LPS-Induced Intracellular Complement 3 Activation Regulated ATP Production in Yak Rumen Epithelial Cells
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Source of Rumen Epithelial Cells and Ethics Statement
2.2. Resuscitation and Cultivation of Rumen Epithelial Cells in Yak
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
2.5. Determination of Inflammatory Cytokine and C3 Level
2.6. RNA Extraction and qRT–PCR Analysis of Gene Expression
2.7. Detection of ATP Concentration
2.8. Mitochondrial Membrane Potential Monitored by JC-1
2.9. Detection of Organic Acids
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
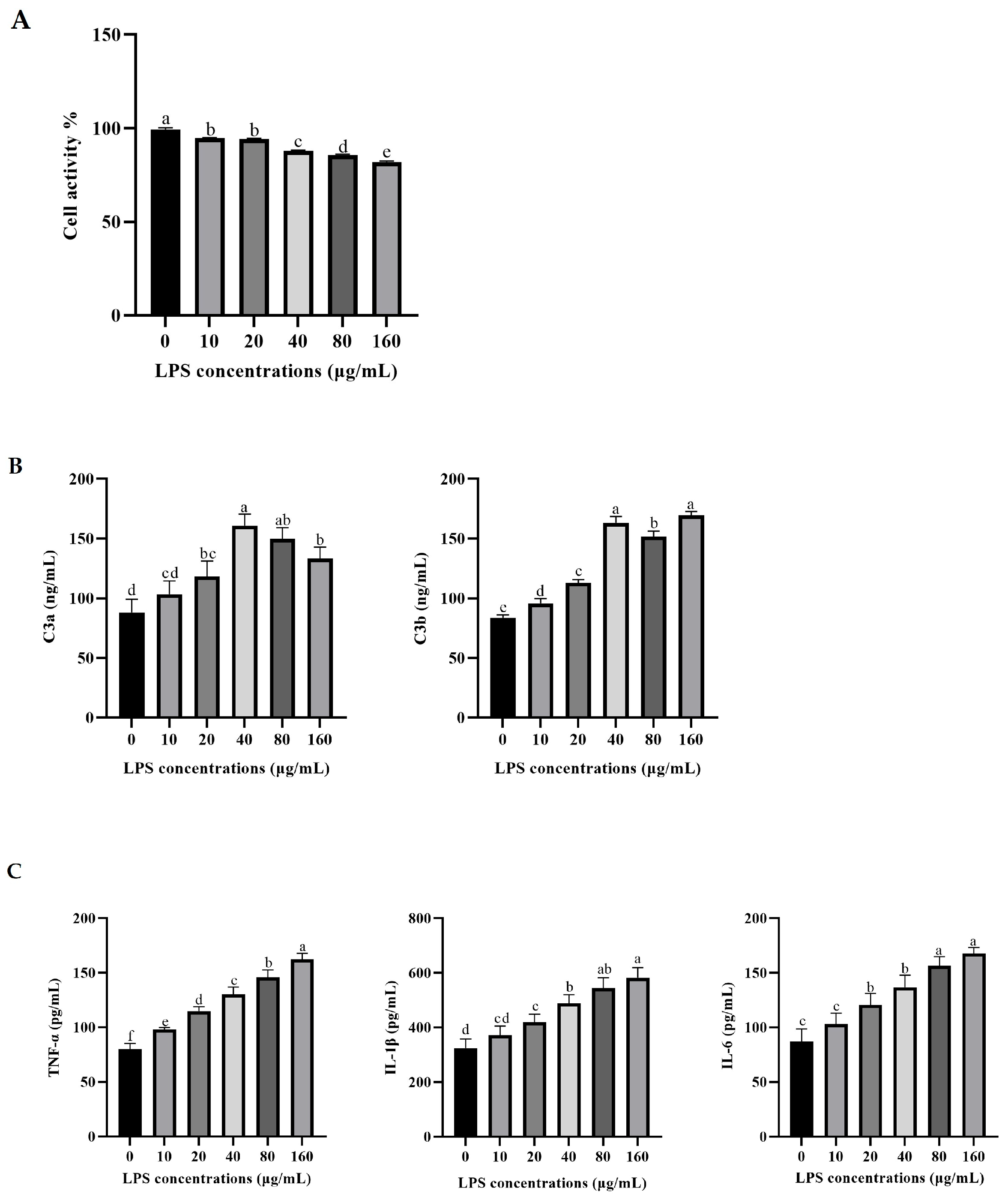
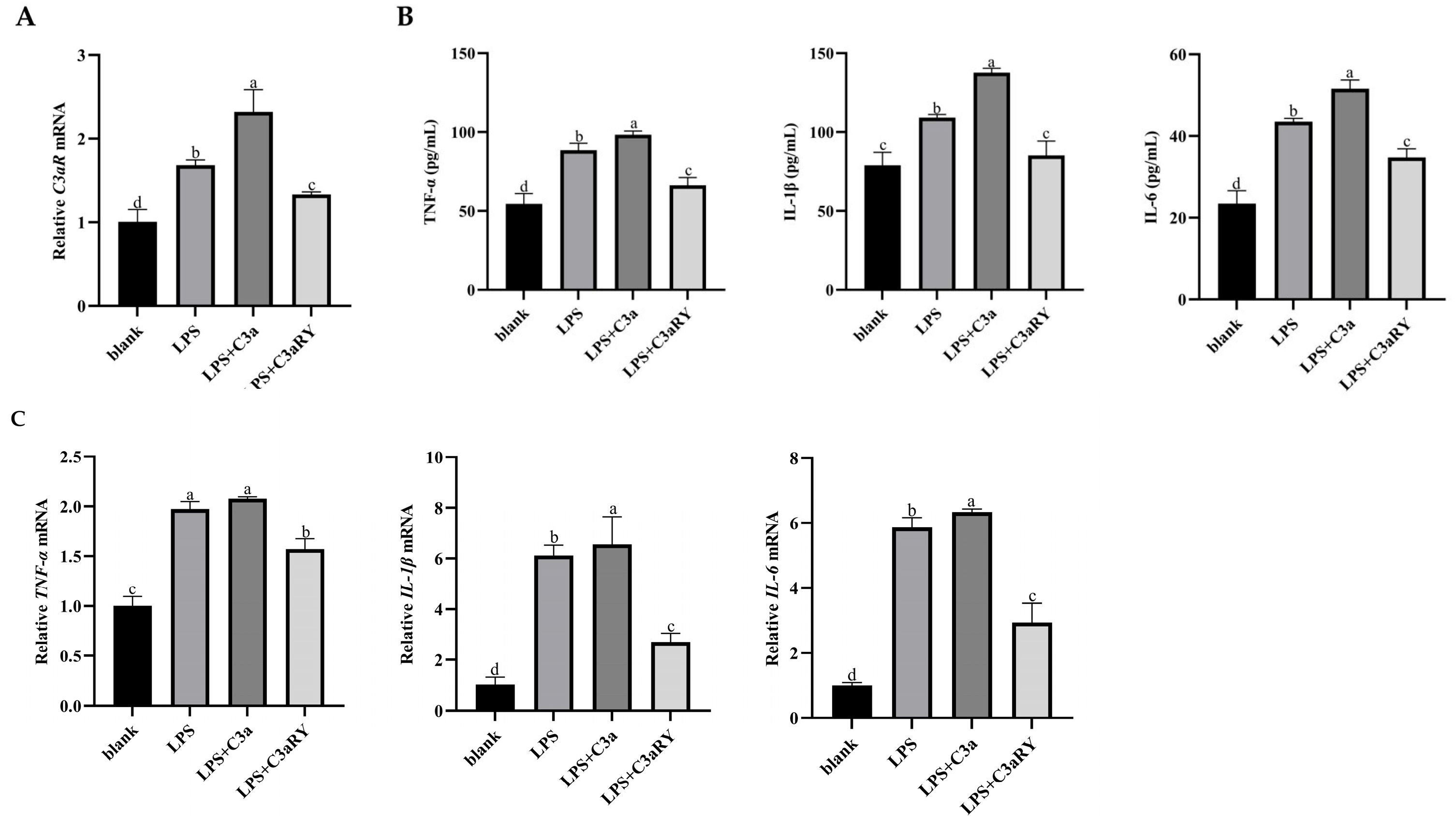
3.1. Effects of LPS on the Secretion of Pro-Inflammatory Factors and the Activation of C3 in Rumen Epithelial Cells of Yaks
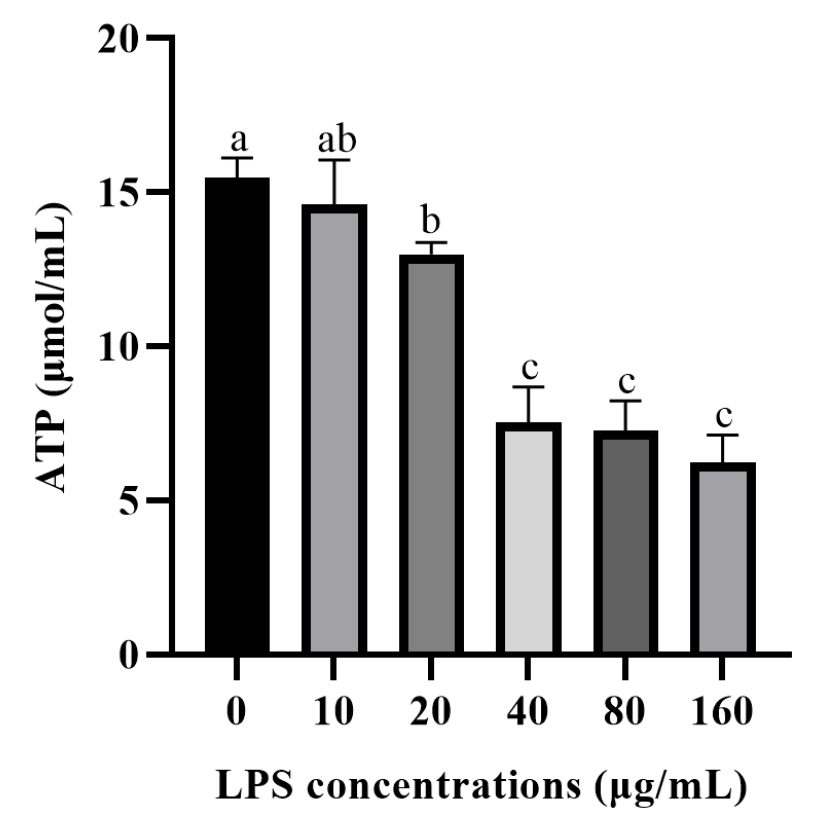
3.2. Effects of LPS on ATP Production in Rumen Epithelial Cells of Yak
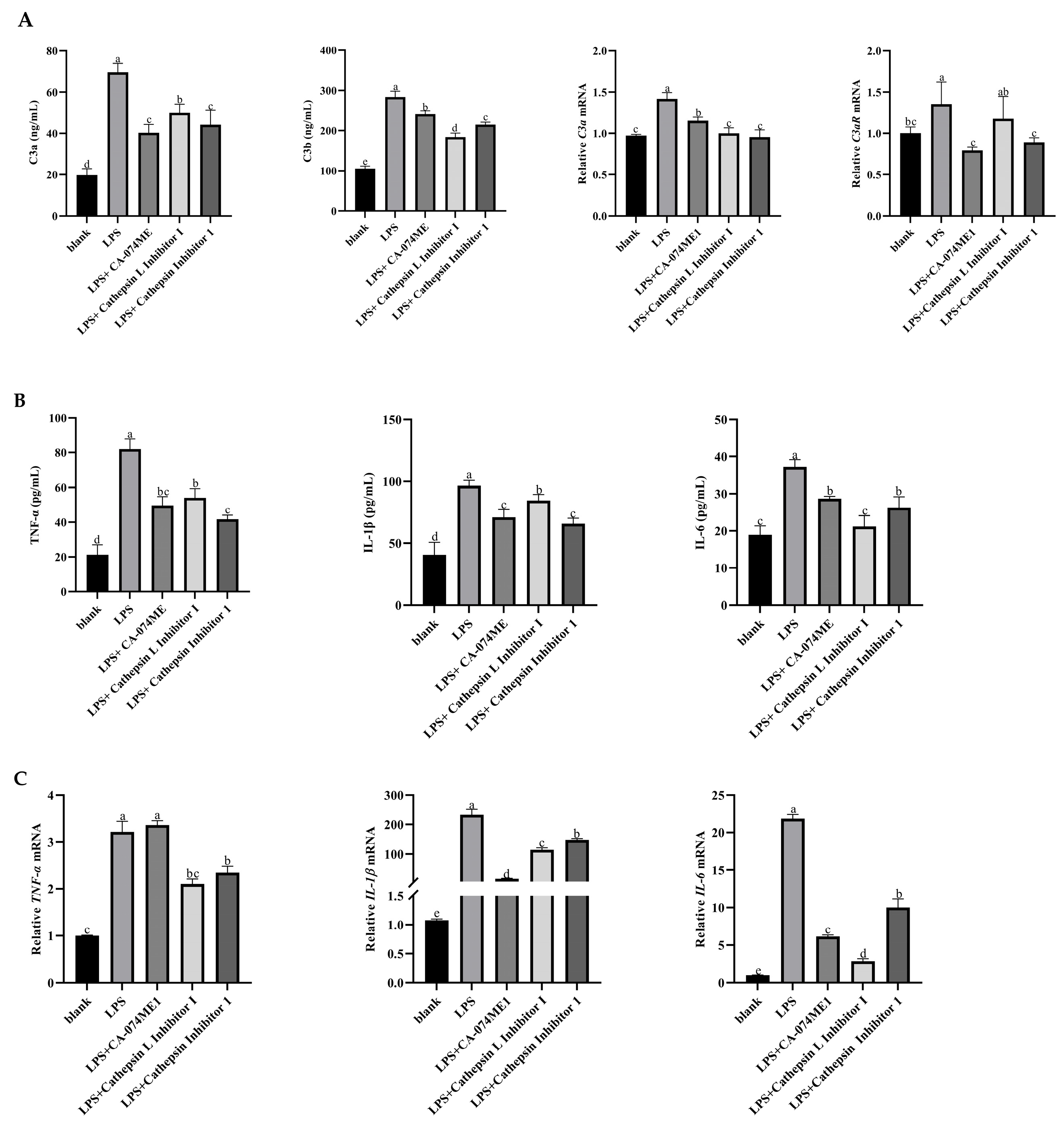
3.3. Effects of Inhibited the C3 Activation on Secretions and mRNA Expressions of Pro-Inflammatory Factors of Yak Rumen Epithelial Cells Under an Inflammatory State
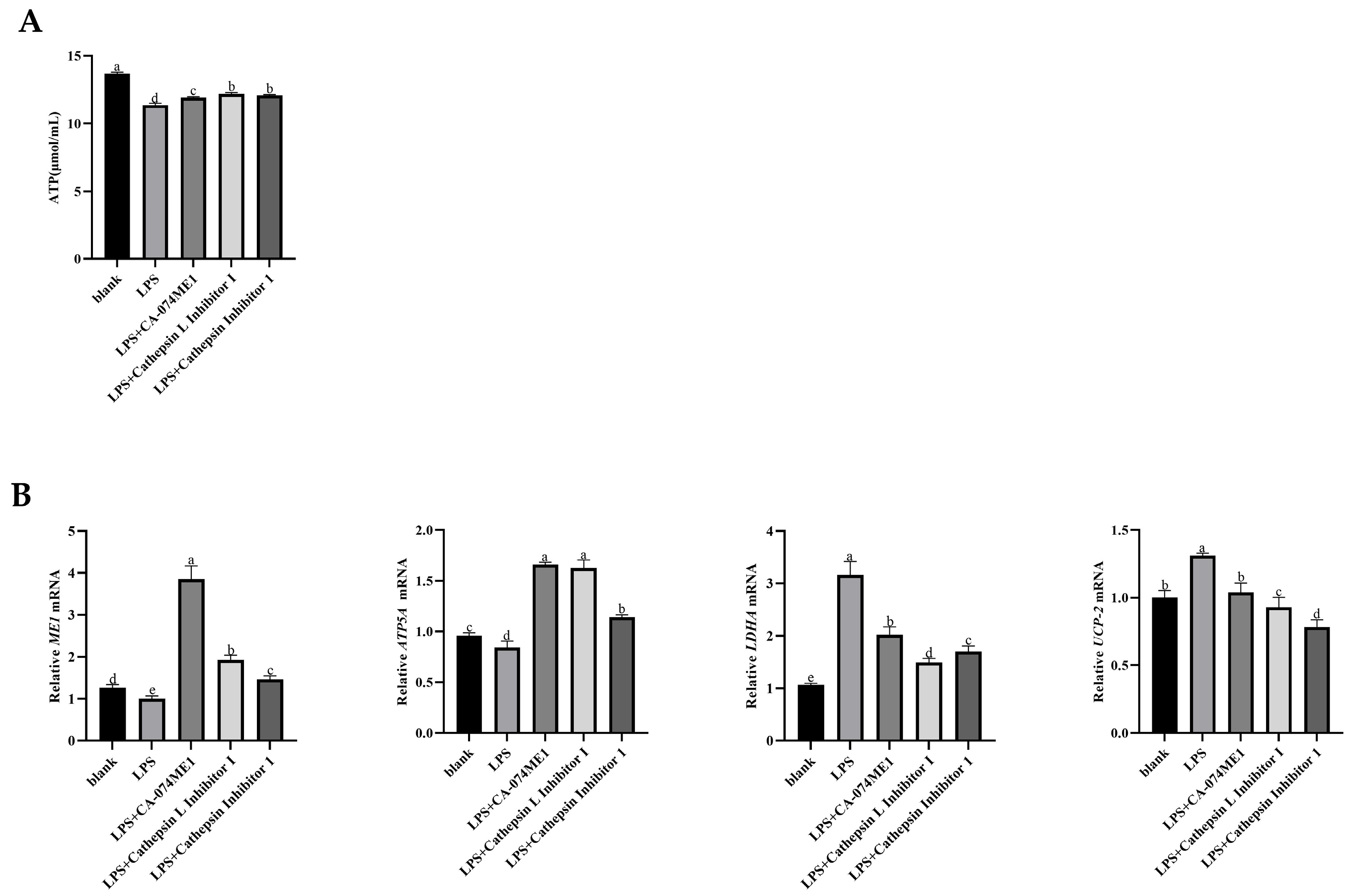
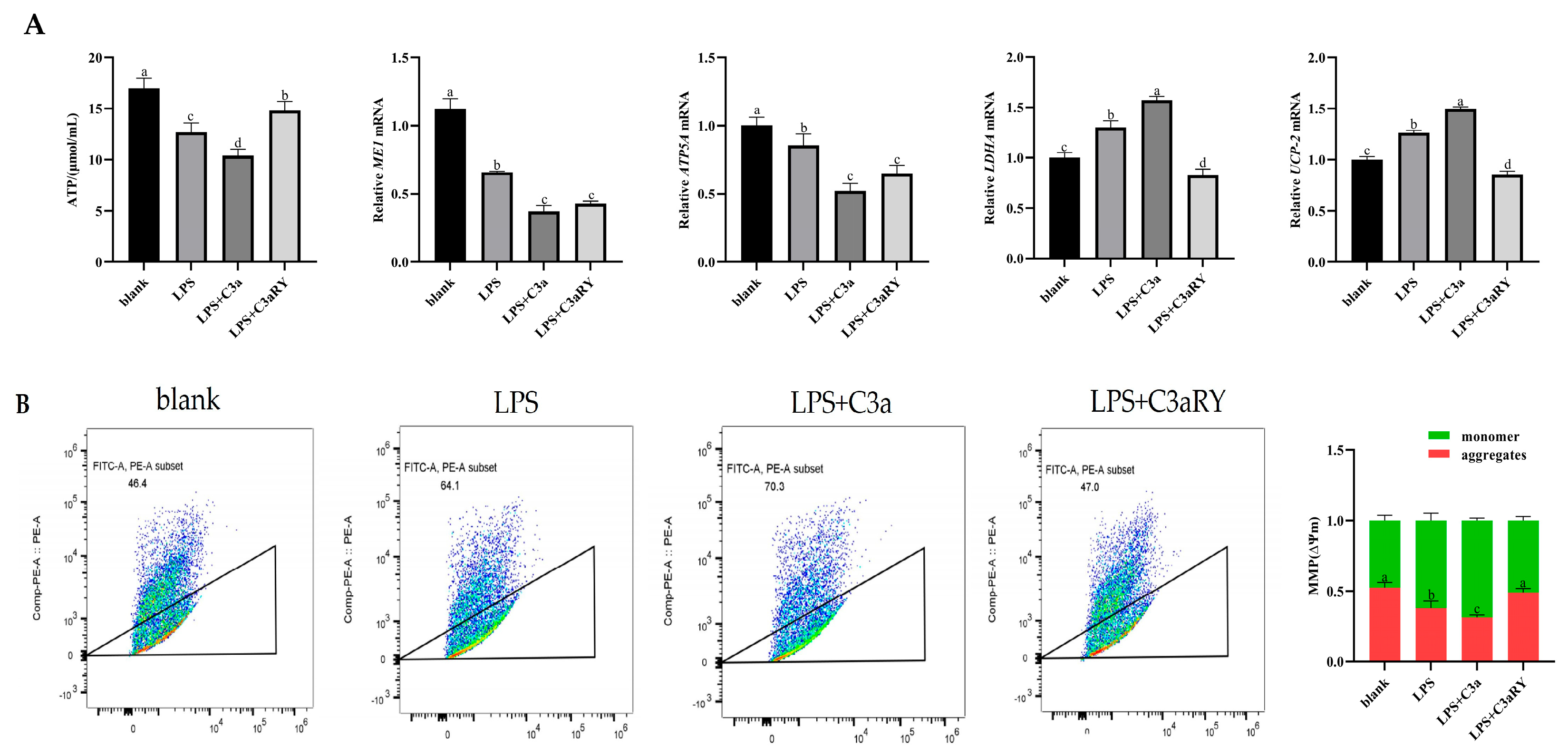
3.4. Effects of Inhibited the C3 Activation on ATP Production of Yak Rumen Epithelial Cells Under an Inflammatory State
3.5. Effects of C3a/C3aR Downstream of C3 on Pro-Inflammatory Factors of Yak Rumen Epithelial Cells Under an Inflammatory State
3.6. Effects of C3a/C3aR Downstream of C3 on ATP Production of Yak Rumen Epithelial Cells Under an Inflammatory State
Effects of C3a/C3aR Downstream of C3 on Concentrations of Tricarboxylic Acid Cycling and Anaerobic Respiratory Metabolites
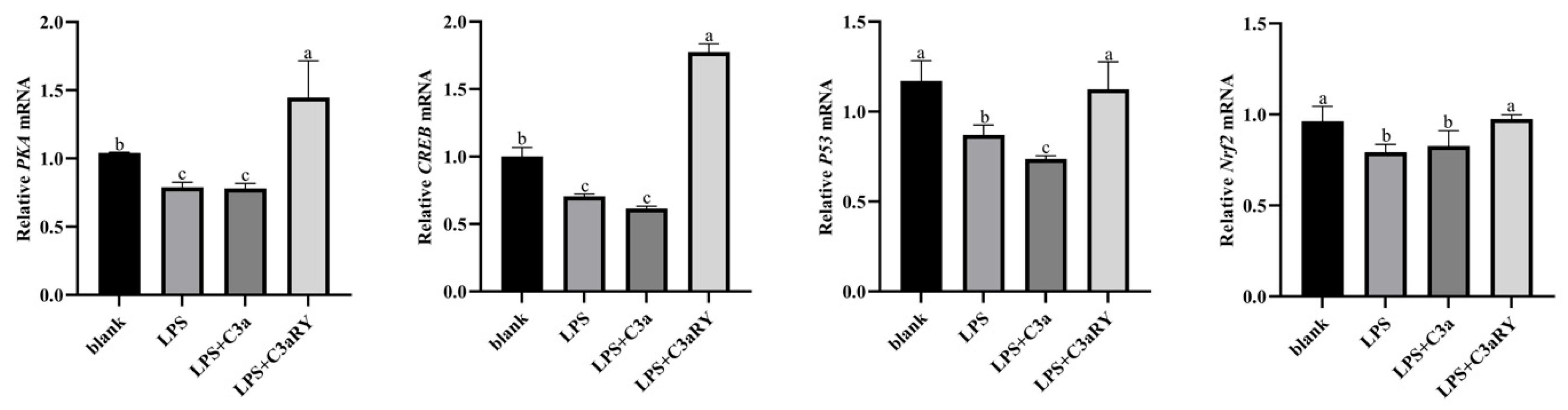
3.7. Effects of C3a/C3aR Downstream of C3 on cAMP/PKA Pathway Related Gene Expression
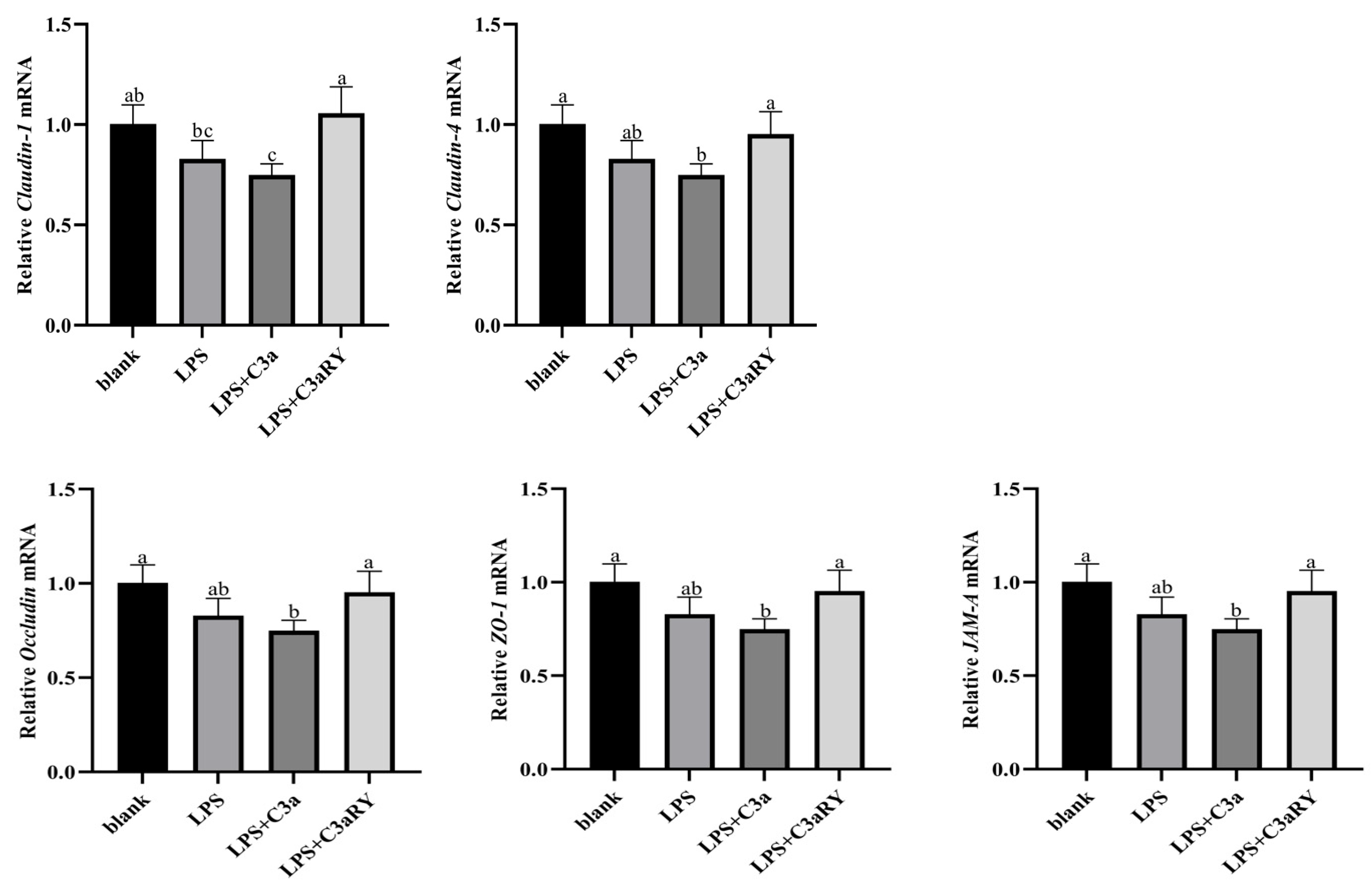
3.8. Effects of C3a/C3aR Downstream of C3 on Expression of Tight Junction Protein Gene
4. Discussion
4.1. LPS-Induced Inflammation Model and Intracellular Activation of C3 in Rumen Epithelial Cells of Yak
4.2. Effects of Inhibition of Intracellular C3 Activation on ATP Production in Rumen Epithelial Cells of Yak Under Inflammatory Conditions
4.3. Effect of C3a/C3aR Downstream of C3 on Pro-Inflammatory Factors and ATP Production of Yak Rumen Epithelial Cells Under an Inflammatory State
4.4. Effects of C3a/C3aR Downstream of C3 on cAMP/PKA Pathway-Related Gene Expression of Yak Rumen Epithelial Cells Under an Inflammatory State
4.5. Effect of C3a/C3aR Downstream of C3 on Expression of Tight Junction Protein Gene
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Ma, T.; Qian, W.; Wang, J.; Ye, Z.; Cao, C.; Hu, Q.; Kim, J.; Larkin, D.M. The yak genome and adaptation to life at high altitude. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 946–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, R.; Shah, A.M.; Han, Q.; Ma, J.; Dai, P.; Meng, Y.; Peng, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Kong, X.; Wang, Z.; et al. Proteomics Reveals the Obstruction of Cellular ATP Synthesis in the Ruminal Epithelium of Growth-Retarded Yaks. Animals 2024, 14, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Tong, J.; Zhao, J.; Underwood, K.; Zhu, M.; Ford, S.; Nathanielsz, P.W. Fetal programming of skeletal muscle development in ruminant animals. J. Anim. Sci. 2010, 88 (Suppl. S13), E51–E60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldwin, R.L.; Connor, E.E. Rumen function and development. Vet. Clin. Food Anim. Pract. 2017, 33, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penner, G.; Steele, M.; Aschenbach, J.R.; McBride, B.W. Ruminant Nutrition Symposium: Molecular adaptation of ruminal epithelia to highly fermentable diets. J. Anim. Sci. 2011, 89, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acin-Perez, R.; Salazar, E.; Kamenetsky, M.; Buck, J.; Levin, L.R.; Manfredi, G. Cyclic AMP produced inside mitochondria regulates oxidative phosphorylation. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Rui, J.; Pei, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhang, S.; Yan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, T.; Li, X. Straw-and slurry-associated prokaryotic communities differ during co-fermentation of straw and swine manure. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 4771–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Beeson, G.; Beeson, C.; Rohrer, B. Mitochondrial C3a receptor activation in oxidatively stressed epithelial cells reduces mitochondrial respiration and metabolism. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 628062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skattum, L. Clinical complement analysis—An overview. Transfus. Med. Rev. 2019, 33, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delanghe, J.R.; Speeckaert, R.; Speeckaert, M.M. Complement C3 and its polymorphism: Biological and clinical consequences. Pathology 2014, 46, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liszewski, M.K.; Kolev, M.; Le Friec, G.; Leung, M.; Bertram, P.G.; Fara, A.F.; Subias, M.; Pickering, M.C.; Drouet, C.; Meri, S.; et al. Intracellular complement activation sustains T cell homeostasis and mediates effector differentiation. Immunity 2013, 39, 1143–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolev, M.; Kemper, C. Keeping It All Going-Complement Meets Metabolism. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freiwald, T.; Afzali, B. The secret life of complement: Challenges and opportunities in exploring functions of the complosome in disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 135, e188350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, E.E.; Kemper, C. Complosome—The intracellular complement system. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Cui, Z.; Zhao, M.-H. The complement C3a and C3a receptor pathway in kidney diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, R.; Wang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Wang, S.; Zou, H.; Peng, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, K. Establishment of Immortalized Yak Ruminal Epithelial Cell Lines by Lentivirus-Mediated SV40T and hTERT Gene Transduction. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8128028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Cao, R. Andrographolide attenuates inflammatory response induced by LPS via activating Nrf2 signaling pathway in bovine endometrial epithelial cells. Res. Vet. Sci. 2021, 134, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, M.; Barbour, T.; Baver, S.; Francois, C.; Deschatelets, P. With complements: C3 inhibition in the clinic. Immunol. Rev. 2023, 313, 358–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, N.; Satyam, A.; Geha, M.; Lapchak, P.H.; Dalle Lucca, J.J.; Tsokos, M.G.; Tsokos, G.C. C3a enhances the formation of intestinal organoids through C3aR1. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, C.; Kemper, C. Complement-Mediated Regulation of Metabolism and Basic Cellular Processes. Immunity 2016, 45, 240–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Iyer, A.; Suen, J.Y.; Seow, V.; Reid, R.C.; Brown, L.; Fairlie, D.P. C5aR and C3aR antagonists each inhibit diet-induced obesity, metabolic dysfunction, and adipocyte and macrophage signaling. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, D.E.; Kehrli Jr, M.E.; Rainard, P.; Paape, M. Complement fragment C5a and inflammatory cytokines in neutrophil recruitment during intramammary infection with Escherichia coli. Infect. Immun. 1997, 65, 3286–3292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, E.; Farahzadi, R.; Valipour, B. Alginate/gelatin encapsulation promotes NK cells differentiation potential of bone marrow resident C-kit+ hematopoietic stem cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 177, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfredi, G.; Yang, L.; Gajewski, C.D.; Mattiazzi, M. Measurements of ATP in mammalian cells. Methods 2002, 26, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reers, M.; Smiley, S.T.; Mottola-Hartshorn, C.; Chen, A.; Lin, M.; Chen, L.B. [29] Mitochondrial membrane potential monitored by JC-1 dye. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1995; Volume 260, pp. 406–417. [Google Scholar]
- Marsili, R.; Ostapenko, H.; Simmons, R.; Green, D.E. High performance liquid chromatographic determination of organic acids in dairy products. J. Food Sci. 1981, 46, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Zou, H.; Wang, Z.; Cao, B.; Peng, Q.; Jing, X.; Wang, Y.; Shao, Y.; Pei, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. Nutritional interventions improved rumen functions and promoted compensatory growth of growth-retarded yaks as revealed by integrated transcripts and microbiome analyses. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, D.-X.; Chen, Y.-H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Wei, W. Reactive oxygen species are involved in lipopolysaccharide-induced intrauterine growth restriction and skeletal development retardation in mice. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 195, 1707–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kent-Dennis, C.; Aschenbach, J.; Griebel, P.; Penner, G. Effects of lipopolysaccharide exposure in primary bovine ruminal epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 9587–9603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolev, M.; Dimeloe, S.; Le Friec, G.; Navarini, A.; Arbore, G.; Povoleri, G.A.; Fischer, M.; Belle, R.; Loeliger, J.; Develioglu, L.; et al. Complement regulates nutrient influx and metabolic reprogramming during Th1 cell responses. Immunity 2015, 42, 1033–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.H.; Zhang, R.H.; Lv, N.N.; Yang, G.P.; Wang, Y.S.; Pan, K.H. The Role of Malic Enzyme on Promoting Total Lipid and Fatty Acid Production in Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Kong, Z.; Miao, J.; Chen, Y.; Bian, Y.; Zeng, L. Emerging roles of lactate in acute and chronic inflammation. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangarajan, S.; Locy, M.L.; Chanda, D.; Kurundkar, A.; Kurundkar, D.; Larson-Casey, J.L.; Londono, P.; Bagchi, R.A.; Deskin, B.; Elajaili, H.; et al. Mitochondrial uncoupling protein-2 reprograms metabolism to induce oxidative stress and myofibroblast senescence in age-associated lung fibrosis. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Jia, B.-B.; Li, M.-F. Complement C3 and activated fragment C3a are involved in complement activation and anti-bacterial immunity. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 813173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, E.; Le Friec, G.; Yamamoto, H.; Perucha, E.; Sacks, S.S.; Köhl, J.; Cook, H.T.; Kemper, C. C3a modulates IL-1β secretion in human monocytes by regulating ATP efflux and subsequent NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Blood 2013, 122, 3473–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, L.; Zang, J.; Tang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bai, L.; Yin, Q.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, J.; et al. C3a and C5a receptor antagonists ameliorate endothelial-myofibroblast transition via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in diabetic kidney disease. Metabolism 2015, 64, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, J.; Singh, P.; Merle, N.S.; Niyonzima, N.; Kemper, C. Complement’s favourite organelle-Mitochondria? Br. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 178, 2771–2785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morken, T.; Kraugerud, O.F.; Barrows, F.T.; Sørensen, M.; Storebakken, T.; Øverland, M. Sodium diformate and extrusion temperature affect nutrient digestibility and physical quality of diets with fish meal and barley protein concentrate for rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Aquaculture 2011, 317, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmhadi, M.E.; Ali, D.K.; Khogali, M.K.; Wang, H. Subacute ruminal acidosis in dairy herds: Microbiological and nutritional causes, consequences, and prevention strategies. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 10, 148–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Kong, Q.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Y.; Hua, H. Complex roles of cAMP–PKA–CREB signaling in cancer. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, H.; Qi, C.; Ji, X.; Yan, H.; Cui, R.; Zhang, G.; Kang, Y.; Shi, G. Pentoxifylline enhances antioxidative capability and promotes mitochondrial biogenesis in D-galactose-induced aging mice by increasing Nrf2 and PGC-1α through the cAMP-CREB pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6695613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simabuco, F.M.; Morale, M.G.; Pavan, I.C.; Morelli, A.P.; Silva, F.R.; Tamura, R.E. Correction: p53 and metabolism: From mechanism to therapeutics. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 34030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Fazekasova, H.; Wang, N.; Peng, Q.; Sacks, S.H.; Lombardi, G.; Zhou, W. Functional modulation of human monocytes derived DCs by anaphylatoxins C3a and C5a. Immunobiology 2012, 217, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, G.; Hagen, F.; Meißner, S.; Shen, Z.; Lu, Z.; Amasheh, S.; Aschenbach, J.R. Effect of individual SCFA on the epithelial barrier of sheep rumen under physiological and acidotic luminal pH conditions. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 96, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Zhang, H.; Ying, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T. Effects of dietary L-methionine supplementation on intestinal integrity and oxidative status in intrauterine growth-retarded weanling piglets. Eur. J. Nutr. 2018, 57, 2735–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Shah, A.M.; Wang, Z.; Hu, R.; Zou, H.; Wang, X.; Cao, G.; Peng, Q.; Xue, B.; Wang, L.; et al. Comparing the gastrointestinal barrier function between growth-retarded and normal yaks on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. PeerJ 2020, 8, e9851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, D.; Yang, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zou, H.; Peng, Q.; Meng, Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. LPS-Induced Intracellular Complement 3 Activation Regulated ATP Production in Yak Rumen Epithelial Cells. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090841
Han Q, Zhang Q, Wu D, Yang Z, Huang J, Wang Z, Zou H, Peng Q, Meng Y, Jiang Y, et al. LPS-Induced Intracellular Complement 3 Activation Regulated ATP Production in Yak Rumen Epithelial Cells. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(9):841. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090841
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Qiang, Qiqi Zhang, Duoting Wu, Zihan Yang, Jinyang Huang, Zhisheng Wang, Huawei Zou, Quanhui Peng, Yukun Meng, Yahui Jiang, and et al. 2025. "LPS-Induced Intracellular Complement 3 Activation Regulated ATP Production in Yak Rumen Epithelial Cells" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 9: 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090841
APA StyleHan, Q., Zhang, Q., Wu, D., Yang, Z., Huang, J., Wang, Z., Zou, H., Peng, Q., Meng, Y., Jiang, Y., Xiao, J., & Hu, R. (2025). LPS-Induced Intracellular Complement 3 Activation Regulated ATP Production in Yak Rumen Epithelial Cells. Veterinary Sciences, 12(9), 841. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12090841






