Evaluation of Toxicity, Bacteriostatic, Analgesic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antipyretic Activities of Huangqin-Honghua-Pugongying-Jinyinhua Extract
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Drugs and Reagents
2.2. Animals and Housing
2.3. Acute Toxicity and 28-Day Sub-Chronic Toxicity
2.4. Bacteriostatic Activity
2.4.1. Oxford Cup Method
2.4.2. MIC and MBC
2.5. Analgesic Activity
2.5.1. Acetic Acid-Induced Writhing Test
2.5.2. Hot Plate Test
2.6. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
2.7. Antipyretic Test
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
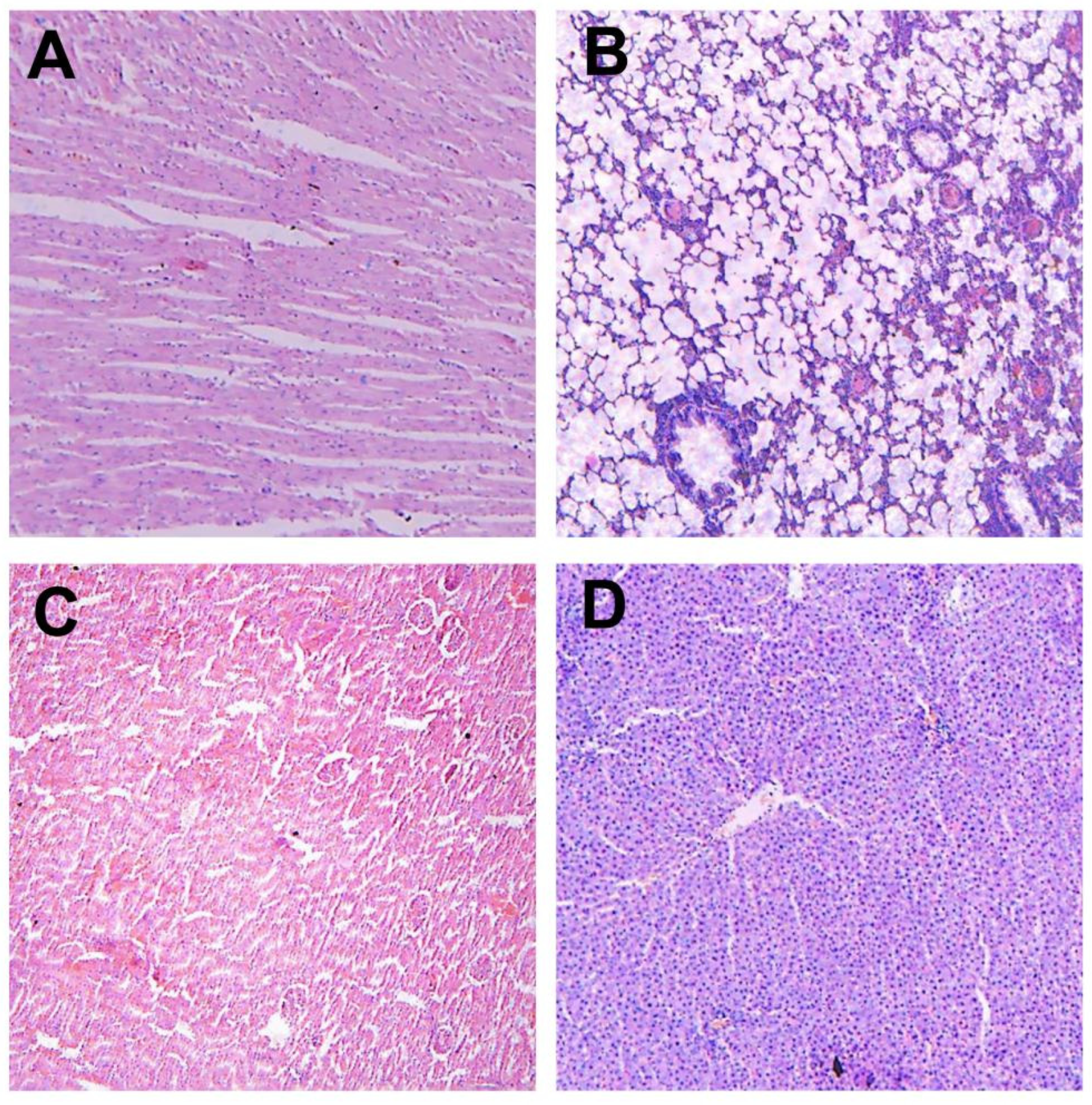
3.1. Toxicity
3.2. Bacteriostatic Activity
3.3. Analgesic Activity
3.3.1. Acetic Acid Induced Writhing Test
3.3.2. Hot Plate Test
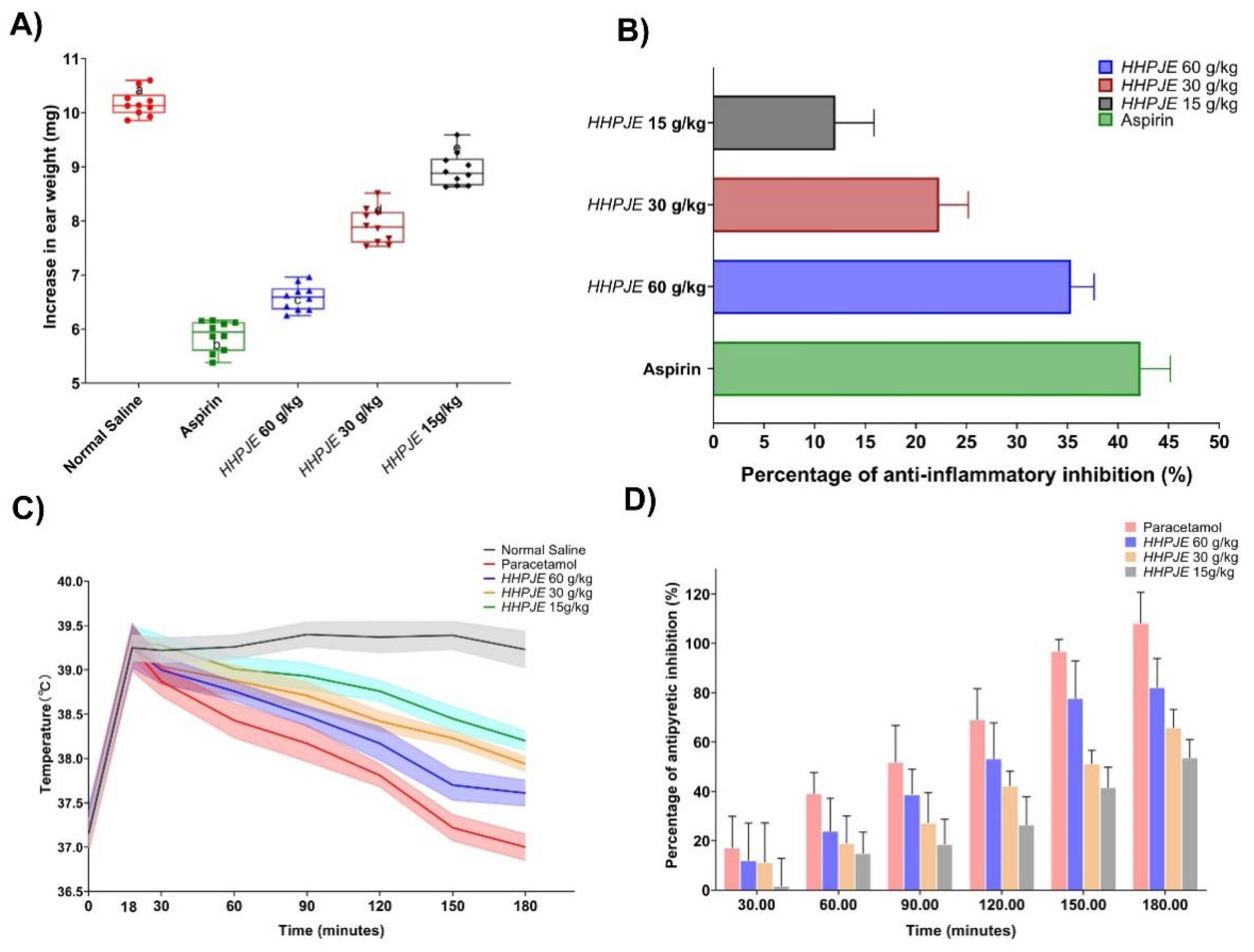
3.4. Anti-Inflammatory Activity
3.5. Antipyretic Activity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maclean, R.C.; San, M.A. The evolution of antibiotic resistance. Science 2019, 365, 1082–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelin, I.; Kishony, R. Antibiotic Resistance. Cell 2018, 172, 1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalski, M.L.; Asero, R.; Bavbek, S.; Blanca, M.; Blanca-Lopez, N.; Bochenek, G.; Brockow, K.; Campo, P.; Celik, G.; Cernadas, J.; et al. Classification and practical approach to the diagnosis and management of hypersensitivity to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Allergy 2013, 68, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteros, M.; Galdeano, C.M.; Balcells, M.F.; Weill, R.; De Paula, J.A.; Perdigon, G.; Cazorla, S.I. Probiotic lactobacilli as a promising strategy to ameliorate disorders associated with intestinal inflammation induced by a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, B.Y.; Gong, F.K.; Chen, Z.H.; Li, Z.X.; Zhang, B. System Prediction and Validation of TCM for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Treatment from the Perspective of Low-Toxicity Chemotherapy: A Stilbene alpha-Viniferin Has a Proapoptotic Effect on K562 Cells via the Mitochondrial Pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2020, 2020, 1986962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantwell, S.L. Traditional Chinese veterinary medicine: The mechanism and management of acupuncture for chronic pain. Top. Companion. Anim. Med. 2010, 25, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Chang, Q.; Hu, Z.; Shen, X.; Feng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, X. Total flavonoid aglycones extract in Radix Scutellariae induces cross-regulation between autophagy and apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 235, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.B.; Choi, J.H.; Park, S.R.; Kim, J.Y.; Hong, J.W.; Kim, G.C. Scutellariae radix induces apoptosis in chemoresistant SCC-25 human tongue squamous carcinoma cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, H.; Yoo, Y.; Won, K.H.; Ngo, H.; Yang, J.E.; Cho, J.G.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, K.Y.; Yi, T.H. Evaluation of in-vitro antimicrobial activity of Artemisia apiacea H. and Scutellaria baicalensis G. extracts. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lin, G.; Zuo, Z. Pharmacological effects and pharmacokinetics properties of Radix Scutellariae and its bioactive flavones. Biopharm. Drug Dispos. 2011, 32, 427–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Yamada, K.; Akiyama, J.; Someya, T.; Odaka, Y.; Takeda, Y.; Tori, M.; Nakashima, K.; Maekawa, T.; Sone, Y. Antioxidation mechanism studies of caffeic acid: Identification of antioxidation products of methyl caffeate from lipid oxidation. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 5947–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Lim, S.K.; Kim, D.I.; Park, M.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Lee, A.C.; Kim, Y.M.; Yang, S.J.; Park, J.H. Safflower bud inhibits RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation and prevents bone loss in ovariectomized mice. Phytomedicine 2017, 34, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Chen, J.; Lin, B.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, D.; Pang, L.; Zeng, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Y. A novel 3D printed bioactive scaffolds with enhanced osteogenic inspired by ancient Chinese medicine HYSA for bone repair. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 394, 112139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faiz, H.C.; Al-Amin, M.; Rahman, K.M.; Sarker, A.; Alam, M.M.; Chowdhury, M.H.; Khan, S.N.; Sultana, G.N. Analgesic principle from Curcuma amada. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 163, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, J.J.; Lin, J.W.; Fang, W.S.; Du, G.H. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of ethanol and aqueous extracts of Pterocephalus hookeri (C.B. Clarke) Hoeck. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 123, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunn, A.; Bobeck, E.N.; Weber, C.; Morgan, M.M. The influence of non-nociceptive factors on hot-plate latency in rats. J. Pain 2011, 12, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, M.; Mazumder, U.K.; Kumar, R.S.; Gomathi, P.; Rajeshwar, Y.; Kakoti, B.B.; Selven, V.T. Anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects of methanol extract from Bauhinia racemosa stem bark in animal models. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 98, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Tao, S.; Zeng, F.; Xie, L.; Shen, Z. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of Schefflera octophylla extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 171, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.; Wan, H.; Su, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Yao, L.; Lin, N. Rheum palmatum L. and Coptis chinensis Franch., exert antipyretic effect on yeast-induced pyrexia rats involving regulation of TRPV1 and TRPM8 expression. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 153, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Nicholson, J.K.; Lu, A.; Wang, Z.; Tang, H.; Holmes, E.; Shen, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, J.V.; Lindon, J.C. Targeting the human genome-microbiome axis for drug discovery: Inspirations from global systems biology and traditional Chinese medicine. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 3509–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mordmuang, A.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Rhodomyrtus tomentosa (Aiton) Hassk. leaf extract: An alternative approach for the treatment of staphylococcal bovine mastitis. Res. Vet. Sci. 2015, 102, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, A.O.; Yahi, A.; Tatonetti, N.P. Artificial Intelligence for Drug Toxicity and Safety. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 624–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changizi, Z.; Moslehi, A.; Rohani, A.H.; Eidi, A. Chlorogenic acid inhibits growth of 4T1 breast cancer cells through involvement in Bax/Bcl2 pathway. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2020, 16, 1435–1442. [Google Scholar]
- Huyut, Z.; Alp, H.H.; Yaman, T.; Keles, O.F.; Yener, Z.; Turkan, F.; Ayengin, K. Comparison of the protective effects of curcumin and caffeic acid phenethyl ester against doxorubicin-induced testicular toxicity. Andrologia 2020, 53, e13919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, I.G.; Jain, R.; Alawi, F.; Nanjan, K.; Bork, O. Translational studies on a ready-to-use intramuscular injection of penethamate for bovine mastitis. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2018, 8, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kot, B.; Kwiatek, K.; Janiuk, J.; Witeska, M.; Pekala-Safinska, A. Antibacterial Activity of Commercial Phytochemicals against Aeromonas Species Isolated from Fish. Pathogens 2019, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.C.; Chu, X.L.; Su, J.Q.; Cui, Z.Q.; Zhang, L.Y.; Yu, Z.J.; Wu, Z.M.; Cai, M.L.; Li, H.X.; Zhang, Z.J. Baicalin protects mice against Salmonella typhimurium infection via the modulation of both bacterial virulence and host response. Phytomedicine 2018, 48, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.Y.; Yuan, M.; Wu, Z.M.; Song, K.; Zhang, C.L.; An, Q.; Xia, F.; Yu, J.L.; Yi, P.F.; Fu, B.D.; et al. Anti-bacterial activity of baicalin against APEC through inhibition of quorum sensing and inflammatory responses. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Feng, C.; Yao, Y.; Qin, A.; Shao, H.; Qian, K. Antiviral effect of baicalin on Marek’s disease virus in CEF cells. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tita, B.; Abdel-Haq, H.; Vitalone, A.; Mazzanti, G.; Saso, L. Analgesic properties of Epilobium angustifolium, evaluated by the hot plate test and the writhing test. Farmaco 2001, 56, 341–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peana, A.T.; D’Aquila, P.S.; Chessa, M.L.; Moretti, M.D.; Serra, G.; Pippia, P. (-)-Linalool produces antinociception in two experimental models of pain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2003, 460, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, T.C.; Chang, L.P.; Li, C.Y.; Wong, C.S.; Yang, S.P. The antiinflammatory and analgesic effects of baicalin in carrageenan-evoked thermal hyperalgesia. Anesth. Analg. 2003, 97, 1724–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liao, X.X.; Liu, W.; Guo, R.X.; Wu, Z.Z.; Zhao, C.M.; Chen, P.X.; Feng, J.Q. A novel role of minocycline: Attenuating morphine antinociceptive tolerance by inhibition of p38 MAPK in the activated spinal microglia. Brain Behav. Immun. 2008, 22, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, K.F. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways in asthma and COPD. Chest 2011, 139, 1470–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, N.K.; Patil, C.S.; Singh, A.; Kulkarni, S.K. Sildenafil-induced peripheral analgesia and activation of the nitric oxide-cyclic GMP pathway. Brain Res. 2001, 909, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, X.S.; He, Y.H.; Chen, S.S.; Bai, X.Y. Hydroxysafflor yellow A suppresses liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride with high-fat diet by regulating PPAR-gamma/p38 MAPK signaling. Pharm. Biol. 2014, 52, 1085–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.W.; Liu, T.T.; Qiu, C.Y.; Li, J.D.; Hu, W.P. Inhibition of acid-sensing ion channels by chlorogenic acid in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Neurosci. Lett. 2014, 567, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, Y.C.; Jeong, Y.H.; Cho, W.K.; Ha, J.H.; Gu, M.J.; Ma, J.Y. Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of pyeongwisan on LPS-stimulated murine macrophages and mouse models of acetic acid-induced writhing response and xylene-induced ear edema. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1232–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, M.; Zhang, N.; Li, D.; Liang, D.; Liu, Z.; Li, F.; Fu, Y.; Cao, Y.; Deng, X.; Yang, Z. Baicalin plays an anti-inflammatory role through reducing nuclear factor-kappaB and p38 phosphorylation in S. aureus-induced mastitis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 16, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, Y.; Xu, W.; Geng, Y.; Su, Y.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J. Baicalin inhibits Salmonella typhimurium-induced inflammation and mediates autophagy through TLR4/MAPK/NF-kappaB signalling pathway. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2021, 128, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; Dai, Y.; Xu, M.; Zhang, C.; Ma, Y.; Gao, P.; Teng, M.; Jiao, K.; Huang, G.; Zhang, J.; et al. The Attenuation of 14-3-3zeta is Involved in the Caffeic Acid-Blocked Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Inflammatory Response in RAW264.7 Macrophages. Inflammation 2017, 40, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, O.H.; Choi, J.G.; Lee, J.H.; Kwon, D.Y. Luteolin isolated from the flowers of Lonicera japonica suppresses inflammatory mediator release by blocking NF-kappaB and MAPKs activation pathways in HMC-1 cells. Molecules 2010, 15, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, D.; Li, X.; Li, Z.; Chao, J.; Qin, X. Metabolomic study of the fever model induced by baker’s yeast and the antipyretic effects of aspirin in rats using nuclear magnetic resonance and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 81-82, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jan, S.; Khan, M.R. Antipyretic, analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects of Kickxia ramosissima. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 182, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidensky, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hand, T.; Goellner, J.; Shaffer, A.; Isakson, P.; Andreasson, K. Neuronal overexpression of COX-2 results in dominant production of PGE2 and altered fever response. Neuromol. Med. 2003, 3, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.F.; Hsiao, P.C.; Kuo, T.C.; Chiang, S.T.; Chen, S.L.; Chiou, S.J.; Ling, X.H.; Liang, M.T.; Cheng, W.Y.; Houng, J.Y. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Lonicera japonica Thunb. var. sempervillosa Hayata flower bud extracts prepared by water, ethanol and supercritical fluid extraction techniques. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 89, 543–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Nan, T.G.; Zhan, Z.L.; Kang, L.P.; Yang, J.; Lai, C.J.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, B.M.; Huang, L.Q. A monoclonal antibody-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the determination of chlorogenic acid in honeysuckle. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 148, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, D.; Sun, J.; Li, Y. Evaluation of Toxicity, Bacteriostatic, Analgesic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antipyretic Activities of Huangqin-Honghua-Pugongying-Jinyinhua Extract. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8120330
Ye D, Sun J, Li Y. Evaluation of Toxicity, Bacteriostatic, Analgesic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antipyretic Activities of Huangqin-Honghua-Pugongying-Jinyinhua Extract. Veterinary Sciences. 2021; 8(12):330. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8120330
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Dongyang, Jing Sun, and Yinqian Li. 2021. "Evaluation of Toxicity, Bacteriostatic, Analgesic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antipyretic Activities of Huangqin-Honghua-Pugongying-Jinyinhua Extract" Veterinary Sciences 8, no. 12: 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8120330
APA StyleYe, D., Sun, J., & Li, Y. (2021). Evaluation of Toxicity, Bacteriostatic, Analgesic, Anti-Inflammatory, and Antipyretic Activities of Huangqin-Honghua-Pugongying-Jinyinhua Extract. Veterinary Sciences, 8(12), 330. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci8120330




