Flow Cytometry-Detected Immunological Markers and on Farm Recorded Parameters in Composite Cow Milk as Related to Udder Health Status
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Milk Samples Collection
2.2. Purification of Milk Somatic Cells
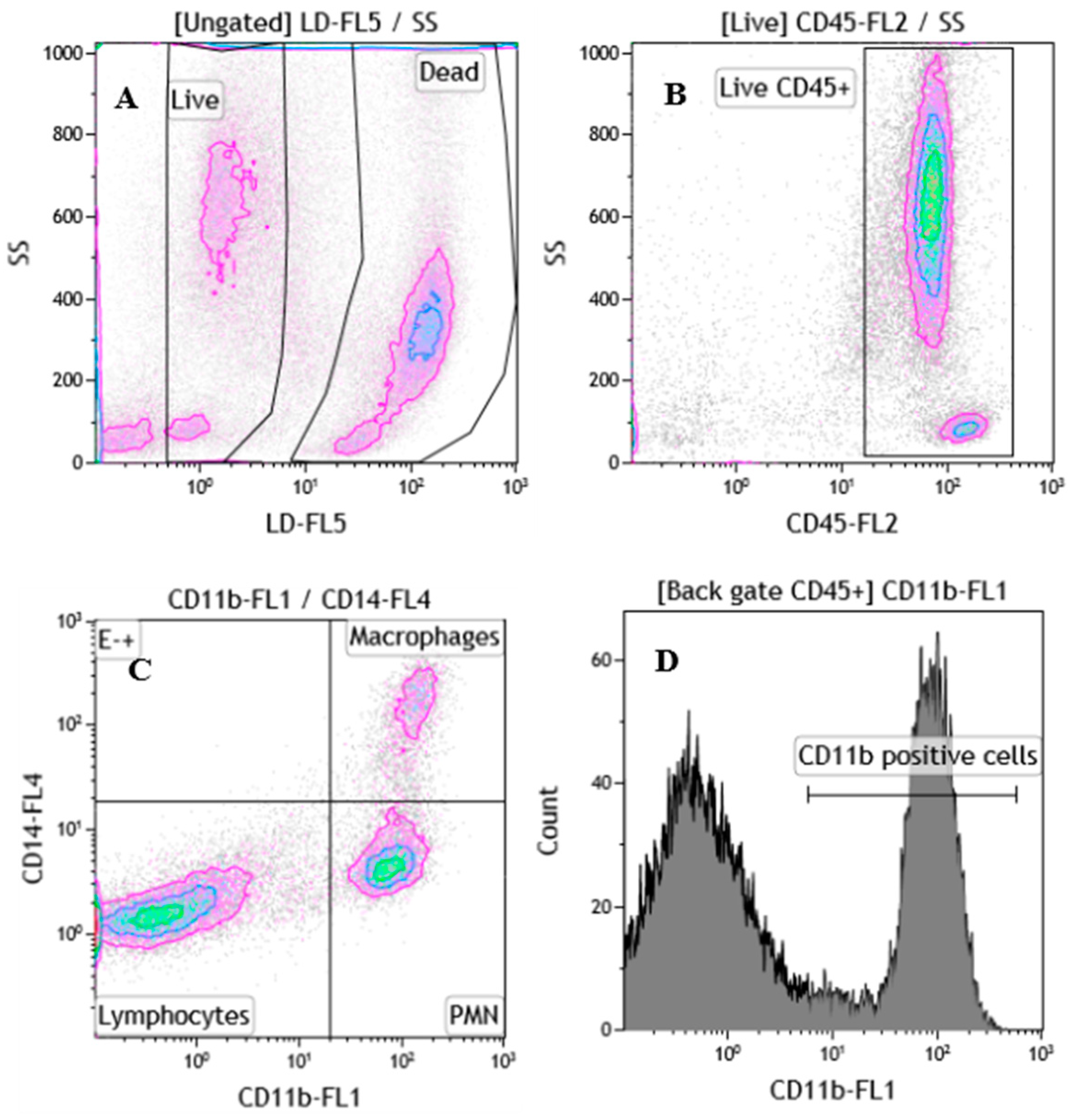
2.3. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Flow Cytometry-Detected Immunological Markers and on Farm Recorded Parameters in Different Bacteriological Conditions
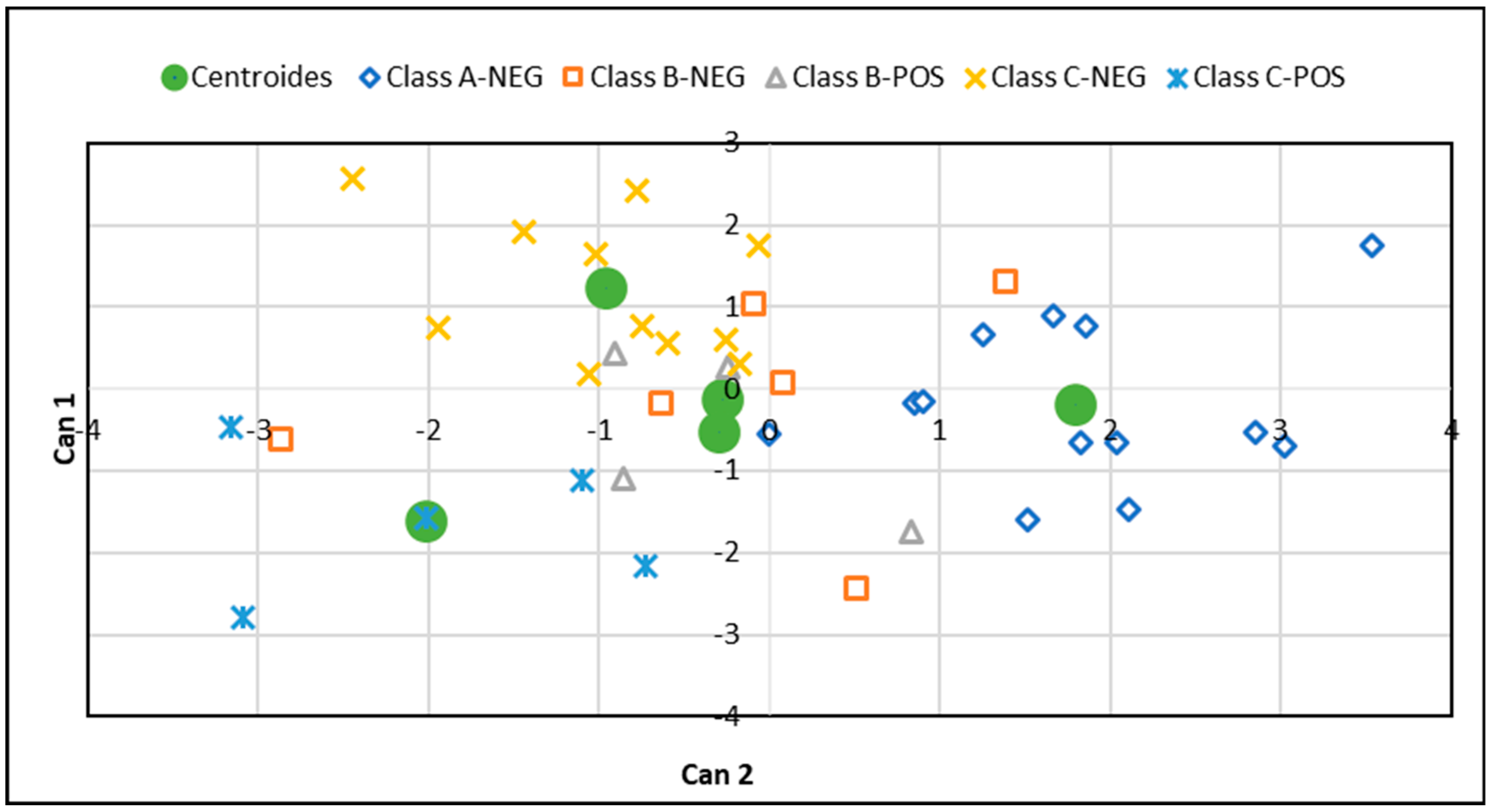
3.2. Linear and Canonical Discriminant Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paape, M.J.; Bannerman, D.D.; Zhao, X.; Lee, J.W. The bovine neutrophil: Structure and function in blood and milk. Vet. Res. 2003, 34, 597–627. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rainard, P.; Riollet, C. Innate immunity of the bovine mammary gland. Vet. Res. 2006, 37, 369–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, D.; Diesterbeck, U.S.; König, S.; Brügemann, K.; Schlez, K.; Zschöck, M.; Wolter, W.; Czerny, C.P. Flow cytometric differential cell counts in milk for the evaluation of inflammatory reactions in clinically healthy and subclinically infected bovine mammary glands. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 5033–5044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilla, R.; Malvisi, M.; Snel, G.G.; Schwarz, D.; König, S.; Czerny, C.P.; Piccinini, R. Differential cell count as an alternative method to diagnose dairy cow mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2013, 96, 1653–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damm, M.; Holm, C.; Blaabjerg, M.; Bro, M.N.; Schwarz, D. Differential somatic cell count-A novel method for routine mastitis screening in the frame of Dairy Herd Improvement testing programs. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4926–4940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, S.K.; Wellnitz, O.; Bruckmaier, R.M.; Schwarz, D. Differential somatic cell count in milk before, during, and after lipopolysaccharide-and lipoteichoic-acid-induced mastitis in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2018, 101, 5362–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecconi, A.; Vairani, D.; Cipolla, M.; Rizzi, N.; Zanini, L. Assessment of Subclinical Mastitis Diagnostic Accuracy by Differential Cell Count in Individual Cow Milk. Ital. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 18, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borjesson, D.L.; Simon, S.I.; Hodzic, E.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Barthold, S.W. Kinetics of CD11b/CD18 up-regulation during infection with the agent of human granulocytic ehrlichiosis in mice. Lab. Investig. 2002, 82, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, H.I.; Nahill, S.R.; Maciaszek, J.W.; Welsh, R.M. CD11b (Mac1): A marker for CD8+ cytotoxic T cell activation and memory in virus infection. J. Immunol. 1992, 149, 1326–1333. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, C.; Hänsch, G.M.; Stegmaier, S.; Denefleh, B.; Hug, F.; Schoels, M. The complement receptor 3, CR3 (CD11b/CD18), on T lymphocytes: Activation-dependent up-regulation and regulatory function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2001, 31, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, H.V.; Christensen, J.P.; Andersson, E.C.; Marker, O.; Thomsen, A.R. Expression of type 3 complement receptor on activated CD8+ T cells facilitates homing to inflammatory sites. J. Immunol. 1994, 153, 2021–2028. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Berckmans, D. Precision livestock farming technologies for welfare management in intensive livestock systems. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2014, 33, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sørensen, L.P.; Bjerring, M.; Løvendahl, P. Monitoring individual cow udder health in automated milking systems using online somatic cell counts. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schukken, Y.H.; Wilson, D.J.; Welcome, F.; Garrison-Tikofsky, L.; Gonzalez, R.N. Monitoring udder health and milk quality using somatic cell counts. Vet. Res. 2003, 34, 579–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyher, K.K.; Dohoo, I.R. Diagnosing intramammary infections: Evaluation of composite milk samples to detect intramammary infections. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 3387–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahalanobis, P.C. On the Generalized Distance in Statistics. Proc. Natl. Inst. Sci. India 1936, 2, 49–55. [Google Scholar]
- Riollet, C.; Rainard, P.; Poutrel, B. Cells and cytokines in inflammatory secretions of bovine mammary gland. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2000, 480, 247–258. [Google Scholar]
- Sarikaya, H.; Schlamberger, G.; Meyer, H.H.; Bruckmaier, R.M. Leukocyte populations and mRNA expression of inflammatory factors in quarter milk fractions at different somatic cell score levels in dairy cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 2479–2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, M.; Steinfort, D.P.; Smallwood, D.; Hew, M.; Chen, W.; Ernst, M.; Irving, L.B.; Anderson, G.P.; Hibbs, M.L. CD11b immunophenotyping identifies inflammatory profiles in the mouse and human lungs. Mucosal Immunol. 2016, 9, 550–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Fraile, A.; Meyer, E.; Duchateau, L.; Burvenich, C. L-Selectin and β2-Integrin expression on circulating bovine polymorphonuclear leukocytes during endotoxin mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2003, 86, 2334–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, K.A.; Maltecca, C.; Bagnato, A.; Doleza, M.; Rossoni, A.; Samore, A.B.; Cassady, J.P. Estimates of marker effects for measures of milk flow in the Italian brown Swiss dairy cattle population. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norberg, E. Electrical conductivity of milk as a phenotypic and genetic indicator of bovine mastitis: A review. Livest. Sci. 2005, 96, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilas Boas, D.F.; Vercesi Filho, A.E.; Pereira, M.A.; Roma Junior, L.C.; El Faro, L. Association between electrical conductivity and milk production traits in Dairy Gyr cows. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2017, 45, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhussien, M.; Manjari, P.; Mohammed, S.; Ahmad Sheikh, A.; Reddi, S.; Dixit, S.; Dang, A.K. Incidence of mastitis and activity of milk neutrophils in Tharparkar cows reared under semi-arid conditions. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2016, 48, 1291–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Item | n | Mean | St. Dev | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell viability (%) | 40 | 54.70 | 17.76 | 15.50 | 91.50 |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 38 | 42.18 | 26.04 | 3.15 | 88.06 |
| PMN (%) | 38 | 43.20 | 24.26 | 6.20 | 90.32 |
| Macrophages (%) | 38 | 14.32 | 9.11 | 2.31 | 35.66 |
| Leucocytes CD11b+ (%) | 40 | 61.80 | 23.99 | 16.00 | 97.00 |
| CD11b PMN (MFI) | 38 | 64.45 | 11.16 | 40.92 | 87.62 |
| CD11b macrophages (MFI) | 38 | 107.53 | 23.91 | 75.09 | 177.47 |
| CD11b leucocytes (MFI) | 40 | 58.99 | 14.89 | 27.36 | 88.47 |
| SCC × 1000 cells/mL | 42 | 501.10 | 952.70 | 10.00 | 5771.00 |
| Milk electrical conductivity (mS/cm) | 42 | 6.11 | 0.41 | 5.15 | 7.15 |
| Milk flow rate (L/min) | 42 | 2.36 | 0.61 | 0.91 | 3.92 |
| Item | Group 1 | LS Mean | SE | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell viability (%) | POS | 56.31 | 6.25 | 0.81 |
| NEG | 54.64 | 3.37 | ||
| Lymphocytes (%) | POS | 26.26 | 8.38 | 0.04 |
| NEG | 45.90 | 4.59 | ||
| PMN (%) | POS | 55.22 | 8.1 | 0.13 |
| NEG | 40.91 | 4.44 | ||
| Macrophages (%) | POS | 18.26 | 2.96 | 0.12 |
| NEG | 12.89 | 1.52 | ||
| Leucocytes CD11b+ (%) | POS | 77.56 | 7.69 | 0.03 |
| NEG | 58.31 | 4.08 | ||
| CD11b PMN (MFI 2) | POS | 67.70 | 4.08 | 0.50 |
| NEG | 64.54 | 2.23 | ||
| CD11b macrophages (MFI 2) | POS | 102.97 | 7.93 | 0.52 |
| NEG | 108.80 | 4.34 | ||
| CD11b leucocytes (MFI 2) | POS | 62.98 | 5.21 | 0.11 |
| NEG | 58.87 | 2.76 | ||
| SCC × 1000 cells/mL | POS | 1428.14 | 419.26 | 0.04 |
| NEG | 448.20 | 203.42 | ||
| Milk electrical conductivity (mS/cm) | POS | 6.45 | 0.14 | 0.01 |
| NEG | 6.03 | 0.07 | ||
| Milk flow rate (L/min) | POS | 1.98 | 0.19 | 0.03 |
| NEG | 2.46 | 0.09 |
| Class | A-NEG | B-NEG | B-POS | C-NEG | C-POS | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-NEG | 13 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 |
| 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | |
| B-NEG | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 6 |
| 16.67 | 33.33 | 0 | 33.33 | 16.67 | 100 | |
| B-POS | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 4 |
| 25 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 25 | 100 | |
| C-NEG | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 11 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 100 | |
| C-POS | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 5 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 100 | |
| Total | 15 | 2 | 2 | 13 | 7 | 39 |
| 38.46 | 5.13 | 5.13 | 33.33 | 17.95 | 100 | |
| Error (%) | 0 | 0.67 | 0.50 | 0 | 0 | 0.15 |
| Prior probability | 0.33 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 0.28 | 0.13 |
| Item | Can1 | Can2 | Can3 | Can4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell viability | −0.05 | 0.05 | 0.01 | 0.00 |
| Lymphocytes (%) | −1.29 | −0.70 | −0.86 | −0.24 |
| PMN (%) | −1.54 | −0.76 | −0.38 | −0.44 |
| Macrophages (%) | −1.67 | −0.75 | −0.44 | −0.51 |
| Leukocytes CD11b+ (%) | 0.22 | 0.03 | −0.49 | 0.24 |
| CD11b PMN (MFI) | −0.12 | 0.03 | 0.03 | −0.02 |
| CD11b macrophages (MFI) | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.03 |
| CD11b leukocytes (MFI) | 0.12 | 0.02 | −0.06 | 0.00 |
| Milk electrical conductivity (mS/cm) | −0.72 | −0.06 | 0.18 | 1.28 |
| Milk flow rate (L/min) | 0.29 | 2.21 | −0.71 | 0.42 |
| Variance | 0.62 | 0.26 | 0.09 | 0.03 |
| Wilks’ Lambda | 0.11 | 0.36 | 0.69 | 0.91 |
| p-Value | 0.007 | 0.272 | 0.796 | 0.897 |
| Class | A-NEG | B-NEG | B-POS | C-NEG | C-POS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-NEG | 1 | 0.1741 | 0.1657 | 0.0017 | 0.0012 |
| B-NEG | 0.1741 | 1 | 0.9438 | 0.542 | 0.2541 |
| B-POS | 0.1657 | 0.9438 | 1 | 0.3011 | 0.2834 |
| C-NEG | 0.0017 | 0.542 | 0.3011 | 1 | 0.038 |
| C-POS | 0.0012 | 0.2541 | 0.2834 | 0.038 | 1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Matteis, G.; Grandoni, F.; Scatà, M.C.; Catillo, G.; Moioli, B.; Buttazzoni, L. Flow Cytometry-Detected Immunological Markers and on Farm Recorded Parameters in Composite Cow Milk as Related to Udder Health Status. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030114
De Matteis G, Grandoni F, Scatà MC, Catillo G, Moioli B, Buttazzoni L. Flow Cytometry-Detected Immunological Markers and on Farm Recorded Parameters in Composite Cow Milk as Related to Udder Health Status. Veterinary Sciences. 2020; 7(3):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030114
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Matteis, Giovanna, Francesco Grandoni, Maria Carmela Scatà, Gennaro Catillo, Bianca Moioli, and Luca Buttazzoni. 2020. "Flow Cytometry-Detected Immunological Markers and on Farm Recorded Parameters in Composite Cow Milk as Related to Udder Health Status" Veterinary Sciences 7, no. 3: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030114
APA StyleDe Matteis, G., Grandoni, F., Scatà, M. C., Catillo, G., Moioli, B., & Buttazzoni, L. (2020). Flow Cytometry-Detected Immunological Markers and on Farm Recorded Parameters in Composite Cow Milk as Related to Udder Health Status. Veterinary Sciences, 7(3), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030114





