Morphological and Immunohistochemical Description of a Splenic Haemangioma in a Captive European Wolf (Canis lupus lupus) and a Review of the Current Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subject
2.2. Pathological Investigations
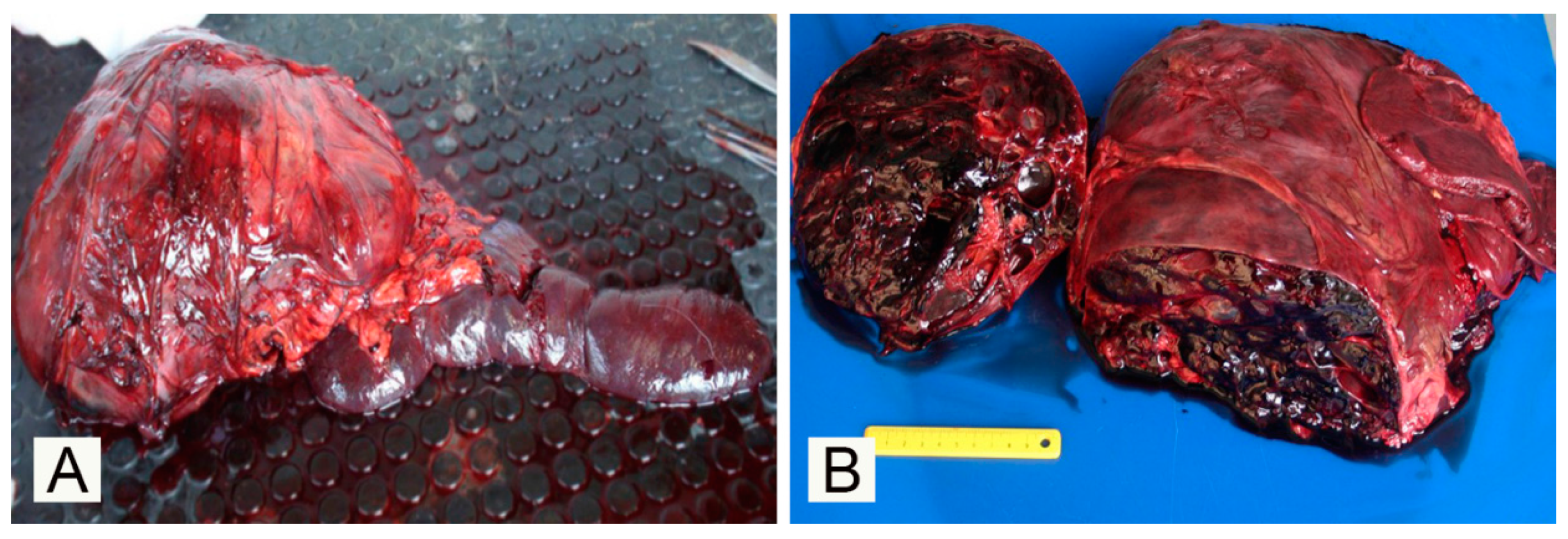
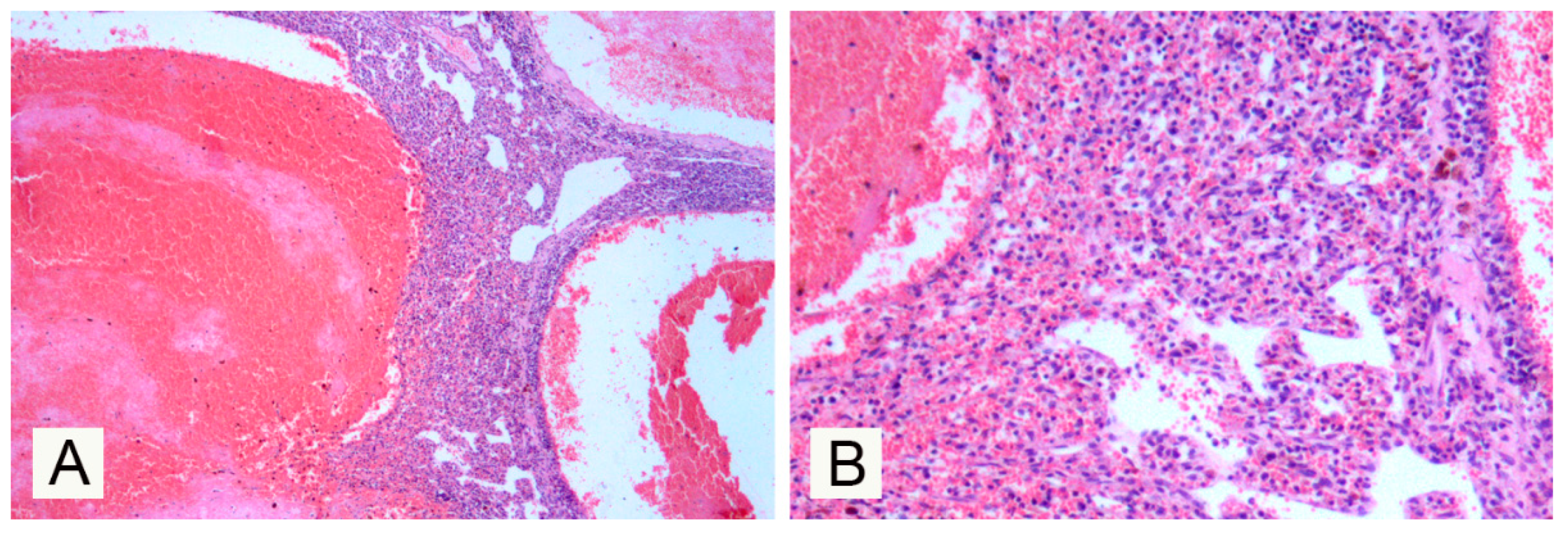
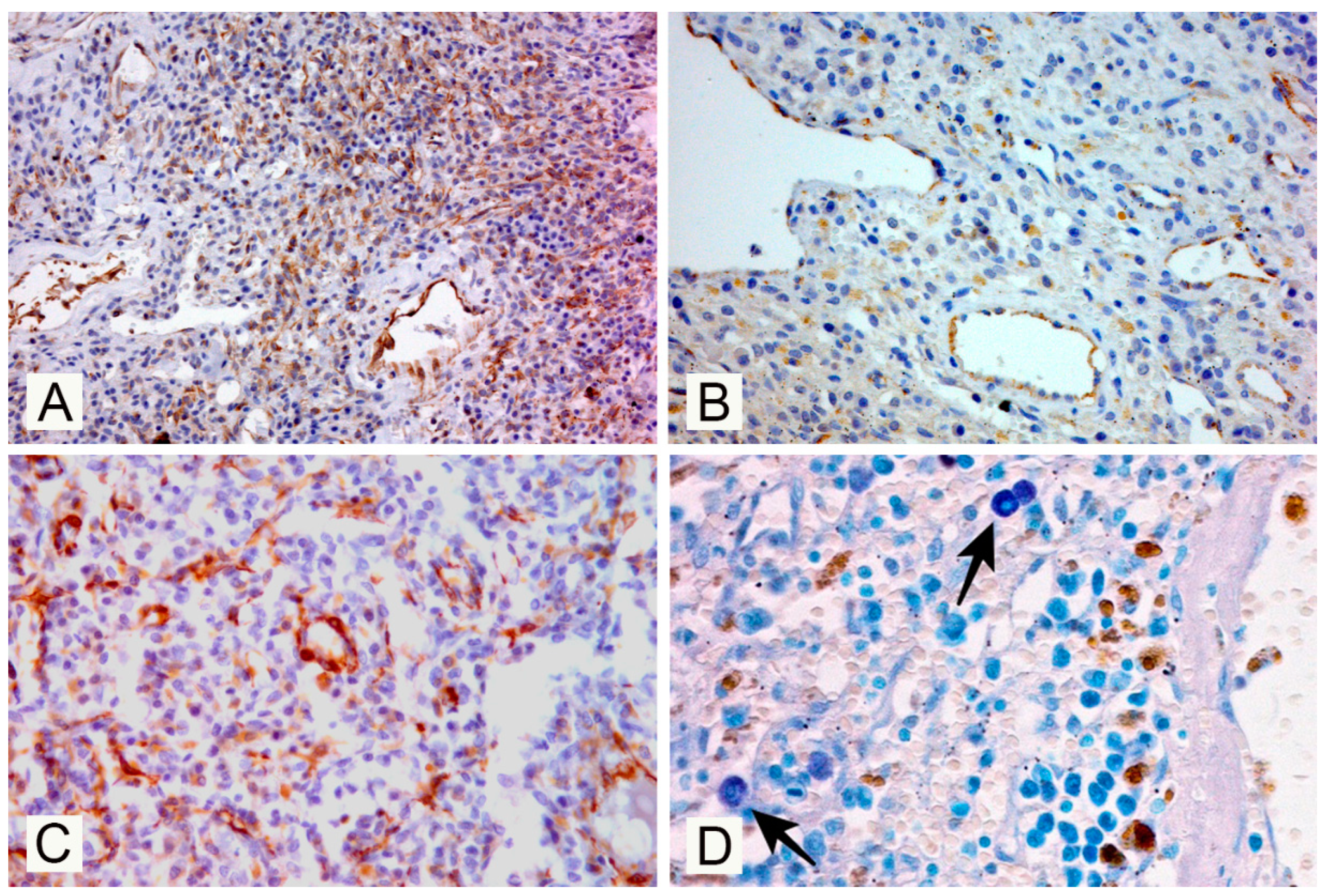
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Robinson, W.F.; Robinson, N.A. Cardiovascular system. In Jubb, Kennedy, and Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals, 6th ed.; Maxie, M.G., Ed.; Elsevier: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2015; pp. 1–101. [Google Scholar]
- Acton, A.E.; Munson, L.; Waddell, W.T. Survey of necropsy results in captive red wolves (Canis rufus), 1992–1996. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2000, 31, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sabattini, S.; Bettini, G. An immunohistochemical analysis of canine haemangioma and haemangiosarcoma. J. Comp. Pathol. 2009, 140, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrick, M.J. Mesenchymal tumors of the skin and soft tissues. In Tumors in Domestic Animals, 5th ed.; Meuten, D.J., Ed.; Wiley Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; p. 142. [Google Scholar]
- Von Beust, B.R.; Suter, M.M.; Summers, B.A. Factor VIII-related antigen in canine endothelial neoplasms: An immunohistochemical study. Vet. Pathol. 1988, 25, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosales Alferez, F.; Tavares Mendoza, F.H.; Pereda Solis, E.M.; Martinez Guerrero, J.H.; Herrera Casio, M.H. Case report of malignant mammary neoplasia in mexican gray wolf (Canis lupus baileyi). J. Anim. Vet. Adv. 2010, 9, 1472–1475. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, P.; Seehusen, F.; Muller, H.; Aupperle, H.; Hewicker-Trautwein, M.; Wohlsein, P. Subcutaneous leiomyosarcoma in a captive European wolf (Canis lupus). Vet. Rec. 2007, 161, 429–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teifke, J.P.; Lohr, C.V.; Langner, C. Tp53 expressing squamous cell carcinoma of the tonsil in a captive polar wolf (Canis lupus arctos). J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2005, 36, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, W.M.; Chalmers, G.A.; Gunson, J.R. Oral papillomatosis in coyotes (Canis latrans) and wolves (Canis lupus) of Alberta. J. Wildl. Dis. 1978, 14, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, K.E.; Garner, M.M.; Waddell, W.T.; Wolf, K.N. A survey of diseases in captive red wolves (Canis Rufus), 1997–2012. J. Zoo Wildl. Med. 2016, 47, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraki, A.; Yoshida, T.; Kawashima, M.; Murayama, H.; Nagahara, R.; Ito, N.; Shibutani, M. Pulmonary neuroendocrine tumor in a female wolf (Canis lupus lupus). J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 79, 588–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rothenburger, J.L.; Myers, S.; Lockerbie, B.; Wobeser, B. Novel papillomaviral sequence detected within epidermal plaques in a wolf (Canis lupus). J. Wildl. Dis. 2016, 52, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brown, N.O.; Patnaik, A.K.; MacEwen, E.G. Canine hemangiosarcoma: Retrospective analysis of 104 cases. J. Am. Vet. Med Assoc. 1985, 186, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.N. Hemangiosarcoma in dogs and cats: Vet. Clin. Nord Am: Small Anim. Pract. 2003, 33, 533–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, G.R.; Head, K.W. Malignant hemangioendothelioma (angiosarcoma) in the dog. J. Small Anim. Pract. 1976, 17, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernades, S.C.; De Nardi, A.B. Hemangiosarcoma. In Oncologia em Cães e Gatos; Daleck, C.R., De Nardi, A.B., Rodaski, S., Eds.; Marca: Roca, Portugal, 2008; pp. 525–537. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, A. Hemangiosarcoma in dogs. J. Comp. Pathol. 1978, 88, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, A.S.; Couto, C.G.; Filppi, J.; Shank, K. Efficacy and toxicity of VAC chemotherapy (vincristine, doxorubicin, and cyclophosphamide) in dogs with hemangiosarcoma. J. Vet. Inter. Med. 1991, 5, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, C.A.; Mackin, A.J.; Henry, C.J. Treatment of canine hemangiosarcoma: 2000 and beyond. J. Vet. Inter. Med. 2000, 14, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorenmo, K.; Duda, L.; Barber, L.; Cronin, K.; Sammarco, C.; Usborne, A.; Goldschmidt, M.; Shofer, F. Canine hemangiosracoma treated with standard chemotherapy and minocycline. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2000, 14, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer, L.; Fondevila, D.; Rabanal, R.M.; Vilafranca, M. Immunohistochemical detection of CD31 antigen in normal and neoplastic canine endothelial cells. J. Comp. Pathol. 1995, 112, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrida, M.A.; Bacon, N.J.; Kamstock, D.A. Use of routine histopathology and factor VIII-related antigen/von Willebrand factor immunohistochemistry to differentiate primary hemangiosarcoma of bone from telangectasic osteosarcoma in 54 dogs. Vet Comp. Oncol. 2017, 15, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laakkonen, P.; Waltari, M.; Holopainen, T.; Takahashi, T.; Pytowski, B.; Steiner, P.; Hicklin, D.; Persaud, K.; Tonra, J.R.; Witte, L.; et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 (VEGFR-3) is involved in tumor angiogenesis and growth. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nóbrega, D.F.; Sehaber, V.F.; Madureira, R.; Bracarense, P.F.R. Canine cutaneous haemangiosarcoma: Biomarkers and survival. J. Comp. Pathol. 2019, 166, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Petrova, T.V.; Bono, P.; Holnthoner, W.; Chesnes, J.; Pytowski, B.; Sihto, H.; Laakkonen, P.; Heikkila, P.; Joensuu, H.; Alitalo, K. VEGFR-3 expression is restricted to blood and lymphatic vessels in solid tumors. Cancer Cell 2008, 13, 554–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Da Silva, L.; Fonseca-Alves, C.E. Pilot assessment of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors and trafficking pathway in recurrent and metastatic canine subcutaneous mast cell tumours. Vet. Med. Sci. 2017, 3, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhauser, T.S.; Derringer, G.A.; Thompson, L.D.; Fanburg-Smith, J.C.; Miettinen, M.; Saaristo, A.; Abbondanzo, S.L. Splenic angiosarcoma: A clinicopathologic and immunophenotypic study of 28 cases. Modern Pathol. 2000, 13, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, S.R.; Scase, T.J.; Adams, V.; Wieczoreck, L.; Miller, J.; Adamo, F.; Long, S. Vascular endothelial growth factor expression in canine intracranial meningiomas and association with patient survival. J. Vet. Inter. Med. 2006, 20, 663–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajita, M.; Itoh, Y.; Chiba, T.; Mori, H.; Okada, A.; Kinoh, H.; Seiki, M. Membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase cleaves CD44 and promotes cell migration. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 153, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Species | Main Findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Mexican gray wolf (Canis lupus baileyi) | Malignant mammary tumor | [6] |
| European wolf (Canis lupus lupus) | Subcutaneous leiomyosarcoma | [7] |
| Polar wolf (Canis lupus arctos) | Oral squamous cell carcinoma | [8] |
| Red wolves (Canis rufus) | Two multicentric lymphomas, one mesenteric round cell tumor, one bronchial carcinoma and two osteosarcomas | [2] |
| American coyotes (Canis latrans) and wolves (Canis lupus). | Oral papillomatosis | [9] |
| Red wolves (Canis rufus) | Forty-three cases in which carcinoma or adenocarcinoma and lymphoma were the most common. There were also reports of pheochromocytomas, osteo-sarcomas, fibrosarcomas, granulosa cell tumors, sarcomas, lymphosarcomas, nerve sheath tumors, sertoli cell tumors, histiocytomas, and adenomas. | [10] |
| Eurasian wolf (Canis lupus lupus) | Pulmonary neuroendocrine tumor | [11] |
| Gray wolf (Canis lupus) | Papillomaviral plaque | [12] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez, J.M.M.; Morandi, F.; Cavicchio, P.; Poli, A.; Verin, R. Morphological and Immunohistochemical Description of a Splenic Haemangioma in a Captive European Wolf (Canis lupus lupus) and a Review of the Current Literature. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030102
Rodríguez JMM, Morandi F, Cavicchio P, Poli A, Verin R. Morphological and Immunohistochemical Description of a Splenic Haemangioma in a Captive European Wolf (Canis lupus lupus) and a Review of the Current Literature. Veterinary Sciences. 2020; 7(3):102. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030102
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez, Josep Maria Monné, Federico Morandi, Paolo Cavicchio, Alessandro Poli, and Ranieri Verin. 2020. "Morphological and Immunohistochemical Description of a Splenic Haemangioma in a Captive European Wolf (Canis lupus lupus) and a Review of the Current Literature" Veterinary Sciences 7, no. 3: 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030102
APA StyleRodríguez, J. M. M., Morandi, F., Cavicchio, P., Poli, A., & Verin, R. (2020). Morphological and Immunohistochemical Description of a Splenic Haemangioma in a Captive European Wolf (Canis lupus lupus) and a Review of the Current Literature. Veterinary Sciences, 7(3), 102. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci7030102





