Wearable Devices for Quantifying Atrial Fibrillation Burden: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
2.4. Risk of Bias
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quality Assessment
3.2. Meta-Analysis Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Clinical Perspectives
- Wearable devices, at least theoretically, could be used in a free-living setting to provide useful information regarding AF burden;
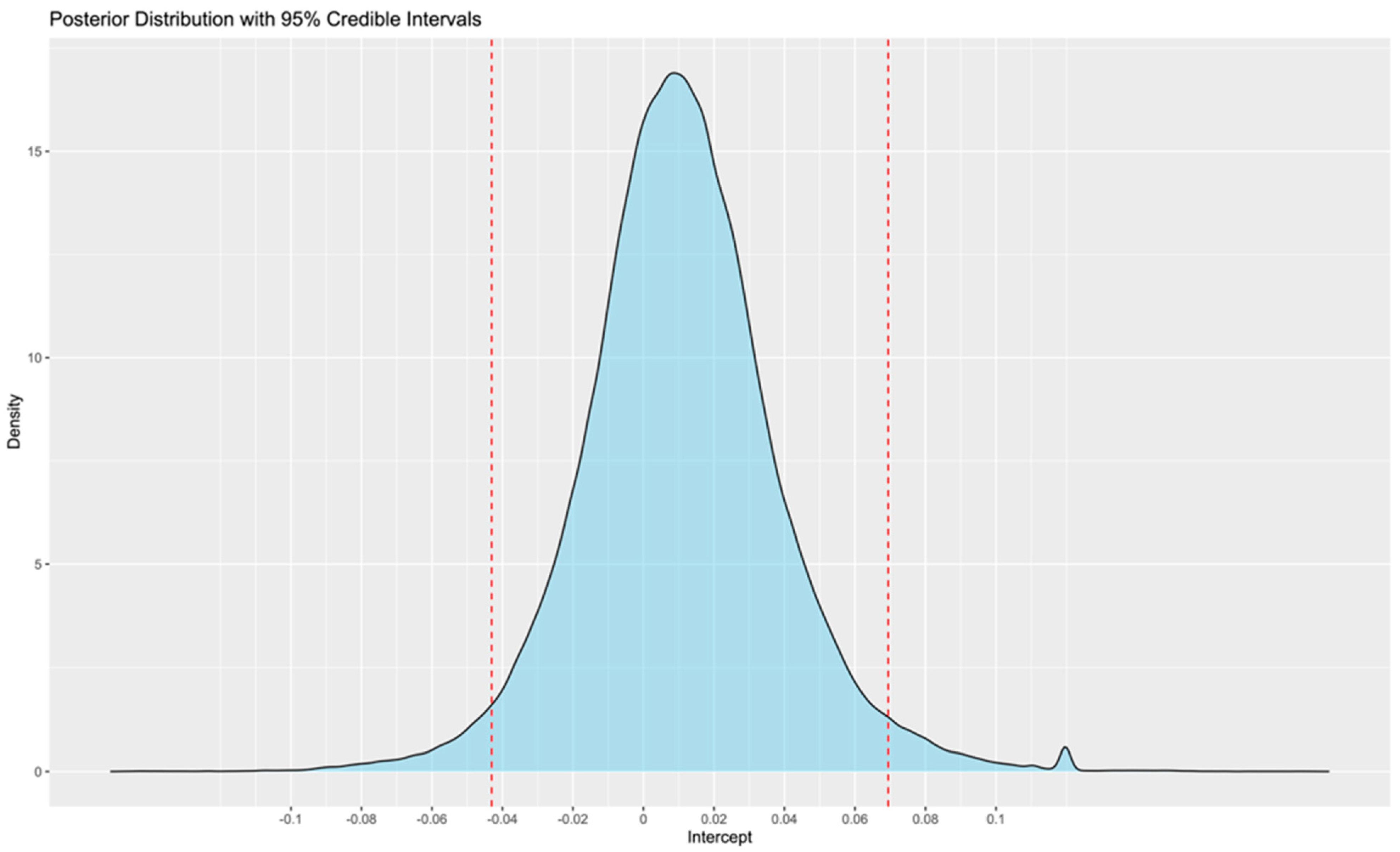
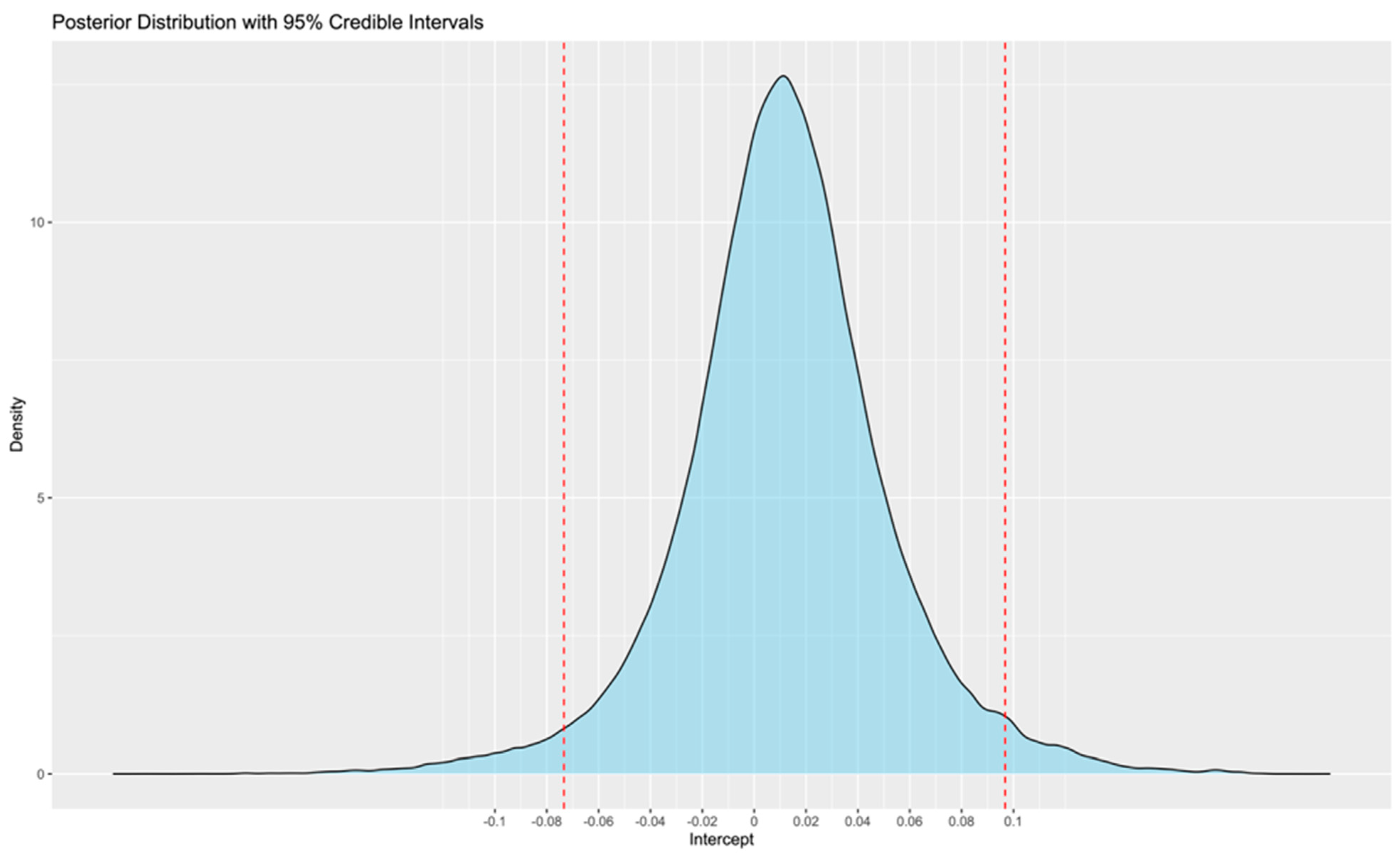
- According to the meta-analysis of the existing literature, no statistically significant difference was observed between wearables and reference ECG monitoring methods, with the mean error estimated at 1% and the 95% CrIS ranging from −4 to 7%;
- This range may be slightly larger for smartwatches;
- These findings support the potential role of wearables in future research and clinical practice. However, the relationship between different levels of burden and outcomes is not yet clear. Therefore, further research is needed to determine whether differences, such as those of the observed magnitude, are clinically significant or not.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Johnson, C.O.; Addolorato, G.; Ammirati, E.; Baddour, L.M.; Barengo, N.C.; Beaton, A.Z.; Benjamin, E.J.; Benziger, C.P.; et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019: Update from the GBD 2019 Study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021, Erratum in J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2021, 77, 1958–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, J.V.; Simon, D.N.; Go, A.S.; Spertus, J.; Fonarow, G.C.; Gersh, B.J.; Hylek, E.M.; Kowey, P.R.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Thomas, L.E.; et al. Association Between Atrial Fibrillation Symptoms, Quality of Life, and Patient Outcomes: Results from the Outcomes Registry for Better Informed Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation (ORBIT-AF). Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2015, 8, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoli, C.D.; O’Neal, W.T.; Levitan, E.B.; Singleton, M.J.; Judd, S.E.; Howard, G.; Safford, M.M.; Soliman, E.Z. Atrial fibrillation and risk of incident heart failure with reduced versus preserved ejection fraction. Heart 2022, 108, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.; Vaishnav, J.; Song, E.; Lee, J.; Schulman, S.; Calkins, H.; Berger, R.; Russell, S.D.; Sharma, K. Atrial fibrillation is an independent risk factor for heart failure hospitalization in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 2918–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruddox, V.; Sandven, I.; Munkhaugen, J.; Skattebu, J.; Edvardsen, T.; Otterstad, J.E. Atrial fibrillation and the risk for myocardial infarction, all-cause mortality and heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2017, 24, 1555–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peigh, G.; Zhou, J.; Rosemas, S.C.; Roberts, A.I.; Longacre, C.; Trinh, K.; Nayak, T.; Soderlund, D.; Passman, R.S. Association of Atrial Fibrillation Burden and Mortality Among Patients with Cardiac Implantable Electronic Devices. Circulation 2024, 150, 350–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becher, N.; Metzner, A.; Toennis, T.; Kirchhof, P.; Schnabel, R.B. Atrial fibrillation burden: A new outcome predictor and therapeutic target. Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 2824–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhn, S.; Axt, M.; Gunga, H.C.; Maggioni, M.A.; Munga, S.; Obor, D.; Sié, A.; Boudo, V.; Bunker, A.; Sauerborn, R.; et al. The Impact of Wearable Technologies in Health Research: Scoping Review. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2022, 10, e34384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedeschi, A.; Palazzini, M.; Trimarchi, G.; Conti, N.; Di Spigno, F.; Gentile, P.; D’Angelo, L.; Garascia, A.; Ammirati, E.; Morici, N.; et al. Heart Failure Management through Telehealth: Expanding Care and Connecting Hearts. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubitz, S.A.; Faranesh, A.Z.; Selvaggi, C.; Atlas, S.J.; McManus, D.D.; Singer, D.E.; Pagoto, S.; McConnell, M.V.; Pantelopoulos, A.; Foulkes, A.S. Detection of Atrial Fibrillation in a Large Population Using Wearable Devices: The Fitbit Heart Study. Circulation 2022, 146, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avram, R.; Ramsis, M.; Cristal, A.D.; Nathan, V.; Zhu, L.; Kim, J.; Kuang, J.; Gao, A.; Vittinghoff, E.; Rohdin-Bibby, L.; et al. Validation of an algorithm for continuous monitoring of atrial fibrillation using a consumer smartwatch. Heart Rhythm 2021, 18, 1482–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: Explanation and elaboration. BMJ 2009, 339, b2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Bossuyt, P.M.; QUADAS-2 Group. QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egger, M.; Smith, G.D.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. Br. Med. J. 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röver, C.; Sturtz, S.; Lilienthal, J.; Bender, R.; Friede, T. Summarizing empirical information on between-study heterogeneity for Bayesian random-effects meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2023, 42, 2439–2454, Erratum in Stat. Med. 2023, 42, 5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamra, G.; MacLehose, R.; Richardson, D. Markov chain Monte Carlo: An introduction for epidemiologists. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2013, 42, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kass, R.E.; Raftery, A.E. Bayes Factors. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1995, 90, 773–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santala, O.E.; Halonen, J.; Martikainen, S.; Jäntti, H.; Rissanen, T.T.; Tarvainen, M.P.; Laitinen, T.P.; Laitinen, T.M.; Väliaho, E.S.; Hartikainen, J.E.K.; et al. Automatic Mobile Health Arrhythmia Monitoring for the Detection of Atrial Fibrillation: Prospective Feasibility, Accuracy, and User Experience Study. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2021, 9, e29933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhu, L.; Nathan, V.; Kuang, J.; Kim, J.; Gao, J.A.; Olgin, J. Towards Early Detection and Burden Estimation of Atrial Fibrillation in an Ambulatory Free-Living Environment. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol. 2021, 5, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Nathan, V.; Kuang, J.; Kim, J.; Avram, R.; Olgin, J.; Gao, J. Atrial Fibrillation Detection and Atrial Fibrillation Burden Estimation via Wearables. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2022, 26, 2063–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reissenberger, P.; Serfözö, P.; Piper, D.; Juchler, N.; Glanzmann, S.; Gram, J.; Hensler, K.; Tonidandel, H.; Börlin, E.; D’Souza, M.; et al. Determine atrial fibrillation burden with a photoplethysmographic mobile sensor: The atrial fibrillation burden trial: Detection and quantification of episodes of atrial fibrillation using a cloud analytics service connected to a wearable with photoplethysmographic sensor. Eur. Heart J. Digit. Health 2023, 4, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poh, M.Z.; Battisti, A.J.; Cheng, L.F.; Lin, J.; Patwardhan, A.; Venkataraman, G.S.; Athill, C.A.; Patel, N.S.; Patel, C.P.; Machado, C.E.; et al. Validation of a Deep Learning Algorithm for Continuous, Real-Time Detection of Atrial Fibrillation Using a Wrist-Worn Device in an Ambulatory Environment. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e030543. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, S.; Guo, Q.; Bo, X.; Kong, X.; Xia, S.; Li, X.; Dai, W.; Guo, L.; et al. Evaluation of an algorithm-guided photoplethysmography for atrial fibrillation burden using a smartwatch. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2024, 47, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Chastin, S.; Miatke, A.; Curtis, R.; Dumuid, D.; Brinsley, J.; Ferguson, T.; Szeto, K.; Simpson, C.; Eglitis, E.; et al. Real-World Accuracy of Wearable Activity Trackers for Detecting Medical Conditions: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. JMIR mHealth uHealth 2024, 12, e56972. [Google Scholar]
- Prasitlumkum, N.; Cheungpasitporn, W.; Chokesuwattanaskul, A.; Thangjui, S.; Thongprayoon, C.; Bathini, T.; Vallabhajosyula, S.; Kanitsoraphan, C.; Leesutipornchai, T.; Chokesuwattanaskul, R. Diagnostic accuracy of smart gadgets/wearable devices in detecting atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 114, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Gelder, I.C.; Rienstra, M.; Bunting, K.V.; Casado-Arroyo, R.; Caso, V.; Crijns, H.J.G.M.; De Potter, T.J.R.; Dwight, J.; Guasti, L.; Hanke, T.; et al. 2024 ESC Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS). Eur. Heart J. 2024, 45, 3314. [Google Scholar]
- Gunawardene, M.A.; Willems, S. Atrial fibrillation progression and the importance of early treatment for improving clinical outcomes. EP Eur. 2022, 24 (Suppl. S2), ii22–ii28. [Google Scholar]
- Boriani, G.; Glotzer, T.V.; Santini, M.; West, T.M.; De Melis, M.; Sepsi, M.; Gasparini, M.; Lewalter, T.; Camm, J.A.; Singer, D.E. Device-detected atrial fibrillation and risk for stroke: An analysis of >10,000 patients from the SOS AF project (Stroke preventiOn Strategies based on Atrial Fibrillation information from implanted devices). Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 508–516. [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg, B.A.; Li, Z.; O’Brien, E.C.; Pritchard, J.; Chew, D.S.; Bunch, T.J.; Mark, D.B.; Nabutovsky, Y.; Greiner, M.A.; Piccini, J.P. Atrial fibrillation burden and heart failure: Data from 39,710 individuals with cardiac implanted electronic devices. Heart Rhythm 2021, 18, 709–716. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, J.G.; Deyell, M.W.; Macle, L.; Steinberg, J.S.; Glotzer, T.V.; Hawkins, N.M.; Khairy, P.; Aguilar, M. Healthcare utilization and quality of life for atrial fibrillation burden: The CIRCA-DOSE study. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachmann, J.; Sohns, C.; Andresen, D.; Siebels, J.; Sehner, S.; Boersma, L.; Merkely, B.; Pokushalov, E.; Sanders, P.; Schunkert, H.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation Burden and Clinical Outcomes in Heart Failure: The CASTLE-AF Trial. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 7, 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terricabras, M.; Mantovan, R.; Jiang, C.Y.; Betts, T.R.; Chen, J.; Deisenhofer, I.; Macle, L.; Morillo, C.A.; Haverkamp, W.; Weerasooriya, R.; et al. Association Between Quality of Life and Procedural Outcome After Catheter Ablation for Atrial Fibrillation: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2025473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samuel, M.; Khairy, P.; Champagne, J.; Deyell, M.W.; Macle, L.; Leong-Sit, P.; Novak, P.; Badra-Verdu, M.; Sapp, J.; Tardif, J.C.; et al. Association of Atrial Fibrillation Burden With Health-Related Quality of Life After Atrial Fibrillation Ablation: Substudy of the Cryoballoon vs Contact-Force Atrial Fibrillation Ablation (CIRCA-DOSE) Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Cardiol. 2021, 6, 1324–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwennesen, H.T.; Andrade, J.G.; Wood, K.A.; Piccini, J.P. Ablation to Reduce Atrial Fibrillation Burden and Improve Outcomes: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2023, 82, 1039–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindricks, G.; Pokushalov, E.; Urban, L.; Taborsky, M.; Kuck, K.H.; Lebedev, D.; Rieger, G.; Pürerfellner, H.; XPECT Trial Investigators. Performance of a new leadless implantable cardiac monitor in detecting and quantifying atrial fibrillation: Results of the XPECT trial. Circ. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. 2010, 3, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, F.J.; Biering-Sørensen, T.; Krieger, D.W. An update on insertable cardiac monitors: Examining the latest clinical evidence and technology for arrhythmia management. Future Cardiol. 2015, 11, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakhi, R.; Theuns, D.A.M.J.; Szili-Torok, T.; Yap, S.C. Insertable cardiac monitors: Current indications and devices. Expert. Rev. Med. Devices 2019, 16, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, C.; Witt, H.; Hindricks, G.; Katra, R.P.; Albert, D.; Belliger, A.; Cowie, M.R.; Deneke, T.; Friedman, P.; Haschemi, M.; et al. Wearables, telemedicine, and artificial intelligence in arrhythmias and heart failure: Proceedings of the European Society of Cardiology Cardiovascular Round Table. Europace 2022, 24, 1372–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, A.; Shandhi, M.M.H.; Master, H.; Dunn, J.; Brittain, E. Wearable Devices in Cardiovascular Medicine. Circ. Res. 2023, 132, 652–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Study | N | Age (y) | Males (%) | PAF (%) | PeAF (%) | FU (d) | Wearable | Noise (%) | Simultaneous Recording (h) | Recording Setting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Santala OE et al., 2021 [18] | 73 | 77 (10) | 52.1 | n/a | n/a | 1 | Heart Belt | 19.6 | 1224 | Hospital |
| Zhang H et al., 2021 [19] | 53 | 66.3 (11.8) | 50.9 | 9.4 | 18.9 | 28 | Smartwatch | 0 | 3812 | Free living |
| Zhu L et al., 2022 [20] | 204 | 62.6 (11.6) | 73 | 77.9 | 7.8 | 28 | Smartwatch | 32.3 | 20,700 | Free living |
| Reissenberger P et al., 2023 [21] | 92 | 73.3 (10.4) | n/a | 100 | 0 | 2 | Smartwatch | 50.7 | 547 | Free living/Hospital |
| Poh MZ et al., 2023 [22] | 111 | 65 (11) | 55 | 100 | 0 | 14 | Smartwatch | 22.8 | 7667 | Free living |
| Zhao Z et al., 2024 [23] | 245 | 63.1 (10.8) | 39.2 | 62.5 | 37.6 | 2 | Smartwatch | 37.2 | 3028 | Hospital |
| Study | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Santala OE et al., 2021 [18] | yes | yes | yes | yes | n/a | Yes | yes | n/a | yes | no | 87.50% |
| Zhang H et al., 2021 [19] | yes | yes | yes | yes | n/a | Yes | yes | n/a | yes | no | 87.50% |
| Zhu L et al., 2022 [20] | yes | yes | yes | yes | n/a | Yes | yes | n/a | yes | no | 87.50% |
| Reissenberger P et al., 2023 [21] | yes | Yes | yes | yes | n/a | Yes | yes | n/a | yes | no | 87.50% |
| Poh MZ et al., 2023 [22] | yes | Yes | yes | yes | n/a | Yes | yes | n/a | yes | no | 87.50% |
| Zhao Z et al., 2024 [23] | yes | Yes | yes | yes | n/a | Yes | yes | n/a | yes | yes | 100% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Anagnostopoulos, I.; Vrachatis, D.; Kousta, M.; Giotaki, S.; Katsoulotou, D.; Karavasilis, C.; Deftereos, G.; Schizas, N.; Avramides, D.; Giannopoulos, G.; et al. Wearable Devices for Quantifying Atrial Fibrillation Burden: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis. J. Cardiovasc. Dev. Dis. 2025, 12, 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12040122
Anagnostopoulos I, Vrachatis D, Kousta M, Giotaki S, Katsoulotou D, Karavasilis C, Deftereos G, Schizas N, Avramides D, Giannopoulos G, et al. Wearable Devices for Quantifying Atrial Fibrillation Burden: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease. 2025; 12(4):122. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12040122
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnagnostopoulos, Ioannis, Dimitrios Vrachatis, Maria Kousta, Sotiria Giotaki, Dimitra Katsoulotou, Christos Karavasilis, Gerasimos Deftereos, Nikolaos Schizas, Dimitrios Avramides, Georgios Giannopoulos, and et al. 2025. "Wearable Devices for Quantifying Atrial Fibrillation Burden: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis" Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease 12, no. 4: 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12040122
APA StyleAnagnostopoulos, I., Vrachatis, D., Kousta, M., Giotaki, S., Katsoulotou, D., Karavasilis, C., Deftereos, G., Schizas, N., Avramides, D., Giannopoulos, G., Papaioannou, T. G., & Deftereos, S. (2025). Wearable Devices for Quantifying Atrial Fibrillation Burden: A Systematic Review and Bayesian Meta-Analysis. Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease, 12(4), 122. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcdd12040122










