Simple Summary
Brucellosis is a bacterial zoonosis that affects both humans and animals, causing significant public health concerns and economic losses, particularly in countries where it is endemic. To prevent the spread of disease, early and accurate diagnosis is critical. Multiple diagnostic tests are used worldwide; however, no single test is sufficient in different epidemiological contexts, and for all relevant host species. This study analyzed data from 135 articles published between 2013 and 2023 that contained relevant data of nearly 20,000 humans and 64,000 animals. The objective of this study was to determine which tests demonstrated superior detection rates when applied simultaneously to the same number of samples. The results of this study revealed that primary binding assays had higher comparative detection rates than the Rose Bengal plate test (RBPT), a commonly used screening test, for diagnosing brucellosis in humans. Slow agglutination tests had lower detection rates than the RBPT, both in humans and cattle. Similarly, the complement fixation test (CFT) had a lower comparative detection rate than the RBPT, both in cattle and sheep. This study will help veterinarians, doctors, and public health authorities in selecting the most suitable tests across different species and epidemiological settings for effective diagnosis and control of brucellosis.
Abstract
Brucellosis is a highly contagious, neglected, and re-emerging zoonotic bacterial disease that poses significant health and economic challenges globally for both humans and animals. Extensive literature is available for various diagnostic strategies; however, no comprehensive meta-analysis comparing the diagnostic tests used has been published. The present study aimed to estimate the relative risk (RR) of diagnostic tests used in humans and animals published between 2013 and 2023. Four databases were systematically searched, and the articles were screened using predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Ultimately, the screening process resulted in a total of 135 studies, including 328 comparisons of relevant data of 19,921 humans and 64,145 animals. The data from these studies were extracted, and the subgroup meta-analyses were conducted using the METABIN procedure in the “meta” package of the R statistical software (version 4.4.1). The forest plots were generated to estimate RR, and the funnel plots were used to assess publication and report bias. The subgroup analysis revealed that primary binding assays had higher comparative detection rates than the Rose Bengal plate test (RBPT) for brucellosis in humans [RR = 1.75 (95% CI: 1.35–2.26), I2 = 73%]. Slow agglutination tests had lower detection rates than the RBPT, both in humans [RR = 0.68 (95% CI: 0.48–0.96), I2 = 90%] and cattle [RR = 0.41 (95% CI: 0.25–0.68), I2 = 96%]. Similarly, the complement fixation test (CFT) had a lower detection rate than the RBPT for brucellosis both in cattle [RR = 0.97 (95% CI: 0.94–0.99), I2 = 9%] and sheep [RR = 0.97 (95% CI: 0.95–0.99), I2 = 0%]. This meta-analysis demonstrated that, for the screening of brucellosis in both humans and animals, primary binding assays are the preferred diagnostic tools, followed by the RBPT and slow agglutination tests. However, their effective implementation requires context-specific diagnostic strategies and combined testing approaches to enhance accuracy and reliability.
1. Introduction
Brucellosis is a highly contagious and often neglected zoonotic bacterial disease that significantly impacts livestock production and poses a considerable public health burden globally.
Brucellosis is caused by Gram-negative, facultative intracellular coccobacilli of the genus Brucella [1]. This genus contains twelve well-characterized Brucella species characterized by specific host preferences. Three species caused significant economic losses and public health hazards, i.e., B. abortus (cattle, buffaloes, and camels), B. melitensis (goats, sheep, and camels), and B. suis (pigs and camels) [2,3]. Brucella canis is also recognized as a potential cause of human brucellosis; however, the disease remains poorly characterized due to its non-specific clinical presentation and the limited research into the condition [4].
Although brucellosis has worldwide distribution, it has been successfully controlled in domestic animals in developed countries, such as Australia, New Zealand, Canada, and Western Europe, through eradication programs. However, in underdeveloped regions of Africa, Asia, the Mediterranean basin, South America, and Latin America, brucellosis remains endemic in humans, farm animals, and wildlife [5,6]. In developing countries, an estimated 3.5 billion people are at risk of getting infected with one or more Brucella spp. [7].
Brucellae are shed by infected animals mainly via secretions and excretions such as milk, semen, vaginal discharge, placental and birth fluids. These are sources of infection for susceptible animals. Direct or indirect transmission involves ingestion, inhalation, or contact, or may occur during mating [8,9]. Brucellae may penetrate mucosa or submucosa, e.g., the conjunctiva. Vertical transmission involves congenital and prenatal infection, when pathogens are passed from mother to offspring [10]. Wildlife species, such as bats, voles, bison, boars, hares, elk, and foxes, serve as reservoirs for Brucella [11,12]. Ticks and lice have also been suggested as potential reservoirs or vectors, although evidence of this remains limited [13,14]. Brucellosis results in a variety of clinical signs in animals with deep economic impacts, e.g., infertility, abortion, retention of fetal membranes, and prolonged calving intervals resulting in reduced productivity of a herd, loss in milk and meat production, reduced weight gain, lost draft power, and culling [15,16,17].
Humans acquire brucellosis primarily through the ingestion of unpasteurized dairy products or by direct contact with infected animals, particularly with excretions, aborted fetuses, etc., during parturition [18]. Occupational infections are commonly seen in veterinarians, farmers, hunters, butchers, and laboratory personnel as they are more often exposed to diseased animals or their products [19]. The most common symptom in the acute stage is undulant fever with chills, headache, fatigue, arthralgia, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, jaundice, and lymphadenopathy. Other symptoms are anorexia, weakness, diarrhea, asthenia, and malaise [20,21,22]. The disease tends to become chronic with chronic fatigue, depression, uveitis, episcleritis, and spondylitis [23]. Localized infections may be seen in all organs after bacteremia. Infection poses a high risk to pregnant women and unborn fetuses. Evidence suggests that Brucella spp. (B. ceti and B. pinnipedialis) found in marine mammals also possesses zoonotic potential. They can be transmitted to humans through the consumption of raw or undercooked seafood, potentially leading to neurobrucellosis, with signs of meningoencephalitis, myelitis, and cerebral involvement [24,25,26].
The gold standard approach for diagnosing brucellosis is isolation and identification of the Brucella organism from cultures of clinical specimens such as blood, tissues, or other body fluids [27]. However, it has certain limitations, such as the availability of samples containing bacteria, increased risk for laboratory personnel during handling, and being time-consuming and labor-intensive [28]. The definitive diagnosis depends upon the detection of Brucella or its DNA through molecular assays, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) [29]. However, these assays are more expensive, require specialized equipment, and may not necessarily represent an active infection [30]. Indirect diagnosis of brucellosis is usually made through various serological assays that detect antibodies against Brucella antigens. These tests include rapid agglutination tests, such as the Rose Bengal plate test (RBPT), slow agglutination tests, such as the standard tube agglutination test (SAT), the complement fixation test (CFT), and primary binding assays, such as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) and the fluorescent polarization assay (FPA) [31]. The agglutination tests are compromised by unacceptably high numbers of false-negative and false-positive results, cross-species reactivity, and lack of common criteria for interpretation [31,32]. ELISAs are widely used for the screening and confirmation of brucellosis due to their high sensitivity and specificity, with competitive ELISA (cELISA) offering improved specificity over indirect ELISA (iELISA) by minimizing cross-reactions, especially with Yersinia species, though sometimes at the cost of reduced sensitivity [33,34].
Due to the lack of specific clinical signs, laboratory testing is currently the cornerstone of brucellosis diagnosis. Choosing an appropriate diagnostic tool is essential for effective disease surveillance and control. However, due to variations in diagnostic sensitivity and specificity, no single test is suitable for different epidemiological contexts or host species, and the performance of tests may vary according to the stage of disease [35,36]. Although previous systematic reviews and meta-analyses have contributed significantly to the understanding of the diagnostic accuracy of tests used for brucellosis. They primarily focused on individual test characteristics (sensitivity/specificity estimates using variable reference standards), specific test formats, or single host species [37,38]. We hypothesized that certain diagnostic methods (e.g., iELISA or PCR) would demonstrate significantly higher detection rates than others (e.g., RBT or SAT) when applied to the same sample sets (parallel testing). By incorporating data from 135 studies, this study provides a broader comparative synthesis by evaluating multiple diagnostic tests across a wide range of host species. By calculating and comparing the relative risk (RR) of test positivity (the likelihood of a test detecting brucellosis compared to another test), this meta-analysis is intended to identify which tests demonstrate superior detection rates when applied simultaneously to the same number of samples. This aims to inform the selection of optimal screening tools, improve the consistency of diagnostic practices, and ultimately support more effective surveillance and control strategies for brucellosis in both animals and humans.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Review Assessment Protocol
This systematic review was performed according to the established principles outlined in the Cochrane Handbook [39], and transparency was maintained by adhering to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines as described by [40]. The review process involved thorough database searches for selecting relevant articles, followed by a rigorous selection based on predefined criteria. The selected articles were then analyzed for their relevance to the research question, and data were extracted, screened, and analyzed following standardized procedures.
2.2. Literature Search Strategy
A systematic and comprehensive search strategy was implemented to identify relevant research articles on the global prevalence and geographical distribution of brucellosis published in English between 2013 and 2023. The major platforms searched include PubMed “https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 15 April 2023)”, Science Direct “https://www.sciencedirect.com/ (accessed on 20 April 2023)”, Web of Science “https://www.webofscience.com/wos/woscc/advanced-search (accessed on 22 April 2023)”, and Scopus “https://www.scopus.com/search/form.uri?display=basic#basic (accessed on 25 April 2023)”. In addition to electronic databases, a supplementary search was conducted in repositories for theses and dissertations; “http://opac.uvas.edu.pk/ (accessed on 27 April 2023)”, at UVAS Pakistan and “https://www.proquest.com (accessed on 28 April 2023)”, in the USA. All electronic databases were comprehensively searched from 15 April to 28 April 2023, to identify the relevant literature on brucellosis prevalence. The search strategy employed a combination of Medical Subject Headings (MeSHs) terms and keywords related to brucellosis prevalence in humans and animals. The keywords were searched by using Boolean operators (AND, OR) to clarify the search, and ensuring that the search captured relevant studies based on the Title, Abstract, or Keywords. The keywords included were ((“Brucellosis” OR “Brucella” OR “Malta fever” OR “Mediterranean fever” OR “Mediterranean remittent fever” OR “Undulant fever” OR “Gibraltar fever” OR “Rock fever” OR “Neapolitan fever”) AND (“Molecular detection” OR “Diagnosis” OR “Prevalence” OR “Seroprevalence” OR “Surveillance” OR “Epidemiological survey” OR “Serology” OR “Serodiagnosis” OR “PCR”) AND (“Human” OR “Animals” OR “Buffalo” OR “Cow” OR “Cattle” OR “Sheep” OR “Goat” OR “Dog” OR “Horse” OR “Camel” OR “Pig” OR “Wildlife” OR “Marine”)) for database search.
2.3. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
Following the initial electronic database search, a two-tiered screening process was implemented. In the first step, duplication was removed. Initial screening of the studies was performed by their titles; subsequently, abstracts were reviewed to select studies published from 2013 to 2023 that investigated brucellosis prevalence either in humans or in animals. In the second stage, an evaluation of full-text articles was conducted to verify the use of a validated diagnostic method. The eligibility criteria were established based on the hypotheses of the meta-analysis. To be included, studies were required to meet the following criteria: (1) they were required to be peer-reviewed, original research articles in English language; (2) published between 1 January 2013 and 28 April 2023 to ensure the most recent data; (3) employed cross-sectional or observational designs at a minimum; (4) reported the total sample size and the number of animals testing positive for brucellosis using a validated diagnostic method; and (5) articles where samples were tested for brucellosis with at least 2 diagnostic tests in parallel. Articles published in other languages and reviews were excluded. Subsequently, articles that satisfied this inclusion criterion were selected for meta-analysis.
2.4. Research Articles Included
Figure 1 illustrates a PRISMA flow diagram outlining the data collection process for the meta-analysis. After the initial search, a total of 6536 records were identified that were published between 2013 and 2023, comprising 6520 records from databases and 16 records from repositories for theses and dissertations. From these records, 1018 studies were removed because of duplication, and 5383 studies were excluded based on predefined eligibility criteria. Ultimately, a total of 135 records, involving 328 comparisons that contained relevant data of 19,921 humans and 64,145 animal samples for brucellosis prevalence, were included. A comprehensive list of records included in the meta-analysis is provided in Supplementary Table S1.
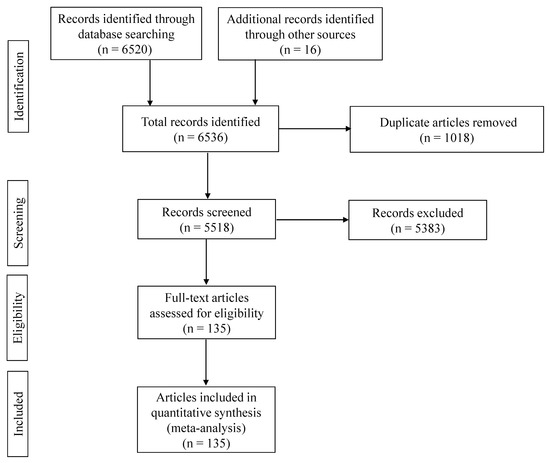
Figure 1.
The PRISMA flow diagram [40] of the systematic review from initial search and screening before final selection of publications to be included in the meta-analysis. After initial identification of the records that appeared in each search engine with certain keywords, the titles of the articles were compared across the search engines to remove duplicates. Records were subsequently screened, and articles related to the hypothesis were assessed based on the eligibility criteria; ultimately, one hundred and thirty-five articles were included in the meta-analysis.
2.5. Data Extraction and Quality Assessment
Two authors independently extracted data from all the eligible studies. All relevant information was recorded in a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet, including the first author’s name, year of publication, study design, country of study, geographical location, animal species, animal species category, sampling information, sample size, diagnostic methods used, the number of samples that were found to be positive for Brucella in each test, and the Brucella species under investigation. The extracted data were then thoroughly reviewed by two other reviewers to ensure the accuracy of the collected information before further analysis. The methodological quality of all included studies was assessed using the Joanna Briggs Institute (JBI) critical appraisal tool [41]. The checklist consists of eight questions evaluating the clarity of inclusion criteria, measurement reliability, validity of outcome measures, confounding factors, and appropriate statistical analysis. Each study was independently assessed by two reviewers and scored using “Yes” or “No” responses for each criterion. Studies scoring positively on ≥6 out of 8 questions were classified as high-quality, ≥4 and 5 as moderate-quality, while those scoring below 4 were designated as low-quality. The quality score and the corresponding quality level for each study are provided in Supplementary Table S1.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The classical meta-analysis was conducted by using the metabin() function in the “meta” package of the R statistical software (version 4.4.1) to calculate pooled relative risk (RR) estimates. RR, a commonly used statistical measure, was selected as the summary measure due to its easy and direct interpretation and suitability for within-study comparisons. It enables a direct comparison of the likelihood of a diagnostic test detecting disease relative to a reference test, and provides a quantitative estimate of how much more or less likely a test is to yield a positive result compared to another.
2.6.1. Reference Standard
Although historically regarded as the gold standard for its high specificity, culture isolation is now considered a suboptimal reference method due to its relatively low sensitivity [37]. Furthermore, a majority of studies included in the meta-analysis did not use culture as a diagnostic test. In this meta-analysis, the Rose Bengal plate test (RBPT) was used as a control or reference for comparisons, whereas the other test was considered experimental. The RBPT is generally considered a rapid screening test, and 70% of the studies in this dataset reported RBPT as one of the tests applied. Where RBPT was not performed, the following tests in a sequence were considered as a control test: rapid agglutination tests [Card test, Brucella-buffered acidified plate antigen test (BAPA), latex agglutination test (LAT)], slow agglutination tests [milk ring test (MRT), standard agglutination test (SAT), serum plate agglutination test (SPAT), Brucellacapt], primary binding assays (IELISA, c-ELISA), precipitation tests [agar gel immunodiffusion test (AGID)], staining techniques [immunohistochemistry (IHC)], and culture. The categorization of the different diagnostic tests according to [33,42], with little modification, is shown in Supplementary Figure S1. The subgroup analyses were conducted by grouping the comparisons based on the diagnostic tests’ classification, as shown in Supplementary Figure S1. When the control was RBPT, the comparisons were grouped based on experimental tests. In contrast, where RBPT was not reported, the comparisons were grouped based on the control test because of multiple control tests. In both cases, the RR (the likelihood of a test detecting brucellosis compared to another test) was estimated for the experimental tests.
2.6.2. Heterogeneity Assessment
Due to the high heterogeneity among the included studies, a random-effects model with the inverse variance method was applied for all analyses. This approach accounts for between-study variability and typically produces wider confidence intervals, providing a more conservative estimate of the central performance measures. Subgroup differences were tested using the Chi-square test for subgroup differences (χ2 test), and heterogeneity was quantified using I2 statistics and τ2. The measure I2 is the transformation of the square root of χ2 heterogeneity statistics divided by the degree of freedom and is a measure of variation in RR beyond chance among comparisons included in the meta-analysis.
2.6.3. Graphical Summaries
The forest plots were generated for each species separately to estimate the RR of different diagnostic methods. The funnel plots were generated to assess potential publication and reporting bias among studies included in this meta-analysis.
In the forest plot, for each comparison, the point estimate (RR) and respective 95% confidence intervals (CIs) are represented by a black point and its associated horizontal lines, respectively. The central vertical black line represents an RR that is equal to 1, and the points located to the left of the central vertical black line indicate the decrease, whereas the points located to the right represent the increase in the relative risk compared to the control. The term “event” in the forest plot refers to the number of samples testing positive out of the total number of samples tested within a group. Each gray box around the point estimate represents the weight of the comparison; the larger the box, the greater the comparison contribution to the overall estimate. The weight that each comparison contributed is shown in the right-hand column. A diamond represents the overall effect at the bottom of the plot, aggregating the RR of all included studies adjusted by the random effect models.
A minimum criterion for test comparison was the availability of at least three valid comparisons per species or group. The number of comparisons for each species is mentioned below the respective forest plots in the Results section.
2.6.4. Subgroup Meta-Analysis by Study Quality
To evaluate the impact of methodological quality on diagnostic test comparisons, subgroup meta-analyses were performed to stratify studies by their quality level (high vs. low/moderate). This was conducted separately for humans, cattle, goats, and sheep, using only studies that employed RBPT as the reference.
2.6.5. Sensitivity Analysis
To assess the robustness of results, a sensitivity analysis was performed by restricting the meta-analysis to high-quality studies only within each species group. Subgroup meta-analyses were again conducted within these high-quality datasets based on the experimental test group variable, allowing comparison of different diagnostic tests against RBPT. Forest plots were generated to visually compare the magnitude and direction of the pooled estimates and to examine the consistency of findings across subgroups.
Statistical significance was considered for p ≤ 0.05 and a tendency at 0.05 < p ≤ 0.10.
2.7. Publication Bias
Funnel plots (species-wise) depicting the publication bias among all studies included in the meta-analysis are presented in Supplementary Figure S2. In the funnel plot, the effect size of each study is plotted on the horizontal axis and the standard error (SE) on the vertical axis.
3. Results
3.1. Comparison of Diagnostic Tests for Brucellosis
A summary of RR estimates for diagnostic test groups compared to RBPT across various species is presented in Table 1. The heatmap depicts the RR of various diagnostic tests compared to RBPT for diagnosing brucellosis across multiple host species (Figure 2).

Table 1.
Summary of relative risk (RR) estimates of diagnostic test groups compared to RBPT in various species.
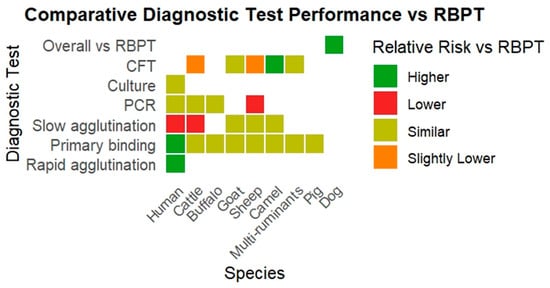
Figure 2.
The heatmap depicts the RR of various diagnostic tests compared to RBPT for diagnosing brucellosis across multiple host species.
3.1.1. Human Medicine
- Comparison with RBPT
The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of six different test groups compared with RBPT for diagnosing brucellosis in humans (Figure 3). Overall, the RR for diagnosing brucellosis when compared to RBPT did not differ significantly [RR (95% CI) = 1.19 (0.88–1.61), I2 = 91%]. In subgroup analysis, rapid agglutination tests had a significantly higher RR compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 3.43 (1.78–6.59), I2 = 18%]. Similarly, primary binding assays also had a significantly higher RR [RR (95% CI) = 1.75 (1.35–2.26), I2 = 73%]. In contrast, slow agglutination tests demonstrated a significantly lower RR [RR (95% CI) = 0.68 (0.48–0.96), I2 = 90%]. The culture, the complement fixation test (CFT), and PCR did not differ significantly from RBPT.
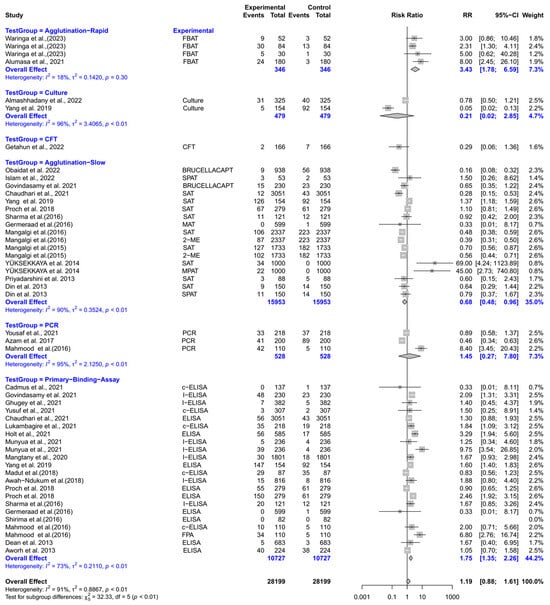
Figure 3.
The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of six different test groups [experimental] compared with the Rose Bengal plate test (RBPT) [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in humans. A total of 49 comparisons are depicted in the forest plot. One comparison was excluded because it had zero positive events in both groups, i.e., experiment and control. In the forest plot, squares represent the point estimate (RR), and their associated horizontal lines indicate the respective 95% CIs. The size of each square reflects the weight of that comparison in the meta-analysis. The diamond represents the overall effect for all studies or within subgroups. The central vertical black line represents an RR of 1, and the dotted red line indicates the pooled RR from the meta-analysis. Overall, the RR for diagnosing brucellosis when compared to RBPT did not differ significantly [RR (95% CI) = 1.19 (0.88–1.61), I2 = 91%]. In subgroup analysis, rapid agglutination tests had a significantly higher RR compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 3.43 (1.78–6.59), I2 = 18%]. Similarly, primary binding assays also had a significantly higher RR [RR (95% CI) = 1.75 (1.35–2.26), I2 = 73%]. In contrast, slow agglutination tests demonstrated a significantly lower RR [RR (95% CI) = 0.68 (0.48–0.96), I2 = 90%]. The culture, the complement fixation test (CFT), and PCR did not differ significantly from RBPT [43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73].
- Comparison across test groups
The forest plot represents the RR of various tests compared to three different test groups for diagnosing brucellosis in humans (Figure 4). The subgroup analyses revealed that experimental tests (Coombs, 2-ME, ELISA, culture, and PCR) had significantly lower RR compared to slow agglutination tests [RR (95% CI) = 0.68 (0.50–0.94), I2 = 82%]. However, the RRs did not differ significantly when experimental tests were compared with rapid agglutination tests and primary binding assays.
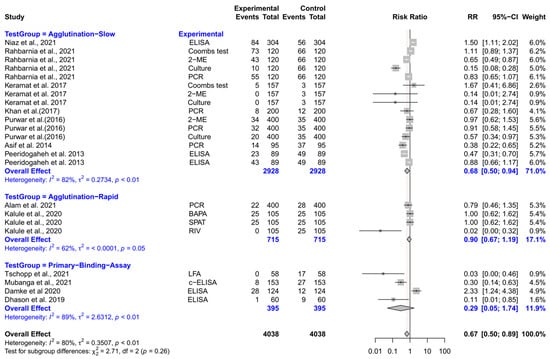
Figure 4.
The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of various tests [experimental] compared to three different test groups [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in humans. A total of 23 comparisons are depicted in the forest plot. In the forest plot, squares represent the point estimate (RR), and their associated horizontal lines indicate the respective 95% CIs. The size of each square reflects the weight of that comparison in the meta-analysis. The diamond represents the overall effect for all studies or within subgroups. The central vertical black line represents an RR of 1, and the dotted red line indicates the pooled RR from the meta-analysis. The subgroup analyses revealed that experimental tests (Coombs, 2-ME, ELISA, culture, and PCR) had significantly lower RR compared to slow agglutination tests [RR (95% CI) = 0.68 (0.50–0.94), I2 = 82%]. However, the RRs did not differ significantly when experimental tests were compared with rapid agglutination tests and primary binding assays [74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86].
3.1.2. Veterinary Medicine
Cattle
- Comparison with RBPT
The forest plot depicts the RR of five different test groups compared with RBPT for diagnosing brucellosis in cattle (Figure 5). Overall, the RR for diagnosing brucellosis when compared to RBPT did not differ significantly [RR (95% CI) = 0.97 (0.81–1.17), I2 = 86%]. In subgroup analysis, slow agglutination tests had a significantly lower RR compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 0.41 (0.25–0.68), I2 = 96%]. The CFT also demonstrated a slightly but significantly lower RR [RR (95% CI) = 0.97 (0.94–0.99), I2 = 9%]. However, the primary binding assays, PCR, and rapid agglutination tests did not differ significantly from RBPT.
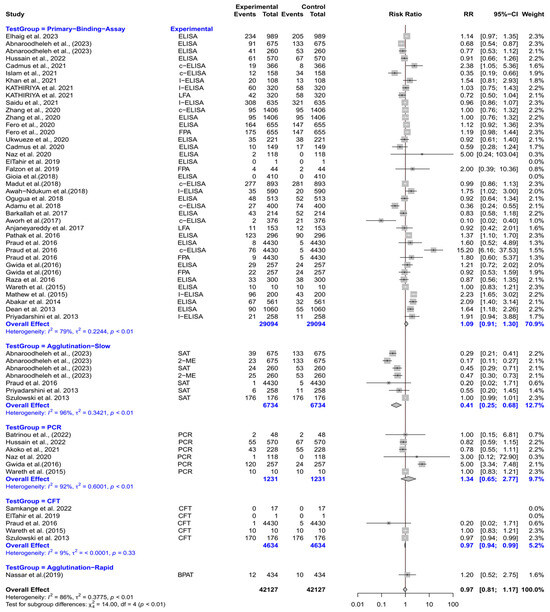
Figure 5.
The forest plot depicts the relative risk (RR) of five different test groups [experimental] compared with the Rose Bengal plate test (RBPT) [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in cattle. A total of 58 comparisons are depicted in the forest plot. Four comparisons were excluded because they had zero positive events in both groups, i.e., the experimental group and the control group. In the forest plot, squares represent the point estimate (RR), and their associated horizontal lines indicate the respective 95% CIs. The size of each square reflects the weight of that comparison in the meta-analysis. The diamond represents the overall effect for all studies or within subgroups. The central vertical black line represents an RR of 1, and the dotted red line indicates the pooled RR from the meta-analysis. Overall, the RR for diagnosing brucellosis when compared to RBPT did not differ significantly [RR (95% CI) = 0.97 (0.81–1.17), I2 = 86%]. In subgroup analysis, slow agglutination tests had a significantly lower RR compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 0.41 (0.25–0.68), I2 = 96%]. The CFT also demonstrated a slightly but significantly lower RR [RR (95% CI) = 0.97 (0.94–0.99), I2 = 9%]. However, the primary binding assays, PCR, and rapid agglutination tests did not differ significantly from RBPT [58,62,69,70,72,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116].
- Comparison across test groups
The forest plot represents the RR of various tests compared with five different test groups (Supplementary Figure S3). The subgroup analyses revealed that the RR did not differ significantly when experimental tests were compared with the control. The control groups included rapid agglutination tests, slow agglutination tests, primary binding assays, staining, and culture.
Buffaloes
- Comparison with RBPT
The forest plot represents the RR of five different test groups compared with RBPT for diagnosing brucellosis in buffaloes (Supplementary Figure S4). Overall, the RR did not differ significantly between the experimental tests and RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 1.11 (0.94–1.32), I2 = 26%]. The subgroup analyses revealed that the primary binding assays, PCR, rapid agglutination tests, slow agglutination tests, and CFT did not differ significantly from RBPT.
- Comparison across test groups
The forest plot represents the RR of various tests compared to three different test groups (Supplementary Figure S5). The subgroup analyses revealed that the RR did not differ significantly when experimental tests were compared with the control. The control groups included rapid agglutination tests, slow agglutination tests, and primary binding assays.
Goats
- Comparison with RBPT
The forest plot represents the RR of five different test groups compared with RBPT (Figure 6). Overall, the RR did not differ significantly compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 1.02 (0.83–1.26), I2 = 58%]. The subgroup analyses revealed that the primary binding assays, CFT, slow agglutination tests, precipitation tests, and PCR did not differ significantly from RBPT.
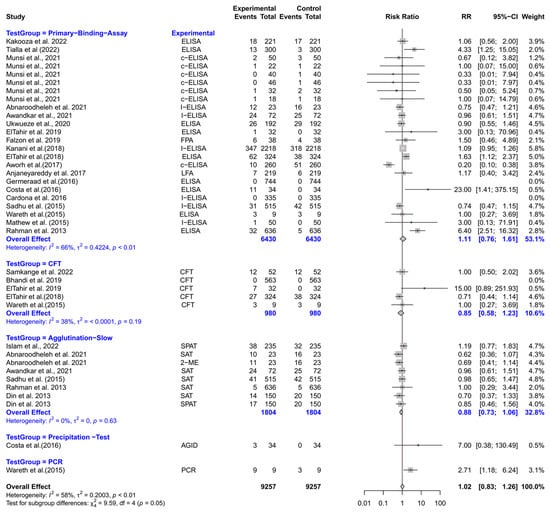
Figure 6.
The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of 5 different test groups [experimental] compared with the Rose Bengal plate test (RBPT) [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in goats. A total of 39 comparisons are depicted in the forest plot. Three comparisons were excluded because they had zero positive events in both groups, i.e., experiment and control. In the forest plot, squares represent the point estimate (RR), and their associated horizontal lines indicate the respective 95% CIs. The size of each square reflects the weight of that comparison in the meta-analysis. The diamond represents the overall effect for all studies or within subgroups. The central vertical black line represents an RR of 1, and the dotted red line indicates the pooled RR from the meta-analysis. Overall, the RR did not differ significantly compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 1.02 (0.83–1.26), I2 = 58%]. The subgroup analyses revealed that the primary binding assays, CFT, slow agglutination tests, precipitation tests, and PCR, did not differ significantly from RBPT [49,54,59,96,99,100,105,106,110,111,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128].
- Comparison across test groups
The forest plot represents the RR of various tests compared to four different test groups (Supplementary Figure S6). The subgroup analyses revealed that the RR did not differ significantly when experimental tests were compared with the control. The control groups consisted of slow agglutination tests, primary binding assays, staining, and culture.
Sheep
- Comparison with RBPT
The forest plot represents the RR of five different test groups compared with RBPT (Figure 7). Overall, the RR did not differ significantly compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 0.97 (0.86–1.09), I2 = 76%]. In subgroup analyses, PCR had a significantly lower RR compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 0.56 (0.32–0.98), I2 = 42%]. The CFT also demonstrated a slightly but significantly lower RR [RR (95% CI) = 0.97 (0.95–0.99), I2 = 0%]. However, primary binding assays, slow agglutination tests, and precipitation tests did not differ significantly from RBPT.
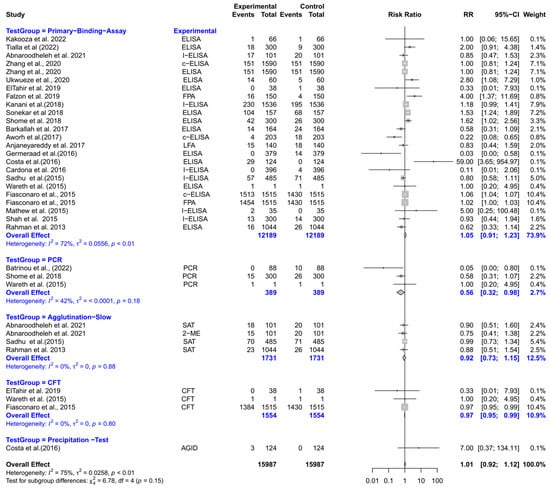
Figure 7.
The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of 5 different test groups [experimental] compared with the Rose Bengal plate test (RBPT) [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in sheep. A total of 35 comparisons are depicted in the forest plot. In the forest plot, squares represent the point estimate (RR), and their associated horizontal lines indicate the respective 95% CIs. The size of each square reflects the weight of that comparison in the meta-analysis. The diamond represents the overall effect for all studies or within subgroups. The central vertical black line represents an RR of 1, and the dotted red line indicates the pooled RR from the meta-analysis. Overall, the RR did not differ significantly compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 0.97 (0.86–1.09), I2 = 76%]. In subgroup analyses, PCR had a significantly lower RR compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 0.56 (0.32–0.98), I2 = 42%]. The CFT also demonstrated a slightly but significantly lower RR [RR (95% CI) = 0.97 (0.95–0.99), I2 = 0%]. However, primary binding assays, slow agglutination tests, and precipitation tests did not differ significantly from RBPT [54,94,96,99,100,104,105,106,110,111,114,117,118,120,122,124,125,126,127,129,130,131].
- Comparison across test groups
The forest plot represents the RR of various tests compared with five different tests (Supplementary Figure S7). The subgroup analyses revealed that the RR did not differ significantly when experimental tests were compared with the control. The control groups included rapid agglutination tests, slow agglutination tests, primary binding assays, staining, and culture.
Camels
- Comparison with RBPT
The forest plot represents the RR of three different test groups compared with RBPT (Figure 8). Overall, the RR did not differ significantly compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 0.96 (0.70–1.32), I2 = 73%]. The subgroup analyses revealed that the CFT had a significantly higher RR compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 1.99 (1.51–2.62), I2 = 0%]. However, the primary binding assays and slow agglutination tests did not differ significantly from RBPT.
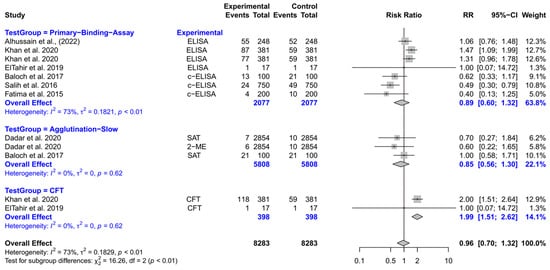
Figure 8.
The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of 3 different test groups [experimental] compared with the Rose Bengal plate test (RBPT) [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in camels. A total of 12 comparisons are depicted in the forest plot. In the forest plot, squares represent the point estimate (RR), and their associated horizontal lines indicate the respective 95% CIs. The size of each square reflects the weight of that comparison in the meta-analysis. The diamond represents the overall effect for all studies or within subgroups. The central vertical black line represents an RR of 1, and the dotted red line indicates the pooled RR from the meta-analysis. Overall, the RR did not differ significantly compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 0.96 (0.70–1.32), I2 = 73%]. The subgroup analyses revealed that the CFT had a significantly higher RR compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 1.99 (1.51–2.62), I2 = 0%]. However, the primary binding assays and slow agglutination tests did not differ significantly from RBPT [3,99,132,133,134,135,136].
Multi-Species Analysis (Ruminants)
- Comparison with RBPT
The forest plot represents the RR of four different test groups compared with RBPT (Supplementary Figure S8). Overall, the RR did not differ significantly compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 0.94 (0.76–1.16), I2 = 88%]. The subgroup analyses revealed that the CFT, primary binding assays, slow agglutination tests, and PCR did not differ significantly compared to RBPT.
- Comparison across test groups
The forest plot represents the RR of various tests compared with three different tests (Supplementary Figure S9). The subgroup analyses revealed that the RR did not differ significantly when experimental tests were compared with the control. The control groups were agglutination slow tests, primary binding assays, and culture.
Pigs
- Comparison with RBPT
The forest plot represents the RR of two different test groups compared with RBPT (Supplementary Figure S10). Overall, the RR did not differ significantly compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 1.22 (0.60–2.46), I2 = 90%]. The subgroup analyses revealed that the primary binding assays and CFT did not differ significantly from RBPT.
Dogs
- Comparison with RBPT
The forest plot represents the RR of five different test groups compared with RBPT (Supplementary Figure S11). Overall, the RR for diagnosing brucellosis was significantly higher compared to RBPT [RR (95% CI) = 1.70 (1.22–2.35), I2 = 48%]. However, the subgroup analyses revealed that the precipitation tests, CFT, PCR, slow agglutination tests, and primary binding assays did not differ significantly from RBPT.
- Comparison across test groups
The forest plot represents the RR of various diagnostic tests compared with five different diagnostic test groups (Supplementary Figure S12). The subgroup analyses revealed that the RR did not differ significantly when experimental tests were compared with the control. The control groups consisted of rapid agglutination tests, primary binding assays, precipitation tests, staining, and culture.
The analysis was not performed for wildlife species (bison, fox, rodents), marine species (dolphin, walrus), or horses because they had fewer than three test comparisons per category.
3.2. Study Quality Assessment
The bar chart illustrates the distribution of study quality based on the JBI critical appraisal checklist (Figure 9a). Out of 135 included studies, 97 (72%) were classified as high-quality, while the remaining 38 (28%) were rated as moderate-quality. The assessment did not identify any studies as being of low quality. The stacked bar plot summarizing responses to the eight JBI checklist questions revealed that the highest proportion of “Yes” responses was observed for Q3: “Was the exposure measured in a valid and reliable way?”. In contrast, the lowest proportion of positive responses was recorded for Q6: “Were strategies to deal with confounding factors stated?” (Figure 9b).
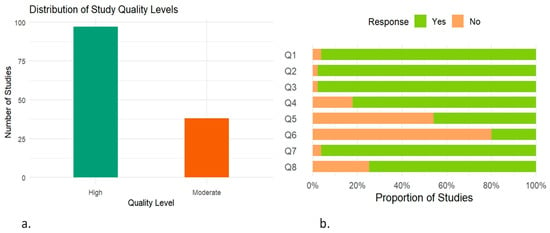
Figure 9.
Assessment of study quality based on JBI critical appraisal checklist. (a) Bar chart showing the overall distribution of included studies categorized by their quality level. (b) Stacked bar chart illustrating the proportion of “Yes” and “No” responses for each of the eight questions (Q1–Q8); 1. Were the criteria for inclusion in the sample clearly defined? 2. Were the study subjects and the setting described in detail? 3. Was the exposure measured in a valid and reliable way? 4. Were objective, standard criteria used for measurement of the condition? 5. Were confounding factors identified? 6. Were strategies to deal with confounding factors stated? 7. Were the outcomes measured in a valid and reliable way? 8. Was appropriate statistical analysis used?
3.3. Subgroup Meta-Analysis by Study Quality
The forest plots represent the subgroup meta-analysis by study quality in humans, cattle, goats, and sheep (Supplementary Figures S13–S16). Subgroup analyses stratified by study quality showed minimal differences in pooled estimates across species. In humans, goats, and sheep, the study quality did not significantly influence the pooled estimates, as the test for subgroup differences was statistically non-significant (p > 0.05). However, in cattle, the difference between high- and moderate-quality studies was statistically significant (p = 0.02), indicating that study quality contributed to the observed heterogeneity.
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis
The forest plots depict the sensitivity analyses based on high-quality studies in humans, cattle, goats, and sheep (Supplementary Figures S17–S20). The pooled RR estimates remained consistent with the main analyses across all species. The overall RR was slightly elevated in humans, slightly lower in cattle, and remained similar in both sheep and goats.
4. Discussion
Brucellosis is a transboundary animal disease classified as a category B infectious disease by the World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH), emphasizing its global importance as a serious health threat to animals and humans alike [137]. Accurate diagnosis of brucellosis is crucial for its effective control, eradication, and surveillance and requires an integrated approach. Multiple diagnostic strategies have been recommended depending upon specific epidemiological contexts. Serial testing (usually a screening test of high sensitivity followed by a confirmatory test of high specificity) is typically employed in low-prevalence areas, pre-movement testing of uninfected herds, and eradication programs. This strategy enhances specificity and minimizes false positives, thereby preventing unnecessary culling or restrictions. In contrast, parallel testing is generally recommended in high-prevalence areas or during outbreak investigations, as it maximizes the sensitivity and reduces the likelihood of false negatives [138,139,140]. This meta-analysis aims to determine the relative risk (RR) of different diagnostic tests used for diagnosing brucellosis in humans and animals, and highlights which tests perform better in parallel testing contexts for improved disease detection. We have further highlighted the strengths and limitations of each diagnostic approach to guide evidence-based decision-making in diverse field settings.
According to the findings of this meta-analysis, primary binding assays detected a higher proportion of positive samples (a higher comparative detection rate) compared to RBPT when both were applied to the same sample sets (parallel testing) in humans. A similar trend was observed in cattle, buffaloes, goats, sheep, and pigs, in which these assays outperformed RBPT in terms of detection. This difference in sensitivity between the primary binding assays and the RBPT for diagnosing brucellosis may be attributed to several factors. Generally, the primary binding assays have higher sensitivities and specificities compared to RBPT [33,141]. As described by [142], the ELISA can be efficiently used to diagnose brucellosis in humans and has a higher sensitivity than RBPT. In the early stages of infection, IgM antibodies predominate, and their strong agglutination capability makes the RBPT, which relies on agglutination, particularly effective for diagnosing the infection during this phase. As the infection progresses to the chronic stage, IgG and non-agglutinating antibodies become more prevalent than agglutinating ones, which can result in the disease going undetected by agglutination tests such as RBPT [143]. All Brucella species, except B. canis and B. ovis, possess a smooth lipopolysaccharide (S-LPS) in their outer cell walls, characterized by an immunodominant O-polysaccharide (OPS) component [144]. Brucella canis and B. ovis lack OPS and their outer surface contains only rough lipopolysaccharide (R-LPS) [145,146]. The RBPT uses S-LPS antigens and is only suitable for detecting antibodies against smooth Brucella species [147]. However, the ELISA can detect antibodies against both the smooth and rough Brucella species when it is properly designed [140]. Furthermore, the RBPT has limitations in detecting non-agglutinating antibodies such as IgA and certain forms of IgG [148,149]. The ELISA can detect both IgG and IgM if designed appropriately, and the use of an IgG conjugate in ELISAs enables the detection of non-agglutinating antibodies as well. The ELISA gives a detailed profile of Brucella-specific antibodies (IgM, IgG, and IgA) and tends to have a higher sensitivity compared to RBPT, making it highly effective for diagnosing both acute and chronic stages of brucellosis and is well-suited for large-scale screening [87,150]. Moreover, the ELISA, as a quantitative assay, can detect lower antibody titers compared to RBPT, and the use of an ELISA reader also provides more objective and consistent results when compared to the visual interpretation of the RBPT. The superior performance of ELISAs is due to the use of S-LPS fragments, thereby reducing the chances of cross-reactions with other Gram-negative bacteria such as Yersinia enterocolitica O:9, Salmonella enterica, Escherichia coli O:116, and O:157, or Vibrio cholerae [33]. Some of the primary binding assays may also distinguish between antibodies produced by vaccination and those resulting from infection [146]. The primary binding assays may help to mitigate the prozone effect, which is often observed with acidified antigens in the RBPT [151,152]. This is a phenomenon where an excess of antibodies or antigens can lead to a false-negative result in an immunoassay. This effect can be avoided by the serial dilution of serum. A 1:8 dilution of serum in RBPT, rather than the standard 1:2 dilution, has been shown to enhance the test’s specificity without significantly impacting sensitivity, increasing complexity, time required, or costs [153]. Additionally, in the RBPT, the acidic nature of the antigen may help to suppress the effects of non-specific agglutinins, potentially leading to reduced detection rates. Despite these prevailing limitations, RBPT is still internationally recommended as a screening test for brucellosis in resource-limited countries because it is rapid, cost-effective, easy to perform, and can be conducted in farm settings. Moreover, rapid laboratory diagnostic procedures for the identification of causative agents are important for the timely implementation of appropriate public health countermeasures. While primary binding assays generally offer better performance compared to rapid diagnostic tests, their higher cost and sophisticated equipment needs often limit their use to a second-line option in low-resource settings [154]. The results of these assays should be interpreted in conjunction with culture and/or molecular identification of Brucella. As in humans, the occurrence of a rheumatoid factor is responsible for false-positive results in the primary binding assays, particularly ELISAs [27].
This meta-analysis revealed that RBPT has a higher comparative detection rate than slow agglutination tests in cattle and humans. Similarly, in goats, sheep, and camels, RBPT is more effective at detecting brucellosis than slow agglutination tests. This difference in detection between RBPT and slow agglutination tests for diagnosing brucellosis could be attributed to several factors. When the analysis was restricted to high-quality studies in humans, the association was attenuated and no longer statistically significant. This shift suggests that study quality may have influenced the originally observed performance difference in slow agglutination tests in humans. The sensitivity of slow agglutination tests is low compared to RBPT [33,155]. The cut-off titers for the standard tube agglutination test (SAT) in determining positive or negative results depend on factors such as the type of specimen, the antigen used, and whether the region is endemic or non-endemic [150]. For instance, in China, the official diagnostic criterion for brucellosis, as stated by [156], is a titer greater than 1:100 with clear agglutination (>50%), which is lower than the WHO’s recommended cut-off of >1:160. In endemic regions, a cut-off titer of 1/320 is recommended for the SAT [157], while the RBT is sensitive to titers below 1:320 [50]. The SAT is more prone to false-negative results than RBPT due to the nature of the antigen used, the presence of prozone phenomenon, blocking, and non-agglutinating antibodies [153]. However, incorporation of certain modifications, such as the addition of EDTA, 2-mercaptoethanol, or antihuman globulin, can enhance accuracy [158]. Slow agglutination tests are less effective for detecting IgG antibodies [147]. In modified slow agglutination tests, reducing agents are added to break the disulfide bridges of IgM to prevent non-specific reactions. However, this process can also affect some IgG molecules, potentially leading to false-negative results as these antibodies lose their ability to agglutinate [42]. The use of mercapto-ethanol in 2ME tests neutralizes IgM, thereby inhibiting serological responses to Yersinia enterocolitica O:9 and other sources of false-positive reactions [159]. Due to their IgM-reducing effect, these tests are not useful during the acute stage of infection. Slow agglutination tests generally exhibit higher specificity compared to RBPT, resulting in fewer false-positive reactions [147,160]. RBPT may sometimes produce false reactions due to fibrin clot formation if samples are incubated for extended periods [42]. The SAT is generally not recommended by the WOAH for diagnosing brucellosis as it is considered inferior to other standard tests. While slow agglutination tests offer better specificity compared to RBPT, they are time-consuming, require labor-intensive protocols, and are prone to false-negative reactions, making them unsuitable for use as screening tests. The findings of this study suggest that the RBPT screening test is preferred to the slow agglutination tests. However, its results must be validated with one of the confirmatory tests, such as primary binding assays, to overcome its limitations and improve diagnostic accuracy.
The results of this meta-analysis illustrate that slow agglutination tests, particularly SAT, have a higher comparative detection rate than various experimental tests, including Coombs, 2-ME, primary binding assays, culture, and PCR in humans. A similar trend has been observed in cattle, goats, and sheep. The SAT is a serological test based on the detection of specific antibodies in a serum sample. While it provides presumptive evidence for infection, it cannot differentiate between active and past infection. The main disadvantages of the SAT are low specificity compared to modified slow agglutination tests, culture, and PCR, and the challenges in interpreting the results, particularly in patients with recurrent exposure to Brucella [148]. Additionally, the diagnostic performance of the SAT can be limited by the presence of non-agglutinating antibodies in chronic cases [161]. Unlike the SAT, culture and PCR are direct diagnostic methods that require the presence of Brucella bacteria or their genetic material in a sample, respectively.
This meta-analysis revealed that compared to molecular assays (PCR), bacterial culture demonstrated a lower comparative detection rate. This can be ascribed to the fastidious nature of Brucella [149]. Isolation failures may arise from a low quantity of viable bacteria in a clinical sample or when the sample is heavily contaminated [162]. Blood cultures are useful only in patients with bacteremia, which may not always occur. Several inhibitor substances, such as anticoagulants, hemoglobin, and host DNA, are present in whole blood [163]. The stage of infection may affect the quantity and localization of the organisms within the different body tissues [164]. During the acute phase of infection, bacterial circulation in the bloodstream often leads to positive blood cultures. However, as the infection progresses to the chronic stage, bacteria may become localized in various body tissues, resulting in negative blood cultures. During the sub-acute stage of disease, culture results are often negative [156]. Additional drawbacks of culture and isolation include that they are time-consuming, labor-intensive, require a BSL-3 laboratory, and pose a significant risk of infection to laboratory workers [165]. To address these challenges, molecular biological techniques, e.g., PCR, are frequently utilized to identify species and characterize strains of Brucella [30]. Although molecular tests are generally expected to have high sensitivity for most diseases, they do possess certain drawbacks in brucellosis testing. They may not identify an active infection, as they can detect a low bacterial count caused by DNA from dead bacteria [37]. The sensitivity of conventional PCR can fluctuate based on the sample type; for instance, the peripheral blood sample may not always contain an adequate amount of bacterial DNA for detection, particularly in chronic or latent cases, leading to reduced sensitivity. These limitations can be addressed by the use of real-time PCR, which provides improved analytical sensitivity and can detect lower levels of bacterial DNA more effectively in clinical samples [166,167].
The findings of this meta-analysis indicate that RBPT has a higher detection rate than CFT for diagnosing brucellosis in cattle and sheep. A similar trend is observed in goats, and when samples of different ruminant species are investigated. CFT has lower sensitivity but higher specificity compared to RBPT. As reported by [168], CFT has demonstrated the highest specificity and shown the fewest false positives. The high specificity of CFT is largely due to its detection of IgG antibodies only, as IgM is partially destroyed during the inactivation process [147]. Since CFT primarily detects IgG1 antibodies, the chances of cross-reactivity with other Gram-negative bacteria are minimized. In contrast, CFT exhibited a higher detection rate than RBPT for diagnosing brucellosis in camels. However, the dataset for this particular subgroup meta-analysis was not robust and comprised only two studies. It is important to note that in one of these studies, 60 out of 118 CFT-positive samples tested negative by other assays, including ELISA and PCR, and showed lower titers of 1:10 or 1:20, and rarely 1:40 [3]. CFT is technically a complex test, requiring careful titration of various test reagents and the inclusion of all control reagents in each test set. The test also has other limitations, including the need for heat-inactivated serum samples to prevent anti-complementary activity, a potential for prozone effects, and the subjective interpretation of results. Additionally, challenges such as the direct activation of the complement by serum (anti-complementary activity), inability to utilize hemolyzed serum samples, the need for well-equipped laboratories, and skilled personnel further complicate its application [144].
Generally, the sensitivity of CFT is lower than that of primary binding assays (ELISAs), which may be due to the fact that ELISA utilizes a protein G conjugate that detects immunoglobulin isotypes IgG1 and IgG2, whereas CFT detects IgG1 only. Additionally, ELISA has been found to detect IgG1 in lower amounts compared to CFT [169]. The CFT can yield false-negative reactions, probably due to hindrance caused by IgG2-type antibodies in complement fixation [170]. The ELISA has been reported to be an effective screening test, whether employed independently or in combination with the RBPT [143]. The competitive ELISA (cELISA) has been demonstrated to eliminate some but not all false-positive serological reactions (FPSRs) produced by cross-reacting microorganisms [171]. These assays avoid the effects of non-agglutinable antibodies. The FPA is a simpler and more cost-effective test than CFT and ELISAs, and can even be conducted outside a laboratory setting with relative ease [35,172]. The primary binding assays, such as ELISAs and the fluorescence polarization assay (FPA), offer comparable or superior diagnostic performance to CFT and are technically simpler and more robust, making them suitable options for use as either a screening or confirmatory tool [168].
In the current study, the febrile antigen Brucella agglutination test (FBAT) has a higher comparative detection rate than RBPT for diagnosing brucellosis in humans. The higher detection rate of FBAT when compared to RBPT in humans could be due to the following findings: FBAT has poor diagnostic specificity and can lead to false-positive reactions [65,173]. The high incidence of potentially false-positive test results has several implications. FBAT’s low positive predictive value has been identified as a factor contributing to frequent over-diagnosis [174]. The sensitivity and the specificity of FBAT are lower than those of RBPT. In comparison to FBAT, the RBPT offers high diagnostic accuracy and lower costs per sample, making it the preferred test for diagnosing brucellosis in humans [44,65].
The sensitivity analysis and subgroup meta-analyses by study quality indicated that study quality had limited influence on the overall estimates and did not substantially alter the direction or significance of the findings. This consistency across quality strata enhances the robustness and generalizability of the pooled estimates. However, in cattle, study quality significantly influenced the results, implying that methodological rigor may impact the diagnostic performance estimates. Furthermore, the persistence of significant subgroup differences across diagnostic tests indicates that variability in test performance is inherent and not solely attributable to study quality. This highlights the need for careful selection and validation of diagnostic tools in future brucellosis research and surveillance efforts.
5. Conclusions
According to the findings of this meta-analysis, primary binding assays should be preferred for large-scale screening of brucellosis in both humans and animals due to their ability to detect more positive cases (a higher comparative detection rate), followed by the RBPT and slow agglutination tests. However, their applicability may vary by host species, epidemiological context, and resource availability. Culture and PCR methods, while definitive, show variable detection rates and were less frequently reported in the included studies. Since no single test proved universally optimal, there is a need for context-specific diagnostic strategies and combined testing approaches. Future studies should aim for standardized reporting of test combinations and relevant contextual factors to enable more tailored and effective diagnostic strategies for brucellosis control.
6. Limitations
This meta-analysis, while comprehensive, is subject to certain limitations that should be acknowledged. Firstly, the use of the RBPT as the primary control in most comparisons, rather than bacterial culture, the gold standard for diagnosing brucellosis, is likely to influence the accuracy of relative risk estimations. While RBPT is widely employed due to its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, its limitations in sensitivity and specificity as compared to culture may affect comparative evaluations. Furthermore, there was significant heterogeneity across the majority of our results. We performed subgroup analyses to better understand the sources of heterogeneity; however, due to the limited number of studies in the majority of subgroups, results should be interpreted with caution, particularly those that had fewer than two studies or with small sample sizes. Variability in diagnostic test protocols, interpretation criteria, and reagent sources further contributes to inter-study differences. These factors collectively emphasize the need for cautious interpretation of the findings and underscore the importance of standardized diagnostic practices in future studies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/vetsci12070638/s1, Table S1: Comprehensive list of records included in the meta-analysis; Figure S1: The tests used for diagnosing brucellosis in humans and animals; Figure S2: Species-wise funnel plots illustrating the publication bias among studies included in the meta-analysis; Figure S3: The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of various tests [experimental] compared with five different test groups [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in cattle; Figure S4:. The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of 5 different test groups [experimental] compared with the Rose Bengal plate test (RBPT) [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in buffaloes; Figure S5: The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of various tests [experimental] compared to three different test groups [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in buffaloes; Figure S6: The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of various tests [experimental] compared to four different test groups [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in goats; Figure S7: The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of various tests [experimental] compared with five different test groups [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in sheep; Figure S8: The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of four different test groups [experimental] compared with the Rose Bengal plate test RBPT [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in samples of multi-species (ruminants); Figure S9: The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of various tests [experimental] compared with three different test groups [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in samples of multi-species (ruminants); Figure S10: The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of two different test groups [experimental] compared with the Rose Bengal plate test (RBPT) [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in pigs; Figure S11: The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of five different test groups [experimental] compared with the Rose Bengal plate test (RBPT) [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in dogs; Figure S12: The forest plot represents the relative risk (RR) of various diagnostic tests [experimental] compared with five different diagnostic test groups [control] for diagnosing brucellosis in dogs; Figure S13: The forest plot represents the subgroup meta-analysis by study quality, with RBPT as reference (control), in humans; Figure S14: The forest plot represents the subgroup meta-analysis by study quality, with RBPT as reference (control), in cattle; Figure S15: The forest plot represents the subgroup meta-analysis by study quality, with RBPT as reference (control), in goats; Figure S16: The forest plot represents the subgroup meta-analysis by study quality, with RBPT as reference (control), in sheep; Figure S17: The forest plot depicts the sensitivity analysis based on high-quality studies, with RBPT as reference (control), in humans; Figure S18: The forest plot depicts the sensitivity analysis based on high-quality studies, with RBPT as reference (control), in cattle; Figure S19: The forest plot depicts the sensitivity analysis based on high-quality studies, with RBPT as reference (control), in goats; Figure S20: The forest plot depicts the sensitivity analysis based on high-quality studies, with RBPT as reference (control), in sheep [175,176,177,178,179,180,181,182,183,184,185,186,187,188,189,190,191,192,193,194,195,196,197,198,199,200,201,202,203,204,205,206,207,208,209,210,211,212,213,214].
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.F., A.U.K. and H.N.; methodology, A.H., R.K., S.N. and M.A.H.; formal analysis, A.H. and S.N.; data acquisition, R.K., S.N. and M.A.H.; writing—original draft preparation, S.N. and R.K.; writing—review and editing, A.U.K., M.F., A.H., H.E.-A. and H.N.; supervision, A.U.K., M.F., H.E.-A. and H.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Fretin, D.; Fauconnier, A.; Köhler, S.; Halling, S.; Léonard, S.; Nijskens, C.; Ferooz, J.; Lestrate, P.; Delrue, R.M.; Danese, I.; et al. The sheathed flagellum of Brucella melitensis is involved in persistence in a murine model of infection. Cell. Microbiol. 2005, 7, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, M.J.; Ballem, A.; Queiroga, C.; Fernandes, C. Etiology: The Genus Brucella. In Brucellosis in Goats and Sheep: An Endemic and Re-Emerging Old Zoonosis in the 21st Century; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 21–58. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, A.U.; Sayour, A.E.; Melzer, F.; El-Soally, S.; Elschner, M.C.; Shell, W.S.; Moawad, A.A.; Mohamed, S.A.; Hendam, A.; Roesler, U.; et al. Seroprevalence and Molecular Identification of Brucella spp. in Camels in Egypt. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weese, J.S.; Weese, H.E. Brucellosis in humans caused by Brucella canis: A scoping review. Can. Vet. J. 2025, 66, 327–334. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho Neta, A.V.; Mol, J.P.; Xavier, M.N.; Paixão, T.A.; Lage, A.P.; Santos, R.L. Pathogenesis of bovine brucellosis. Vet. J. 2010, 184, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.; Khan, A. Epidemiology and epizootology of brucellosis: A review. Pak. Vet. J. 2007, 27, 145. [Google Scholar]
- Akinyemi, K.O.; Fakorede, C.O.; Amisu, K.O.; Wareth, G. Human and Animal Brucellosis in Nigeria: A Systemic Review and Meta-Analysis in the Last Twenty-One Years (2001–2021). Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxie, G. Jubb, Kennedy & Palmer’s Pathology of Domestic Animals; Elsevier Health Sciences: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Godfroid, J.; Garin-Bastuji, B.; Saegerman, C.; Blasco, J.M. Brucellosis in terrestrial wildlife. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2013, 32, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meltzer, E.; Sidi, Y.; Smolen, G.; Banai, M.; Bardenstein, S.; Schwartz, E. Sexually transmitted brucellosis in humans. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2010, 51, e12–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Espinoza, G.; Arce-Gorvel, V.; Mémet, S.; Gorvel, J.P. Brucella: Reservoirs and Niches in Animals and Humans. Pathogens 2021, 10, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Urushadze, L.; Osikowicz, L.; McKee, C.; Kuzmin, I.; Kandaurov, A.; Babuadze, G.; Natradze, I.; Imnadze, P.; Kosoy, M. Molecular Survey of Bacterial Zoonotic Agents in Bats from the Country of Georgia (Caucasus). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Li, C.; Gao, A.; Jiang, N.; Feng, X.; Li, J.; Hu, W. Evidence-practice gap analysis in the role of tick in brucellosis transmission: A scoping review. Infect. Dis. Poverty 2024, 13, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urge, B.; Tadele, M.; Siyoum, T. Infestation of ectoparasites in dairy calves reared by smallholder farmers in central areas of Ethiopia. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2020, 10, 20016–20020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, F.M. The pathogenesis and pathobiology of Brucella infection in domestic animals. Anim. Brucell. 1990, 301, 320. [Google Scholar]
- Suresh, K.P.; Patil, S.S.; Nayak, A.; Dhanze, H.; Rajamani, S.; Shivamallu, C.; Cull, C.A.; Amachawadi, R.G. Prevalence of brucellosis in livestock of African and Asian continents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 923657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, R.P.; Magnusson, U.; Grace, D.; Lindahl, J. Bovine brucellosis: Prevalence, risk factors, economic cost and control options with particular reference to India- a review. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2018, 8, 1556548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capparelli, R.; Parlato, M.; Iannaccone, M.; Roperto, S.; Marabelli, R.; Roperto, F.; Iannelli, D. Heterogeneous shedding of Brucella abortus in milk and its effect on the control of animal brucellosis. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 106, 2041–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, C.R.; Cotrim de Almeida, J.V.F.; Cardoso de Oliveira, I.R.; Faria de Oliveira, L.; Pereira, L.J.; Zangerônimo, M.G.; Lage, A.P.; Dorneles, E.M.S. Occupational exposure to Brucella spp.: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kydyshov, K.; Usenbaev, N.; Sharshenbekov, A.; Aitkuluev, N.; Abdyraev, M.; Chegirov, S.; Kazybaeva, J.; Brangsch, H.; Melzer, F.; Neubauer, H.; et al. Brucellosis in Humans and Animals in Kyrgyzstan. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareth, G.; Dadar, M.; Ali, H.; Hamdy, M.E.R.; Al-Talhy, A.M.; Elkharsawi, A.R.; Tawab, A.; Neubauer, H. The perspective of antibiotic therapeutic challenges of brucellosis in the Middle East and North African countries: Current situation and therapeutic management. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2022, 69, e1253–e1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantur, B.; Amarnath, S.; Shinde, R. Review of clinical and laboratory features of human brucellosis. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 25, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skendros, P.; Pappas, G.; Boura, P. Cell-mediated immunity in human brucellosis. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodur, H.; Erbay, A.; Akinci, E.; Colpan, A.; Cevik, M.A.; Balaban, N. Neurobrucellosis in an endemic area of brucellosis. Scand. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 35, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohn, A.H.; Probert, W.S.; Glaser, C.A.; Gupta, N.; Bollen, A.W.; Wong, J.D.; Grace, E.M.; McDonald, W.C. Human neurobrucellosis with intracerebral granuloma caused by a marine mammal Brucella spp. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2003, 9, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, W.L.; Jamaludin, R.; Mackereth, G.; Hansen, M.; Humphrey, S.; Short, P.; Taylor, T.; Swingler, J.; Dawson, C.E.; Whatmore, A.M.; et al. Characterization of a Brucella sp. strain as a marine-mammal type despite isolation from a patient with spinal osteomyelitis in New Zealand. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 4363–4370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bonaventura, G.; Angeletti, S.; Ianni, A.; Petitti, T.; Gherardi, G. Microbiological Laboratory Diagnosis of Human Brucellosis: An Overview. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, A.U.; Melzer, F.; Hendam, A.; Sayour, A.E.; Khan, I.; Elschner, M.C.; Younus, M.; Ehtisham-Ul-Haque, S.; Waheed, U.; Farooq, M.; et al. Seroprevalence and Molecular Identification of Brucella spp. in Bovines in Pakistan-Investigating Association With Risk Factors Using Machine Learning. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 594498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, G.N.; Tuon, F.F. Comparative study of IS711 and bcsp31-based polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for the diagnosis of human brucellosis in whole blood and serum samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2021, 183, 106182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnova, E.; Vasin, A.; Sandybaev, N.; Klotchenko, S.; Plotnikova, M.; Chervyakova, O.; Sansyzbay, A.; Kiselev, O. Current methods of human and animal brucellosis diagnostics. Adv. Infect. Dis. 2013, 3, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagupsky, P.; Morata, P.; Colmenero, J.D. Laboratory Diagnosis of Human Brucellosis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 33, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araj, G.F. Update on laboratory diagnosis of human brucellosis. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 36 (Suppl. 1), S12–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfroid, J.; Nielsen, K.; Saegerman, C. Diagnosis of brucellosis in livestock and wildlife. Croat. Med. J. 2010, 51, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, M.; Nieto, J.; Rosa, C.; Geijo, P.; Escribano, M.; Munoz, A.; López, C. Evaluation of seven tests for diagnosis of human brucellosis in an area where the disease is endemic. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2008, 15, 1031–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, R.S.; Oliveira, M.M.; Bueno Filho, J.S.S.; Ferreira, F.; Godfroid, J.; Lage, A.P.; Dorneles, E.M.S. Accuracy of serological tests for bovine brucellosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2024, 222, 106079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Grady, D.; Byrne, W.; Kelleher, P.; O’Callaghan, H.; Kenny, K.; Heneghan, T.; Power, S.; Egan, J.; Ryan, F. A comparative assessment of culture and serology in the diagnosis of brucellosis in dairy cattle. Vet. J. 2014, 199, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, M.L.; Machado de Assis, T.S.; Silva, S.N.; Cota, G. Diagnosis of human brucellosis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2024, 18, e0012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, M.S.; Mushtaq, M.H.; Rehman, A. A systematic review and meta-analysis study to evaluate the accuracy of various PCR methods for diagnosing brucellosis in animals and humans. Heliyon 2025, 11, e42728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, P.M.; Deeks, J.J.; Leeflang, M.M.; Takwoingi, Y.; Flemyng, E. Evaluating medical tests: Introducing the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Diagnostic Test Accuracy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2023, 7, Ed000163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA Statement. Open Med. 2009, 3, e123–e130. [Google Scholar]
- Moola, S.; Munn, Z.; Tufanaru, C.; Aromataris, E.; Sears, K.; Sfetcu, R.; Currie, M.; Qureshi, R.; Mattis, P.; Lisy, K.; et al. Chapter 7: Systematic reviews of etiology and risk. In JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis; Aromataris, E., Munn, Z., Eds.; JBI: Adelaide, Australia, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Poester, F.P.; Nielsen, K.; Samartino, L.E.; Yu, W.L. Diagnosis of brucellosis. Open Vet. Sci. J. 2010, 4, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waringa, N.M.A.; Waiboci, L.W.; Bebora, L.; Kinyanjui, P.W.; Kosgei, P.; Kiambi, S.; Osoro, E. Human brucellosis in Baringo County, Kenya: Evaluating the diagnostic kits used and identifying infecting Brucella species. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0269831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alumasa, L.; Thomas, L.F.; Amanya, F.; Njoroge, S.M.; Moriyón, I.; Makhandia, J.; Rushton, J.; Fèvre, E.M.; Falzon, L.C. Hospital-based evidence on cost-effectiveness of brucellosis diagnostic tests and treatment in Kenyan hospitals. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0008977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almashhadany, D.A.; Fetehallah Zefenkey, Z.; Naji Ahmed Odhah, M. Epidemiological study of human brucellosis among febrile patients in Erbil-Kurdistan region, Iraq. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2022, 16, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, G.; Luo, P.; He, Z.; Hu, F.; Li, L.; Allain, J.P.; Li, C.; Wang, W. Detection of Brucellae in peripheral blood mononuclear cells for monitoring therapeutic efficacy of brucellosis infection. Antimicrob. Resist. Infect. Control 2019, 8, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, T.K.; Urge, B.; Mamo, G. Seroprevalence of human brucellosis in selected sites of Central Oromia, Ethiopia. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obaidat, M.M.; Malania, L.; Arner, R.J.; Roess, A.A. Seroprevalence and risk factors for Brucella infections in Jordan. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2022, 107, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, B.; Rahman, H.U.; Islam, Z.U.; Rehman, S.U.; Rashid, A. Seroepidemiological analysis of brucellosis in goat and household animal keepers of District Swat. Egypt. J. Vet. Sci. 2022, 53, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy, K.; Thompson, P.N.; Harris, B.N.; Rossouw, J.; Abernethy, D.A.; Etter, E.M.C. Bovine Brucellosis in Gauteng, South Africa: Seroprevalence amongst Cattle Handlers and Variables Associated with Seropositive Cattle Herds, 2014–2016. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, S.P.; Kalorey, D.R.; Awandkar, S.P.; Kurkure, N.V.; Narang, R.; Kashyap, R.S.; Rahi, M.; Barbuddhe, S.B. Journey towards National Institute of One Health in India. Indian J. Med. Res. 2021, 153, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proch, V.; Singh, B.B.; Schemann, K.; Gill, J.P.S.; Ward, M.P.; Dhand, N.K. Risk factors for occupational Brucella infection in veterinary personnel in India. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2018, 65, 791–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.K.; Kotwal, S.K.; Singh, D.K.; Malik, M.A.; Kumar, A.; Rajagunalan; Singh, M. Seroprevalence of human brucellosis in and around Jammu, India, using different serological tests. Vet. World 2016, 9, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germeraad, E.A.; Hogerwerf, L.; Faye-Joof, T.; Goossens, B.; van der Hoek, W.; Jeng, M.; Lamin, M.; Manneh, I.L.; Nwakanma, D.; Roest, H.I.; et al. Low Seroprevalence of Brucellosis in Humans and Small Ruminants in the Gambia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangalgi, S.S.; Sajjan, A.G.; Mohite, S.T.; Gajul, S. Brucellosis in Occupationally Exposed Groups. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, Dc24–Dc27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangalgi, S.S.; Sajjan, A.G.; Mohite, S.T.; Kakade, S.V. Serological, Clinical, and Epidemiological Profile of Human Brucellosis in Rural India. Indian J. Community Med. 2015, 40, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüksekkaya, S.; Aras, Z.; Uçan, U.S. Investigation of Brucella canis Seroprevalence in Brucellosis Suspected Cases. Mikrobiyol. Bul. 2013, 47, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priyadarshini, A.; Sarangi, L.; Palai, T.; Panda, H.; Mishra, R.; Behera, P. Brucellosis in cattle and occupationally exposed human beings: A serosurvey in Odisha, India. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2013, 7, 3255–3260. [Google Scholar]
- Din, A.; Khan, S.; Ahmad, I.; Rind, R.; Hussain, T.; Shahid, M.; Ahmed, S. A study on the seroprevalence of brucellosis in human and goat populations of district Bhimber, Azad Jammu and Kashmir. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2013, 23, 113–118. [Google Scholar]
- Yousaf, R.; Khan, I.; Shehzad, W.; Hussain, R.; Ali, S.; Neubauer, H.; Wareth, G. Seroprevalence and Molecular Detection of Brucellosis in Hospitalized Patients in Lahore Hospitals, Pakistan. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2021, 13, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, R.; Ali, T.; Waheed, U.; Asif, M.; Khan, Q.M. Application of serum based PCR and fluorescence polarization assay for diagnosis of brucellosis among people occupationally at risk to disease. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2016, 18, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadmus, S.; Salam, S.P.; Adesokan, H.K.; Akporube, K.; Ola-Daniel, F.; Awosanya, E.J. Seroprevalence of brucellosis and Q fever infections amongst pastoralists and their cattle herds in Sokoto State, Nigeria. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0254530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghugey, S.L.; Setia, M.S.; Deshmukh, J.S. Human brucellosis: Seroprevalence and associated exposure factors among the rural population in Nagpur, Maharashtra, India. J. Family Med. Prim. Care 2021, 10, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.A.; Hassan-Kadle, A.A.; Ibrahim, A.M.; Hassan-Kadle, M.A.; Yasin, A.M.; Khojaly, M.; Garcia, J.L.; Vieira, R.F.C. Prevalence of Anti-Toxoplasma gondii and Anti-Brucella Spp. Antibodies in Pregnant Women From Mogadishu, Somalia. Front. Reprod. Health 2021, 3, 672885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukambagire, A.S.; Mendes, Â.J.; Bodenham, R.F.; McGiven, J.A.; Mkenda, N.A.; Mathew, C.; Rubach, M.P.; Sakasaka, P.; Shayo, D.D.; Maro, V.P.; et al. Performance characteristics and costs of serological tests for brucellosis in a pastoralist community of northern Tanzania. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holt, H.R.; Bedi, J.S.; Kaur, P.; Mangtani, P.; Sharma, N.S.; Gill, J.P.S.; Singh, Y.; Kumar, R.; Kaur, M.; McGiven, J.; et al. Epidemiology of brucellosis in cattle and dairy farmers of rural Ludhiana, Punjab. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyua, P.; Osoro, E.; Hunsperger, E.; Ngere, I.; Muturi, M.; Mwatondo, A.; Marwanga, D.; Ngere, P.; Tiller, R.; Onyango, C.O.; et al. High incidence of human brucellosis in a rural Pastoralist community in Kenya, 2015. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangtani, P.; Berry, I.; Beauvais, W.; Holt, H.R.; Kulashri, A.; Bharti, S.; Sagar, V.; Nguipdop-Djomo, P.; Bedi, J.; Kaur, M.; et al. The prevalence and risk factors for human Brucella species infection in a cross-sectional survey of a rural population in Punjab, India. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2020, 114, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madut, N.A.; Muwonge, A.; Nasinyama, G.W.; Muma, J.B.; Godfroid, J.; Jubara, A.S.; Muleme, J.; Kankya, C. The sero-prevalence of brucellosis in cattle and their herders in Bahr el Ghazal region, South Sudan. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awah-Ndukum, J.; Mouiche, M.M.M.; Kouonmo-Ngnoyum, L.; Bayang, H.N.; Manchang, T.K.; Poueme, R.S.N.; Kouamo, J.; Ngu-Ngwa, V.; Assana, E.; Feussom, K.J.M.; et al. Seroprevalence and risk factors of brucellosis among slaughtered indigenous cattle, abattoir personnel and pregnant women in Ngaoundéré, Cameroon. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirima, G.M.; Kunda, J.S. Prevalence of brucellosis in the human, livestock and wildlife interface areas of Serengeti National Park, Tanzania. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2016, 83, a1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, A.S.; Bonfoh, B.; Kulo, A.E.; Boukaya, G.A.; Amidou, M.; Hattendorf, J.; Pilo, P.; Schelling, E. Epidemiology of brucellosis and q Fever in linked human and animal populations in northern togo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aworh, M.K.; Okolocha, E.; Kwaga, J.; Fasina, F.; Lazarus, D.; Suleman, I.; Poggensee, G.; Nguku, P.; Nsubuga, P. Human brucellosis: Seroprevalence and associated exposure factors among abattoir workers in Abuja, Nigeria—2011. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2013, 16, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niaz, S.; Raqeeb, A.; Khan, A.; Nasreen; Amir, S.; Zhu, L.; Kumar, S. Status of human brucellosis in district Malakand, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. J. Infect. Public Health 2021, 14, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbarnia, L.; Farajnia, S.; Naghili, B.; Saeedi, N. Comparative Evaluation of Nested Polymerase Chain Reaction for Rapid Diagnosis of Human Brucellosis. Arch. Razi Inst. 2021, 76, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keramat, F.; Majzobi, M.M.; Poorolajal, J.; Ghane, Z.Z.; Adabi, M. Seroprevalence of Brucellosis in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infected Patients in Hamadan, Iran. Osong Public Health Res. Perspect. 2017, 8, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.Z.; Tahir Usman, T.U.; Ummer Sadique, U.S.; Qureshi, M.S.; Hassan, M.F.; Muhammad Shahid, M.S.; Adnan Khan, A.K. Molecular characterization of Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis in cattle and humans at the North West of Pakistan. Pak. Vet. J. 2017, 37, 360–363. [Google Scholar]
- Purwar, S.; Metgud, S.C.; Mutnal, M.B.; Nagamoti, M.B.; Patil, C.S. Utility of Serological Tests in the Era of Molecular Testing for Diagnosis of Human Brucellosis in Endemic Area with Limited Resources. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2016, 10, Dc26–Dc29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asif, M.; Waheed, U.; Farooq, M.; Ali, T.; Khan, Q.M. Frequency of Brucellosis in High Risk Human Groups in Pakistan Detected through Polymerase Chain Reaction and its Comparison with Conventional Slide Agglutination Test. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2014, 16, 986–990. [Google Scholar]
- Peeridogaheh, H.; Golmohammadi, M.G.; Pourfarzi, F. Evaluation of ELISA and Brucellacapt tests for diagnosis of human Brucellosis. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2013, 5, 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, M.; Paul, S.K.; Haque, N.; Ahmad, F.U.; Mazid, R.; Al Amin, M.M.; Aziz, M.A.; Paul, A.; Ahmed, S.; Nasreen, S.A.; et al. Seropositivity of Human Brucellosis among Patients with Pyrexia of Unknown Origin on Both Risk and Non-Risk Group of Individuals and Molecular Detection by Real-time PCR. Mymensingh Med. J. 2021, 30, 936–942. [Google Scholar]
- Kalule, J.B.; Tomusange, J.; Namatovu, T. Serological detection of brucellosis among febrile, malaria-negative children and domesticated dogs in an urban African setting. Afr. J. Lab. Med. 2020, 9, 864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschopp, R.; Gebregiorgis, A.; Tassachew, Y.; Andualem, H.; Osman, M.; Waqjira, M.W.; Hattendorf, J.; Mohammed, A.; Hamid, M.; Molla, W.; et al. Integrated human-animal sero-surveillance of Brucellosis in the pastoral Afar and Somali regions of Ethiopia. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubanga, M.; Mfune, R.L.; Kothowa, J.; Mohamud, A.S.; Chanda, C.; McGiven, J.; Bumbangi, F.N.; Hang’ombe, B.M.; Godfroid, J.; Simuunza, M.; et al. Brucella Seroprevalence and Associated Risk Factors in Occupationally Exposed Humans in Selected Districts of Southern Province, Zambia. Front. Public. Health 2021, 9, 745244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damke, S.S.; Damke, S.G. Seroprevalence of Brucella agglutinins in patients with pyrexia of unknown origin attending a tertiary care rural hospital. J. Evol. Med. 2020, 3, 162–165. [Google Scholar]
- DHASON, T.; SUBRAMANIAN, M.; MANI, A.; AURLENE, N. Seroprevalence of Anti-Brucella Antibodies IgG and IgM in Acute Polyarthritis in a Tertiary Care Center in Southern India. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2019, 13, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elhaig, M.M.; Wahdan, A. Seroprevalence, associated risk factors, and molecular detection of bovine brucellosis in rural areas of Egypt. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2023, 95, 101971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abnaroodheleh, F.; Emadi, A.; Dashtipour, S.; Jamil, T.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A.; Dadar, M. Shedding rate of Brucella spp. in the milk of seropositive and seronegative dairy cattle. Heliyon 2023, 9, e15085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Hussain, A.; Aziz, M.U.; Song, B.; Zeb, J.; Hasib, F.M.Y.; Li, J.; Rehman, A.; George, D.; Cabezas-Cruz, A.; et al. First serological evidence of Q fever in large ruminants and its associated risk factors in Punjab, Pakistan. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, S.; Barua, S.R.; Moni, S.P.; Islam, A.; Rahman, A.; Chowdhury, S. Seroprevalence and risk factors for bovine brucellosis in the Chittagong Metropolitan Area of Bangladesh. Vet. Med. Sci. 2021, 7, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.R.; Rehman, A.; Khalid, S.; Ahmad, M.U.D.; Avais, M.; Sarwar, M.; Awan, F.N.; Melzer, F.; Neubauer, H.; Jamil, T. Seroprevalence and Associated Risk Factors of Bovine Brucellosis in District Gujranwala, Punjab, Pakistan. Animals 2021, 11, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathiriya, J.B.; Shah, N.M.; Trangadia, B.J.; Bhedi, K.R.; Sindhi, S.H.; Montagnaro, S. Evaluation of lateral flow assay as a field test for sero-diagnosis of bovine brucellosis. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 2021, 91, 1050–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidu, A.S.; Mahajan, N.K.; Musallam, I.I.; Holt, H.R.; Guitian, J. Epidemiology of bovine brucellosis in Hisar, India: Identification of risk factors and assessment of knowledge, attitudes, and practices among livestock owners. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2021, 53, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, X.; Cui, B.; Shao, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yang, Q.; Song, S.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Abortion and various associated risk factors in dairy cow and sheep in Ili, China. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0232568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fero, E.; Juma, A.; Koni, A.; Boci, J.; Kirandjiski, T.; Connor, R.; Wareth, G.; Koleci, X. The seroprevalence of brucellosis and molecular characterization of Brucella species circulating in the beef cattle herds in Albania. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukwueze, K.O.; Ishola, O.O.; Dairo, M.D.; Awosanya, E.J.; Cadmus, S.I. Seroprevalence of brucellosis and associated factors among livestock slaughtered in Oko-Oba abattoir, Lagos State, southwestern Nigeria. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2020, 36, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadmus, S.I.; Akporube, K.A.; Ola-Daniel, F.; Adelakun, O.D.; Akinseye, V.O. Seroprevalence and associated factors of brucellosis and Q-fever in cattle from Ibarapa area, Oyo State, South-western Nigeria. Pan Afr. Med. J. 2020, 36, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Azeem, M.; Hafeez, M.; Ashraf, K.; Asif, K.; Ali, A.; Ashfaq, H.; Shehzad, W.; Imran, M.; Tayyub, M. Comparison of molecular and serological tests for detection of Brucella abortus in asymptomatic bovine breeding bulls. JAPSJ. Anim. Plant Sci. 2020, 30. [Google Scholar]
- ElTahir, Y.; Al-Farsi, A.; Al-Marzooqi, W.; Al-Toobi, A.; Gaafar, O.M.; Jay, M.; Corde, Y.; Bose, S.; Al-Hamrashdi, A.; Al-Kharousi, K.; et al. Investigation on Brucella infection in farm animals in Saham, Sultanate of Oman with reference to human brucellosis outbreak. BMC Vet. Res. 2019, 15, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzon, L.C.; Traoré, S.; Kallo, V.; Assamoi, J.B.; Bonfoh, B.; Schelling, E. Evaluation of the Fluorescence Polarization Assay as a Rapid On-Spot Test for Ruminant Brucellosis in Côte d’Ivoire. Front. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioia, G.; Vinueza, R.L.; Cruz, M.; Jay, M.; Corde, Y.; Marsot, M.; Zanella, G. Estimating the probability of freedom from bovine brucellosis in the Galapagos Islands. Epidemiol. Infect. 2018, 147, e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogugua, A.J.; Akinseye, V.O.; Cadmus, E.O.; Jolaoluwa Awosanya, E.A.; Alabi, P.I.; Idowu, O.S.; Akinade, S.A.; Dale, E.J.; Perrett, L.; Taylor, A.; et al. Prevalence and risk factors associated with bovine brucellosis in herds under extensive production system in southwestern Nigeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 1573–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamu, S.G.; Kabir, J.; Umoh, J.U.; Raji, M.A. Seroprevalence of brucellosis and Q fever (Coxiellosis) in cattle herds in Maigana and Birnin Gwari agro-ecological zone of Kaduna State, Nigeria. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkallah, M.; Gharbi, Y.; Zormati, S.; Karkouch, N.; Mallek, Z.; Gautier, M.; Gdoura, R.; Fendri, I. A mixed methods study of ruminant brucellosis in central-eastern Tunisia. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2017, 49, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aworh, M.K.; Okolocha, E.C.; Awosanya, E.J.; Fasina, F.O. Sero-prevalence and intrinsic factors associated with Brucella infection in food animals slaughtered at abattoirs in Abuja, Nigeria. BMC Res. Notes 2017, 10, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjaneyareddy, K.B.; Muniveerappa, V.B.; ISLOOR, S.; Gowda, L.; Kamran, C.; Gomes, A.R.; Kalleshamurthy, T.; Shankaranarayana, P.B.; Shome, R. Comparative evaluation of blood based lateral flow assay for diagnosis of brucellosis in livestock species. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 87, 1068–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, A.D.; Dubal, Z.B.; Karunakaran, M.; Doijad, S.P.; Raorane, A.V.; Dhuri, R.B.; Bale, M.A.; Chakurkar, E.B.; Kalorey, D.R.; Kurkure, N.V.; et al. Apparent seroprevalence, isolation and identification of risk factors for brucellosis among dairy cattle in Goa, India. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2016, 47, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praud, A.; Durán-Ferrer, M.; Fretin, D.; Jaÿ, M.; O’Connor, M.; Stournara, A.; Tittarelli, M.; Travassos Dias, I.; Garin-Bastuji, B. Evaluation of three competitive ELISAs and a fluorescence polarisation assay for the diagnosis of bovine brucellosis. Vet. J. 2016, 216, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwida, M.; El-Ashker, M.; Melzer, F.; El-Diasty, M.; El-Beskawy, M.; Neubauer, H. Use of serology and real time PCR to control an outbreak of bovine brucellosis at a dairy cattle farm in the Nile Delta region, Egypt. Ir. Vet. J. 2015, 69, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareth, G.; Melzer, F.; Tomaso, H.; Roesler, U.; Neubauer, H. Detection of Brucella abortus DNA in aborted goats and sheep in Egypt by real-time PCR. BMC Res. Notes 2015, 8, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, C.; Stokstad, M.; Johansen, T.B.; Klevar, S.; Mdegela, R.H.; Mwamengele, G.; Michel, P.; Escobar, L.; Fretin, D.; Godfroid, J. First isolation, identification, phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Brucella abortus biovar 3 from dairy cattle in Tanzania. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abakar, M.F.; Naré, N.B.; Schelling, E.; Hattendorf, J.; Alfaroukh, I.O.; Zinsstag, J. Seroprevalence of Rift Valley fever, Q fever, and brucellosis in ruminants on the southeastern shore of Lake Chad. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2014, 14, 757–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szulowski, K.; Iwaniak, W.; Weiner, M.; Złotnicka, J. Brucella suis biovar 2 isolations from cattle in Poland. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2013, 20, 672–675. [Google Scholar]
- Batrinou, A.; Strati, I.F.; Tsantes, A.G.; Papaparaskevas, J.; Dimou, I.; Vourvidis, D.; Kyrma, A.; Antonopoulos, D.; Halvatsiotis, P.; Houhoula, D. The Importance of Complementary PCR Analysis in Addition to Serological Testing for the Detection of Transmission Sources of Brucella spp. in Greek Ruminants. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akoko, J.M.; Pelle, R.; Lukambagire, A.S.; Machuka, E.M.; Nthiwa, D.; Mathew, C.; Fèvre, E.M.; Bett, B.; Cook, E.A.J.; Othero, D.; et al. Molecular epidemiology of Brucella species in mixed livestock-human ecosystems in Kenya. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samkange, A.; van der Westhuizen, J.; Voigts, A.S.; Chitate, F.; Kaatura, I.; Khaiseb, S.; Hikufe, E.H.; Kabajani, J.; Bishi, A.S.; Mbiri, P.; et al. Investigation of the outbreaks of abortions and orchitis in livestock in Namibia during 2016–2018. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2022, 54, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakooza, S.; Watuwa, J.; Ipola, P.A.; Munyiirwa, D.F.N.; Kayaga, E.; Nabatta, E.; Mahero, M.; Ssajjakambwe, P.; Kaneene, J.B. Seromonitoring of brucellosis in goats and sheep slaughtered at an abattoir in Kampala, Uganda. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2022, 34, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tialla, D. The first study on seroprevalence and risk factors for zoonotic transmission of ovine and caprine brucellosis in the Province of Bam, Burkina Faso. Vet. World 2022, 15, 262–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munsi, M.N.; Akther, S.; Rahman, M.H.; Hassan, M.Z.; Ali, M.Z.; Ershaduzzaman, M. Seroprevalence of Brucellosis in goats in some selected areas of Bangladesh. J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2021, 8, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abnaroodheleh, F.; Emadi, A.; Dadar, M. Seroprevalence of brucellosis and chlamydiosis in sheep and goats with history of abortion in Iran. Small Rumin. Res. 2021, 202, 106459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awandkar, S.; Kale, S.; Sonekar, C.; Gabhane, G.; Chaudhari, S.; Kurkure, N. Gynaecological disorders associated with Brucella melitensis in goat flocks with potential risk of occupational zoonoses in Central India. Curr. Sci. 2021, 120, 1912–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanani, A.; Dabhi, S.; Patel, Y.; Chandra, V.; Kumar, O.R.V.; Shome, R. Seroprevalence of brucellosis in small ruminants in organized and unorganized sectors of Gujarat state, India. Vet. World 2018, 11, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElTahir, Y.; Al Toobi, A.G.; Al-Marzooqi, W.; Mahgoub, O.; Jay, M.; Corde, Y.; Al Lawati, H.; Bose, S.; Al Hamrashdi, A.; Al Kharousi, K.; et al. Serological, cultural and molecular evidence of Brucella melitensis infection in goats in Al Jabal Al Akhdar, Sultanate of Oman. Vet. Med. Sci. 2018, 4, 190–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.F.; Pessoa, M.S.; Guimarães, L.B.; Faria, A.K.; Morão, R.P.; Mol, J.P.; Garcia, L.N.; Almeida, A.C.; Gouveia, A.M.; Silva, M.X.; et al. Serologic and molecular evidence of Brucella ovis infection in ovine and caprine flocks in the State of Minas Gerais, Brazil. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linderot de Cardona, K.; De Gracia Scanapieco, A.; Braun, P.G. First results on small ruminant brucellosis and tuberculosis and caprine arthritis-encephalitis in El Salvador. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2016, 48, 1083–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadhu, D.B.; Panchasara, H.H.; Chauhan, H.C.; Sutariya, D.R.; Parmar, V.L.; Prajapati, H.B. Seroprevalence and comparison of different serological tests for brucellosis detection in small ruminants. Vet. World 2015, 8, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.K.; Saegerman, C.; Berkvens, D.; Fretin, D.; Gani, M.O.; Ershaduzzaman, M.; Ahmed, M.U.; Emmanuel, A. Bayesian estimation of true prevalence, sensitivity and specificity of indirect ELISA, Rose Bengal Test and Slow Agglutination Test for the diagnosis of brucellosis in sheep and goats in Bangladesh. Prev. Vet. Med. 2013, 110, 242–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandi, S.; Pfukenyi, D.M.; Matope, G.; Murondoti, A.; Tivapasi, M.; Ndengu, M.; Scacchia, M.; Bonfini, B.; De Garine-Wichatitsky, M. Brucellosis and chlamydiosis seroprevalence in goats at livestock-wildlife interface areas of Zimbabwe. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2019, 86, e1–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonekar, C.P.; Kale, S.; Bhoyar, S.; Paliwal, N.; Shinde, S.V.; Awandkar, S.P.; Khan, W.; Chaudhari, S.P.; Kurkure, N.V. Brucellosis in migratory sheep flock from Maharashtra, India. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2018, 50, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shome, R.; Sahay, S.; Triveni, K.; Krithiga, N.; Shome, B.; Rahman, H. Evidence of ovine brucellosis due to Brucella ovis and Brucella melitensis in Karnataka, India. Indian J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 88, 522–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiasconaro, M.; Mannelli, A.; Rappazzo, E.; Aronica, V.; Ferrara, M.C.; Vesco, G.; Presti, V.D.M.L. Field evaluation of fluorescence polarization assay, and comparison with competitive ELISA for the detection of antibodies against Brucella melitensis in sheep in Sicily, Italy. Small Rumin. Res. 2015, 130, 252–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhussain, H.; Zughaier, S.M.; Gawish, A.; Mahmoud, M.H.; Yassine, H.M.; Al Thani, A.; Obied, T.E.; Al-Zeyara, A.M.; Eltai, N.O. Seroprevalence of camel brucellosis in Qatar. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2022, 54, 351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, A.S.; Rasheed, A.; Rind, R.; Sahito, J.K.; Buriro, R.; Ayoob, M.F.; Dewani, P. Seroprevalence of brucellosis in camels in Sindh, Pakistan. Pak. J. Zool. 2017, 49, 367–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salih, M.E.; Shuaib, Y.A.; Suliman, S.E.; Abdalla, M.A. Seroprevalence and risk factors of brucellosis in camels in and around Alzulfi, Saudi Arabia. J. Camel Pract. Res. 2016, 23, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadar, M.; Alamian, S. Isolation of Brucella melitensis from seronegative camel: Potential implications in brucellosis control. Prev. Vet. Med. 2020, 185, 105194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, S.; Khan, I.; Nasir, A.; Younus, M.; Saqib, M.; Melzer, F.; Neubauer, H.; El-Adawy, H. Serological, molecular detection and potential risk factors associated with camel brucellosis in Pakistan. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2016, 48, 1711–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetaruk, E.W. Brucella Species (Brucellosis) Attack. In Ciottone’s Disaster Medicine; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; pp. 751–753. [Google Scholar]
- OIE. Brucellosis (infection with Brucella abortus, B. melitensis and B. suis). In Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals; World Organisation for Animal Health Paris: Paris, France, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Godfroid, J.; Al Dahouk, S.; Pappas, G.; Roth, F.; Matope, G.; Muma, J.; Marcotty, T.; Pfeiffer, D.; Skjerve, E. A “One Health” surveillance and control of brucellosis in developing countries: Moving away from improvisation. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2013, 36, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praud, A.; Champion, J.L.; Corde, Y.; Drapeau, A.; Meyer, L.; Garin-Bastuji, B. Assessment of the diagnostic sensitivity and specificity of an indirect ELISA kit for the diagnosis of Brucella ovis infection in rams. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, E.M.; Naguib, D.; Mazeed, A.M.; Ahmed, A.E.; El-tarabili, R.M. Comparative Diagnostic Efficacy of Commonly used Serological Assays for Brucellosis. Pak. Vet. J. 2023, 43, 665–670. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N.; Qu, C.; Sai, L.; Wen, S.; Yang, L.; Wang, S.; Yang, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, G. Evaluating the efficacy of serological testing of clinical specimens collected from patients with suspected brucellosis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legesse, A.; Mekuriaw, A.; Gelaye, E.; Abayneh, T.; Getachew, B.; Weldemedhin, W.; Tesgera, T.; Deresse, G.; Birhanu, K. Comparative evaluation of RBPT, I-ELISA, and CFT for the diagnosis of brucellosis and PCR detection of Brucella species from Ethiopian sheep, goats, and cattle sera. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K. Diagnosis of brucellosis by serology. Vet. Microbiol. 2002, 90, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain-Gupta, N.; Waldrop, S.G.; Tenpenny, N.M.; Witonsky, S.G.; Boyle, S.M.; Sriranganathan, N. Rough Brucella neotomae provides protection against Brucella suis challenge in mice. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 239, 108447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, K.; Yu, W. Serological diagnosis of brucellosis. Prilozi 2010, 31, 65–89. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaltungo, B.; Saidu, S.; Sackey, A.; Kazeem, H. A review on diagnostic techniques for brucellosis. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 13, 7C9F42D42549. [Google Scholar]
- Al Dahouk, S.; Nöckler, K. Implications of laboratory diagnosis on brucellosis therapy. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2011, 9, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alton, G.G.; Jones, L.M.; Angus, R.; Verger, J. Techniques for the Brucellosis Laboratory; Institut National de la recherche Agronomique (INRA): Paris, France, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Araj, G.F.; Lulu, A.R.; Mustafa, M.Y.; Khateeb, M.I. Evaluation of ELISA in the diagnosis of acute and chronic brucellosis in human beings. Epidemiol. Infect. 1986, 97, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meena, D.S.; Sharma, L.; Bishnoi, J.; Soni, M.; Jeph, N.K.; Galav, V.; Sharma, S.K. Serological and molecular prevalence of Brucella spp. among livestock species in Rajasthan, India. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1157211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdenebaatar, J.; Bayarsaikhan, B.; Yondondorj, A.; Watarai, M.; Shirahata, T.; Jargalsaikhan, E.; Kawamoto, K.; Makino, S. Epidemiological and serological survey of brucellosis in Mongolia by ELISA using sarcosine extracts. Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 48, 571–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz, R.; Casanova, A.; Ariza, J.; Moriyón, I. The Rose Bengal Test in human brucellosis: A neglected test for the diagnosis of a neglected disease. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieckhaus, K.D.; Kyebambe, P.S. Human Brucellosis in Rural Uganda: Clinical Manifestations, Diagnosis, and Comorbidities at Kabale Regional Referral Hospital, Kabale, Uganda. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2017, 4, ofx237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, M.; Verloo, D.; de Massis, F. Meta-analytical equivalence studies on diagnostic tests for bovine brucellosis allowing assessment of a test against a group of comparative tests. Prev. Vet. Med. 2009, 92, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Wang, W.; Chen, F.; Li, W.; Wang, G. ELISA is superior to bacterial culture and agglutination test in the diagnosis of brucellosis in an endemic area in China. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.P.; Mulder, M.; Gilman, R.H.; Smits, H.L. Human brucellosis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2007, 7, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiros, A.; Asgedom, H.; Abdi, R.D. A review on bovine brucellosis: Epidemiology, diagnosis and control options. ARC J. Anim. Vet. Sci. (AJAVS) 2016, 2, 8–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sareyyüpoğlu, B.; Cantekin, Z.; Müştak, H.K. Investigation of Brucella antibodies in bovine sera by rose bengal plate test (RBPT), serum agglutination test (SAT), microagglutination test (MAT) and 2-mercaptoethanol-microagglutination (2-ME-MAT) test. Ank. Üniversitesi Vet. Fakültesi Derg. 2010, 57, 157–160. [Google Scholar]
- Gall, D.; Nielsen, K. Serological diagnosis of bovine brucellosis: A review of test performance and cost comparison. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2004, 23, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, E.; Blasco, J.M.; Moriyón, I. Facing the Human and Animal Brucellosis Conundrums: The Forgotten Lessons. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seleem, M.N.; Boyle, S.M.; Sriranganathan, N. Brucellosis: A re-emerging zoonosis. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 140, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alikhani, M.Y.; Hashemi, S.H.; Naseri, Z.; Farajnia, S.; PEERI, D.H. Diagnosis of human brucellosis by blood culture (BACTEC) and PCR method via whole blood and serum. Jundishapur J. Microbiol. 2013, 6, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbani, A.; Rabbani Khorasgani, M.; Zarkesh-Esfahani, H.; Sharifiyazdi, H.; Kashani, A.D.; Emami, H. Comparison of serology, culture, and PCR for detection of brucellosis in slaughtered camels in Iran. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 22, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.U.; Melzer, F.; Sayour, A.E.; Shell, W.S.; Linde, J.; Abdel-Glil, M.; El-Soally, S.; Elschner, M.C.; Sayour, H.E.M.; Ramadan, E.S.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing for Tracing the Genetic Diversity of Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis Isolated from Livestock in Egypt. Pathogens 2021, 10, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Hamid, N.H.; Beleta, E.I.M.; Kelany, M.A.; Ismail, R.I.; Shalaby, N.A.; Khafagi, M.H.M. Validation of real-time polymerase chain reaction versus conventional polymerase chain reaction for diagnosis of brucellosis in cattle sera. Vet. World 2021, 14, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dal, T.; Kara, S.S.; Cikman, A.; Balkan, C.E.; Acıkgoz, Z.C.; Zeybek, H.; Uslu, H.; Durmaz, R. Comparison of multiplex real-time polymerase chain reaction with serological tests and culture for diagnosing human brucellosis. J. Infect. Public Health 2019, 12, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosein, H.; Abdel-Raouf, A.; Madkour, B.; Mazeed, A.; Rouby, S. Comparative assessment of sensitivity and specificity of some diagnostic procedures of brucellosis using different approaches. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2021, 9, 2176–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paweska, J.T.; Potts, A.D.; Harris, H.J.; Smith, S.J.; Viljoen, G.J.; Dungu, B.; Brett, O.L.; Bubb, M.; Prozesky, L. Validation of an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the detection of antibody against Brucella abortus in cattle sera using an automated ELISA workstation. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res. 2002, 69, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- MacMillan, A.P.; Greiser-Wilke, I.; Moennig, V.; Mathias, L.A. A competition enzyme immunoassay for brucellosis diagnosis. Dtsch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 1990, 97, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Praud, A.; Gimenez, O.; Zanella, G.; Dufour, B.; Pozzi, N.; Antras, V.; Meyer, L.; Garin-Bastuji, B. Estimation of sensitivity and specificity of five serological tests for the diagnosis of porcine brucellosis. Prev. Vet. Med. 2012, 104, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, K.; Gall, D.; Smith, P.; Balsevicius, S.; Garrido, F.; Ferrer, M.D.; Biancifiori, F.; Dajer, A.; Luna, E.; Samartino, L.; et al. Comparison of serological tests for the detection of ovine and caprine antibody to Brucella melitensis. Rev. Sci. Tech. 2004, 23, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Glanville, W.A.; Conde-Álvarez, R.; Moriyón, I.; Njeru, J.; Díaz, R.; Cook, E.A.J.; Morin, M.; Bronsvoort, B.M.C.; Thomas, L.F.; Kariuki, S.; et al. Poor performance of the rapid test for human brucellosis in health facilities in Kenya. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0005508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiambi, S.G.; Fèvre, E.M.; Omolo, J.; Oundo, J.; de Glanville, W.A. Risk factors for acute human brucellosis in Ijara, north-eastern Kenya. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020, 14, e0008108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías Luaces, L.; Boll, K.; Klose, C.; Domogalla-Urbansky, J.; Müller, M.; Eisenberger, D.; Riehm, J.M. Seroprevalence of Brucella Infection in Wild Boars (Sus. scrofa) of Bavaria, Germany, 2019 to 2021 and Associated Genome Analysis of Five B. suis Biovar 2 Isolates. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Afifi, A.H.; Alewy Almashhadany, D.; Al-Azazi, A.S.H.; Khalaf, A.M.; Naji Ahmed Odhah, M.; Al-Gabri, N.A. Prevalence of Brucella spp. in milk from aborted and non-aborted animals in Dhamar governorate, Yemen. Ital. J. Food Saf. 2022, 11, 10370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Marzooqi, W.; Elshafie, E.I.; Al-Toobi, A.; Al-Hamrashdi, A.; Al-Kharousi, K.; El-Tahir, H.; Jay, M.; Corde, Y.; ElTahir, Y. Seroprevalence and Risk Factors of Brucellosis in Ruminants in Dhofar Province in Southern Oman. Vet. Med. Int. 2022, 2022, 3176147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ZareBidaki, M.; Allahyari, E.; Zeinali, T.; Asgharzadeh, M. Occurrence and risk factors of brucellosis among domestic animals: An artificial neural network approach. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2022, 54, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šerić-Haračić, S.; Velić, L.; Šaljić, E.; Čengić, B.; Tandir, F.; Hadžimusić, N. Agreement Among Rose Bengal, Complement Fixation Test, and iELISA in Diagnostic Discrimination of Sheep and Goat Brucellosis (Brucella melitensis). Acta Vet. Eurasia 2022, 48, 30–34. [Google Scholar]
- Barreto, J.V.P.; Oliveira, P.A.M.; Pertile, S.F.N.; Sbizera, M.C.R.; Rego, F.C.A.; Queiroz, G.R.; Cunha Filho, L.F.C. Non-agreement between 2 serologic techniques for detecting antibody to Brucella ovis in naturally infected sheep. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2022, 34, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber Marouf, A.; Hanifian, S.; Shayegh, J. Prevalence of Brucella spp. in raw milk and artisanal cheese tested via real-time qPCR and culture assay. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2021, 347, 109192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Meng, Y.; Ren, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z. A Retrospective Survey of the Abortion Outbreak Event Caused by Brucellosis at a Blue Fox Breeding Farm in Heilongjiang Province, China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 666254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy, K.; Etter, E.M.C.; Harris, B.N.; Rossouw, J.; Abernethy, D.A.; Thompson, P.N. Knowledge of Brucellosis, Health-Seeking Behaviour, and Risk Factors for Brucella Infection amongst Workers on Cattle Farms in Gauteng, South Africa. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzo, P.; Migliore, S.; Cascio, S.; Barreca, S.; Alfano, M.; Tagliarini, A.; Candela, A.; Piraino, C.; Galuppo, L.; Condorelli, L.; et al. Diagnostic Findings in a Confirmed Outbreak of Brucella ovis Infection in a Traditional Sheep Farm in Sicily (South-Italy). Pathogens 2021, 10, 1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeni, D.K.; Doğan, A. Evaluation of the analytical efficiency of Real-Time PCR in the diagnosis of Brucellosis in cattle and sheep. Kafkas Üniv. Vet. Fakültesi Derg. 2021, 27, 503–509. [Google Scholar]
- Suárez-Esquivel, M.; Ruiz-Villalobos, N.; Hidalgo-Jara, W.; Chacón-Díaz, C.; Zúñiga-Pereira, A.M.; Masís-Mora, M.; Fernández-Fernández, E.; Hernández-Mora, G.; Barquero-Calvo, E.; Chaves-Olarte, E.; et al. Canine brucellosis in Costa Rica reveals widespread Brucella canis infection and the recent introduction of foreign strains. Vet. Microbiol. 2021, 257, 109072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.; Khan, I.; Shakeel, M.; Yousaf, A.; Naseer, Z.; Zohaib, A.; Ullah, Q. Bovine and caprine brucellosis detected by milk indirect ELISA and milk ring test in Islamabad Capital Territory, Pakistan. Pak. J. Zool. 2021, 53, 391–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo-Castañeda, A.M.; Stranahan, L.W.; Edwards, J.F.; Garcia-Gonzalez, D.G.; Roa, L.; Avila-Granados, L.M.; Hensel, M.E.; Arenas-Gamboa, A.M. Characterization of epididymal and testicular histologic lesions and use of immunohistochemistry and PCR on formalin-fixed tissues to detect Brucella canis in male dogs. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2021, 33, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mol, J.P.S.; Guedes, A.C.B.; Eckstein, C.; Quintal, A.P.N.; Souza, T.D.; Mathias, L.A.; Haddad, J.P.A.; Paixão, T.A.; Santos, R.L. Diagnosis of canine brucellosis: Comparison of various serologic tests and PCR. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2020, 32, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sherida, Y.; El-Gohary, A.H.; Mohamed, A.; El-Diasty, M.; Wareth, G.; Neubauer, H.; Abdelkhalek, A. Sheep Brucellosis in Kuwait: A Large-Scale Serosurvey, Identification of Brucella Species and Zoonotic Significance. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montagnaro, S.; D’Ambrosi, F.; Petruccelli, A.; Ferrara, G.; D’Alessio, N.; Iovane, V.; Veneziano, V.; Fioretti, A.; Pagnini, U. A Serological Survey of Brucellosis in Eurasian Wild Boar (Sus scrofa) in Campania Region, Italy. J. Wildl. Dis. 2020, 56, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leahy, E.; Shome, R.; Deka, R.P.; Sahay, S.; Grace, D.; Mazeri, S.; Lindahl, J.F. Risk factors for Brucella spp. and Coxiella burnetii infection among small ruminants in Eastern India. Infect. Ecol. Epidemiol. 2020, 10, 1783091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainaina, M.; Aboge, G.O.; Omwenga, I.; Ngaywa, C.; Ngwili, N.; Kiara, H.; Wamwere-Njoroge, G.; Bett, B. Detection of Brucella spp. in raw milk from various livestock species raised under pastoral production systems in Isiolo and Marsabit Counties, northern Kenya. Trop. Anim. Health Prod. 2020, 52, 3537–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alamian, S.; Dadar, M. Brucella abortus contamination of camel milk in two Iranian regions. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 169, 104708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harms, N.J.; Jung, T.S.; Andrew, C.L.; Surujballi, O.P.; VanderKop, M.; Savic, M.; Powell, T. Health Status of Reintroduced Wood Bison (Bison bison athabascae): Assessing the Conservation Value of an Isolated Population in Northwestern Canada. J. Wildl. Dis. 2019, 55, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotter, S.E.; Tryland, M.; Nymo, I.H.; Hanssen, L.; Harju, M.; Lydersen, C.; Kovacs, K.M.; Klein, J.; Fisk, A.T.; Routti, H. Contaminants in Atlantic walruses in Svalbard part 1: Relationships between exposure, diet and pathogen prevalence. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 244, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.V.; Krishnaiah, N.; Rao, L.V.; Reddy, Y.N.; Reddy, K.K.; Narayana, B. Seroprevalence of brucellosis in buffaloes of Telangana state, India. Buffalo Bull. 2018, 37, 303–311. [Google Scholar]
- Yesilmen, S.; Yaman, T.; Sağsöz, H.; Bademkiran, S. Diagnosis of Q fever and Brucellosis in aborted ovine fetuses by microbiological, pathological and immunohistochemical methods. Acta Vet. 2018, 68, 168–177. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, M.A.; Muhammid, H.A.; AL-Shemmari, I.G.; Jameel, Y.J. Efficacy of Different ELISA, Histopathology and PCR Assays for the Diagnosis of Ovine Brucellosis in Ram. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 12, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, T.I.; Ehtisham-ul-Haque, S.; Waheed, U.; Khan, I.; Younus, M.; Ali, S. Milk Indirect-ELISA and Milk Ring Test for Screening of Brucellosis in Buffaloes, Goats and Bulk Tank Milk Samples Collected from Two Districts of Punjab, Pakistan. Pak. Vet. J. 2018, 38, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailat, N.; Khlouf, S.; Ababneh, M.; Brown, C. Pathological, Immunohistochemical and Molecular Diagnosis of Abortions in Small Ruminants in Jordan with Reference to Chlamydia abortus and Brucella melitensis. Pak. Vet. J. 2018, 38, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckstein, C.; Moustacas, V.S.; Lopes, L.B.; da Silva Mol, J.P.; Gomes, S.C.; dos Santos, R.; de Castro, B.G.; Santos, R.L. Differential diagnosis of infectious reproductive diseases in sheep flocks of Mato Grosso State, Brazil. Small Rumin. Res. 2017, 153, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Saegerman, C.; Berkvens, D.; Melzer, F.; Neubauer, H.; Fretin, D.; Abatih, E.; Dhand, N.; Ward, M.P. Brucella abortus is Prevalent in Both Humans and Animals in Bangladesh. Zoonoses Public Health 2017, 64, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.R.A.; de Souza Lima, G.M.; da Silva, J.D.; da Costa, D.F.; dos Santos, F.A.; dos Santos Higino, S.S.; de Azevedo, S.S.; Alves, C.J. Epidemiological characterization and risk factors associated with leptospirosis and brucellosis in small ruminants sold at animal fair in the Sertão Region of Pernambuco State, a semiarid Region of Northeastern Brazil. Semin. Ciênc. Agrár. 2017, 38, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, S.K.; Yiğin, A.; Gürbilek, S.E.; Gürbüz, S.; Demirci, M.; Keskin, O.; Tel, O.Y. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Brucella specific antibody and real-time PCR for detecting Brucella spp. in milk and cheese in Şanlıurfa, Turkey. Pak. Vet. J. 2017, 37, 39–42. [Google Scholar]
- Azam, A. Molecular Diagnosis of Brucella Zoonosis as Blood Transfusion Hazard in Metropolitan Population of Lahore and Okara; University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences: Lahore, Pakistan, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, A. Seroprevalence of Brucellosis in Dairy Cattle in Three Selected Districts of Punjab, Pakistan; University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences: Lahore, Pakistan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Tanner, M.; Inlameia, O.; Michel, A.; Maxlhuza, G.; Pondja, A.; Fafetine, J.; Macucule, B.; Zacarias, M.; Manguele, J.; Moiane, I.C.; et al. Bovine Tuberculosis and Brucellosis in Cattle and African Buffalo in the Limpopo National Park, Mozambique. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2015, 62, 632–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlozzari, G.; Franco, A.; Macrì, G.; Lorenzetti, S.; Maggiori, F.; Dottarelli, S.; Maurelli, M.; Di Giannatale, E.; Tittarelli, M.; Battisti, A.; et al. First report of Brucella suis biovar 2 in a semi free-range pig farm, Italy. Vet. Ital. 2015, 51, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.T.H. Sero-Prevalence of Brucellosis in Sheep in Hazara Region; University of Veterinary and Animal Sciences: Lahore, Pakistan, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.; McFee, W.E.; Goldstein, T.; Tiller, R.V.; Schwacke, L. Real-time PCR assays for detection of Brucella spp. and the identification of genotype ST27 in bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). J. Microbiol. Methods 2014, 100, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wareth, G.; Melzer, F.; Elschner, M.C.; Neubauer, H.; Roesler, U. Detection of Brucella melitensis in bovine milk and milk products from apparently healthy animals in Egypt by real-time PCR. J. Infect. Dev. Ctries. 2014, 8, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, P.E.; Stanchi, N.O.; Silvestrini, M.; Brihuega, B.; Samartino, L.; Parrado, E. Seroprevalence for selected pathogens of zoonotic importance in wild nutria (Myocastor coypus). Eur. J. Wildl. Res. 2014, 60, 551–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, S.T.; Khan, A.; Ahmad, M.; Hussain, I. Seroprevalence of Brucellosis and Associated Hematobiochemical Changes in Pakistani Horses. Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 50, 745–750. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).