Abstract
Proteases (EC 3.4) are hydrolytic enzymes widely used in biotechnological processes, representing about 60 to 70% of the global industrial enzyme market. Edible mushrooms of the genus Pleurotus stand out as excellent producers of these enzymes, in addition to exhibiting high nutritional value and medicinal properties. The proteases produced by these species exhibit broad adaptability to different experimental conditions, including variations in optimal pH and temperature, as well as distinct sensitivities to inhibitors. The production of these enzymes can be intensified by solid-state fermentation (SSF) using low-cost agro-industrial substrates, such as wheat bran, which favors sustainable applications aligned with the circular economy. Parameters such as carbon/nitrogen (C/N) ratio, medium pH, cultivation time, and inoculum age directly influence enzyme productivity. Proteases from Pleurotus spp. show high potential in the biochemical control of parasites such as Meloidogyne incognita, Haemonchus spp., Taenia solium, and Moniezia sp., catalyzing the degradation of the cuticle or eggshell. Other biotechnological applications include milk coagulation, thrombolytic therapies, keratin bioconversion, increased protein digestibility, and use as additives in the food, detergent, and pharmaceutical industries.
1. Introduction
Proteases (EC 3.4) are a type of enzyme that helps break down peptide bonds, leading to the formation of peptides and amino acids [1,2,3]. All forms of life contain proteins in their constitution, which play essential roles in fundamental physiological processes such as immune defense, cell growth and death, sporulation, blood coagulation, enzymatic modification, and regulation of gene expression [4,5,6]. These functions confer great biological importance to proteins and, consequently, to proteases. In addition to their physiological relevance, these enzymes occupy a significant share of the industrial market, accounting for approximately 60% to 70% of the enzymes sold worldwide [7,8,9].
Fungi stand out as important microorganisms for protease production [8]. Within this group, edible mushrooms, especially those belonging to the genus Pleurotus (phylum Basidiomycota), have gained prominence [10]. The genus Pleurotus comprises more than 40 species [4], among which the edible mushrooms P. ostreatus (oyster) and P. eryngii (king oyster or shimeji) stand out, being widely appreciated and consumed. Globally, P. ostreatus is the second most produced mushroom [10,11]. Several factors justify its importance, including medicinal properties, reduced cultivation time compared to other edible mushroom genera, and the ability to colonize and degrade various types of lignocellulosic waste, which favors practices associated with the circular economy [7,9,12].
Proteases of Pleurotus spp. have been used promisingly in the biochemical control of different parasites of importance in the context of One Health, such as Taenia solium, Moniezia sp. [13], Meloidogyne incognita [14], Trichostrongylus spp., and Strongyloides papillosus [15]. They act to catalyze the degradation of proteins present in the structure of the parasites [13]. In addition, these enzymes have potential applications in milk coagulation for cheese production, thrombolytic therapy for the treatment and prevention of thrombosis, and various industrial processes in the detergent, food, and pharmaceutical sectors [3,16,17].
Given the favorable characteristics of proteases from the genus Pleurotus and the growing industrial demand for biodegradable methods with low operating costs [18], research involving these fungi has gained increased attention, even though the genera Aspergillus and Penicillium have historically been the most widely used for protease production [4]. In this context, this review aims to compile up-to-date information on the classification and biochemical characterization of proteases produced by different Pleurotus species, as well as discussing their various biotechnological applications.
2. Classification and Biochemical Characterization of Pleurotus Proteases
The genus Pleurotus encompasses a large number of species of protease-producing edible mushrooms [4] such as P. ostreatus [11], P. eryngii [1], P. citrinopileatus [19], P. pulmonarius [12], P. sajor-caju [18], P. djamor [20], P. albidus [21], and P. tuber-regium [22]. Among these species, the most investigated is P. ostreatus [4], due to several factors, such as its high nutritional and medicinal value, excellent yield, ease of large-scale cultivation, and ability to produce a variety of enzymes [4,11].
Among the enzymes produced by species of the genus Pleurotus, proteases stand out as one of the most relevant [4,12]. These enzymes can be classified based on their mechanism of action, dividing them into exopeptidases, which promote the catalysis of peptide bond cleavage at the N- or C-terminals, and endopeptidases, responsible for the catalysis of internal bond cleavage in the polypeptide chain [1,23]. In addition, another important classification criterion is the catalytic mechanism involved in hydrolysis, which can be determined by analyzing the amino acid residues or cofactors present at the enzyme’s active site [24,25].
Additionally, proteases can also be classified into families, according to the MEROPS database, which organizes these enzymes based on structural, functional, and evolutionary characteristics. Each family receives an alphanumeric designation, such as S8 (serine proteases) or M36 (metalloproteases/fungalisins) [26].
The most common class of proteases produced by Pleurotus spp. is that of serine proteases, whose catalytic triad is composed of aspartate, histidine, and serine residues [9]. During the peptide bond cleavage process, the serine residue acts as a nucleophile, initiating the catalytic reaction. In the industrial context, this type of protease is highly relevant, which explains its great demand on a global scale [9,21]. In MEROPS, these enzymes are mainly assigned to the S8 family. Their activity can be affected by certain inhibitors, such as diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DFP) [27], 3,4-dichloroisocoumarin (DCI), 4-(2-aminoethyl) benzenesulfonyl fluoride (AEBSF), leupeptin, aprotinin, and PMSF (phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride), the latter being the most cited inhibitor in the literature [2].
On the other hand, although to a lesser extent, aspartic proteases are also produced by Pleurotus spp. [28]. These enzymes share several biochemical and structural features, such as sequence similarity, predominance of beta-sheet secondary structures, and the presence of aspartate residues at the active site, which are responsible for catalytic activity [29]. Due to their optimal performance under acidic pH conditions, these enzymes are classified as acid proteases [12]. In MEROPS, they mainly +6 correspond to the A1 family. Inhibitors such as diazoacetylnorleucine (DAN) methyl ester, 1,2-epoxy-3-(p-nitrophenoxy) propane (EPNP), and pepstatin A affect the activity of aspartic proteases, with pepstatin A being the best known and most widely used [2].
Another group of proteases present in the genus Pleurotus is the cysteine proteases, also known as thiol proteases. The active site of these enzymes contains three amino acids that form the catalytic triad Cys/His/Asn (or Asp), whose residues act in a coordinated manner in the hydrolysis of the peptide bond [30]. Although they are not the most frequently found proteases, studies indicate their occurrence in P. ostreatus, P. albidus, and P. sajor-caju [4,21]. In MEROPS, they are grouped into families such as C1. Their activity is inhibited by thiol group-chelating compounds, such as iodoacetic acid [2].
Metalloproteases are also present in Pleurotus species, such as P. ostreatus and P. eryngii [17,31]. The enzymatic catalysis of these proteases requires the coordination of a metal ion at the active site. During peptide bond hydrolysis, the water molecule, acting as a nucleophile, is activated by the metal ion [32]. In MEROPS, metalloproteases of the M36 family, also known as fungalisins, are particularly noteworthy and are frequently found in basidiomycetes. The activity of these enzymes is inhibited by metal-chelating agents, such as EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid) and 1,10-phenanthroline [2,29].
The presence of different classes of proteases may be associated with the different morphological stages of edible mushrooms. In the study by Genier et al. (2015), for example, the authors suggested that the protease produced by P. ostreatus is a serine protease, based on the total inhibition of enzymatic activity observed in the presence of a specific inhibitor of this class [33]. On the other hand, Choi and Shin (1998), using the fruiting body as the enzyme source in the purification and characterization stage, identified a cysteine protease produced by P. ostreatus [34].
In genomic terms, the genome of the PC9_AS strain of P. ostreatus was annotated with approximately 11,875 genes, a number similar to that found in strains PC15 and PC9_JGI, which have 12,330 and 12,206 genes, respectively [35]. The annotation includes, among other elements, protease-encoding genes classified by the MEROPS database, suggesting considerable diversity of these enzymes in the genome. Transcriptomic studies reinforce this enzymatic diversity: Alfaro et al. (2016) identified at least 18 peptidase families, including serine, cysteine, aspartic, and metalloproteases, with emphasis on the S8 (serine proteases) and M36 (metalloproteases) families, which showed high expression under different culture conditions [36]. In addition, Faraco et al. (2005) characterized a new subfamily of serine proteases in P. ostreatus, describing the structure and function of an extracellular protease encoded by the posl gene, belonging to the S8 family, confirming its relevant role in the degradation of lignocellulosic substrates [37]. The review by Inácio et al. (2015) highlights that the genus Pleurotus possesses a variety of extracellular proteases, reflecting an adaptive strategy that contributes to its efficiency in decomposing organic matter, especially in environments rich in lignin and cellulose [4]. However, despite the identification of multiple peptidase families and the functional annotation of the genome, to date there are no studies that present, in a consolidated manner, the total number of protease-encoding genes in the genus Pleurotus, which remains a gap in the literature.
Table 1 presents the main biochemical properties of proteases produced by various Pleurotus species, including molecular weight, optimal pH and temperature, sensitivity to inhibitors, and response to metal ions. These parameters can vary significantly between and within species due to differences in the media used to induce enzyme production, which highlights the functional diversity of fungal proteases.

Table 1.
Biochemical properties of proteases from species of the genus Pleurotus.
When analyzing Table 1, the wide adaptability of Pleurotus spp. proteases to environmental conditions can be observed. These enzymes show significant variations in their optimal pH and temperature ranges [2,23]. In addition, the use of specific inhibitors for different classes of proteases, such as PMSF, pepstatin A, and EDTA, has revealed the presence of multiple classes of proteases in the same species [2,5]. The relevance of metal ions in enzymatic catalysis further reinforces the importance of detailed characterization of these enzymes, especially for their application in biotechnological processes involving different matrices and physicochemical conditions [5,12].
3. Physiological Aspects of Protease Production by Pleurotus spp.
The presence of different classes of proteases may be associated with the different morphological stages of the edible mushrooms. In the study by Genier et al. (2015), for example, the authors suggested that the protease produced by P. ostreatus is a serine pro-tease, based on the total inhibition of enzymatic activity observed in the presence of a specific inhibitor of this class [33]. On the other hand, Choi and Shin (1998), using the fruiting body as an enzyme source in the purification and characterization stage, identified a cysteine protease produced by P. ostreatus [34].
The age of the inoculum is a critical and easily controlled factor that directly impacts protease production yield [4]. Previous studies indicate that a young inoculum in an active growth phase results in significantly higher enzyme production [21]. The study by Martim et al. (2017) [21] using P. albidus found maximum activity (80.33 U/mL) with a five-day-old inoculum. Subsequently, the authors observed a gradual decrease in activity with increasing inoculum age, with reductions of 28.57%, 47.40%, and 77.39% in proteolytic activities for inocula aged 8, 12, and 20 days, respectively [21].
The cultivation time determines the peak production of both biomass and enzymes, varying significantly among Pleurotus spp. species (P. sajor-caju at 4 days, P. djamor at 5 days, and P. pulmonarius at 10 days) [4,45]. Exceeding the ideal time results in a decrease in enzymatic activity, possibly due to enzymatic degradation or toxin accumulation [7,24].
A key variable that controls both microbial growth and protease production for Pleurotus spp. is the C/N ratio in the substrate [45]. Adequate amounts of carbon, particularly from lignocellulosic sources such as wheat, stimulate the development of the fungus, as protease production is often inhibited by a lack of carbon and nitrogen, forcing the fungus to secrete these enzymes to obtain nutrients from the medium. On the other hand, an excess of nitrogen can be toxic and inhibit mycelial growth [7].
In addition to hydrolyzing proteins, Pleurotus spp. proteases play an important role in regulating other enzymes produced by the fungus. It has been demonstrated that the extracellular acid and neutral proteases produced by P. ostreatus modulate the activity of laccase isoforms by degrading enzymes such as POXA1b via the serine protease PoSl [2,18]. Conversely, when these proteases are inhibited by inhibitors such as PMSF and pepstatin A, laccase activity increases by a factor of 1.35 [2,37].
In contrast, alkaline proteases have been shown to have a low or even positive effect on P. ostreatus activity. This indicates that laccase is not sensitive to this type of enzyme and can therefore act as an activator of laccase activity [4,10]. The literature also highlights possible synergistic or competitive interactions between proteases and laccases influenced by substrate composition, revealing a highly adaptive enzyme system [2].
At the physiological level, these enzymes act in spore germination, sporulation, and substrate degradation, being fundamental for the survival of the fungus in lignocellulosic environments [2,4]. The co-expression of proteases and laccases produced by P. sapidus suggests the presence of integrated enzyme systems, although these are still poorly understood [11].
4. Production and Optimization of Pleurotus Proteases
The production of enzymes by mushrooms of the genus Pleurotus mainly uses two different strategies: solid-state fermentation (SSF) and submerged fermentation (SmF) [7,24]. These fungi are significant producers of various enzymes, among which proteases stand out for their extensive industrial applications. Therefore, selecting an appropriate cultivation method is essential to increase enzyme production and economic viability [9,19].
Solid-state fermentation (SSF) mimics the natural habitat of many fungi, cultivating microorganisms in isolated or low-moisture substrates [47]. Because it uses less water and energy and produces less harmful waste, this process is believed to be more cost-effective [48]. On the other hand, submerged fermentation (SmF) (Table 2) involves the cultivation of microorganisms in a liquid medium. Immersing the fungus provides greater control over culture parameters such as pH, temperature, oxygen levels, and humidity, in addition to simplifying the purification of extracellular enzymes and large-scale production [21,49,50].

Table 2.
Submerged fermentation (SmF) for protease production by Pleurotus spp. species.
The choice between SSF and SmF requires a strategic assessment of the various possibilities and production interests. On the one hand, SSF is commonly chosen because it generates a more concentrated enzyme product, which facilitates and reduces the costs of the extraction and purification phases, making it attractive in some biocatalysis processes [12]. However, despite higher initial costs, SmF offers better process control and greater scalability, essential factors for consistent industrial production. Both approaches are being actively investigated to maximize protein yield for the growing biotechnology market [2,20].
In general, the success of this species in bioprocesses is due to its ability to grow easily in tropical and subtropical regions. Pleurotus spp. species are especially suitable for SSF because they can thrive on a variety of lignocellulosic agricultural wastes and are mainly capable of mimicking their natural growth environment, as shown in Table 3 [52].

Table 3.
Lignocellulosic and agroindustrial residues used as alternative substrates for protease production by Pleurotus spp. species.
The proteases produced by fungi of the Pleurotus genus show highly competitive enzymatic activity, with values that often exceed those of other fungi in specific applications, although direct comparison requires methodological caution [24]. An example of this is the fibrinolytic activity of the P. eryngii species, which showed larger activity halos (63 mm2) than Agaricus blazei (35 mm2) and a specific activity of 226.47 U/mL, higher than that of P. ostreatus (71.5 U/mL) [6,17]. Even more significantly, the serine protease produced by P. sajor-caju showed a catalytic efficiency up to 8.48 times greater than that of Aspergillus oryzae [18]. On the other hand, in some cases it is possible to observe that genera that belong to the Ascomycota phylum excelled in proteolytic activity, such as Duddingtonia flagrans (56.34 U/mL) [53], Beauveria bassiana ESALQ PL63, and Metarhizium anisopliae ESALQ E9 (36 U/mg and 52 U/mg), respectively [54]. During the milk curdling process, the gross activity of P. albidus (153 U/mL) remained lower than that of Aspergillus sp. (240 U/mL) [5]. It is important to note that these values are dependent on the substrate and test conditions, but the consolidated evidence positions Pleurotus as a versatile and potent source of proteases with high biotechnological potential [4].
The efficiency of the Pleurotus genus in degrading lignocellulosic substrates is what underpins its use in circular economy applications, such as the production of proteases from agro-industrial waste [55,56]. As decomposition is necessary for its growth, the fungus actively seeks out these materials, which are rich in cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin [57]. These fungi are able to carry out this process because they produce a complex of ligninolytic and hydrolytic enzymes, including proteases, which act synergistically to catalyze the breakdown of vegetative cell wall polymers [52,58]. Thus, while the fungus performs its ecological function of recycling nutrients, it also produces high-value biotechnological enzymes, converting waste into a product [3,59].
For the enzymatic production process to transcend the laboratory scale and become an industrially viable process, it is important to rigorously optimize the cultivation parameters [51]. Variables such as pH, temperature, incubation time, agitation, and the nutritional composition of the substrate, particularly the carbon/nitrogen (C/N) ratio, interact synergistically to modulate the fungus’s metabolism and directly affect its production process. Precise control of these variables is what determines the commercial success of the bioprocess, maximizing productivity, reducing operating costs, and ensuring the acquisition of enzymes with the desired activity and stability [48].
The pH of the culture medium influences the activity, production, and stability of Pleurotus spp. proteases [23]. Each species and even each type of protease may have a distinct optimum pH (e.g., pH 6.5 for P. eryngii, pH 9.0 for P. ostreatus alkaline) [1,33]. The pH of the medium is also dynamic, being influenced by factors such as the C/N ratio, and its optimization is vital not only for production but also for specific applications, such as milk coagulation in cheese making [23].
5. Applications of Pleurotus Proteases
5.1. Nematicide Applications and Biological Control
In addition to their importance in human nutrition and biotechnological processes, mushrooms of the Pleurotus genus have attracted growing interest for their potential in the biological control of animal parasites such as Moniezia sp., T. solium, and Haemonchus spp. and plant parasites such as M. incognita [13,14,15,46]. The use of Pleurotus spp. as biocontrol agents represents a promising alternative to reduce dependence on chemical pesticides, contributing to more sustainable and environmentally friendly agricultural practices [11].
These fungal species act through different mechanisms to control parasites, one of which is the production of toxins, such as trans-2-decenedioic acid, capable of paralyzing target organisms. Once paralyzed, the parasites become entangled in the fungal hyphae and exhibit morphological deformities, such as a reduction in head volume [60,61].
Another important mechanism involves the secretion of extracellular proteases. The cuticle of nematodes, composed predominantly of proteins, functions as a protective barrier. Proteases produced by Pleurotus spp. act directly on this structure, catalyzing the hydrolysis of cuticular proteins, leading to its degradation and, consequently, to the death of the parasite [14] (Figure 1).
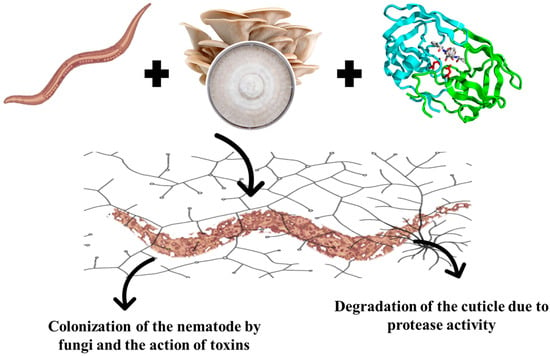
Figure 1.
Mechanism of nematophagy of edible mushroom.
In vitro studies have used free-living nematodes, such as Panagrellus sp., as models to evaluate the efficacy of compounds produced by Pleurotus spp. Genier et al. (2015) [33] evaluated the predatory activity of P. ostreatus (strain PLO 06) on Panagrellus sp. larvae, observing a 65.6% reduction in the number of larvae on the first day, 77.4% on the second day, and 95.2% on the third day. In the same study, in another trial, only the extracellular proteases from the same isolate were used, resulting in a 42% reduction in the number of larvae. This result indicates that the proteases produced by P. ostreatus (90 U/mL) are essential for the cuticle degradation process, enhancing the nematicidal effect [33].
The combined action of toxins that paralyze nematodes and hydrolytic enzymes contributes to the biocidal effect promoted by species of the genus Pleurotus. Plant parasitic nematodes cause great damage to agriculture worldwide, directly affecting crop yields and requiring more effective control strategies [14]. In this context, Sufiate et al. (2017) demonstrated that P. eryngii has nematicidal activity on eggs and juveniles of M. javanica, with a reduction of more than 50%, attributed to the production of proteases (32.74 U/mL) and chitinases (3.57 U/mL) [62].
Tests conducted with animal parasitic nematodes also demonstrate the nematicidal potential of Pleurotus spp. proteases. Silva et al. (2025) evaluated the effect of the cell-free crude extract, rich in P. djamor proteases (proteolytic activity of 7.5 U/mL and specific activity of 30 U/mL), on ruminant coprocultures and observed a 35% reduction in the number of Haemonchus spp. and Trichostrongylus spp. larvae, a result considered promising, especially as it was obtained in a fecal environment [46].
In addition to nematodes, in vitro tests on T. solium and Moniezia sp. eggs demonstrated the potential of P. djamor proteases (31.61 U/mL) in controlling these parasites. Silva et al. (2025) reported reductions of 33.44% in the hatching of T. solium eggs and 45.43% in Moniezia sp. eggs, highlighting the role of proteases in the degradation of eggshells [13].
The synergistic action between toxins and enzymes intensifies the observed effects. Trans-2-decenedioic acid, for example, initially acts by paralyzing the parasites, compromising their ability to respond and making them more susceptible to enzymatic action [20]. In turn, the degradation of the cuticle promoted by proteases facilitates toxin penetration, establishing an effective cycle of action. This synergy gives Pleurotus spp. a significant advantage as biocontrol agents [33].
The use of Pleurotus spp. or its cell-free crude extracts has several ecological advantages. However, further advances are still needed in the standardization of fermentation processes, purification of bioactive compounds, and more in-depth field studies to assess enzyme stability [11]. Pleurotus spp. and their proteases thus prove to be a promising biotechnological tool in controlling different parasites. The combined action of toxic metabolites and extracellular proteases confers high efficacy in the immobilization and degradation of these organisms. Case studies with different species of the genus [33,62] reinforce this potential, indicating the possibility of developing effective and sustainable bio-inputs for modern agriculture.
5.2. Food
Cheese production reflects the cultural and culinary traditions of each country and region. In 2019, the global cheese market was valued at approximately US$114.1 billion. Europe is the leading producer, accounting for nearly half of the total market value. In terms of consumption, the United States ranks first, followed by Germany and France. It is estimated that by the end of 2030, global cheese production will reach 27 million tons, underscoring the relevance of cheese as a key product in the food sector [63].
An essential step in cheese production is milk coagulation. This process occurs through the hydrolysis of peptide bonds in κ-casein, a protein present in milk, which leads to micelle destabilization and, consequently, the precipitation of casein [42]. One of the main methods used for inducing milk coagulation involves the action of hydrolytic enzymes, with chymosin (EC 3.4.23.4) being the most widely employed. This protease is considered the standard enzyme for milk coagulation in the production of various types of cheese due to characteristics such as high coagulating activity and specificity for cleaving the Phe105–Met106 peptide bond in κ-casein [23].
Renin, a complex of aspartic endopeptidases, is the main source of proteases used in cheese production. However, the use of raw materials of animal origin, such as bovine stomachs, has prompted the search for alternative sources of milk-coagulating enzymes. Species of the Pleurotus genus have a remarkable ability to adapt to different environments, since they are able to colonize and degrade a wide variety of lignocellulosic residues, in addition to growing in different temperature ranges and geographical regions [18,33]. It is one of the most widely distributed genera of edible mushrooms in the world, and its cultivation is facilitated by its low nutritional requirements [4,18]. In addition, they produce high levels of various enzymes, particularly proteases that are essential for the hydrolysis of milk proteins, making them promising alternatives as sources of enzymes for cheese production [18,21,42].
Studies have shown that one species of this genus, P. albidus, native to the Amazon, is capable of synthesizing milk-coagulating proteases in liquid culture media. Martim et al. (2021) [23] demonstrated that the proteases produced by P. albidus (DPUA 1692), when cultivated on açaí seeds supplemented with rice bran, were effective in the production of Minas frescal cheese. Fermentation time and temperature, as well as the concentration of certain metal ions such as calcium, influenced their coagulating activity [23].
A previous study by Martim et al. (2017) also reported that P. albidus (DPUA 1692) produces milk-coagulating enzymes with optimal activity at 60 °C and pH 6 [21]. Nolli et al. (2022) observed that the crude extract of P. albidus with an activity value of 153 U/mL was sufficient to coagulate milk [5].
In addition, another edible mushroom species that has shown the ability to produce milk-coagulating proteases is P. djamor. Research conducted by Silva et al. (2025) [9] reported the production of these enzymes by P. djamor PLO13 cultivated in wheat bran, identifying them as serine proteases. These enzymes were capable of coagulating both whole and skimmed pasteurized milk, even at room temperature and in the presence or absence of calcium. According to the authors, 1.875 mg/mL of protease-containing protein in the crude extract of P. djamor is required to coagulate milk at a temperature of 50 °C in 30 min for pasteurized whole milk and in 45 min for reconstituted skimmed milk [9].
5.3. Biomedical
According to an article published by Mensah et al. (2023), the global death toll from cardiovascular disease rose from 12.4 million in 1990 to 19.8 million in 2022, reflecting the growth and aging of the world’s population, as well as the influence of preventable risk factors of a metabolic, behavioral, and environmental nature [64]. In addition, although the available drugs are safe, they are still expensive [65]. In this context, there is evidence that enzymes produced by microorganisms, such as fungi, may be useful in controlling cardiovascular diseases due to their ability to produce fibrinolytic enzymes [24].
Fibrinolytic enzymes are proteases capable of promoting the catalysis of the degradation of the fibrin mesh, the main protein component present in blood clots. Among the species capable of producing fibrinolytic enzymes are mushrooms of the genus Pleurotus, such as P. ferulae, P. ostreatus, P. eryngii, and P. pulmonarius (Table 4). The fibrinolytic proteases produced by these fungi have been identified as SPPs, metalloproteases, serine proteases, and serine metalloproteases, showing therapeutic potential against thrombosis [4,17].

Table 4.
Studies of fungi of the genus Pleurotus that showed fibrinolytic enzyme production and activity.
5.4. Industrial
Keratinases are extracellular proteases capable of catalyzing the degradation of insoluble keratin-rich substrates such as feathers, hair, and nails, which are highly stable structures due to their high content of disulfide bonds, making them resistant to most common proteases [4,19,37]. These enzymes, generally classified as serine or metalloproteases, have been investigated in ligninolytic fungi such as Pleurotus spp., whose enzymatic diversity reveals applications in sustainable processes [2,4,10].
The products of keratin hydrolysis are mainly amino acids and smaller peptides. These compounds can be applied in various sectors, such as in the production of fertilizers, in the pharmaceutical and food industries, in environmental pollution control, and in leather processing, among others [10,43].
For example, in P. pulmonarius, a 16 kDa protease with proven keratinolytic activity on feathers, hair, and human keratin, both in vitro and in vivo, was identified, indicating its value in the bioconversion of keratinous waste [4,43]. Its effectiveness has also been demonstrated in lignocellulosic substrates, extending its scope beyond keratins [12]. In addition, enzymes from P. ostreatus and P. sapidus have been associated with the degradation of structural proteins in lignin-rich environments, which highlights the adaptive role of these proteases in various biotechnological systems [2,11,37].
The application of Pleurotus spp. proteases in protein hydrolysis has proven effective in increasing digestibility and generating bioactive peptides with functional potential. Alkaline proteases obtained from P. eryngii were applied in the pretreatment and promoted an increase of up to 7.54 times in the release of amino acids, with emphasis on the L isomers of lysine and arginine, in addition to the generation of up to 19,870 short peptides (<800 Da), which are highly bioavailable. This result is noteworthy because the amino acids mentioned are important in the context of human health and muscle recovery. Making their bioavailability more efficient contributes to their nutritional value [10].
Proteases from Pleurotus spp. are promising biocatalysts for industrial applications, given their specificity, efficiency, and biodegradability [4,19]. They are used in detergents, food, leather, silk, cosmetics, wastewater treatment, and metal recovery, such as silver. Their stability in alkaline pH favors their use as additives for detergents [37].
In this context, subtilisin PPP1 from P. pulmonarius has proven effective in removing organic stains, while the thermostable protease SPPS, isolated from P. sajor-caju, performs well under industrial conditions [18,66]. Serine proteases, PoSl, are widely researched and dominate the industrial enzyme market [67]. In addition, native strains such as P. albidus, from the Amazon, produce high levels of proteases (34.00 U/mL), highlighting the regional value of these species [21].
6. Conclusions and Future Prospects
The Pleurotus genus of fungi stands out as an important producer of proteases, whose biochemical properties offer broad potential for applications in areas such as medicine, agriculture, the food industry, and biotechnology. In addition to their functional diversity, these enzymes exhibit promising nematicidal potential and can be obtained from agro-industrial residual substrates, providing environmental and economic benefits by adding value to materials that would otherwise be discarded.
Despite recent advances, significant gaps remain in the understanding of the metabolic and molecular processes involved in the production of these enzymes, making it essential to explore new biotechnological strategies to enhance their efficiency and stability. Modern approaches, such as the immobilization of cells or enzymes on innovative supports, including nanoparticles, mesoporous materials, hydrogels, and structures derived from agro-industrial residues, have shown promising results by increasing catalytic activity, resistance to adverse conditions, and the potential for reuse in industrial processes.
In parallel, genetic engineering techniques offer pathways for obtaining more robust variants with higher yield and specificity, including in recombinant hosts, thereby expanding prospects for large-scale production. The growing demand for proteases with high stability, specificity, and sustainability creates a favorable environment for the development of innovative solutions based on Pleurotus spp.
Pleurotus proteases exhibit promising characteristics, including stability under alkaline conditions and high catalytic activity in challenging environments. These attributes enhance their potential for industrial, agricultural, and biomedical applications, highlighting their biotechnological value and reinforcing their potential as sustainable and competitive alternatives to existing market solutions.
Thus, the development of enzyme formulations derived from Pleurotus spp. for biochemical pest control, industrial processes, and high-precision biomedical applications represents a strategic pathway for innovation. Continuous investment in scientific research and technological development is essential to establish Pleurotus proteases as sustainable, innovative alternatives with economic and social relevance, promoting solutions aligned with current trends in biotechnology.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.T.d.S. and F.E.d.F.S.; Methodology, A.T.d.S. and A.T.d.S.; Investigation, A.T.d.S.; Writing—Original Draft Preparation, A.T.d.S., A.d.C.A., D.C.T.d.S., A.C.S., J.C.d.S.A., Y.L.L. and E.H.G.; Writing—Review & Editing, A.T.d.S., A.d.C.A., D.C.T.d.S., A.C.S., J.C.d.S.A., Y.L.L. and E.H.G.; Supervision., F.E.d.F.S. and L.A.-M.; Funding Acquisition, F.E.d.F.S. and L.A.-M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the Minas Gerais Research Funding Foundation (FAPEMIG) (RED-00161-23) and by the project CBF2023-2024-387 of SECIHTI, Mexico. National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) provided the grant PQ 306615/2025-8 for F.E.d.F. Soares.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicsable.
Data Availability Statement
No new data were created or analyzed in this study. Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank CAPES (Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel), FAPEMIG (Minas Gerais Research Funding Foundation) and National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) for all the financial support throughout the research.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bano, S.; Dahot, M.U.; Naqvi, S.H.A. Optimization of culture conditions for the production of protease by Pleurotus eryngii. Pak. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 13, 193–198. [Google Scholar]
- Cruz-Vázquez, A.; Tomasini, A.; Armas-Tizapantzi, A.; Marcial-Quino, J.; Montiel-González, A.M. Extracellular proteases and laccases produced by Pleurotus ostreatus PoB: The effects of proteases on laccase activity. Int. Microbiol. 2022, 25, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, G.L.; Chevreuil, L.R.; Vasconcelos, A.D.S.; Aguiar, L.V.B.; Pessoa, V.A.; Pereira, D.B.; Soares, L.B.N.; Gouvêa, P.R.S.; Campos, C.S. Destacando o potencial de um shimeji amazônico (Pleurotus ostreatus) por meio da comparação com linhagens comerciais: Crescimento micelial e produção de protease em diferentes meios de cultura. SSRN 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inácio, F.D.; Ferreira, R.O.; Araújo, C.A.; Brugnari, T.; Castoldi, R.; Peralta, R.M.; Souza, C.G. Proteases of wood rot fungi with emphasis on the genus Pleurotus. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 290161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolli, M.M.; Contato, A.G.; Brugnari, T.; Buzzo, A.J.D.R.; Aranha, G.M.; Inácio, F.D.; Souza, C.G.M. Evaluation of the milk clotting potential and characterization of proteases from Aspergillus sp. and Pleurotus albidus. Acta Sci. Technol. 2022, 44, e57766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessoa, V.A.; Soares, L.B.N.; Silva, G.L.; Vasconcelos, A.S.; Silva, J.F.; Fariña, J.I.; Chevreuil, L.R. Production of mycelial biomass, proteases and protease inhibitors by Ganoderma lucidum under different submerged fermentation conditions. Braz. J. Biol. 2023, 83, e270316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, A.K.P.; Pimenta, L.; Barbosa, E.E.P.; Batista, S.C.P.; Coelho, M.P.S.L.V.; Castillo, T.A.; Teixeira, M.F.S. Evaluation of tropical forest substrates for cultivation and production of proteases by Pleurotus djamor. Res. Soc. Dev. 2021, 10, e31810313385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naureen, U.; Kayani, A.; Akram, F.; Rasheed, A.; Saleem, M. Protease production and molecular characterization of a protease dipeptidyl aminopeptidase gene from different strains of Sordaria fimicola. Braz. J. Biol. 2022, 84, e255692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, M.D.C.; Costa, R.B.; do Nascimento, J.S.; Gomes, M.M.O.d.S.; Ferreira, A.N.; Grillo, L.A.M.; Pereira, H.J.V. Production of milk-coagulating protease by fungus Pleurotus djamor through solid state fermentation using wheat bran as the low-cost substrate. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2025, 55, 278–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Wan, J.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, R.; Wu, Y.; Bao, D.; Chen, H.; Zou, G.; et al. Enhancing digestibility and intestinal peptide release of Pleurotus eryngii protein: An enzymatic approach. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, B.; Majumdar, S.; Dutta, R.; Bhowal, J. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of Pleurotus ostreatus derived proteins through RSM and evaluation of nutritional and functional qualities of mushroom protein hydrolysates. Braz. J. Food Technol. 2022, 25, e2020186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contato, A.G.; Inácio, F.D.; Bueno, P.S.A.; Nolli, M.M.; Janeiro, V.; Peralta, R.M.; Souza, C.G.M. Pleurotus pulmonarius: A protease-producing white rot fungus in lignocellulosic residues. Int. Microbiol. 2023, 26, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.T.D.; Figueroa, L.B.P.; Souza, D.C.; Ferreira, D.P.; Santos, P.H.D.; Dias, E.S.; Braga, F.R.; Soares, F.E.F. Use of agricultural waste for optimization of protease production by Pleurotus djamor and evaluation of its anthelmintic activity. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2025, 56, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.T.D.; Ferreira, D.P.; de Souza, D.C.D.; de Araújo, J.C.; Silva, A.C.; Dias, E.S.; de Freitas Soares, F.E.D.F. Nematicidal activity of metabolites from Pleurotus djamor on Meloidogyne incognita under greenhouse conditions. Cad. Pedagógico 2024, 21, e9944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.T.D.; Figueroa, L.B.P.; de Souza, D.C.D.; Dias, E.S.; Albuquerque, L.B.; Moreira, T.F.; Soares, F.E.F. Evaluation of the nematicidal and enzymatic activity of Pleurotus djamor on Trichostrongylus spp. and Strongyloides papillosus. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2024, 34, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Xu, W.; Wang, F.; Fu, R.; Wei, F. Microbial proteases and their applications. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1236368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santana, R.D.S.; Mendes, F.D.S.; Paula da Silva, B.J.; Lima, E.S.; Nascimento, T.P.; Carneiro da Cunha, M.N.; Gomes, W.R. Recovery and partial purification of fibrinolytic protease from Pleurotus ostreatus and P. eryngii and cytotoxic and antioxidant activity of their extracts. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2024, 54, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benmrad, M.O.; Mechri, S.; Jaouadi, N.Z.; Elhoul, M.B.; Rekik, H.; Sayadi, S.; Bejar, S.; Kechaou, N.; Jaouadi, B. Purification and biochemical characterization of a novel thermostable protease from the oyster mushroom Pleurotus sajor-caju strain CTM10057 with industrial interest. BMC Biotechnol. 2019, 19, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, L.; Liu, Q.H.; Wang, H.X.; Ng, T.B. An alkaline protease from fresh fruiting bodies of the edible mushroom Pleurotus citrinopileatus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 75, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.T.D.; de Souza, D.C.D.; de Souza, S.A.; de Souza Alves, J.C.; Dias, E.S.; Aguilar-Marcelino, L.; Soares, F.E.F. Linking the protease activity to the nematicidal action of edible mushroom. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martim, S.R.; Silva, L.S.C.; de Souza, L.B.; do Carmo, E.J.; Alecrim, M.M.; de Vasconcellos, M.C.; Oliveira, I.M.A.; Teixeira, M.F.S. Pleurotus albidus: A new source of milk-clotting proteases. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 11, 660–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kuforiji, O.O.; Fasidi, I.O. Enzyme activities of Pleurotus tuber-regium (Fries) Singer, cultivated on selected agricultural wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 4275–4278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martim, S.R.; Silva, L.S.C.; Alecrim, M.M.; Teixeira, L.S.; Teixeira, M.F.S. Milk-clotting proteases from Pleurotus albidus: An innovative alternative for the production of Minas frescal cheese. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2021, 43, e57275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.S.; de Farias, V.G.; de Souza Sevalho, E.; Candido, K.; Carpio, K.C.R.; Gomes, W.R.; Carvalho, R.P. Cultivation conditions and biochemical characterization of the proteolytic enzymes with fibrinolytic action obtained from mushrooms in the last ten years. Res. Soc. Dev. 2022, 11, e530111436652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, E.; Bendre, A.D.; Gaikwad, S.M. Hydrolases: The most diverse class of enzymes. In Hydrolases; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J.; Thomas, P.D.; Huang, X.; Bateman, A.; Finn, R.D. The MEROPS database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors in 2017 and a comparison with peptidases in the PANTHER database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D624–D632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, W.S.; Park, S.S.; Kim, S.J.; Choi, D. Biochemical and enzymatic properties of a fibrinolytic enzyme from Pleurotus eryngii cultivated under solid-state conditions using corn cob. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6475–6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petraglia, T.; Latronico, T.; Fanigliulo, A.; Crescenzi, A.; Rossano, R. Hydrolytic enzymes in the secretome of the mushrooms P. eryngii and P. ostreatus: A comparison between the two species. Molecules 2025, 30, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Zheng, L.; Chen, L.; Tan, Q.; Shang, X.; Ma, A. Cloning, expression, and characterization of a milk-clotting aspartic protease gene (Po-Asp) from Pleurotus ostreatus. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 2119–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, N.; Matthew, M.A.; Yao, C. Roles of cysteine proteases in biology and pathogenesis of parasites. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.J. Purification and partial characterization of a fibrinolytic enzyme from the fruiting body of the medicinal and edible mushroom Pleurotus ferulae. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2017, 47, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joh, J.H.; Kim, B.G.; Kong, W.S.; Yoo, Y.B.; Kim, N.K.; Park, H.R.; Lee, C.S. Cloning and developmental expression of a metalloprotease cDNA from the metzincin family of the oyster mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 239, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Genier, H.L.A.; Soares, F.E.F.; Queiroz, J.H.; Gouveia, A.S.; Araújo, J.V.; Braga, F.R.; Kasuya, M.C.M. Activity of the fungus Pleurotus ostreatus and of its proteases on Panagrellus sp. larvae. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.S.; Shin, H.H. Purification and partial characterization of a fibrinolytic protease in Pleurotus ostreatus. Mycologia 1998, 90, 674–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-Y.; Vidal-Diez de Ulzurrun, G.; Schwarz, E.M.; Stajich, J.E.; Hsueh, Y.-P. Genome sequence of the oyster mushroom Pleurotus ostreatus strain PC9. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2021, 11, jkaa008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaro, M.; Castanera, R.; Lavín, J.L.; Grigoriev, I.V.; Oguiza, J.A.; Ramírez, L.; Pisabarro, A.G. Comparative and transcriptional analysis of the predicted secretome in the lignocellulose-degrading basidiomycete fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 821–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faraco, V.; Palmieri, G.; Festa, G.; Monti, M.; Sannia, G.; Giardina, P. A new subfamily of fungal subtilases: Structural and functional analysis of a Pleurotus ostreatus member. Microbiology 2005, 151, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ng, T.B. Pleureryn, a novel protease from fresh fruiting bodies of the edible mushroom Pleurotus eryngii. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 289, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmieri, G.; Bianco, C.; Cennamo, G.; Giardina, P.; Marino, G.; Monti, M.; Sannia, G. Purification, characterization, and functional role of a novel extracellular protease from Pleurotus ostreatus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 2754–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.H.; Kim, J.S.; Sapkota, K.; Park, S.E.; Choi, B.S.; Kim, S.; Kim, S.J. Purification, characterization, and cloning of fibrinolytic metalloprotease from Pleurotus ostreatus mycelia. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2007, 17, 1271–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Sakovich, V.V.; Zhernosekov, D.D.; Rebriev, A.V.; Korolova, D.S.; Marunych, R.Y.; Chernyshenko, V.O. Metalloprotease from the cultural liquid of Pleurotus ostreatus. Biotechnol. Acta 2019, 12, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Campos, C.; Dias, D.C.; Valle, J.S.D.; Colauto, N.B.; Linde, G.A. Produção de biomassa, proteases e exopolissacarídeos por Pleurotus ostreatus em cultivo líquido. Arq. Ciênc. Vet. Zool. UNIPAR 2010, 13. Available online: https://revistas.unipar.br/index.php/veterinaria/article/view/3372 (accessed on 24 September 2025).
- Inácio, F.D.; Martins, A.F.; Contato, A.G.; Brugnari, T.; Peralta, R.M.; Souza, C.G.M. Biodegradation of human keratin by protease from the basidiomycete Pleurotus pulmonarius. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 127, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.R.G.; Martim, S.R.; Alecrim, M.M.; Teixeira, M.F.S. Production and characterization of proteases from edible mushrooms cultivated on Amazonian tubers. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 16, 2160–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, G.; Gomathi, D.; Kalaiselvi, M.; Uma, C. A protease from the medicinal mushroom Pleurotus sajor-caju: Production, purification and partial characterization. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 2012, 2, S411–S417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.T.D.; Figueroa, L.B.P.; de Souza, D.C.D.; do Carmo Alves, A.; Facury, T.M.; Dias, E.S.; Braga, F.R.; de Freitas Soares, F.E.F. Proteolytic profile and nematicidal potential of proteases produced by Pleurotus djamor in coprocultures. Res. Vet. Sci. 2025, 184, 105528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, S.S.; Ray, R.C.; Das, U.; Panda, S.K.; Saranraj, P. Microorganisms in fermentation. In Essentials of Fermentation Technology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosa-Martínez, J.D.; Montañez, J.; Contreras-Esquivel, J.C.; Balagurusamy, N.; Gadi, S.K.; Morales-Oyervides, L. Agroindustrial and food processing residues valorization for solid-state fermentation processes: A case for optimizing the co-production of hydrolytic enzymes. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.L.; Zheng, X.Q.; Qian, P.Z.; Kopparapu, N.K.; Deng, Y.P.; Nonaka, M.; Harada, N. Purification and characterization of a novel fibrinolytic enzyme from culture supernatant of Pleurotus ostreatus. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benmrad, M.O.; Gargouri, W.; Mahfoudh, D.; Kriaa, M.; Jaouadi, B.; Kechaou, N. Response surface methodology optimization of milk-clotting protease produced by Pleurotus sajor-caju strain CTM 10057 and its technico-economical evaluation. Alger. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, E.E.P.; Pimenta, L.; Araújo, K.S.; Brito, A.K.P.; Batista, S.C.P.; Martim, S.R.; Teixeira, M.F.S. Production and partial characterization of a new fibrinolytic protease from salmon oyster mushroom from Amazonia. Braz. J. Biol. 2025, 85, e289933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergun, S.O.; Urek, R.O. Production of ligninolytic enzymes by solid state fermentation using Pleurotus ostreatus. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2017, 15, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, D.C.; Gomes, E.H.; Puentes, L.B.F. Duddingtonia flagrans and its crude proteolytic extract: Concomitant action in sheep coprocul-tures. Vet. Res. Commun. 2024, 48, 3423–3427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa, L.B.P.; Mamani, R.C.C.; Souza, D.C.; Alves, J.C.D.S.; Souza, S.A.; Ferreira, C.B.; Soares, F.E.F. Enzyme production by the entomopathogenic fungi Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae and their application in the control of nematodes (Haemonchus spp. and Meloidogyne incognita) in vitro. J. Nat. Pestic. Res. 2024, 8, 100077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainos, E.; Díaz-Godínez, G.; Loera, O.; Montiel-González, A.M.; Sánchez, C. Growth of Pleurotus ostreatus on wheat straw and wheat-grain-based media: C. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 812–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, D.; Wösten, H.A.B. Mushroom cultivation in the circular economy. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 102, 7795–7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, A.R.G.; Teixeira, M.F.S.; Kirsch, L.S.; Campelo, M.C.L.; Oliveira, I.M.A. Nutritional value and proteases of Lentinus citrinus produced by solid state fermentation of lignocellulosic waste from tropical region. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2016, 23, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elissishvili, V.; Kachishvili, E.; Penninckx, M.J. Profile of lignocellulolytic enzymes during the growth and fruiting of Pleurotus ostreatus in wheat straw and tree leaves. Microbiol. Minutes 2008, 55, 157–168. [Google Scholar]
- Mujtaba, M.; Fraceto, L.; Fazeli, M.; Mukherjee, S.; Savassa, S.M.; de Medeiros, G.A.; Vilaplana, F. Lignocellulosic biomass from agricultural waste to the circular economy: A review with focus on biofuels, biocomposites and bioplastics. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 400, 136815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degenkolb, T.; Vilcinskas, A. Metabolites from nematophagous fungi and nematicidal natural products from fungi as alternatives for biological control. Part II: Metabolites from nematophagous basidiomycetes and non-nematophagous fungi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 3813–3824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Arévalo, J.; Hernández-Velázquez, V.M.; Cardoso-Taketa, A.T.; González-Cortazar, M.; Sánchez-Vázquez, J.E.; Peña-Chora, G.; Aguilar-Marcelino, L. Hydroalcoholic extracts from Pleurotus ostreatus spent substrate with nematocidal activity against Nacobbus aberrans phytonematode and the non-target species Panagrellus redivivus. Plants 2024, 13, 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufiate, B.L.; Soares, F.E.F.; Moreira, S.S.; Gouveia, A.S.; Monteiro, T.S.A.; Freitas, L.G.; Queiroz, J.H. Nematicidal action of Pleurotus eryngii metabolites. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 12, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, S.J.P.; de Oliveira Barretto, L.C.; de Oliveira Júnior, A.M. Estudos prospectivos da produção de queijos nacionais e do seu potencial para a indicação geográfica. Obs. Econ. Latinoamericana 2023, 21, 11932–11954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensah, G.A.; Fuster, V.; Roth, G.A. A Heat-Healthy and Stroke-Free World: Using Data to Inform Global Action. JACC J. 2023, 82, 2343–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimenta, L.; Barbosa, E.E.P.; Araújo, K.S.; Brito, A.K.P.; Batista, S.C.P.; Martim, S.R.; Teixeira, M.F.S. Bioconversion of Amazonian vegetables by Pleurotus albidus: Production of fibrinolytic enzyme. Braz. J. Biol. 2025, 85, e290015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonhardt, R.H.; Krings, U.; Berger, R.G.; Linke, D. Heterologous production of the stain-solving peptidase PPP1 from Pleurotus pulmonarius. Bioproc. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 39, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, G.P.; Zhang, G.Q.; Wu, Y.Y.; Wang, H.X.; Ng, T.B. Purification and characterization of a novel serine protease from the mushroom Pholiota nameko. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 111, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).