modulates intestinal microbiota composition in mice exposed to alcohol intake. Foods 2021, 10, 2436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, F.Q.; Zhang, F.P.; Li, X.M.; Wu, X.P.; Fu, J.S. Hepatoenteric protective effect of melanin from Inonotus hispidus on acute alcoholic liver injury in mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, 2200562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsouko, E.; Tolia, E.; Sarris, D. Microbial melanin: Renewable feedstock and emerging applications in food-related systems. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, T.; Matsuura, T.; Izawa, H.; Kishikawa, K.; Kohri, M. Melanin upcycling: Creation of polymeric materials from melanin decomposition products. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 7115–7125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Torres, P.; Cárdenas-Ninasivincha, S.; Aguilar, Y. Exploring the agricultural applications of microbial melanin. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidzadeh, E.; Kalra, A.P.; Shankar, K. Melanin-based electronics: From proton conductors to photovoltaics and beyond. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 122, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.Q.; Rong, P.X.; Liu, H.Y.; Gan, B.C.; Wu, D.T.; Li, H.B.; Gan, R.Y. Co-fermentation of edible mushroom by-products with soybeans enhances nutritional values, isoflavone aglycones, and antioxidant capacity of Douchi Koji. Foods 2022, 11, 2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.J.; Deng, Z.Y.; Liu, T.Y.; Liang, J.F.; Liu, J. Fermentation with edible mushroom mycelia improves flavor characteristics and techno-functionalities of soybean protein. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 104123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.L.; Yi, X.T.; Wu, Z.C.; Zhou, H.B.; Yang, H.L. Synchronous reducing anti-nutritional factors and enhancing biological activity of soybean by the fermentation of edible fungus Auricularia auricula. Food Microbiol. 2024, 120, 104486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karyani, T.Z.; Homaei, A.; Vianello, F. Green pigment hybrid of natural melanin and cellulose nanofibers for sustainable UV-shielding and antioxidant activity. Dyes Pigment. 2025, 244, 113153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.J.; Xia, Z.P.; Deng, N.P.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.B.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gao, H. Eumelanin-inspired nanomaterials in electrochemical energy storage devices: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 452, 138607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Shamery, N.; Heppner, F.; Dosche, C.; Morgenschweis, S.; Bredow, T.; Wittstock, G.; Lee, P.S. Functionalized melanin for enhanced energy storage in aqueous and ionic liquid electrolytes. Commun. Chem. 2025, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; He, S.B.; Wang, T.Y.; Wang, C.C.; Tao, J.R.; Li, Y.W. Melanin-like nanofibers with highly ordered structures achieve ultrahigh specific electromagnetic interference shielding efficiency. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 7127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, R.T.; Chen, W.; Zhu, H.J.; Li, Y.X.; Ou, Y.L.; Wang, J.; Ruan, Q.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, J.B.; Zhang, Y.X.; et al. Molecular engineering of melanin for enhanced biological γ-ray protection. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 7895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, J.; Shen, H.; Lv, W.; Zhang, J.; Fu, J. Edible Fungi Melanin: Recent Advances in Extraction, Characterization, Biological Activity and Applications. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11100738
Tang J, Shen H, Lv W, Zhang J, Fu J. Edible Fungi Melanin: Recent Advances in Extraction, Characterization, Biological Activity and Applications. Journal of Fungi. 2025; 11(10):738. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11100738
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Jiandong, Hebin Shen, Wenyu Lv, Jingxuan Zhang, and Junsheng Fu. 2025. "Edible Fungi Melanin: Recent Advances in Extraction, Characterization, Biological Activity and Applications" Journal of Fungi 11, no. 10: 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11100738
APA StyleTang, J., Shen, H., Lv, W., Zhang, J., & Fu, J. (2025). Edible Fungi Melanin: Recent Advances in Extraction, Characterization, Biological Activity and Applications. Journal of Fungi, 11(10), 738. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof11100738





