Changes in Perioperative Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Regimens for Colic Surgery in Horses: A Single Center Report
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population
3.2. Surgery
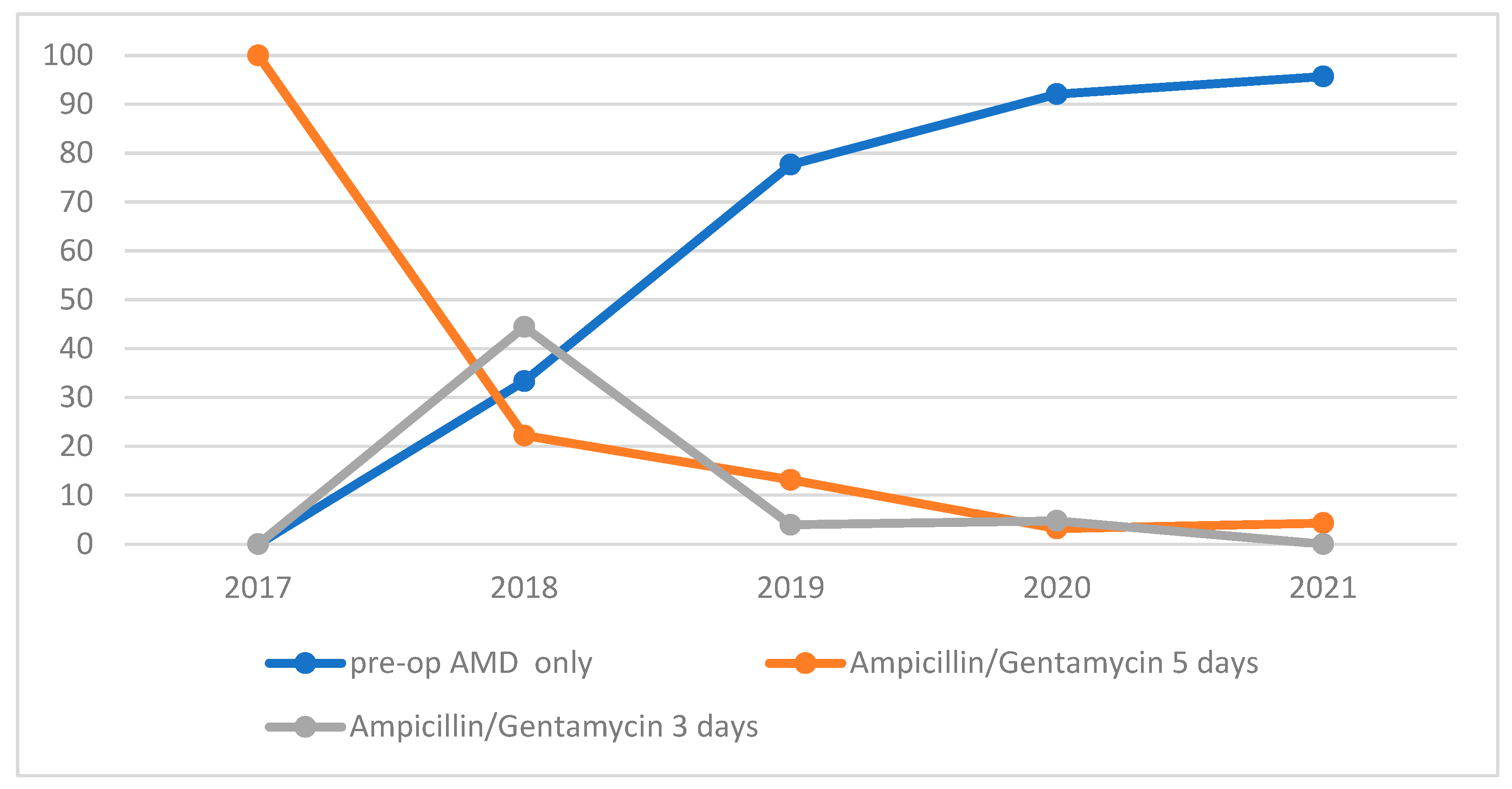
3.3. Pre and Intra-Operative AMDs and AIDs Administration
3.4. Postoperative AMDs during Hospitalization
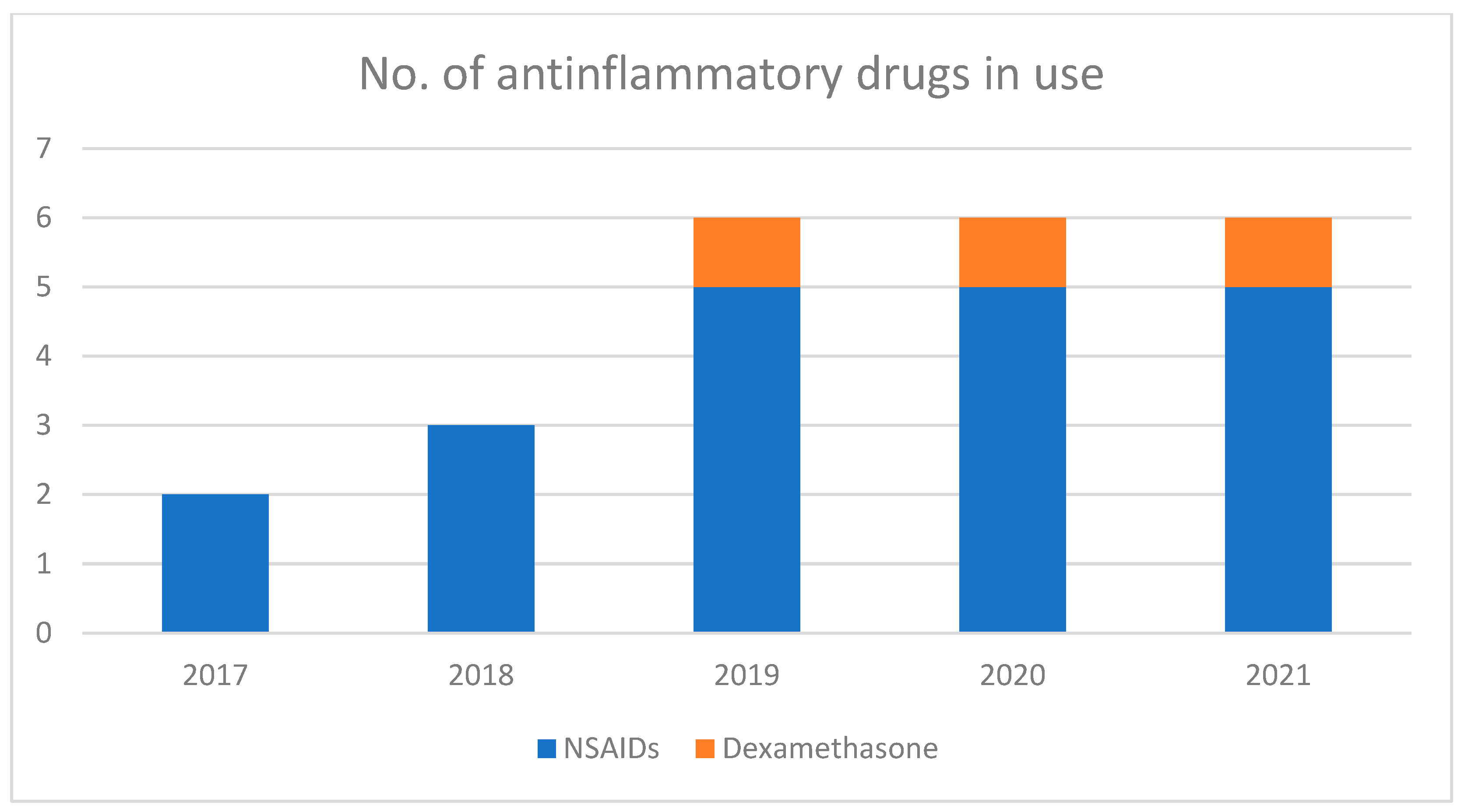
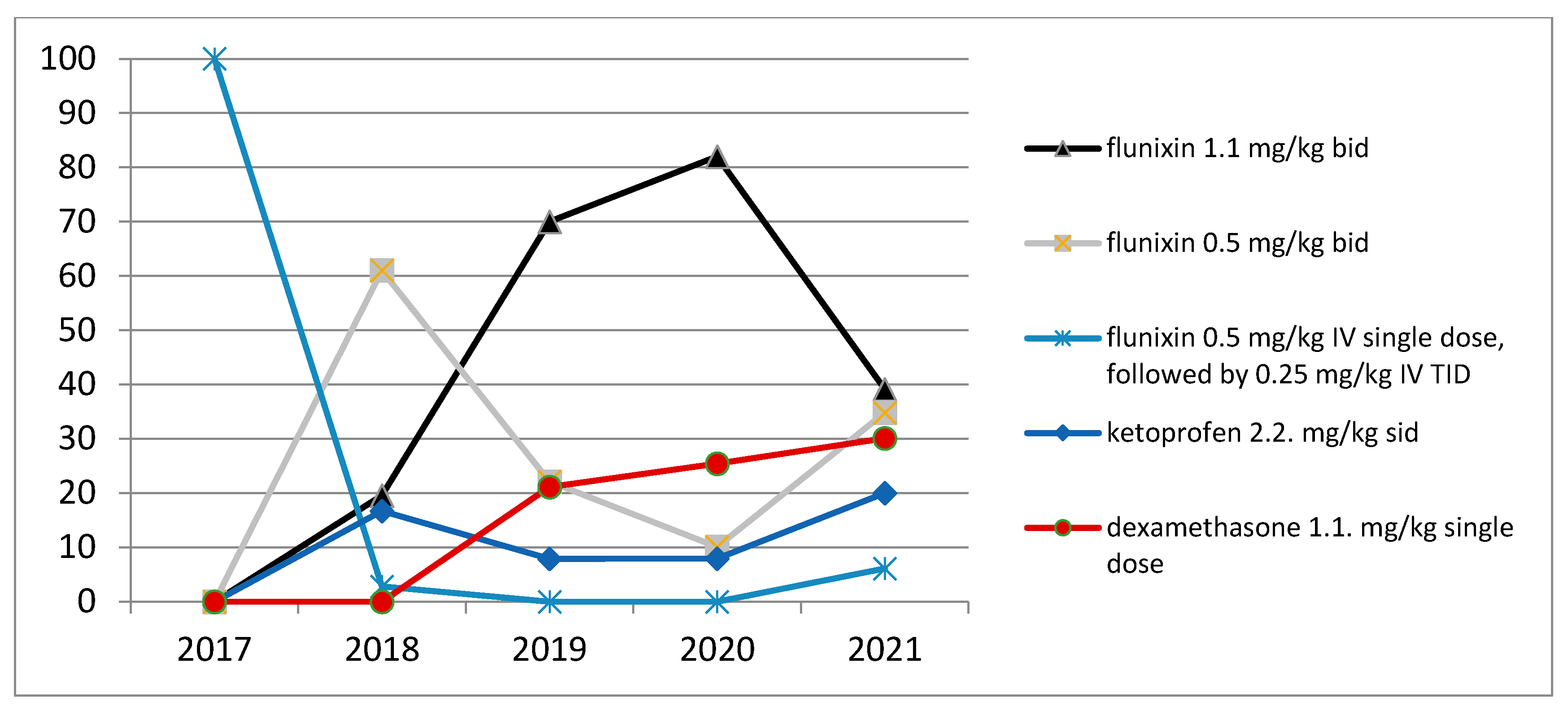
3.5. Postoperative AIDs Drugs Administration during Hospitalization
3.6. Short-Term Follow Up
Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fogle, C. Postoperative Care, Complications, and Reoperation of the Colic Patient. In Equine Surgery, 5th ed.; Saunders Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2019; pp. 660–677. [Google Scholar]
- Southwood, L.L. Principles of antimicrobial therapy: What should we be using? Vet. Clin. N. Am. Equine Pract. 2006, 22, 279–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, D.E. Antimicrobial use during colic surgery: Finding the right strategy. Vet. Rec. 2013, 172, 285–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, K.D.; Southwood, L.L.; Lane, J.; Lindborg, S.; Aceto, H.W. Post operative infection, pyrexia and perioperative antimicrobial drug use in surgical colic patients. Equine Vet. J. 2012, 44, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morley, P.S.; Apley, M.D.; Besser, T.E.; Burney, D.P.; Fedorka-Cray, P.J.; Papich, M.G.; Traub-Dargatz, J.L.; Weese, J.S. Antimicrobial drug use in veterinary medicine. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2005, 19, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryden, M.; Johnson, A.P.; Ashiru-Oredope, D.; Sharland, M. Using antibiotics responsibly: Right drug, right time, right dose, right duration. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 2441–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, V.L.; Blikslager, A.T. The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in critically ill horses. J. Vet. Emerg. Crit. Care 2015, 25, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durward-Akhurst, S.A.; Mair, T.S.; Boston, R.; Dunkel, B. Comparison of two antimicrobial regimens on the prevalence of incisional infections after colic surgery. Vet. Rec. 2013, 172, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, R.; McGovern, K. Trends in antimicrobial use for exploratory laparotomy. Equine Vet. J. 2019, 51 (Suppl. 53), 5–31. [Google Scholar]
- Stöckle, S.D.; Kannapin, D.A.; Kauter, A.M.L.; Lübke-Becker, A.; Walther, B.; Merle, R.; Gehlen, H. A Pilot Randomised Clinical Trial Comparing a Short-Term Perioperative Prophylaxis Regimen to a Long-Term Standard Protocol in Equine Colic Surgery. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Båverud, V.; Gustafsson, A.; Franklin, A.; Lindholm, A.; Gunnarsson, A. Clostridium difficile associated with acute colitis in mature horses treated with antibiotics. Equine Vet. J. 1997, 29, 279–284. [Google Scholar]
- Isgren, C.M. Improving clinical outcomes via responsible antimicrobial use in horses. Equine Vet. Educ. 2021, 34, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redding, L.; Grunwald, H.; Cole, S.; Rankin, S.; Nolen-Walston, R. Modification of empirical antimicrobial regimens in large animal medicine. Vet. Rec. 2020, 187, e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muntwyler, N.; Dubois, M.S.; Weese, J.S. Retrospective assessment of perioperative antimicrobial use for elective arthroscopy in horses. Vet. Surg. 2020, 49, 427–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, D.P.M.; de Lacerda Neto, J.C. Jugular thrombophlebitis in horses: A review of fibrinolysis, thrombus formation, and clinical management. Can. Vet. J. 2013, 54, 65–71. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, V. Abdominal closure. In The Equine Acute Abdomen, 3rd ed.; Blikslager, A., Mair, T.S., White, N., Moore, J.N., Eds.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017; Chapter 46; pp. 606–608. [Google Scholar]
- Hubbell, J.A.; Muir, W.W.; Robertson, J.T.; Sams, R.A. Cardiovascular effects of intravenous sodium penicillin, sodium cefazolin, and sodium citrate in awake and anesthetized horses. Vet. Surg. 1987, 16, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaer, D.B.L.; Linton, J.K.; Aceto, H. Antimicrobial use in horses undergoing colic surgery. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2012, 26, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torfs, S.; Levet, T.; Delesalle, C.; Dewulf, J.; Vlaminck, L.; Pille, F.; Lefere, L.; Martens, A. Risk factors for incisional complications after exploratory celiotomy in horses: Do skin staples increase the risk? Vet. Surg. 2010, 39, 616–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heal, C.F.; Banks, J.L.; Lepper, P.D.; Kontopantelis, E.; van Driel, M.L. Topical antibiotics for preventing surgical site infection in wounds healing by primary intention. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 11, CD011426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isgren, C.M.; Salem, S.E.; Archer, D.C.; Worsman, F.C.; Townsend, N.B. Risk factors for surgical site infection following laparotomy: Effect of season and perioperative variables and reporting of bacterial isolates in 287 horses. Equine Vet. J. 2017, 49, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, S.L.; Devick, I.; Bracamonte, J.L.; Hendrick, S.; Barber, S.M.; Carmalt, J.L.; Wilson, D.G. Occurrence of Incisional Complications After Closure of Equine Celiotomies with USP 7 Polydioxanone. Vet. Surg. 2015, 44, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnaud, S.J.; Southwood, L.L.; Aceto, H.W.; Stefanovski, D.; Tomassone, L.; Zarucco, L. Are horse age and incision length associated with surgical site infection following equine colic surgery? Vet. J. 2016, 217, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colbath, A.C.; Patipa, L.; Berghaus, R.D.; Parks, A.H. The influence of suture pattern on the incidence of incisional drainage following exploratory laparotomy. Equine Vet. J. 2014, 46, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirosh-Levy, S.; Gottlieb, Y.; Fry, L.M.; Knowles, D.P.; Steinman, A. Twenty Years of Equine Piroplasmosis Research: Global Distribution, Molecular Diagnosis, and Phylogeny. Pathogens 2020, 9, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fugler, L.A. Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Equine Systemic Inflammatory Response: Implications for Equine Laminitis. Ph.D. Thesis, Louisiana State University, Baton Rouge, LA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mair, T.S.; Smith, L.J. Survival and complication rates in 300 horses undergoing surgical treatment of colic. Part 1: Short-term survival following a single laparotomy. Equine Vet. J. 2005, 37, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Liu, S.; Hu, Y.; Yu, M.; Chen, J.; Liu, C. Influence of perioperative nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on complications after gastrointestinal surgery: A meta-analysis. Acta Anaesthesiol. Taiwan. 2016, 54, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brune, K.; Dietzel, K.; Nürnberg, B.; Schneider, H.T. Recent insight into the mechanism of gastrointestinal tract ulceration. Scand. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 1987, 65, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushfeldt, C.F.; Sveinbjørnsson, B.; Søreide, K.; Vonen, B. Risk of anastomotic leakage with use of NSAIDs after gastrointestinal surgery. Int J. Colorectal. Dis. 2011, 26, 1501–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naylor, R.J.; Taylor, A.H.; Knowles, E.J.; Wildford, S.; Linnenkohl, W.; Mair, T.S.; Johns, I.C. Comparison of flunixin meglumine and meloxicam for post operative management of horses with strangulating small intestinal lesions. Equine Vet. J. 2014, 46, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, A.L.; Freeman, C.K.; Fogle, C.A.; Burke, M.J.; Davis, J.L.; Cook, V.L.; Southwood, L.L.; Blikslager, A.T. Multicentre, blinded, randomised clinical trial comparing the use of flunixin meglumine with firocoxib in horses with small intestinal strangulating obstruction. Equine Vet. J. 2019, 51, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| AMD | No AMD | Total | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | Test | p | ||
| Total cases | 92 | 142 | 234 | ||||||
| Postoperative euthanasia | 14 | 15.2 | 17 | 12 | 31 | 13.3 | Chi-square | 0.51 | |
| Discharged | 78 | 84.8 | 125 | 88 | 203 | 86.7 | |||
| Female | 35 | 38 | 54 | 38 | 89 | 38 | Chi-square | 0.99 | |
| Gelding | 41 | 44.6 | 67 | 47.2 | 108 | 46.2 | |||
| Stallion | 16 | 17.4 | 21 | 14.8 | 37 | 15.8 | |||
| Pathology | Small intestine—Strangulating lesions | 23 | 25 | 33 | 23.2 | 56 | 24 | Chi-square | 1 |
| Small intestine—Non-Strangulating lesions | 11 | 12 | 25 | 17.6 | 36 | 15.4 | |||
| Large intestine—Strangulating lesions | 12 | 13 | 16 | 11.3 | 28 | 12 | Chi-square | 0.06 | |
| Large intestine—Non-Strangulating lesions | 46 | 50 | 68 | 47.9 | 114 | 48.6 | |||
| Enterotomy/anastomosis | 80 | 87 | 131 | 92.3 | 211 | 90.2 | Chi-square | 0.18 | |
| AMD | NO AMD | Total | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | Test | p | ||
| Number of horses per group | 92 | 142 | 234 | ||||||
| AMD prophylaxis | 5-day course | 70 | 0 | 70 | |||||
| 3-day course | 22 | 0 | 22 | ||||||
| AMD extra prophylaxis protocol | 30/92 | 32.6 | 51/142 | 35.9 | 81/234 | 34.6 | Chi-square | 0.603 | |
| Reason | SSI | 6/30 | 20 | 5/51 | 9.8 | 11/81 | 13.6 | Chi-square | 0.195 |
| Thrombophlebitis | 0 | 2 | 2 | Fisher exact | 0.52 | ||||
| Piroplasmosis | 18/30 | 60 | 43/51 | 84.3 | 61/81 | 75.3 | Chi-square | 0.014 | |
| Peritonitis | 0 | 2 | 2 | Fisher exact | 0.52 | ||||
| Laminitis | 3 | 4 | 7 | Fisher exact | 0.7 | ||||
| Others (DPJ, Abortus) | 3 | 5 | 8 | Fisher exact | 1 | ||||
| AMD | NO AMD | Total | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | Test | p | ||
| Number of horses per group | 92 | 142 | 234 | ||||||
| Intraoperative dexamethasone (0.05 mg/kg) | 8/92 | 30/142 | 38/234 | Chi-square | 0.01 | ||||
| AIDs extra protocol | 35/92 | 38 | 74/142 | 52.1 | 109/234 | 46.6 | Chi-square | 0.03 | |
| Flunixin | 11 | 6 | 17 | Chi-square | 0.001 | ||||
| Phenylbutazone | 19 | 46 | 65 | Chi-square | 0.43 | ||||
| Ketoprofen | 5 | 20 | 25 | Fisher exact | 0.22 | ||||
| Acetylsalicylate | 1 | 2 | 3 | Fisher exact | 1 | ||||
| Multiple drugs | 11 | 0 | 11 | Fisher exact | 0.001 | ||||
| Reason | Pyrexia | 21/35 | 60 | 50/74 | 67.6 | 71/109 | 65.2 | Chi-square | 0.024 |
| Colic | 8 | 15 | 23 | Chi-square | 0.76 | ||||
| Laminitis | 5 | 7 | 12 | Fisher exact | 0.5 | ||||
| Other | 1 | 2 | 3 | Fisher exact | 1 | ||||
| AMD | NO AMD | Total | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | n | % | Test | p | ||
| Number of horses per group | 92 | 142 | 234 | ||||||
| Pyrexia | 40 | 43.5 | 63 | 44.4 | 103 | 44 | Chi-square | 0.893 | |
| Duration (hours) | <48 | 31 | 77.5 | 39 | 61.9 | 70 | 68 | Chi-square | 0.098 |
| °C | <39.5 | 31 | 77.5 | 53 | 84.1 | 84 | 81.6 | Chi-square | 0.398 |
| Enterotomy/anastomosis + pyrexia | 32/80 | 40 | 56/131 | 42.8 | 88/211 | 41.8 | Chi-square | 0.694 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gandini, M.; Cerullo, A.; Franci, P.; Giusto, G. Changes in Perioperative Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Regimens for Colic Surgery in Horses: A Single Center Report. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100546
Gandini M, Cerullo A, Franci P, Giusto G. Changes in Perioperative Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Regimens for Colic Surgery in Horses: A Single Center Report. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(10):546. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100546
Chicago/Turabian StyleGandini, Marco, Anna Cerullo, Paolo Franci, and Gessica Giusto. 2022. "Changes in Perioperative Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Regimens for Colic Surgery in Horses: A Single Center Report" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 10: 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100546
APA StyleGandini, M., Cerullo, A., Franci, P., & Giusto, G. (2022). Changes in Perioperative Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Regimens for Colic Surgery in Horses: A Single Center Report. Veterinary Sciences, 9(10), 546. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100546








