Molecular and Pathological Detection of Hepatitis E Virus in Roe Deer (Capreolus capreolus) and Fallow Deer (Dama dama) in Central Italy
Abstract
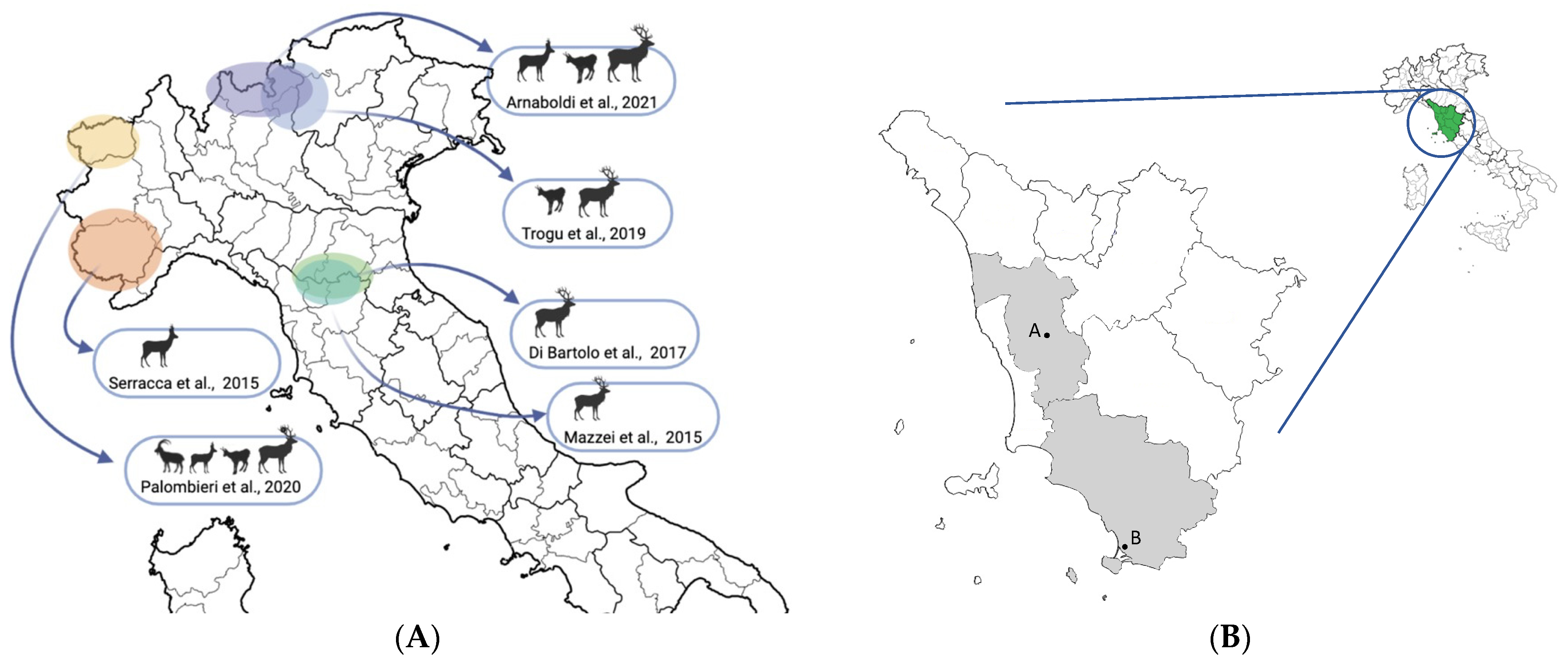
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Estimation
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. ELISA Screening
2.4. Molecular Analysis
2.5. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Statistic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Animals
3.2. Virological Investigation
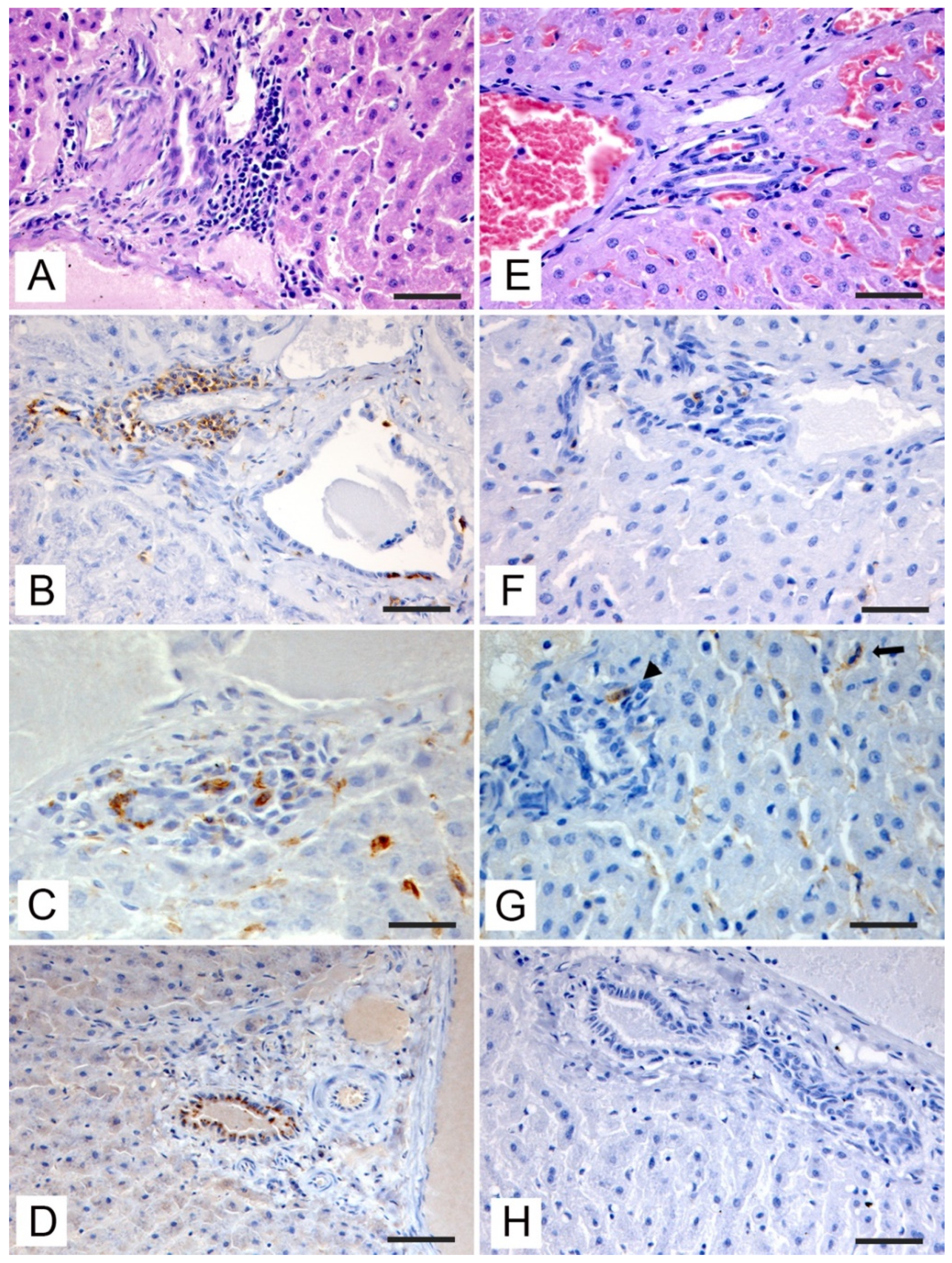
3.3. Histopathologic and Immunohistochemical Investigations
3.4. Statistical Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nimgaonkar, I.; Ding, Q.; Schwartz, R.E.; Ploss, A. Hepatitis e virus: Advances and challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purdy, M.A.; Harrison, T.J.; Jameel, S.; Meng, X.J.; Okamoto, H.; Van Der Poel, W.H.M.; Smith, D.B. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Hepeviridae. J. Gen. Vir. 2017, 98, 2645–2646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lhomme, S.; Marion, O.; Abravanel, F.; Izopet, J.; Kamar, N. Clinical Manifestations, Pathogenesis and Treatment of Hepatitis E Virus Infections. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- King, N.J.; Hewitt, J.; Perchec-Merien, A.M. Hiding in Plain Sight? It’s Time to Investigate Other Possible Transmission Routes for Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) in Developed Countries. Food Environ. Virol. 2018, 10, 225–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicot, F.; Dimeglio, C.; Migueres, M.; Jeanne, N.; Latour, J.; Abravanel, F.; Ranger, N.; Harter, A.; Dubois, M.; Lameiras, S.; et al. Classification of the Zoonotic Hepatitis E Virus Genotype 3 Into Distinct Subgenotypes. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 634430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierini, I.; Di Bartolo, I.; Manuali, E.; Pirani, S.; Bazzucchi, M.; Moscati, L.; De Mia, G.M.; Giammarioli, M. Hepatitis E virus (HEV) genotype 3 diversity: Identification of a novel HEV subtype in wild boar in Central Italy. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2020, 68, 2121–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sabato, L.; Di Bartolo, I.; Lapa, D.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Garbuglia, A.R. Molecular Characterization of HEV Genotype 3 in Italy at Human/Animal Interface. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, G.; Vergara, A. Hepatitis E Virus in the Food of Animal Origin: A Review. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2021, 18, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forzan, M.; Pacini, M.I.; Periccioli, M.; Mazzei, M. Hepatitis E Virus RNA Presence in Wild Boar Carcasses at Slaughterhouses in Italy. Animals 2021, 11, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, J.D.; Riddell, M.A.; Li, F.; Love, R.J.; Anderson, D.A. Serological evidence for swine hepatitis E virus infection in Australian pig herds. Vet. Microbiol. 1999, 68, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boadella, M. Hepatitis E in wild ungulates: A review. Small Rumin. Res. 2015, 128, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tei, S.; Kitajima, N.; Takahashi, K.; Mishiro, S. Zoonotic transmission of hepatitis E virus from deer to human beings. Lancet 2003, 362, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, R.M.; Roe, R.T. Livestock Disease Surveys: A Field Manual for Veterinarians; Australian Government Publishing Service: Canberra, Australia, 1982; pp. 32–34. [Google Scholar]
- Forgách, P.; Nowotny, N.; Erdélyi, K.; Boncz, A.; Zentai, J.; Szucs, G.; Reuter, G.; Bakonyi, T. Detection of hepatitis E virus in samples of animal origin collected in Hungary. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 143, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rutjes, S.A.; Lodder-Verschoor, F.; Lodder, W.J.; van der Giessen, J.; Reesink, H.; Bouwknegt, M.; de Roda Husman, A.M. Seroprevalence and molecular detection of hepatitis E virus in wild boar and red deer in The Netherlands. J. Virol. Methods 2010, 168, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boadella, M.; Casas, M.; Martín, M.; Vicente, J.; Segalés, J.; de la Fuente, J.; Gortázar, C. Increasing contact with hepatitis E virus in red deer, Spain. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1994–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubankova, M.; Kralik, P.; Lamka, J.; Zakovcik, V.; Dolanský, M.; Vasickova, P. Prevalence of Hepatitis E Virus in Populations of Wild Animals in Comparison with Animals Bred in Game Enclosures. Food Environ. Virol. 2015, 7, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, S.; Hackl, S.S.; Piepenschneider, M.; Vina-Rodriguez, A.; Dremsek, P.; Ulrich, R.G.; Groschup, M.H.; Eiden, M. Serologic and Molecular Survey of Hepatitis E Virus in German Deer Populations. J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anheyer-Behmenburg, H.E.; Szabo, K.; Schotte, U.; Binder, A.; Klein, G.; Johne, R. Hepatitis E Virus in Wild Boars and Spillover Infection in Red and Roe deer, Germany, 2013–2015. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2017, 23, 130–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiry, D.; Mauroy, A.; Saegerman, C.; Licoppe, A.; Fett, T.; Thomas, I.; Brochier, B.; Thiry, E.; Linden, A. Belgian Wildlife as Potential Zoonotic Reservoir of Hepatitis E Virus. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spancerniene, U.; Grigas, J.; Buitkuviene, J.; Zymantiene, J.; Juozaitiene, V.; Stankeviciute, M.; Razukevicius, D.; Zienius, D.; Stankevicius, A. Prevalence and phylogenetic analysis of hepatitis E virus in pigs, wild boars, roe deer, red deer and moose in Lithuania. Acta Vet. Scand. 2018, 60, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Di Bartolo, I.; Ponterio, E.; Angeloni, G.; Morandi, F.; Ostanello, F.; Nicoloso, S.; Ruggeri, F.M. Presence of Hepatitis E Virus in a RED Deer (Cervus elaphus) Population in Central Italy. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnevali, L.; Pedrotti, L.; Riga, F.; Toso, S. Banca Dati Ungulati. Status, Distribuzione, Consistenza, Gestione e Prelievo Venatorio delle Popolazioni di Ungulati in Italia; Rapporto/Report 2001–2005; ISPRA—Settore Editoria: Rome, Italy, 2009; Volume 117, pp. 1–168. [Google Scholar]
- Serracca, L.; Battistini, R.; Rossini, I.; Mignone, W.; Peletto, S.; Boin, C.; Pistone, G.; Ercolini, R.; Ercolini, C. Molecular Investigation on the Presence of Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) in Wild Game in North-Western Italy. Food Environ. Virol. 2015, 7, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzei, M.; Forzan, M.; Pizzurro, F.; Picciolli, F.; Bandecchi, P.; Poli, A. Detection of Hepatitis E Virus Antibodies in Domestic and Wild Animal Species in Central Italy. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 4, 1000227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trogu, T.; Ferrari, N.; Formenti, N.; Virginia, F.; Pedrotti, L.; Viganò, R.; Lanfranchi, P.; Luzzago, C. Low Serologic Prevalences Suggest Sporadic Infections of Hepatitis E Virus in Chamois (Rupicapra rupicapra) and Red Deer (Cervus elaphus) in the Italian Alps. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 56, 443–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palombieri, A.; Robetto, S.; Di Profio, F.; Sarchese, V.; Fruci, P.; Bona, M.C.; Ru, G.; Orusa, R.; Marsilio, F.; Martella, V.; et al. Surveillance study of hepatitis E virus (HEV) in domestic and wild ruminants in northwestern Italy. Animals 2020, 10, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaboldi, S.; Righi, F.; Carta, V.; Bonardi, S.; Pavoni, E.; Bianchi, A.; Losio, M.N.; Filipello, V. Hepatitis E Virus (HEV) Spread and Genetic Diversity in Game Animals in Northern Italy. Food Environ. Virol. 2021, 13, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marinis, A.M.; Toso, S. Valutazione dell’età nei Cervidi Tramite Esame della Dentatura; Manuali e Linee guida n. 90/2013; ISPRA—Settore Editoria: Rome, Italy, 2015; pp. 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Parisi, F.; Mazzei, M.; Verin, R.; Forzan, M.; Rocchigiani, G.; Roper, C.; Bertelloni, G.; Poli, A. Hepatitis E virus infection in wild rabbit (Oryctolagus cuniculus) in Italy and in the UK: A serological, molecular, and pathological study. Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2019, 65, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jothikumar, N.; Cromeans, T.L.; Robertson, B.H.; Meng, X.J.; Hill, V.R. A broadly reactive one-step real-time RT-PCR assay for rapid and sensitive detection of hepatitis E virus. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 131, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A.T. BioEdit: A user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucl. Acids Symp. Ser. 1999, 41, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Aprea, G.; Scattolini, S.; D’Angelantonio, D.; Chiaverini, A.; Di Lollo, V.; Olivieri, S.; Marcacci, M.; Mangone, I.; Salucci, S.; Antoci, S.; et al. Whole Genome Sequencing Characterization of HEV3-e and HEV3-f Subtypes among the Wild Boar Population in the Abruzzo Region, Italy: First Report. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reuter, G.; Fodor, D.; Forgách, P.; Kátai, A.; Szucs, G. Characterization and zoonotic potential of endemic hepatitis E virus (HEV) strains in humans and animals in Hungary. J. Clin. Virol. 2009, 44, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacristán, C.; Madslien, K.; Sacristán, I.; Klevar, S.; das Neves, C.G. Seroprevalence of Hepatitis E Virus in Moose (Alces alces), Reindeer (Rangifer tarandus), Red Deer (Cervus elaphus), Roe Deer (Capreolus capreolus), and Muskoxen (Ovibos moschatus) from Norway. Viruses 2021, 13, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, A.C.; Kroneman, A.; Franz, E.; Vennema, H.; Tulen, A.D.; Takkinen, J.; Hofhuis, A.; Adlhoch, C. HEVnet: A One Health, collaborative, interdisciplinary network and sequence data repository for enhanced hepatitis E virus molecular typing, characterisation and epidemiological investigations. Euro Surveill. 2019, 24, 1800407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, M.; Nishizawa, T.; Sato, H.; Sato, Y.; Jirintai; Nagashima, S.; Okamoto, H. Analysis of the full-length genome of a Hepatitis E Virus isolate obtained from a wild boar in Japan that is classifiable into a Novel Genotype. J. Gen. Virol. 2011, 92, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crotta, M.; Pellicioli, L.; Guffari, A.; Trogu, T.; Formenti, N.; Tranquillo, V.; Luzzago, C.; Ferrari, N.; Lanfranchi, P. Analysis of seroprevalence data on Hepatitis E virus and Toxoplasma gondii in wild ungulates for the assessment of human exposure to zoonotic meat-borne pathogens. Food Microbiol. 2022, 101, 103890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzei, M.; Nardini, R.; Verin, R.; Forzan, M.; Poli, A.; Tolari, F. Serologic and molecular survey for hepatitis E virus in wild boar (Sus scrofa) in Central Italy. New Microbes New Infect. 2015, 7, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullen, J.M.; Lemon, S.M. Comparative Pathology of Hepatitis A Virus and Hepatitis E Virus Infection. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a033456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.J.; Halbur, P.G.; Haynes, J.S.; Tsareva, T.S.; Bruna, J.D.; Royer, R.L.; Purcel, R.H.; Emerson, S. Experimental infection of pigs with the newly identified swine hepatitis E virus (swine HEV), but not with human strains of HEV. Arch. Virol. 1998, 143, 1405–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primadharsini, P.P.; Nagashima, S.; Okamoto, H. Mechanism of Cross-Species Transmission, Adaptive Evolution and Pathogenesis of Hepatitis E Virus. Viruses 2021, 13, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczynski, K.; Meng, X.J.; Rybczynska, J. Pathogenetic elements of hepatitis E and animal models of HEV infection. Virus Res. 2011, 161, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lhomme, S.; Marion, O.; Abravanel, F.; Chapuy-Regaud, S.; Kamar, N.; Izopet, J. Hepatitis E pathogenesis. Viruses 2016, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolios, G.; Valatas, V.; Kouroumalis, E. Role of Kupffer cells in the pathogenesis of liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 7413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Wang, L. An overview: Rabbit hepatitis E virus (HEV) and rabbit providing an animal model for HEV study. Rev. Med. Virol. 2018, 28, e1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardini, R.; Verin, R.; Mazzei, M.; Forzan, M.; Poli, A. Hepatitis E virus-related liver alterations and viral antigen localization in European wild boar (Sus scrofa). Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2014, 60, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronesi, R.; Morach, M.; Hübschke, E.; Bachofen, C.; Stephan, R.; Nüesch-Inderbinen, M. Seroprevalence of hepatitis E virus in dogs in Switzerland. Zoonoses Public Health 2021, 68, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavio, N.; Doceul, V.; Bagdassarian, E.; Johne, R. Recent knowledge on hepatitis e virus in Suidae reservoirs and transmission routes to human. Vet. Res. 2017, 48, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liberg, O.; Johansson, A.; Andersen, R.; Linnell, J.D.C. Mating system, mating tactics and the function of male territory in roe deer. In The European Roe Deer: The Biology of Success; Andersen, R., Duncan, P., Linnell, J.D.C., Eds.; Scandinavian University Press: Oslo, Norway, 1998; pp. 221–256. [Google Scholar]
- Sridhar, S.; Yip, C.C.; Wu, S.; Chew, N.F.; Leung, K.H.; Chan, J.F.; Zhao, P.S.; Chan, W.M.; Poon, R.W.; Tsoi, H.W.; et al. Transmission of Rat Hepatitis E Virus Infection to Humans in Hong Kong: A Clinical and Epidemiological Analysis. Hepatology 2021, 73, 10–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinelli, N.; Pavoni, E.; Filogari, D.; Ferrari, N.; Chiari, M.; Canelli, E.; Lombardi, G. Hepatitis E virus in wild boar in the central northern part of Italy. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonardi, S.; Filipello, V.; Pavoni, E.; Carta, V.; Bolzoni, L.; Corradi, M.; Gilioli, S.; Losio, M.N. Geographical restriction of Hepatitis E virus circulation in wild boars (Sus scrofa) in Emilia-Romagna region, Northern Italy. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2020, 9, 8463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, J.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Jo, Y.W.; Min, H.J.; Kim, H.J.; Jung, W.T.; Lee, O.J.; Yun, H.; Yoon, Y.S. Genotype-4 hepatitis E in a human after ingesting roe deer meat in South Korea. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2013, 19, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Antibody | Ag Retrieval | Peroxidase Block | Protein Block | Dilution | II Ab |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-HEV | Tris-EDTA (pH 9) | H2O2 3% | UV | 1:200 | Goat anti-M |
| Anti-CD3 | Citric acid (pH 6) | BLOXALL B.S. | UV | 1:200 | Horse anti-M/R |
| Anti-CD20 | Citric acid (pH 6) | BLOXALL B.S. | UV | 1:100 | Horse anti-M/R |
| Anti-Iba-1 | Citric acid (pH 6) | BLOXALL B.S. | UV | 1:300 | Horse anti-M/R |
| Species | Age | Pisa | Grosseto | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | Female | Total | Male | Female | Total | |||
| Roe deer | Yearlings (1–2 years) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 | 5 | 11 | 14 |
| Mature (>2 years) | - | 9 | 9 | 9 | 10 | 19 | 28 | |
| Age n.d. | - | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 5 | 6 | |
| Total | 1 | 12 | 13 | 16 | 19 | 35 | 48 | |
| Fallow deer | Yearlings (1–2 years) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 15 | 11 | 26 | 29 |
| Mature (>2 years) | 3 | 1 | 4 | 12 | 5 | 17 | 21 | |
| Age n.d. | - | 1 | 1 | 7 | 2 | 9 | 10 | |
| Total | 4 | 4 | 8 | 34 | 18 | 52 | 60 | |
| Total cervids | 5 | 16 | 21 | 50 | 37 | 87 | 108 | |
| Species | N° | Sex | Age Class | Sampling Date | Hunting Area | PCR Viral Load |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roe deer | #1 | F | yearling | 04/03/21 | Magliano in Toscana (GR) | 1.40 × 103 |
| #2 | M | yearling | 14/04/21 | Scansano (GR) | 2.03 × 104 | |
| #3 | M | mature | 08/04/21 | Scansano (GR) | 1.25 × 104 | |
| #4 | M | yearling | 26/03/21 | Capalbio (GR) | 1.06 × 104 | |
| #5 | M | yearling | 10/04/21 | Magliano in Toscana (GR) | 2.75 × 104 | |
| Fallow deer | #6 | M | - | 07/11/19 | Parco Maremma (GR) | 9.3 × 103 |
| Species | Province | Virological Analysis | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AgELISA | RT-qPCR | ||
| Roe deer | Grosseto | 12/35 | 5/12 |
| Pisa | 4/13 | 0/4 | |
| Total | 16/48 | 5/16 | |
| Fallow deer | Grosseto | 3/52 | 1/3 |
| Pisa | 0/8 | - | |
| Total | 3/60 | 1/3 | |
| Total cervids | 19/108 | 6/19 | |
| Markers | Histopathological Changes | #1 | #2 | #3 | #4 | #5 | #6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roe Deer | Fallow Deer | ||||||
| Anti-HEV | Positive hepatocytes | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Positive cholangiocytes | 3 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Anti-Iba1 | Kupffer cells hyperplasia | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Periportal macrophage infiltration | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 1 | |
| Anti-CD3 | Periportal T-cells infiltration | 3 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| Sinusoidal T-cells infiltration | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | |
| Anti-CD20 | Periportal B-cells infiltration | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Sinusoidal B-cells infiltration | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fonti, N.; Pacini, M.I.; Forzan, M.; Parisi, F.; Periccioli, M.; Mazzei, M.; Poli, A. Molecular and Pathological Detection of Hepatitis E Virus in Roe Deer (Capreolus capreolus) and Fallow Deer (Dama dama) in Central Italy. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030100
Fonti N, Pacini MI, Forzan M, Parisi F, Periccioli M, Mazzei M, Poli A. Molecular and Pathological Detection of Hepatitis E Virus in Roe Deer (Capreolus capreolus) and Fallow Deer (Dama dama) in Central Italy. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(3):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030100
Chicago/Turabian StyleFonti, Niccolò, Maria Irene Pacini, Mario Forzan, Francesca Parisi, Marcello Periccioli, Maurizio Mazzei, and Alessandro Poli. 2022. "Molecular and Pathological Detection of Hepatitis E Virus in Roe Deer (Capreolus capreolus) and Fallow Deer (Dama dama) in Central Italy" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 3: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9030100






