Hemophilia A Resulting in Severe Hyperesthesia Due to Extraparenchymal Spinal Cord Hemorrhage in a Young Golden Retriever Puppy
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
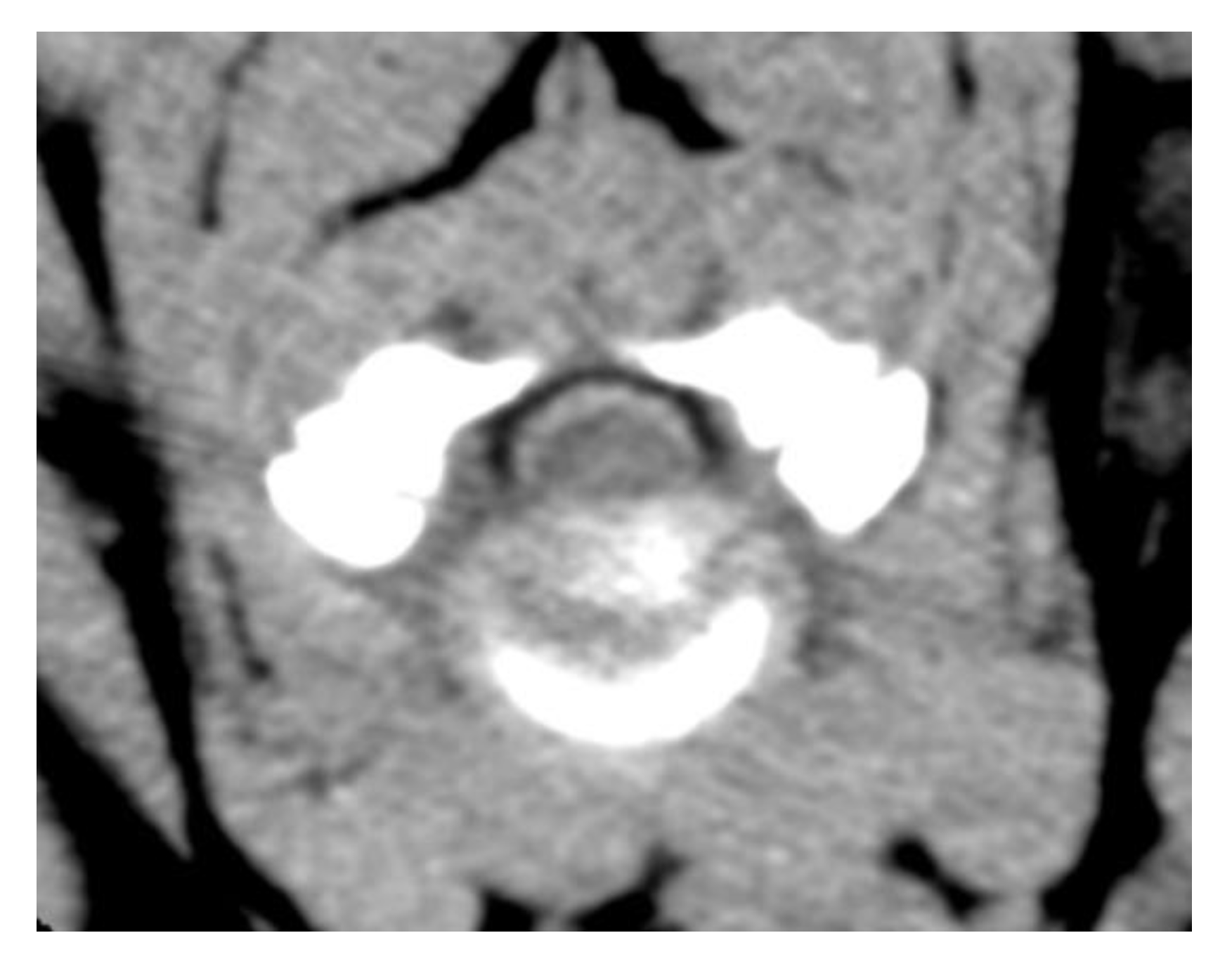
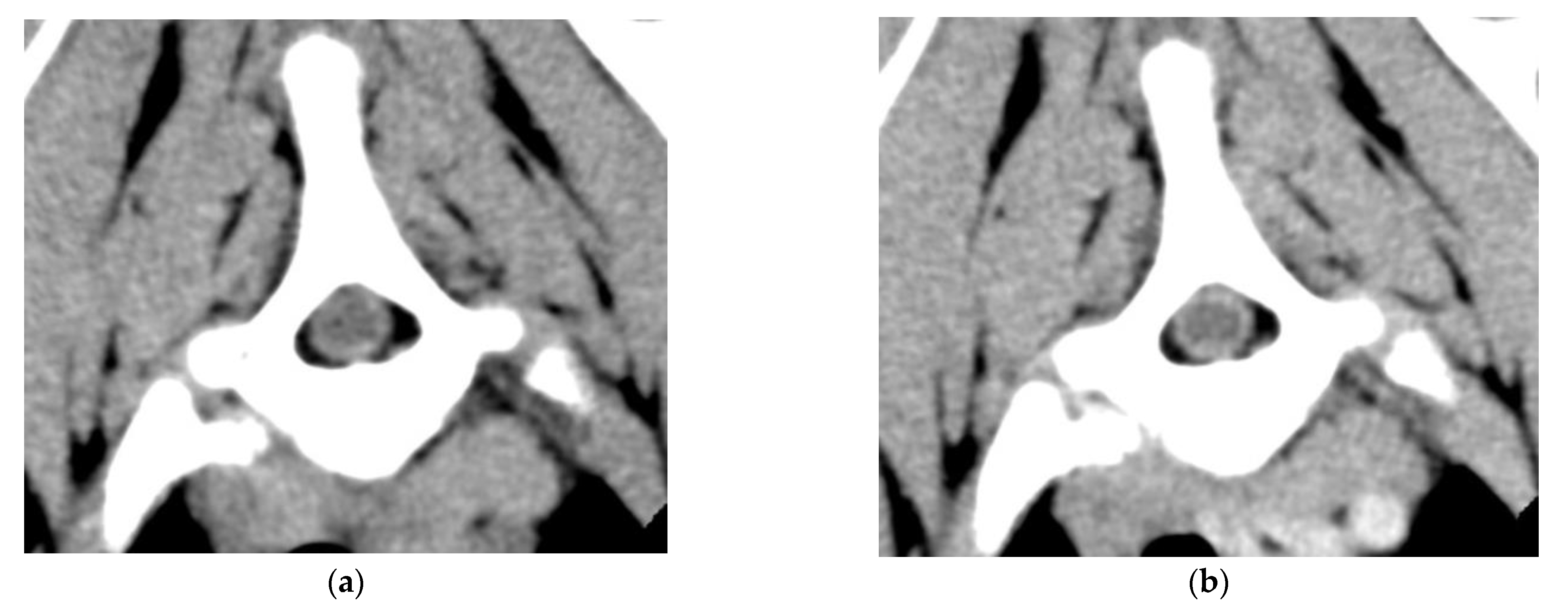
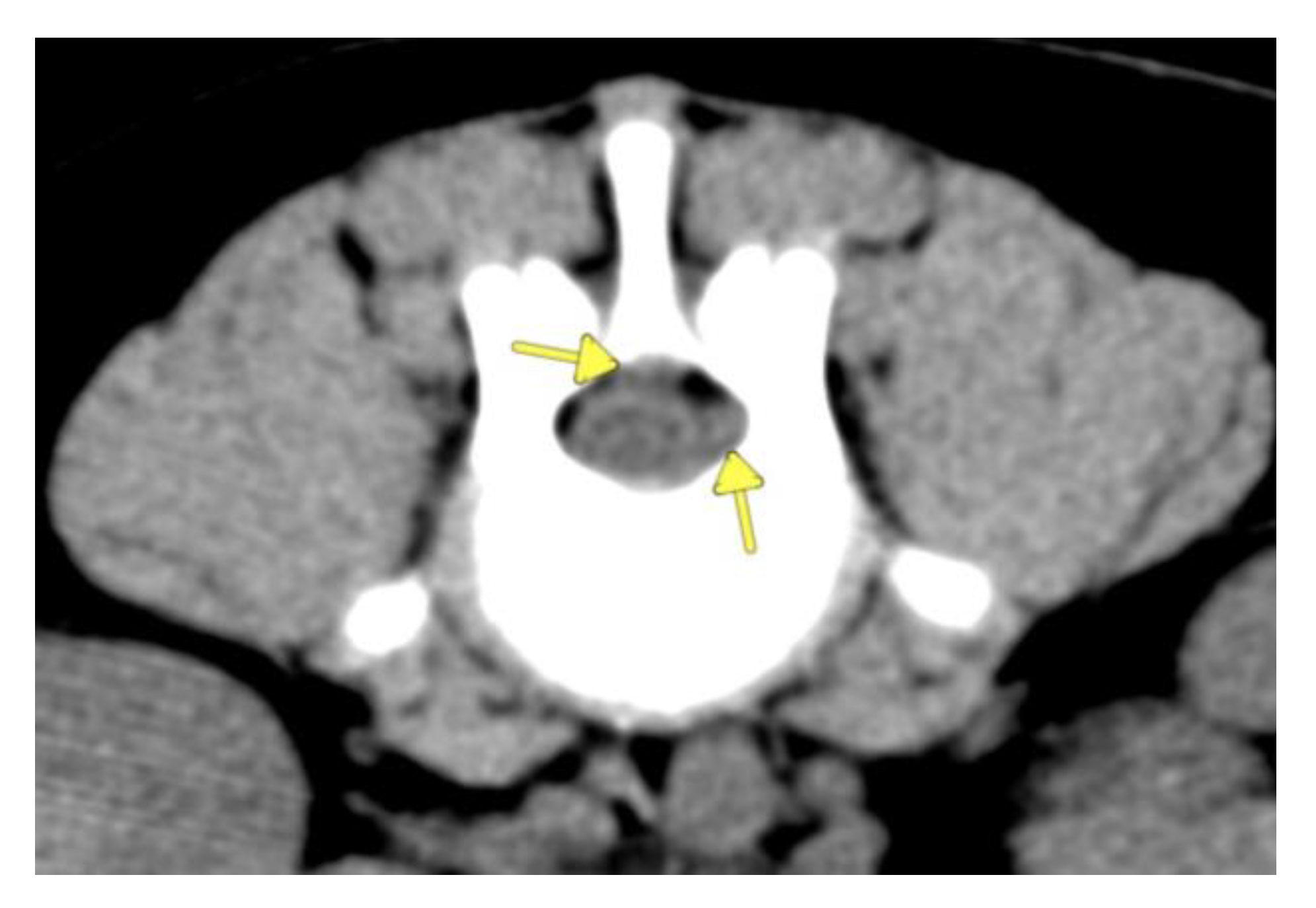
2. Case Description
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brooks, M. A review of canine inherited bleeding disorders: Biochemical and molecular strategies for disease characterization and carrier detection. J. Hered. 1999, 90, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausman, L.; Pack, A.; Hausmann, S.; Neiger, R. Acquired von-Willebrand factor and factor-VIII deficiencies caused by angiostrongylosis in a dog. Tierarztl. Prax. Ausg. K. Kleintiere/Heimtiere 2016, 44, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Aslanian, M.E.; Sharp, C.R.; Rozanski, E.A.; de Laforcade, A.M.; Rishniw, M.; Brooks, M.B. Clinical outcome after diagnosis of hemophilia A in dogs. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2014, 245, 667–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benn, D.M.; Gentry, P.A.; Johnstone, I.B. Classic hemophilia (hemophilia A) in a family of collies. Can. Vet. J. 1978, 19, 221–225. [Google Scholar]
- Parry, B.; Howard, M.; Mansell, P.; Holloway, S. Haemophilia A in German shepherd dogs. Aust. Vet. J. 1988, 65, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.; Kreeger, J. Acute paraplegia in a puppy with hemophilia A. J. Am. Anim. Hosp. Assoc. 1999, 35, 36–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokol, T.; Parry, B.W.; Richardson, J.L. Hematorrhachis associated with hemophilia A in three German shepherd dogs. J. Am. Hosp. Assoc. 1994, 30, 239–243. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, M.A.; Sharp, N.J.H. What is your neurological diagnosis? Parenchymal bleeding, irritation of the meninges and nerve roots, prior hemorrhage, and hemophilia A. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2002, 221, 1253–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, K.M.; Bolton, T.A.; Rossmeisl, J.H.; Arendse, A.U.; Vernau, K.M.; Li, R.H.L.; Parker, R.L. Clinical, diagnostic, and imaging findings in three juvenile dogs with paraspinal hyperesthesia or myelopathy as a consequence of Hemophilia A: A case report. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 871029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, J.; Windsor, R.; Stewart, S.D.; Fuerher-Senecal, L.; Khanna, C. Prevalence and clinical features of thoracolumbar intervertebral disc-associated epidural hemorrhage in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2022, 36, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, K.L.; Stieger-Vanegas, S.M.; Valentine, B.A. Hemorrhage in the central canal of the cervical spinal cord in a coonhound diagnosed with canine juvenile polyarteritis (steroid responsive meningitis-arteritis. Can. Vet. J. 2015, 56, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poli, F.; Calistri, M.; Meucci, V.; Di Gennaro, G.; Baroni, M. Prevalence, clinical features, and outcome of intervertebral disc extrusion associated with extensive epidural hemorrhage in a population of French Bulldogs compared to Dachshunds. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2022, 84, 1307–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang-Leandro, A.; Huenerfauth, E.; Heissl, K.; Tipold, A. MRI findings of early-stage hyperacute hemorrhage causing extramedullary compression of the cervical spinal cord in a dog with suspected steroid-responsive meningitis-arteritis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2017, 4, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilli, J.; Olszewska, A.; Farke, D.; Schmidt, M.J. Successful surgical and medical treatment of a severe, acute epidural bleed in a young dog due to steroid responsive meningitis-arteritis. Acta Vet. Scand. 2021, 63, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigrist, N.E.; Tritten, L.; Kümmerle-Fraune, C.; Hofer-Inteeworn, N.; Schefer, R.J.; Schnyder, M.; Kutter, A.P.N. Coagulation status in dogs naturally infected with Angiostrongylus vasorum. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessmann, A.; Lu, D.; Lamb, C.R.; Smyth, B.; Mantis, P.; Chandler, K.; Boag, A.; Cherubini, G.B.; Cappello, R. Brain and spinal cord haemorrhages associated with Angiostrongylus vasorum infection in four dogs. Vet. Rec. 2006, 158, 858–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, S.J.; Feldman, E.C.; Coté, E. Textbook of Veterinary Interal Medicine: Diseases of the Dog and Cat, 8th ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2017; Volume 1, p. 828. [Google Scholar]
- Gavazza, A.; Lubas, G.; Trotta, M.; Caldin, M. Hemophilia A in a Belgian shepherd malinois dog: Case report. Res. Vet. Sci. 2014, 97, 96–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, J.W.; McMichael, M. Inherited disorders of hemostasis in dogs and cats. Top. Companion Anim. Med. 2012, 27, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokol, T.; Parry, B.W. Efficacy of fresh-frozen plasma and cryoprecipitate in dogs with von Willebrand’s disease of hemophilia A. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 1998, 12, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callan, M.B.; Haskins, M.E.; Wang, P.; Zhou, S.; High, K.A.; Arruda, V.R. Successful phenotype improvement following gene therapy for severe hemophilia A in privately owned dogs. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’kelley, B.M.; Whelan, M.F.; Brooks, M.B. Factor VIII inhibitors complicating treatment of postoperative bleeding in a dog with hemophilia A. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2009, 19, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, G.N.; Everett, J.K.; Kafle, S.; Roche, A.M.; Raymond, H.E.; Leiby, J.; Wood, C.; Assenmacher, C.; Merricks, E.P.; Long, C.T.; et al. A long-term study of AAV gene therapy in hemophilia A dogs identifies clonal expansions of transduced liver cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricciardi, M.; Campanella, A.; Grieco, G.; Zammit, R. Usefulness of spinal unenhanced computed tomography and CT-myelography in the age of multidetector CT technology and magnetic resonance imaging—Preliminary considerations. Open Vet. J. 2018, 8, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, R.C.; Moore, S.A. Differential diagnosis of spinal diseases. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 40, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamir, M.H.; Tavor, N.; Aizenberg, T. Radiographic findings during recovery from discospondylitis. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2001, 42, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.B. Diskospondylitis and other vertebral infections. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2000, 30, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalo-Orden, J.M.; Altonaga, J.R.; Orden, M.A.; Gonzalo, J.M. Magnetic resonance, computed thomographic and radiologic findings in a dog with discospondylitis. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound 2000, 41, 142–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, J.F.; Levine, J.; Kerwin, S.; Cole, R. Canine thoracolumbar invertebral disk disease: Diagnosis, prognosis and treatment. Compend. Contin. Educ. Vet. 2009, 31, E3. [Google Scholar]
- Tipold, A.; Schatzberg, S.J. An update on steroid responsive meningitis-arteritis. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2010, 51, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Hehn, C.A.; Baron, R.W. Deconstructing the neuropathic pain phenotype to reveal neural mechanisms. Neuron 2012, 73, 638–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, S.E.; Hendrix, D.V.H. Unilateral subconjunctival and retrobulbar hemorrhage secondary to brodifacoum toxicity in a dog. Case Rep. Vet. Med. 2013, 2013, 417808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, O.L.; Andreasen, C. The utility of plasma D-dimer to identify thromboembolic disease in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2003, 17, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, M.B.; Barnas, J.L.; Fremont, J.; Ray, J. Cosegregation of factor VIII microsatellite marker with mild hemophilia A in golden retriever dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2005, 19, 205–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, J.L.; Donahue, J.H.; Nacey, N.C.; Quirk, C.R.; Perry, M.T.; Faulconer, N.; Gene, A.F.; Maldonado, M.D.; Schaeffer, C.A.; Shen, F.H. Spinal hematomas: What a radiologist needs to know. RadioGraphics 2018, 38, 1516–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaumet, A.C.S.G.; Rossi, T.A.; Murphy, L.A.; Nakamura, R.K. Evaluation of owners’ attitudes towards veterinary insurance in a specialty hospital. J. Small Anim. Pract. 2021, 62, 805–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leebeek, F.W.G.; Miesbach, W. Gene therapy for hemophilia: A review on clinical benefit, limitations, and remaining issues. Blood 2021, 138, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Measurement | 1 | 2 | Reference Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| PT (s) | 13.0 | 11.0 | 11.0–17.0 |
| aPPT (s) | 142.0 | 187.0 | 72.0–102.0 |
| FVIII:C (%) | 6 | 7 | 60–150 |
| FXI:C (%) | 35 | 60 | 60–150 |
| D-dimers (µg/mL) | 0.7 | - | 0.023–0.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lubbers, C.; Beukers, M.; Bergknut, N.; Paes, G. Hemophilia A Resulting in Severe Hyperesthesia Due to Extraparenchymal Spinal Cord Hemorrhage in a Young Golden Retriever Puppy. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110638
Lubbers C, Beukers M, Bergknut N, Paes G. Hemophilia A Resulting in Severe Hyperesthesia Due to Extraparenchymal Spinal Cord Hemorrhage in a Young Golden Retriever Puppy. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(11):638. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110638
Chicago/Turabian StyleLubbers, Charlotte, Martijn Beukers, Niklas Bergknut, and Geert Paes. 2022. "Hemophilia A Resulting in Severe Hyperesthesia Due to Extraparenchymal Spinal Cord Hemorrhage in a Young Golden Retriever Puppy" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 11: 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110638
APA StyleLubbers, C., Beukers, M., Bergknut, N., & Paes, G. (2022). Hemophilia A Resulting in Severe Hyperesthesia Due to Extraparenchymal Spinal Cord Hemorrhage in a Young Golden Retriever Puppy. Veterinary Sciences, 9(11), 638. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9110638






