Oxygenase Ppo-Regulated Moldy Volatiles Affect Growth, Pathogenicity and Patulin Biosynthesis of Penicillium expansum Through G Protein Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fungal Strains and Culture Conditions
2.2. Bioinformatic Analysis
2.3. Construction of Knockout and Complementary Strains
2.4. C8 MVOC Production
2.5. Observation of Colony Growth and Sporulation
2.6. Pathogenicity Assay
2.7. Patulin Production
2.8. RNA Isolation and RT-qPCR Analysis of Gene Expression
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Bioinformatic Analysis of PePpoA and PePpoC
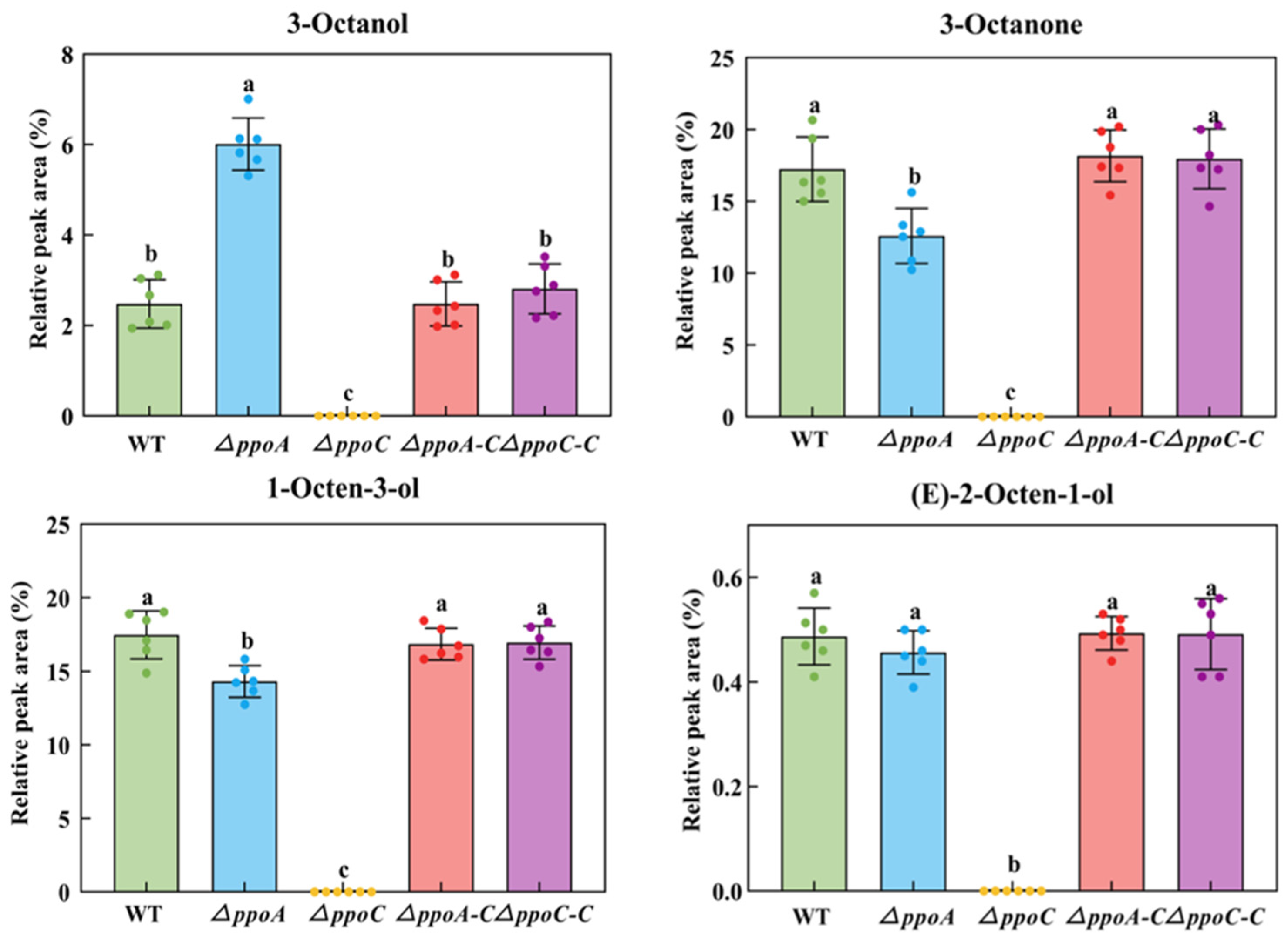
3.2. PePpoC Is Required for C8 MVOC Production in P. expansum
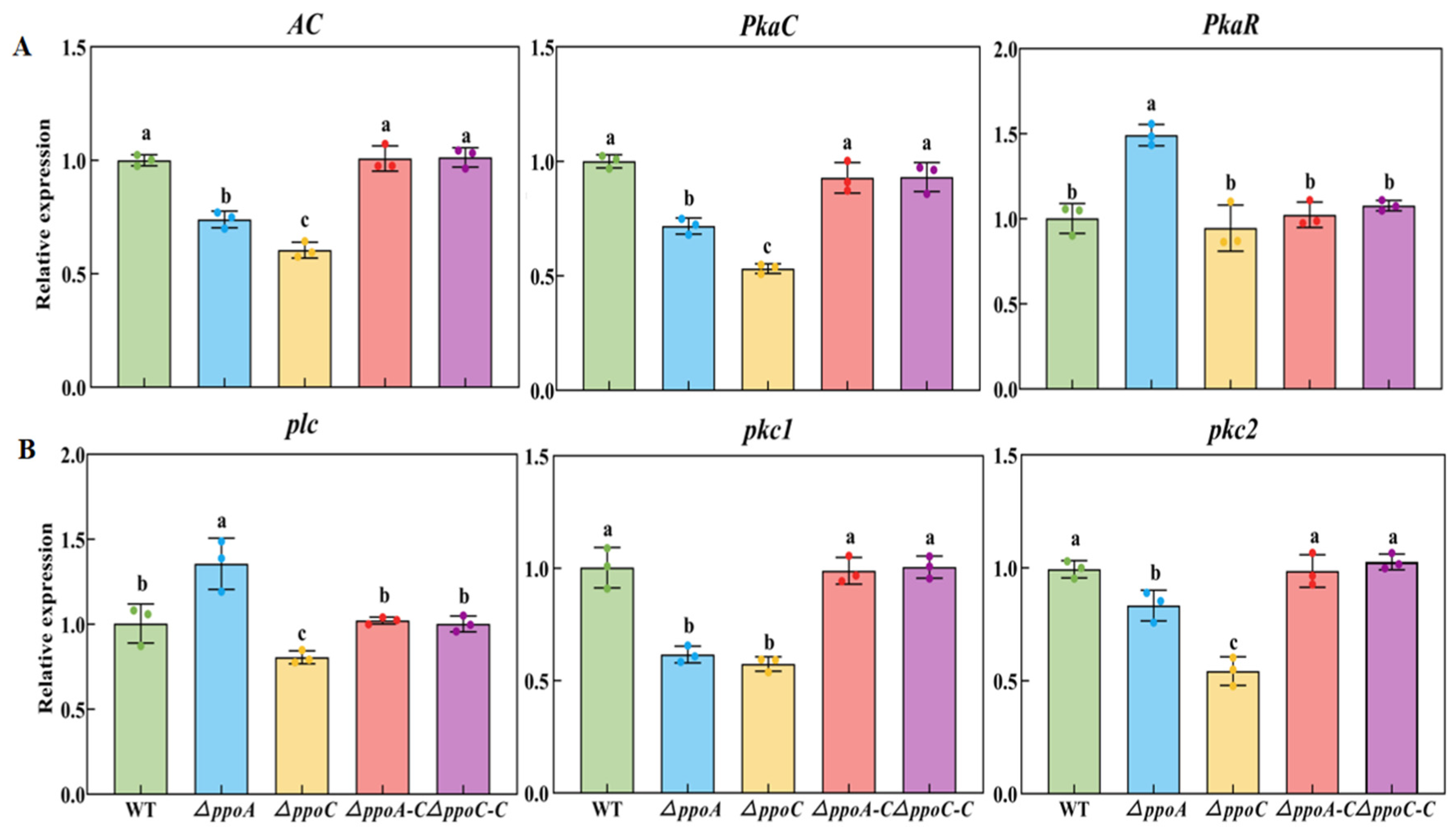
3.3. Loss of PePpoA and PePpoC Down-Regulated the Gene Expression Involved in cAMP-PKA and PLC/PKC Signaling Pathways in P. expansum
3.4. Loss of PePpoA or PePpoC Affects Colony Growth and Hyphal Morphology of P. expansum
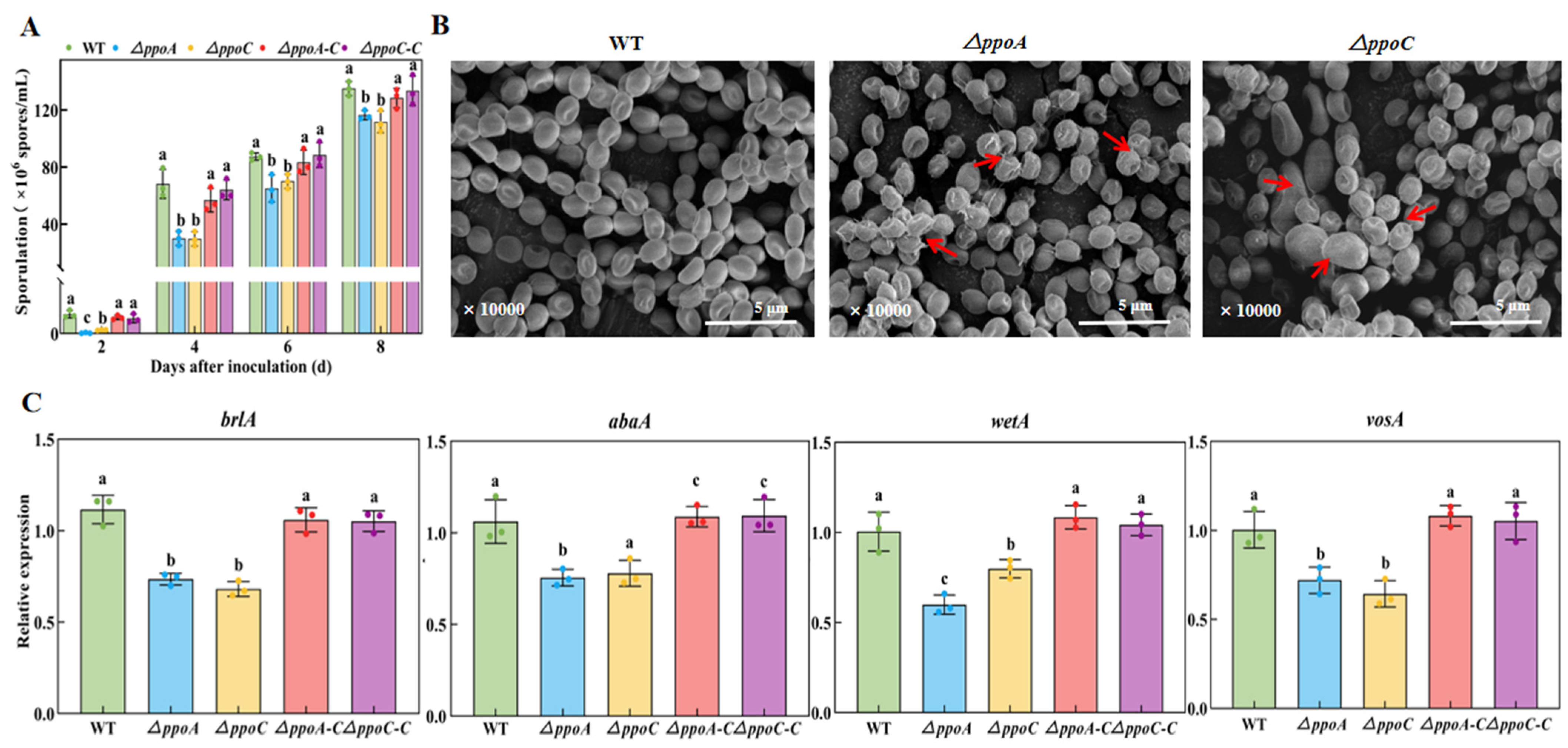
3.5. Loss of PePpoA or PePpoC Affects Sporulation and Spore Morphology of P. expansum
3.6. Loss of PePpoA or PePpoC Decreases Pathogenicity of P. expansum on Apple Fruit
3.7. Loss of PePpoA or PePpoC Inhibits Patulin Biosynthesis in P. expansum
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Inamdar, A.A.; Morath, S.; Bennett, J.W. Fungal volatile organic compounds: More than just a funky smell? Annu. Rev. Virol. 2020, 74, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Prusky, D.; Long, D.F.; Bi, Y.; Zhang, Y. Moldy odors in food-a review. Food Chem. 2024, 458, 140210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaddaoui, I.E.; Rangel, D.E.N.; Bennett, J.W. Fungal volatiles have physiological properties. Fungal Biol. 2023, 127, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Bi, Y.; Zong, Y.Y.; Li, Y.C.; Sionov, E.; Prusky, D. Characterization and sources of volatile organic compounds produced by postharvest pathogenic fungi colonized fruit. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 188, 111903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Son, S.Y.; Lee, C.H. Critical thresholds of 1-octen-3-ol shape inter-species Aspergillus interactions modulating the growth and secondary metabolism. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Chen, Y.; Tian, S.P. Mushroom alcohol controls gray mold caused by Botrytis cinerea in harvested fruit via activating the genes involved in jasmonic acid signaling pathway. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 186, 111843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.K.; Li, G.J.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Tian, S.P. 3-Octanol controls gray mold on postharvest fruit by inducing autophagy of Botrytis cinerea. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 205, 112525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennerman, K.K.; Scarsella, J.B.; Yin, G.H.; Hua, S.S.T.; Hartman, T.G.; Bennett, J.W. Volatile 1-octen-3-ol increases patulin production by Penicillium expansum on a patulin-suppressing medium. Mycotoxin Res. 2019, 35, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliw, E.H. Fatty acid dioxygenase-cytochrome P450 fusion enzymes of filamentous fungal pathogens. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2021, 157, 103623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodhun, F.; Feussner, I. Oxylipins in fungi. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 1047–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, R.; Watanabe, T.; Yano, S.; Mizutani, O.; Yamada, O.; Kasumi, T.; Ogihara, J. Aspergillus luchuensis fatty acid oxygenase ppoC is necessary for 1-octen-3-ol biosynthesis in rice koji. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 129, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, R.; Lacaze, I.; Faouder, P.L.; Bertrand-Michel, J.; Oger, C. Cyclooxygenases and lipoxygenases are used by the fungus Podospora anserina to repel nematodes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 2174–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Zarnowski, R.; Keller, N.P. The lipid body protein, PpoA, coordinates sexual and asexual sporulation in Aspergillus nidulans. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 11344–11353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Kowieski, T.M.; Zarnowski, R.; Keller, N.P. Three putative oxylipin biosynthetic genes integrate sexual and asexual development in Aspergillus nidulans. Microbiolology 2005, 151, 1809–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Keller, N.P. Oxylipins act as determinants of natural product biosynthesis and seed colonization in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 59, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagenais, T.R.; Chung, D.; Giles, S.S.; Hull, C.M.; Andes, D.; Keller, N.P. Defects in conidiophore development and conidium-macrophage interactions in a dioxygenase mutant of Aspergillus fumigatus. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 3214–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.H.; Scott, J.B.; Bhaheetharan, J.; Sharpee, W.C.; Milde, L.; Wilson, R.A.; Keller, N.P. Oxygenase coordination is required for morphological transition and the host-fungus interaction of Aspergillus flavus. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2009, 22, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsitsigiannis, D.I.; Keller, N.P. Oxylipins as developmental and host-fungal communication signals. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, C. The regulatory functions of oxylipins in fungi: A review. J. Basic Microbiol. 2023, 63, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.M.; Wang, X.X.; Gong, D.; Xu, X.B.; Tang, Y.B.; Prusky, P.; Zong, Y.Y.; Bi, Y. Gα3 regulates growth and development, stress response, patulin synthesis and pathogenicity of Penicillium expansum by mediating cAMP/PKA and PKC signaling. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 213, 112967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zong, Y.; Du, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, G.; Tian, S. Genomic characterization reveals insights into patulin biosynthesis and pathogenicity in Penicillium species. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2015, 28, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Zong, Y.Y.; Gong, D.; Yu, L.R.; Sionov, E.; Bi, Y.; Prusky, D. NADPH oxidase regulates the growth and pathogenicity of Penicillium expansum. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 696210–696221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Bi, Y.; Zong, Y.Y.; Li, Y.C.; Sionov, E.; Prusky, D. Penicillium expansum-induced release of branched-chain volatile compounds in apple fruit by increasing amino acids accumulation. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2021, 173, 111432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Zong, Y.; Zhang, X.; Gong, D.; Wang, B.; Prusky, D.; Sionov, E.; Xue, H.; Bi, Y. Erg4 is involved in ergosterol biosynthesis, conidiation and stress response in Penicillium expansum. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.M.; Zong, Y.Y.; Gong, D.; Zhang, F.; Yu, L.R.; Bi, Y.; Sionov, S.; Prusky, D. Small GTPase RacA is critical for spore growth, patulin accumulation, and virulence of Penicillium expansum. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2022, 191, 111964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notardonato, I.; Gianfagna, S.; Castoria, R.; Ianiri, G.; De Curtis, F.; Russo, M.V.; Avino, P. Critical review of the analytical methods for determining the mycotoxin patulin in food matrices. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2021, 40, 144–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Y.Y.; Li, B.Q.; Tian, S.P. Effects of carbon, nitrogen and ambient pH on patulin production and related gene expression in Penicillium expansum. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2015, 206, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, S.A.I.; de Felice, D.V.; Ianiri, G.; Pinedo-Rivilla, C.; De Curtis, F.; Castoria, R. Two rapid assays for screening of patulin biodegradation. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 11, 1387–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil-Serna, J.; García-Díaz, M.; González-Jaén, M.T.; Vázquez, C.; Patiño, B. Description of an orthologous cluster of ochratoxin A biosynthetic genes in Aspergillus and Penicillium species. A comparative analysis. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 268, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, K.; Murakami, T.; Kakumyan, P.; Keller, N.P.; Matsui, K. Formation of 1-octen-3-ol from Aspergillus flavus conidia is accelerated after disruption of cells independently of Ppo oxygenases, and is not a main cause of inhibition of germination. PeerJ 2014, 2, e395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Steffan, B.N.; Fischer, G.J.; Venkatesh, N.; Raffa, N.L.; Wettstein, M.A.; Bok, J.W.; Greco, C.; Zhao, C.; Berthier, E.; et al. Fungal oxylipins direct programmed developmental switches in filamentous fungi. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, R.; Watanabe, T.; Hayashi, R.; Isogai, A.; Yamada, O.; Ogihara, J. Awamori fermentation test and 1-octen-3-ol productivity analysis using fatty acid oxygenase disruptants of Aspergillus luchuensis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2020, 130, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wasternack, C.; Feussner, I. The oxylipin pathways: Biochemistry and function. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2018, 69, 363–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafon, A.; Seo, J.A.; Han, K.H.; Yu, J.H.; Enfert, C. The heterotrimeric G-protein GanB(alpha)-SfaD(beta)-GpgA(gamma) is a carbon source sensor involved in early cAMP-dependent germination in Aspergillus nidulans. Genetics 2005, 171, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Rico, R.O.; Fierro, F. Role of G-protein alpha sub-units in the morphogenic processes of filamentous Ascomycota fungi. Rev. Iberoam Micol. 2017, 34, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gresset, A.; Sondek, J.; Harden, T.K. The phospholipase C isozymes and their regulation. Subcell Biochem. 2012, 58, 61–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barman, A.; Gohain, D.; Bora, U.; Tamuli, R. Phospholipases play multiple cellular roles including growth, stress tolerance, sexual development, and virulence in fungi. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 209, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affeldt, K.J.; Brodhagen, M.; Keller, N.P. Aspergillus oxylipin signaling and quorum sensing pathways depend on g protein-coupled receptors. Toxins 2012, 4, 695–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; He, H.; Dong, Y.; Pan, H. Hyphae-specific genes HGC1, ALS3, HWP1, and ECE1 and relevant signaling pathways in Candida albicans. Mycopathologia 2013, 176, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, J.G.; Jackson, C.L. ARF family G proteins and their regulators: Roles in membrane transport, development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, X.M.; Gong, D.; Rong, Y.L.; Prusky, P.; Bi, Y.; Zong, Y.Y. ArfA and SarA small GTPases involved in growth, patulin biosynthesis and virulence of Penicillium expansum. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2023, 205, 112506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wright, S.J.; Krystofova, S.; Park, G.; Borkovich, K.A. Heterotrimeric G protein signaling in filamentous fungi. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 61, 423–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.; Xia, X.; Su, C.; Dong, W.; Xian, Y.; Wang, W.; Song, Y. Hepatotoxicity and genotoxicity of patulin in mice, and its modulation by green tea polyphenols administration. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 71, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, D.; Yan, T.; Wang, X.; Prusky, D.; Long, D.; Zhang, Y.; Bi, Y. Oxygenase Ppo-Regulated Moldy Volatiles Affect Growth, Pathogenicity and Patulin Biosynthesis of Penicillium expansum Through G Protein Signaling. J. Fungi 2024, 10, 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120827
Gong D, Yan T, Wang X, Prusky D, Long D, Zhang Y, Bi Y. Oxygenase Ppo-Regulated Moldy Volatiles Affect Growth, Pathogenicity and Patulin Biosynthesis of Penicillium expansum Through G Protein Signaling. Journal of Fungi. 2024; 10(12):827. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120827
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Di, Tingting Yan, Xuexue Wang, Dov Prusky, Danfeng Long, Ying Zhang, and Yang Bi. 2024. "Oxygenase Ppo-Regulated Moldy Volatiles Affect Growth, Pathogenicity and Patulin Biosynthesis of Penicillium expansum Through G Protein Signaling" Journal of Fungi 10, no. 12: 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120827
APA StyleGong, D., Yan, T., Wang, X., Prusky, D., Long, D., Zhang, Y., & Bi, Y. (2024). Oxygenase Ppo-Regulated Moldy Volatiles Affect Growth, Pathogenicity and Patulin Biosynthesis of Penicillium expansum Through G Protein Signaling. Journal of Fungi, 10(12), 827. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof10120827






