Environmental Microbiome Characteristics and Disinfection Strategy Optimization in Intensive Dairy Farms: Bactericidal Efficacy of Glutaraldehyde-Based Combination Disinfectants and Regulation of Gut Microbiota
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dairy Barns
2.2. Sample Collection and Processing
2.3. Genomic DNA Extraction and Sample Analysis
2.4. Bioinformatics Analysis
3. Results
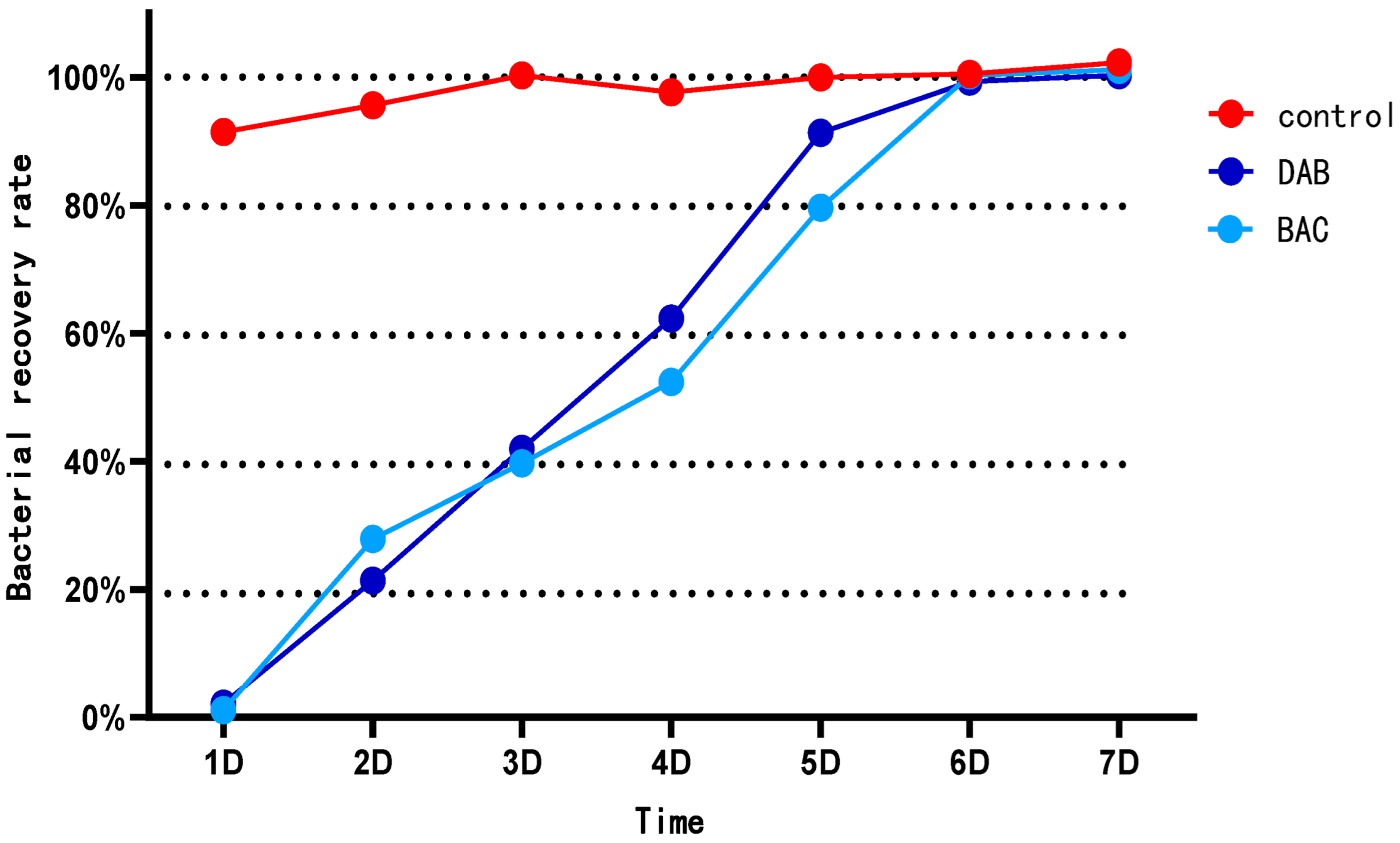
3.1. Analysis of Disinfection Efficacy for Two Disinfectants
3.2. 16S Amplicon Sequencing Analysis of Disinfectant Effects on Gut and Environmental Microbiota
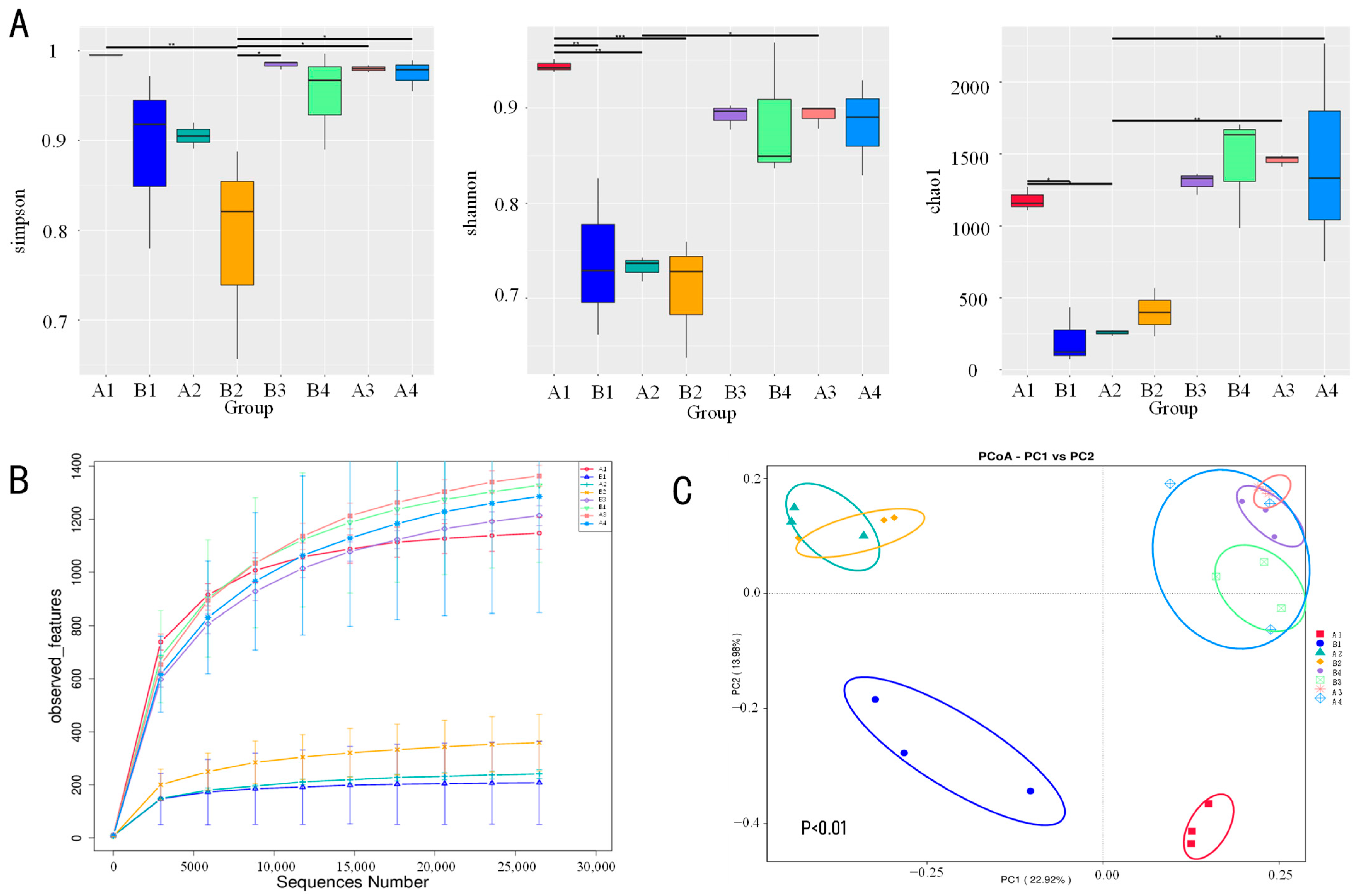
3.2.1. Impact of Disinfection Regimens on Microbial Community Alpha Diversity
3.2.2. Microbial Community Beta Diversity and Structural Differentiation
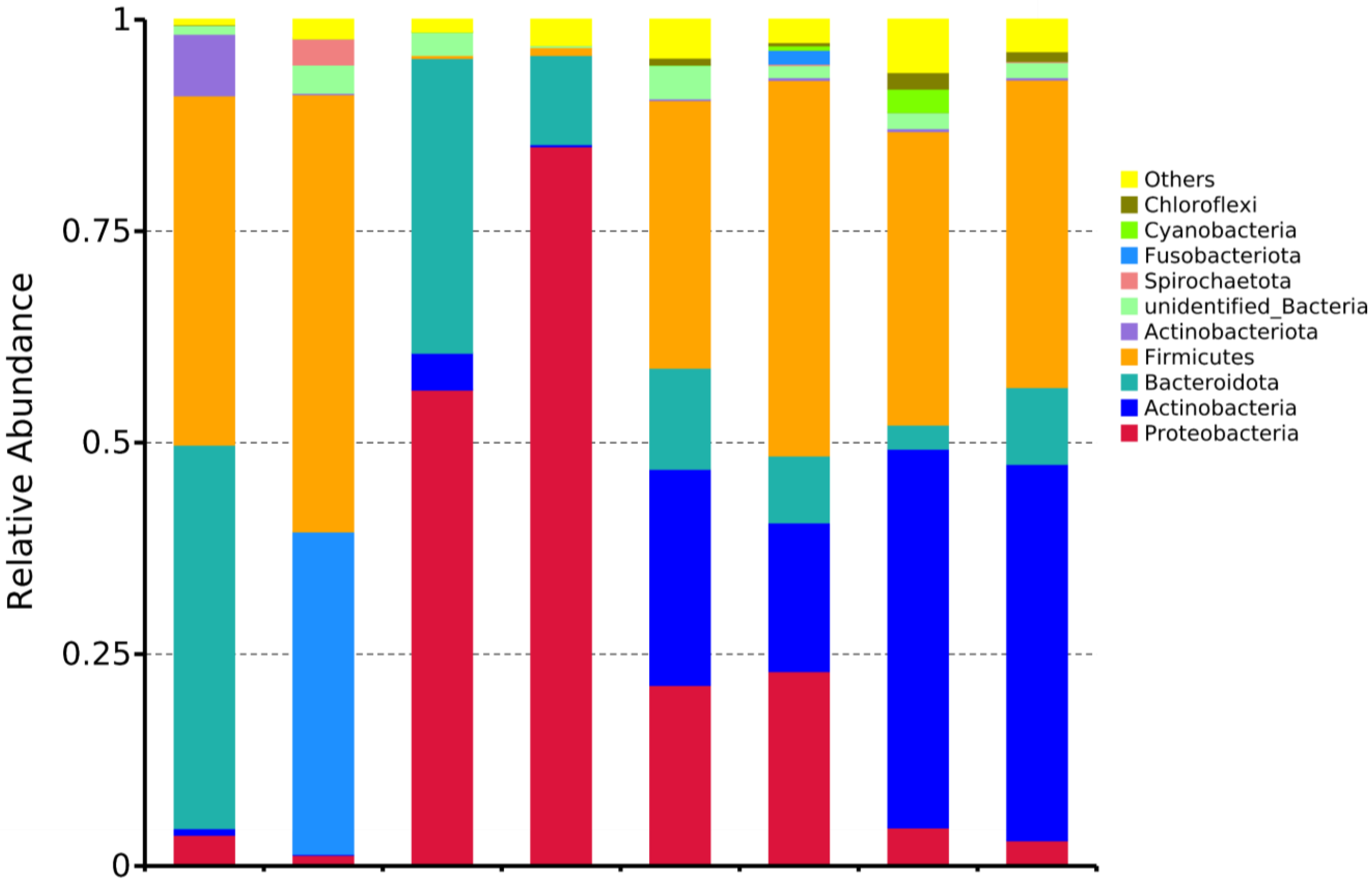
3.2.3. Phylum- and Genus-Level Analysis of Microbial Community Composition
Dominant Phyla Distribution
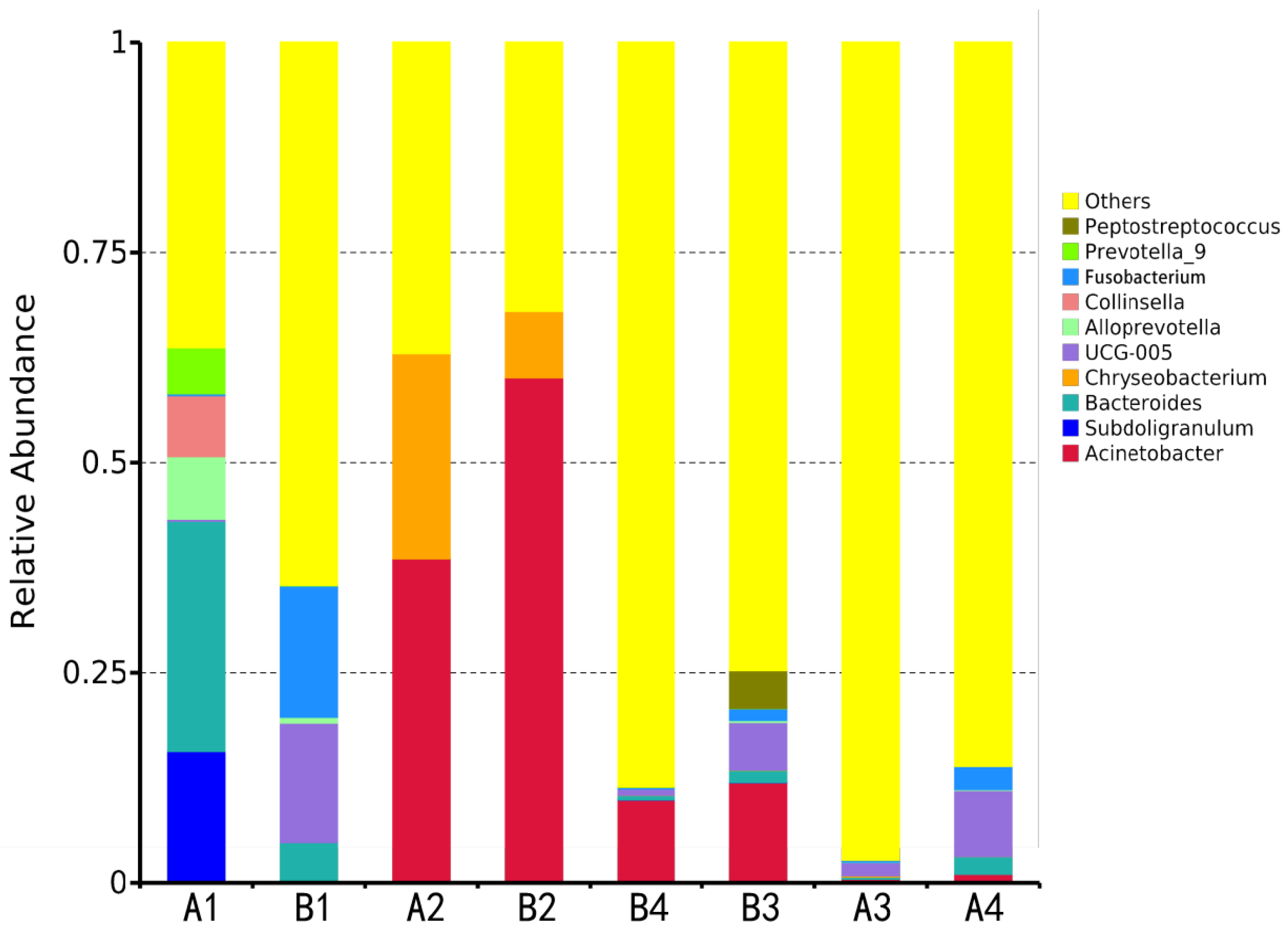
Dominant Genera Distribution
3.2.4. OTU Sharing Patterns and Community Similarity
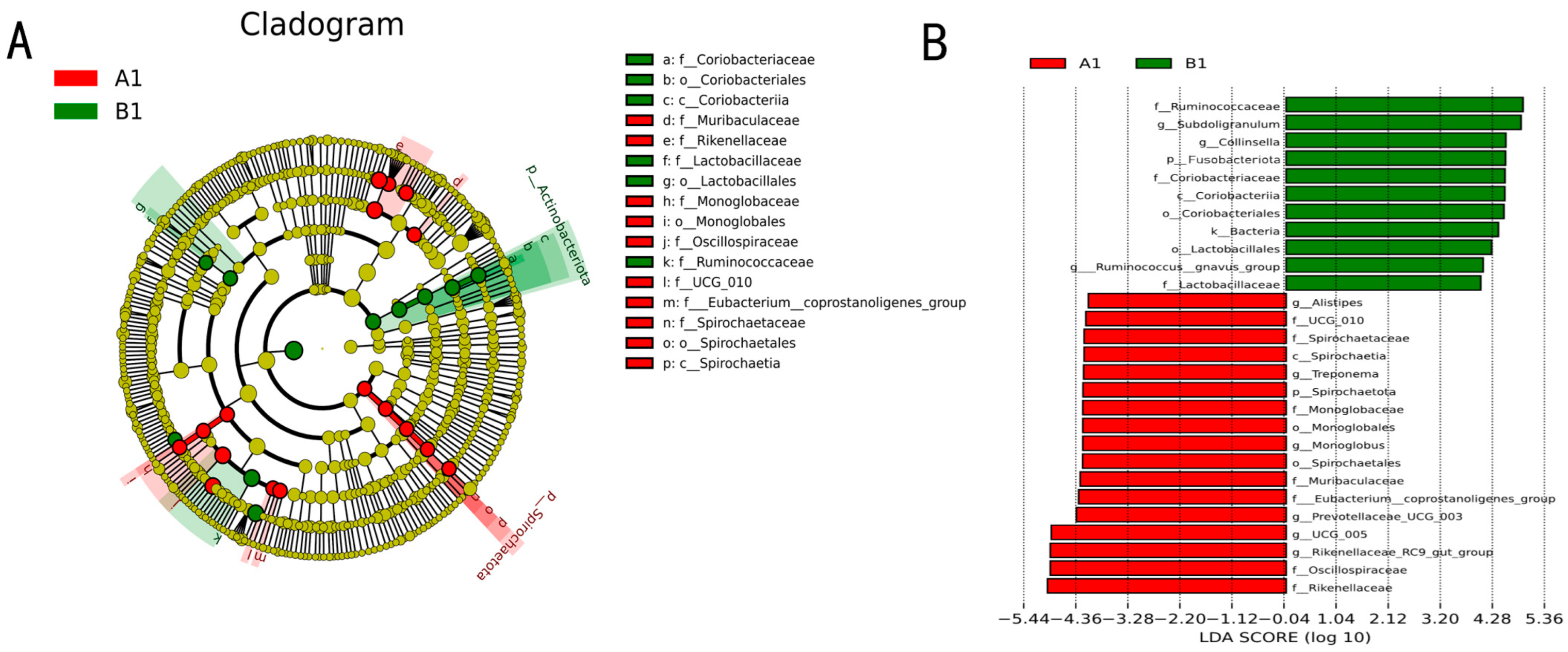
3.2.5. Biomarker Screening for Differentially Enriched Genera
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berhanu, L.; Gume, B.; Kassa, T.; Dadi, L.S.; Tegegne, D.; Getnet, M.; Bediru, H.; Getaneh, A.; Suleman, S.; Mereta, S.T. Microbial quality of raw cow milk and its predictors along the dairy value chain in Southwest Ethiopia. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 350, 109228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majadi, M.; Barkó, A.; Varga-Tóth, A.; Maukenovna, Z.S.; Batirkhanovna, D.Z.; Dilora, S.; Lukacs, M.; Kaszab, T.; Mednyánszky, Z.; Kovacs, Z. Quality Assessment of Reconstructed Cow, Camel and Mare Milk Powders by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Molecules 2024, 29, 3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Yan, M.; Yao, Z.; Dou, J. Antibiotic residues in milk and dairy products in China: Occurrence and human health concerns. Environ. Sci. Pollut Res. Int. 2023, 30, 113138–113150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Khan, N.; Yu, P.; Ali, M.; Cone, J.W.; Hendriks, W.H. Nutritive value of maize silage in relation to dairy cow performance and milk quality. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2015, 95, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azooz, M.F.; El-Wakeel, S.A.; Yousef, H.M. Financial and economic analyses of the impact of cattle mastitis on the profitability of Egyptian dairy farms. Vet. World 2020, 13, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.M.; Wang, J.L.; Gou, W.Q.; Tian, Y.; Wang, J. Research Progress on Bovine Mastitis Abroad—Based on Web of Science Core Database. China Dairy Ind. 2023, 9, 89–97. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Irie, Y.; Ono, M.; Aritsune, M.; Imamura, Y.; Nishioka, S.; Akiyama, K.; Enokidani, M.; Horikita, T. Cleaning procedures and cleanliness assessments of bucket milkers and suckling buckets on Japanese dairy farms. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 83, 863–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowbotham, R.; Ruegg, P. Bacterial counts on teat skin and in new sand, recycled sand, and recycled manure solids used as bedding in freestalls. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 6594–6608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, B.; Li, H.; Ren, Z.; Zhu, R.; Zhu, Z. Recent advances in sterilization and disinfection technology: A review. Chemosphere 2022, 308, 136404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falagas, M.; Thomaidis, P.; Kotsantis, I.; Sgouros, K.; Samonis, G.; Karageorgopoulos, D. Airborne hydrogen peroxide for disinfection of the hospital environment and infection control: A systematic review. J. Hosp. Infect. 2011, 78, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, W.; Meng, F.; Cui, H.; Lin, Y.; Wang, G.; Wu, J. Ecotoxicity of phenol and cresols to aquatic organisms: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 157, 441–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyneau, M.; de Chaisemartin, L.; Gigant, N.; Chollet-Martin, S.; Kerdine-Römer, S. Quaternary ammonium compounds in hypersensitivity reactions. Front. Toxicol. 2022, 4, 973680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; Mcmurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.; Lozinski, B.; Torres, I.; Davison, S.; Hilbrands, A.; Nelson, E.; Parra-Suescun, J.; Johnston, L.; Gomez, A.; Young, V.B. Disinfection of maternal environments is associated with piglet microbiome composition from birth to weaning. MSphere 2021, 6, e0066321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, A.Z.; He, M.; Li, D.; Chen, J. Subinhibitory Concentrations of Disinfectants Promote the Horizontal Transfer of Multidrug Resistance Genes within and across Genera. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annaleise, W.; Narelle, F.; Mark, S.T. Co-culture with Acinetobacter johnsonii enhances benzalkonium chloride resistance in Salmonella enterica via triggering lipid A modifications. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2022, 381, 109905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frentzel, H.; Menrath, A.; Tomuzia, K.; Braeunig, J.; Appel, B. Decontamination of high-risk animal and zoonotic pathogens. Biosecur. Bioterror. 2013, 11 (Suppl. S1), S102–S114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.-B.; Wang, Y.-F.; Meng, S.-Y.; Zhang, X.-T.; Wang, Y.-R.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Qian, P.-Y. Effects of antibiotic and disinfectant exposure on the mouse gut microbiome and immune function. Microbiol. Spectr. 2024, 12, e0061124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Ma, L.; Chen, Z.; Huang, Y.; Lin, L.; Qin, Z. Long-term disinfectant exposure on intestinal immunity and microbiome variation of grass carp. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 272, 106942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grillitsch, B.; Gans, O.; Kreuzinger, N.; Scharf, S.; Uhl, M.; Fuerhacker, M. Environmental risk assessment for quaternary ammonium compounds: A case study from Austria. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 54, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdomo, A.; Calle, A. Assessment of microbial communities in a dairy farm from a food safety perspective. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2024, 423, 110827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Rodríguez, M.; Cabo, M.L.; Balsa-Canto, E.; García, M.R. Mechanisms of Listeria monocytogenes Disinfection with Benzalkonium Chloride: From Molecular Dynamics to Kinetics of Time-Kill Curves. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorman, S.; Scott, E. Potentiation and stabilization of glutaraldehyde biocidal activity utilizing surfactant-divalent cation combinations. Int. J. Pharm. 1979, 4, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crnčević, D.; Krce, L.; Brkljača, Z.; Cvitković, M.; Brčić, S.B.; Čož-Rakovac, R.; Odžak, R.; Šprung, M. A dual antibacterial action of soft quaternary ammonium compounds: Bacteriostatic effects, membrane integrity, and reduced in vitro and in vivo toxicity. RSC Adv. 2025, 15, 1490–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérdy, J. Bioactive microbial metabolites. J. Antibiot. 2005, 58, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.L.; Li, W.P. Research Progress on Disinfectant Resistance Produced by Microorganisms. Chin. J. Infect. Control 2016, 15, 633–636. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.D.; Chen, J.; Hoffmann, C.; Bittinger, K.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Keilbaugh, S.A.; Bewtra, M.; Knights, D.; Walters, W.A.; Knight, R.; et al. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science 2011, 334, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.A.; Pandupuspitasari, N.S.; Huang, C.; Negara, W.; Ahmed, B.; Putri, E.M.; Lestari, P.; Priyatno, T.P.; Prima, A.; Restitrisnani, V.; et al. Unlocking gut microbiota potential of dairy cows in varied environmental conditions using shotgun metagenomic approach. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciurba, J.D.; E Chlipala, G.; Green, S.J.; A Delaney, M.; Fortman, J.D.; E Purcell, J. Evaluation of effects of laboratory disinfectants on mouse gut microbiota. Comp. Med. 2021, 71, 492–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.F.; Reis, M.P.; Acurcio, L.B.; Carmo, A.O.; Diamantino, C.F.; Motta, A.M.; Kalapothakis, E.; Nicoli, J.R.; Nascimento, A.M. Changes in mouse gut bacterial community in response to different types of drinking water. Water Res. 2018, 132, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Kokubu, E.; Kawana, T.; Saito, A.; Okuda, K.; Ishihara, K. Synergy in biofilm formation between Fusobacterium nucleatum and Prevotella species. Anaerobe 2012, 18, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Fujii, R.; Nakagawa, K.; Kuramitsu, H.K.; Okuda, K.; Ishihara, K. Stimulation of Fusobacterium nucleatum biofilm formation by Porphyromonas gingivalis. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2008, 23, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela, M.; Biagi, E.; Maccaferri, S.; Turroni, S.; Brigidi, P. Intestinal microbiota is a plastic factor responding to environmental changes. Trends Microbiol. 2012, 20, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanhua, Y.; Huihui, C.; Lixue, D.; Ruihuan, D.; Baiqin, Z.; Aijun, L. Study on the Structure and Diversity of Environmental Microbial Communities in Dairy Farms. Anim. Husb. Vet. Med. 2021, 53, 31–37. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Fiorentino, M.A.; Acuña, Y.; Sosa, E.; Cantón, G.J.; Erreguerena, I.; Malena, R.; Mendez, M.A.; Morrell, E.L.; García, J.A. Infectious sporadic bovine abortions: Retrospective analysis. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2024, 56, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maki, J.J.; Bobeck, E.A.; Sylte, M.J.; Looft, T. Eggshell and environmental bacteria contribute to the intestinal microbiota of growing chickens. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X. Analysis of Environmental Management and Disinfection Technology in Dairy Farms. Mod. Anim. Husb. Sci. Technol. 2019, 149–150. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dimitracopoulos, G.; Kalkani-Boussiakou, H.; Papavassiliou, J. Animal fecal carriership and biotypes of Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1977, 34, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuter, T.; Alexander, T.W.; McAllister, T.A. Viability of Bacillus licheniformis and Bacillus thuringiensis spores as a model for predicting the fate of bacillus anthracis spores during composting of dead livestock. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 1588–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, A.M.; Nascimento, J.D. Acinetobacter: An underrated foodborne pathogen? J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2017, 11, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hantsis-Zacharov, E.; Halpern, M. Culturable psychrotrophic bacterial communities in raw milk and their proteolytic and lipolytic traits. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 7162–7168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berchieri, A.; Barrow, P.A., Jr. The antibacterial effects for Salmonella Enteritidis phage type 4 of different chemical disinfectants and cleaning agents tested under different conditions. Avian Pathol. 1996, 25, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleeson, D.; Flynn, J.; Brien, B.O. Effect of pre-milking teat disinfection on new mastitis infection rates of dairy cows. Ir. Vet. J. 2018, 71, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Liu, S.; Gao, D.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Chen, T.; Xiao, J.; Wang, J.; Hou, G.; Li, S.; et al. The Bifidobacterium-dominated fecal microbiome in dairy calves shapes the characteristic growth phenotype of host. NPJ Biofilms Microbiomes 2024, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansilla, F.I.; Ficoseco, C.A.; Miranda, M.H.; Puglisi, E.; Nader-Macías, M.E.F.; Vignolo, G.M.; Fontana, C.A. Administration of probiotic lactic acid bacteria to modulate fecal microbiome in feedlot cattle. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catozzi, C.; Bonastre, A.S.; Francino, O.; Lecchi, C.; De Carlo, E.; Vecchio, D.; Martucciello, A.; Fraulo, P.; Bronzo, V.; Cuscó, A.; et al. The microbiota of water buffalo milk during mastitis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Items | Didecyl Dimethyl Ammonium Bromide (DAB) | Benzalkonium Chloride (BAC) |
|---|---|---|
| Disinfectant Information | Manufacturer: Sichuan Dingjian Animal Health Co., Ltd., Sichuan, China Composition: 100 mL contains 10 g glutaraldehyde + 10 g didecyl dimethyl ammonium bromide | Manufacturer: Coventry Chemicals Ltd., Coventry, UK Composition: 100 mL contains 15 g glutaraldehyde + 10 g benzalkonium chloride |
| Barn Conditions | Independent barns housing 30 healthy lactating cows with rice straw bedding | Independent barns housing 30 healthy lactating cows with rice straw bedding |
| Sampling Time | 7 days post-disinfection | 7 days post-disinfection |
| Application Parameters | Equipment: electric sprayer (0.3 MPa) Application rate: 300 mL/m2 | Equipment: electric sprayer (0.3 MPa) Application rate: 300 mL/m2 |
| Environmental Controls | Temperature: 25 ± 2 °C Humidity: 50 ± 5% RH Ammonia concentration: 5.2–7.8 ppm Bedding pH: 6.5–7.2 Bedding dry matter content: oven-dried at 65 °C for 24 h, 35–40% | Temperature: 25 ± 2 °C Humidity: 50 ± 5% RH Ammonia concentration: 5.2–7.8 ppm Bedding pH: 6.5–7.2 Bedding dry matter content: oven-dried at 65 °C for 24 h, 35–40% |
| Group | Before Disinfection (104 CFU/mL) | After Disinfection (104 CFU/mL) | Disinfection Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control group | 82.00 | 75.00 | 8.54 |
| DAB group | 83.00 | 0.64 | 97.87 |
| BAC group | 76.00 | 0.51 | 99.33 |
| Sample Type | DAB Group Dominant Phyla | BAC Group Dominant Phyla |
|---|---|---|
| Gut | Firmicutes (51.71%) Bacteroidota (38.08%) | Bacteroidota (45.28%) Firmicutes (41.30%) Actinobacteria (8.80%) |
| Drinking Water | Proteobacteria (56.27%) Bacteroidota (34.86%) | Firmicutes (44.38%) Proteobacteria (23.00%) Actinobacteria (17.57%) Bacteroidota (7.92%) |
| Environment | Actinobacteria (44.71%) Firmicutes (34.71%) | Proteobacteria (85.06%) Bacteroidota (10.53%) |
| Teat Surface | Actinobacteria (44.46%) Firmicutes (36.31%) Bacteroidota (9.11%) | Firmicutes (31.64%) Actinobacteria (25.55%) Proteobacteria (21.39%) Bacteroidota (11.95%) |
| Sample Type | DAB Group Dominant Genera | BAC Group Dominant Genera |
|---|---|---|
| Gut | Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group (15.63%) UCG-005 (14.23%) Bacteroides (4.83%) | Bacteroides (27.42%) Fusobacterium (15.67%) Alloprevotella (7.42%) Collinsella (7.27%) Prevotella_9 (5.47%) |
| Drinking Water | Acinetobacter (38.60%) Chryseobacterium (24.43%) | Acinetobacter (60.14%) Chryseobacterium (7.93%) |
| Environment | UCG-005 (1.56%) Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group (0.24%) | Acinetobacter (11.95%) UCG-005 (5.65%) |
| Teat Surface | UCG-005 (7.86%) Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group (2.74%) Bacteroides (2.11%) | Acinetobacter (9.88%) UCG-005 (0.75%) Rikenellaceae_RC9_gut_group (0.17%) |
| Group | Drinking Water | Environment |
|---|---|---|
| Gut (DAB group) | 0 | 4.37 |
| Gut (BAC group) | 0 | 8.27 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, T.; He, T.; Chai, M.; Zhang, L.; Han, X.; Jiang, S. Environmental Microbiome Characteristics and Disinfection Strategy Optimization in Intensive Dairy Farms: Bactericidal Efficacy of Glutaraldehyde-Based Combination Disinfectants and Regulation of Gut Microbiota. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080707
Wang T, He T, Chai M, Zhang L, Han X, Jiang S. Environmental Microbiome Characteristics and Disinfection Strategy Optimization in Intensive Dairy Farms: Bactericidal Efficacy of Glutaraldehyde-Based Combination Disinfectants and Regulation of Gut Microbiota. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(8):707. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080707
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Tianchen, Tao He, Mengqi Chai, Liyan Zhang, Xiangshu Han, and Song Jiang. 2025. "Environmental Microbiome Characteristics and Disinfection Strategy Optimization in Intensive Dairy Farms: Bactericidal Efficacy of Glutaraldehyde-Based Combination Disinfectants and Regulation of Gut Microbiota" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 8: 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080707
APA StyleWang, T., He, T., Chai, M., Zhang, L., Han, X., & Jiang, S. (2025). Environmental Microbiome Characteristics and Disinfection Strategy Optimization in Intensive Dairy Farms: Bactericidal Efficacy of Glutaraldehyde-Based Combination Disinfectants and Regulation of Gut Microbiota. Veterinary Sciences, 12(8), 707. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12080707






