Transcriptional Profiles of Murine Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells in Response to Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus
Abstract
1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Animals and Cells
2.2. PPRV Inoculation
2.3. Indirect Immunofluorescence Assay
2.4. Library Construction and RNA Sequencing
2.5. Data Processing and Transcriptome Analysis
2.6. Verification of DEGs by qRT-PCR
3. Results
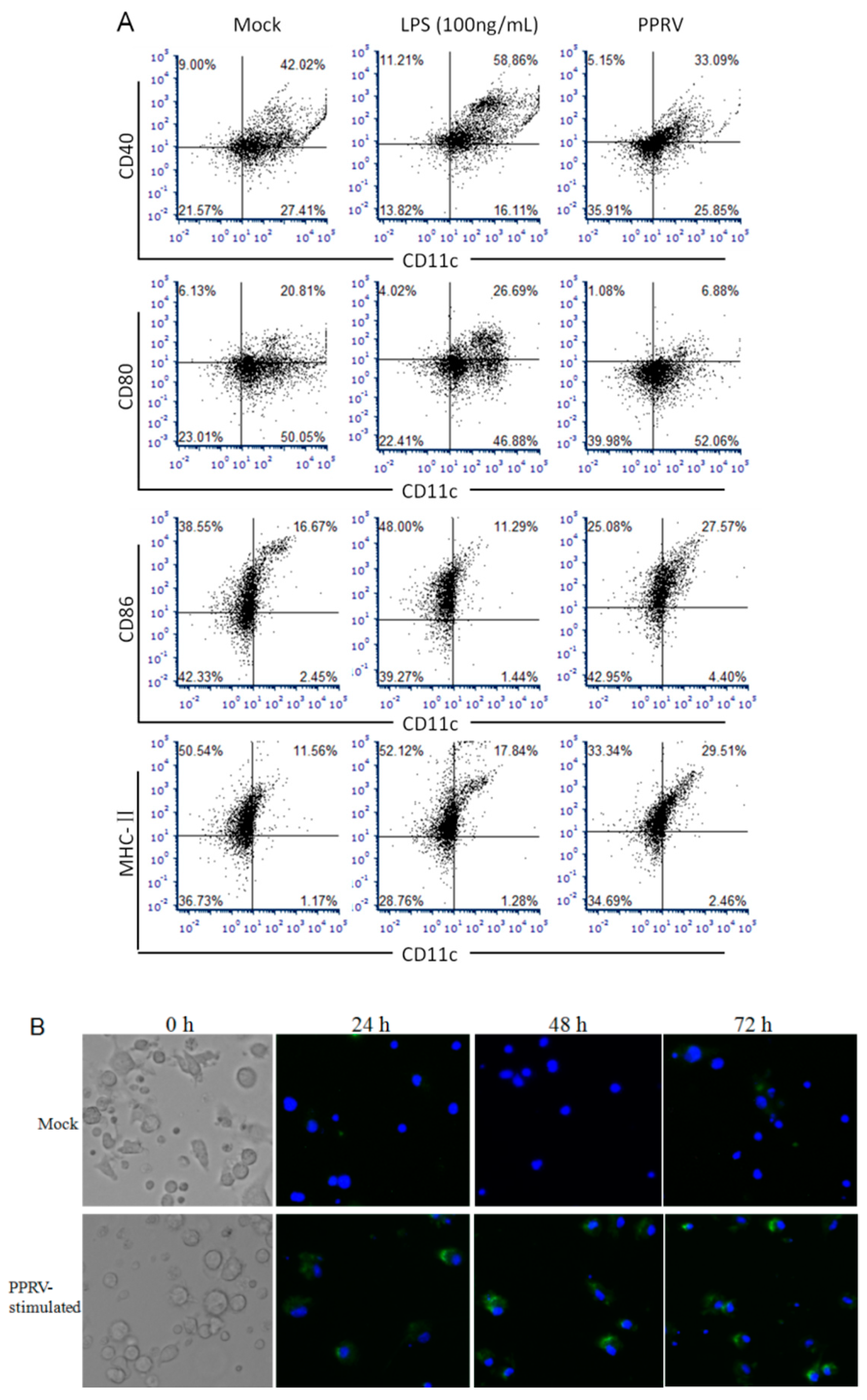
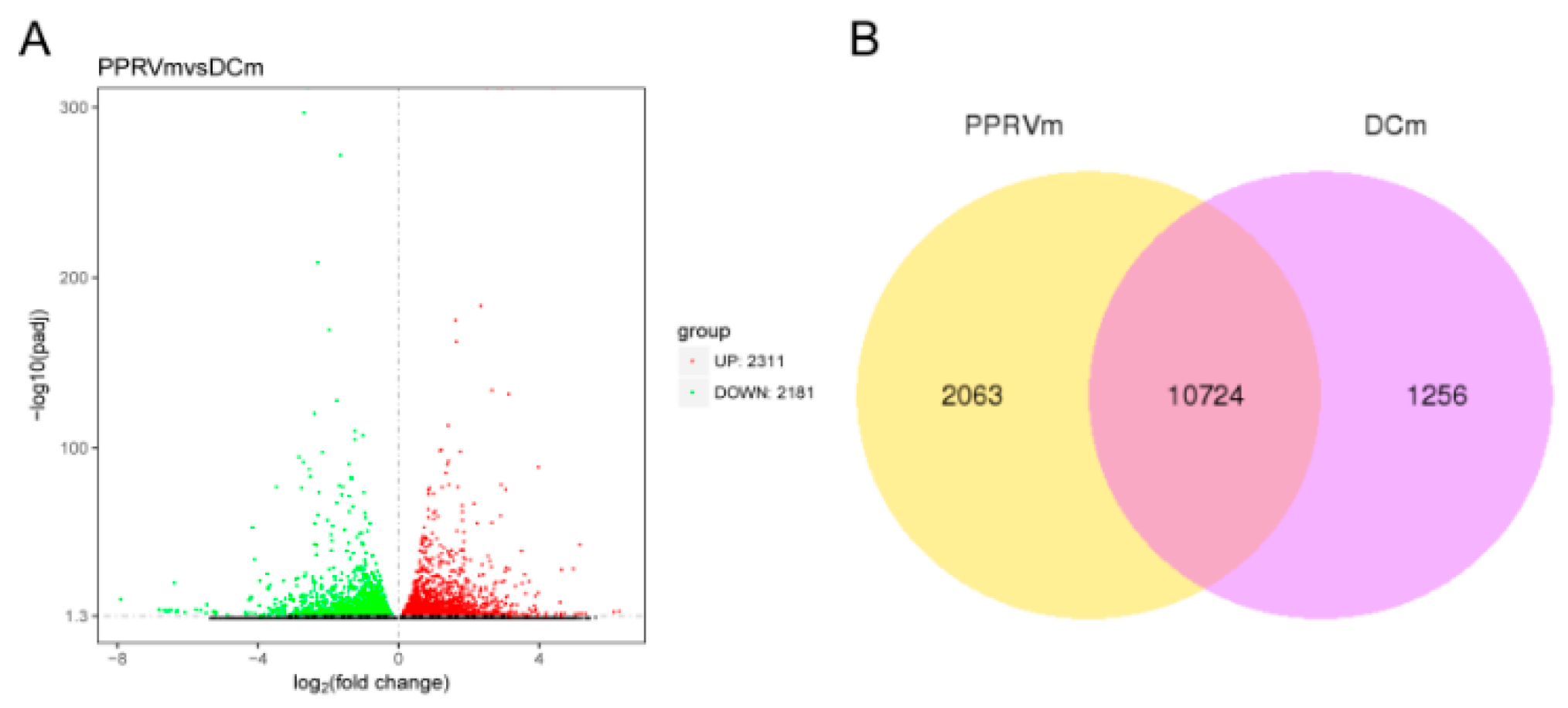
3.1. Responses of BMDCs in Response to PPRV
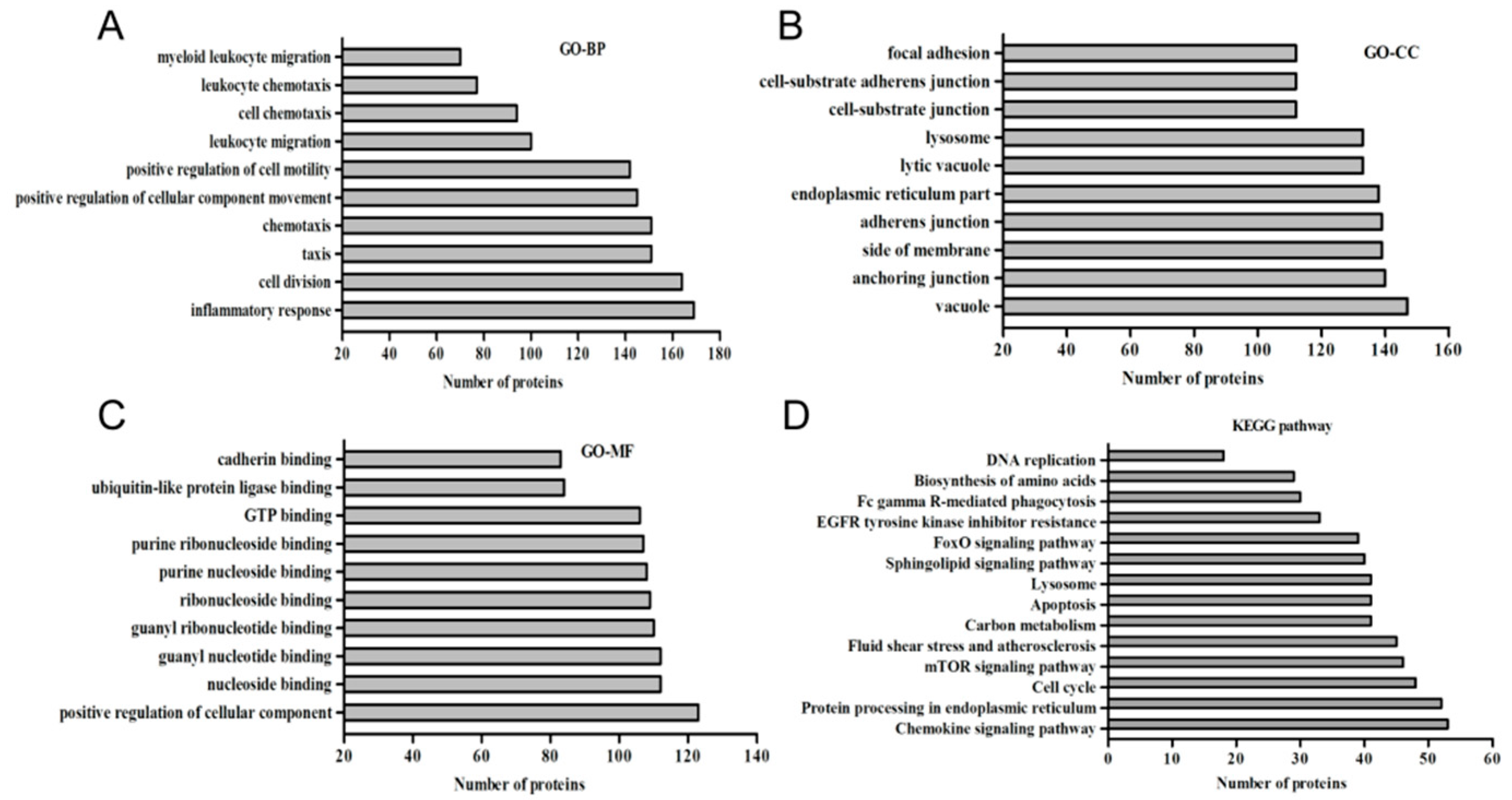
3.2. Function Classification of the DEGs in Response to PPRV
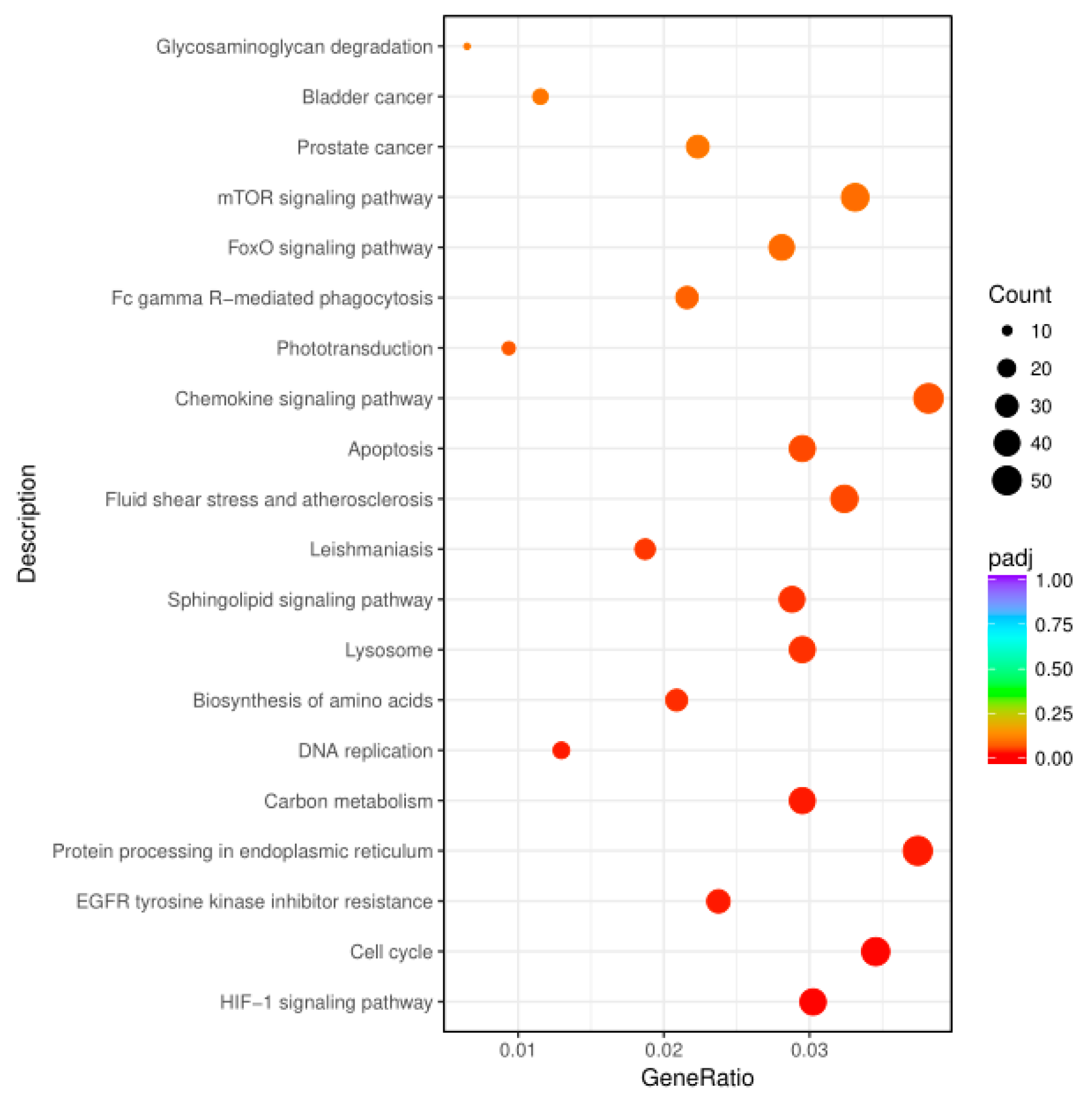
3.3. KEGG Enrichment of Key Genes Related to Signal Pathways
3.4. Validation of DEGs by Quantitative RT-PCR
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
References
- Gari, G.; Serda, B.; Negesa, D.; Lemma, F.; Asgedom, H. Serological Investigation of Peste Des Petits Ruminants in East Shewa and Arsi Zones, Oromia Region, Ethiopia. Vet. Med. Int. 2017, 2017, 9769071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Hassen, S.; Monaco, F.; Sghaier, S.; Orsini, M.; Valleriani, F.; Haj Ammar, H.; Petrini, A.; Hammami, S.; Cosseddu, G.M. Peste des Petits Ruminants outbreaks in Tunisia in 2016. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubakar, M.; Jamal, S.M.; Arshed, M.J.; Hussain, M.; Ali, Q. Peste des petits ruminants virus (PPRV) infection; its association with species, seasonal variations and geography. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2009, 41, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reperant, L.A.; Brown, I.H.; Haenen, O.L.; de Jong, M.D.; Osterhaus, A.D.; Papa, A.; Rimstad, E.; Valarcher, J.F.; Kuiken, T. Companion Animals as a Source of Viruses for Human Beings and Food Production Animals. J. Comp. Pathol. 2016, 155, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, D.; Banyard, A.; Dash, P.; Ozkul, A.; Barrett, T. Full genome sequence of peste des petits ruminants virus, a member of the Morbillivirus genus. Virus Res. 2005, 110, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baron, M.D.; Diallo, A.; Lancelot, R.; Libeau, G. Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus. Adv. Virus Res. 2016, 95, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Muniraju, M.; Munir, M.; Parthiban, A.R.; Banyard, A.C.; Bao, J.; Wang, Z.; Ayebazibwe, C.; Ayelet, G.; El Harrak, M.; Mahapatra, M.; et al. Molecular evolution of peste des petits ruminants virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 2023–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Xue, Q.; Qi, X.; Wang, X.; Jia, P.; Chen, S.; Wang, T.; Xue, T.; Wang, J. Autophagy enhances the replication of Peste des petits ruminants virus and inhibits caspase-dependent apoptosis in vitro. Virulence 2018, 9, 1176–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prajapati, M.; Alfred, N.; Dou, Y.; Yin, X.; Prajapati, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z. Host Cellular Receptors for the Peste des Petits Ruminant. Viruses 2019, 11, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldrich, W.A.; Ren, C.; White, A.F.; Zhou, S.Z.; Kumar, S.; Jenkins, C.B.; Shaw, D.R.; Strong, T.V.; Triozzi, P.L.; Ponnazhagan, S. Enhanced transduction of mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells by repetitive infection with self-complementary adeno-associated virus 6 combined with immunostimulatory ligands. Gene Ther. 2006, 13, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosavi, R.A.; Salwe, S.; Mukherjee, S.; Dahake, R.; Kothari, S.; Patel, V.; Chowdhary, A.; Deshmukh, R.A. Optimization of Ex Vivo Murine Bone Marrow Derived Immature Dendritic Cells: A Comparative Analysis of Flask Culture Method and Mouse CD11c Positive Selection Kit Method. Bone Marrow Res. 2018, 2018, 3495086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashayekhi, M.; Sandau, M.M.; Dunay, I.R.; Frickel, E.M.; Khan, A.; Goldszmid, R.S.; Sher, A.; Ploegh, H.L.; Murphy, T.L.; Sibley, L.D.; et al. CD8alpha(+) dendritic cells are the critical source of interleukin-12 that controls acute infection by Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites. Immunity 2011, 35, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contractor, N.; Louten, J.; Kim, L.; Biron, C.A.; Kelsall, B.L. Cutting edge: Peyer’s patch plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs) produce low levels of type I interferons: Possible role for IL-10, TGFbeta, and prostaglandin E2 in conditioning a unique mucosal pDC phenotype. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 2690–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Zhao, L.; Li, D.; Xu, S.; Hou, X.; Li, Z. Low risk HPV-6E6 induces apoptosis in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szulc-Dabrowska, L.; Struzik, J.; Ostrowska, A.; Guzera, M.; Toka, F.N.; Bossowska-Nowicka, M.; Gierynska, M.M.; Winnicka, A.; Nowak, Z.; Niemialtowski, M.G. Functional paralysis of GM-CSF-derived bone marrow cells productively infected with ectromelia virus. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegemund, S.; Hartl, A.; von Buttlar, H.; Dautel, F.; Raue, R.; Freudenberg, M.A.; Fejer, G.; Büttner, M.; Köhler, G.; Kirschning, C.J.; et al. Conventional bonemarrow-derived dendritic cells contribute to toll-like receptor-independent production of alpha/beta interferon in response to inactivated Parapoxvirus ovis. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 9411–9422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Yu, J.; Li, Z.; Lin, W.; Lin, X. Systematically integrated metabonomic-proteomic studies of Escherichia coli under ciprofloxacin stress. J. Proteom. 2018, 179, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.X.; Yan, R.; Shi, H.Y.; Shi, D.; Fang, D.Q.; Jiang, H.Y.; Wu, W.R.; Guo, F.F.; Jiang, X.W.; Gu, S.L.; et al. Integrated transcriptomic and proteomic analysis of the bile stress response in probiotic Lactobacillus salivarius LI01. J. Proteom. 2017, 150, 216–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Hwang, Y.H.; Kim, K.J.; Park, A.K.; Paik, M.J.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, S.U.; Yee, S.T.; Son, Y.J. Proteomic and transcriptomic analysis of lung tissue in OVA-challenged mice. Arch. Pharmacal Res. 2018, 41, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, C.S.; Chong, P.K.; Pham, T.K.; Wright, P.C. Technical, experimental, and biological variations in isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation (iTRAQ). J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 821–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, J.Y.; Du, G.Y.; Feng, Q.; Wang, G.X.; Chen, Y.; Cao, X.A.; Liu, Y.S.H.; Liu, X.T.; Shang, Y.J. Effects of peste des petits ruminants virus on the maturation and differentiation of murine bone marrow derived dendritic cells. Immunol. J. 2018, 34, 369–377. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Wu, J.; Cao, X.; Zhou, J.; Yin, S.; Yang, S.; Feng, Q.; Du, P.; Liu, Y.; Shang, Y.; et al. Proteomic analysis of murine bone marrow derived dendritic cells in response to peste des petits ruminants virus. Res. Vet. Sci. 2019, 125, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, M.B.; Kukutsch, N.; Ogilvie, A.L.; Rossner, S.; Koch, F.; Romani, N.; Schuler, G. An advanced culture method for generating large quantities of highly pure dendritic cells from mouse bone marrow. J. Immunol. Methods 1999, 223, 77–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfield, A.; Auray, G.; Ricklin, M. Comparative dendritic cell biology of veterinary mammals. Annu. Rev. Anim. Biosci. 2015, 3, 533–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, N.; Pimentel, H.; Melsted, P.; Pachter, L. Erratum: Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.R.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.L.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 562–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Hattori, M.; Aoki-Kinoshita, K.F.; Itoh, M.; Kawashima, S.; Katayama, T.; Araki, M.; Hirakawa, M. From genomics to chemical genomics: New developments in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D354–D357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Chen, Z.; Li, C.; Shi, L.; Li, W.; Huang, H.; Tao, C.; Cheng, C.; Xu, B.; et al. Recombinant adenovirus expressing F and H fusion proteins of peste des petits ruminants virus induces both humoral and cell-mediated immune responses in goats. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2013, 154, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yue, X.; Jin, H.; Liu, G.; Pan, L.; Wang, G.; Guo, H.; Li, G.; Li, Y. A suicidal DNA vaccine expressing the fusion protein of peste des petits ruminants virus induces both humoral and cell-mediated immune responses in mice. J. Virol. Methods 2015, 225, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjunath, S.; Mishra, B.P.; Mishra, B.; Sahoo, A.P.; Tiwari, A.K.; Rajak, K.K.; Muthuchelvan, D.; Saxena, S.; Santra, L.; Sahu, A.R.; et al. Comparative and temporal transcriptome analysis of peste des petits ruminants virus infected goat peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Virus Res. 2017, 229, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manjunath, S.; Mishra, B.; Mishra, B.P.; Saxena, S.; Mondal, P.; Sahu, A.R.; Sahoo, A.P.; Tiwari, A.K.; Gandham, R.K. Identification of suitable reference gene in goat peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) infected with peste des petits ruminants virus (PPRV). Livest. Sci. 2015, 181, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, O.M.; Levert-Mignon, A.J.; Lord, S.J.; Botelho, N.K.; Freeman, A.K.; Thomas, M.L.; Falkenback, D.; Wettstein, A.; Whiteman, D.C.; Bobryshev, Y.V.; et al. High Expression of Cathepsin E in Tissues but Not Blood of Patients with Barrett’s Esophagus and Adenocarcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 2431–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, M.; Bartelt, J.; Reichling, C.; Winnig, M.; Kuhn, C.; Meyerhof, W. Members of RTP and REEP gene families influence functional bitter taste receptor expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 20650–20659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annaert, W.G.; Becker, B.; Kistner, U.; Reth, M.; Jahn, R. Export of cellubrevin from the endoplasmic reticulum is controlled by BAP31. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 139, 1397–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.; Breckenridge, D.G.; Ducret, A.; Shore, G.C. Caspase-resistant BAP31 inhibits fas-mediated apoptotic membrane fragmentation and release of cytochrome c from mitochondria. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 6731–6740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, B.; Sreenivasa, B.P.; Dhar, P.; Singh, R.P.; Bandyopadhyay, S.K. Apoptosis induced by peste des petits ruminants virus in goat peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Virus Res. 2001, 73, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Lv, J.; Feng, C.; Deng, J.; Wang, C.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, T.; Lin, X. Peste des petits ruminants virus exploits cellular autophagy machinery for replication. Virology 2013, 437, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Sahu, A.R.; Wani, S.A.; Saxena, S.; Kanchan, S.; Sah, V.; Rajak, K.K.; Khanduri, A.; Sahoo, A.P.; Tiwari, A.K.; et al. Modulation of Host miRNAs Transcriptome in Lung and Spleen of Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus Infected Sheep and Goats. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadahi, J.A.; Yongqian, B.; Ehsan, M.; Zhang, Z.C.; Wang, S.; Yan, R.F.; Song, X.K.; Xu, L.X.; Li, X.R. Haemonchus contortus excretory and secretory proteins (HcESPs) suppress functions of goat PBMCs in vitro. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 35670–35679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehsan, M.; Gao, W.; Gadahi, J.; Lu, M.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, R.; Xu, L.; Song, X.; Li, X. Arginine kinase from Haemonchus contortus decreased the proliferation and increased the apoptosis of goat PBMCs in vitro. Parasit. Vectors 2017, 10, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehsan, M.; Wang, W.; Gadahi, J.; Hasan, M.; Lu, M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Haseeb, M.; Yan, R.; Xu, L.; et al. The Serine/Threonine-Protein Phosphatase 1 From Is Actively Involved in Suppressive Regulatory Roles on Immune Functions of Goat Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Front. Immunol 2018, 9, 1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Name | Primer Sequence (5′ to 3′) | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| Pfn2 | F: GAAGGTTTCTTTACCAACGGTT | 81 |
| R: GTCACCATCAACGTATAGGCTA | ||
| Pf4 | F: TCTCCTCTGGGATCCATCTTAA | 114 |
| R: GGCAAATTTTCCTCCCATTCTT | ||
| Gm5483 | F: ATCCAGGAGATTGCTGATAAGG | 81 |
| R: CTCAACAGCTTTGAACACTTCA | ||
| Cd14 | F: GACCTTAGTCACAATTCACTGC | 87 |
| R: GAAAGACAGATTGAGCGAGTTT | ||
| Fbp1 | F: GATCTTTTTATACCCCGCCAAC | 93 |
| R: GCCTTCTCCATGACATAAGCTA | ||
| Tarsl2 | F: CGATGTGGACTTAGATGACAGT | 104 |
| R: TGATCTTTTCCTTTTCGCCAAC | ||
| Bcap31 | F: CTTTGTGGTTCTCATCGTCATC | 92 |
| R: GGTTCACCTTTTCTGTCACATC | ||
| Il1b | F: TGAATGAAGCACCAGCACAT | 140 |
| R: AGCCTCATGGCCCAATTTCT | ||
| Cstb | F: TCTGATTCGGGGCTCCTTTG | 74 |
| R: TCCCTTCTCTCCATCACCGA | ||
| Atp5e | F: CGACAGGCTGGACTCAGCTA | 115 |
| R: TTATGCTGCTGCCCGAAGTC | ||
| Klk1b11 | F: AGTCTCGAATTGTTGGAGGATT | 187 |
| R: GTTCACGTTGGAATAGCTTTGT | ||
| Rapgef3 | F: AACTTGCTGAGGGAACAGTATC | 84 |
| R: CTTGGTCTGAGGAGATACGTTC | ||
| Romo1 | F: CTGTCTCAGGATCGGAATGC | 103 |
| R: CATTCCAATGGCCATGAAAGTG | ||
| Fblim1 | F: CTCCATCAAAGGGATCGTCTG | 108 |
| R: CTTCTCTCTCTGGAAGTGTGAC | ||
| Tppp3 | F: TGACGGACACCAGTAAGTATAC | 125 |
| R: GTTTTTGTAGGCACTCACGTAG | ||
| Cd9 | F: ATCAAATACCTGCTCTTCGGAT | 83 |
| R: AATCGGAGCCATAGTCCAATAG | ||
| Gpr15 | F: CACATCTGTCTTCCTCCCTATC | 118 |
| R: GATGTCGATCAATCTTCGGTTG | ||
| Reep5 | F: CATCTCAATGAAAGCCATCGAG | 88 |
| R: ATGCTGAACACACCATATACCA | ||
| Tagln2 | F: GTAAAGAAGATCCAGGCCTCTT | 136 |
| R: TGTTCTTTCCTTCCCAGAGATC | ||
| Poglut1 | F: TAAAGCCATGGGTTCACTACAT | 262 |
| R: AGTTCAGTTTTCAAACGTCTGG | ||
| Pcna | F: GAAGTTTTCTGCAAGTGGAGAG | 107 |
| R: CAGGCTCATTCATCTCTATGGT | ||
| C3ar1 | F: GTGCAAACTTATCCCATCCATC | 92 |
| R: GTACTATCAGACATCGGTCCAG | ||
| Hal | F: CAACGTCTTAGCCAAAGGTTAC | 230 |
| R: GTCCATGGGCTTCTAGAACATA | ||
| Cmklr1 | F: GCGTCTTCCTGCTGACTGTCATC | 85 |
| R: CGGATGCTGCGGTGGTTCTG | ||
| Ldha | F:AAGACTACTGTGTAACTGCGAA | 114 |
| R: ACTTGAAGATGTTCACGTTTCG | ||
| Fam63b | F: CAAAGAAACTCCAGGAAGAGGA | 198 |
| R: CTTTGTCTTTTTCCCGAGGTTC | ||
| Cd74 | F: GTGAACTGGAAGATCTTCGAGA | 115 |
| R: ACTTGGTCAGTACTTTAGGTGG | ||
| β-actin | F: AGTGTGACGTTGACATCCGT | 126 |
| R: GCAGCTCAGTAACAGTCCGC |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Wu, J.; Liu, D.; Du, G.; Liu, Y.; Shang, Y.; Liu, X. Transcriptional Profiles of Murine Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells in Response to Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci6040095
Li L, Wu J, Liu D, Du G, Liu Y, Shang Y, Liu X. Transcriptional Profiles of Murine Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells in Response to Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus. Veterinary Sciences. 2019; 6(4):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci6040095
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lingxia, Jinyan Wu, Dan Liu, Guoyu Du, Yongsheng Liu, Youjun Shang, and Xiangtao Liu. 2019. "Transcriptional Profiles of Murine Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells in Response to Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus" Veterinary Sciences 6, no. 4: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci6040095
APA StyleLi, L., Wu, J., Liu, D., Du, G., Liu, Y., Shang, Y., & Liu, X. (2019). Transcriptional Profiles of Murine Bone Marrow-Derived Dendritic Cells in Response to Peste des Petits Ruminants Virus. Veterinary Sciences, 6(4), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci6040095




