Immunomolecular Characterization of MIC-1, a Novel Antigen in Babesia bigemina, Which Contains Conserved and Immunodominant B-Cell Epitopes that Induce Neutralizing Antibodies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Babesia bigemina Strains, Parasite Culture and Bovine Sera
2.2. Identification of mic-1 Gene in the Babesia bigemina Genome
2.3. Isolation of DNA and Amplification and Sequencing of B. bigemina mic-1
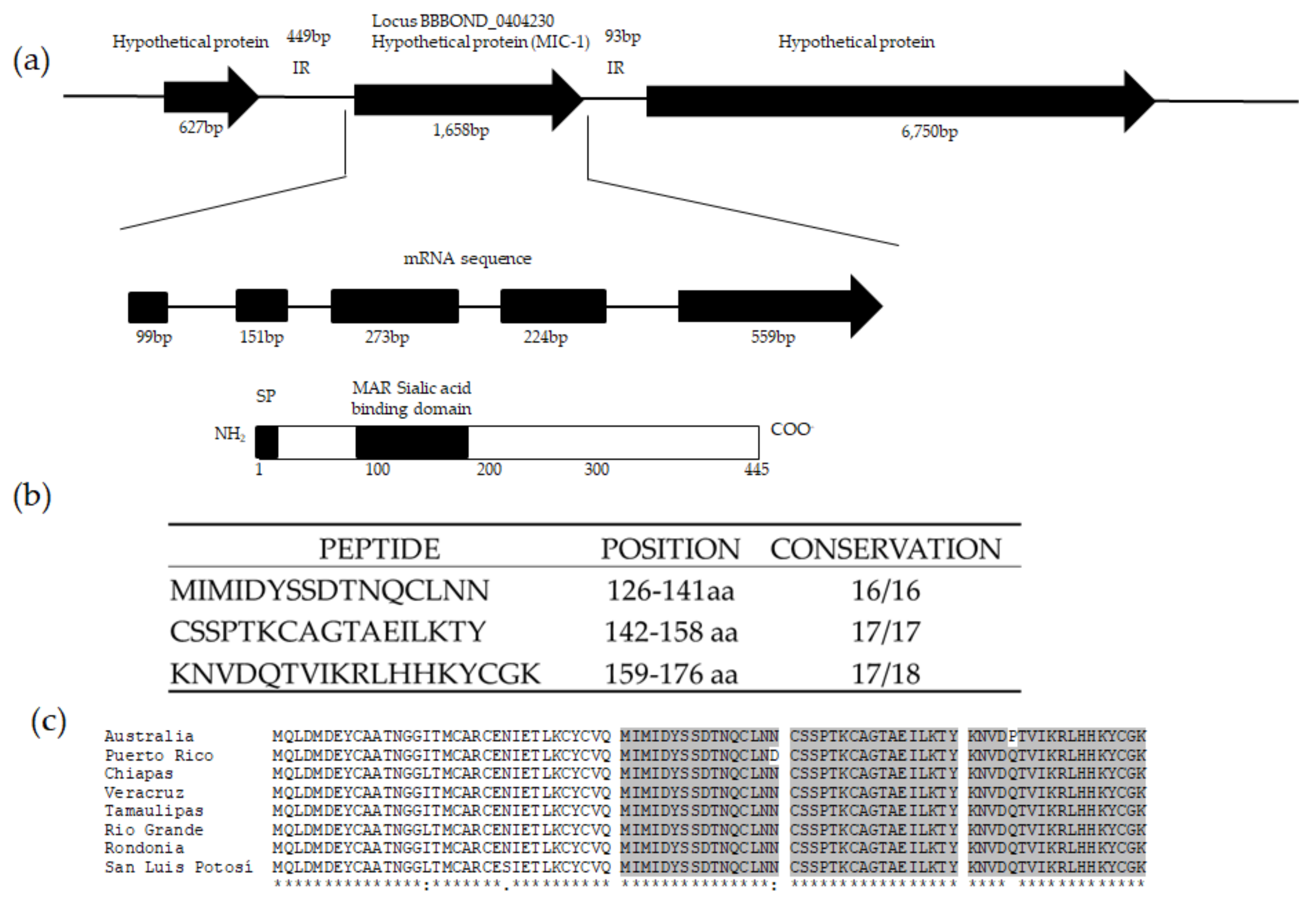
2.4. B. bigemina mic-1 Sequence Analysis
2.5. mic-1 Gene Transcription Analysis
2.6. Anti-MIC-1 Antibody Production
2.7. MIC-1 Protein Expression Analysis
2.7.1. Western Blot
2.7.2. Evaluation of the Presence of Anti-Babesia bigemina MIC-1 Antibodies in Cattle from Endemic Areas
2.8. Neutralization Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification of a mic-1 Homologous Gene in the Babesia bigemina Genome
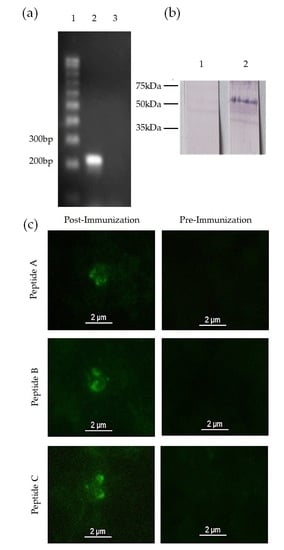
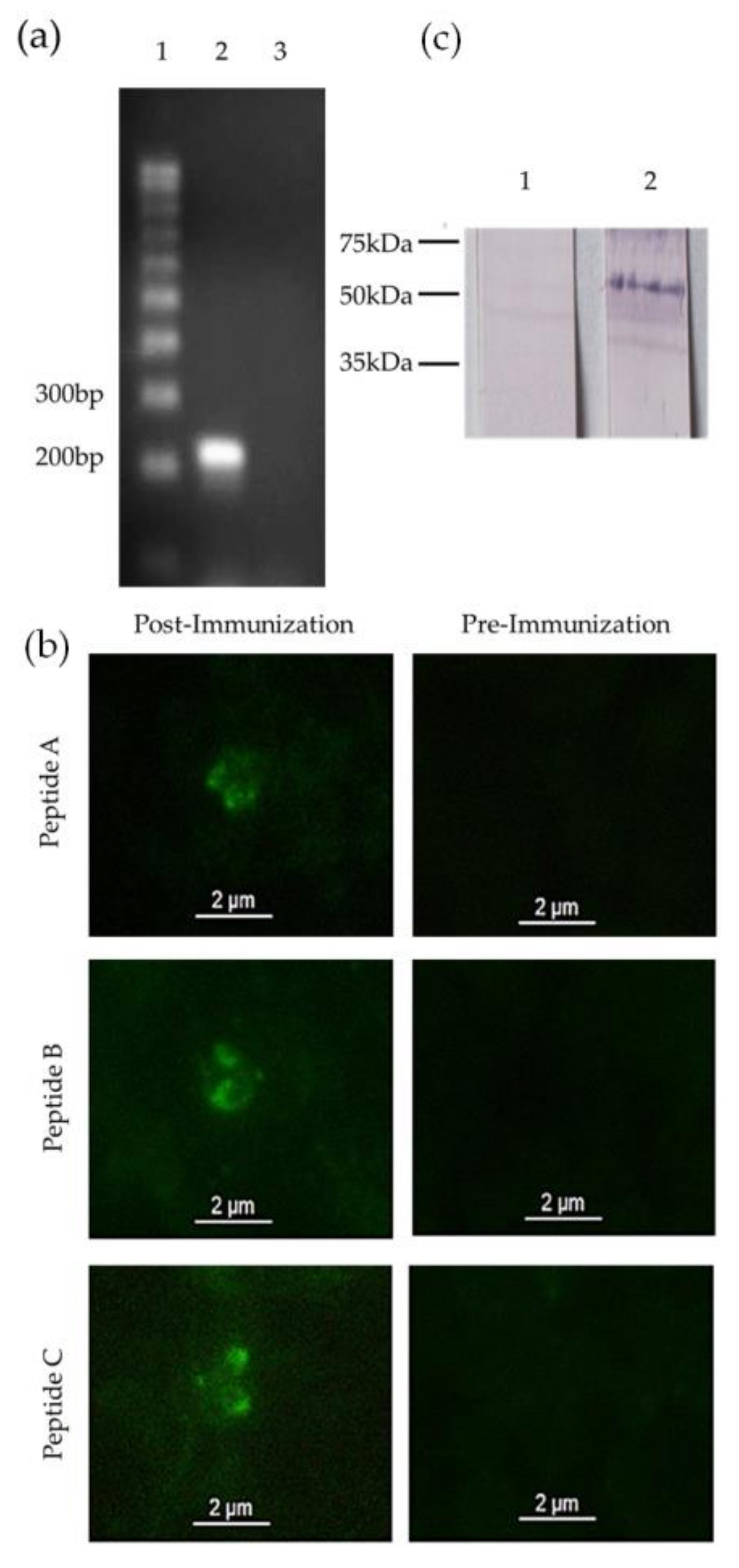
3.2. mic-1 Is Transcribed and Expressed in Blood Stages of Babesia Bigemina
3.3. Anti-MIC-1 Antibodies Are Present in Bovine Naturally Infected with Babesia Bigemina
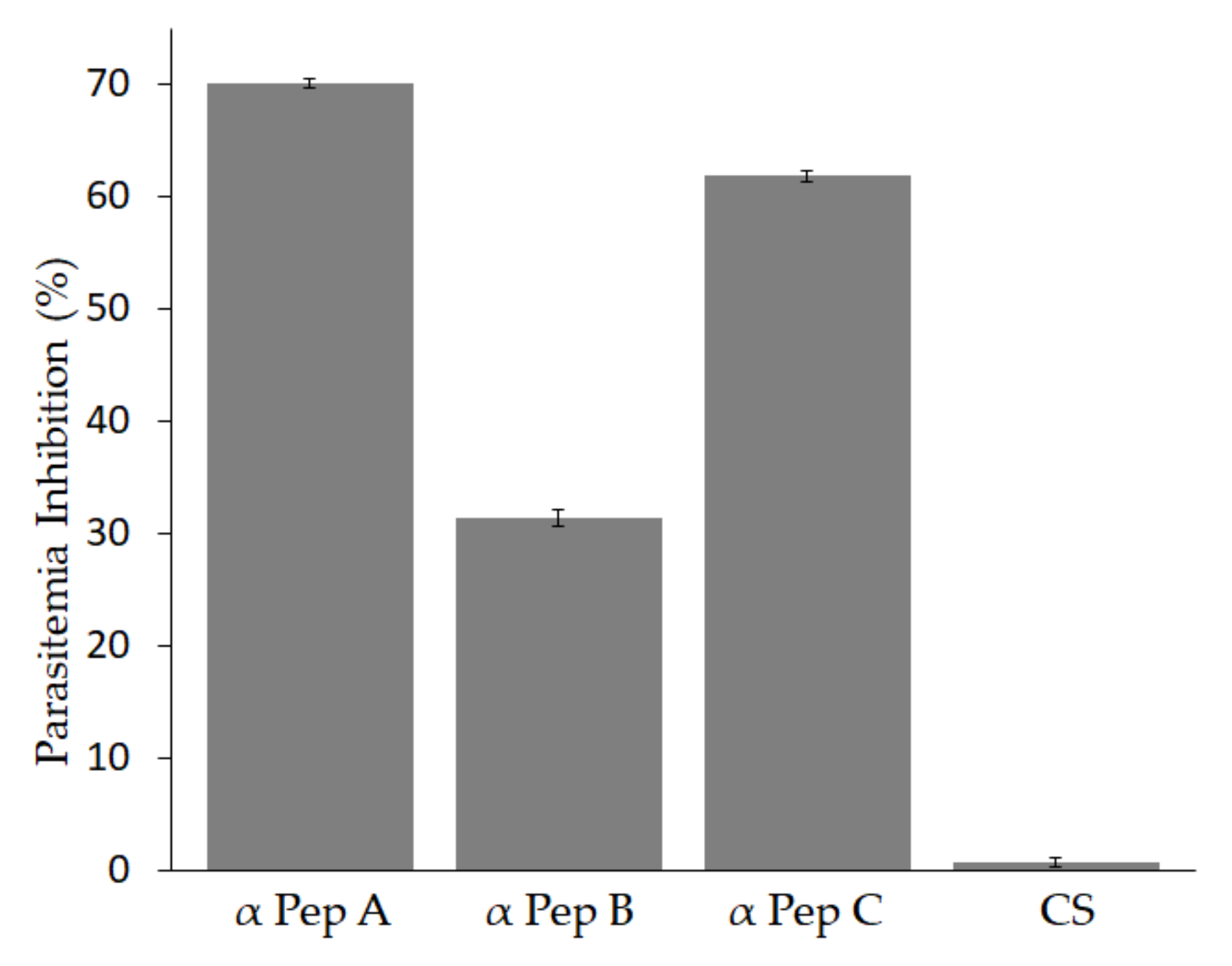
3.4. Antibodies against Babesia bigemina MIC-1 Block Parasite Invasion In-Vitro
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bock, R.; Jackson, L.; De Vos, A.; Jorgensen, W. Babesiosis of cattle. Parasitology 2004, 129, S247–S269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lew, A.; Jorgensen, W. Molecular approaches to detect and study the organisms causing bovine tick borne diseases: babesiosis and anaplasmosis. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2005, 4, 292–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, M.G.; Ristic, M. Babesia bovis: continuous cultivation in a microaerophilous stationary phase culture. Science 1980, 207, 1218–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnittger, L.; Rodriguez, A.E.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Morrison, D.A. Babesia: A world emerging. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2012, 12, 1788–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubremetz, J.F.; Garcia-Réguet, N.; Conseil, V.; Fourmaux, M.N. Invited review Apical organelles and host-cell invasion by Apicomplexa. Int. J. Parasitol. 1998, 28, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, N.; Okamura, M.; Igarashi, I. Erythrocyte invasion by Babesia parasites: current advances in the elucidation of the molecular interactions between the protozoan ligands and host receptors in the invasion stage. Vet. Parasitol. 2006, 138, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowman, A.F.; Berry, D.; Baum, J. The cellular and molecular basis for malaria parasite invasion of the human red blood cell. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 198, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldati, D.; Foth, B.J.; Cowman, A.F. Molecular and functional aspects of parasite invasion. Trends Parasitol. 2004, 20, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lobo, C.A.; Cursino-Santos, J.R.; Rodriguez, M.; Ord, R.; Singh, M. Receptor–ligand interactions underlying RBC invasion in Babesia. ISBT Sci. Ser. 2015, 10, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, V.B.; Tomley, F.M. Receptor-ligand interaction and invasion: Microneme proteins in apicomplexans. Subcell. Biochem. 2008, 47, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fourmaux, M.N.; Achbarou, A.; Mercereau-Puijalon, O.; Biderre, C.; Briche, I.; Loyens, A.; Odberg-Ferragut, C.; Camus, D.; Dubremetz, J.F. The MIC1 microneme protein of Toxoplasma gondii contains a duplicated receptor-like domain and binds to host cell surface. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1996, 83, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenço, E.V.; Pereira, S.R.; Faça, V.M.; Coelho-Castelo, A.A.M.; Mineo, J.R.; Roque-Barreira, M.-C.; Greene, L.J.; Panunto-Castelo, A. Toxoplasma gondii micronemal protein MIC1 is a lactose-binding lectin. Glycobiology 2001, 11, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiss, M.; Viebig, N.; Brecht, S.; Fourmaux, M.N.; Soete, M.; Di Cristina, M.; Dubremetz, J.F.; Soldati, D. Identification and characterization of an escorter for two secretory adhesins in Toxoplasma gondii. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 152, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchant, J.; Cowper, B.; Liu, Y.; Lai, L.; Pinzan, C.; Marq, J.B.; Friedrich, N.; Sawmynaden, K.; Liew, L.; Chai, W.; et al. Galactose Recognition by the Apicomplexan Parasite Toxoplasma gondii. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 16720–16733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, M.G.; Ueti, M.W.; Norimine, J.; Florin-Christensen, M.; Bastos, R.G.; Goff, W.L.; Brown, W.C.; Oliva, A.; Suarez, C.E. Babesia bovis expresses a neutralization-sensitive antigen that contains a microneme adhesive repeat (MAR) domain. Parasitol. Int. 2010, 59, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosqueda-Gualito, J.J. Extracción de Ácidos Nucleicos de Hemoparásitos. Diagnóstico de Enfermedades Parasitarias Selectas de Rumiantes; INIFAP: Mexico City, Mexico, 2010; ISBN 978-607-425-476-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett, J.M.S.; Stirling, D. PCR Protocols; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; ISBN 978-1-59259-384-2. [Google Scholar]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.; Appel, R.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Emanuelsson, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. Locating proteins in the cell using TargetP, SignalP and related tools. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 953–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.D.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Mistry, J.; Mitchell, A.L.; Potter, S.C.; Punta, M.; Qureshi, M.; Sangrador-Vegas, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database: Towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D279–D285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Raghava, G.P.S. Prediction of continuous B-cell epitopes in an antigen using recurrent neural network. Proteins 2006, 65, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Raghava, G.P.S. BcePred: Prediction of Continuous B-Cell Epitopes in Antigenic Sequences Using Physico-chemical Properties. In Artificial Immune Systems; Nicosia, G., Cutello, V., Bentley, P.J., Timmis, J., Eds.; Lecture Notes in Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Vita, R.; Overton, J.A.; Greenbaum, J.A.; Ponomarenko, J.; Clark, J.D.; Cantrell, J.R.; Wheeler, D.K.; Gabbard, J.L.; Hix, D.; Sette, A.; et al. The immune epitope database (IEDB) 3.0. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D405–D412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosqueda, J.; McElwain, T.F.; Stiller, D.; Palmer, G.H. Babesia bovis Merozoite Surface Antigen 1 and Rhoptry-Associated Protein 1 Are Expressed in Sporozoites, and Specific Antibodies Inhibit Sporozoite Attachment to Erythrocytes. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 1599–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hines, S.A.; Palmer, G.H.; Jasmer, D.P.; McGuire, T.C.; McElwain, T.F. Neutralization-sensitive merozoite surface antigens of Babesia bovis encoded by members of a polymorphic gene family. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1992, 55, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 22.0; IBM: Armonk, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Blumenschein, T.M.; Friedrich, N.; Childs, R.A.; Saouros, S.; Carpenter, E.P.; Campanero-Rhodes, M.A.; Simpson, P.; Chai, W.; Koutroukides, T.; Blackman, M.J.; et al. Atomic resolution insight into host cell recognition by Toxoplasma gondii. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 2808–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holec-Gąsior, L.; Ferra, B.; Drapała, D.; Lautenbach, D.; Kur, J. A New MIC1-MAG1 Recombinant Chimeric Antigen Can Be Used Instead of the Toxoplasma gondii Lysate Antigen in Serodiagnosis of Human Toxoplasmosis. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosqueda-Gualito, J.J.; Falcón Neri, A.; Aragón, R.; Alberto, J.; Alarcón, C.; Jorge, G.; Camacho-Nuez, M. Estrategias genómicas y moleculares para el control de la babesiosis bovina. Rev. Mex. Cienc. Pecu. 2012, 3, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
| State | Farm/Ranch | Peptide A | Peptide B | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Positive | Negative | Total | Positive | Negative | Total | ||
| Aguascalientes | A | 7 | 2 | 38 | 9 | 0 | 38 |
| B | 24 | 1 | 25 | 0 | |||
| C | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 | |||
| Queretaro | A | 4 | 0 | 10 | 3 | 1 | 10 |
| B | 6 | 0 | 5 | 1 | |||
| Sinaloa | A | 7 | 0 | 26 | 4 | 3 | 26 |
| B | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | |||
| C | 3 | 0 | 3 | 0 | |||
| D | 11 | 0 | 9 | 2 | |||
| E | 4 | 0 | 3 | 1 | |||
| Veracruz | A | 2 | 0 | 42 | 2 | 0 | 42 |
| B | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | |||
| C | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |||
| D | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | |||
| E | 4 | 0 | 3 | 1 | |||
| F | 6 | 0 | 5 | 1 | |||
| G | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | |||
| H | 16 | 0 | 13 | 3 | |||
| I | 3 | 0 | 2 | 1 | |||
| Total positive/negative | 113 | 3 | 96 | 20 | |||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernández-Silva, D.J.; Valdez-Espinoza, U.M.; Mercado-Uriostegui, M.A.; Aguilar-Tipacamú, G.; Ramos-Aragón, J.A.; Hernández-Ortiz, R.; Ueti, M.; Mosqueda, J. Immunomolecular Characterization of MIC-1, a Novel Antigen in Babesia bigemina, Which Contains Conserved and Immunodominant B-Cell Epitopes that Induce Neutralizing Antibodies. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci5020032
Hernández-Silva DJ, Valdez-Espinoza UM, Mercado-Uriostegui MA, Aguilar-Tipacamú G, Ramos-Aragón JA, Hernández-Ortiz R, Ueti M, Mosqueda J. Immunomolecular Characterization of MIC-1, a Novel Antigen in Babesia bigemina, Which Contains Conserved and Immunodominant B-Cell Epitopes that Induce Neutralizing Antibodies. Veterinary Sciences. 2018; 5(2):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci5020032
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernández-Silva, Diego Josimar, Uriel Mauricio Valdez-Espinoza, Miguel Angel Mercado-Uriostegui, Gabriela Aguilar-Tipacamú, Juan Alberto Ramos-Aragón, Ruben Hernández-Ortiz, Massaro Ueti, and Juan Mosqueda. 2018. "Immunomolecular Characterization of MIC-1, a Novel Antigen in Babesia bigemina, Which Contains Conserved and Immunodominant B-Cell Epitopes that Induce Neutralizing Antibodies" Veterinary Sciences 5, no. 2: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci5020032
APA StyleHernández-Silva, D. J., Valdez-Espinoza, U. M., Mercado-Uriostegui, M. A., Aguilar-Tipacamú, G., Ramos-Aragón, J. A., Hernández-Ortiz, R., Ueti, M., & Mosqueda, J. (2018). Immunomolecular Characterization of MIC-1, a Novel Antigen in Babesia bigemina, Which Contains Conserved and Immunodominant B-Cell Epitopes that Induce Neutralizing Antibodies. Veterinary Sciences, 5(2), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci5020032