Genetic Relatedness, Antibiotic Resistance, and Effect of Silver Nanoparticle on Biofilm Formation by Clostridium perfringens Isolated from Chickens, Pigeons, Camels, and Human Consumers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling
2.2. Bacteriological Examination
2.3. Molecular Identification
2.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
2.5. Biofilm Formation
2.6. Anti-Biofilm Activity of AgNPs-H2O2
2.7. Genotyping
2.8. Data Analysis
3. Results
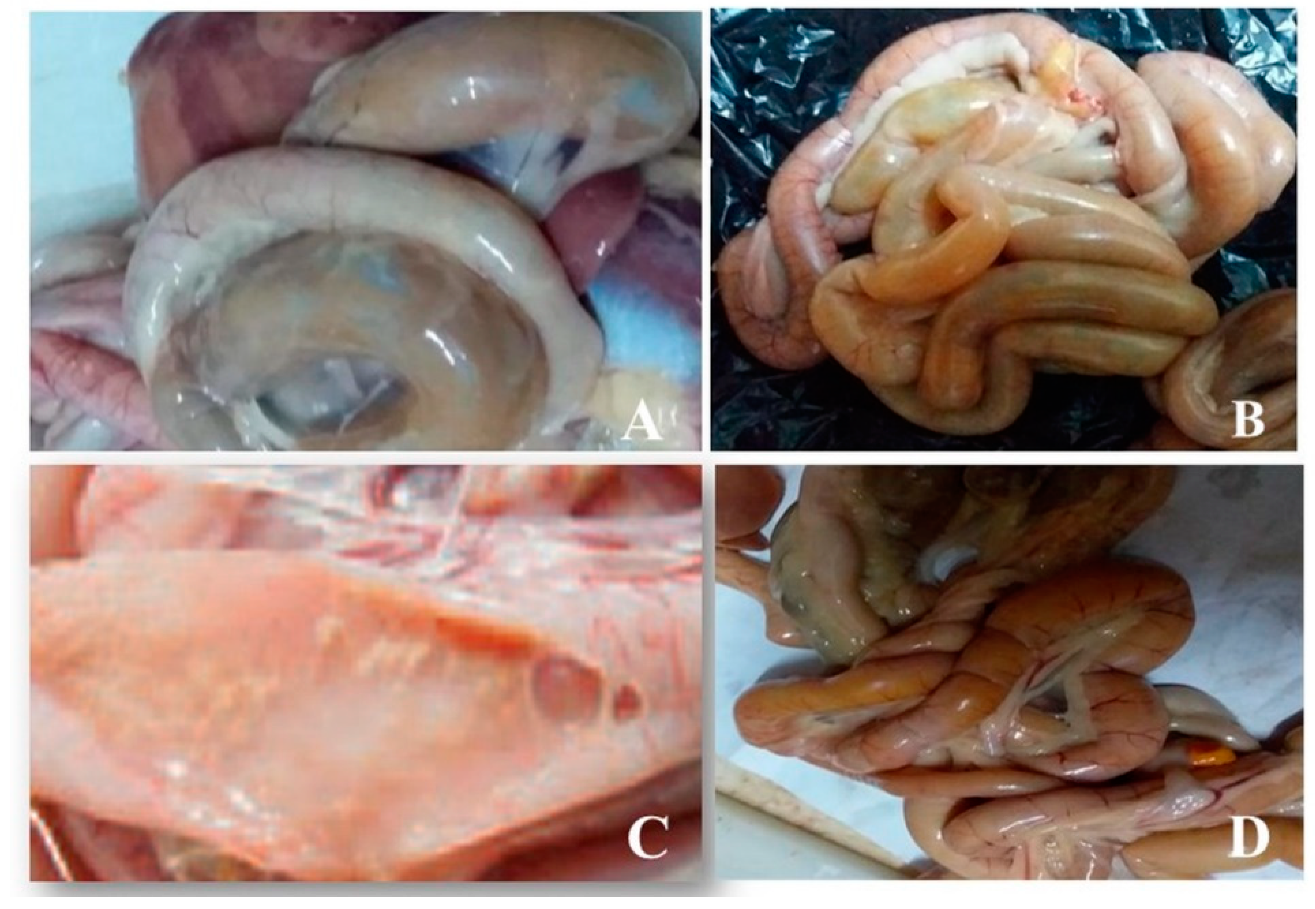
3.1. Postmortem Examination of Intestinal Samples from Birds
3.2. Prevalence of C. perfringens in the Examined Samples
3.3. Toxinotyping of C. perfringens Isolates
3.4. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
3.5. Biofilm Formation
3.6. Anti-Biofilm Activity of AgNPs-H2O2
3.7. Genotyping
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stanley, D.; Wu, S.B.; Rodgers, N.; Swick, R.A.; Moore, R.J. Differential responses of cecal microbiota to fishmeal, Eimeria and Clostridium perfringens in a necrotic enteritis challenge model in chickens. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernery, U.; Seifert, H.S.; Billah, A.M.; Ali, M. Predisposing factors in enterotoxemias of camels (Camelus dromedarius) caused by Clostridium perfringens type A. Rev. Elev. Med. Vet. Pays Trop. 1991, 44, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ignacio, A.; Fernandes, M.R.; Rodrigues, V.A.A.; Groppo, F.C.; Cardoso, A.L.; Avila-Campos, M.J.; Nakano, V. Correlation between body mass index and faecal microbiota from children. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 258.e251–258.e258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, W.; Ai, D.; Zhang, R.; Lu, Q.; Luo, Q.; Shao, H. Prevalence and characterization of Clostridium perfringens in broiler chickens and retail chicken meat in central China. Anaerobe 2018, 54, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, R.J.; Sayeed, S.; Li, J.; Genheimer, C.W.; Hiltonsmith, M.F.; Wilkins, T.D.; McClane, B.A. Clostridium perfringens toxin genotypes in the feces of healthy North Americans. Anaerobe 2008, 14, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagpal, R.; Ogata, K.; Tsuji, H.; Matsuda, K.; Takahashi, T.; Nomoto, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Kawashima, K.; Nagata, S.; Yamashiro, Y. Sensitive quantification of Clostridium perfringens in human feces by quantitative real-time PCR targeting alpha-toxin and enterotoxin genes. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rood, J.I.; Adams, V.; Lacey, J.; Lyras, D.; McClane, B.A.; Melville, S.B.; Moore, R.J.; Popoff, M.R.; Sarker, M.R.; Songer, J.G.; et al. Expansion of the Clostridium perfringens toxin-based typing scheme. Anaerobe 2018, 53, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, K.; Wen, Q.; McClane, B.A. Multiplex PCR genotyping assay that distinguishes between isolates of Clostridium perfringens type A carrying a chromosomal enterotoxin gene (cpe) locus, a plasmid cpe locus with an IS1470-like sequence, or a plasmid cpe locus with an IS1151 sequence. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 1552–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Songer, J.G.; Uzal, F.A. Clostridial enteric infections in pigs. J. Vet. Diagn. Invest. 2005, 17, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miki, Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Kaneko-Hirano, I.; Fujiuchi, K.; Akimoto, S. Prevalence and characterization of enterotoxin gene-carrying Clostridium perfringens isolates from retail meat products in Japan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 5366–5372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueschel, D.M.; Jost, B.H.; Billington, S.J.; Trinh, H.T.; Songer, J.G. Prevalence of cpb2, encoding beta2 toxin, in Clostridium perfringens field isolates: Correlation of genotype with phenotype. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.-S.; Kim, D.-H.; Bae, D.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, H.; Moon, J.-S.; Song, K.-Y.; Chon, J.-W.; Seo, K.-H. Prevalence, toxin-typing, and antimicrobial susceptibility of Clostridium perfringens from retail meats in Seoul, Korea. Anaerobe 2020, 64, 102235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwood, J.E.; Fraser, S.; Citron, D.M.; Wexler, H.; Blakely, G.; Jobling, K.; Patrick, S. Multi-drug resistant Bacteroides fragilis recovered from blood and severe leg wounds caused by an improvised explosive device (IED) in Afghanistan. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.O.S.; Salvarani, F.M.; Assis, R.A.; Martins, N.R.S.; Pires, P.S.; Lobato, F.C.F. Antimicrobial susceptibility of Clostridium perfringens strains isolated from broiler chickens. Brazil. J. Microbiol. Publ. Brazil. Soc. Microbiol. 2009, 40, 262–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulaz, S.; Vitale, S.; Quinn, L.; Casey, E. Nanoparticle–Biofilm Interactions: The Role of the EPS Matrix. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 915–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestby, L.K.; Grønseth, T.; Simm, R.; Nesse, L.L. Bacterial Biofilm and its Role in the Pathogenesis of Disease. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, M.; Ahmad, W.; Andleeb, S.; Jalil, F.; Imran, M.; Nawaz, M.A.; Hussain, T.; Ali, M.; Rafiq, M.; Kamil, M.A. Bacterial biofilm and associated infections. J. Chin. Med. Assoc. 2018, 81, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jong, W.H.; Borm, P.J.A. Drug delivery and nanoparticles:applications and hazards. Int. J. Nanomed. 2008, 3, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, N.; Ray, B.; Ranjit, K.T.; Manna, A.C. Antibacterial activity of ZnO nanoparticle suspensions on a broad spectrum of microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 279, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, A.; Jamshidi, A.; Razmyar, J.; Rad, M. Genomic diversity of Clostridium perfringens strains isolated from food and human sources. Iran. J. Vet. Res. 2016, 17, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.S.; Lee, S.U.; Park, K.Y.; Park, Y.H. Molecular typing and epidemiological survey of prevalence of Clostridium perfringens types by multiplex PCR. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1997, 35, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herholz, C.; Miserez, R.; Nicolet, J.; Frey, J.; Popoff, M.; Gibert, M.; Gerber, H.; Straub, R. Prevalence of beta2-toxigenic Clostridium perfringens in horses with intestinal disorders. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1999, 37, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. In 21st Informational Supplement. CLSI Supplement M100-S21; Wayne, P.A., Ed.; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2011; Volume 31, no. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Krumperman, P.H. Multiple antibiotic resistance indexing of Escherichia coli to identify high-risk sources of fecal contamination of foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1983, 46, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-resistant, extensively drug-resistant and pandrug-resistant bacteria: An international expert proposal for interim standard definitions for acquired resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlebois, A.; Jacques, M.; Archambault, M. Biofilm formation of Clostridium perfringens and its exposure to low-dose antimicrobials. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charlebois, A.; Jacques, M.; Boulianne, M.; Archambault, M. Tolerance of Clostridium perfringens biofilms to disinfectants commonly used in the food industry. Food Microbiol. 2017, 62, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.; Banerjee, G.; Garg, R.; Singh, M. Comparative Study of Biofilm Formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolates from Patients of Lower Respiratory Tract Infection. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. JCDR 2014, 8, DC09–DC11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Toole, G.A.; Kolter, R. Initiation of biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 proceeds via multiple, convergent signalling pathways: A genetic analysis. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 28, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalishwaralal, K.; BarathManiKanth, S.; Pandian, S.R.K.; Deepak, V.; Gurunathan, S. Silver nanoparticles impede the biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus epidermidis. Coll. Surf. Bioint. 2010, 79, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leflon-Guibout, V.; Pons, J.L.; Heym, B.; Nicolas-Chanoine, M.H. Typing of Clostridium perfringens strains by use of Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) system in comparison with zymotyping. Anaerobe 1997, 3, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, P.R. Reproducibility and indices of discriminatory power of microbial typing methods. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1990, 28, 1903–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Eils, R.; Schlesner, M. Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2847–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tansuphasiri, U.; Matra, W.; Sangsuk, L. Antimicrobial resistance among Clostridium perfringens isolated from various sources in Thailand. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 2005, 36, 954–961. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Craven, S.E.; Stern, N.J.; Bailey, J.S.; Cox, N.A. Incidence of Clostridium perfringens in broiler chickens and their environment during production and processing. Avian Dis. 2001, 45, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, K.M.; Soliman, Y.A.; Amin, Z.M.; Aly, M.A. Prevalence of Clostridium perfringens type A isolates in commercial broiler chickens and parent broiler breeder hens in Egypt. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2012, 31, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharaibeh, S.; Al Rifai, R.; Al-Majali, A. Molecular typing and antimicrobial susceptibility of Clostridium perfringens from broiler chickens. Anaerobe 2010, 16, 586–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaldhusdal, M.; Lovland, A. The economical impact of Clostridium perfringens is greater than anticipated. World Poult. 2000, 16, 50–51. [Google Scholar]
- Kaldhusdal, M.; Schneitz, C.; Hofshagen, M.; Skjerve, E. Reduced incidence of Clostridium perfringens-associated lesions and improved performance in broiler chickens treated with normal intestinal bacteria from adult fowl. Avian Dis. 2001, 45, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDevitt, R.; Brooker, J.; Acamovic, T.; Sparks, N. Necrotic enteritis; a continuing challenge for the poultry industry. Worlds Poult. Sci. J. 2006, 62, 221–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Sharma, R.; Borah, P.; Chakraborty, A.; Devi, M.R.; Longjam, N. Characterization of Clostridium perfringens isolated from mammals and birds from Guwahati city, India. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2012, 18, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Harlin, R.; Wade, L. Bacterial and parasitic diseases of Columbiformes. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Exot. Anim. Pract. 2009, 12, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canard, B.; Saint-Joanis, B.; Cole, S.T. Genomic diversity and organization of virulence genes in the pathogenic anaerobe Clostridium perfringens. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engström, B.E.; Fermér, C.; Lindberg, A.; Saarinen, E.; Båverud, V.; Gunnarsson, A. Molecular typing of isolates of Clostridium perfringens from healthy and diseased poultry. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, S.; Timmons, J.; Fitz-coy, S.; Parveen, S. Characterization of Clostridium perfringens recovered from broiler chicken affected by necrotic enteritis. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikinheimo, A.; Korkeala, H. Multiplex PCR assay for toxinotyping Clostridium perfringens isolates obtained from Finnish broiler chickens. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2005, 40, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Asten, A.J.A.M.; Nikolaou, G.N.; Gröne, A. The occurrence of cpb2-toxigenic Clostridium perfringens and the possible role of the β2-toxin in enteric disease of domestic animals, wild animals and humans. Vet. J. 2010, 183, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamiandehkordi, A.; Eeckhaut, V.; Lanckriet, A.; Timbermont, L.; Bjerrum, L.; Ducatelle, R.; Haesebrouck, F.; Van Immerseel, F. Antimicrobial resistance in Clostridium perfringens isolates from broilers in Belgium. Vet. Res. Commun. 2009, 33, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, L.; Gibert, M.; Popoff, M.R. Clostridium perfringens: Toxinotype and genotype. Trends Microbiol. 1999, 7, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.-S.; Kim, H.; Koo, O.K. Molecular genotyping, biofilm formation and antibiotic resistance of enterotoxigenic Clostridium perfringens isolated from meat supplied to school cafeterias in South Korea. Anaerobe 2018, 52, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparks, S.G.; Carman, R.J.; Sarker, M.R.; McClane, B.A. Genotyping of enterotoxigenic Clostridium perfringens fecal isolates associated with antibiotic-associated diarrhea and food poisoning in North America. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2001, 39, 883–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, J.C.; Shrestha, A.; McClane, B.A. Clostridium perfringens Enterotoxin: Action, Genetics, and Translational Applications. Toxins 2016, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; McClane, B.A. Detection of enterotoxigenic Clostridium perfringens type A isolates in American retail foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 2685–2691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibert, M.; Jolivet-Reynaud, C.; Popoff, M.R. Beta2 toxin, a novel toxin produced by Clostridium perfringens. Gene 1997, 203, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, T.; Ohtani, K.; Hirakawa, H.; Ohshima, K.; Yamashita, A.; Shiba, T.; Ogasawara, N.; Hattori, M.; Kuhara, S.; Hayashi, H. Complete genome sequence of Clostridium perfringens, an anaerobic flesh-eater. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Praveen Kumar, N.; Vinod Kumar, N.; Karthik, A. Molecular detection and characterization of Clostridium perfringens toxin genes causing necrotic enteritis in broiler chickens. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2019, 51, 1559–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolooe, A.; Shojadoost, B.; Peighambari, S. Molecular detection and characterization of cpb2 gene in Clostridium perfringens isolates from healthy and diseased chickens. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins incl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 17, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forti, K.; Ferroni, L.; Pellegrini, M.; Cruciani, D.; De Giuseppe, A.; Crotti, S.; Papa, P.; Maresca, C.; Severi, G.; Marenzoni, M.L.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Clostridium perfringens Strains Isolated in Italy. Toxins 2020, 12, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharieb, R.; Saad, M.; Abdallah, K.; Khedr, M.; Farag, E.; Abd El-Fattah, A. Insights on toxin genotyping, virulence, antibiogram profiling, biofilm formation and efficacy of disinfectants on biofilms of Clostridium perfringens isolated from poultry, animals and humans. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2021, 130, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Rafii, F. The prevalence of plasmid-coded cpe enterotoxin, β2 toxin, tpeL toxin, and tetracycline resistance in Clostridium perfringens strains isolated from different sources. Anaerobe 2019, 56, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packer, S.; Day, J.; Hardman, P.; Cameron, J.; Kennedy, M.; Turner, J.; Willis, C.; Amar, C.; Nozad, B.; Gobin, M. A cohort study investigating a point source outbreak of Clostridium perfringens associated with consumption of roasted meat and gravy at a buffet on Mothering Sunday 2018, South West, England. Food Control. 2020, 112, 107097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayez, M.; Elsohaby, I.; Al-Marri, T.; Zidan, K.; Aldoweriej, A.; El-Sergany, E.; Elmoslemany, A. Genotyping and antimicrobial susceptibility of Clostridium perfringens isolated from dromedary camels, pastures and herders. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 101460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, Z.A.M. The Role of Clostridium Perfringens in Camel Calf Diarrhoea with Special Reference to the Pathogenesis and Pathology in the Sudan. Ph.D. Thesis, Microbiology Department, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, University of Khartoum, Khartoum, Sudan, 2004; pp. 1–138. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, E.M.; Suelam, I.; Saleh, M. The presence of toxin genes of Clostridium perfringens isolated from camels and humans in Egypt. Vet. Arhiv 2010, 80, 383–392. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, E.; Gamboa Mdel, M.; Vargas, P. [Clostridium perfringens in raw and cooked meats and its relation with the environment in Costa Rica]. Arch. Latinoam. Nutr. 2002, 52, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Samuel, S.C.; Hancock, P.; Leigh, D.A. An investigation into Clostridium perfringens enterotoxin-associated diarrhoea. J. Hosp. Infect. 1991, 18, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshminarayanan, B.; Harris, H.M.B.; Coakley, M.; O’Sullivan, Ó.; Stanton, C.; Pruteanu, M.; Shanahan, F.; O’Toole, P.W.; Ross, R.P.; On Behalf Of The Eldermet, C. Prevalence and characterization of Clostridium perfringens from the faecal microbiota of elderly Irish subjects. J. Med. Microbiol. 2013, 62, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, J.P.; Das, S.C.; Dhaka, P.; Vijay, D.; Kumar, M.; Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Chowdhury, G.; Chauhan, P.; Singh, R.; Dhama, K.; et al. Molecular characterization and antimicrobial resistance profile of Clostridium perfringens type A isolates from humans, animals, fish and their environment. Anaerobe 2017, 47, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diarra, M.S.; Malouin, F. Antibiotics in Canadian poultry productions and anticipated alternatives. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhi, M.T.; Bidar Asl, S.; Pirzadeh, T.; Naghili, B.; Yeganeh, F.; Memar, Y.; Mohammadzadeh, Y. Antibiotic Sensitivity of Clostridium perfringens Isolated From Faeces in Tabriz, Iran. Jundis. J. Microbiol. 2015, 8, e20863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, N. Clindamycin-resistant Clostridium perfringens cellulitis. J. Tissue Viab. 2008, 17, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyras, D.; Adams, V.; Ballard, S.A.; Teng, W.L.; Howarth, P.M.; Crellin, P.K.; Bannam, T.L.; Songer, J.G.; Rood, J.I. tISCpe8, an IS1595-family lincomycin resistance element located on a conjugative plasmid in Clostridium perfringens. J. Bacteriol. 2009, 191, 6345–6351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landers, T.F.; Cohen, B.; Wittum, T.E.; Larson, E.L. A review of antibiotic use in food animals: Perspective, policy, and potential. Publ. Health Rep. 2012, 127, 4–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varga, J.J.; Therit, B.; Melville, S.B. Type IV pili and the CcpA protein are needed for maximal biofilm formation by the gram-positive anaerobic pathogen Clostridium perfringens. Infect. Immun. 2008, 76, 4944–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmølle, M.; Ren, D.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Sørensen, S.J. Interactions in multispecies biofilms: Do they actually matter? Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giaouris, E.; Heir, E.; Desvaux, M.; Hébraud, M.; Møretrø, T.; Langsrud, S.; Doulgeraki, A.; Nychas, G.-J.; Kačániová, M.; Czaczyk, K.; et al. Intra- and inter-species interactions within biofilms of important foodborne bacterial pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderl, J.N.; Franklin, M.J.; Stewart, P.S. Role of antibiotic penetration limitation in Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilm resistance to ampicillin and ciprofloxacin. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2000, 44, 1818–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitesides, G.M. Nanoscience, Nanotechnology, and Chemistry. Small 2005, 1, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Gohary, F.A.; Abdel-Hafez, L.J.M.; Zakaria, A.I.; Shata, R.R.; Tahoun, A.; El-Mleeh, A.; Abo Elfadl, E.A.; Elmahallawy, E.K. Enhanced Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Combined with Hydrogen Peroxide Against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogens Isolated from Dairy Farms and Beef Slaughterhouses in Egypt. Infect Drug. Resist. 2020, 13, 3485–3499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsayed, M.M.; Elgohary, F.A.; Zakaria, A.I.; Elkenany, R.M.; El-Khateeb, A.Y. Novel eradication methods for Staphylococcus aureus biofilm in poultry farms and abattoirs using disinfectants loaded onto silver and copper nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 30716–30728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.H.; Aslam, B.; Imran, M.; Ashraf, A.; Nadeem, H.; Hayat, S.; Khurshid, M.; Afzal, M.; Malik, I.R.; Shahzad, M.; et al. Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Biofilm Formation and EPS Production of Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 6398165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.R.; Sahareen, T.; Singh, M.; Kumar, S. Role of biogenic silver nanoparticles in disruption of cell–cell adhesion in Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli biofilm. J. Indust. Eng. Chem. 2015, 26, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah, K.; Gamal, A.; Ibrahim, S.; Mohamed, E.; Saleh, A. Investigation of the efficacy of synthesized silver and zinc oxide nanoparticles against multi-drug resistant gram negative bacterial clinical isolates. Arch Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 67. [Google Scholar]
- Hastey, C.J.; Boyd, H.; Schuetz, A.N.; Anderson, K.; Citron, D.M.; Dzink-Fox, J.; Hackel, M.; Hecht, D.W.; Jacobus, N.V.; Jenkins, S.G.; et al. Changes in the antibiotic susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria from 2007-2009 to 2010-2012 based on the CLSI methodology. Anaerobe 2016, 42, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Species | Type of Sample | Number Examined | Number Positive | Genotyping | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cpa+ | cpe+ | cpb2+ | ||||
| Chickens | Intestinal content | 50 | 10 (20%) | 10 | 0 | 9 (90%) |
| Meat | 50 | 5 (10%) | 5 | 0 | 2 (40%) | |
| Pigeons | Intestinal content | 30 | 20 (66.7%) | 20 | 0 | 4 (20%) |
| Camels | Diarrheic feces | 50 | 9 (18%) | 9 | 3 (33.3%) | 7 (77.8%) |
| Meat | 50 | 2 (4%) | 2 | 1 (50%) | 2 (100%) | |
| Humans | Diarrheic stool | 100 | 4 (4%) | 4 | 2 (50%) | 4 (100%) |
| Antibiotic Class | Antimicrobial Agent (Abbreviation) | S | R |
|---|---|---|---|
| Penicillins | Penicillin (PEN) | 9 (18%) | 41 (82%) |
| Ampicillin (AMP) | 37 (74%) | 13 (26%) | |
| β-lactamas | Amoxicillin (AMX) | 37 (74%) | 13 (26%) |
| Ampicillin-sulbactam (SAM) | 37 (74%) | 13 (26%) | |
| Lincosamides | Clindamycin (CLI) | 3 (6%) | 47 (94%) |
| Nitroimidazole | Metronidazole (MTZ) | 43 (86%) | 7 (14%) |
| Glycopeptides | Vancomycin (VAN) | 50 (100%) | 0 |
| Carbapenems | Imipenem (IPM) | 25 (50%) | 25 (50%) |
| Meropenem (MEM) | 22 (44%) | 28 (56%) | |
| Phenolics | Chloramphenicole (CHL) | 3 (6%) | 47 (94%) |
| Tetracyclines | Tetracycline (TET) | 27 (54%) | 23 (46%) |
| Cephems | Cefotaxime (CTX) | 7 (14%) | 43 (86%) |
| Cefoxitin (FOX) | 7 (14%) | 43 (86%) | |
| Ceftriaxone (CRO) | 7 (14%) | 43 (86%) |
| ID | Source | Virulence Profile | Biofilm Category | Resistance Pattern | MAR Index | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cpa | cpe | cpb2 | |||||
| CT1 | CT | + | - | + | W | PEN | - |
| CT4 | CT | + | - | + | W | PEN | - |
| CT7 | CT | + | - | + | W | PEN-MEM | - |
| CT11 | CT | + | - | + | S | PEN-AMP-AMX-SAM-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-MTZ-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO * | 0.9 |
| CT13 | CT | + | - | + | S | PEN-AMP-AMX-SAM-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO * | 0.8 |
| CT18 | CT | + | - | + | M | PEN-IPM-MEM-CLI-MTZ-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.6 |
| CT21 | CT | + | - | + | M | MEM-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.4 |
| CT25 | CT | + | - | + | M | PEN-MEM-TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.5 |
| CT29 | CT | + | - | + | M | PEN-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.6 |
| CT48 | CT | + | - | - | M | CLI-CHL | - |
| CM7 | CM | + | - | - | M | PEN-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.5 |
| CM13 | CM | + | - | + | M | CLI-CLI-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.3 |
| CM18 | CM | + | - | - | S | PEN-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-MTZ-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO * | 0.7 |
| CM25 | CM | + | - | + | M | PEN-IPM-CLI-CHL | 0.28 |
| CM48 | CM | + | - | - | M | TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 04 |
| PT1 | PT | + | - | - | M | PEN-TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.5 |
| PT2 | PT | + | - | - | M | PEN-TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.5 |
| PT3 | PT | + | - | + | M | PEN-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.4 |
| PT4 | PT | + | - | - | M | PEN-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.4 |
| PT5 | PT | + | - | - | M | PEN-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.6 |
| PT6 | PT | + | - | - | M | PEN-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.4 |
| PT8 | PT | + | - | - | M | PEN-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.4 |
| PT11 | PT | + | - | - | S | (PEN-AMP-AMX-SAM-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO) * | 0.8 |
| PT12 | PT | + | - | + | S | (PEN-AMP-AMX-SAM-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO) * | 0.8 |
| PT14 | PT | + | - | - | M | TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.4 |
| PT15 | PT | + | - | + | M | CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.3 |
| PT16 | PT | + | - | + | M | CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.3 |
| PT20 | PT | + | - | - | M | CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.3 |
| PT21 | PT | + | - | - | M | PEN-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.4 |
| PT22 | PT | + | - | - | M | PEN-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.4 |
| PT26 | PT | + | - | - | M | IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.57 |
| PT27 | PT | + | - | - | M | PEN-CLI-CHL | 0.2 |
| PT28 | PT | + | - | - | M | PEN-IPM-MEM-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.57 |
| PT29 | PT | + | - | - | M | PEN-MEM-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.5 |
| PT30 | PT | + | - | - | S | (PEN-AMP-AMX-SAM-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO) * | 0.8 |
| CF8 | CF | + | - | + | M | PEN-CLI-CHL | 0.2 |
| CF13 | CF | + | - | - | S | (PEN-AMP-AMX-SAM-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-MTZ-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO) * | 0.9 |
| CF16 | CF | + | - | - | S | (PEN-AMP-AMX-SAM-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO) * | 0.8 |
| CF17 | CF | + | - | + | M | PEN-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.4 |
| CF18 | CF | + | - | + | M | PEN-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.4 |
| CF21 | CF | + | + | + | S | (PEN-AMP-AMX-SAM-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO) * | 0.8 |
| CF22 | CF | + | - | + | M | PEN-IPM-MEM-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.57 |
| CF28 | CF | + | + | + | S | (PEN-AMP-AMX-SAM-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO) * | 0.8 |
| CF31 | CF | + | + | + | M | PEN-IPM-MEM-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.57 |
| CA38 | CA | + | - | + | S | (PEN-AMP-AMX-SAM-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-MTZ-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO) * | 0.9 |
| CA49 | CA | + | + | + | S | (PEN-AMP-AMX-SAM-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO) * | 0.8 |
| HU11 | HU | + | - | + | M | PEN-IPM-MEM-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.57 |
| HU19 | HU | + | + | + | S | (PEN-AMP-AMX-SAM-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-MTZ-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO) * | 0.9 |
| HU38 | HU | + | - | + | M | PEN-IPM-MEM-CLI-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO | 0.57 |
| HU47 | HU | + | + | + | S | (PEN-AMP-AMX-SAM-IPM-MEM-TET-CLI-MTZ-CHL-CTX-FOX-CRO) * | 0.9 |
| Isolate | Positive Control | Negative Control | AgNP Concentrations (µg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 25 | 50 | 75 | 100 | |||
| CT11 | ++++ | - | +++ | ++ | + | - |
| CM18 | ++++ | - | +++ | ++ | + | - |
| PT11 | ++++ | - | +++ | + | - | - |
| CF13 | ++++ | - | +++ | ++ | + | - |
| CA49 | ++++ | - | +++ | ++ | + | - |
| HU19 | ++++ | - | +++ | ++ | + | - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, H.A.; El Bayomi, R.M.; Hamed, R.I.; Mohsen, R.A.; El-Gohary, F.A.; Hefny, A.A.; Elkhawaga, E.; Tolba, H.M.N. Genetic Relatedness, Antibiotic Resistance, and Effect of Silver Nanoparticle on Biofilm Formation by Clostridium perfringens Isolated from Chickens, Pigeons, Camels, and Human Consumers. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030109
Ahmed HA, El Bayomi RM, Hamed RI, Mohsen RA, El-Gohary FA, Hefny AA, Elkhawaga E, Tolba HMN. Genetic Relatedness, Antibiotic Resistance, and Effect of Silver Nanoparticle on Biofilm Formation by Clostridium perfringens Isolated from Chickens, Pigeons, Camels, and Human Consumers. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(3):109. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030109
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Heba A., Rasha M. El Bayomi, Rehab I. Hamed, Rasha A. Mohsen, Fatma A. El-Gohary, Ahmed A. Hefny, Eman Elkhawaga, and Hala M. N. Tolba. 2022. "Genetic Relatedness, Antibiotic Resistance, and Effect of Silver Nanoparticle on Biofilm Formation by Clostridium perfringens Isolated from Chickens, Pigeons, Camels, and Human Consumers" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 3: 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030109
APA StyleAhmed, H. A., El Bayomi, R. M., Hamed, R. I., Mohsen, R. A., El-Gohary, F. A., Hefny, A. A., Elkhawaga, E., & Tolba, H. M. N. (2022). Genetic Relatedness, Antibiotic Resistance, and Effect of Silver Nanoparticle on Biofilm Formation by Clostridium perfringens Isolated from Chickens, Pigeons, Camels, and Human Consumers. Veterinary Sciences, 9(3), 109. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030109






