The Application of MALDI-TOF MS for a Variability Study of Paenibacillus larvae
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
2.2. MALDI-TOF Identification of Bacteria
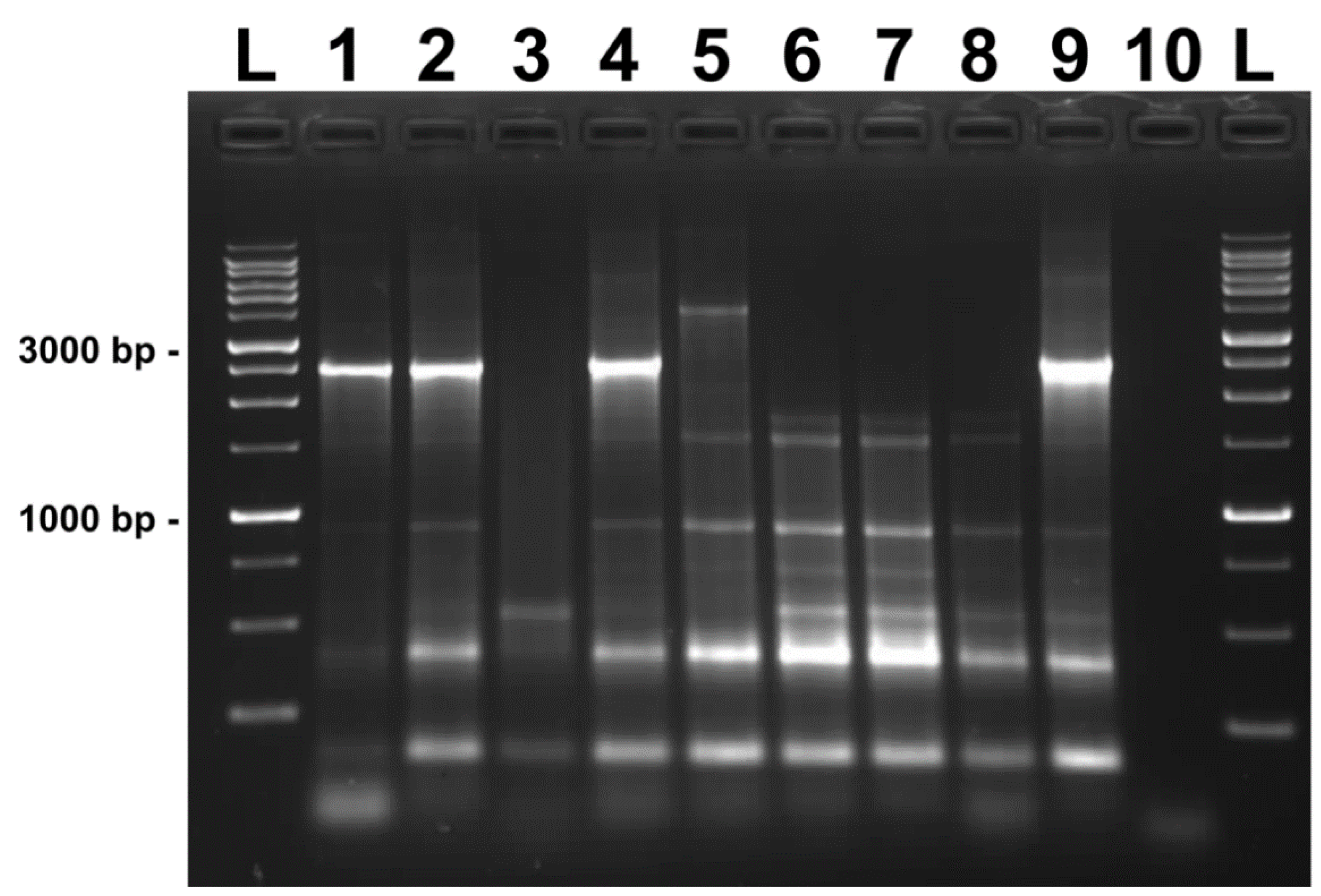
2.3. DNA Isolation, PCR Amplification, and the Phylogenetic Analysis of P. larvae Isolates
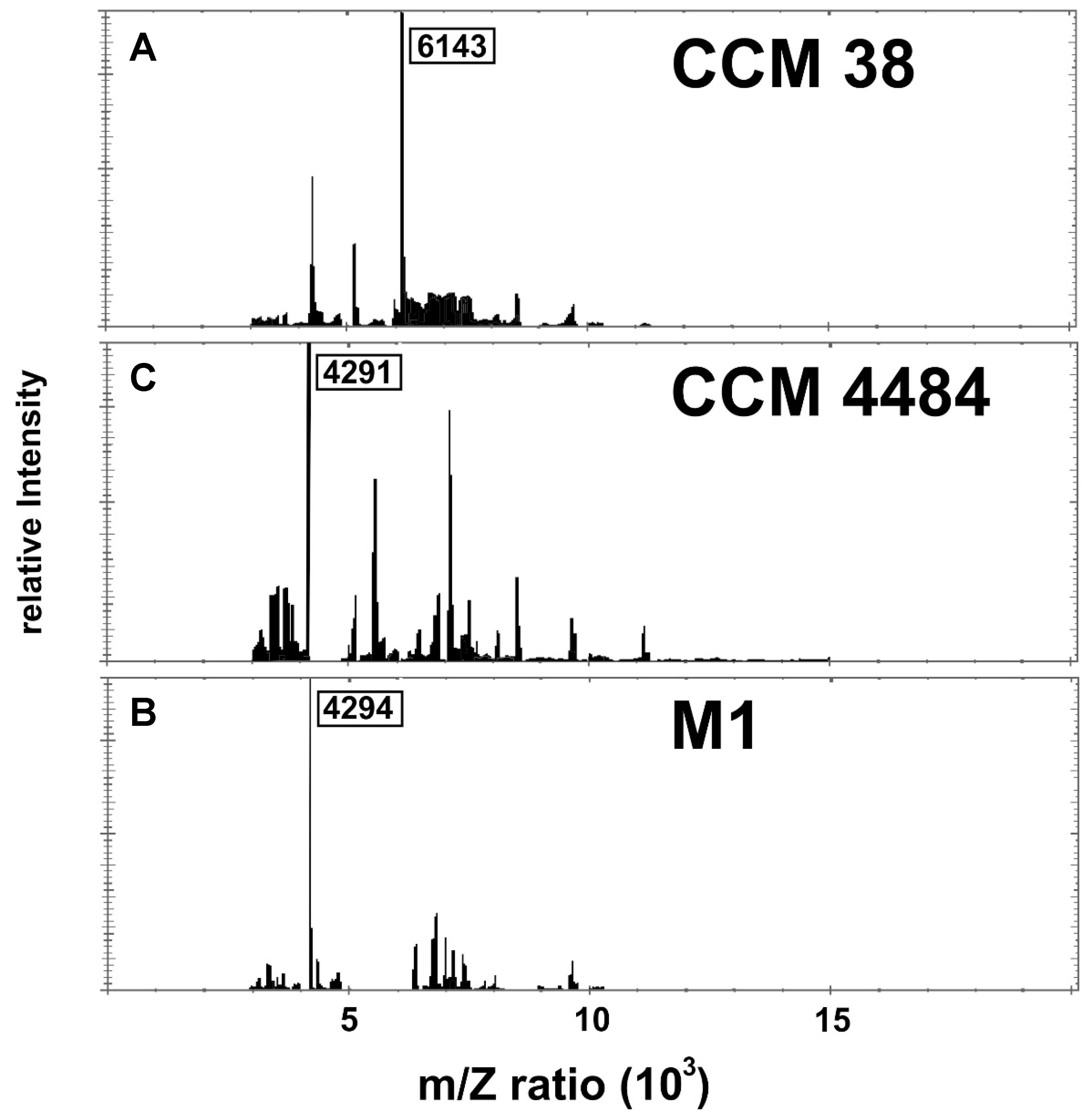
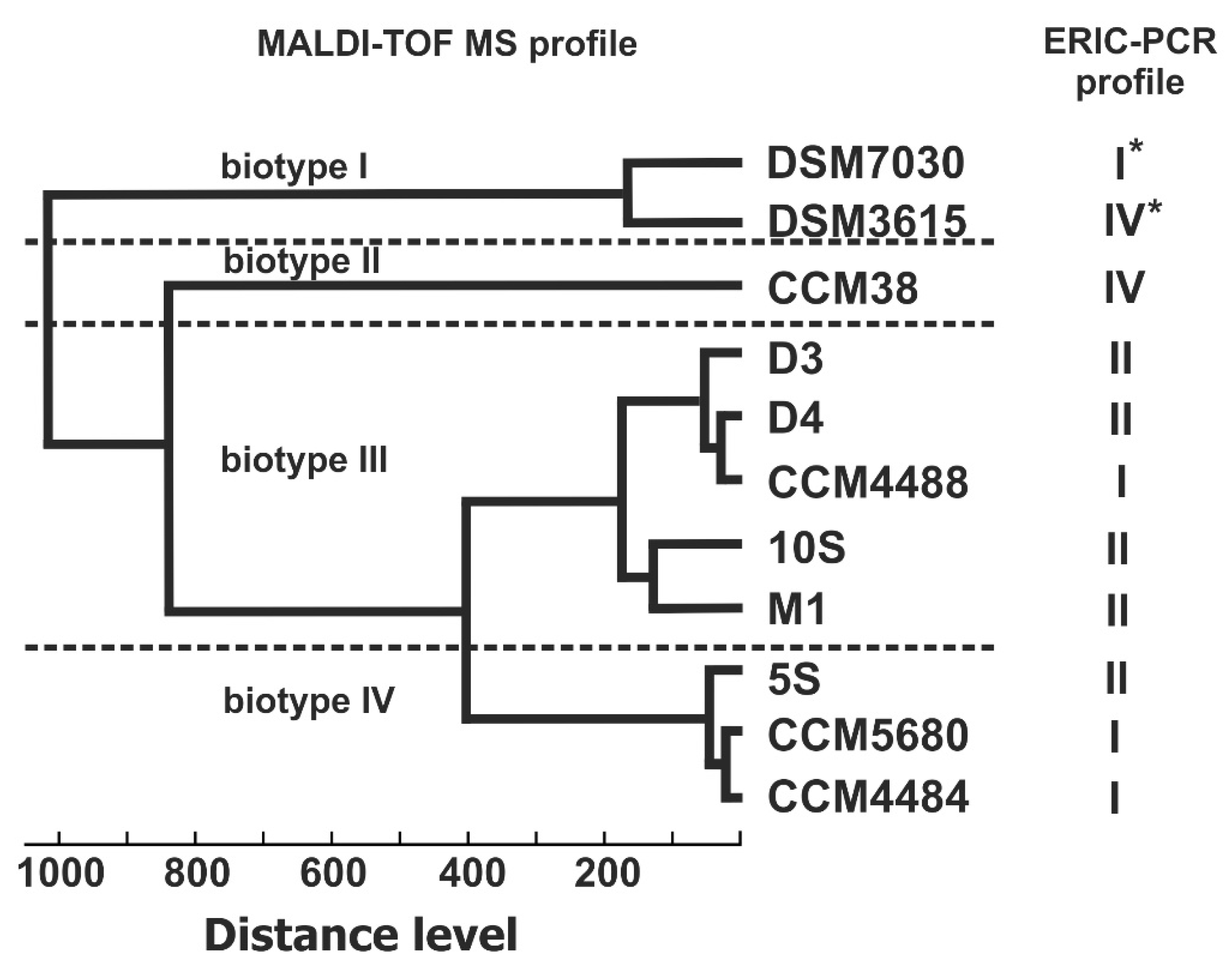
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Genersch, E. American Foulbrood in honeybees and its causative agent, Paenibacillus larvae. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 103, S10–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashiralieva, A.; Genersch, E. Reclassification, genotypes and virulence of Paenibacillus larvae, the etiological agent of American foulbrood in honeybees—A review. Apidologie 2006, 37, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antúnez, K.; Piccini, C.; Castro-Sowinski, S.; Rosado, A.S.; Seldin, L.; Zunino, P. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Paenibacillus larvae isolates. Vet. Microbiol. 2007, 124, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genersch, E.; Otten, C. The use of repetitive element PCR fingerprinting (rep-PCR) for genetic subtyping of German field isolates of Paenibacillus larvae subsp. larvae. Apidologie 2003, 34, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kilwinski, J.; Peters, M.; Ashiralieva, A.; Genersch, E. Proposal to reclassify Paenibacillus larvae subsp. pulvifaciens DSM 3615 (ATCC 49843) as Paenibacillus larvae subsp. larvae. Results of a comparative biochemical and genetic study. Vet. Microbiol. 2004, 104, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loncaric, I.; Derakhshifar, I.; Oberlerchner, J.T.; Köglberger, H.; Moosbeckhofer, R. Genetic diversity among isolates of Paenibacillus larvae from Austria. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2009, 100, 44–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuendorf, S.; Hedtke, K.; Tangen, G.; Genersch, E. Biochemical characterization of different genotypes of Paenibacillus larvae subsp. larvae, a honey bee bacterial pathogen. Microbiology 2004, 150, 2381–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genersch, E.; Forsgren, E.; Pentikäinen, J.; Ashiralieva, A.; Rauch, S.; Kilwinski, J.; Fries, I. Reclassification of Paenibacillus larvae subsp. pulvifaciens and Paenibacillus larvae subsp. larvae as Paenibacillus larvae without subspecies differentiation. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beims, H.; Bunk, B.; Erler, S.; Mohr, K.I.; Spröer, C.; Pradella, S.; Günther, G.; Rohde, M.; von der Ohe, W.; Steinert, M. Discovery of Paenibacillus larvae ERIC V: Phenotypic and genomic comparison to genotypes ERIC I-IV reveal different inventories of virulence factors which correlate with epidemiological prevalences of American Foulbrood. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2020, 310, 151394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carolis, E.; Vella, A.; Vaccaro, L.; Torelli, R.; Spanu, T.; Fiori, B.; Posteraro, B.; Sanguinetti, M. Application of MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry in clinical diagnostic microbiology. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2014, 8, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabrolier, N.; Sauget, M.; Bertrand, X.; Hocquet, D. Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry identifies Pseudomonas aeruginosa high-risk clones. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 1395–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordström, S.; Fries, I. A comparison of media and cultural conditions for identification of Bacillus larvae in honey. J. Apic. Res. 1995, 34, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; Sánchez-Juanes, F.; García-Fraile, P.; Rivas, R.; Mateos, P.F.; Martínez-Molina, E.; González-Buitrago, J.M.; Velázquez, E. MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry is a fast and reliable platform for identification and ecological studies of species from family Rhizobiaceae. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pospiech, A.; Neumann, B. A versatile quick-prep of genomic DNA from Gram-positive bacteria. Trends Genet. 1995, 11, 217–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versalovic, J.; Schneider, M.; De Bruijn, F.J.; Lupski, J.R. Genomic fingerprinting of bacteria using repetitive sequence-based polymerase chain reaction. Methods Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 5, 25–40. [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg, W.G.; Barns, S.M.; Pelletier, D.A.; Lane, D.J. 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 697–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maniatis, T.; Fritsch, E.F.; Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1982; ISSN 0307-4412. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T. The enveomics collection: A toolbox for specialized analyses of microbial genomes and metagenomes. PeerJ Prepr. 2016, 4, e1900v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alippi, A.M.; Reynaldi, F.J.; Lopez, A.C.; De Giusti, M.R.; Aguilar, O.M. Molecular epidemiology of Paenibacillus larvae larvae and incidence of American foulbrood in Argentinean honeys from Buenos Aires province. J. Apic. Res. 2004, 43, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katznelson, H. Bacillus pulvifaciens (n. sp.), an organism associated with powdery scale of honeybee larvae. J. Bacteriol. 1950, 59, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culebras, E. The Use of Mass Spectrometry Technology (MALDI-TOF) in Clinical Microbiology; Cobo, F., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 213–233. ISBN 9780128144510. [Google Scholar]
- Celandroni, F.; Salvetti, S.; Gueye, S.A.; Mazzantini, D.; Lupetti, A.; Senesi, S.; Ghelardi, E. Identification and pathogenic potential of clinical Bacillus and Paenibacillus isolates. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Sánchez, B.; Sánchez-Carrillo, C.; Ruiz, A.; Marín, M.; Cercenado, E.; Rodríguez-Créixems, M.; Bouza, E. Direct identification of pathogens from positive blood cultures using matrix-assisted laser desorption-ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, O421–O427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Bai, F.; Li, T.; Yan, H. An endophytic strain of genus Paenibacillus isolated from the fruits of Noni (Morinda citrifolia L.) has antagonistic activity against a Noni’s pathogenic strain of genus Aspergillus. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 125, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schäfer, M.O.; Genersch, E.; Fünfhaus, A.; Poppinga, L.; Formella, N.; Bettin, B.; Karger, A. Rapid identification of differentially virulent genotypes of Paenibacillus larvae, the causative organism of American foulbrood of honey bees, by whole cell MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 170, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, L.J.; Yang, Y.L. Bacillus classification based on matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry—Effects of culture conditions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, S.; Freiwald, A.; Maier, T.; Kube, M.; Reinhardt, R.; Kostrzewa, M.; Geider, K. Classification and identification of bacteria by mass spectrometry and computational analysis. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loucif, L.; Bendjama, E.; Gacemi-Kirane, D.; Rolain, J.M. Rapid identification of Streptomyces isolates by MALDI-TOF MS. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 69, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| P. larvae Strain | MALDI Identification | 16S rRNA GenBank Accession Number | Nucleotide in Variable Positions in 16S rRNA Gene | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Score | Biotype | 57 | 731 | 1022 | ||
| 5S | 2.094 | IV | MN613427 | T | A | C |
| 10S | 2.095 | III | MN613428 | T | A | C |
| CCM 4488 | 2.014 | III | MN613430 | C | G | T |
| CCM 4484 | 1.937 | IV | MN613429 | C | G | C |
| CCM 38 | 2.081 | II | MN613431 | C | A | T |
| CCM 5680 | 2.072 | IV | MN613432 | C | G | C |
| D3 | 2.021 | III | MN613433 | T | A | C |
| D4 | 1.988 | III | MN982887 | C | A | C |
| M1 | 2.104 | III | MN982886 | T | A | C |
| DSM 7030 | NA | I | AY530294 | C | A | T |
| DSM 3615 | NA | I | AY530295 | C | A | T |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kopcakova, A.; Salamunova, S.; Javorsky, P.; Sabo, R.; Legath, J.; Ivorova, S.; Piknova, M.; Pristas, P. The Application of MALDI-TOF MS for a Variability Study of Paenibacillus larvae. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100521
Kopcakova A, Salamunova S, Javorsky P, Sabo R, Legath J, Ivorova S, Piknova M, Pristas P. The Application of MALDI-TOF MS for a Variability Study of Paenibacillus larvae. Veterinary Sciences. 2022; 9(10):521. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100521
Chicago/Turabian StyleKopcakova, Anna, Slavomira Salamunova, Peter Javorsky, Rastislav Sabo, Jaroslav Legath, Silvia Ivorova, Maria Piknova, and Peter Pristas. 2022. "The Application of MALDI-TOF MS for a Variability Study of Paenibacillus larvae" Veterinary Sciences 9, no. 10: 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100521
APA StyleKopcakova, A., Salamunova, S., Javorsky, P., Sabo, R., Legath, J., Ivorova, S., Piknova, M., & Pristas, P. (2022). The Application of MALDI-TOF MS for a Variability Study of Paenibacillus larvae. Veterinary Sciences, 9(10), 521. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci9100521





