The Early Prediction of Patient Outcomes in Acute Heart Failure: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Setting
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Outcomes and Predictor Variables
2.4. Data Collection and Management
2.5. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
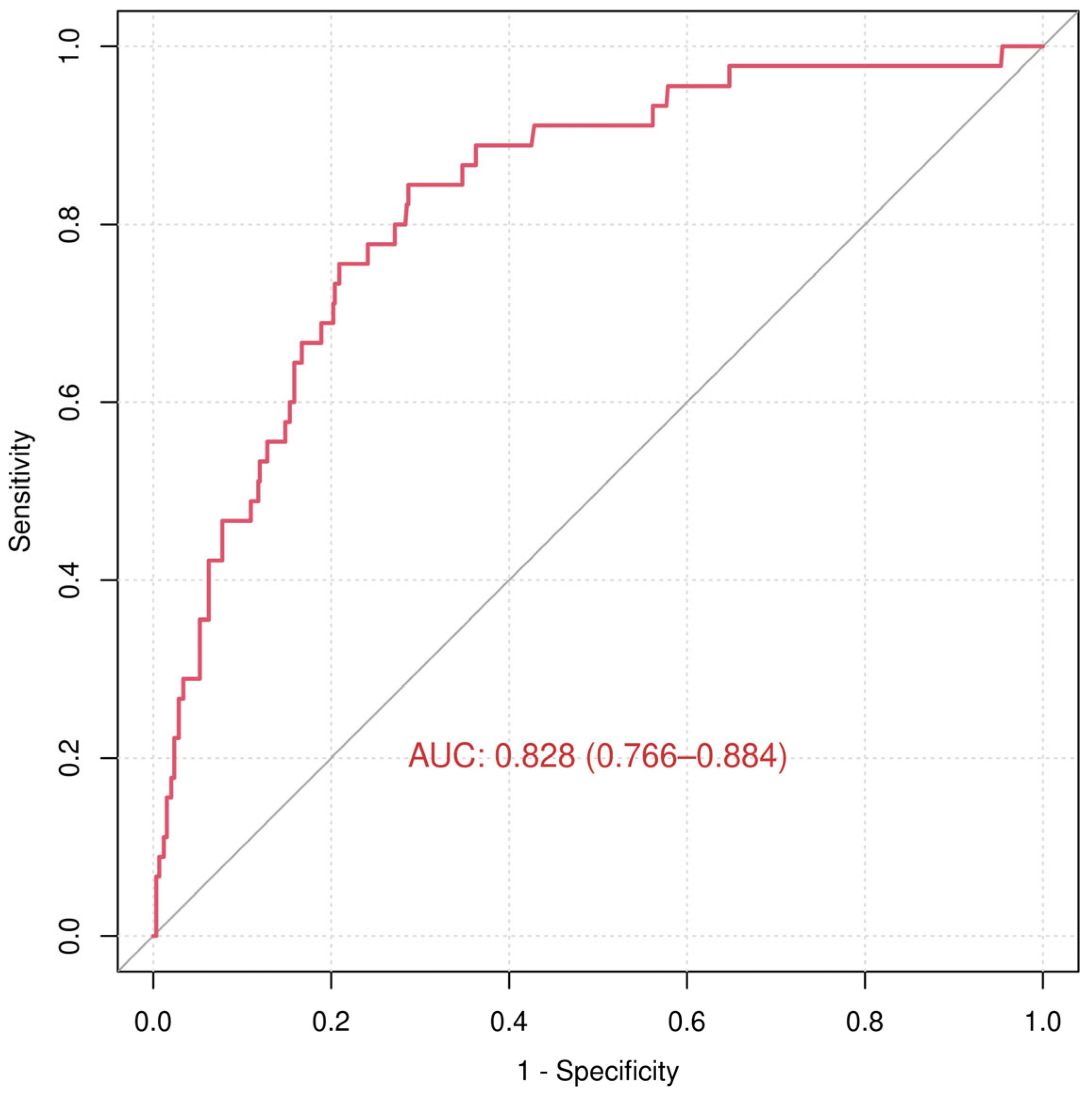
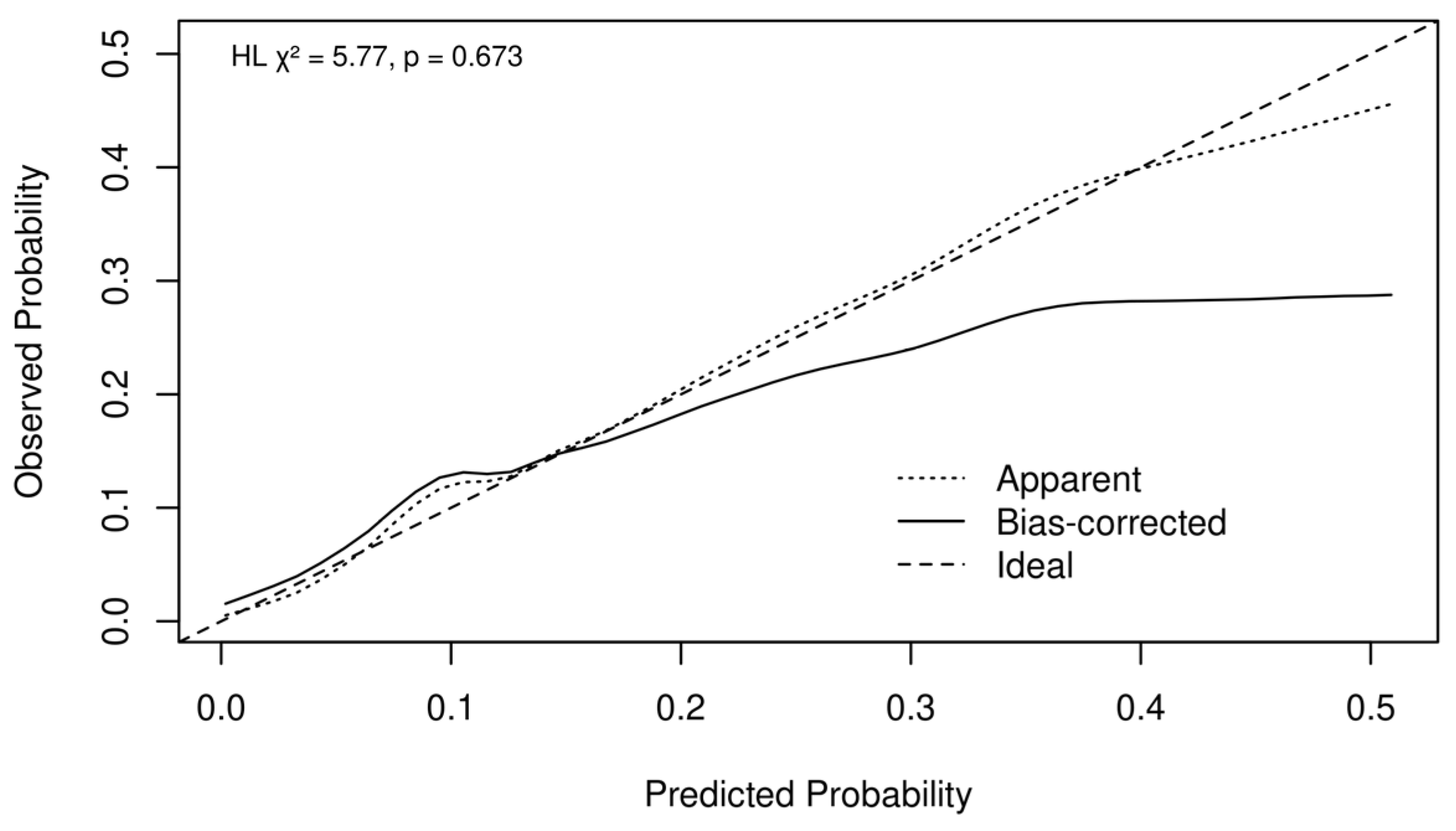
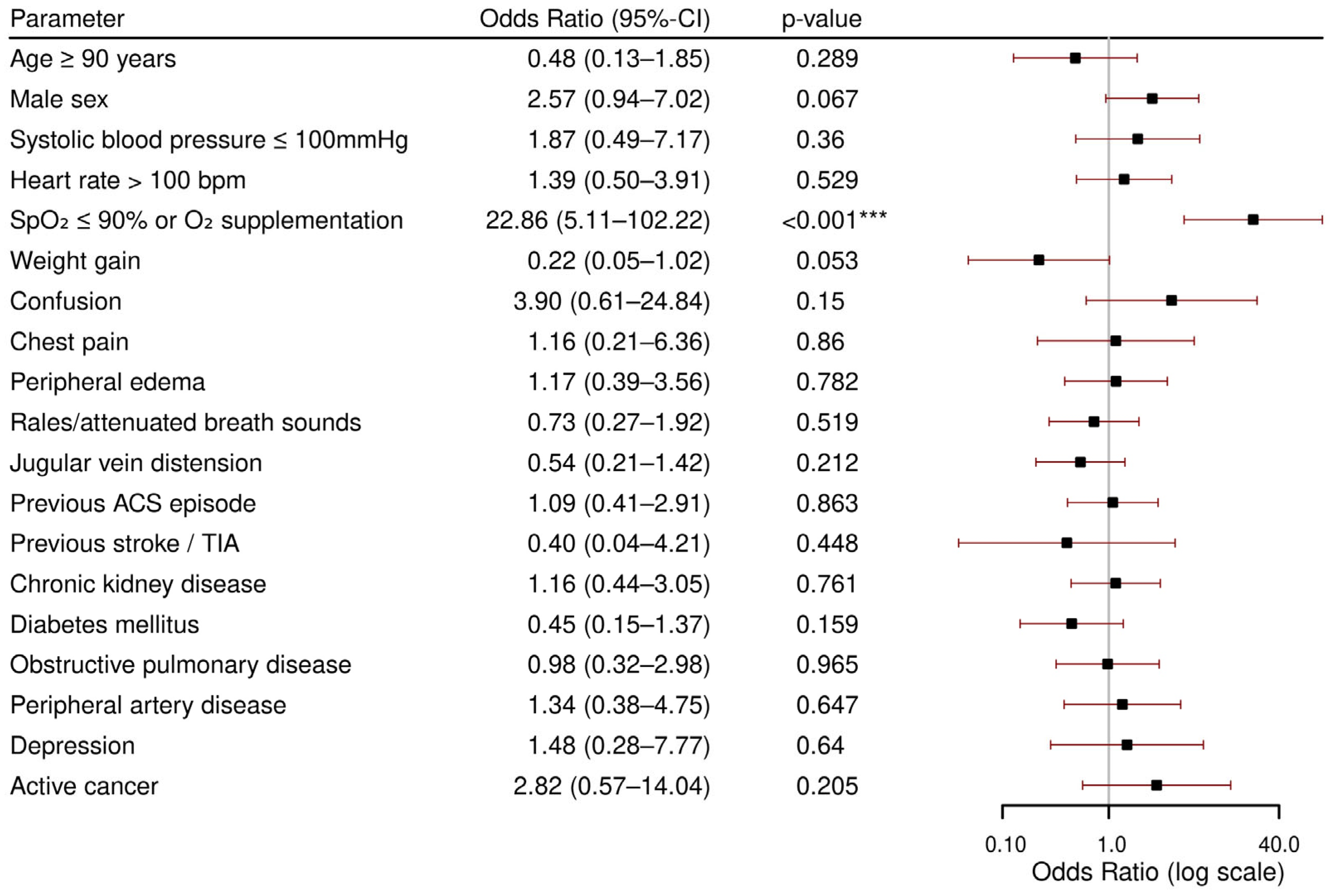
3.2. In-Hospital Death
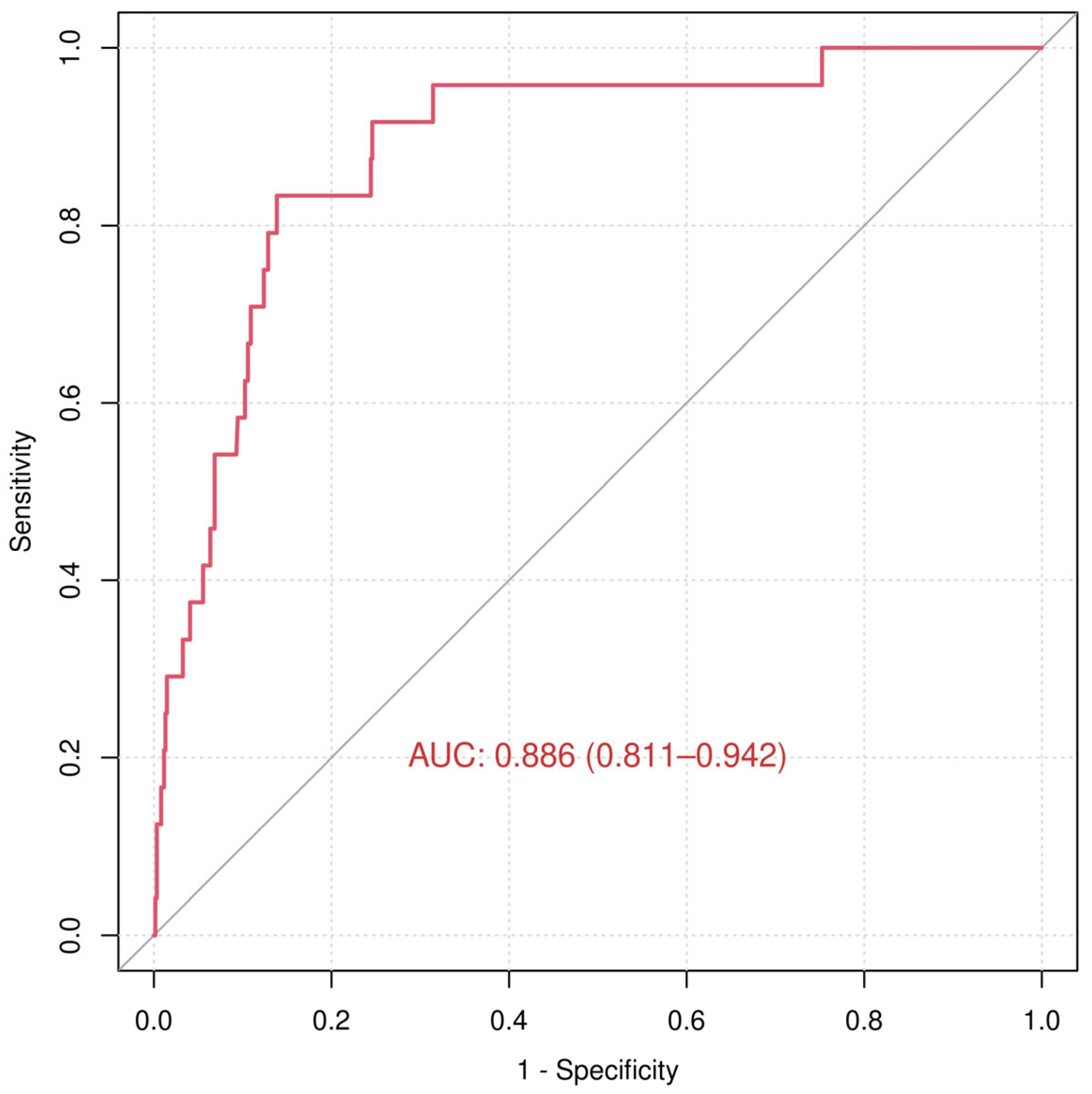
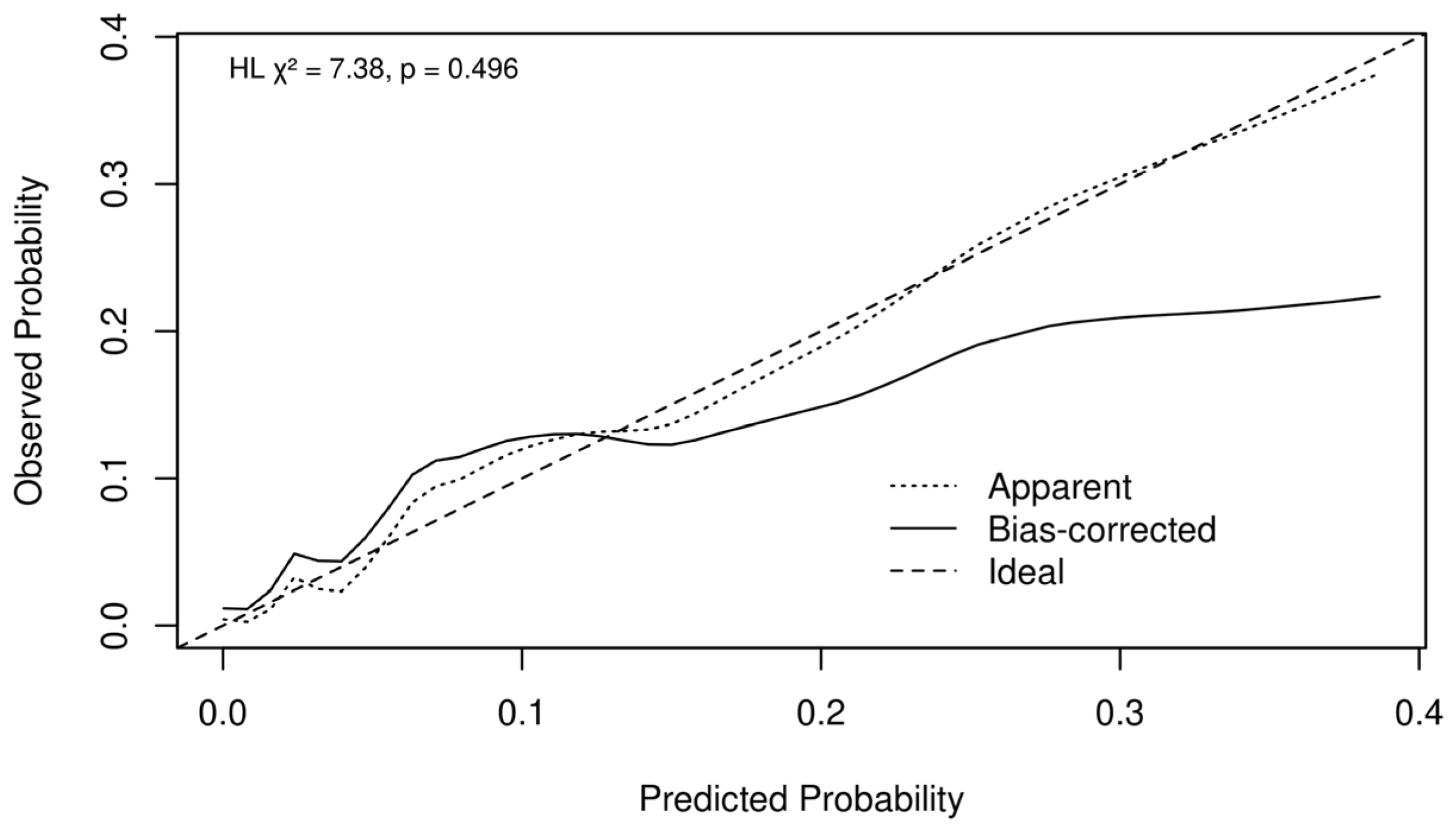
3.3. Admission to Intensive Care Unit (ICU)
3.4. Length of Hospital Stay (LOHS)
4. Discussion
- Low systolic blood pressure, low peripheral oxygen saturation or oxygen supplementation, peripheral edema at admission, and previous stroke or TIA were independently associated with in-hospital death.
- Patients with low peripheral oxygen saturation or oxygen supplementation at admission were more likely to experience more intensive care needs, including a higher likelihood of ICU admission and prolonged hospitalization. Additionally, patients with recent weight gain and CKD were prone to be hospitalized longer than the average patient.
4.1. Patient Characteristics
4.2. In-Hospital Death
4.3. ICU Admission
4.4. Length of Hospital Stay (LOHS)
4.5. Implications for Clinical Practice
4.6. Limitations and Strengths
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACS | Acute coronary syndrome |
| AHF | Acute heart failure |
| AUROC | Area under the receiver operating characteristic curves |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| bpm | Beats per minute |
| brpm | Breaths per minute |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| CRT | Cardiac resynchronization therapy |
| ED | Emergency department |
| EHMRG | Emergency Heart Failure Mortality Risk Grade |
| ICD | Implantable cardioverter defibrillator |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| IQR | Interquartile range |
| LOHS | Length of hospital stay |
| MEESSI-AHF | Multiple Estimation of Risk Based on the Emergency Department Spanish Score in Patients with AHF |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| TIA | Transient ischemic attack |
Appendix A
| ICD-10 Code | Diagnosis Description |
|---|---|
| I11.0 | Hypertensive heart disease with (congestive) heart failure |
| I13.0 | Hypertensive heart and kidney disease with (congestive) heart failure. |
| I50.0 | Congestive heart failure |
| I50.1 | Left ventricular failure |
| I50.2 | Systolic heart failure |
| I50.3 | Diastolic heart failure |
| I50.4 | Combined systolic and diastolic heart failure |
| I50.8 | Other heart failure |
| I50.9 | Unspecified heart failure |
| Parameter | VIF In-Hospital Death | VIF ICU Admission |
|---|---|---|
| Age ≥ 90 years | 1.14 | 1.07 |
| Male sex | 1.10 | 1.14 |
| Systolic blood pressure ≤ 100 mmHg | 1.16 | 1.18 |
| Heart rate > 100 bpm | 1.07 | 1.10 |
| SpO2 ≤ 90% or O2 supplementation | 1.07 | 1.04 |
| Weight gain | 1.14 | 1.05 |
| Confusion | 1.04 | 1.12 |
| Chest pain | 1.07 | 1.19 |
| Peripheral edema | 1.13 | 1.20 |
| Rales/attenuated breath sounds | 1.10 | 1.11 |
| Jugular vein distension | 1.10 | 1.09 |
| Previous ACS episode | 1.16 | 1.19 |
| Previous stroke/TIA | 1.11 | 1.15 |
| Chronic kidney disease | 1.09 | 1.17 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.18 | 1.13 |
| Obstructive pulmonary disease | 1.11 | 1.17 |
| Peripheral artery disease | 1.10 | 1.10 |
| Depression | 1.03 | 1.08 |
| Active cancer | 1.15 | 1.30 |
References
- Seferovic, P.M.; Vardas, P.; Jankowska, E.A.; Maggioni, A.P.; Timmis, A.; Milinkovic, I.; Polovina, M.; Gale, C.P.; Lund, L.H.; Lopatin, Y.; et al. The Heart Failure Association Atlas: Heart Failure Epidemiology and Management Statistics 2019. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2021, 23, 906–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutz, A.; Gut, L.; Ebrahimi, F.; Wagner, U.; Schuetz, P.; Mueller, B. Association of the Swiss Diagnosis-Related Group Reimbursement System With Length of Stay, Mortality, and Readmission Rates in Hospitalized Adult Patients. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e188332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Matteis, G.; Covino, M.; Burzo, M.L.; Della Polla, D.A.; Franceschi, F.; Mebazaa, A.; Gambassi, G. Clinical Characteristics and Predictors of In-Hospital Mortality among Older Patients with Acute Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinar, J.; Parenica, J.; Vitovec, J.; Widimsky, P.; Linhart, A.; Fedorco, M.; Malek, F.; Cihalik, C.; Spinarova, L.; Miklik, R.; et al. Baseline characteristics and hospital mortality in the Acute Heart Failure Database (AHEAD) Main registry. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parissis, J.T.; Mantziari, L.; Kaldoglou, N.; Ikonomidis, I.; Nikolaou, M.; Mebazaa, A.; Altenberger, J.; Delgado, J.; Vilas-Boas, F.; Paraskevaidis, I.; et al. Gender-related differences in patients with acute heart failure: Management and predictors of in-hospital mortality. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundaram, V.; Nagai, T.; Chiang, C.E.; Reddy, Y.N.V.; Chao, T.F.; Zakeri, R.; Bloom, C.; Nakai, M.; Nishimura, K.; Hung, C.L.; et al. Hospitalization for Heart Failure in the United States, UK, Taiwan, and Japan: An International Comparison of Administrative Health Records on 413,385 Individual Patients. J. Card. Fail. 2022, 28, 353–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atherton, J.J.; Hayward, C.S.; Wan Ahmad, W.A.; Kwok, B.; Jorge, J.; Hernandez, A.F.; Liang, L.; Kociol, R.D.; Krum, H.; Committee, A.I.-A.P.S.A. Patient characteristics from a regional multicenter database of acute decompensated heart failure in Asia Pacific (ADHERE International-Asia Pacific). J. Card. Fail. 2012, 18, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajayi, A.A.; Sofowora, G.G.; Ladipo, G.O. Explaining Heart Failure Hyper-mortality in Sub Saharan Africa: Global Genomic and Environmental Contribution Review. J. Natl. Med. Assoc. 2020, 112, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollenberg, S.M.; Warner Stevenson, L.; Ahmad, T.; Amin, V.J.; Bozkurt, B.; Butler, J.; Davis, L.L.; Drazner, M.H.; Kirkpatrick, J.N.; Peterson, P.N.; et al. 2019 ACC Expert Consensus Decision Pathway on Risk Assessment, Management, and Clinical Trajectory of Patients Hospitalized With Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology Solution Set Oversight Committee. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 1966–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebazaa, A.; Yilmaz, M.B.; Levy, P.; Ponikowski, P.; Peacock, W.F.; Laribi, S.; Ristic, A.D.; Lambrinou, E.; Masip, J.; Riley, J.P.; et al. Recommendations on pre-hospital & early hospital management of acute heart failure: A consensus paper from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology, the European Society of Emergency Medicine and the Society of Academic Emergency Medicine. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2015, 17, 544–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagyu, T.; Kumada, M.; Nakagawa, T. Novel risk stratification with time course assessment of in-hospital mortality in patients with acute heart failure. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parissis, J.T.; Ikonomidis, I.; Rafouli-Stergiou, P.; Mebazaa, A.; Delgado, J.; Farmakis, D.; Vilas-Boas, F.; Paraskevaidis, I.; Anastasiou-Nana, M.; Follath, F. Clinical characteristics and predictors of in-hospital mortality in acute heart failure with preserved left ventricular ejection fraction. Am. J. Cardiol. 2011, 107, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, Y.; Kunii, H.; Yoshihisa, A.; Takiguchi, M.; Shimizu, T.; Yamauchi, H.; Iwaya, S.; Owada, T.; Abe, S.; Sato, T.; et al. Impact of peripheral artery disease on prognosis in hospitalized heart failure patients. Circ. J. 2015, 79, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miro, O.; Conde-Martel, A.; Llorens, P.; Salamanca-Bautista, P.; Gil, V.; Gonzalez-Franco, A.; Jacob, J.; Casado, J.; Tost, J.; Montero-Perez-Barquero, M.; et al. The influence of comorbidities on the prognosis after an acute heart failure decompensation and differences according to ejection fraction: Results from the EAHFE and RICA registries. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2023, 111, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chioncel, O.; Mebazaa, A.; Harjola, V.P.; Coats, A.J.; Piepoli, M.F.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Laroche, C.; Seferovic, P.M.; Anker, S.D.; Ferrari, R.; et al. Clinical phenotypes and outcome of patients hospitalized for acute heart failure: The ESC Heart Failure Long-Term Registry. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 1242–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chioncel, O.; Benson, L.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Anker, S.D.; Coats, A.J.S.; Filippatos, G.; McDonagh, T.; Margineanu, C.; Mebazaa, A.; Metra, M.; et al. Comprehensive characterization of non-cardiac comorbidities in acute heart failure: An analysis of ESC-HFA EURObservational Research Programme Heart Failure Long-Term Registry. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2023, 30, 1346–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castello, L.M.; Molinari, L.; Renghi, A.; Peruzzi, E.; Capponi, A.; Avanzi, G.C.; Pirisi, M. Acute decompensated heart failure in the emergency department: Identification of early predictors of outcome. Medicine 2017, 96, e7401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.S.; Lee, J.S.; Schull, M.J.; Borgundvaag, B.; Edmonds, M.L.; Ivankovic, M.; McLeod, S.L.; Dreyer, J.F.; Sabbah, S.; Levy, P.D.; et al. Prospective Validation of the Emergency Heart Failure Mortality Risk Grade for Acute Heart Failure. Circulation 2019, 139, 1146–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, B.; Keim, S.M.; Gottlieb, M.; Collins, S.P. What are the Data for Current Prognostic Tools Used to Determine the Risk of Short-Term Adverse Events in Patients with Acute Heart Failure? J. Emerg. Med. 2023, 65, e600–e613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, Y.; Kohsaka, S.; Abe, T.; Nagai, T.; Goda, A.; Nishihata, Y.; Nagatomo, Y.; Saji, M.; Toyosaki, Y.; Takei, M.; et al. Derivation and Validation of Clinical Prediction Models for Rapid Risk Stratification for Time-Sensitive Management for Acute Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sax, D.R.; Mark, D.G.; Huang, J.; Sofrygin, O.; Rana, J.S.; Collins, S.P.; Storrow, A.B.; Liu, D.; Reed, M.E. Use of Machine Learning to Develop a Risk-Stratification Tool for Emergency Department Patients With Acute Heart Failure. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2021, 77, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miro, O.; Rossello, X.; Gil, V.; Martin-Sanchez, F.J.; Llorens, P.; Herrero-Puente, P.; Jacob, J.; Bueno, H.; Pocock, S.J.; Group, I.-S.R. Predicting 30-Day Mortality for Patients With Acute Heart Failure in the Emergency Department: A Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2017, 167, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, M.J.; Collins, S.P.; Liu, D.; Froehle, C.M. Preventable delays to intravenous furosemide administration in the emergency department prolong hospitalization for patients with acute heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 269, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, P.A.; Taylor, R.; Thielke, R.; Payne, J.; Gonzalez, N.; Conde, J.G. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—A metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mucherino, A.; Papajorgji, P.J.; Pardalos, P.M.; Mucherino, A.; Papajorgji, P.J.; Pardalos, P.M. K-nearest neighbor classification. In Data Mining in Agriculture; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 83–106. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. 2021. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 7 January 2025).
- Ponikowski, P.; Voors, A.A.; Anker, S.D.; Bueno, H.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Coats, A.J.S.; Falk, V.; Gonzalez-Juanatey, J.R.; Harjola, V.P.; Jankowska, E.A.; et al. 2016 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: The Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC)Developed with the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 2129–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvao, M.; Kalman, J.; DeMarco, T.; Fonarow, G.C.; Galvin, C.; Ghali, J.K.; Moskowitz, R.M. Gender differences in in-hospital management and outcomes in patients with decompensated heart failure: Analysis from the Acute Decompensated Heart Failure National Registry (ADHERE). J. Card. Fail. 2006, 12, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, Y.; Tajiri, K.; Nagata, H.; Kojima, M. Determinants of In-Hospital Mortality in Elderly Patients Aged 80 Years or above with Acute Heart Failure: A Retrospective Cohort Study at a Single Rural Hospital. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebazaa, A.; Erhardt, L. Levosimendan: A new dual-action drug in the treatment of acute heart failure. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2003, 57, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milo-Cotter, O.; Cotter, G.; Kaluski, E.; Rund, M.M.; Felker, G.M.; Adams, K.F.; O’Connor, C.M.; Weatherley, B.D. Rapid clinical assessment of patients with acute heart failure: First blood pressure and oxygen saturation--is that all we need? Cardiology 2009, 114, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossello, X.; Bueno, H.; Gil, V.; Jacob, J.; Martin-Sanchez, F.J.; Llorens, P.; Herrero Puente, P.; Alquezar-Arbe, A.; Espinosa, B.; Raposeiras-Roubin, S.; et al. Synergistic Impact of Systolic Blood Pressure and Perfusion Status on Mortality in Acute Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2021, 14, e007347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, F.L.; Pugliese, N.R.; Ameri, P.; Attanasio, U.; Badagliacca, R.; Correale, M.; Mercurio, V.; Tocchetti, C.G.; Agostoni, P.; Palazzuoli, A.; et al. Right ventricular failure in left heart disease: From pathophysiology to clinical manifestations and prognosis. Heart Fail. Rev. 2023, 28, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoaib, A.; Mamas, M.A.; Ahmad, Q.S.; McDonagh, T.M.; Hardman, S.M.C.; Rashid, M.; Butler, R.; Duckett, S.; Satchithananda, D.; Nolan, J.; et al. Characteristics and outcome of acute heart failure patients according to the severity of peripheral oedema. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 285, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, G.E.; Kaboli, P.J.; Barnett, M.J.; Sirio, C.A. Age and the risk of in-hospital death: Insights from a multihospital study of intensive care patients. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2002, 50, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luthi-Corridori, G.; Boesing, M.; Roth, A.; Giezendanner, S.; Leuppi-Taegtmeyer, A.B.; Schuetz, P.; Leuppi, J.D. Predictors of Length of Stay, Rehospitalization and Mortality in Community-Acquired Pneumonia Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Targher, G.; Dauriz, M.; Laroche, C.; Temporelli, P.L.; Hassanein, M.; Seferovic, P.M.; Drozdz, J.; Ferrari, R.; Anker, S.; Coats, A.; et al. In-hospital and 1-year mortality associated with diabetes in patients with acute heart failure: Results from the ESC-HFA Heart Failure Long-Term Registry. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunlay, S.M.; Givertz, M.M.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Chan, M.; Desai, A.S.; Deswal, A.; Dickson, V.V.; Kosiborod, M.N.; Lekavich, C.L.; et al. Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association and the Heart Failure Society of America: This statement does not represent an update of the 2017 ACC/AHA/HFSA heart failure guideline update. Circulation 2019, 140, e294–e324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wussler, D.; Kozhuharov, N.; Sabti, Z.; Walter, J.; Strebel, I.; Scholl, L.; Miro, O.; Rossello, X.; Martin-Sanchez, F.J.; Pocock, S.J.; et al. External Validation of the MEESSI Acute Heart Failure Risk Score: A Cohort Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 170, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miro, O.; Llorens, P.; Rossello, X.; Gil, V.; Sanchez, C.; Jacob, J.; Herrero-Puente, P.; Lopez-Diez, M.P.; Llauger, L.; Romero, R.; et al. Impact of the MEESSI-AHF tool to guide disposition decision-making in patients with acute heart failure in the emergency department: A before-and-after study. Emerg. Med. J. 2023, 41, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miro, O.; Rossello, X.; Gil, V.; Martin-Sanchez, F.J.; Llorens, P.; Herrero-Puente, P.; Jacob, J.; Pinera, P.; Mojarro, E.M.; Lucas-Imbernon, F.J.; et al. Analysis of How Emergency Physicians’ Decisions to Hospitalize or Discharge Patients With Acute Heart Failure Match the Clinical Risk Categories of the MEESSI-AHF Scale. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2019, 74, 204–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American College of Emergency Physicians Clinical Policies Subcommittee (Writing Committee) on Acute Heart Failure Syndromes. Clinical Policy: Critical Issues in the Evaluation and Management of Adult Patients Presenting to the Emergency Department With Acute Heart Failure Syndromes: Approved by ACEP Board of Directors, June 23, 2022. Ann. Emerg. Med. 2022, 80, e31–e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.M.; Madsen, B.E.; Kopecky, S.L.; Jenson, C.E.; Loth, A.R.; Mullan, A.F.; Clements, C.M.; Lin, G. Retrospective validation of acute heart failure risk stratification in the emergency department. Heart Lung 2023, 57, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsetti, L.; Zaccone, V.; Guerrieri, E.; Perrotta, G.; Diblasi, I.; Giuliani, L.; Palma, L.E.G.; Viticchi, G.; Fioranelli, A.; Moroncini, G.; et al. Implementation of EHMRG Risk Model in an Italian Population of Elderly Patients with Acute Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Bohm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Celutkiene, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure: Developed by the Task Force for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). With the special contribution of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the ESC. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 4–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.P.; Verouhis, D.; Gamble, G.; Swedberg, K.; Sharpe, N.; Doughty, R.N. Factors influencing the length of hospital stay of patients with heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2003, 5, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minhas, A.M.K.; Bhopalwala, H.M.; Dewaswala, N.; Ijaz, S.H.; Khan, M.S.; Khan, M.Z.; Dani, S.S.; Warraich, H.J.; Greene, S.J.; Edmonston, D.L.; et al. Association of Chronic Renal Insufficiency with Inhospital Outcomes in Primary Heart Failure Hospitalizations (Insights from the National Inpatient Sample 2004 to 2018). Am. J. Cardiol. 2023, 202, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forman, D.E.; Butler, J.; Wang, Y.; Abraham, W.T.; O’Connor, C.M.; Gottlieb, S.S.; Loh, E.; Massie, B.M.; Rich, M.W.; Stevenson, L.W.; et al. Incidence, predictors at admission, and impact of worsening renal function among patients hospitalized with heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Rosano, G.; Herzog, C.A. Management of Heart Failure Patient with CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2021, 16, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2022, 145, e895–e1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Overall (n = 638) | Missing (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Demographics | Age (years), median [IQR] (range) | 84 [77, 89] (45–101) | - |
| Male sex, n (%) | 320 (50.2) | - | |
| Vital signs at admission | Systolic BP (mmHg), median [IQR] | 135 [118, 153] | 2.0 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg), median [IQR] | 79 [69, 90] | 2.0 | |
| Heart rate (bpm), median [IQR] | 84 [70, 100] | 1.6 | |
| Peripheral O2 saturation %, median [IQR] | 94 [91, 96] | 4.2 | |
| Respiratory rate ≥ 22 brpm, n (%) | 215 (41.8) | 19.4 | |
| O2 supplementation, n (%) | 168 (26.3) | - | |
| Fever (body temperature ≥ 38 °C) | 13 (2.2) | 7.2 | |
| Symptoms at admission, | Dyspnea | 556 (87.1) | - |
| n (%) | Weight gain | 194 (30.4) | - |
| Fatigue | 128 (20.1) | - | |
| Chest pain | 65 (10.2) | - | |
| Confusion | 15 (2.4) | - | |
| Nycturia | 21 (3.3) | - | |
| Nocturnal cough | 16 (2.5) | - | |
| Clinical examination, | Peripheral edema | 486 (76.2) | - |
| n (%) | Pulmonary rales | 351 (55.0) | - |
| Jugular vein distension | 301 (47.2) | - | |
| Hepato-jugular reflux | 41 (6.4) | - | |
| Attenuated breath sounds | 126 (19.7) | - | |
| Cardiac medical history, | Previously diagnosed heart failure | 505 (79.2) | - |
| n (%) | GDMT for heart failure 1 (n = 505) | 378 (74.9) | - |
| Previous hospitalization for AHF 2 (n = 505) | 128 (25.3) | - | |
| Previous ACS episode | 217 (34.0) | - | |
| Pacemaker or ICD | 87 (13.6) | - | |
| Previous CRT | 6 (0.9) | - | |
| Previous valvular surgery | 38 (6.0) | - | |
| Mechanical circulatory support (IABP, VAD) | 0 | - | |
| Comorbidities, | Arterial hypertension | 487 (76.3) | - |
| n (%) | Valvular heart disease | 288 (45.1) | - |
| Coronary artery disease | 238 (37.3) | - | |
| Atrial fibrillation | 374 (58.6) | - | |
| Chronic kidney disease | 370 (58.0) | - | |
| Anemia | 207 (32.4) | - | |
| Diabetes mellitus | 196 (30.7) | - | |
| Obstructive pulmonary disease | 107 (16.8) | - | |
| Peripheral artery disease | 77 (12.1) | - | |
| Previous stroke or TIA | 54 (8.5) | - | |
| Depression | 35 (5.5) | ||
| Active cancer | 44 (6.9) | - | |
| Obesity | 106 (29.9) | 44.4 |
| Outcome | |
|---|---|
| In-hospital death, n (%) | 45 (7.1) |
| Admission to intensive care unit, n (%) | 24 (3.8) |
| Length of hospital stay (nights), median [IQR] 1 | 8 [5, 12] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boesing, M.; Suchina, J.; Lüthi-Corridori, G.; Jaun, F.; Brändle, M.; Leuppi, J.D. The Early Prediction of Patient Outcomes in Acute Heart Failure: A Retrospective Study. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12070236
Boesing M, Suchina J, Lüthi-Corridori G, Jaun F, Brändle M, Leuppi JD. The Early Prediction of Patient Outcomes in Acute Heart Failure: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(7):236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12070236
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoesing, Maria, Justas Suchina, Giorgia Lüthi-Corridori, Fabienne Jaun, Michael Brändle, and Jörg D. Leuppi. 2025. "The Early Prediction of Patient Outcomes in Acute Heart Failure: A Retrospective Study" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 7: 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12070236
APA StyleBoesing, M., Suchina, J., Lüthi-Corridori, G., Jaun, F., Brändle, M., & Leuppi, J. D. (2025). The Early Prediction of Patient Outcomes in Acute Heart Failure: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(7), 236. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12070236





