Human and Animal Brucellosis in Nigeria: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis in the Last Twenty-One Years (2001–2021)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
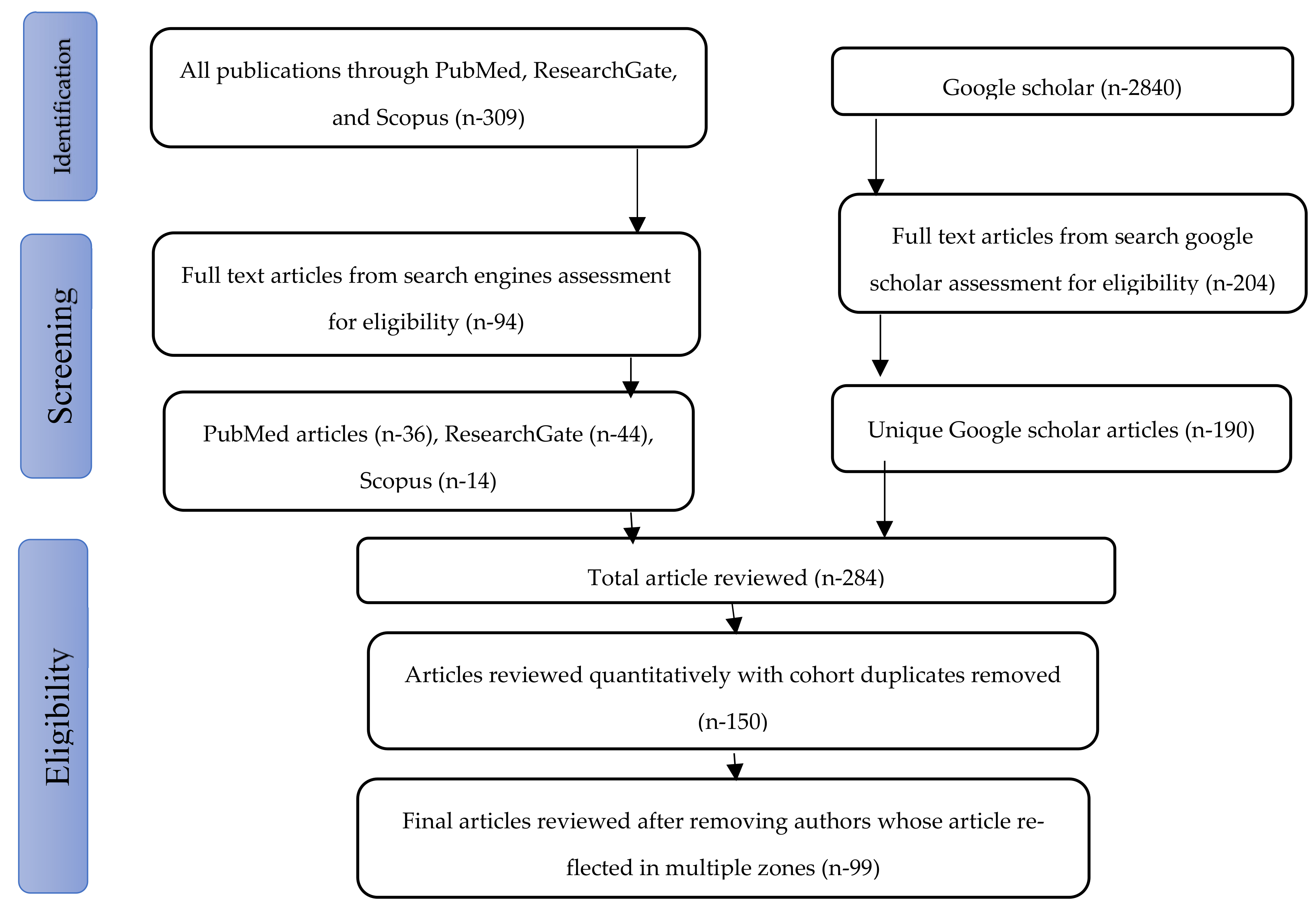
2.2. Search Strategy and Data Acquisition
2.3. Selection Criteria
2.4. Inclusion Criteria
2.5. Exclusion Criteria
2.6. Data Extraction
3. Results
3.1. Data Analysis
3.2. Prevalence of Human and Animal Brucellosis in Nigeria
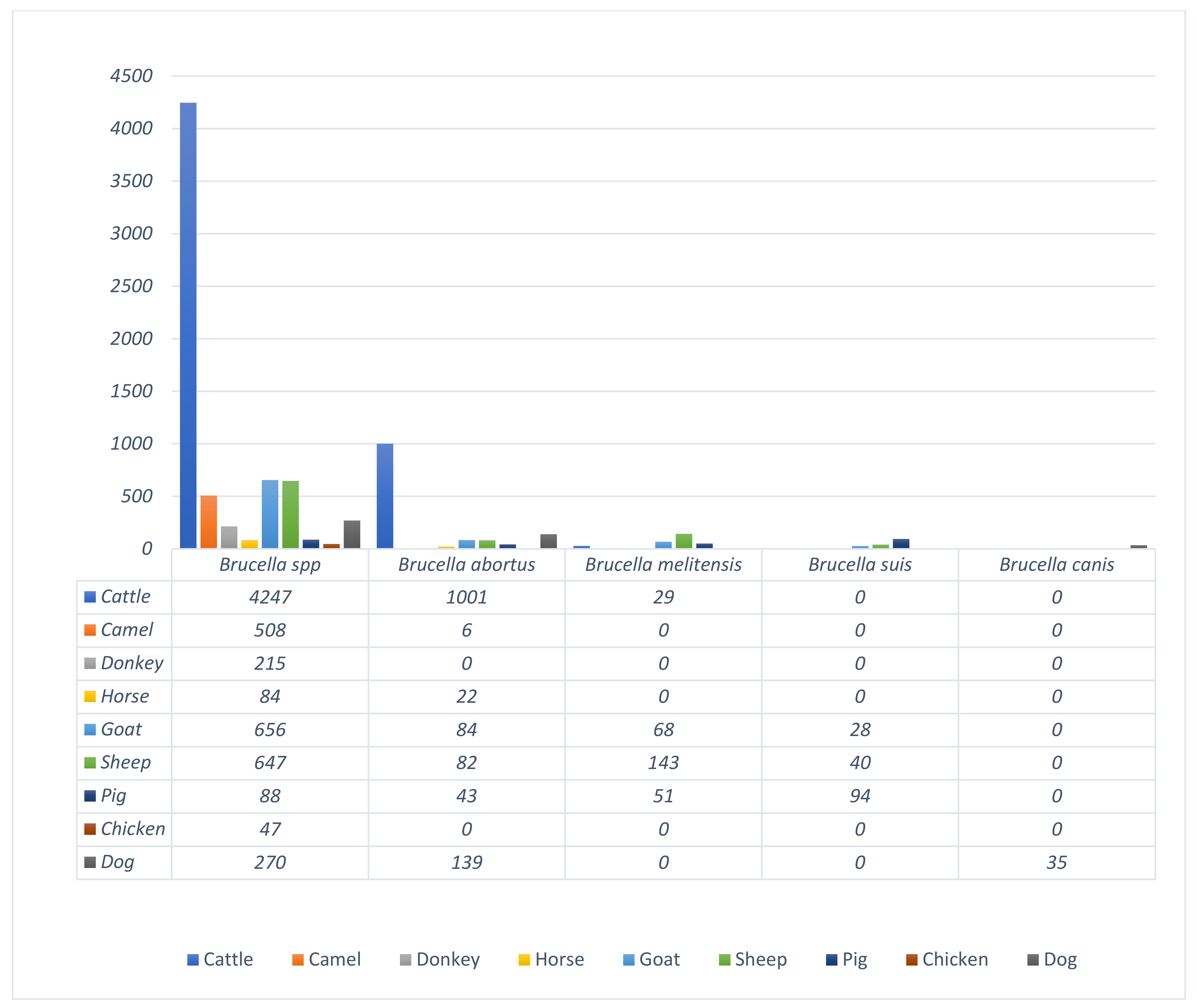
3.3. Regional Prevalence of Brucellosis in Common Domestic Animals in Nigeria
3.4. Prevalence of Brucella Infection According to Sample Type
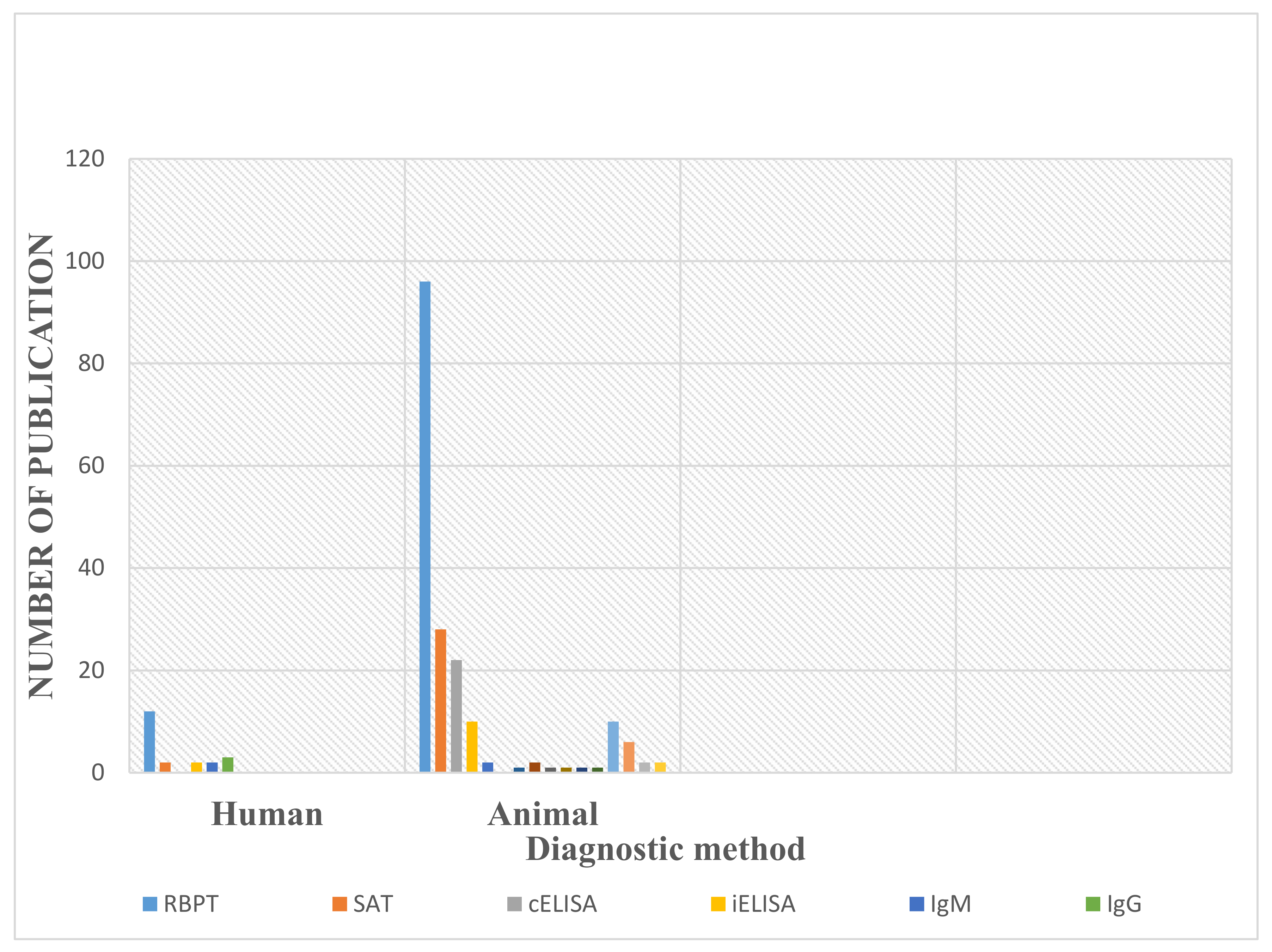
3.5. Diagnostic Methods Used in the Detection of Human and Animal Brucellosis in Nigeria
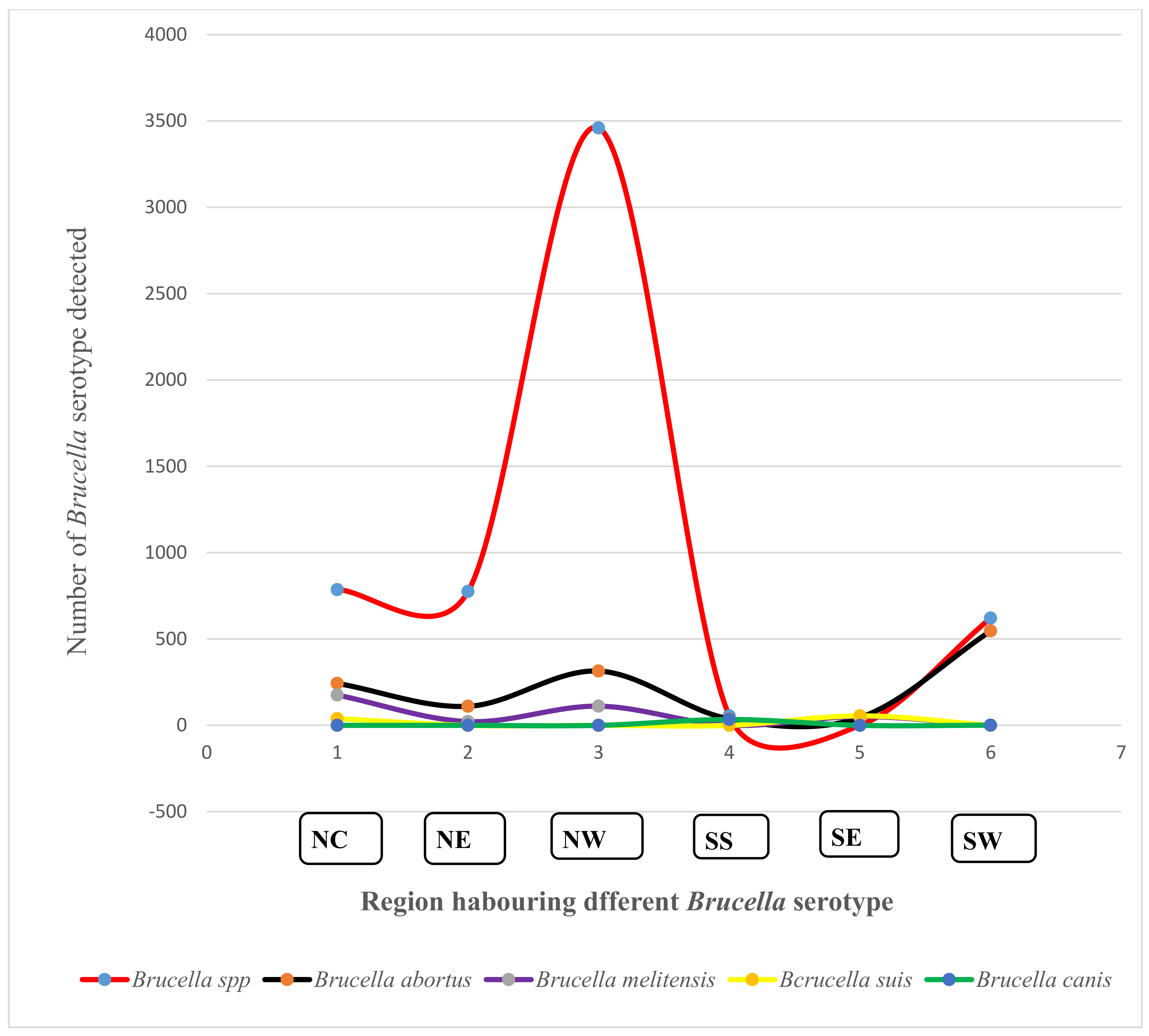
3.6. Prevalence and Diversity of Brucella Species from Humans and Animals within the Six Geopolitical Zones of Nigeria
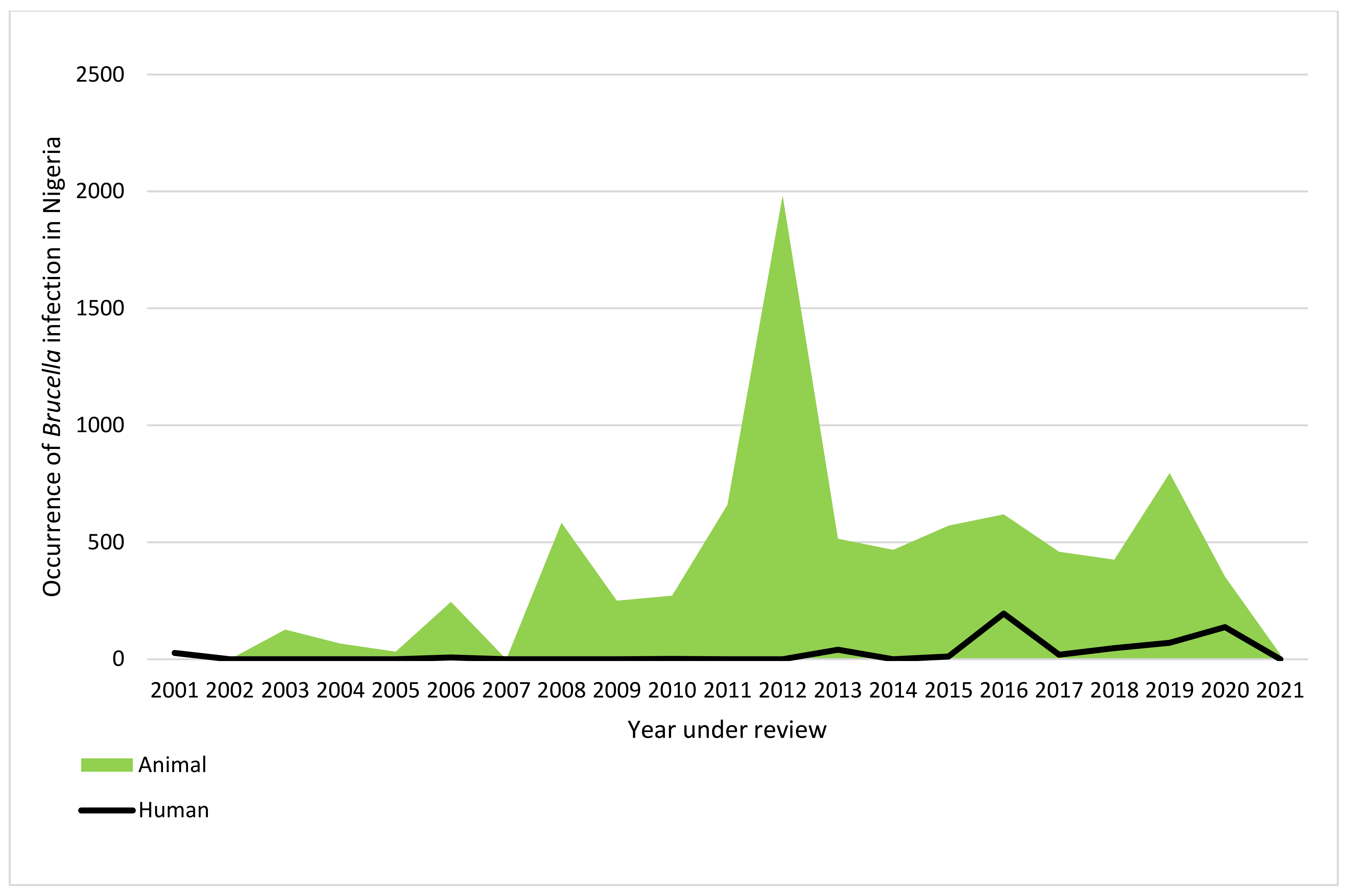
3.7. The Trend of Reported Human and Animal Brucella Infection in Nigeria (2001 to 2021)
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Corbel, M.J. Brucellosis in Humans and Animals; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ducrotoya, M.; Bertub, W.J.; Matopec, G.; Cadmusd, S.; Conde-Álvareze, R.; Gusib, A.M.; Welburna, S.; Ocholib, R.; Blascof, J.M.; Moriyón, I. Brucellosis in Sub-Saharan Africa: Current challenges for management, diagnosis and control. Acta Tropica. 2017, 165, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, N.J.; Bronze, M.S. Brucellosis. Available online: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/213430-print (accessed on 20 April 2022).
- World Health Organization. Home/Newsroom/Fact sheets/Detail/Brucellosis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti, C.A.; Arenas-Gamboa, A.M.; Maurizio, E. Caprine brucellosis: A historically neglected disease with significant impact on public health. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosilkovski, M.; Keramat, F.; Arapovic, J. The current therapeutic strategies in human brucellosis. Infection 2021, 49, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadmus, S.I.; Akporube, K.A.; Ola-Daniel, F.; Adelakun, O.D.; Akinseye, V.O. Seroprevalence and associated factors of brucellosis and Q-fever in cattle from Ibarapa area, Oyo state, south-western Nigeria. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2020, 36, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wareth, G.; Dadar, M.; Ali, H.; Hamdy, M.E.R.; Al-Talhy, A.M.; Elkharsawi, A.R.; El Tawab, A.A.A.; Neubauer, H. The perspective of antibiotic therapeutic challenges of brucellosis in the Middle East and North African countries: Current situation and therapeutic management. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Diasty, M.; El-Said, R.; Abdelkhalek, A. Seroprevalence and molecular diagnosis of sheep brucellosis in Dakahlia governorate, Egypt. Ger. J. Vet. Res. 2021, 1, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, J.J.; Arimi, S. Brucellosis in sub-Saharan Africa: Epidemiology, control and impact. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 90, 111–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division. World Population Prospects 2019: Highlights; ST/ESA/SER.A/423; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Adamu, N.N.; Ajogi, I. Serological investigations of camels (Camelus dromedarius) slaughtered at Kano municipal abattoir for evidence of brucellosis. Trop. Vet. 1999, 18, 45–48. [Google Scholar]
- Ducrotoy, M.J.; Bertu, W.J.; Ocholi, R.A.; Gusi, A.M.; Bryssinckx, W.; Welburn, S.; Moriyón, I. Brucellosis as an Emerging Threat in Developing Economies: Lessons from Nigeria. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, e3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aworh, M.K.; Okolocha, E.C.; Awosanya, E.J.; Fasina, F.O. Sero-prevalence and intrinsic factors associated with Brucella infection in food animals slaughtered at abattoirs in Abuja, Nigeria. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogugua, A.; Akinseye, V.; Ayoola, M.; Oyesola, O.; Shima, F.; Tijjani, A.; Musa, A.N.A.; Adesokan, H.; Perrett, L.; Taylor, A.; et al. Seroprevalence and risk factors of brucellosis in goats in selected states in Nigeria and the public health implications. Afr. J. Med. Med Sci. 2014, 43 (Suppl. 1), 121–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ehizibolo, D.O.; Gusi, A.M.; Ehizibolo, P.O.; Mbuk, E.U.; Ocholi, R.A. Serologic Prevalence of Brucellosis in Horse Stables in Two Northern States of Nigeria. J. Equine Sci. 2011, 22, 17–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhaji, N.B.; Wungak, Y.S.; Bertu, W.J. Serological survey of bovine brucellosis in Fulani nomadic cattle breeds (Bos indicus) of North-central Nigeria: Potential risk factors and zoonotic implications. Acta Trop. 2016, 153, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertu, W.J.; Ajogi, I.; Bale, J.O.O.; Kwaga, J.K.P.; Ocholi, R.A. Sero-epidemiology of brucellosis in small ruminants in Plateau State, Nigeria. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2010, 4, 1935–1938. [Google Scholar]
- Bamidele, F.; Gidado, S.; Edukugho, A.; Cadmus, S. Seroprevalence of Brucellosis in abattoir workers and slaughtered cattle in Ilorin metropolis Kwara State Nigeria. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 101, 532–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.Y.; Ameen, S.A.; Ambali, H.M.; Adah, A.D.; Abdulmajeed, I.; Furo, N.A.; Kadir, R.A.; Olajide, E.O. Seroprevalence of brucellosis in horses in Ilorin metropolis, Kwara State, Nigeria. J. Vet. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 2, 210–217. [Google Scholar]
- Bertu, W.; Ocholi, R.; Gusi, A.; Ngulukun, S.; Ducrotoy, M.; Moriyon, I. Isolation of brucella strains in cattle from sedentary and nomadic communities and its public health implication. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 101, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndumari, W.; Se-ember, A.D.; Oluwatosin, A.; Terzugwe, T. Seroprevalence of Brucellosis in Nigerian Breed of Dog in North Bank Area of Makurdi, Benue State Nigeria. Int. J. Intern. Med. Geriatr. 2020, 2, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Bertu, W.J.; Dapar, M.; Gusi, A.M.; Ngulukun, S.S.; Leo, S.; Jw, L.D. Prevalence of Brucella antibodies in marketed milk in Jos and environs. Afr. J. Food. Sci. 2010, 4, 62–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wungak, Y.S.; Aworh, M.K.F.; Maurice, N.; Balami, A.G.; Danmarwa, A.; Danthe, H.D. Serological survey of antibodies against Brucella abortus in cattle in Jos south local government area. Vom. J. Vet. Sci. 2011, 8, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Momoh, H.A.; Ijale, G.O.; Ajogi, I.; Okolocha, E.C. Risk factors and level of awareness of canine brucellosis in Jos, Plateau State, Nigeria. J. Vet. Med. Anim. Health 2015, 7, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Agada, C.A.; Goden, C.P.; Ogugua, J.O. Prevalence of bovine brucellosis and analysis of risk factors in resident cattle herds of Kanke Local Government Area, Plateau State, Nigeria. Niger. Vet. J. 2017, 38, 104–116. [Google Scholar]
- Dawang, N.D.; Danahap, L.S.; Nash, K.N.; Oluseye, E.; Kalejaye, O. Occurrence of Brucella spp. in slaughtered sheep and goats in Jos main abattoir, Jos, Plateau State, Nigeria. Afr. J. Nat. Sci. AJNS 2016, 17, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Alhaji, N.B.; Wungak, Y. Epizootiological survey of bovine brucellosis in nomadic pastoral camps in Niger state, Nigeria. Niger. Vet. J. 2013, 34, 795–800. [Google Scholar]
- Agada, C.; Ogugua, A.; Anzaku, E. Occurrence of brucellosis in small ruminants slaughtered in Lafia central abattoir, Nasarawa State, Nigeria. Sokoto J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 16, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aworh, M.; Okolocha, E.; Kwaga, J.; Fasina, F.; Lazarus, D.; Suleman, I.; Poggensee, G.; Nguku, P.; Nsubuga, P. Human brucellosis: Seroprevalence and associated exposure factors among abattoir workers in Abuja, Nigeria—2011. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2013, 16, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agada, C.; Mohammed, J.; Okoh, A.E.J.; Ogugua, J.A. Prevalence and risk factors associated with brucellosis among high-risk individuals in Lafia, Nasarawa state, Nigeria. Int. J. One Health 2018, 4, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngbede, E.O.; Momoh, A.H.; Bala, R.S.; Madaki, B.D.; Maurice, N.A. An abattoir-based study on sero-diagnosis of swine brucellosis in Makurdi, Benue State, North-Central Nigeria. J. Adv. Vet. Res. 2013, 3, 57–59. [Google Scholar]
- Bertu, W.J.; Ocholi, R.A.; Gusi, A.M.; Abdullahi, S.; Zwandor, N.J.; Durbi, I.A.A.; Opara, J.; Okewole, P.A. Brucella abortus infection in a multispecies livestock farm in Nigeria. Int. J. Biotec. Food Sci. 2015, 3, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Ior, D.D.; Chukwu, C.C. Prevalence of Brucella antibodies in marketed cow milk in Benue State, Nigeria. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 9, 1752–1757. [Google Scholar]
- Cadmus, S.; Adesokan, H.; Oluwayelu, D.; Idris, A.; Stack, J. Short Communication: Brucella Abortus Antibodies in The Sera of Indigenous and Exotic Avian Species In Nigeria. Bull. Anim. Health Prod. Afr. 2011, 58, 382–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocholi, R.; Kwaga, J.; Ajogi, I.; Bale, J. Phenotypic characterization of Brucella strains isolated from livestock in Nigeria. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 103, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusi, A.M.; Bertu, W.J.; De Miguel, M.J.; Dieste-Pérez, L.; Smits, H.L.; Ocholi, R.A.; Blasco, J.M.; Moriyon, I.; Muñoz, P.M. Comparative performance of lateral flow immunochromatography, iELISA and Rose Bengal tests for the diagnosis of cattle, sheep, goat and swine brucellosis. PLOS Neglected Trop. Dis. 2019, 13, e0007509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tijjani, A.O.; Junaidu, A.U.; Salihu, M.D.; Farouq, A.A.; Faleke, O.O.; Adamu, S.G.; Musa, H.I.; Hambali, I.U. Serological survey for Brucella antibodies in donkeys of north-eastern Nigeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 1211–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamu, S.G.; Hassan, M.; Ardo, M.B. Seroprevalence of Brucella antibodies in Donkeys (Equus asinus) in Yobe south senatorial zone, Northeastern Nigeria. J. Equine Sci. 2020, 31, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Mai, H.M.; Irons, P.C.; Kabir, J.; Thompson, P.N. A large seroprevalence survey of brucellosis in cattle herds under diverse production systems in northern Nigeria. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamu, N.B.; Adamu, S.G.; Jajere, M.S.; Atsanda, N.N.; Mustapha, F.B.; Mama, M. Serological survey of brucellosis in slaughtered local chicken, guinea fowl, duck and turkey in North eastern Nigeria. Inter. J. Poultry Sci. 2014, 13, 340–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ocholi, R.A.; Kwaga, J.K.; Ajogi, I.; Bale, J.O. Abortion due to Brucella abortus in sheep in Nigeria. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2005, 24, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olufemi, O.T.; Dantala, D.B.; Shinggu, P.; Dike, U.A.; Otolorin, G.R.; Nwuku, J.A.; Baba-Onoja, E.B.T.; Jatau, T.D.; Amama, F.I. Seroprevalence of Brucellosis and Associated Risk Factors among Indigenous Breeds of Goats in Wukari, Taraba State, Nigeria. J. Pathog. 2008, 1, 5257926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jajere, S.M.; Atsanda, N.N.; Bitrus, A.A.; Hamisu, T.M.; Ayo, A.O. Seroprevalence of brucellosis among cattle slaughtered in three municipal abattoirs of Gombe state, Northeastern Nigeria. Vet. World 2016, 9, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Baba, M.M.; Sarkindared, S.E.; Brisibe, F. Serological evidence of brucellosis among predisposed patients with pyrexia of unknown origin in the north eastern Nigeria. Central Eur. J. Public Health 2001, 9, 158–161. [Google Scholar]
- Ardo, M.B.; Abubakar, D.M. Seroprevalence of horse (Equus caballus) brucellosis on the Mambilla plateau of Taraba State, Nigeria. J. Equine Sci. 2016, 27, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, M.A.; Ajogi, I.; Bale, J.O.O.; Mosimabale, F.B.; Tijjani, A.N.; Auwal, M.S.; Mustapha, A.R.; Kudi, A.C. Epidemiological investigation of brucellosis in one humped camel (Camelus dromedarius) in Lake Chad area of Borno state, Nigeria. J. Camel Pract. Res. 2010, 17, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Mai, H.M.; Irons, P.C.; Thompson, P.N. Brucellosis, genital campylobacteriosis and other factors affecting calving rate of cattle in three states of Northern Nigeria. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, Y.; Mai, H.M.; Kalla, D.J.U.; Kabir, J.; Nathaniel, J. Seroprevalence and potential risk factors of bovine brucellosis at the livestock-wildlife interface area of Yankari game reserve, Bauchi State, Nigeria. Niger. J. Anim. Prod. 2019, 46, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsanda, N.; Liba, J.; Francis, M.; Malgwi, H. Serological survey of brucellosis among internally displaced persons in Maiduguri, North eastern Nigeria. Sokoto J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 16, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, M.A.; Ajogi, I.; Bale, J.O.O.; Mosimabale, F.B.; Tijjani, A.N.; Kaikabo, A.A. Serological survey of antibodies against Brucella organism in one-humped camels (Camelus dromedarius) in Lake Chad area of Borno state, North-eastern Nigeria. Nig. Vet. J. 2011, 32, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Audu, Y.; Maikai, B.V.; Okolocha, E.C. Survey for Brucella antibodies in dogs in Billiri local government area of Gombe State, Nigeria. Sci. Res. J. 2018, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, S.G.; Atsanda, N.N.; Tijjani, A.O.; Usur, A.M.; Sule, A.G.; Gulani, I.A. Epidemiological study of bovine brucellosis in three senatorial zones of Bauchi State, Nigeria. Vet. World 2016, 9, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Adamu, S.; Tijjani, A.; Adamu, N.; Atsanda, N.; Ali, S.; Gashua, M.; Simon, C. Seroprevalence of Brucellosis in one-humped camel (Camelus dromedarius) herds in Yobe State, Nigeria. Int. J. Livest. Res. 2014, 4, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, M.A.; Tijjani, A.-N.; Auwal, M.S.; Mustapha, A.R.; Gulani, I. Serological Prevalence of Brucellosis among Donkeys (Equus asinus) in Some Local Government Areas of Yobe State, Nigeria. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 2013, 33, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, N.B.; Adeniyi, S.O.; Adamu, S.G.; Bale, J.O.O.; Okoh, A.E.J.; Umaru, G.A.; Umar, Y.A. Seroprevalence of brucellosis among livestock workers at Maiduguri cattle market, Borno State, North-Eastern, Nigeria. J. Public Health Epidemiol. 2015, 7, 253–257. [Google Scholar]
- Igawe, P.B.; Okolocha, E.; Kia, G.S.; Irmiya, I.B.; Balogun, M.S.; Nguku, P.; Bugun, I.I. Seroprevalence of brucellosis and associated exposure factors among in Bauchi state, Nigeria. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2020, 35, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusi, A.M.; Ocholi, R.A.; Bertu, W.J.; Moses, H.; Ibrahim, L.; Mwankon, E.; Wungak, Y.; Woma, T.Y.; Wularamu, H.G.; Madu, G.A.; et al. Sero-prevalence of camel brucellosis in three abbatoirs of Nothern Nigeria. J. Vet. Med. Anim. Health 2016, 8, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, M.; Mshelia, G.D.; Adamu, N.; Ouda, L.; Egwu, G.O. Studies on farmer awareness on caprine abortion and the presence of Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis in selected flocks in an arid zone of Nigeria. J. Vet. Med. Anim. Health 2012, 4, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Junaidu, A.U.; Oboegbulem, S.I.; Salihu, M.D. Serological survey of Brucella antibodies in breeding herds. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Res. 2011, 11, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Nathaniel, J.; Kalla, D.J.U.; Mai, H.M.; Ibrahim, Y.; Mujitaba, M.A.; Amaduruonye, W.; Akinsola, K.L.; Obasi, E.N.; Suleiman, Y. Seroprevalence of brucellosis in donkeys (Equus asinus) and assessment of donkey management practices in Gamawa local government area, Bauchi state, Nigeria. Niger. J. Anim. Sci. 2019, 21, 134–144. [Google Scholar]
- Akinseye, V.O.; Adesokan, H.K.; Ogugua, A.J.; Adedoyin, F.J.; Otu, P.I.; Kwaghe, A.V.; Kolawole, N.O.; Okoro, O.J.; Agada, C.; Tade, A.O.; et al. Sero-epidemiological survey and risk factors associated with bovine brucellosis among slaughtered cattle in Nigeria. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2016, 83, 1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salisu, U.; Kudi, C.; Bale, J.; Babashani, M.; Kaltungo, B.; Saidu, S.; Asambe, A.; Baba, A. Seroprevalence of Brucella antibodies in camels in Katsina State, Nigeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, S.G.; Kabir, J.; Umoh, J.U.; Raji, M.A. Seroprevalence of brucellosis and Q fever (Coxiellosis) in cattle herds in Maigana and Birnin Gwari agro-ecological zone of Kaduna State, Nigeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltungo, B.Y.; Saidu, S.N.A.; Sackey, A.K.B.; Kazeem, H.M. Serological Evidence of Brucellosis in Goats in Kaduna North Senatorial District of Kaduna State, Nigeria. ISRN Vet. Sci. 2013, 2013, 963673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Obiako, O.R.; Ogoina, D.; Danbauchi, S.S.; Kwaifa, S.I.; Chom, N.D.; Nwokorie, E. Neurobrucellosis—a case report and review of literature. Niger. J. Clin. Pract. 2010, 13, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, F.U.; Ibrahim, S.; Ajogi, I.; Olaniyi, B.J.O. Prevalence of Bovine Brucellosis and Risk Factors Assessment in Cattle Herds in Jigawa State. ISRN Vet. Sci. 2011, 27, 132897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junaidu, A.U.; Salihu, M.D.; Gulumbe, M.L. Seroprevalence of Brucellosis in sheep in Sokoto city abattoir. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2006, 9, 2696–2698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Buhari, H.U.; Sn, A.S.; Mohammed, G.; Raji, M.A. Serological evaluation of bovine brucellosis in the North Senatorial District of Kaduna State, Nigeria. Int. J. Vet. Sci. 2016, 5, 24–28. [Google Scholar]
- Onoja, I.I.; Mshelia, W.P.; Andrew, A.; Usman, B.; Sambo, K.W. A Case of Brucellosis in a One and Half-year-old Uda Sheep in Zaria. Sahel J. Vet. Sci. 2012, 11, 7–10. [Google Scholar]
- Junaidu, A.U.; Garba, B. Seroprevalence of Brucella antibodies in horses in Sokoto metropolis, Nigeria. J. Anim. Sci. Vet. Med. 2019, 4, 173–177. [Google Scholar]
- Adesiyun, A.G.; Folagbade, O.B.; Olayinka, A.T.; Randawa, A.; Bawa, U. Seroprevalence of brucellosis among women with miscarriage at Ahmadu Bello University Teaching Hospital, Zaria. Trop. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2017, 34, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu’Aibu, G.; Kabir, J.; Umoh, J.; Raji, M.; Tijjani, A.; Umaru, G. Seroprevalence of Brucellosis in sheep in Maigana and Birnin Gwari agro-ecological zones of Kaduna State, Nigeria. Niger. Vet. J. 2018, 39, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, F.; Ibrahim, S.; Musa, G.; Kaltungo, B.; Danbirni, S.; Kwaga, J. Brucella infection in migratory cattle herds in Jigawa State Nigeria: A cross sectional study. Sokoto J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 14, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onoja, I.I.; Ajani, A.J.; Mshelia, W.P.; Andrew, A.; Ogunkoya, A.B.; Achi, C.R.; Sambo, K.W. Brucellosis outbreak in a flock of seventeen sheep in Zaria. Sokoto J. Vet. Sci. 2008, 7, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Cadmus, S.; Salam, S.P.; Adesokan, H.K.; Akporube, K.; Ola-Daniel, F.; Awosanya, E.J. Seroprevalence of brucellosis and Q fever infections amongst pastoralists and their cattle herds in Sokoto State, Nigeria. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaltungo, B.; Saidu, S.; Kudi, C.; Isma’Il, M.; Jacob, R.; Salisu, U.; Baba, Y.; Buhari, H. Geo-spatial distribution of Brucella melitensis infection in selected local government areas of Katsina and Sokoto States, Nigeria. Niger. Vet. J. 2019, 40, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yusuf, Y.; Abdulrasheed, A. Survey on Bovine Brucellosis in Sokoto Metropolitan Abattoir, Nigeria. J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2019, 18, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junaidu, A.U.; Garba, H.S. Application of competitive ELISA (cELISA) Rose Bengal plate test (RBPT) and serum agglutination test (SAT) for detection of antibodies to Brucella infection in slaughter cattle in Sokoto, Nigeria. Sahel J. Vet. Sci. 2006, 5, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Buhari, H.; Saidu, S.; Kudi, C.; Okolocha, E.; Kaltungo, B. Seroprevalence of Brucella infection in small ruminants from two institutional farms and a slaughter slab in Zaria, Nigeria. Sokoto J. Vet. Sci. 2020, 18, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogo, R.; Maikai, B.V.; Musa, J.A.; Tizhe, J.Q. Brucella Prevalence in Goats and Farmers’ Awareness and Practices towards Brucella Infection in Giwa Area of Kaduna State Nigeria. Br. Microbiol. Res. J. 2016, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubairu, A.; Ardo, M.; Mai, H. Seroprevalence of ruminant brucellosis in three selected local government areas of Taraba state. Sokoto J. Vet. Sci. 2014, 12, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Farouk, U.M.; Bale, J.O.O.; Kwaga, J.K.P.; Abdullahi, U.S.; Ibrahim, S.; Madobi, I.S. Preliminary study on brucellosis in cattle in Jigawa state Nigeria. In Proceedings of the 54th Annual Congress of the Nigerian Veterinary Medical Association, Kaduna State, Nigeria, 7 November 2017; Nigerian Veterinary Association: Kano, Nigeria, 2017; pp. 66–71. [Google Scholar]
- Lawal, N.; Egwu, G.O.; Tambuwal, F.M.; Junaidu, A.U.; Abubakar, M.B.; Magaji, A.A.; Rabi’u, M.A.; Saulawa, M.A.; Mamuda, A.; Jibrin, M.S.; et al. Prevalence of Brucella abortus antibodies in bovine serum from gusau modern abattoir, Zamfara state, Nigeria. Sci. J. Microbiol. 2012, 1, 91–96. [Google Scholar]
- Kaltungo, B.Y.; Saidu, S.N.A.; Sackey, A.K.B.; Kazeem, H.M. Sero-prevalence of brucellosis in sheep in North Senatorial District of Kaduna State, Nigeria. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Dis. 2015, 5, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bale, J.O.O.; Nuru, S.; Addo, P.B.; Adeyinka, I.A. Bacteriological investigation of sheep and goats milk for brucellosis in government farms in Northern Nigeria. Niger. J. Anim. Prod. 2013, 30, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbuk, E.U.; Ajogi, I.; Bale, J.; Umoh, J.U. Prevalence of Brucella Antibodies in Migratory Fulani Cattle Herds in Kaduna State, Nigeria. Niger. Vet. J. 2011, 32, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Osinubi, M.; Ajogi, I.; Ehizibol, O. Brucella abortus agglutinins in dogs in Zaria, Nigeria. Niger. Vet. J. 2004, 25, 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekere, S.O.; Njoga, E.O.; Onunkwo, J.I.; Njoga, U.J. Brucella seropositivity in slaughter food animals and role of slaughterhouse workers in spread of Brucella infection in Southeast Nigeria. Vet. World 2018, 11, 1171–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anyaoha, C.O.; Majesty-Alukagberie, L.O.; Ugochukwu, I.C.I.; Nwanta, J.A.; Anene, B.M.; Oboegbulam, S.I. Seroprevalencia y factores de riesgo de la brucelosis en perros de los Estados Enugu y Anambra, Nigeria. Rev. Med. Vet. 2020, 1, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbodo, S.O.; Isiofia, O.P.; Uzodinma, B.A. Co-existence and seroprevalence of brucellosis in a malaria-endemic metropolis of south-eastern Nigeria. J. Exp. Res. 2016, 4, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Onunkwo, J.I.; Njoga, E.O.; Njoga, U.J.; Ezeokafor, E.; Ekere, S.O. Brucella seropositivity in chicken and risk factors for Brucella infection at the animal-human interface in Anambra State, Nigeria. Int. J. One Health 2018, 4, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onunkwo, J.; Njoga, E.; Nwanta, J.; Shoyinka, S.; Onyenwe, I.; Eze, J. Serological Survey of Porcine Brucella Infection in SouthEast, Nigeria. Niger. Vet. J. 2011, 32, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Njoga, E.O.; Onunkwo, J.I.; Ekere, S.O.; Njoga, U.J.; Okoro, W.N. Seroepidemiology of Equine Brucellosis and Role of Horse Carcass Processors in Spread of Brucella Infection in Enugu State, Nigeria. Int. J. Curr. Res. Rev. 2018, 10, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bello-Onaghise, G.; Vaikosen, S.E.; Evivie, S.E. Abortion cases in pig farms in Benin city and some surrounding communities in Edo State, Nigeria. Niger. J. Agri. Food Env. 2012, 8, 37–42. [Google Scholar]
- Owowo, E.E.; Antia, U.E.; Christopher, M.A.; Okon, I.E. Sero-Prevalence of Brucellosis among Nomadic Herdsmen, Abattoir and Livestock Workers in Niger-Delta Region, Nigeria. J. Biosci. Med. 2019, 7, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurice, N.A. Bacteriological and serological studies of bovine brucellosis in Obudu cattle ranch, Cross River State. Nigeria. Eur. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 3, 484–488. [Google Scholar]
- Cadmus, S.I.B.; Adesokan, H.K.; Ajala, O.O.; Odetokun, W.O.; Perrett, L.L.; Stack, J.A. Seroprevalence of Brucella abortus and B. canis in household dogs in southwestern Nigeria: A preliminary report. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2011, 82, 56–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayoola, M.C.; Akinseye, V.O.; Cadmus, E.; Awosanya, E.; Popoola, O.A.; Akinyemi, O.O.; Perrett, L.; Taylor, A.; Stack, J.; Moriyon, I.; et al. Prevalence of bovine brucellosis in slaughtered cattle and barriers to better protection of abattoir workers in Ibadan, South-Western Nigeria. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2017, 28, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukwueze, K.O.; Ishola, O.O.; Dairo, M.D.; Awosanya, E.J.; Cadmus, S.I. Seroprevalence of brucellosis and associated factors among livestock slaughtered in Oko-Oba abattoir, Lagos State, southwestern Nigeria. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2020, 36, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadmus, S.I.; Alabi, P.I.; Adesokan, H.K.; Dale, E.J.; Stack, J.A. Serological investigation of bovine brucellosis in three cattle production systems in Yewa Division, south-western Nigeria. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2013, 84, E1–E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayinmode, A.; Akinseye, V.; Schares, G.; Cadmus, S. Serological survey of toxoplasmosis, neosporosis, and brucellosis among cattle herds in Oyo State, south-western Nigeria. Afr. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 11, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadmus, S.; Adesokan, H.; Stack, J. The use of the milk ring test and rose bengal test in brucellosis control and eradication in Nigeria. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2008, 79, 113–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadmus, S.I.; Adesokan, H.K.; Adedokun, B.O.; Stack, J.A. Seroprevalence of bovine brucellosis in trade cattle slaughtered in Ibadan, Nigeria, from 2004–2006. J. S. Afr. Vet. Assoc. 2010, 81, 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Adeyemi, A.K. Survey of Brucellosis among People at Risk in Lagos, Nigeria. Master’s Dissertation, University of South Africa, Pretoria, South Africa, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cadmus, S.; Osikoya, I.; Adesokan, H. Brucellosis in trade cattle in Lagos state: An investigation of two Abattoirs. Niger. Vet. J. 2008, 29, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwala, D.G.; McCrindle, C.; Fasina, F.O.; Ijagbone, I. Abattoir characteristics and seroprevalence of bovine brucellosis in cattle slaughtered at Bodija Municipal Abattoir, Ibadan, Nigeria. J. Vet. Med. Anim. Health 2015, 7, 164–168. [Google Scholar]
- Ogugua, A.J.; Akinseye, V.O.; Cadmus, E.O.; Awosanya, E.A.J.; Alabi, P.I.; Idowu, O.S.; Akinade, S.A.; Dale, E.J.; Perrett, L.; Taylor, A.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors associated with bovine brucellosis in herds under extensive production system in southwestern Nigeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comfort, A.M.; Joseph, O.A.; Oluwatoyin, A.V.; Joshua, T.O.; Folusho, B.M.; Julianah, A.F.; Kehinde, A.H.; Olutayo, O.T.; Olusoji, A.J.; Ihuaku, O.P.; et al. Sero-epidemiological survey and risk factors associated with brucellosis in dogs in south-western Nigeria. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2016, 23, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadmus, S.; Ijagbone, I.; Oputa, H.; Adesokan, H.; Stack, J. Serological survey of Brucellosis in livestock animals and workers in Ibadan, Nigeria. Afr. J. Biomed. Res. 2009, 9, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, A.S.; Crump, L.; Greter, H.; Hattendorf, J.; Schelling, E.; Zinsstag, J. Clinical Manifestations of Human Brucellosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 6, e1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laine, C.G.; Wade, A.; Scott, H.M.; Krecek, R.C.; Arenas-Gamboa, A.M. Scoping review of brucellosis in Cameroon: Where do we stand, and where are we going? PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahariri, S.M.; Kitala, P.M.; Muchemi, G.M.; Njenga, K.; Nanyingi, M. Sero-prevalence and risk factors for human brucellosis in Marsabit county, Kenya (2014). PAMJ One Health 2021, 4, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehari, S.; Zerfu, B.; Desta, K. Prevalence and risk factors of human brucellosis and malaria among patients with fever in malaria-endemic areas, attending health institutes in Awra and Gulina district, Afar Region, Ethiopia. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tumwine, G.; Matovu, E.; Kabasa, J.D.; Owiny, D.O.; Majalija, S. Human brucellosis: Sero-prevalence and associated risk factors in agro-pastoral communities of Kiboga District, Central Uganda. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, M.S.; Zidan, S.A.A.; Hassan, N.A.A.; Elaadli, H.; Bayoumi, A.M. Seroprevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Brucellosis in Livestock and Residents of New Valley Governorate, Egypt. World’s Vet. J. 2020, 10, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagamiko, F.D.; Mfune, R.L.; Hang’Ombe, B.M.; Karimuribo, E.D.; Mwanza, A.M.; Sindato, C.; Muma, J.B. Seroprevalence of human Brucellosis and associated risk factors among high-risk occupations in Mbeya Region of Tanzania. J. Epidemiol. Res. 2020, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njeru, J.; Wareth, G.; Melzer, F.; Henning, K.; Pletz, M.W.; Heller, R.; Neubauer, H. Systematic review of brucellosis in Kenya: Disease frequency in humans and animals and risk factors for human infection. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bale, J.O.; Kumi-Diaka, J. Serological and bacteriological study of bovine Brucellae from livestock investigation and breeding centers in Nigeria. Br. Vet. J. 1981, 37, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gameel, S.E.A.M.; Mohamed, S.O.; Mustafa, A.A.; Azwai, S.M. Prevalence of camel brucellosis in Libya. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 1993, 25, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucero, N.E.; Ayala, S.M.; Escobar, G.I.; Jacob, N.R. Brucella isolated in humans and animals in Latin America from 1968 to 2006. Epidemiol. Infect. 2008, 136, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minharro, S.; Mol, J.P.S.; Dorneles, E.M.S.; Pauletti, R.B.; Neubauer, H.; Melzer, F.; Poester, F.P.; Dasso, M.G.; Pinheiro, E.S.; Filho, P.M.S.; et al. Biotyping and Genotyping (MLVA16) of Brucella abortus Isolated from Cattle in Brazil, 1977 to 2008. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e81152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanogo, M.; Thys, E.; Achi, Y.L.; Fretin, D.; Michel, P.; Abatih, E.; Berkvens, D.; Saegerman, C. Bayesian estimation of the true prevalence, sensitivity and specificity of the Rose Bengal and indirect ELISA tests in the diagnosis of bovine brucellosis. Vet. J. 2013, 195, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Li, J.-M.; Zeng, F.-L.; Zong, Y.; Leng, X.; Shi, K.; Diao, N.-C.; Li, D.; Li, B.-Y.; Zhao, Q.; et al. Prevalence and Risk Factors of Brucellosis, Chlamydiosis, and Bluetongue Among Sika Deer in Jilin Province in China. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2018, 18, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alton, G.G.; Jones, L.M.; Angus, R.D.; Verger, J.M. Techniques for the Brucellosis Laboratory; INRA: Paris, France, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Bricker, B.J.; Ewalt, D.R.; Halling, S.M. Brucella ‘HOOF-Prints’: Strain typing by multi-locus analysis of variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs). BMC Microbiol. 2003, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Flèche, P.; Jacques, I.; Grayon, M.; Al Dahouk, S.; Bouchon, P.; Denoeud, F.; Nöckler, K.; Neubauer, H.; Guilloteau, L.A.; Vergnaud, G. Evaluation and selection of tandem repeat loci for a Brucella MLVA typing assay. BMC Microbiol. 2006, 6, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, R. Emergency Prevention System for Transboundary Animal and Plant Pests and Diseases. In Guidelines for Coordinated Human and Animal Brucellosis Surveillance; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- World Organization for Animal Health (OIE). Bovine Brucellosis. In Manual of Diagnostic Test and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals; OIE: Paris, France, 2009; Chapter 2.4.3.; pp. 1–35. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, M.Z.; Zahoor, M. An Overview of Brucellosis in Cattle and Humans, and its Serological and Molecular Diagnosis in Control Strategies. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Region | State | No of Samples Tested | No of Positive Sample | Seroprevalence % | Detection Methods | Brucella Type | Reference | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBPT | SAT | cELISA | iELISA | IgM | IgG | IgG/IgM ELISA | Brucella spp. | Brucella abortus | Brucella melitensis | ||||||
| NC | Kwara | 189 | 42 | 22.2% | 42 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 42 | 0 | 0 | [19] |
| Abuja | 224 | 40 | 17.9% | 40 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 22 | 18 | 0 | 40 | 0 | 0 | [30] | |
| Nasarawa | 160 | 16 | 10% | 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 16 | 0 | 0 | [31] | |
| Total | 573 | 98 | 17.1% | 98 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 22 | 18 | 0 | 98 | 0 | 0 | ||
| NE | Bauchi | 285 | 95 | 33.3% | 95 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 18 | 0 | 95 | 0 | 0 | [57] |
| Not indicated | 500 | 26 | 5.2% | 26 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 26 | 0 | 0 | [45] | |
| Borno | 106 | 4 | 3.8% | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | [50] | |
| Borno | 100 | 11 | 11% | 11 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 0 | [56] | |
| Total | 990 | 136 | 13.7% | 136 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 18 | 0 | 125 | 11 | 0 | ||
| NW | Kaduna | 1 | 1 | 100% | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | [66] |
| Kaduna | 100 | 19 | 19% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 0 | [72] | |
| Sokoto | 137 | 1 | 0.7% | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | [76] | |
| Total | 238 | 21 | 8.8% | 1 | 1 | 0 | 19 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19 | 2 | 0 | ||
| SE | Enugu | 682 | 195 | 28.6% | 195 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 195 | 0 | 0 | [91] |
| Total | 682 | 195 | 28.6% | 195 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 195 | 0 | 0 | ||
| SS | Akwa Ibom | 228 | 70 | 30.7% | 29 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 41 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 70 | [96] |
| Total | 228 | 70 | 30.7% | 29 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 41 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 70 | ||
| SW | Lagos | 422 | 27 | 6.4% | 27 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 27 | 0 | 0 | [105] |
| Oyo | 11 | 7 | 63.6% | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | [110] | |
| Total | 433 | 34 | 7.9% | 34 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 34 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Grand Total | 3144 | 554 | 17.6% | 493 | 1 | 0 | 22 | 28 | 77 | 0 | 471 | 13 | 70 | ||
| Animal | Variable | The Six Geopolitical Zones in Nigeria | Total Nationwide | National Prevalence % | Odd Ratio | 95% CL | Z Statistics | p-Value | Number of Publications | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NC | NE | NW | SE | SS | SW | |||||||||
| Cattle | Sample screened | 3213 | 5253 | 19,648 | 1567 | 369 | 12,458 | 42,508 | 12.2% | 0.1390 | 0.1346 to 0.1435 | 120.853 | <0.0001 | 43 |
| + ve samples | 277 | 1154 | 2617 | 51 | 151 | 937 | 5187 | |||||||
| Regional prevalence | 8.6% | 22% | 13.3% | 3.3% | 40.9% | 7.5% | ||||||||
| Donkey | Sample screened | 0 | 2101 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2101 | 10.2% | 0.2427 | 0.2046 to 0.2879 | 16.247 | <0.0001 | 4 |
| + ve samples | 0 | 215 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 215 | |||||||
| Regional prevalence | 0% | 10.2% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | ||||||||
| Camel | Sample screened | 0 | 1267 | 1192 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2459 | 20.9% | 0.2024 | 0.1796 to 0.2281 | 26.196 | <0.0001 | 5 |
| + ve samples | 0 | 398 | 116 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 514 | |||||||
| Regional prevalence | 0% | 31.4% | 9.7% | 0% | 0% | 0% | ||||||||
| Horse | Sample screened | 86 | 100 | 400 | 402 | 0 | 0 | 988 | 10.7% | 0.0941 | 0.0729 to 0.1214 | 18.190 | <0.0001 | 8 |
| + ve samples | 24 | 16 | 54 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 106 | |||||||
| Regional prevalence | 27.9% | 16% | 13.5% | 3% | 0% | 0% | ||||||||
| Goat | Sample screened | 2134 | 831 | 2191 | 340 | 0 | 2813 | 8309 | 10.2% | 0.1013 | 0.0931 to 0.1102 | 53.357 | <0.0001 | 20 |
| + ve samples | 410 | 75 | 303 | 12 | 0 | 46 | 846 | |||||||
| Regional prevalence | 19.2% | 9% | 13.8% | 3.5% | 0% | 1.6% | ||||||||
| Sheep | Sample screened | 1308 | 57 | 2449 | 0 | 0 | 94 | 3908 | 23.3% | 0.2831 | 0.2569 to 0.3119 | 25.465 | <0.0001 | 22 |
| + ve samples | 322 | 14 | 562 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 912 | |||||||
| Regional prevalence | 24.6% | 24.6% | 22.9% | 0% | 0% | 14.9% | ||||||||
| Pig | Sample screened | 369 | 0 | 0 | 351 | 55 | 200 | 975 | 18.7% | 0.1731 | 0.1420 to 0.2110 | 17.371 | <0.0001 | 5 |
| + ve samples | 125 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 55 | 0 | 182 | |||||||
| Regional prevalence | 34% | 0% | 0% | 0.6% | 100% | 0% | ||||||||
| Chicken | Sample screened | 275 | 730 | 0 | 410 | 0 | 140 | 1555 | 8.4% | 0.0298 | 0.0213 to 0.0417 | 20.498 | <0.0001 | 3 |
| + ve samples | 10 | 18 | 0 | 14 | 0 | 5 | 47 | |||||||
| Regional prevalence | 3.6% | 2.5% | 0% | 3.4% | 0% | 3.6% | ||||||||
| Dog | Sample screened | 492 | 374 | 200 | 123 | 0 | 1102 | 2291 | 19.4% | 0.2337 | 0.2037 to 0.2680 | 20.767 | <0.0001 | 8 |
| + ve samples | 115 | 76 | 43 | 34 | 0 | 176 | 444 | |||||||
| Regional prevalence | 23.4% | 20.3% | 21.5% | 27.6% | 0% | 16% | ||||||||
| Region | Types of Animals | Types of Samples Investigated | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood | Milk | Vaginal Swab | Hygroma Fluid | Aborted Foetus | Lymph Node | ||||||||
| No Tested | +ve Sample | Not Tested | +ve Sample | No Tested | +ve Sample | No Tested | +ve Sample | No Tested | +ve Sample | No Tested | +ve Sample | ||
| NC | Cattle | 2397 | 212 | 428 | 52 | 374 | 11 | 4 | 1 | 10 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Donkey | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Camel | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Horse | 77 | 20 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Goat | 2099 | 410 | 18 | 0 | 17 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Sheep | 1242 | 322 | 20 | 0 | 44 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pig | 366 | 125 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Chicken * | 275 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Dog | 483 | 115 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 6939 | 1214 | 470 | 52 | 443 | 14 | 5 | 2 | 20 | 1 | 0 | 0 | |
| NE | Cattle | 5047 | 1120 | 144 | 27 | 56 | 3 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Donkey | 2101 | 215 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Camel | 1267 | 398 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Horse | 100 | 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Goat | 831 | 75 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Sheep | 28 | 4 | 8 | 7 | 21 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pig | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Chicken * | 730 | 18 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Dog | 374 | 76 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 10,478 | 1922 | 152 | 34 | 77 | 6 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| NW | Cattle | 16,008 | 2456 | 3307 | 111 | 161 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 170 | 50 |
| Donkey | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Camel | 1192 | 116 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Horse | 400 | 54 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Goat | 1937 | 214 | 254 | 89 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| Sheep | 2248 | 522 | 201 | 40 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pig | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Chicken * | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Dog | 200 | 43 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 21,985 | 3405 | 3762 | 240 | 161 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 170 | 50 | |
| SE | Cattle | 1566 | 51 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Donkey | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Camel | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Horse | 402 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Goat | 340 | 12 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Sheep | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pig | 351 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Chicken * | 410 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Dog | 123 | 34 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 3192 | 125 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| SS | Cattle | 354 | 149 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Donkey | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Camel | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Horse | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Goat | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Sheep | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pig | 30 | 81 | 0 | 0 | 25 | 68 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Chicken * | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Dog | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 384 | 230 | 0 | 0 | 39 | 69 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| SW | Cattle | 11,234 | 689 | 1224 | 248 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Donkey | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Camel | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Horse | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Goat | 2813 | 46 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Sheep | 94 | 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pig | 200 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Chicken * | 140 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Dog | 1102 | 176 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Total | 15,583 | 930 | 1224 | 248 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Grand Total | 58,561 | 7826 | 5608 | 574 | 720 | 89 | 14 | 7 | 20 | 1 | 170 | 50 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Akinyemi, K.O.; Fakorede, C.O.; Amisu, K.O.; Wareth, G. Human and Animal Brucellosis in Nigeria: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis in the Last Twenty-One Years (2001–2021). Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9080384
Akinyemi KO, Fakorede CO, Amisu KO, Wareth G. Human and Animal Brucellosis in Nigeria: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis in the Last Twenty-One Years (2001–2021). Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(8):384. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9080384
Chicago/Turabian StyleAkinyemi, Kabiru O., Christopher O. Fakorede, Kehinde O. Amisu, and Gamal Wareth. 2022. "Human and Animal Brucellosis in Nigeria: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis in the Last Twenty-One Years (2001–2021)" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 8: 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9080384
APA StyleAkinyemi, K. O., Fakorede, C. O., Amisu, K. O., & Wareth, G. (2022). Human and Animal Brucellosis in Nigeria: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis in the Last Twenty-One Years (2001–2021). Veterinary Sciences, 9(8), 384. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9080384







