Characterization of Biofilm Producing Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Bulk Tank Milk
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. CoNS Isolates
2.2. Biofilm Formation Assay
2.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Detection of Biofilm-Associated Genes
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
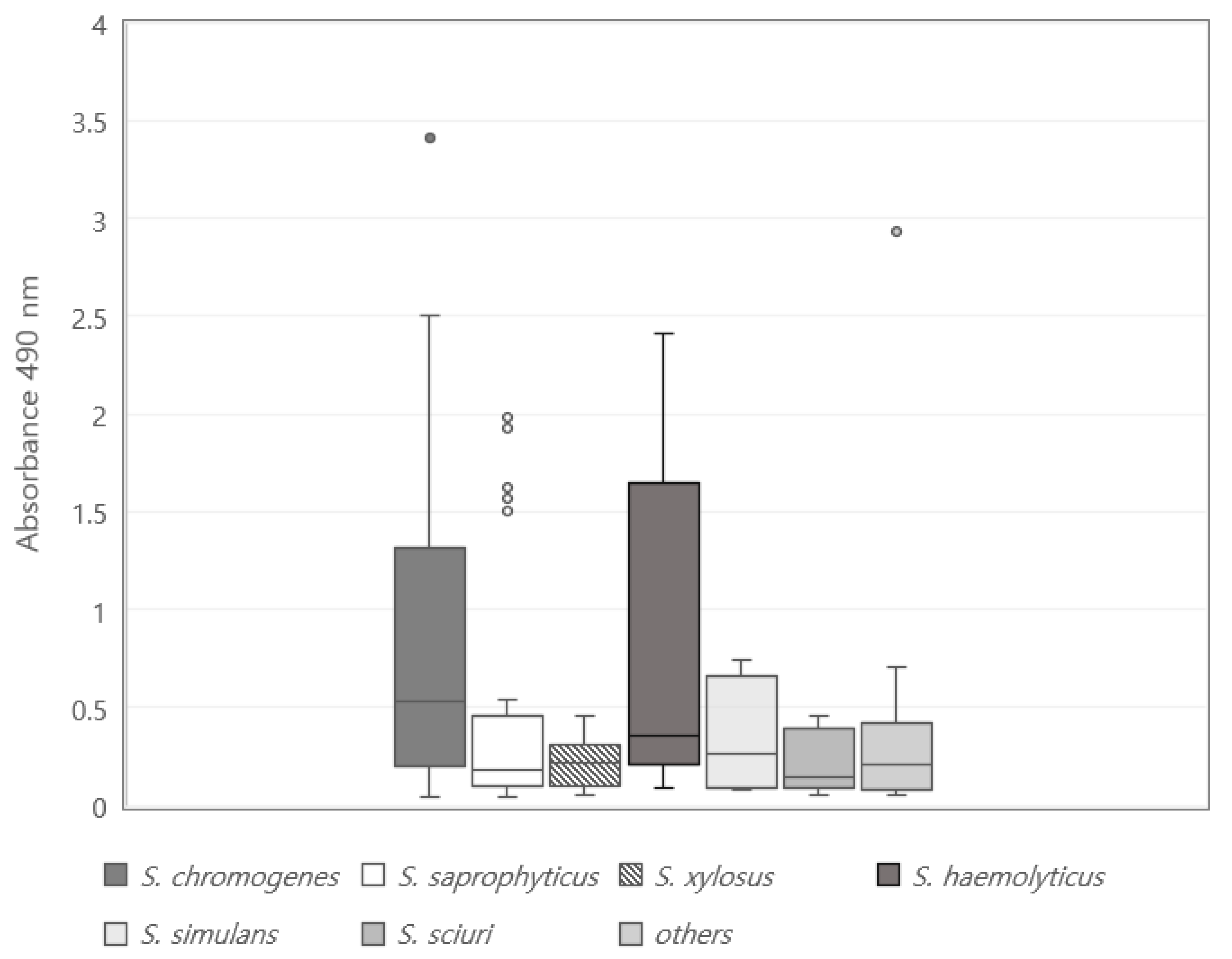
3.1. Biofilm Formation Potential
3.2. Distribution of Biofilm-Associated Genes
3.3. Relationship between Biofilm-Associated Genes and Biofilm-Forming Ability
3.4. Relationship between MDR and Biofilm-Forming Ability
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- França, A.; Gaio, V.; Lopes, N.; Melo, D.R. Virulence Factors in Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. Pathogens 2021, 10, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marek, A.; Pyzik, E.; Stępień-Pyśniak, D.; Dec, M.; Jarosz, Ł.S.; Nowaczek, A.; Sulikowska, M. Biofilm-formation ability and the presence of adhesion genes in coagulase-negative staphylococci isolates from chicken broilers. Animals 2021, 11, 728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, D.A.; Motta, C.C.; Rojas, A.C.C.M.; Soares, B.S.; Coelho, I.S.; Coelho, S.M.O.; Souza, M.M.S. Characterization of Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci and pheno-genotypic beta lactam resistance evaluation in samples from bovine Intramammary infection. Arq. Bras. De Med. Veteriná Ria E Zootec. 2018, 70, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klibi, A.; Maaroufi, A.; Torres, C.; Jouini, A. Detection and characterization of methicillin-resistant and susceptible coagulase-negative staphylococci in milk from cows with clinical mastitis in Tunisia. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 52, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirwa, E.; Gabriel, A.O.; Maitho, T.E.; Mbindyo, C.M.; Abuom, T.O.; Mainga, A.O. Antibiotic profile of Staphylococcus aureus and Coagulase negative Staphylococci species isolated from raw camel milk from Garissa County, Kenya. East African J. Sci. Technol. Innov. 2021, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, C.; Tremblay, Y.D.N.; Lamarche, D.; Blondeau, A.; Gaudreau, A.M.; Labrie, J.; Malouin, F.; Jacques, M. Coagulase-negative staphylococci species affect biofilm formation of other coagulase-negative and coagulase-positive staphylococci. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 6454–6464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffey, B.M.; Anderson, G.G. Biofilm formation in the 96-well microtiter plate. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1149, 631–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gajewska, J.; Chajęcka-Wierzchowska, W. Biofilm formation ability and presence of adhesion genes among coagulase-negative and coagulase-positive staphylococci isolates from raw cow’s milk. Pathogens 2020, 9, 654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaweera, T.S.P.; Ruwandeepika, H.A.D.; Deekshit, V.K.; Kodithuwakku, S.P.; Cyril, H.W.; Karunasagar, I.; Vidanarachchi, J.K. Biofilm Forming Ability of Broiler Chicken Meat Associated Salmonella spp. on Food Contact Surfaces. Trop. Agric. Res. 2021, 32, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, H.M.; Lim, S.K.; Moon, J.S.; Kang, H.M.; Kim, J.M.; Jang, K.C.; Kim, J.M.; Kang, M.I.; Joo, Y.S.; Jung, S.C. Antimicrobial resistance of enterococci isolated from mastitic bovine milk samples in Korea. Zoonoses Public Health 2010, 57, 698–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Moon, D.C.; Park, S.C.; Kang, H.Y.; Na, S.H.; Lim, S.K. Antimicrobial resistance and genetic characterization of coagulase-negative staphylococci from bovine mastitis milk samples in Korea. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 11439–11448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, M.J.; Yoon, S.; Lee, Y.J. Monitoring and characteristics of major mastitis pathogens from Bulk tank milk in Korea. Animals 2020, 10, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS). Processing Standards and Ingredient Specifications for Livestock Products; NIFDS: Cheong ju, Korea, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Martineau, F.; Picard, F.J.; Ke, D.; Paradis, S.; Roy, P.H.; Ouellette, M.; Bergeron, M.G. Development of a PCR assay for identification of staphylococci at genus and species levels. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 2541–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, G.; Séguin, D.L.; Asselin, A.E.; Déziel, E.; Cantin, A.M.; Frost, E.H.; Michaud, S.; Malouin, F. Staphylococcus aureus sigma B-dependent emergence of small-colony variants and biofilm production following exposure to Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline-N-oxide. BMC Microbiol. 2010, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Ren, S.X.; Li, H.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Fu, G.; Yang, J.; Qin, Z.Q.; Miao, Y.G.; Wang, W.Y.; Chen, R.S.; et al. Genome-based analysis of virulence genes in a non-biofilm-forming Staphylococcus epidermidis strain (ATCC 12228). Mol. Microbiol. 2003, 49, 1577–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.R.; Fouts, D.E.; Archer, G.L.; Mongodin, E.F.; DeBoy, R.T.; Ravel, J.; Paulsen, I.T.; Kolonay, J.F.; Brinkac, L.; Beanan, M.; et al. Insights on evolution of virulence and resistance from the complete genome analysis of an early methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strain and a biofilm-producing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis strain. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 2426–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toledo-Silva, B.; de Souza, F.N.; Mertens, K.; Piepers, S.; Haesebrouck, F.; De Vliegher, S. Bovine-associated non-aureus staphylococci suppress Staphylococcus aureus biofilm dispersal in vitro yet not through agr regulation. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 28th ed.; CLSI: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018; ISBN 156238838X. [Google Scholar]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakshi, C.S.; Shah, D.H.; Verma, R.; Singh, R.K.; Malik, M. Rapid differentiation of Mycobacterium bovis and Mycobacterium tuberculosis based on a 12.7-kb fragment by a single tube multiplex-PCR. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 109, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cucarella, C.; Tormo, M.Á.; Úbeda, C.; Trotonda, M.P.; Monzón, M.; Peris, C.; Amorena, B.; Lasa, Í.; Penadés, J.R. Role of Biofilm-Associated Protein Bap in the Pathogenesis of Bovine Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Immun. 2004, 72, 2177–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohde, H.; Burdelski, C.; Bartscht, K.; Hussain, M.; Buck, F.; Horstkotte, M.A.; Knobloch, J.K.M.; Heilmann, C.; Herrmann, M.; Mack, D. Induction of Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilm formation via proteolytic processing of the accumulation-associated protein by staphylococcal and host proteases. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 55, 1883–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohde, H.; Burandt, E.C.; Siemssen, N.; Frommelt, L.; Burdelski, C.; Wurster, S.; Scherpe, S.; Davies, A.P.; Harris, L.G.; Horstkotte, M.A.; et al. Polysaccharide intercellular adhesin or protein factors in biofilm accumulation of Staphylococcus epidermidis and Staphylococcus aureus isolated from prosthetic hip and knee joint infections. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simojoki, H.; Hyvönen, P.; Plumed Ferrer, C.; Taponen, S.; Pyörälä, S. Is the biofilm formation and slime producing ability of coagulase-negative staphylococci associated with the persistence and severity of intramammary infection? Vet. Microbiol. 2012, 158, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovačević, Z.; Radinović, M.; Čabarkapa, I.; Kladar, N.; Božin, B. Natural agents against bovine mastitis pathogens. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyatov, V.; Vrtková, I.; Knoll, A. Detection of selected antibiotic resistance genes using multiplex PCR assay in mastitis pathogens in the Czech Republic. Acta Vet. Brno 2017, 86, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbindyo, C.M.; Gitao, G.C.; Mulei, C.M. Prevalence, Etiology, and Risk Factors of Mastitis in Dairy Cattle in Embu and Kajiado Counties, Kenya. Vet. Med. Int. 2020, 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Fox, L.K.; Seo, K.S.; McGuire, M.A.; Park, Y.H.; Rurangirwa, F.R.; Sischo, W.M.; Bohach, G.A. Comparison of phenotypic and genotypic methods for the species identification of coagulase-negative staphylococcal isolates from bovine intramammary infections. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 147, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walid, M.S. Antibiogram and antibiotic resistance genes among coagulase-negative staphylococci recovered from bovine mastitis. Arch. Anesthesiol. Crit. Care 2021, 9, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, S.; Ambatipudi, K. Mammary microbial dysbiosis leads to the zoonosis of bovine mastitis: A One-Health perspective. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tremblay, Y.D.N.; Lamarche, D.; Chever, P.; Haine, D.; Messier, S.; Jacques, M. Characterization of the ability of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from the milk of Canadian farms to form biofilms. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srednik, M.E.; Tremblay, Y.D.N.; Labrie, J.; Archambault, M.; Jacques, M.; Cirelli, A.F.; Gentilini, E.R. Biofilm formation and antimicrobial resistance genes of coagulase-negative staphylococci isolated from cows with mastitis in Argentina. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2017, 364, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, K.; Heilmann, C.; Peters, G. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 870–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Meervenne, E.; De Weirdt, R.; Van Coillie, E.; Devlieghere, F.; Herman, L.; Boon, N. Biofilm models for the food industry: Hot spots for plasmid transfer? Pathog. Dis. 2014, 70, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Secondary, C.A.; Author, C.; Lin, J.; Jin, Y.; Pang, Q.; Lin, J. Application of ica D, eno, sar A and agr gene testing in early diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. Int. Surg. 2021, 106, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibtissem, K.T.; Hafida, H.; Salwa, O.; Samia, B.; Imen, M.; Meriem, L.; Mohammed, T. Detection of icaA and icaD genes and biofilmformation in Staphylococcus spp. isolated from urinary catheters at the University Hospital of Tlemcen (Algeria). African J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 7, 5350–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Osman, K.M.; Abd El-Razik, K.A.; Marie, H.S.H.; Arafa, A. Relevance of biofilm formation and virulence of different species of coagulase-negative staphylococci to public health. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 34, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saidi, R.; Cantekin, Z.; Mimoune, N.; Ergun, Y.; Solmaz, H.; Khelef, D.; Kaidi, R. Investigation of the presence of slime production, VanA gene and antiseptic resistance genes in Staphylococci isolated from bovine mastitis in Algeria. Vet. Stanica 2021, 52, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, T.S.; Pinheiro, F.R.; Soares, L.; Andre, P.; Freire, R.; Pereira, A.; Correa, R.F.; De Mello, G.C.; Aparecida, T.; Ribeiro, N.; et al. Virulence Factors Found in Nasal Colonization and Infection of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) Isolates and Their Ability to Form a Biofilm. Toxins 2020, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poppele, E.H.; Hozalski, R.M. Micro-cantilever method for measuring the tensile strength of biofilms and microbial flocs. J. Microbiol. Methods 2003, 55, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Bai, H.; Kong, F.; Liss, S.N.; Liao, B. Recent advances in membrane aerated biofilm reactors. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 649–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, K.; Zarei, O.; Sedighi, P.; Taheri, M.; Doosti-Irani, A.; Shokoohizadeh, L. Investigation of Antibiotic Resistance and Biofilm Formation in Clinical Isolates of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Microbiol. 2021, 2021, 5573388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phophi, L.; Petzer, I.M.; Qekwana, D.N. Antimicrobial resistance patterns and biofilm formation of coagulase-negative Staphylococcus species isolated from subclinical mastitis cow milk samples submitted to the Onderstepoort Milk Laboratory. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Oliveira, A.; Pereira, V.C.; Pinheiro, L.; Riboli, D.F.M.; Martins, K.B.; Ribeiro de Souza da Cunha, M.D.L. Antimicrobial resistance profile of planktonic and biofilm cells of staphylococcus aureus and coagulase-negative staphylococci. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Staphylococcus chromogenes (n = 65) | Staphylococcus saprophyticus (n = 46) | Staphylococcus xylosus (n = 17) | Staphylococcus haemolyticus (n = 11) | Staphylococcus simulans (n = 4) | Staphylococcus sciuri (n = 5) | Others 2 (n = 14) | Total (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biofilm formation(A490) 1 | ||||||||
| Negative | 5 (7.7) c | 17 (37.0) a | 5 (29.4) a,b | 1 (9.1) b,c | 1 (25.0) a,b | 1 (20.0) a,b | 5 (35.7) a | 35 (21.6) |
| Positive | 60 (92.3) a* | 29 (63.0) c* | 12 (70.6) c* | 10 (90.9) a,b* | 3 (75.0) b,c* | 4 (80.0) a,b,c* | 9 (64.3) c* | 127 (78.4) * |
| Weak | 26 (40.0) cA | 18 (39.1) cA | 12 (70.6) a,bA | 5 (45.5) cA | 2 (50.0) b,cA | 4 (80.0) aA | 6 (42.9) c A | 73 (45.1) A |
| Moderate | 18 (27.7) aB | 1 (2.2) b,cC | 0 (0.0) cB | 1 (9.1) b,cC | 1 (25.0) aB | 0 (0.0) cB | 2 (14.3) a,bB | 23 (14.2) B |
| Strong | 16 (24.6) a,bB | 10 (21.7) a,bB | 0 (0.0) cB | 4 (36.4) aB | 0 (0.0) cC | 0 (0.0) cB | 1 (7.1) b,cC | 31 (19.1) B |
| Biofilm-associated gene | ||||||||
| None | 4 (6.2) b,cD | 2 (4.3) b,cD | 2 (11.8) a,bC | 1 (9.1) a,bC | 1 (25.0) aB | 0 (0.0) cC | 0 (0.0) cD | 10 (6.2) D |
| aap | 20 (30.8) B,C | 15 (32.6) B,C | 3 (17.6) B,C | 4 (36.4) B,C | 1 (25.0) B | 1 (20.0) B | 5 (35.7) B,C | 49 (30.2) B,C |
| atlE | 12 (18.5) C,D | 6 (13.0) C,D | 4 (23.5) B,C | 2 (18.2) C | 1 (25.0) B | 1 (20.0) B | 4 (28.6) C | 30 (18.5) C |
| bap | 15 (23.1) b,cC,D | 17 (37.0) aB,C | 2 (11.8) cC | 3 (27.3) b,cB,C | 1 (25.0) b,cB | 0 (0.0) cC | 5 (35.7) a,bB,C | 43 (26.5) C |
| embP | 14 (21.5) b,cC,D | 5 (10.9) b,cC,D | 3 (17.6) b,cB,C | 1 (9.1) cC | 1 (25.0) a,bB | 0 (0.0) cC | 6 (42.9) aB,C | 30 (18.5) C |
| eno | 27 (41.5) cB,C | 38 (82.6) aA | 11 (64.7) a,bA | 9 (81.8) aA | 2 (50.0) b,cA | 4 (80.0) aA | 10 (71.4) a,bA | 101 (62.3) A |
| fbe | 32 (49.2) a,bB,C | 25 (54.3) a,bB | 7 (41.2) b,cB | 3 (27.3) cB,C | 1 (25.0) cB | 3 (60.0) aB | 5 (35.7) b,cB,C | 76 (46.9) B |
| icaA | 40 (61.5) aA | 15 (32.6) a,bB,C | 4 (23.5) b,cB,C | 0 (0.0) cD | 1 (25.0) b,cB | 1 (20.0) b,cB | 3 (21.4) b,cC | 64 (39.5) B,C |
| Antimicrobial Resistance | Biofilm Producer | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Strong or Moderate Biofilm Former (n = 54) | Weak Biofilm Former (n = 73) | Non-Former (n = 35) | |
| Non-MDR | 10 (18.5) cB | 24 (32.9) bB | 28 (80.0) aA |
| MDR | 44 (81.5) aA | 49 (67.1) bA | 7 (20.0) cB |
| Biofilm-Associated Gene | Biofilm Producer | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Strong or Moderate Biofilm Former (n = 54) | Weak Biofilm Former (n = 73) | Non-Former (n = 35) | |
| None | 0 (0.0) bE | 6 (8.2) a,bD | 4 (11.4) aC,D |
| aap | 28 (51.9) aA,B,C | 16 (21.9) bB,C | 5 (14.3) cC,D |
| atlE | 18 (33.3) aC,D | 9 (12.3) bC,D | 3 (8.6) cD |
| bap | 22 (40.7) aB,C,D | 16 (21.9) bB,C | 5 (14.3) cC,D |
| embP | 12 (22.2) a,bD | 9 (12.3) bC,D | 9 (25.7) aB,C |
| eno | 35 (64.8) a,bA | 38 (52.1) bA | 28 (80.0) aA |
| fbe | 32 (59.3) aA,B | 28 (38.4) bA,B | 16 (45.7) a,bB |
| icaA | 35 (64.8) aA | 24 (32.9) bA,B | 5 (14.3) cC,D |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.J.; Lee, Y.J. Characterization of Biofilm Producing Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Bulk Tank Milk. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9080430
Lee YJ, Lee YJ. Characterization of Biofilm Producing Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Bulk Tank Milk. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(8):430. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9080430
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Yu Jin, and Young Ju Lee. 2022. "Characterization of Biofilm Producing Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Bulk Tank Milk" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 8: 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9080430
APA StyleLee, Y. J., & Lee, Y. J. (2022). Characterization of Biofilm Producing Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci Isolated from Bulk Tank Milk. Veterinary Sciences, 9(8), 430. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9080430






