Diagnosis and Prognosis of Canine Melanocytic Neoplasms
Abstract
1. Introduction
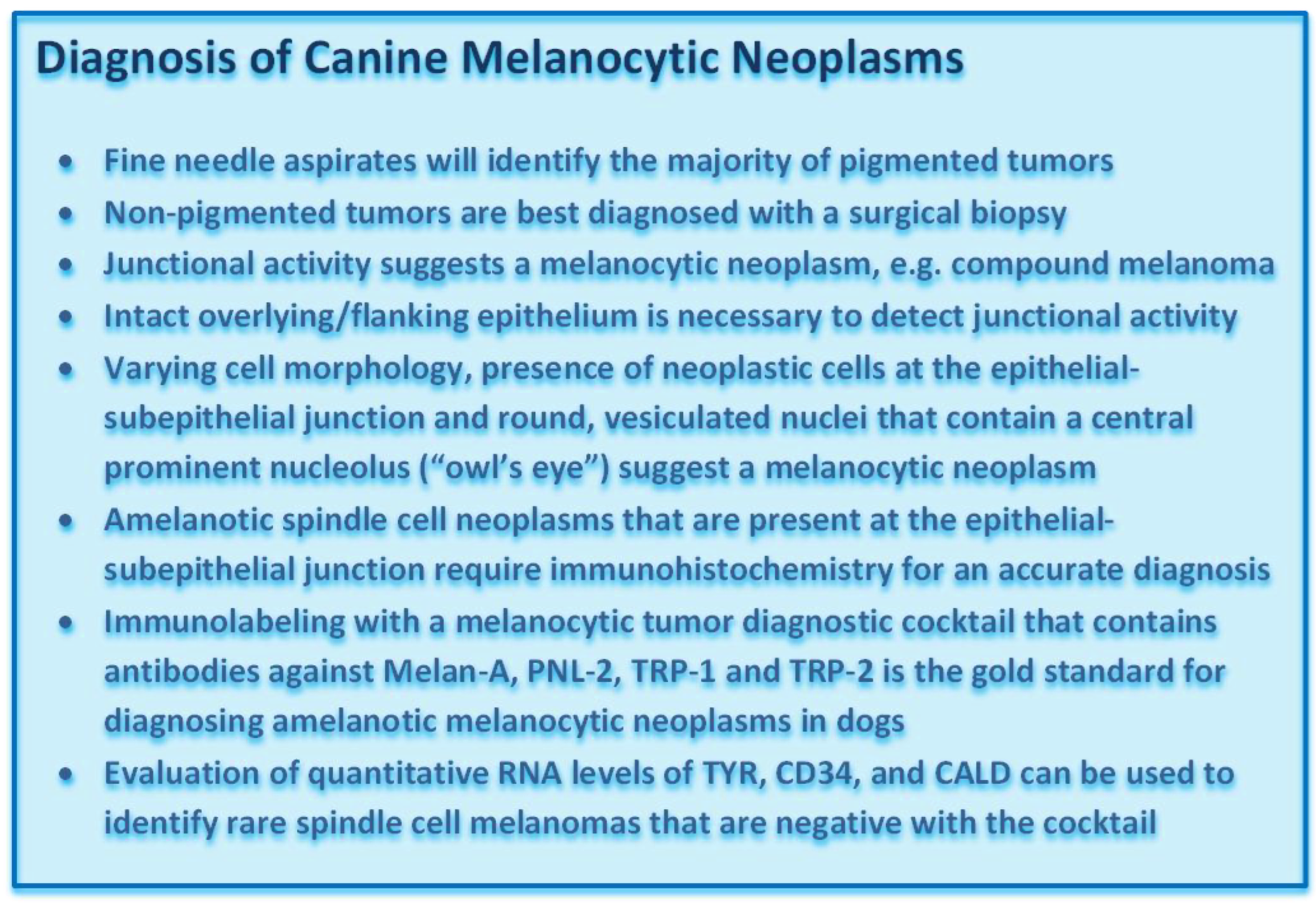
2. Diagnosis of Canine Melanocytic Neoplasms
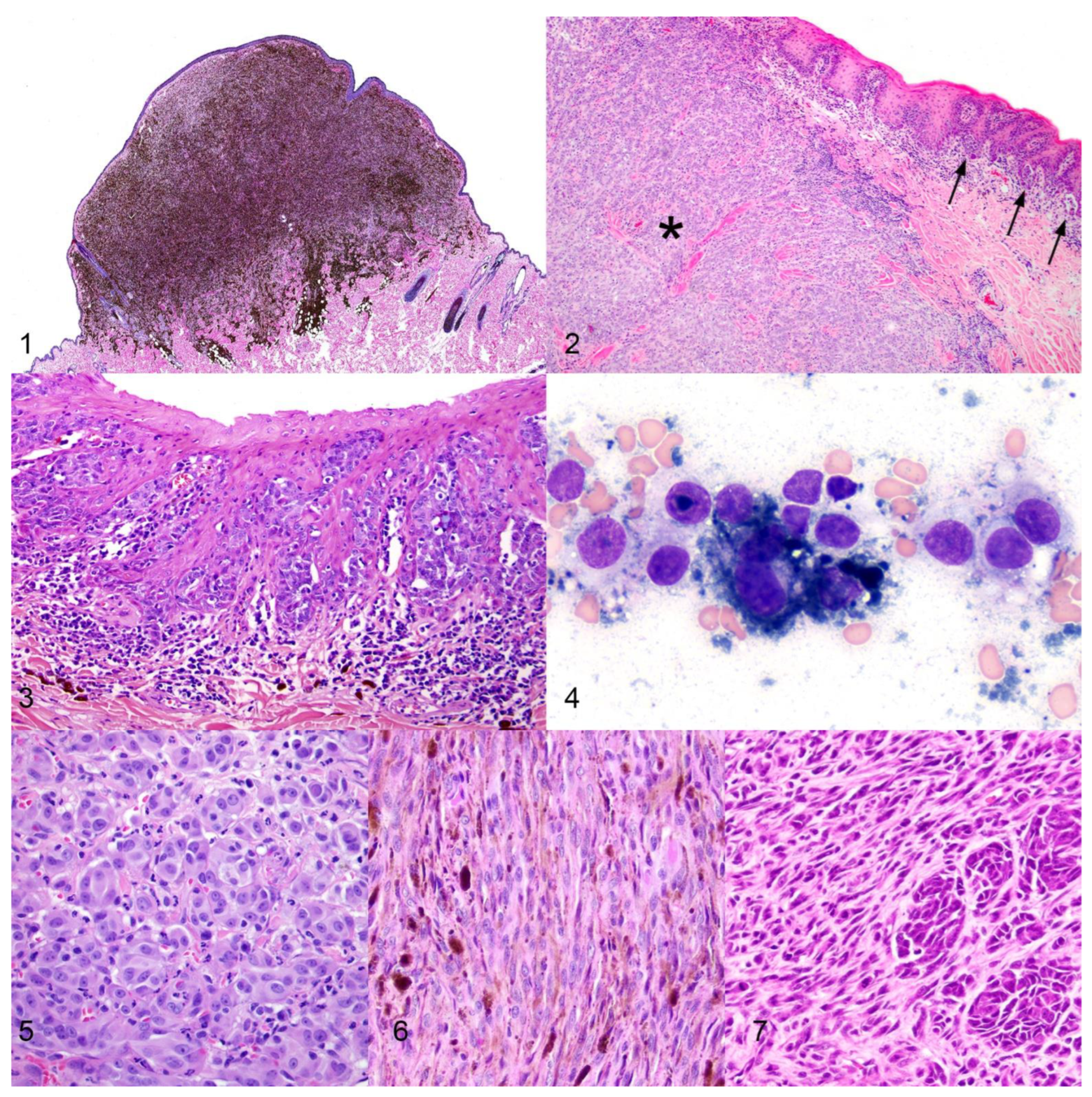
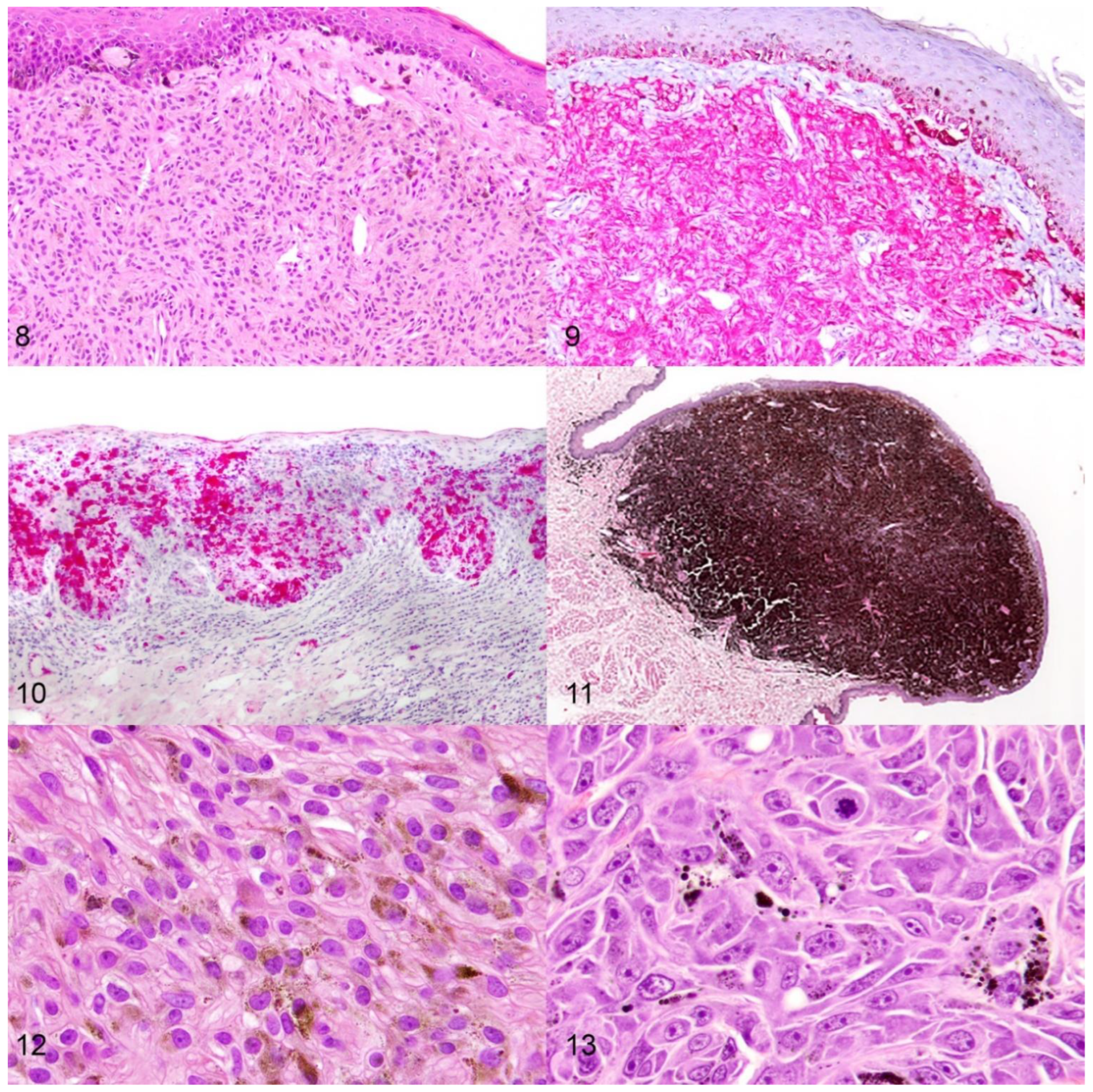
3. Prognosis of Canine Melanocytic Neoplasms
3.1. Signalment
3.2. Location
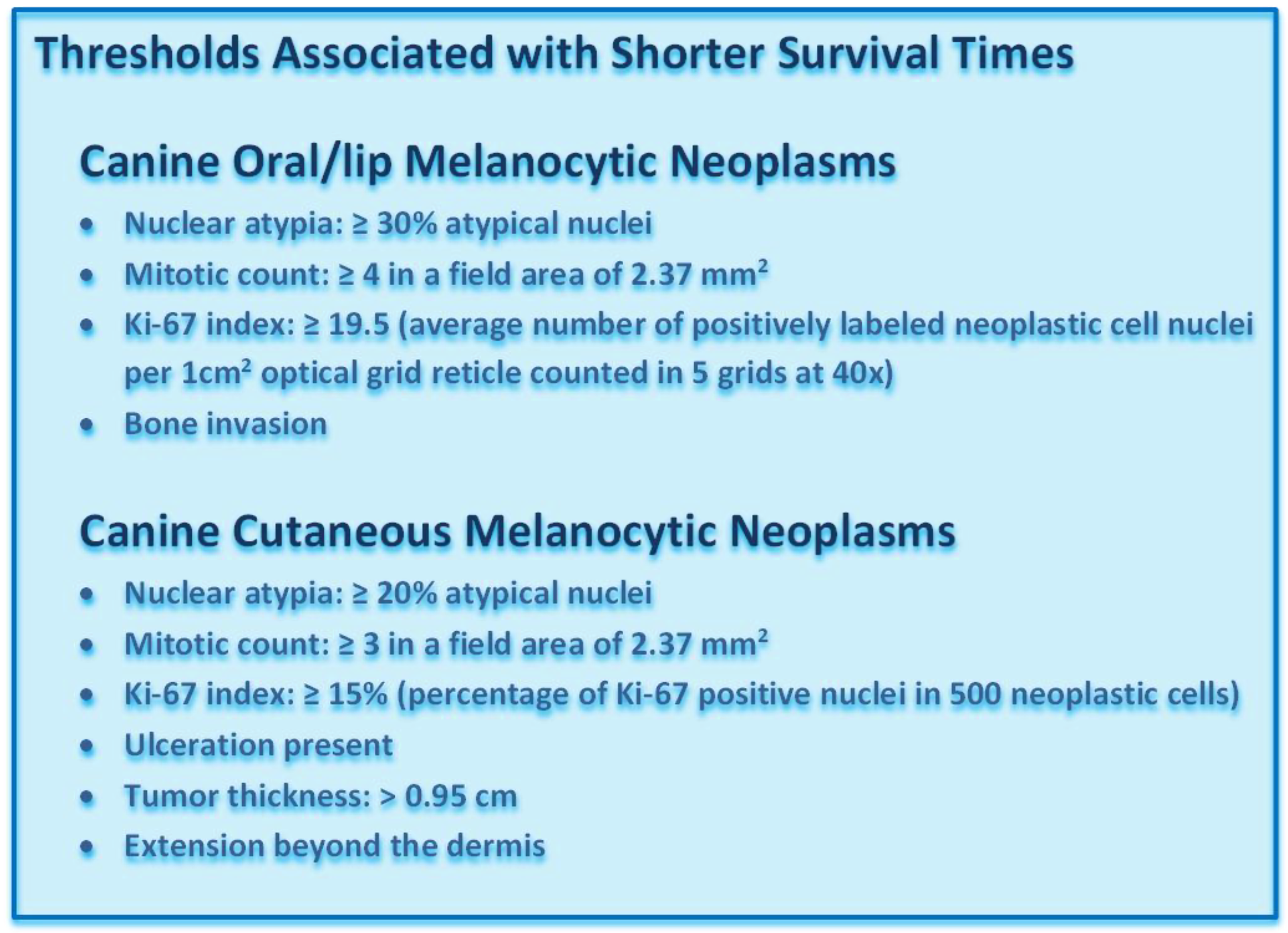
3.3. Histologic Parameters
3.3.1. Nuclear Atypia
3.3.2. Mitotic Count
3.3.3. Pigmentation
3.3.4. Level of Infiltration
3.3.5. Vascular Invasion
3.3.6. Ulceration
3.3.7. Tumor Thickness

3.4. Molecular Parameters
Ki-67 Index
3.5. Margin Evaluation
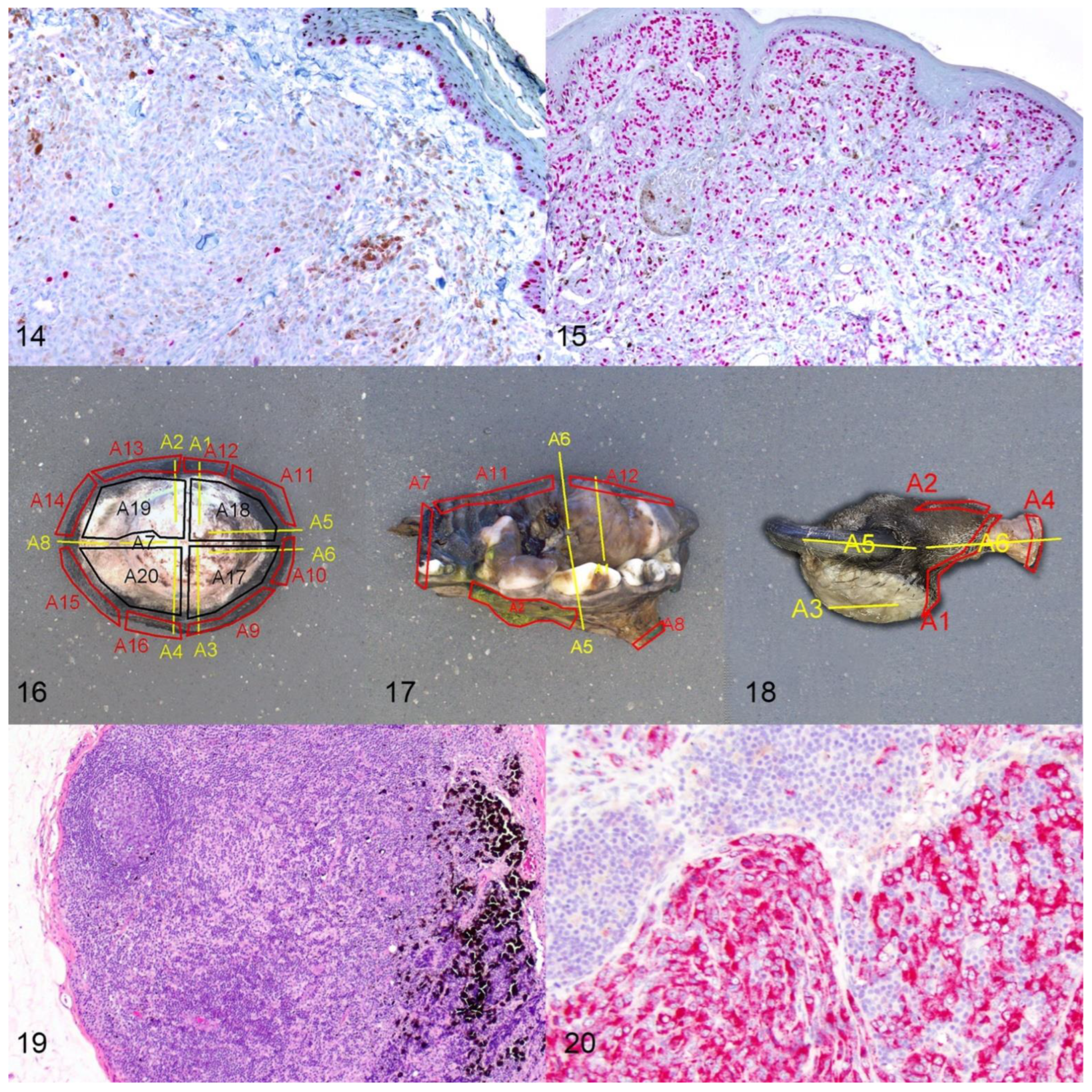

3.6. Lymph Node Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobson, J.M.; Samuel, S.; Milstein, H.; Rogers, K.; Wood, J.L. Canine neoplasia in the UK: Estimates of incidence rates from a population of insured dogs. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2002, 43, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todoroff, R.J.; Brodey, R.S. Oral and pharyngeal neoplasia in the dog: A retrospective survey of 361 cases. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 1979, 175, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smedley, R.C.; Lamoureux, J.; Sledge, D.G.; Kiupel, M. Immunohistochemical Diagnosis of Canine Oral Amelanotic Melanocytic Neoplasms. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergman, P.J. Canine Oral Melanoma. Clin. Tech. Small Anim. Pract. 2007, 22, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacroux, C.; Raymond-Letron, I.; Bourges-Abella, N.; Lucas, M.N.; Deviers, A.; Serra, F.; Degorce-Rubiales, F.; Delverdier, M. Study of canine cutaneous melanocytic tumours: Evaluation of histological and immunohistochemical prognostic criteria in 65 cases. Rev. Med. Vet. 2012, 163, 393–401. [Google Scholar]
- Laver, T.; Feldhaeusser, B.R.; Robat, C.S.; Baez, J.L.; Cronin, K.L.; Buracco, P.; Annoni, M.; Regan, R.C.; McMillan, S.K.; Curran, K.M.; et al. Post-surgical outcome and prognostic factors in canine malignant melanomas of the haired skin: 87 cases (2003–2015). Can. Vet. J. 2018, 59, 981–987. [Google Scholar]
- Munday, J.; Kiupel, M.; Loehr, C. Tumors of the Alimentary Tract. In Tumors of Domestic Animals, 5th ed.; Meuten, D.J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: Ames, IA, USA, 2017; pp. 515–524. [Google Scholar]
- Proulx, D.R.; Dvm, D.M.R.; Ms, R.K.D.; Hauck, M.L.; Dvm, L.E.W.; Horn, B.; Dvm, G.S.P.; Thrall, D.E. A Retrospective Analysis of 140 Dogs with Oral Melanoma Treated with External Beam Radiation. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2003, 44, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, R.C.; Spangler, W.L.; Esplin, D.G.; Kitchell, B.E.; Bergman, P.J.; Ho, H.-Y.; Bergin, I.L.; Kiupel, M. Prognostic Markers for Canine Melanocytic Neoplasms: A comparative review of the literature and goals for future investigation. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 54–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.M.; Bastian, B.; Michael, H.; Webster, J.D.; Prasad, M.L.; Conway, C.M.; Prieto, V.M.; Gary, J.M.; Goldschmidt, M.; Esplin, D.G.; et al. Sporadic naturally occurring melanoma in dogs as a preclinical model for human melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014, 27, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.H.; Goldschmidt, M.; McManus, P.M. A Comparative Review of Melanocytic Neoplasms. Vet. Pathol. 2002, 39, 651–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smedley, R.C.; Thaiwong, T.; Deeth, L.E.; Kiupel, M. Correlation Between KIT Expression and c-Kit Mutations in 2 Subtypes of Canine Oral Melanocytic Neoplasms. Vet. Pathol. 2021, 58, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghisleni, G.; Roccabianca, P.; Ceruti, R.; Stefanello, D.; Bertazzolo, W.; Bonfanti, U.; Caniatti, M. Correlation between fine-needle aspiration cytology and histopathology in the evaluation of cutaneous and subcutaneous masses from dogs and cats. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 35, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, G.L.; Lumsden, J.H.; Valli, V.E. Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology and Histologic Correlation in Canine Tumors. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 1984, 13, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Przeździecki, R.; Czopowicz, M.; Sapierzyński, R. Accuracy of routine cytology and immunocytochemistry in preoperative diagnosis of oral amelanotic melanomas in dogs. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 2015, 44, 597–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostock, D.E. Prognosis after Surgical Excision of Canine Melanomas. Vet. Pathol. 1979, 16, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyamada, T.; Tanaka, H.; Park, C.-H.; Ueki, H.; Komiya, T.; Arai, S. Pathology of Canine Oral Malignant Melanoma with Cartilage and/or Osteoid Formation. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2007, 69, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tsoi, M.F.; Thaiwong, T.; Smedley, R.C.; Noland, E.; Kiupel, M. Quantitative Expression of TYR, CD34, and CALD1 Discriminates Between Canine Oral Malignant Melanomas and Soft Tissue Sarcomas. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 701457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, C.; Kusewitt, D.F. Comparison of Tyrosinase-related Protein-2, S-100, and Melan A Immunoreactivity in Canine Amelanotic Melanomas. Vet. Pathol. 2003, 40, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudice, C.; Ceciliani, F.; Rondena, M.; Stefanello, D.; Grieco, V. Immunohistochemical investigation of PNL2 reactivity of canine melanocytic neoplasms and comparison with Melan, A. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2010, 22, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Vara, J.A.; Miller, M.A.; Johnson, G.C.; Turnquist, S.E.; Kreeger, J.M.; Watson, G.L. Melan A and S100 protein immunohistochemistry in feline melanomas: 48 cases. Vet. Pathol. 2002, 39, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos-Vara, J.A.; Beissenherz, M.E.; Miller, M.A.; Johnson, G.C.; Pace, L.W.; Fard, A.; Kottler, S.J. Retrospective Study of 338 Canine Oral Melanomas with Clinical, Histologic, and Immunohistochemical Review of 129 Cases. Vet. Pathol. 2000, 37, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergin, I.L.; Smedley, R.C.; Esplin, D.G.; Spangler, W.L.; Kiupel, M. Prognostic Evaluation of Ki67 Threshold Value in Canine Oral Melanoma. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolon, B.; Hall, B.J.; Mays, M.B.C. Characteristics of Canine Melanomas and Comparison of Histology and DNA Ploidy to Their Biologic Behavior. Vet. Pathol. 1990, 27, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spangler, W.L.; Kass, P.H. The Histologic and Epidemiologic Bases for Prognostic Considerations in Canine Melanocytic Neoplasia. Vet. Pathol. 2006, 43, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcellato, I.; Silvestri, S.; Menchetti, L.; Dvm, F.R.; Mechelli, L.; Sforna, M.; Iussich, S.; Bongiovanni, L.; Lepri, E.; Brachelente, C. Tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes in canine melanocytic tumours: An investigation on the prognostic role of CD3+ and CD20+ lymphocytic populations. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2020, 18, 370–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esplin, D.G. Survival of Dogs Following Surgical Excision of Histologically Well-differentiated Melanocytic Neoplasms of the Mucous Membranes of the Lips and Oral Cavity. Vet. Pathol. 2008, 45, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuten, D.J.; Moore, F.M.; George, J.W. Mitotic Count and the Field of View Area: Time to standardize. Vet. Pathol. 2015, 53, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meuten, D.J.; Moore, F.M.; Donovan, T.A.; Bertram, C.A.; Klopfleisch, R.; Foster, R.A.; Smedley, R.C.; Dark, M.J.; Milovancev, M.; Stromberg, P.; et al. International Guidelines for Veterinary Tumor Pathology: A Call to Action. Vet. Pathol. 2021, 58, 766–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laprie, C.; Abadie, J.; Amardeilh, M.; Net, J.; Lagadic, M.; Delverdier, M. MIB-1 immunoreactivity correlates with biologic behaviour in canine cutaneous melanoma. Vet. Dermatol. 2001, 12, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, I.; Chung, T.F.; Huang, W.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Liu, C.C.; Chiu, Y.H.; Huang, K.C.; Liao, A.T.; Lin, C.S. Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO), and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) expression is involved in tumour proliferation and predicts poor survival in canine melanoma. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2021, 19, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porcellato, I.L.; Brachelente, C.; Cappelli, K.; Menchetti, L.; Silvestri, S.; Sforna, M.; Mecocci, S.; Iussich, S.; Leonardi, L.; Mechelli, L. FoxP3, CTLA-4, and IDO in Canine Melanocytic Tumors. Vet. Pathol. 2021, 58, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prouteau, A.; Chocteau, F.; De Brito, C.; Cadieu, E.; Primot, A.; Botherel, N.; Degorce, F.; Cornevin, L.; Lagadic, M.A.; Cabillic, F.; et al. Prognostic value of somatic focal amplifications on chromosome 30 in canine oral melanoma. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2020, 18, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestri, S.; Porcellato, I.; Mechelli, L.; Menchetti, L.; Rapastella, S.; Brachelente, C. Tumor Thickness and Modified Clark Level in Canine Cutaneous Melanocytic Tumors. Vet. Pathol. 2018, 56, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, T.H.M.; Pulz, L.H.; Ferro, D.G.; Sobral, R.A.; Venturini, M.A.F.A.; Corrêa, H.L.; Strefezzi, R.F. Galectin-3 Expression Correlates with Post-surgical Survival in Canine Oral Melanomas. J. Comp. Pathol. 2019, 173, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongiovanni, L.; D’Andrea, A.; Porcellato, I.; Ciccarelli, A.; Malatesta, D.; Romanucci, M.; Della Salda, L.; Mechelli, L.; Brachelente, C. Canine cutaneous melanocytic tumours: Significance of β-catenin and survivin immunohistochemical expression. Vet. Dermatol. 2015, 26, 270-e59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camerino, M.; Giacobino, D.; Manassero, L.; Iussich, S.; Riccardo, F.; Cavallo, F.; Tarone, L.; Olimpo, M.; Lardone, E.; Martano, M.; et al. Prognostic impact of bone invasion in canine oral malignant melanoma treated by surgery and anti-CSPG4 vaccination: A retrospective study on 68 cases (2010–2020). Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2022, 20, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roels, S.; Tilmant, K.; Ducatelle, R. PCNA and Ki67 Proliferation Markers as Criteria for Prediction of Clinical Behaviour of Melanocytic Tumours in Cats and Dogs. J. Comp. Pathol. 1999, 121, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagne, C.; Julé, S.; Alleaume, C.; Bernex, F.; Ezagal, J.; Château-Joubert, S.; Estrada, M.; Aubin-Houzelstein, G.; Panthier, J.-J.; Egidy, G. Canine Melanoma Diagnosis: RACK1 as a potential biological marker. Vet. Pathol. 2013, 50, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iussich, S.; Maniscalco, L.; Di Sciuva, A.; Iotti, B.; Morello, E.; Martano, M.; Gattino, F.; Buracco, P.; De Maria, R. PDGFRs expression in dogs affected by malignant oral melanomas: Correlation with prognosis. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2017, 15, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamstock, D.A.; Ehrhart, E.J.; Getzy, D.M.; Bacon, N.J.; Rassnick, K.M.; Moroff, S.D.; Liu, S.M.; Straw, R.C.; McKnight, C.A.; Amorim, R.L.; et al. Recommended Guidelines for Submission, Trimming, Margin Evaluation, and Reporting of Tumor Biopsy Specimens in Veterinary Surgical Pathology. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herring, E.S.; Smith, M.M.; Robertson, J.L. Lymph Node Staging of Oral and Maxillofacial Neoplasms in 31 Dogs and Cats. J. Vet. Dent. 2002, 19, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimes, J.A.; Mestrinho, L.A.; Berg, J.; Cass, S.; Oblak, M.L.; Murphy, S.; Amsellem, P.M.; Brown, P.; Hamaide, A.; Matz, B.M. Histologic evaluation of mandibular and medial retropharyngeal lymph nodes during staging of oral malignant melanoma and squamous cell carcinoma in dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med Assoc. 2019, 254, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skinner, O.T.; Boston, S.E.; Souza, C.H.D.M. Patterns of lymph node metastasis identified following bilateral mandibular and medial retropharyngeal lymphadenectomy in 31 dogs with malignancies of the head. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2017, 15, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, L.E.; Packer, R.A. Association between lymph node size and metastasis in dogs with oral malignant melanoma: 100 cases (1987–2001). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2003, 222, 1234–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Congiusta, M.; Lawrence, J.; Rendahl, A.; Goldschmidt, S. Variability in Recommendations for Cervical Lymph Node Pathology for Staging of Canine Oral Neoplasia: A Survey Study. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, J.A.; Secrest, S.A.; Wallace, M.L.; Laver, T.; Schmiedt, C.W. Use of indirect computed tomography lymphangiography to determine metastatic status of sentinel lymph nodes in dogs with a pre-operative diagnosis of melanoma or mast cell tumour. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2020, 18, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willcox, J.L.; Spriet, M.; Zwingenberger, A.L.; Phillips, K.L.; Burton, J.H.; Skorupski, K.A.; Hansen, K.S.; Affolter, V.K.; Woolard, K.D.; Beylin, D.; et al. Evaluation of accuracy for 18 F-FDG positron emission tomography and computed tomography for detection of lymph node metastasis in canine oral malignant melanoma. Vet. Comp. Oncol. 2021, 19, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimes, J.A.; Matz, B.M.; Christopherson, P.W.; Koehler, J.W.; Cappelle, K.K.; Hlusko, K.C.; Smith, A. Agreement Between Cytology and Histopathology for Regional Lymph Node Metastasis in Dogs With Melanocytic Neoplasms. Vet. Pathol. 2017, 54, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.L.; Balch, C.M.; Hurley, P.; Agarwala, S.S.; Akhurst, T.J.; Cochran, A.; Cormier, J.N.; Gorman, M.; Kim, T.Y.; McMasters, K.M.; et al. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy for Melanoma: American Society of Clinical Oncology and Society of Surgical Oncology Joint Clinical Practice Guideline. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 19, 3313–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhn, A.K.; Brambs, C.E.; Erber, R.; Hiller, G.G.R.; Mayr, D.; Schmidt, D.; Schmoeckel, E.; Horn, L.C. Reporting and handling of lymphonodectomy specimens in gynecologic malignancies and sentinel lymph nodes. Pathologe 2021, 42, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, D.L.; Le, U.P.; Dupuis, S.L.; Weaver, K.A.; Harlow, S.P.; Ashikaga, T.; Krag, D.N. Metastasis Detection in Sentinel Lymph Nodes: Comparison of a Limited Widely Spaced (NSABP Protocol B-32) and a Comprehensive Narrowly Spaced Paraffin Block Sectioning Strategy. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2009, 33, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiupel, M.; Camus, M. Diagnosis and Prognosis of Canine Cutaneous Mast Cell Tumors. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2019, 49, 819–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grindem, C.B. What Is Your Diagnosis? Lymph node aspirate from a dog with carcinoma. Vet. Clin. Pathol. 1994, 23, 72–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutt, J.H.C.; Dunn, K.A.; Scase, T.J.; Shipstone, M.A. A preliminary survey of the histopathological features of skin from the planum nasale and adjacent skin of dogs unaffected by dermatological or respiratory disease. Vet. Dermatol. 2015, 26, 359–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Smedley, R.C.; Sebastian, K.; Kiupel, M. Diagnosis and Prognosis of Canine Melanocytic Neoplasms. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9040175
Smedley RC, Sebastian K, Kiupel M. Diagnosis and Prognosis of Canine Melanocytic Neoplasms. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(4):175. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9040175
Chicago/Turabian StyleSmedley, Rebecca C., Kimberley Sebastian, and Matti Kiupel. 2022. "Diagnosis and Prognosis of Canine Melanocytic Neoplasms" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 4: 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9040175
APA StyleSmedley, R. C., Sebastian, K., & Kiupel, M. (2022). Diagnosis and Prognosis of Canine Melanocytic Neoplasms. Veterinary Sciences, 9(4), 175. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9040175





