Population Dynamics of Off-Host Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) Larvae in Response to Habitat and Seasonality in South Texas
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Rearing of Ticks
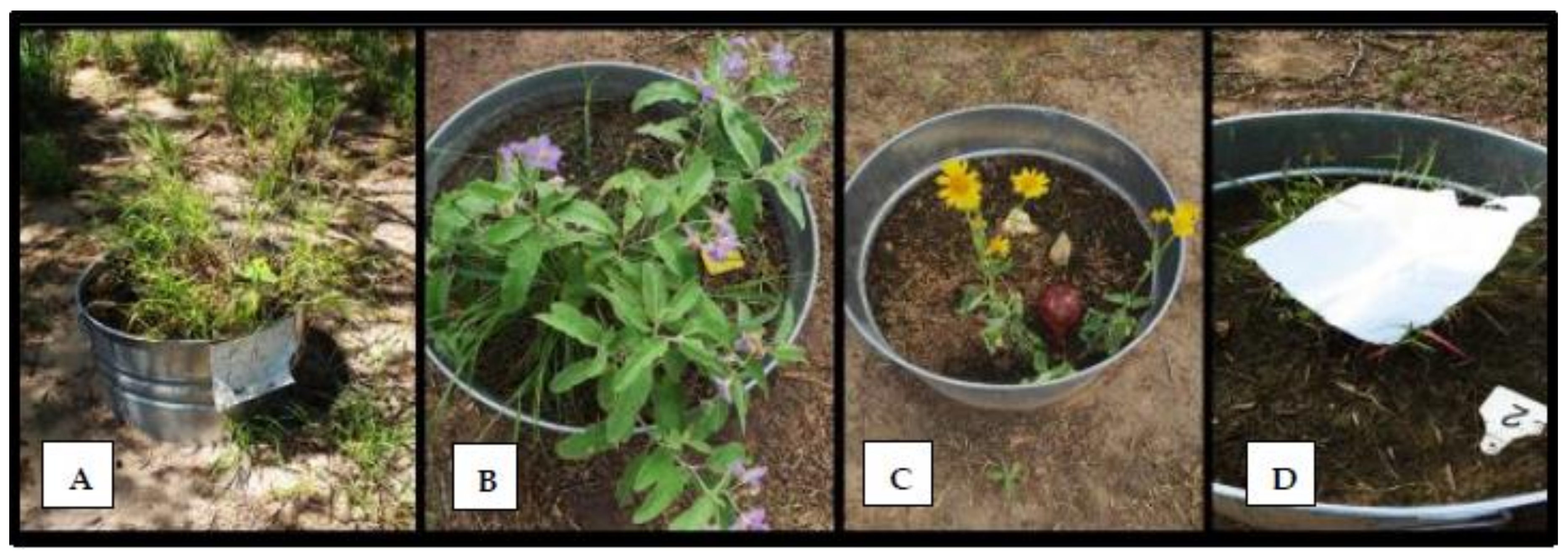
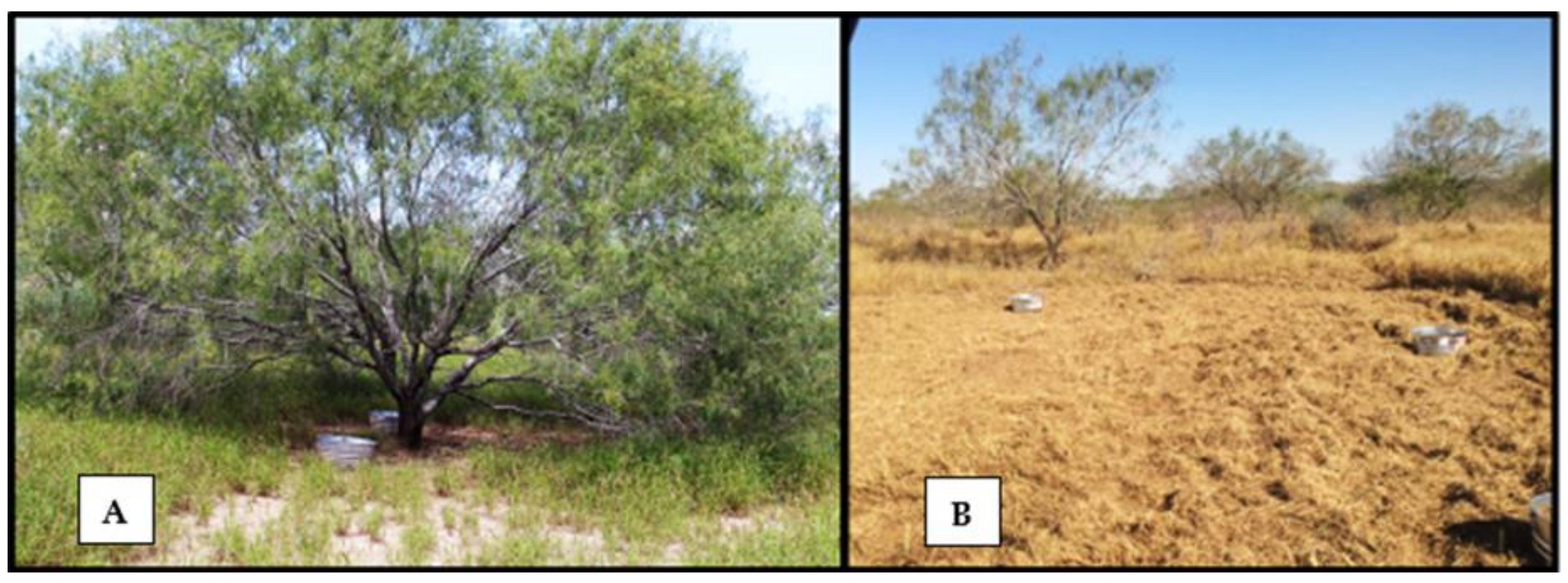
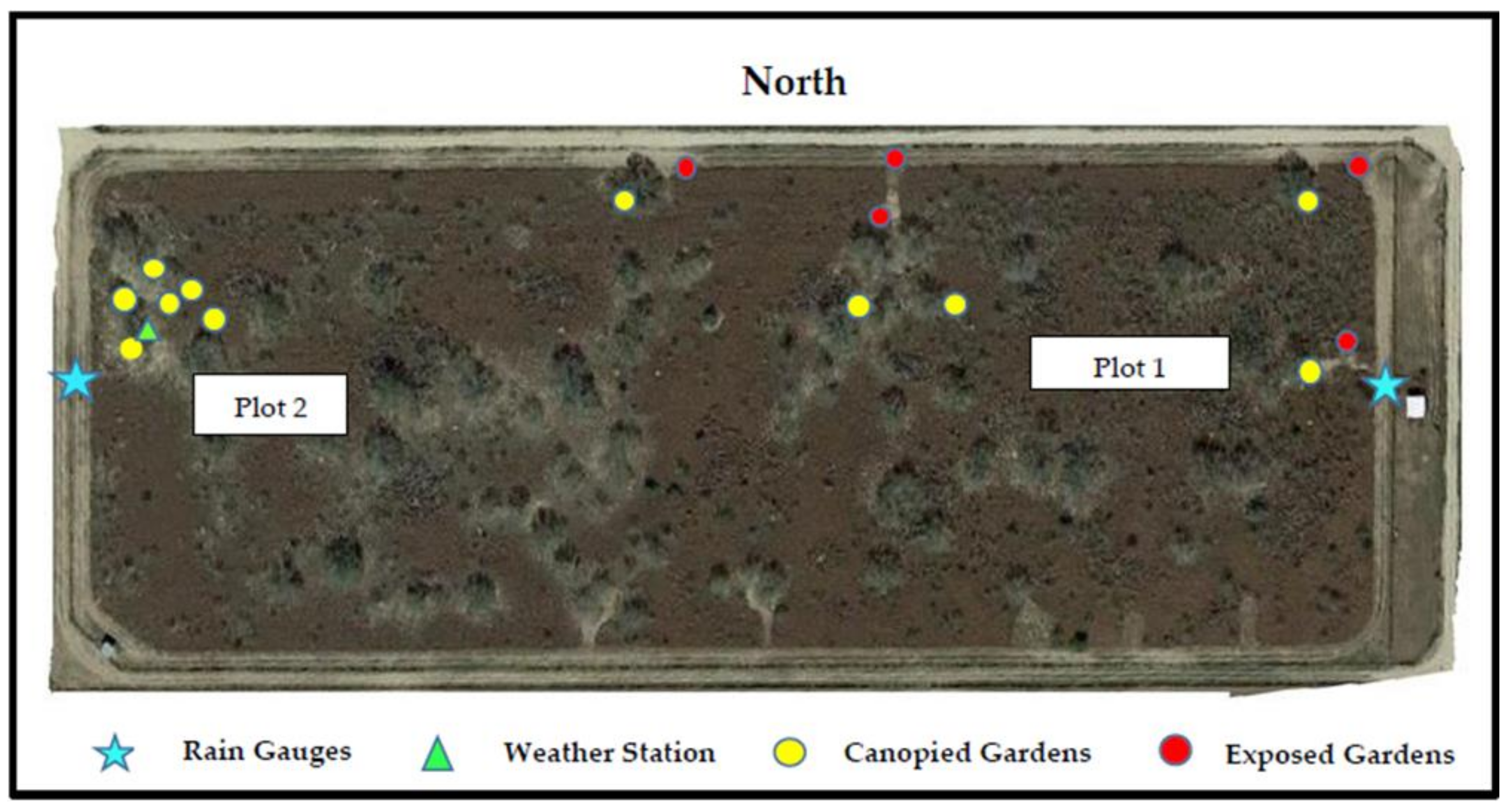
2.3. Tick Gardens
2.4. Data Collection
2.5. Cohorts
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nuñez, J.L.; Muñoz-Cobeñas, M.E.; Horacio, L.M. Boophilus microplus: The Common Cattle Tick; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, Germany, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Kocan, K.M.; Blouin, E.F.; Barbet, A.F. Anaplasmosis control: Past, present, and future. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2000, 916, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uilenberg, G. Babesia—A historical overview. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 138, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez de León, A.A.; Vannier, E.; Alamazán, C.; Krause, P.J. Tick-borne protozoa. In Biology of Ticks; Sonenshine, D.E., Roe, R.M., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 2, pp. 147–179. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, O.H.; Hourrigan, J.L. Eradication programs for the arthropods parasites of livestock. J. Med. Entomol. 1977, 13, 629–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmeyer, K.H.; Pound, J.M.; May, M.A.; Kammlah, D.M.; Davey, R.B. Distribution of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus and Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) annulatus (Acari: Ixodidae) infestations detected in the United States along the Texas/Mexico border. J. Med. Entomol. 2011, 48, 770–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey, R.B. Daily dynamics of egg development and fecundity and effect of age of larvae on attachment rate to cattle in Boophilus annulatus. Southwest. Entomol. 1986, 11, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Teel, P.D.; Marin, S.L.; Grant, W.E. Simulation of host-parasite-landscape interactions: Influence of season and habitat on cattle fever tick (Boophilus spp.) population dynamics. Ecol. Model. 1996, 84, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parola, P.; Raoult, D. Ticks and tickborne bacterial diseases in humans: An emerging infectious threat. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 32, 897–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooker, W.A.; Bishopp, F.C.; Wood, H.P. The Life History and Bionomics of Some North American Ticks; U.S. Deptartment of Agriculture, Bureau of Entomology: Washington, DC, USA, 1912. [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, L.F. Studies on the parasitic stages of the cattle fever tick, Boophilus microplus (Canestrini) (Acarina: Ixodidae). Austral. J. Zool. 1955, 3, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, G.R.; Teel, P.D. Off-host physiological ecology of Ixodid ticks. Ann. Rev. Entomol. 1991, 36, 659–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utech, K.; Sutherst, M.; Dallwitz, M.J.; Wharton, R.H.; Maywald, G.F.; Sutherland, I.D. A model of the survival of larvae of the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus, on pasture. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1983, 34, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lees, A.D. Transpiration and the structure of the epicuticle in ticks. J. Exp. Biol. 1946, 23, 379–410. [Google Scholar]
- Randolph, S.E.; Bowman, A.S.; Nuttall, P.A. Ticks: Biology, Disease, and Control; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; pp. 40–72. [Google Scholar]
- Knap, N.; Durmiši, E.; Saksida, A.; Korva, M.; Petrovec, M.; Avšič-Županc, T. Influence of climatic factors on dynamics of questing Ixodes ricinus ticks in Slovenia. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 164, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cumming, G.S. Host distributions do not limit the species ranges of most African ticks (Acari: Ixodida). Bull. Entomol. Res. 1999, 89, 303–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, T.D.; Shao, R.; Barker, S.C. Phylogenetic analysis of mitochondria genome sequences indicates that the cattle tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus, contains a cryptic species. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2014, 76, 241–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, V.N.; Tay, S.T.; Kho, K.L.; Koh, F.X.; Tan, T.K.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Ong, B.L.; Pachadcharam, C.; Norma-Rashid, Y.; Sofian-Azirun, M. Molecular characterisation of the tick Rhipicephalus microplus in Malaysia: New insights into the cryptic diversity and distinct genetic assemblages throughout the world. Parasit. Vectors 2015, 8, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Peña, A.; Venzal, J.M.; Santiago, N.; Mangold, A.; Guglielmone, A.A.; Labruna, M.B.; De la Fuente, J. Reinstatement of Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) australis (Acari: Ixodidae) with redescription of the adult and larval stages. J. Med. Entomol. 2012, 49, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). U.S. Department of Commerce. Available online: http://www.noaa.gov (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Crosswhite, F.S. Dry country plants of the south Texas plains. Desert Plants 1980, 2, 141–179. [Google Scholar]
- Clover, E.U. Vegetational survey of the Lower Rio Grande Valley, Texas. Madroño 1937, 4, 41–66. [Google Scholar]
- Jahrsdoefer, S.E.; Leslie, D.M., Jr. Tamaulipan Brushland of the Lower Rio Grande Valley of South Texas: Description, Human Impacts, and Management Options; U.S. Department of the Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service: Fairfax, VA, USA, 1988.
- Correll, E.F.; Johnston, M.C. Manual of the Vascular Plants of Texas; Texas Research Foundation: Renner, TX, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- United States Department of Agriculture Plants Database. Available online: https://www.plants.usda.gov/java/ (accessed on 22 March 2018).
- Leal, B.; Thomas, D.B.; Dearth, R.K. Cattle fever tick, Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae): Potential control on pastures by the application of urea fertilizer. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 241, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey, R.B.; Osburn, R.L.; Miller, J.A. Ovipositional and morphological comparisons of Boophilus (Acari: Ixodidae) collected from different geographic areas. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1984, 77, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriaga, L.; Castellanos, A.E.; Moreno, E.; Alarcón, J. Potential ecological distribution of alien invasive species and risk assessment: A case study of buffel grass in arid regions of Mexico. Conserv. Biol. 2001, 18, 1504–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekki, M. Biology, distribution, and impacts of silverleaf nightshade (Solanum elaeagnifolium Cav). EPPO Bull. 2007, 37, 114–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grichar, W.J.; Sestak, D.C. Control of golden crownbeard (Verbesina encelioides) in peanut (Arachis hypogaea) with postemergence herbicides. Peanut Sci. 1998, 25, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, P.R. The use of sampling methods in studies of the distribution of larvae of Boophilus microplus on pastures. Aust. J. Zool. 1961, 9, 752–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- QuickCalcs Graph Pad Software. Available online: https://www.graphpad.com/quickcalcs/linear1/ (accessed on 20 February 2018).
- Shapiro, S.S.; Wilk, M.B. An analysis of variance test for normality (complete samples). Biometrika 1965, 52, 591–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, P.R.; Wilson, J.T. Survival of cattle ticks in central Queensland pastures. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1959, 10, 129–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitchcock, L.F. Studies on the non-parasitic stages on the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus (Canestrini) (Acarina: Ixodidae). Austral. J. Zool. 1955, 3, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harley, K.L.S. Studies on the survival of the non-parasitic stages of the cattle tick Boophilus microplus in three climatically dissimilar districts of north Queensland. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1966, 17, 387–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legg, J. Some observations on the life history of the cattle tick (Boophilus australis). Proc. Roy. Soc. Qd. 1930, 41, 121–132. [Google Scholar]
- Australian Government. Bureau of Meteorology (BOM). Available online: http://www.bom.gov.au/ (accessed on 6 February 2018).
- Davey, R.B.; Cooksey, L.M.; Despins, J.L. Survival of larvae of Boophilus annulatus, Boophilus microplus, and Boophilus hybrids (Acari: Ixodidae) in different temperatures and humidity regimes in the laboratory. Vet. Parasitol. 1991, 28, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.V.; Monteiro, A.C.; Szabó, M.P.J.; Mochi, D.A.; Detogni-Simi, L.; Mendes-Carvalho, W.; Akemi-Tsurtua, S.; Barbosa, J.C. Effect of Metarhizium anisopliae fungus on off-host Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus from tick-infested pasture under cattle grazing in Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2011, 181, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branagan, D. The developmental periods of the Ixodid tick Rhipicephalus appendiculatus Nuem. under laboratory conditions. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1973, 63, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherst, R.W.; Dallwitz, M.J. Progress in the development of a population model for the cattle tick Boophilus microplus. In Proceedings of the 4th International Congress of Acarology, Saalfelden, Austria, 12–19 August 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Garris, G.I.; Popham, T.W. Vertical distribution and longevity of Boophilus microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) larvae in moist tropical grass environment in Puerto Rico. Environ. Entomol. 1990, 19, 1403–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, N.J.; Floyd, R.B.; Norval, R.A.I.; Sutherst, R.W. Survival and Behaviour of Unfed stages of the ticks Rhipicephalus appendiculatus, Boophilus decoloratus and B. microplus under field conditions in Zimbabwe. Exp. App. Acarol. 1989, 6, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teel, P.D.; Marin, S.; Grant, W.E.; Stuth, J.W. Simulation of host-parasite-landscape interactions: Influence of season and habitat on cattle fever tick (Boophilus sp.) population dynamics in rotational grazing systems. Ecol. Model. 1997, 97, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherst, R.W. Variation in the numbers of the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus (Canestrini), in a moist habitat made marginal by low temperatures. J. Aust. Entomol. Soc. 1983, 22, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowball, G.J. Ecological observations on the cattle tick, Boophilus microplus (Canestrini). Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1957, 8, 394–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabó, M.P.J.; Castro, M.B.; Ramos, H.G.C.; Garcia, M.V.; Castagnolli, K.C.; Pinter, A.; Veronez, V.A.; Magalhães, G.M.; Duarte, J.M.B.; Labruna, M.B. Species diversity and seasonality of free-living ticks (Acari: Ixodidae) in the natural habitat of wild Marsh deer (Blastocerus dichotomus) in Southeastern Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 2007, 143, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogden, N.H.; Lindsay, L.R.; Beauchamp, G.; Charron, D.; Maarouf, A.; O’Callaghan, C.J.; Waltner-Toews, D.; Barker, I.K. Investigation of Relationships between temperatures and developmental rates of tick Ixodes scapularis (Acari: Ixodidae) in the laboratory and field. J. Med. Entomol. 2004, 41, 622–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, M.L.; Adler, G.H.; Speilman, A. Correlation between abundance of deer and that of the deer tick, Ixodes dammini (Acari: Ixodidae). Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 1985, 78, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


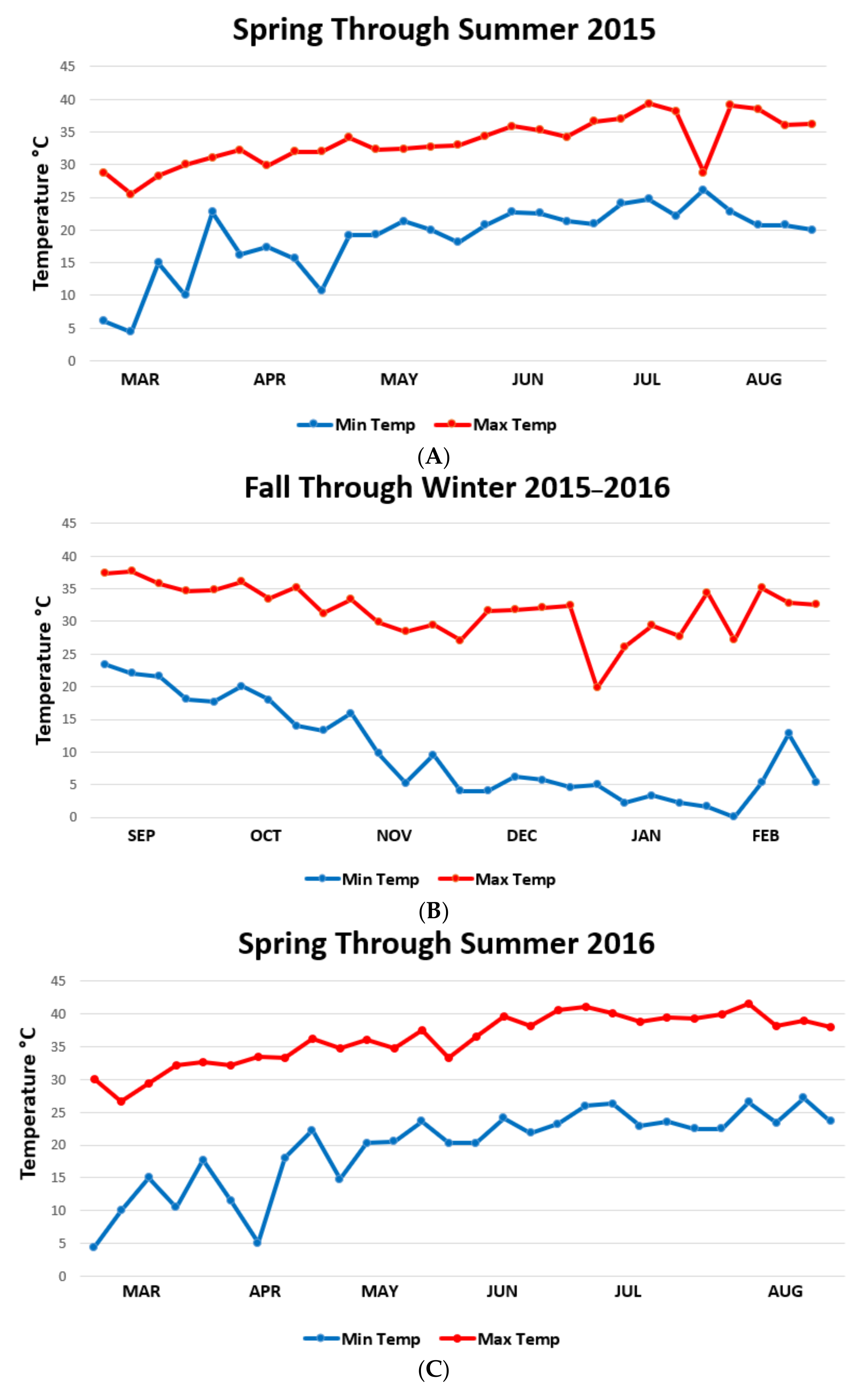
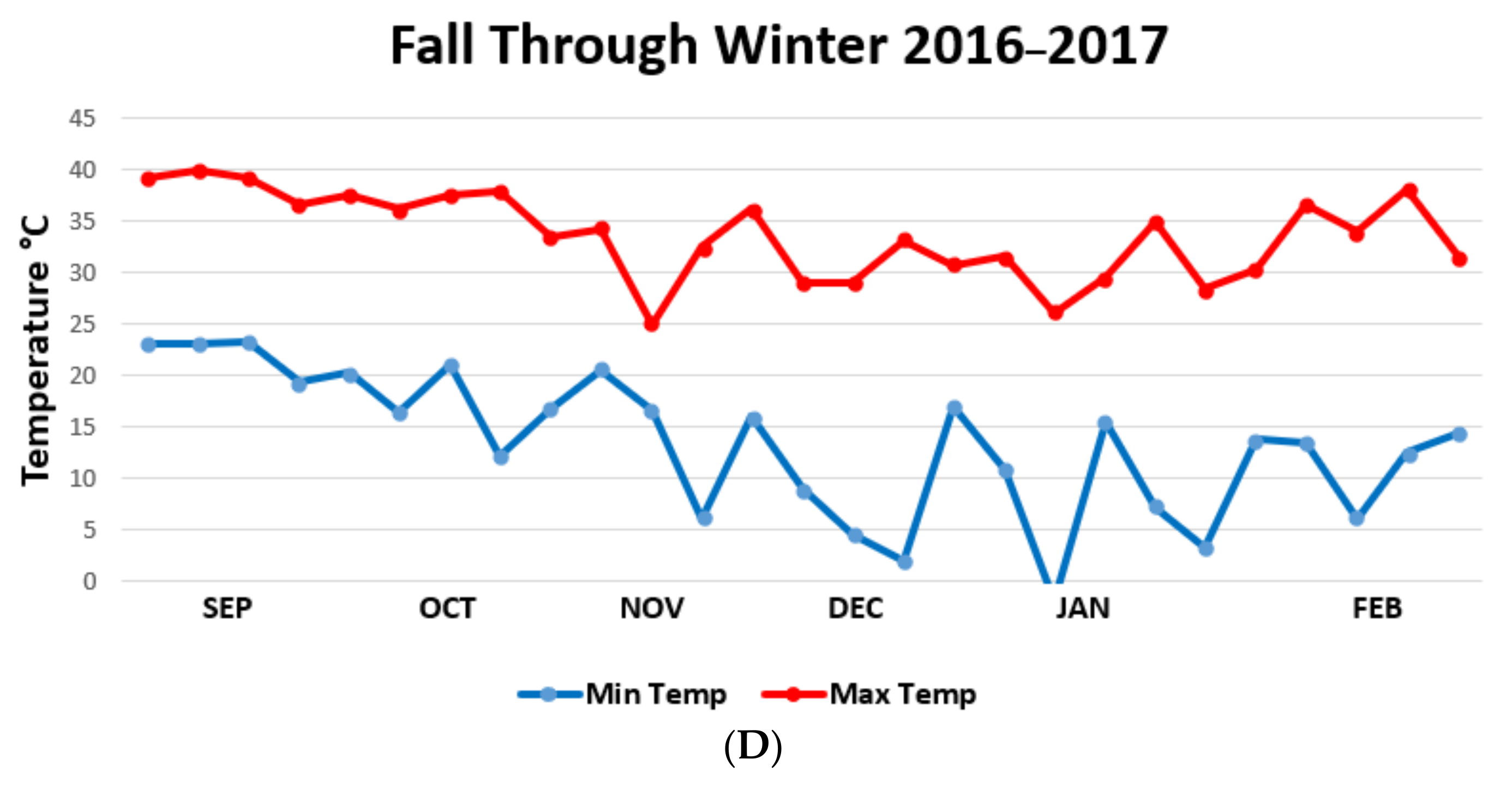
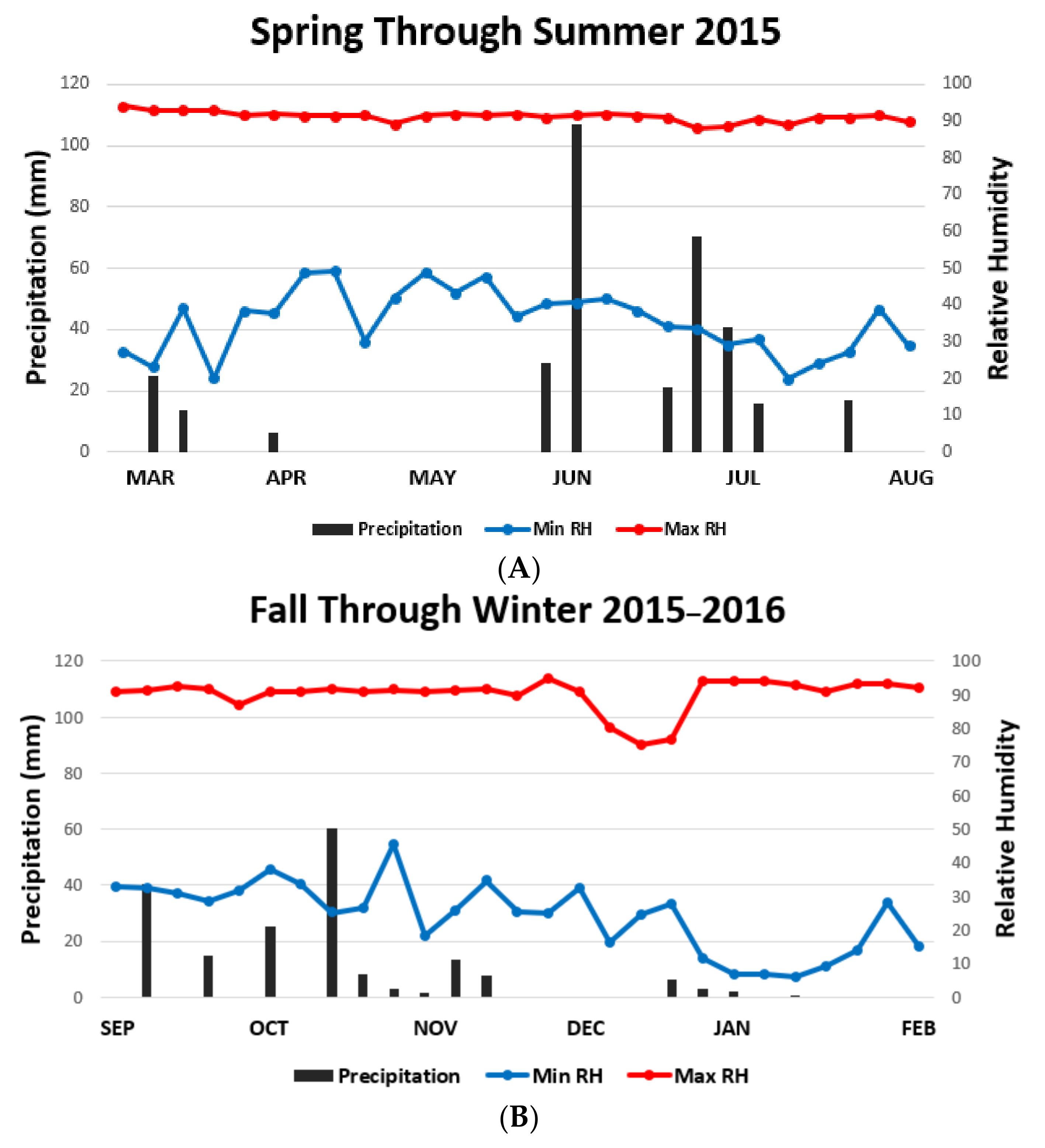
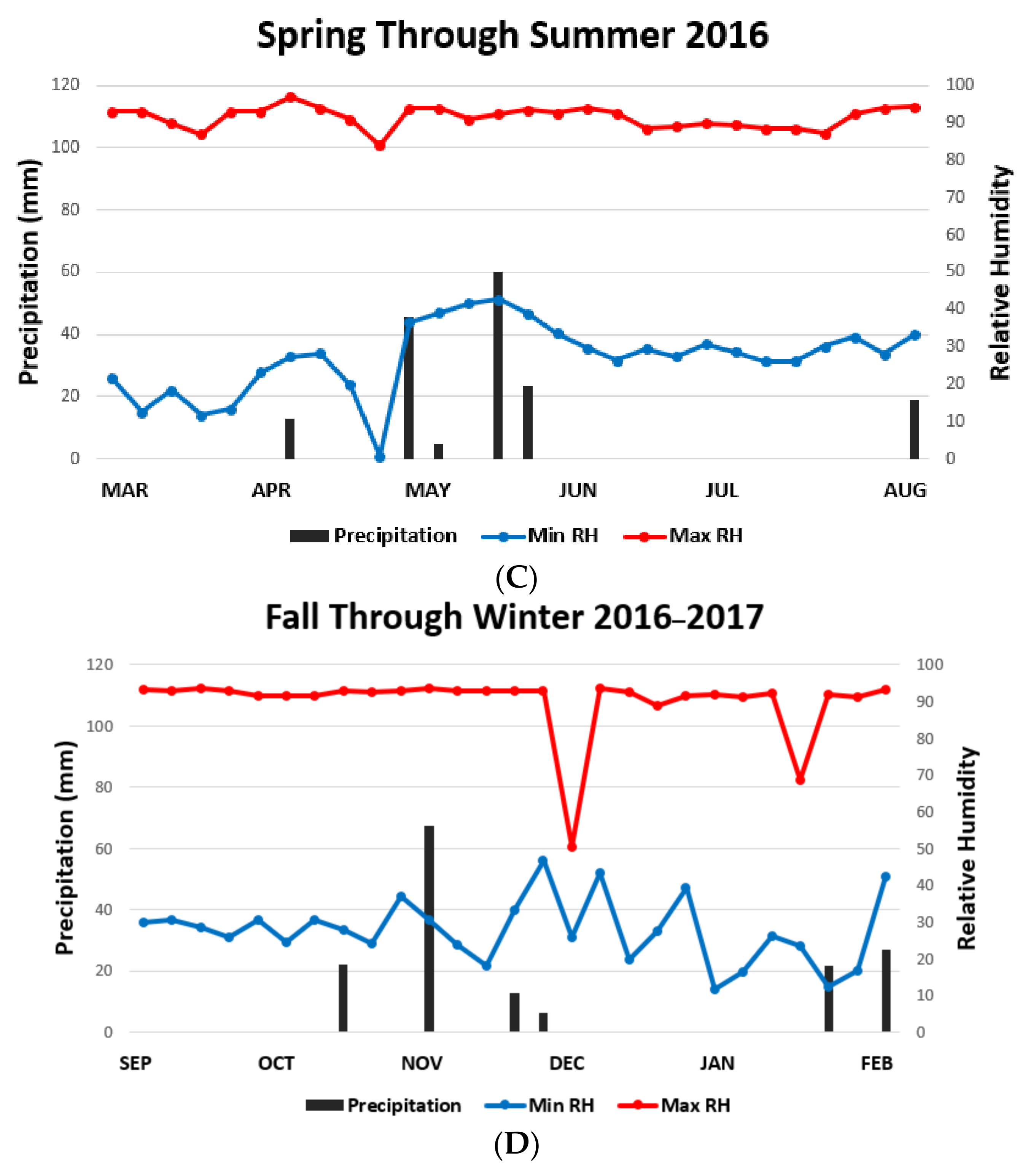
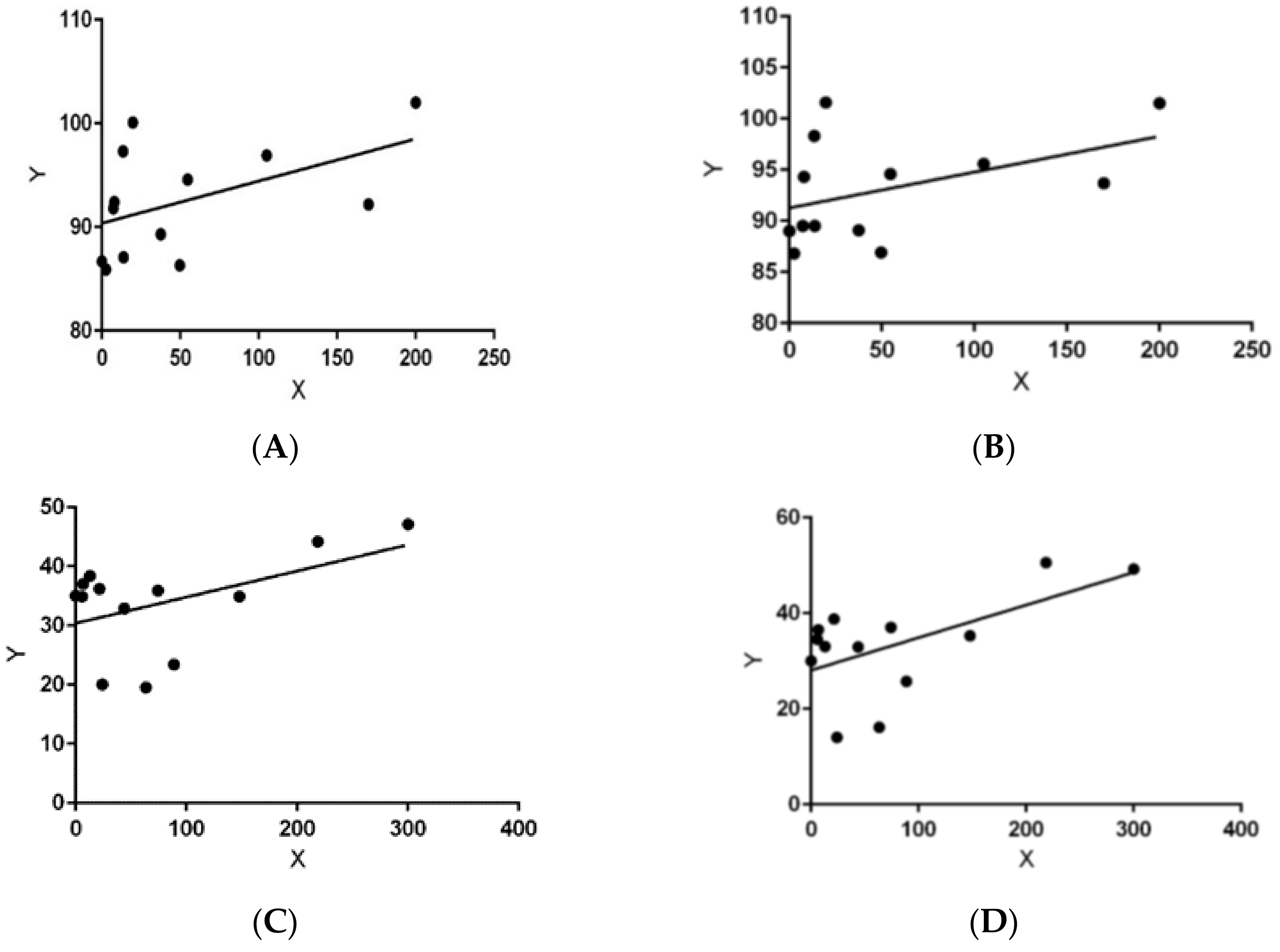
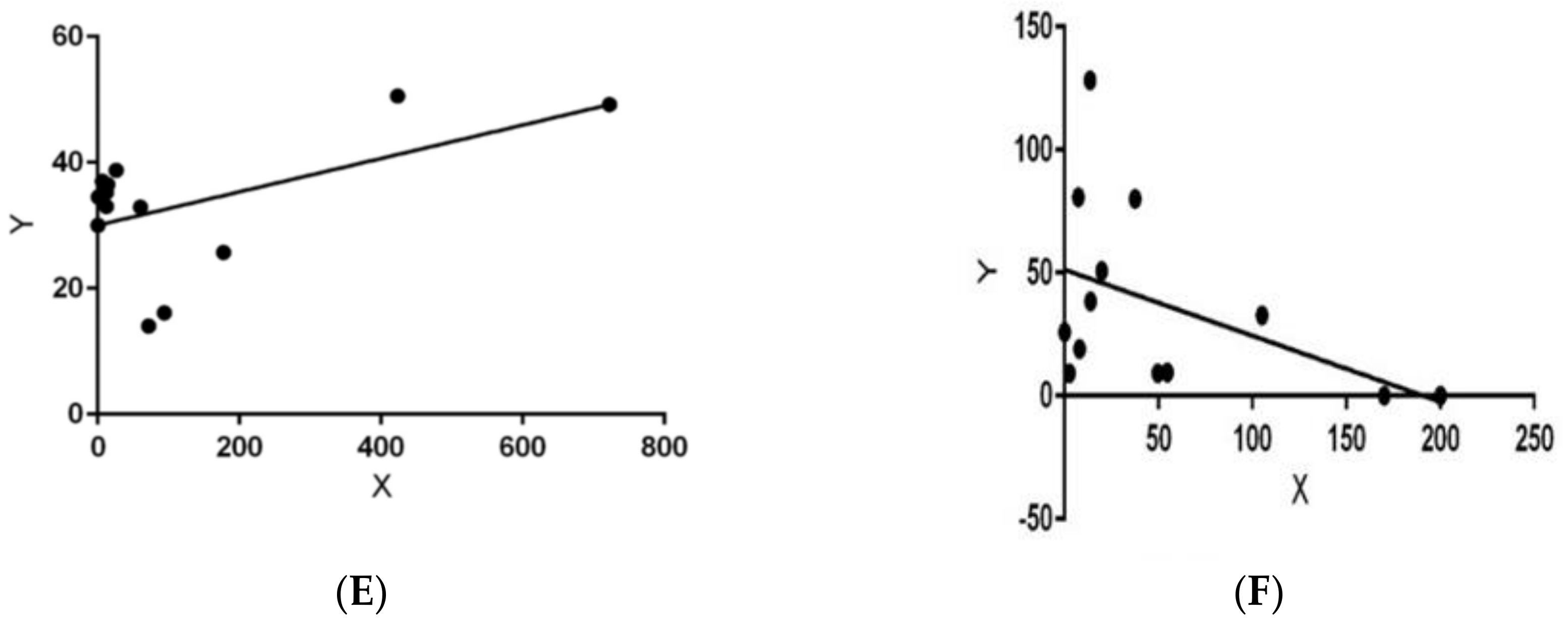
| Habitat | Fall ± SD | Winter ± SD | Spring ± SD | Summer ± SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Canopied | 7.3 ± 15.6 A | 27.5 ± 71.8 A | 76.7 ± 179.4 B | 111.6 ± 193.1 B |
| Exposed | 5.4 ± 9.9 A | 162.3 ± 250.5 B | 263.2 ± 540.8 B | 10.3 ± 19.5 A |
| All gardens | 6.6 ± 19.5 A | 72.9 ± 166.6 B | 130.5 ± 3321B | 81.2 ± 167.9 B |
| Positive gardens only | 11.8 ± 22 A | 93.1 ± 183.6 B | 147.5 ± 349.9 B | 115.94 ± 191 B |
| Cohorts | Season | N Gardens | Positive Gardens | Total Larvae | () Larvae | () Larvae Canopied | () Larvae Exposed | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | (%) | |||||||
| 1 | Winter | 10 | 9 | 90 | 2185 | 218.5 | 13.8 | 123.2 |
| 2 | Spring | 16 | 15 | 93 | 4801 | 300.6 | 169.9 | 586.4 |
| 3 | Summer | 16 | 4 | 25 | 209 | 13.1 | 13.5 | 12 |
| 4 | Summer | 16 | 14 | 87 | 1188 | 74.3 | 84.9 | 6.4 |
| 5 | Fall | 16 | 12 | 75 | 107 | 6.7 | 7.3 | 5.4 |
| 6 | Fall | 16 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | Winter | 16 | 8 | 50 | 385 | 24.1 | 2.4 | 71.8 |
| 8 | Winter | 16 | 16 | 100 | 1016 | 63.5 | 45.5 | 78.3 |
| 9 | Spring | 18 | 15 | 83 | 1598 | 88.8 | 54.7 | 319.6 |
| 10 | Spring | 18 | 16 | 88 | 387 | 21.5 | 19.8 | 77.4 |
| 11 | Summer | 18 | 18 | 100 | 2662 | 147.9 | 200.1 | 12.2 |
| 12 | Fall | 18 | 7 | 38 | 107 | 5.9 | 8.2 | 21.4 |
| 13 | Winter | 18 | 14 | 77 | 789 | 43.8 | 52.6 | 157.8 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leal, B.; Thomas, D.B.; Dearth, R.K. Population Dynamics of Off-Host Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) Larvae in Response to Habitat and Seasonality in South Texas. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci5020033
Leal B, Thomas DB, Dearth RK. Population Dynamics of Off-Host Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) Larvae in Response to Habitat and Seasonality in South Texas. Veterinary Sciences. 2018; 5(2):33. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci5020033
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeal, Brenda, Donald B. Thomas, and Robert K. Dearth. 2018. "Population Dynamics of Off-Host Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) Larvae in Response to Habitat and Seasonality in South Texas" Veterinary Sciences 5, no. 2: 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci5020033
APA StyleLeal, B., Thomas, D. B., & Dearth, R. K. (2018). Population Dynamics of Off-Host Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus (Acari: Ixodidae) Larvae in Response to Habitat and Seasonality in South Texas. Veterinary Sciences, 5(2), 33. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci5020033




