Simple Summary
Klebsiella pneumoniae can be spread between humans and animals through close contact with food and the environment, and there is a risk of transmission from animals to humans. However, the correlation between human and avian sources of Klebsiella pneumoniae is not clear. Firstly, Klebsiella pneumoniae strains origined from human/avian in Jiangsu province, China, were isolated and identified. Secondly, the pathogenicity was evaluated in vitro and in vivo. We found that both avian-origin and human-origin strains possessed the ability to form biofilms and exhibited multi-drug resistantance, but with different ST types distributions. Additionally, the number of virulence genes in human-origin strains was found to be higher than that in avian-origin strains, and a positive correlation was observed between the number of virulence genes and pathogenicity. This study provided a theoretical basis for the prevention and control of diseases associated with Klebsiella pneumoniae by revealing the difference of biological characteristics between avian and human sources.
Abstract
Klebsiella pneumoniae, a zoonotic pathogen of global concern, poses significant threats to both veterinary and public health. Here, a comparative study characterized 14 clinical isolates (7 avian-derived, 7 human-derived) from Jiangsu, China, through integrated genomic and phenotypic analyses. Firstly, multilocus sequence typing (MLST) revealed distinct epidemiological patterns: the same ST type in avian isolates was circulating between different species and different regions, whereas it was not found in human isolates. In addition, hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (hvKP) phenotypes confirmed by string test were exclusive to two human isolates (KP15, KP20). Secondly, biofilm detection demonstrated 78.6% (11/14) of isolates possessed biofilm-forming capacity, with cellulose but not curli as the predominant matrix component. Human-derived KP15 and KP20 had the strongest biofilm formation ability in all isolates. Antimicrobial susceptibility profiling identified serious multidrug resistance in both avian and human isolates. Virulence gene analysis revealed striking disparities, with human isolates harboring 10–20 virulence factors (median 15) versus 6–7 (median 6.5) in avian counterparts. Finally, functional pathogenesis assessments demonstrated human-derived strains exhibited stronger epithelial cell adhesion (2-fold higher) and invasion (1.97-fold higher) in Calu-3 cell models and paradoxically showed reduced macrophage phagocytosis (2.85-fold lower at 2 h) for immune escape. In vivo models confirmed dose-dependent mortality, with human isolates demonstrating higher lethality in both Galleria mellonella and mice. Virulence gene burden positively correlated with mortality outcomes. These findings delineate critical host adaptation differences in Klebsiella pneumoniae populations and provide empirical evidence for pathogen transmission dynamics at the human-animal interface.
1. Introduction
Klebsiella pneumoniae (K. pneumoniae) is one of the most important enterobacteria of the Klebsiella genus, and diseases caused by K. pneumoniae account for more than 95% of Klebsiella infections [1]. K. pneumoniae is common in the respiratory tract and digestive tract of humans and animals, as well as in the natural environment, such as water and soil [2]. K. pneumoniae is an important pathogen of community-acquired pneumonia and can cause a variety of human infections, including pneumonia, bloodstream infections, meningitis, urinary tract infections, and invasive diseases [3]. K. pneumoniae not only has a serious impact on human health but also causes huge economic losses to the aquaculture industry. In recent years, K. pneumoniae has caused great harm to the health of poultry, domestic animals, and wild animals all over the world, and its morbidity and mortality have increased significantly [4]. K. pneumoniae can infect animals with different clinical symptoms, such as mastitis, pneumonia, and septicemia infection in pigs [5]; mastitis and respiratory tract infection in cows [6]; pneumonia and upper respiratory tract infection in sheep and goats [7]; and pneumonia, enteritis, liver abscess, and septicemia in poultry [8]. According to the expression level of virulence factors, clinical infection characteristics, and molecular biological characteristics such as the carriage of virulence genes and capsular serotypes, K. pneumoniae can be divided into classical K. pneumoniae (cKP) and hypervirulent K. pneumoniae (hvKP) [9]. According to data provided by the China Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (CARSS), the national Bacterial Resistance Detection Report for 2022 shows that K. pneumoniae ranks second in prevalence among isolated Gram-negative pathogens with 21.2%.
The pathogenicity of K. pneumoniae is jointly determined by a variety of virulence genes, including capsular polysaccharide (CPS), lipopolysaccharide (LPS), fimbriae, iron carrier, and biofilm [10]. Capsular polysaccharide is an acidic polysaccharide matrix wrapped on the surface of K. pneumoniae, which can protect the bacteria against harsh environments or harmful substances and from the influence of host immune response and is one of the main virulence factors of K. pneumoniae [11]. The synthesis of CPS is regulated by genes rmpA, rmpA2, and magA [12]. The synthesis of fimbriae is encoded by the fim and mrk gene cluster [13]. Iron is an indispensable metal element for bacterial growth and plays a crucial role in the infection process of K. pneumoniae [14]. The synthesis of iron carriers is regulated by genes ureA, entB, iutA, iucA, iroB, ybtS, irp2, fyuA, aerobactin, kfu, and peg-344. The bacteria in the biofilm are not easily killed by the host defense system, and the biofilm can promote the substance transfer of antibiotic resistance [15].
There have been a lot of studies on the epidemic transmission of K. pneumoniae, but there are few studies on the transmission between animals and humans, especially the transmission between avian and human. Alexis Dereeper et al. discovered human multidrug-resistant and high-risk K. pneumoniae in a pet hospital, indicating that STs are shared between pets and humans, and companion animals had the potential risk of transmitting K. pneumoniae to humans [16]. Sandra Pulss et al. found that bacterial sequence types and OXA-48 plasmids had significant overlap between humans and animals, reinforcing the idea of transmission between humans and animals [17]. In addition, Jun Sung Hong et al.’s study in South Korea also observed that the increase of CTX-M-55 in companion animals may affect antimicrobial resistance (AMR) transmission between humans and companion animals [18]. Fan Yang et al. found that K. pneumoniae strains from different hosts (including humans and animals) had common molecular types and similar phenotypes and speculated that these strains may be transmitted between humans and animals [19]. Thongpan Leangapichart et al. found pig-to-human transmission in a pig farm, indicating the possibility of zoonotic transmission in the K. pneumoniae clonal subpopulation [20]. Agricultural workers face a heightened occupational risk of exposure to livestock-associated K. pneumoniae and can become carriers, potentially transmitting it to close contacts like family members and the general public [21]. Studies have shown that the same sequence type of K. pneumoniae exists in a human blood specimen and a sample of retail chicken meat [22]. A study in Norway showed that K. pneumoniae from the cecum of broilers and turkeys belongs to the same sublineage as K. pneumoniae from human blood, urine, and feces [23]. Some research showed that there was a relatively higher presence of carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae among hospital inpatients (7.3%) compared to that in the meat products (2.7%) and farm animals (pig, 4.6%; chicken, 0.63%) in Qingdao, China [24]. To explore the correlation and differences in biological characteristics of K. pneumoniae from different host sources, K. pneumoniae from the avian and human were isolated in the Jiangsu region. We conducted comparative studies on the homology analysis, virulence factors, drug resistance, and pathogenicity to mammals of K. pneumoniae and analyzed the possibility of transmission of K. pneumoniae between avian and human. This study provided data reference for the epidemiological study of K. pneumoniae.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
The animal studies were in accordance with the Laboratory Animal Welfare and Ethics guidelines of the Jiangsu Provincial Laboratory Animal Management Committee and have been approved by it (permission number: SYXK(SU)2022-0044).
2.2. Reagents
Defibrinated sheep blood was purchased from SenBeiJia Biological Technology (Nanjing, China). Tryptone and yeast extract were purchased from OXOID (Basingstoke, UK). NaCl was obtained from National Pharmaceutical Group (Shanghai, China). Agar was purchased from Sincere Biotech (Shanghai, China). 2 × FineTaq PCR SuperMix (+dye) was purchased from TransGen Biotech (Shanghai, China). DL1000 DNA marker and DL2000 DNA marker were purchased from Takara (Kyoto, Japan). Antimicrobial discs were derived from Microbial Reagent (Hangzhou, China). Crystal violet, Congo red, and Triton X-100 were purchased from Sangon Biotech (Shanghai, China). LB broth was purchased from Hope Biotechnology (Qingdao, China). Calofluor White Stain was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). DMEM medium, fetal bovine serum (FBS), and penicillin-streptomycin were sourced from Thermo Fisher Scientific (Waltham, MA, USA).
2.3. Isolation and Identification of K. pneumoniae
K. pneumoniae were isolated from sputum, blood, liver, heart, and feces of Xuzhou Central Hospital, Northern Jiangsu People’s Hospital, and animals’ tissues of Jiangsu Province from 2020 to 2023 (Table 1). The samples in this study followed the principle of randomization. Each sample was streaked on blood agar and incubated for 12–18 h at 37 °C. A single colony exhibiting suspicious characteristics, including white coloration, mucus-like consistency, and rounded morphology, was selected and purified two times. The genomic DNA of bacterial isolates was extracted by the boiling method as a template. PCR detection was performed using universal bacterial primers to amplify the 16S rRNA gene of the isolated strains. PCR program: 4 min pre-denaturation at 94 °C; 30 s denaturation at 94 °C; 45 s annealing at 51 °C; 1 min extension at 72 °C, for a total of 30 cycles; 10 min extension at 72 °C. Use 1% agarose gel electrophoresis to validate the PCR products. The purified PCR products were sent to Nanjing Qingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China) for sequencing. The assembled complete sequences were subjected to nucleic acid sequence alignment on NCBI. The primers were synthesized by Sangon Biotech Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China), and the primer sequences are shown in Table S1. The bacterial liquid is mixed with sterile 50% glycerol in a 1:1 ratio and stored at −80 °C for further studies.

Table 1.
The distribution and origin of K. pneumoniae isolates.
2.4. Multilocus Sequence Typing and Homology Analysis
Molecular typing of K. pneumoniae was performed using the multilocus sequence typing (MLST) method. The seven housekeeping genes of K. pneumoniae (gapA, infB, mdh, phoE, pgi, rpoB, and tonB) were amplified by PCR and sequenced. PCR program: 5 min pre-denaturation at 94 °C; 45 s denaturation at 94 °C; 30 s annealing at 50 °C; 1 min extension at 72 °C, for a total of 30 cycles; 5 min extension at 72 °C. PCR products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis in a 1% (w/v) gel. The purified PCR products were sent to Nanjing Qingke Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Nanjing, China) for sequencing. The alleles and STs were determined by matching the sequence from the database in the Pasteur Institute MLST website (http://www.pasteur.fr/en (accessed on 2 June 2025)). The complete sequences of corresponding ST types were downloaded from the database and uploaded to MEGA11. The phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method to analyze the genetic relationship between K. pneumoniae with different ST types.
2.5. String Test and Mucoviscosity Assay
The strains were inoculated onto LB agar plates and incubated at 37 °C for 12–18 h. The bacterial colonies were elongated using a typical bacteriologic loop stretched a mucoviscous string from the colony. The positive result of the string test was defined as the formation of viscous strings ≥5 mm [25]. The mucoviscosity assay was performed with the previous method [26]. Both the string test and mucoviscosity test are used to detect the viscosity of Klebsiella pneumoniae.
2.6. Biofilm Formation Assay
To test the biofilm formation ability of K. pneumoniae isolates, we used test tubes as described previously [27]. Briefly, K. pneumoniae isolates were at 37 °C for 8–10 h. After the OD600 of the bacteria solution reached 0.8~1.1, the bacteria were inoculated in test tubes and then incubated for 24 h at 37 °C. Next, the test tubes were washed with PBS. Subsequently, 0.4% crystal violet (CV) solution was added to the test tubes and incubated at room temperature for 30 min away from light. Then, the test tubes were washed three times with PBS and allowed to dry. The CV was dissolved using absolute ethanol, and the absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 550 nm using a microplate reader. The experiment was independently repeated three times.
The biofilm formation ability of K. pneumoniae isolates was divided according to the ODc [28] (ODc = mean absorbance of negative controls + 3SD (the standard deviation)). OD550 ≤ ODc indicated that the strain was unable to form biofilms; ODc < OD550 ≤ 2ODc indicated that the strain had a weak ability to form biofilms. 2ODc < OD550 ≤ 4ODc indicated that the strain had moderate biofilm formation ability. OD550 > 4ODc indicated that the strain had a strong ability to form biofilms.
Curli and cellulose production were detected by Congo Red (CR) plates and Calcofluor (CF) plates [29]. 10 μL of bacterial solution was inoculated on Congo Red plates and Calcofluor plates and incubated at 28 °C for 96 h. Expression of curli fimbriae and cellulose nanofibers shows the dry, red, and rough morphotype on Congo red agar plates. Only expression of cellulose nanofibers shows the pink and smooth morphotype, while only expression of curli fimbriae has the brown, dry, and rough morphotype [30]. Colony morphology on the Calcofluor plate was observed under an Ultraviolet (UV) light at 365 nm [31]. The experiment was independently repeated three times.
2.7. Antibiotic Susceptibility Test
Antibiotic susceptibility testing was performed and interpreted using the standard Kirby–Bauer disk diffusion method according to CLSI (2020) [32]. In this study, a total of 20 antibiotics were tested. Escherichia coli ATCC25922 was used as a quality control strain for parallel testing to ensure the validity of the results.
2.8. Virulence Gene Detection
To determine the virulence profile of the K. pneumoniae isolates, 21 virulence genes were tested by PCR. These virulence genes include lipopolysaccharide-related genes (uge [33], wabG [34]), capsular polysaccharide synthesis and synthesis regulation-related genes (rmpA [35], rmpA2 [36], magA [35], K2 [35], wcaG [37]), fimbriae synthesis-related genes (fimH [34], mrkD [35]), urease-related gene (ureA [33]), allantoin-related gene (allS [35]), and iron uptake system genes (entB [35], iutA [35], iucA [36], iroB [36], ybtS [35], irp2 [36], fyuA [38], kfu [35], aerobactin [39], peg-344 [36]). Primers used in this study are listed in Table S1. The PCR program refers to the references of each virulence gene. PCR products were analyzed on a 1% agarose gel. The presence of a target gene was confirmed if amplicons were of the expected size.
2.9. Adhesion and Invasion Assay of K. pneumoniae to Calu-3 Cell
The adhesion and invasion of epithelial cells by Klebsiella pneumoniae are mainly based on relevant references [40]. Calu-3 cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM) with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 °C and 5% CO2, respectively. For adhesion assays, bacterial strains were added at an MOI of 10:1 bacteria/cell proportion and incubated for 1 h. Non-adherent bacteria were removed by washing 3 times with 1 mL sterile PBS. Then, cells were lysed with 0.5% TritonX-100 at 37 °C for 10 min. The cell lysates were serially diluted with PBS and cultured on LB plates to calculate the number of viable bacteria. For invasion assays, after 1 h of incubation with bacteria, 100 μg/mL gentamicin was added and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h. The cell lysates were cultured on LB plates after cell washing and lysing. The experiment was independently repeated three times.
2.10. Phagocytosis and Clearance Assay
To detect the ability of K. pneumoniae to resist phagocytosis and clearance of macrophages. RAW264.7 cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium (DMEM) with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 °C and 5% CO2. For the phagocytosis assay, bacterial strains were added at an MOI of 100:1 bacteria/cell proportion and incubated for 1 h. The initial number of cells was 2.5 × 105 per well in a 24-well plate. After incubation, the cells were washed with sterile PBS. 100 μg/mL gentamicin was added and incubated at 37 °C for 1 h to kill bacteria that did not enter cells. Then, the cells were washed with sterile PBS and lysed with 0.5% TritonX-100 at 37 °C for 10 min. The cell lysates were cultured on LB plates to calculate the number of viable bacteria. For the clearance assay, after 1 h of incubation with 100 μg/mL gentamicin, the cells were washed with sterile PBS, and 10 μg/mL gentamicin was added and incubated at 37 °C for 7 h and 20 h. The cell lysates were cultured on LB plates. The experiment was independently repeated three times.
2.11. Pathogenicity of K. pneumoniae in Galleria Mellonella and Mice
To evaluate the virulence of K. pneumoniae isolates, the Galleria mellonella infection model was established as described previously [41]. The larvae of the Galleria mellonella were fed at 37 °C for 24 h and then were randomly divided into seventy-three groups (n = 10 per group). The penultimate left foot of larvae in each group was injected with 20 μL of the bacterial suspension or sterile PBS. Survival rates of Galleria mellonella were recorded for 5 days. The lethal dose 50 (LD50) was calculated by the modified Koch’s method.
The pneumonia murine model was established as previously described [42]. Female SPF C57BL/6 mice aged 6–8 weeks were used in this study. Five mice were randomly assigned to each cage. Food and water can be freely obtained. Mice were weighed and anesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of tribromoethanol. Then, each mouse was intratracheally injected with 20 μL bacterial suspension or sterile PBS. After the injection, the incision was glued with tissue adhesive. Weight change was assessed daily for the next 15 days, and the survival of the mice was recorded. The LD50 was calculated by a modified Koch’s method. In addition, in the group of KP820 and KP20, mice were euthanized at 24 h, 48 h, and 72 h after bacterial infection, and the heart, liver, spleen, and lung tissues were aseptically separated and weighed. Tissue weight/body weight ratio was calculated. Meanwhile, the heart, liver, spleen, and lung tissues were homogenized and plated onto LB plates to calculate the number of viable bacteria. The mice were euthanized with CO2.
2.12. Statistical Analysis
All the quantitative experiments were independently performed at least in triplicate. All data are expressed as mean and standard deviations (SD). The data were visualized using GraphPad Prism 9.5. ANOVA in SPSS 27.0 software was used to compare the statistical differences between different groups. The LSD method was used for multiple comparisons. * p < 0.05 indicated a statistically significant difference. Spearman’s correlation coefficient (r) was calculated to evaluate the correlation. |r| ≥ 0.8 indicated high correlation, 0.5 ≤ |r| < 0.8 indicated moderate correlation, 0.3 ≤ |r| < 0.5 indicated low correlation, and |r| < 0.3 indicated no correlation.
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Identification of K. pneumoniae
In our study, a total of 14 K. pneumoniae strains were isolated from Jiangsu, China, during 2020 to 2023 (Table 1). Among these, seven strains of K. pneumoniae isolated from avian were named KP820, KP826, KP911, KP926, KP1016, KP1103, and KP1116, respectively. Seven strains of K. pneumoniae isolated from humans were named KP33, KP34, KP35, KP36, KP37, KP15, and KP20, respectively.
MLST has been used for a variety of bacteria detection and evolutionary studies of epidemiology [43]. The technique was applied to the genotyping of K. pneumoniae in 2005 [44]. First, we examined the ST type of 14 K. pneumoniae isolates. As shown in Table 2, the MLST analysis revealed 9 different STs among 14 K. pneumoniae. KP826, KP1116, and KP15 were classified as two new STs (ST7640 and ST7641). ST37, ST3410, ST5491, and ST7640 were found in K. pneumoniae isolated from avian. KP820, KP926, and KP1103 belong to ST5491. KP826 and KP1116 belong to ST7640. ST11, ST15, ST23, ST431, and ST7641 were found in K. pneumoniae isolated from humans. KP33 and KP34 belong to ST11. KP35 and KP36 belong to ST15. Next, we conducted phylogenetic analyses to investigate the evolutionary distances between these isolates. As shown in Figure 1, KP820, KP926, KP1103, and KP1016 showed a high homology. KP35, KP36, and KP37 showed a high homology. KP20, KP826, and KP1116 also showed a high homology.

Table 2.
Allele profile and ST typing of K. pneumoniae strains.
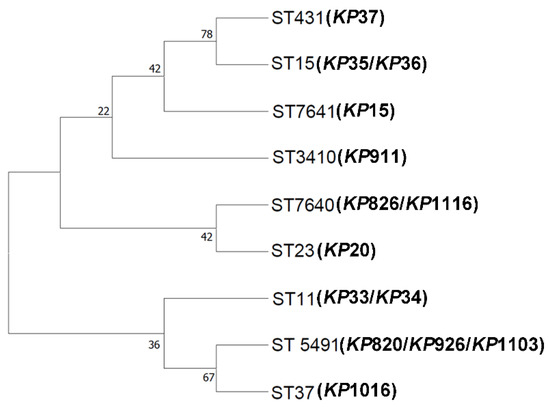
Figure 1.
Neighbor-joining phylogeny was constructed using seven MLST genes for 14 K. pneumoniae isolates with 1000 bootstrap replicates. The high bootstrap values implied a high level of confidence in the tree.
String testing is commonly used to determine the hypermucoviscosity (hmv) phenotype of K. pneumoniae, which is typical of most hvKP [45]. The evaluation of mucoviscosity can also be used to distinguish between hvKP and cKP strains [46]. Here, we conducted a string test and mucoviscosity assay for K. pneumoniae. As shown in Figure 2 and Table 3, only KP15 and KP20 from human K. pneumoniae could form a long string, while other strains did not have the ability. In addition, mucoviscosity was also detected. As shown in Figure 2E, KP15 and KP20, isolated from humans, had a higher mucoviscosity than other strains, which was consistent with the results of the string test. KP15 and KP20 were hvKP, while the remaining strains were cKP. Besides, the capsules of K. pneumoniae were stained with the Congo red negative staining method according to the reference [47]. As shown in Figure 2F, KP20 had the thickest capsule among the 14 strains of K. pneumoniae.
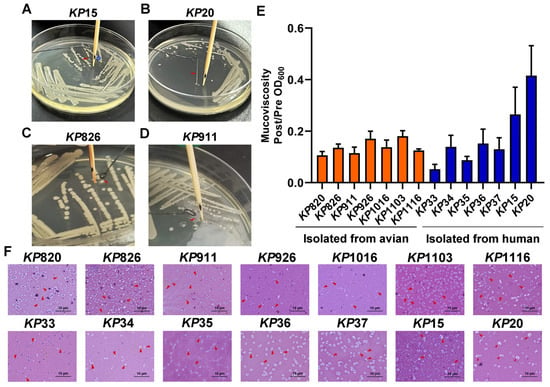
Figure 2.
Results of viscosity assay. (A,B) KP15 and KP20 could form a string on the LB agar plate. Generally, a string 5 mm or longer was defined as positive. *, the distance from the bottom of the toothpick to the black spot is 5 mm. (C,D) KP826 and KP911 could not form a string on the LB agar plate. (E) Mucoviscosity assay of K. pneumoniae isolates. (F) The bacteria were evenly mixed on the slide with Congo red and serum mixture solution and then were pushed into a thin layer. The bacteria were decolonized with 5% dilute hydrochloric acid for 1 min, washed with water, and then stained with 0.1% crystal violet for 1 min, washed with water, dried naturally, and observed under the oil microscope. Bars: 10 μm. Capsules are indicated by short red arrows.

Table 3.
The results of the string test.
3.2. Biofilm Formation Ability of K. pneumoniae Strains
Biofilm formation is one of the major virulence properties of K. pneumoniae [48]. We evaluated the biofilm formation ability of K. pneumoniae isolates by using test tubes. As shown in Figure 3A, it is stated that 11 strains formed biofilms, with KP820/KP926 being the most potent in avian species and KP15/KP20 in humans. Next, the OD value was statistically analyzed, and biofilm formation ability was classified according to the OD value. As shown in Figure 3B, KP820, KP926, KP1103, KP1116, KP35, KP15, and KP20 had a strong biofilm formation ability; KP36 and KP37 had a moderate biofilm formation ability; KP1016 had a weak biofilm formation ability; and KP911, KP33, and KP34 had no biofilm formation ability. These data suggested that the majority of K. pneumoniae can form the biofilm. Meanwhile, biofilm structure of KP826 and KP15 was observed by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) in Figure 3C. In the process of biofilm formation, Alexa FluorTM 647 dextran was added, the biofilm matrix showed red fluorescence, and bacterial nucleic acids were stained with Syto 9 (green fluorescence). Compared with KP826, KP15 had a higher ability to form biofilms. Furthermore, we evaluated the curli and cellulose production of the K. pneumoniae strains on CR and CF agar plates. As shown in Figure 3D,E, 14 K. pneumoniae strains produced a pink colony, indicating a lack of curli production. We found that KP820 and KP1103 displayed strong fluorescence under UV light illumination, indicating their strong cellulose production capacity.
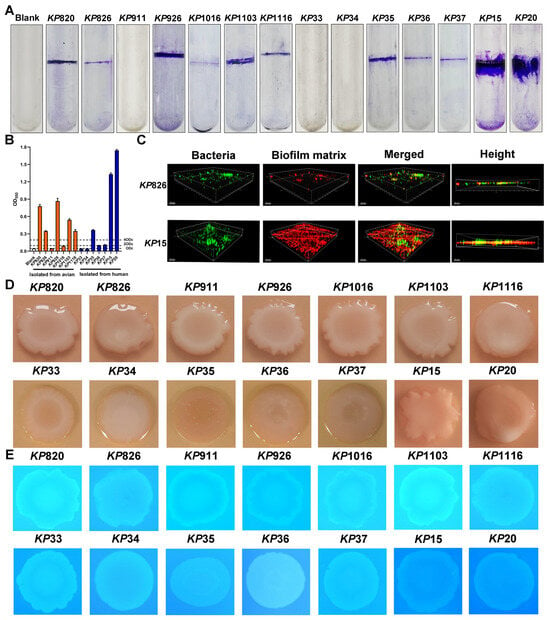
Figure 3.
Results of biofilm formation ability of K. pneumoniae isolates. (A) The biofilm formation was detected by the crystal violet in the test tube. (B) The crystal violet was dissolved using absolute ethanol, and the absorbance was measured at a wavelength of 550 nm. (C) Biofilm structure of KP826 and KP15 was observed by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). (D) Colony morphology of 14 K. pneumoniae isolates growing on Congo red plates. (E) Colony morphology of 14 K. pneumoniae isolates growing on Calcofluor plates. Photographs represent one of three experiments, which gave similar results.
3.3. Antibiotic Susceptibility Patterns and Virulence Factors Distribution of K. pneumoniae Isolates
The antimicrobial resistance results are presented in Table 4 and Table 5. Among the strains isolated from avian, the resistance rate to cotrimoxazole, florfenicol, chloramphenicol, ampicillin, carbenicillin, erythromycin, tetracycline, doxycycline, nitrofurantoin, and rifampin was 100%. The resistance rate to ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, cephalexin, cefotaxime, amikacin, and aztreonam was 71.43%. The resistance rate to cefoxitin was 57.14%. The resistance rate to meropenem, imipenem, and polymyxin B was 0%. KP820, KP926, KP1016, and KP1103 were resistant to 17 antibiotics. KP911 was resistant to 16 antibiotics. KP826 and KP1116 were resistant to 10 antibiotics. Among the strains isolated from humans, the resistance rate to cephalexin, ampicillin, carbenicillin, erythromycin, tetracycline, doxycycline, nitrofurantoin, and rifampin was 100%. The resistance rate to ciprofloxacin, norfloxacin, and aztreonam was 85.71%. The resistance rate to cotrimoxazole, cefotaxime, amikacin, and imipenem was 71.43%. The resistance rate to cefoxitin and meropenem was 57.14%. The resistance rate to chloramphenicol and polymyxin B was 28.57%. The resistance rate to florfenicol was 14.29%. KP34 and KP35 were resistant to 18 antibiotics. KP33 was resistant to 17 antibiotics. KP36 was resistant to 16 antibiotics. KP37 and KP15 were resistant to 15 antibiotics. KP20 was resistant to 8 antibiotics. We found that all K. pneumoniae were completely resistant to ampicillin, carbenicillin, erythromycin, tetracycline, doxycycline, nitrofurantoin, and rifampin. It was noted that the isolates in this study were all multi-drug resistant (MDR) strains, indicating that the resistance status of K. pneumoniae is severe.

Table 4.
Antimicrobial susceptibility profile of K. pneumoniae isolated from avian.

Table 5.
Antimicrobial susceptibility profile of K. pneumoniae isolated from humans.
To further investigate the molecular characteristics of these K. pneumoniae strains, we analyzed their virulence gene profiles. As shown in Table 6 and Table 7, 21 virulence genes in this study were detected. All K. pneumoniae strains carried uge, wabG, fimH, mrkD, ureA, and entB. All strains isolated from humans carried ybtS, irp2, and fyuA. All strains isolated from avian did not carry ybtS, irp2, and fyuA. RmpA, rmpA2, magA, K2, wcaG, allS, iutA, iucA, iroB, aerobactin, and peg-344 can be found in some strains isolated from humans, but not in strains isolated from avian. The kfu gene was found in KP820, KP926, KP1103, KP35, KP36, KP37, and KP20. All K. pneumoniae isolates had three or more virulence genes, and the number of virulence genes of KP20 reached 20. The virulence genes of K. pneumoniae isolated from avian and human sources were 6–7 and 10–20, respectively. We conducted a statistical analysis on the difference in the number of virulence genes carried by avian and human K. pneumoniae. As shown in Figure S1. The number of virulence genes carried by human strains is significantly higher than that of avian strains. Besides, we found no differences in the virulence genes carried by strains of the same ST except for ST11. These data suggested that the virulence of K. pneumoniae isolated from humans may be stronger than K. pneumoniae isolated from avian.

Table 6.
Distribution of virulence genes of K. pneumoniae isolates from avian.

Table 7.
Distribution of virulence genes of K. pneumoniae isolates from humans.
3.4. Adhesion and Invasion of K. pneumoniae to Calu-3 Cells
To evaluate the adhesive and invasive capacity of K. pneumoniae, strains infected Calu-3 cells. As shown in Figure 4A,B, the average adhesion (a = 1.54%, b = 3.08%) and invasion rate (a = 0.35%, b = 0.69%) of strains isolated from humans to Calu-3 cells were higher than that of strains isolated from avian. Among the strains isolated from avian, KP820 showed the highest adhesion rate to Calu-3 cells. KP926 showed the highest invasion rate to Calu-3 cells. Among the strains isolated from humans, KP35 showed the highest adhesion rate and invasion rate to Calu-3 cells. Statistical analysis was conducted on the differences in adhesion and invasion of Calu-3 cells between avian strains and human strains. As shown in Figure S2. The adhesion rate and invasion rate of human strains to Calu-3 cells were significantly higher than those of avian strains. These data suggested that the adhesion and invasion ability of strains isolated from humans to Calu-3 cells was stronger than that of strains isolated from avian.
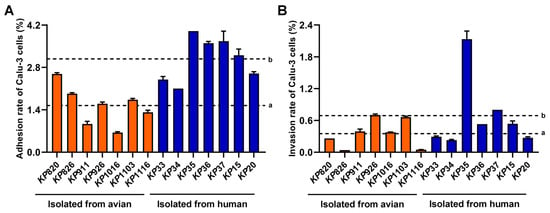
Figure 4.
Result of epithelial cell adhesion and invasion assay. (A) Adhesion ability of K. pneumoniae to Calu-3 cells. (B) Invasion ability of K. pneumoniae to Calu-3 cells. a: The average adhesion rate or invasion rate of strains isolated from avian to Calu-3 cells. b: The average adhesion rate or invasion rate of strains isolated from humans to Calu-3 cells.
3.5. Phagocytosis of K. pneumoniae by Macrophages and Proliferation of K. pneumoniae in Macrophages
We evaluated the phagocytic ability of macrophages to K. pneumoniae. As shown in Figure 5B, the phagocytosis rate of macrophages to strains isolated from avian was higher than that of strains isolated from human (a = 6.18%, b = 2.17%) at 2 h. Among the strains isolated from avian, macrophages had the strongest phagocytic ability to KP820. Among the strains isolated from humans, macrophages had the strongest phagocytic ability to KP34. Statistical analysis was conducted on the differences in macrophage phagocytosis between avian strains and human strains. As shown in Figure S3. The phagocytic rate of avian strains by macrophages was significantly higher than that of human strains. Next, we counted the number of K. pneumoniae in macrophages after infection with K. pneumoniae at 7 and 20 h, respectively. As shown in Figure 5A,C, compared to that at 2 h, the intracellular replication of K. pneumoniae was significantly increased at 20 h (p < 0.05). Among the strains isolated from avian, KP1116 had the strongest intracellular replication ability in macrophages. Among the strains isolated from humans, KP15 had the strongest intracellular replication ability in macrophages.
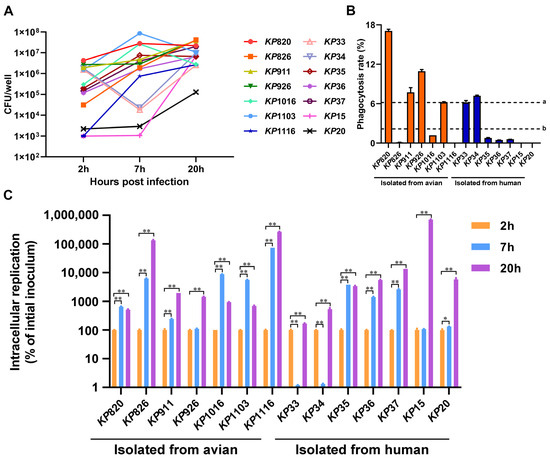
Figure 5.
Results of K. pneumoniae infection in macrophage RAW264.7. (A) The amount of K. pneumoniae strains inside macrophage RAW264.7 at 2, 7, and 20 h after infection, respectively. (B) Phagocytosis rate of macrophages RAW264.7 against K. pneumoniae. a: The average phagocytosis rate of macrophages to strains isolated from avian. b: The average phagocytosis rate of macrophages to strains isolated from humans. (C) The intracellular replication rates of K. pneumoniae strains inside macrophage RAW264.7. The intracellular replication at 7 and 20 h was calculated by comparing to the CFUs at 2 h *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.
3.6. The Results of K. pneumoniae Infection in Galleria Mellonella and Mice
The Galleria mellonella infection model has been employed to investigate various bacteria and assess the virulence of K. pneumoniae due to the ease and cost-effectiveness of obtaining larvae [49]. In this study, we counted the survival rate of Galleria mellonella infected with K. pneumoniae for 5 days and calculated the LD50 by modified Koch’s method. As shown in Figure 6A–C and Figure S4, the LD50 of strains isolated from avian was above 2.5 × 103, and the LD50 of strains isolated from human was below 2 × 103. Among the strains isolated from avian, KP911 and KP1103 were the most virulent to Galleria mellonella. Among the strains isolated from humans, KP15 was the most virulent to Galleria mellonella.
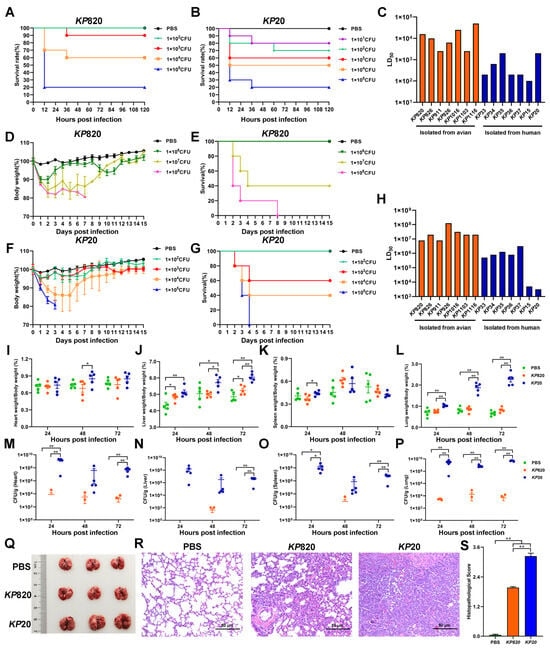
Figure 6.
Evaluation of pathogenicity of K. pneumoniae isolates. (A) Survival rate of Galleria mellonella (n = 10) infected with KP820. (B) Survival rate of Galleria mellonella (n = 10) infected with KP20. (C) K. pneumoniae strains infected Galleria mellonella, then calculated median lethal dose. (D,E) The body weight changes and survival rate of mice (n = 5) intratracheally injected with KP820. (F,G) The body weight changes and survival rate of mice (n = 5) intratracheally injected with KP20. (H) K. pneumoniae strains infected mice, then calculated the median lethal dose. (I–L) The wet weight of the tissue (heart, liver, spleen, and lung) in mice (n = 5) intratracheally injected with PBS, KP820, and KP20 at 24, 48, and 72 h post infection. (M–P) The bacterial load of the tissue (heart, liver, spleen, and lung) in mice (n = 5) intratracheally injected with PBS, KP820, and KP20 at 24, 48, and 72 h post infection. The pathology images in lungs (n = 3 per group) (Q), histopathological images in H&E-stained lung tissues (n = 3) (R), and histopathologic scores in the lungs (S) of mice intratracheally injected with PBS, KP820, and KP20 at 72 h post infection. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.
Mouse infection models remain a standard for assessing pathogen virulence, including that for K. pneumoniae, which is an accurate method for identifying hvKP and differentiating it from cKP [45]. In this study, we evaluated the body weight, survival rate, and median lethal dose of mice intratracheally injected with K. pneumoniae. The results are shown in Figure 6D–H, Figures S5 and S6. The LD50 of strains isolated from avian was above 8 × 106, and the LD50 of strains isolated from humans was below 3.2 × 106. Among the strains isolated from avian, KP820 and KP911 were the most virulent to mice. Among the strains isolated from humans, KP20 was the most virulent to mice. In addition, the correlation between the number of virulence genes and the LD50 of the Galleria mellonella and mice was analyzed. As shown in Table 8. The number of virulence genes was moderately negatively correlated with the LD50 of Galleria mellonella and highly negatively correlated with the LD50 of mice.

Table 8.
Spearman correlation analysis.
According to the results of LD50 to mice, KP820 and KP20 were the most virulent strains isolated from avian and human, respectively. Next, we measured the tissues’ wet weight and bacterial load of mice infected with PBS, KP820, and KP20. As shown in Figure 6I–L, compared to the PBS group, the wet liver weights were significantly (p < 0.05) increased in the KP820 group after 24 and 72 h post infection. Compared to the KP820 group, the wet liver weights and wet lung weights were significantly (p < 0.05) increased in the KP20 group after 48 and 72 h post infection. As shown in Figure 6M–P, compared to the PBS group, the bacterial loads of the heart, liver, spleen, and lung were significantly (p < 0.01) increased in the KP20 group after 72 h post infection. Compared to the KP820 group, the bacterial loads of the lung were significantly (p < 0.01) increased in the KP20 group after 24, 48, and 72 h post infection. At 72 h post infection, the lungs of challenged mice in the KP20 group showed swelling (Figure 6Q) and severe pneumonia with inflammatory cellular infiltration and alveolar wall thickening by an H&E staining (Figure 6R). Compared to the KP20 group, the pathological changes in the lungs of mice in the KP820 group were milder, and the pathological index was lower (Figure 6S).
4. Discussion
K. pneumoniae is a zoonotic pathogen widely distributed in nature, which can cause respiratory tract and urethral infections, meningitis, enteritis, and other tissue and organ inflammation and septicemia in humans and animals [50]. K. pneumoniae has caused economic losses to the breeding industry and posed a long-term threat to public health security and human health [51]. In this study, a total of 14 strains of K. pneumoniae were isolated from avian-origin samples and human hospitals, respectively, and their biological characteristics were compared. We found that the same ST type in K. pneumoniae isolated from avian was prevalent between different species and different regions. Most of K. pneumoniae isolated from avian and human sources could form biofilms, and the biofilms were mainly composed of cellulose and did not contain culri. K. pneumoniae isolated from avian and human sources are multi-drug resistant strains, but there were different drug resistance profiles, which were related to the use of specific antibiotics. K. pneumoniae isolated from avian had certain pathogenicity to Galleria mellonella and mice; K. pneumoniae isolated from humans had stronger pathogenicity.
The phylogenetic tree showed the relationship between the ST types of different strains. Generally, strains belonging to the same branch were closely related. There are 9 ST types of K. pneumoniae in this study, among which ST7640 and ST7641 are newly discovered ST types. Notably, ST5491 was found in chickens, ducks, and Grus Japonensis, and ST7640 was found in ducks and Grus Japonensis, indicating possible cross-species transmission of K. pneumoniae. ST11, ST15, and ST431 were prevalent in Xuzhou. ST5491 was found in Dongtai, Jiangyin, and Sheyang, indicating that ST5491 may be transmitted across regions. Although this study did not detect the same ST type in animals and humans, ST7640 and ST23 belong to the same clade, indicating that there may be mutual transmission between animals and humans. The results of this study were consistent with a study in Qingdao. There was no overlap in STs between the isolates from hospitalized patients and those from meat products or farm animals [24]. More studies are needed to confirm the possibility of transmission of K. pneumoniae between animals and humans. This study confirmed that K. pneumoniae has cross-species and cross-regional transmission, which is not conducive to the prevention and control of K. pneumoniae, and strict infection prevention and control measures should be implemented to reduce the risk of transmission and infection.
K. pneumoniae can form biofilms, which can enhance resistance to the attack of the host immune system [52]. The existence of the biofilm is also closely related to its virulence and drug resistance [53]. In this study, the results of the test tube showed that 78.6% of K. pneumoniae formed biofilms. Sanchez et al. have shown that MDR strains had a high positive rate of biofilm formation, and MDR K. pneumoniae that can form biofilms may cause the infection to become difficult to treat [53]. Curli and cellulose are the primary extracellular components that play crucial roles in the adhesion of bacteria to surfaces and the formation of biofilms [54]. In this study, 14 K. pneumoniae strains lacked curli in biofilms. KP820 and KP1103 contained a higher cellulose production. Studies have shown that cellulose is an important protective scaffold for biofilm formation, and the increase of its synthesis can enhance the stability of biofilm [55].
In recent years, the resistance rate of K. pneumoniae has gradually increased, and more and more MDR strains have appeared [56]. MDR is a key problem in the control of K. pneumoniae [57]. The 14 strains of K. pneumoniae in this study were all multidrug-resistant strains. Multiple drug resistance and high virulence have long been considered two different evolutionary directions, and hvKP is usually sensitive to antibiotics [58]. KP20 in this study fits this profile. Avian strains were completely sensitive to meropenem, imipenem, and polymyxin B, which may be because carbapenems and polymyxins are not approved for feeding food animals [59]. Human strains had a relatively high resistance rate to imipenem and meropenem. Research showed that the resistance rates of K. pneumoniae to imipenem and meropenem increased from 7.8% and 9.6% in 2019 to 11.6% and 13.2% in 2023, respectively, much higher than the resistance rates of E. coli to carbapenem antibiotics (<2%) [60]. It indicated that the current situation of drug resistance of clinical patients to carbapenem antibiotics is becoming increasingly serious. Sulfonamide antibiotics had been used as feed additives to improve the growth and yield of livestock and poultry food animals [33], which was consistent with the complete resistance of K. pneumoniae isolated from avian to sulfonamide antibiotics in this study. Among the K. pneumoniae isolated from avian, two strains came from the feces of Grus Japonensis. Studies have shown that contaminated feed, soil, and surface water can spread antibiotic resistance [61], that feces can become a reservoir of antibiotic compounds and resistant bacteria [62], and that birds become vectors for the spread of resistant bacteria across geographic distances [63]. K. pneumoniae can be transmitted to humans by infecting livestock and poultry or contaminating retail meat [64]. Resistant bacteria can be enriched by selection and return to human patients via direct contact, the environment, or the food chain [65]. Therefore, strict prevention and control measures should be implemented to prevent the transmission of K. pneumoniae between humans and avian, such as regular cleaning and disinfection of farms, improving sanitation, and minimizing contact with livestock and poultry.
Virulence factors play important roles in different stages of pathogen infection and pathogenicity [66]. Compared with cKP, hvKP produces more iron carriers with stronger activity [67]. A study found that the virulence of K. pneumoniae may mainly depend on the number of virulence factors it contains [10]. In our study, there was no difference in the distribution of lipopolysaccharide virulence genes uge and wabG, fimH and mrkD, allantoin virulence gene ureA, and iron carrier virulence gene entB in K. pneumoniae isolated from avian and human sources. However, capsule virulence genes rmpA, rmpA2, magA, K2, wcaG, and other siderophore virulence genes except kfu were only present in some strains isolated from humans, but not in strains isolated from birds. Similar to a study in Faisalabad, Pakistan, none of the six strains of K. pneumoniae isolated from broilers carried rmpA, rmpA2, magA, iucA, iroB, and irp2, but all carried fimH, mrkD, ureA and entB [68]. Therefore, it is speculated that capsule virulence genes and siderophore virulence genes are the key factors for determining the difference in virulence between K. pneumoniae isolated from avian and humans.
K. pneumoniae can naturally exist in the gut and respiratory tract of healthy individuals, and when the body’s resistance is reduced, it can invade epithelial cells by adhesion or break the tight connections between epithelial cells, cross the epithelial cell barrier, and infect the body [69]. Our results showed that the adhesion and invasion ability of different K. pneumoniae to epithelial cells was different. KP35 has the strongest adhesion and invasion ability to epithelial cells.
After K. pneumoniae crosses the epithelial barrier, macrophages are involved in mediating congenital and acquired immune responses to reduce the harm to the body by phagocytosis to eliminate K. pneumoniae [70]. The ability to replicate within the macrophage is associated with virulence [71]. In this study, it was observed that macrophages had weak phagocytic capacity for KP826, KP1016, KP1116, KP35, KP36, KP37, KP15, and KP20. K. pneumoniae proliferated abundantly in macrophages after 20 h, indicating that K. pneumoniae could resist macrophage clearance capacity. In addition, the string test indicated that KP15 and KP20 were hvKP. Determination of virulence genes revealed that KP15 carried the capsular virulence gene K2, and KP20 carried the capsular virulence genes magA and wcaG. Meanwhile, KP15 and KP20 had a strong ability to resist phagocytosis by macrophages, and KP15 had the strongest intracellular replication ability in macrophages. Therefore, the ability of K. pneumoniae to resist phagocytosis by macrophages and its intracellular replication ability in macrophages may be related to the capsular structure. Similarly, Wanford, Joseph J., et al. found that hvKP resisted phagocyte-mediated clearance and replicated in mouse liver macrophages [72]. Combined with the results of the invasion assay, it can be found that KP35 has a strong ability to adhere to and invade Calu-3 cells and resist phagocytosis of macrophages. However, KP35 was not hvKP; it was speculated that this situation may be related to other pathogenicity of K. pneumoniae.
The virulence of both K. pneumoniae isolated from avian and human sources towards Galleria mellonella and mice was approximately identical. The virulence of K. pneumoniae isolated from humans was stronger than that of K. pneumoniae isolated from avian, and this finding was in line with the results of the virulence gene tests. According to the study results of Yee-Huang Ku et al., the carriage rate of virulence factors in isolates with LD50 < 106 (high virulence) was significantly higher than in isolates with LD50 > 106 (low virulence) [73]. In this study, we found that the number of virulence genes was positively correlated with the pathogenicity of mice and Galleria mellonella. It was speculated that the more virulence genes there are, the stronger the pathogenicity to mammals. In this study, the LD50 of the hvKP strain was about 103, which was consistent with the results of Travis J. Kochan et al. [74]. The wet weight in the liver and lung of mice infected with K. pneumoniae isolated from humans was much higher than that of mice infected with K. pneumoniae isolated from avian. The bacterial load in the heart, liver, spleen, and lung of mice infected with K. pneumoniae isolated from humans was much higher than that of mice infected with K. pneumoniae isolated from avian. The wet weight and bacterial load in the lungs of mice infected with strains isolated from humans were about 2 to 3 times those of those infected with strains isolated from avian. Studies have shown that the lung is an organ directly connected with the external environment, which increases the chance of lung infection. The alveolar structure of the lung is also conducive to the adhesion and colonization of bacteria [75]. The liver is an organ with abundant blood circulation and is also vulnerable to bacterial invasion [76].
At present, existing studies have shown that plasmid-mediated horizontal gene transfer is an important factor for the widespread of bacteria within and between species. For example, several intestinal bacteria, including K. pneumoniae, have the ability to acquire and retransfer a broad-host-range plasmid, RP4. The RP4 plasmid can transfer to multiple clinically relevant bacterial species without antibiotic selection pressure [77]. The Klebsiella genus is highly mature in the microbiota of wild animals, making them a perfect reservoir for bacteria and the subsequent gene exchange [78]. K. pneumoniae, due to its outstanding ability to integrate β-lactamase genes, can efficiently insert these drug-resistant genes into mobile plasmids. This unique genetic plasticity, combined with the inherent horizontal transfer characteristics of the plasmid itself, directly promotes the evolution and global spread of plasmid-mediated cephalosporin enzymes in this strain [79].
This study had some limitations, such as a small sample size, the main sample sources being from the Jiangsu region, and the lack of complete genomic analysis. In the future, we will expand the sample size, extend the sampling range, and use whole-genome sequencing to strengthen the hypothesis of the transmission of K. pneumoniae between avian and human.
5. Conclusions
In summary, our study showed that different strains of avian origin had the same ST type, and this phenomenon existed in human strains. The same ST type existed in different regions and among different species. In addition, we found that the multiple drug resistance of K. pneumoniae isolated from avian and human sources was relatively serious. It was also found that K. pneumoniae strains isolated from humans were more pathogenic to mammals than K. pneumoniae strains isolated from avian. Therefore, it is more important to monitor the epidemiological spread of K. pneumoniae further and strengthen the management of its prevention and control to prevent it from causing more serious consequences.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/vetsci12070628/s1, Table S1: Primers used in this study; Figure S1: The number of virulence genes carried by avian and human K. pneumoniae. **, p < 0.01; Figure S2: The adhesion and invasion rate of Calu-3 cells by avian and human Klebsiella pneumoniae. *, p < 0.05, **, p < 0.01; Figure S3: The phagocytic rate of macrophages to avian strains and human strains. **, p < 0.01; Figure S4: (A)–(L) Survival rate of Galleria mellonella (n = 10) infected with K. pneumoniae isolates; Figure S5: (A)–(L) The body weight changes of mice (n = 5) intratracheally injected with K. pneumoniae isolates; Figure S6: (A)–(L) Survival rate of mice (n = 5) intratracheally injected with K. pneumoniae isolates.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Y. (Yinyan Yin) and D.P.; methodology, Y.X., Y.Y. (Yinyan Yin), and D.P.; software, Y.X., F.S., J.Z., and Y.Y. (Yinyan Yin); validation, Y.X. and W.L.; formal analysis, Y.X. and Y.Y. (Yinyan Yin); investigation, Y.X., F.S., and Y.Y. (Yinyan Yin); isolation and identification of Klebsiella pneumoniae from human, F.S., B.Z., and Y.S.; the provider of animals’ tissues, Y.Y. (Yang Yang) and S.C.; data curation, Y.X.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.X., Y.Y. (Yinyan Yin), and T.Q.; writing—review and editing, Y.Y. (Yinyan Yin), T.Q., and D.P.; visualization, Y.X. and Y.Y. (Yinyan Yin); supervision, Y.Y. (Yinyan Yin), T.Q., S.C., and D.P.; project administration, Y.Y. (Yinyan Yin), T.Q., S.C., and D.P.; funding acquisition, Y.Y. (Yinyan Yin), T.Q., S.C., and D.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32172942), the Key Research and Development Program of Social Development of Jiangsu Province (BE2022774), the Agricultural Science and Technology Independent Innovation Fund of Jiangsu Province (CX(23)3071), the Jiangsu Provincial Natural Science Fund for Excellent Young Scholars (BK20240045), the Forestry Science and Technology Innovation and Promotion Project of Jiangsu Province (LYKJ[2024]16), the Open Project Program of Jiangsu Key Laboratory of Zoonosis (No. R2403), Yangzhou University Interdisciplinary Research Foundation for Veterinary Medicine Discipline of Targeted Support (yzuxk202004), the 111 Project (D18007), and a Project Funded by the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions (PAPD).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Jiangsu Laboratory Animal Welfare and Ethical Committee and approved by the Jiangsu Administrative Committee of Laboratory Animals (permission number: SYXK(SU)2022-0044).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data are contained within this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
References
- Liang, J.; Lin, S.; He, L. Formation ability and drug resistance mechanism of Klebsiella pneumoniae biofilm and capsule for multidrug-resistant. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riwu, K.H.P.; Effendi, M.H.; Rantam, F.A.; Khairullah, A.R.; Widodo, A. A review: Virulence factors of Klebsiella pneumonia as emerging infection on the food chain. Vet. World 2022, 15, 2172–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bina, X.R.; Weng, Y.; Budnick, J.; Van Allen, M.E.; Bina, J.E. Klebsiella pneumoniae TolC contributes to antimicrobial resistance, exopolysaccharide production, and virulence. Infect. Immun. 2023, 91, e0030323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Xie, Y. A systematic review on antibiotics misuse in livestock and aquaculture and regulation implications in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 798, 149205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasseri, G.; Teh, C.S.J.; Ooi, P.T.; Thong, K.L. The emergence of colistin-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae strains from swine in Malaysia. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2019, 17, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, B.; Barkema, H.W.; Cobo, E.R.; Kastelic, J.P.; Zhou, M.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, R.; et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from bovine mastitis is cytopathogenic for bovine mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3493–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrous, S.H.; El-Balkemy, F.A.; Abo-Zeid, N.Z.; El-Mekkawy, M.F.; Damaty, H.M.E.; Elsohaby, I. Antibacterial and Anti-Biofilm Activities of Cinnamon Oil against Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Pneumonic Sheep and Goats. Pathogens 2023, 12, 1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Xin, L.; Peng, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, P.; Yu, L.; Liu, M.; Wang, F. Prevalence and antimicrobial susceptibility profiles of ESBL-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae from broiler chicken farms in Shandong Province, China. Poult. Sci. 2022, 101, 102002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Marr, C.M. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00001-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shon, A.S.; Bajwa, R.P.; Russo, T.A. Hypervirulent (hypermucoviscous) Klebsiella pneumoniae: A new and dangerous breed. Virulence 2013, 4, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhao, G.; Chao, X.; Xie, L.; Wang, H. The Characteristic of Virulence, Biofilm and Antibiotic Resistance of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.Y.; Chen, Y.S.; Wu, C.Y.; Chang, H.Y.; Lai, Y.C.; Peng, H.L. RmpA regulation of capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae CG43. J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 3144–3158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, S.; Murphy, C.N. Epidemiology and virulence of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Urin. Tract Infect. Mol. Pathog. Clin. Manag. 2017, 435–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.R.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Jeon, J.H.; Kim, Y.B.; Cha, C.J.; Jeong, B.C.; Lee, S.H. Antimicrobial Resistance of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: Epidemiology, Hypervirulence-Associated Determinants, and Resistance Mechanisms. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennequin, C.; Aumeran, C.; Robin, F.; Traore, O.; Forestier, C. Antibiotic resistance and plasmid transfer capacity in biofilm formed with a CTX-M-15-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2123–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dereeper, A.; Gruel, G.; Pot, M.; Couvin, D.; Barbier, E.; Bastian, S.; Bambou, J.C.; Gelu-Simeon, M.; Ferdinand, S.; Guyomard-Rabenirina, S.; et al. Limited Transmission of Klebsiella pneumoniae among Humans, Animals, and the Environment in a Caribbean Island, Guadeloupe (French West Indies). Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0124222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulss, S.; Stolle, I.; Stamm, I.; Leidner, U.; Heydel, C.; Semmler, T.; Prenger-Berninghoff, E.; Ewers, C. Multispecies and Clonal Dissemination of OXA-48 Carbapenemase in Enterobacteriaceae from Companion Animals in Germany, 2009–2016. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.S.; Song, W.; Park, H.-M.; Oh, J.-Y.; Chae, J.-C.; Shin, S.; Jeong, S.H. Clonal Spread of Extended-Spectrum Cephalosporin-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae Between Companion Animals and Humans in South Korea. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Deng, B.; Liao, W.; Wang, P.; Chen, P.; Wei, J. High rate of multiresistant Klebsiella pneumoniae from human and animal origin. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 2729–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leangapichart, T.; Lunha, K.; Jiwakanon, J.; Angkititrakul, S.; Järhult, J.D.; Magnusson, U.; Sunde, M. Characterization of Klebsiella pneumoniae complex isolates from pigs and humans in farms in Thailand: Population genomic structure, antibiotic resistance and virulence genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 2012–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.S.; Price, L.B. Recent Research Examining Links Among Klebsiella pneumoniae from Food, Food Animals, and Human Extraintestinal Infections. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2016, 3, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overdevest, I.T.; Heck, M.; van der Zwaluw, K.; Huijsdens, X.; van Santen, M.; Rijnsburger, M.; Eustace, A.; Xu, L.; Hawkey, P.; Savelkoul, P.; et al. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase producing Klebsiella spp. in chicken meat and humans: A comparison of typing methods. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 251–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hetland, M.A.K.; Winkler, M.A.; Kaspersen, H.; Håkonsholm, F.; Bakksjø, R.J.; Bernhoff, E.; Delgado-Blas, J.F.; Brisse, S.; Correia, A.; Fostervold, A.; et al. Complete genomes of 568 diverse Klebsiella pneumoniae species complex isolates from humans, animals, and marine sources in Norway from 2001 to 2020. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2025, 14, e0093124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, R.; Wang, X.; Zou, Z.; Zhou, W.; Tan, C.; Cao, Y.; Fu, B.; Zhai, W.; Hu, F.; Wang, Y.; et al. Limited transmission of carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae between animals and humans: A study in Qingdao. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2024, 13, 2387446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; Olson, R.; Fang, C.T.; Stoesser, N.; Miller, M.; MacDonald, U.; Hutson, A.; Barker, J.H.; Hoz, R.M.L.; Johnson, J.R. Identification of Biomarkers for Differentiation of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae from Classical K. pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00776-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, T.A.; MacDonald, U.; Hassan, S.; Camanzo, E.; LeBreton, F.; Corey, B.; McGann, P.; Young, V.B. An Assessment of Siderophore Production, Mucoviscosity, and Mouse Infection Models for Defining the Virulence Spectrum of Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae. mSphere 2021, 6, e00045-21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghofaili, F. Use of bacterial culture supernatants as anti-biofilm agents against Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2022, 26, 1388–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, M.A.F.; Ahmed, F.A.; Elkhateeb, A.F.; Mahmoud, E.E.; Ahmed, M.I.; Ahmed, R.I.; Hosni, A.; Alghamdi, S.; Kabrah, A.; Dablool, A.S.; et al. Virulence Characteristics of Biofilm-Forming Acinetobacter baumannii in Clinical Isolates Using a Galleria mellonella Model. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cimdins, A.; Simm, R. Semiquantitative Analysis of the Red, Dry, and Rough Colony Morphology of Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium and Escherichia coli Using Congo Red. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1657, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosharaf, M.; Tanvir, M.; Haque, M.; Haque, M.; Khan, M.; Molla, A.; Alam, M.Z.; Islam, M.; Talukder, M.R. Metal-adapted bacteria isolated from wastewaters produce biofilms by expressing proteinaceous curli fimbriae and cellulose nanofibers. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Chen, J. Antibiotic resistance profiles and cell surface components of Salmonellae. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphries, R.; Bobenchik, A.M.; Hindler, J.A.; Schuetz, A.N. Overview of Changes to the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, M100, 31st Edition. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2021, 59, e0021321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, G.; Ahmad, S.; Li, Y.; Yan, D.; Yang, S.; Chen, S.; Qiu, Z.; Yu, X.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; et al. Epidemiological, Virulence, and Antibiotic Resistance Analysis of Klebsiella pneumoniae, a Major Source of Threat to Livestock and Poultry in Some Regions of Xinjiang, China. Animals 2024, 14, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Fu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xu, H.; Kong, H.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, L. High prevalence of KPC-2-producing hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae causing meningitis in Eastern China. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compain, F.; Babosan, A.; Brisse, S.; Genel, N.; Audo, J.; Ailloud, F.; Kassis-Chikhani, N.; Arlet, G.; Decré, D.; Doern, G.V. Multiplex PCR for Detection of Seven Virulence Factors and K1/K2 Capsular Serotypes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 4377–4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, S.; Doi, Y.; Diekema, D.J. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae: A Call for Consensus Definition and International Collaboration. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2018, 56, e00959-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turton, J.F.; Perry, C.; Elgohari, S.; Hampton, C.V. PCR characterization and typing of Klebsiella pneumoniae using capsular type-specific, variable number tandem repeat and virulence gene targets. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballén, V.; Gabasa, Y.; Ratia, C.; Ortega, R.; Tejero, M.; Soto, S. Antibiotic Resistance and Virulence Profiles of Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains Isolated From Different Clinical Sources. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 738223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Zhou, M.; Nobrega, D.B.; Cao, Z.; Yang, J.; Zhu, C.; Han, B.; Gao, J. Virulence profiles of Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from 2 large dairy farms in China. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 9027–9036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Xiao, W.; Tang, Y.; Guan, W.; Wang, J.; Shu, F.; Shen, J.; Gu, S.; Zhang, L.; et al. Inosine and D-Mannose Secreted by Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Affect Viability of Lung Epithelial Cells. Molecules 2022, 27, 2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, D.; Wu, A.; Li, R.; Cai, D.; Tong, H.; Wang, N.; Tan, J. Identification of hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae based on biomarkers and Galleria mellonella infection model. BMC Microbiol. 2023, 23, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, H.; Lu, J.; Lin, Y.; Zhu, J.; Lai, M.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Zheng, J. Protective effect and mechanism of nanoantimicrobial peptide ND-C14 against Streptococcus pneumoniae infection. World J. Emerg. Med. 2024, 15, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiden, M.C. Multilocus sequence typing of bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 561–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yang, X.; Wu, Y.; Yang, H.; Han, Y.; Yang, R.; Hu, L.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, D. MLST-based inference of genetic diversity and population structure of clinical Klebsiella pneumoniae, China. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, D.A.; Campos-Madueno, E.I.; Donà, V.; Endimiani, A. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae (hvKp): Overview, Epidemiology, and Laboratory Detection. Pathog. Immun. 2024, 10, 80–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Yang, X.; Chan, E.W.C.; Chen, S. The hypermucoviscosity of hypervirulent K. pneumoniae confers the ability to evade neutrophil-mediated phagocytosis. Virulence 2021, 12, 2050–2059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, K.; Shah, N.; Lewin, M. AL-Amyloidosis Presenting with Negative Congo Red Staining in the Setting of High Clinical Suspicion: A Case Report. Case Rep. Nephrol. 2012, 2012, 593460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surgers, L.; Boyd, A.; Girard, P.M.; Arlet, G.; Decré, D. Biofilm formation by ESBL-producing strains of Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. IJMM 2019, 309, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.B.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, S.; Rong, Y.J.; Huang, Z.A.; Sun, L.W.; Cai, T. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae detection methods: A minireview. Arch. Microbiol. 2023, 205, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Anes, J.; Devineau, S.; Fanning, S. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Prevalence, Reservoirs, Antimicrobial Resistance, Pathogenicity, and Infection: A Hitherto Unrecognized Zoonotic Bacterium. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2021, 18, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almansour, A.M.; Alhadlaq, M.A.; Alzahrani, K.O.; Mukhtar, L.E.; Alharbi, A.L.; Alajel, S.M. The Silent Threat: Antimicrobial-Resistant Pathogens in Food-Producing Animals and Their Impact on Public Health. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, V.; Ferrières, L.; Klemm, P. The ferric yersiniabactin uptake receptor FyuA is required for efficient biofilm formation by urinary tract infectious Escherichia coli in human urine. Microbiology 2008, 154, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, C.J., Jr.; Mende, K.; Beckius, M.L.; Akers, K.S.; Romano, D.R.; Wenke, J.C.; Murray, C.K. Biofilm formation by clinical isolates and the implications in chronic infections. BMC Infect. Dis. 2013, 13, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnhart, M.M.; Chapman, M.R. Curli biogenesis and function. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.P.; Qing, T.; Zhang, P.; Feng, B. Quantitative proteomics and phosphoproteomics elucidate the molecular mechanism of nanostructured TiO(2)-stimulated biofilm formation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 432, 128709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Kumar, S.; Zhang, L.; Wu, H.; Wu, H. Characteristics of antibiotic resistance mechanisms and genes of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Open Med. 2023, 18, 20230707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassetti, M.; Righi, E.; Carnelutti, A.; Graziano, E.; Russo, A. Multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: Challenges for treatment, prevention and infection control. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2018, 16, 749–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyres, K.L.; Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Froumine, R.; Tokolyi, A.; Gorrie, C.L.; Lam, M.M.C.; Duchêne, S.; Jenney, A.; Holt, K.E. Distinct evolutionary dynamics of horizontal gene transfer in drug resistant and virulent clones of Klebsiella pneumoniae. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1008114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, H.; Chen, B.H.; Kuca, K.; Nepovimova, E.; Kaushal, A.; Nagraik, R.; Bhatia, S.K.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, A.; et al. Understanding of Colistin Usage in Food Animals and Available Detection Techniques: A Review. Animals 2020, 10, 1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Huang, X.; Liu, X.; Yu, H.; Long, S. Analysis of the Distribution Characteristics and Changes of Drug Resistance of Pathogens in Patients with Urinary Tract Infection Across Southwest China From 2019 to 2023. Infect. Drug Resist. 2025, 18, 1491–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wareth, G.; Neubauer, H. The Animal-foods-environment interface of Klebsiella pneumoniae in Germany: An observational study on pathogenicity, resistance development and the current situation. Vet. Res. 2021, 52, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuer, H.; Schmitt, H.; Smalla, K. Antibiotic resistance gene spread due to manure application on agricultural fields. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, J.; Ji, F.; Wang, M.; Wu, B.; Qin, J.; Dong, G.; Zhao, R.; Wang, C. Genomic Characteristics and Molecular Epidemiology of Multidrug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae Strains Carried by Wild Birds. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e0269122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.S.; Waits, K.; Nordstrom, L.; Weaver, B.; Aziz, M.; Gauld, L.; Grande, H.; Bigler, R.; Horwinski, J.; Porter, S.; et al. Intermingled Klebsiella pneumoniae Populations Between Retail Meats and Human Urinary Tract Infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Infect. Dis. Soc. Am. 2015, 61, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.L. The role of natural environments in the evolution of resistance traits in pathogenic bacteria. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2009, 276, 2521–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fittipaldi, N.; Segura, M.; Grenier, D.; Gottschalk, M. Virulence factors involved in the pathogenesis of the infection caused by the swine pathogen and zoonotic agent Streptococcus suis. Future Microbiol. 2012, 7, 259–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choby, J.E.; Howard-Anderson, J.; Weiss, D.S. Hypervirulent Klebsiella pneumoniae—Clinical and molecular perspectives. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 287, 283–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.; Mushtaq, M.A.; Abbas, N.; Fatima, F.; Gibbon, M.J.; Schierack, P.; Mohsin, M. Occurrence, antimicrobial resistance and genomic features of Klebsiella pneumoniae from broiler chicken in Faisalabad, Pakistan. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1433124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, D. Molecular pathogenesis of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Future Microbiol. 2014, 9, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinton, L.J.; Walkey, A.J.; Mizgerd, J.P. Integrative physiology of pneumonia. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1417–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hondalus, M.K. Pathogenesis and virulence of Rhodococcus equi. Vet. Microbiol. 1997, 56, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanford, J.J.; Hames, R.G.; Carreno, D.; Jasiunaite, Z.; Chung, W.Y.; Arena, F.; Pilato, V.D.; Straatman, K.; West, K.; Farzand, R. Interaction of Klebsiella pneumoniae with tissue macrophages in a mouse infection model and ex-vivo pig organ perfusions: An exploratory investigation. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e695–e703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, Y.H.; Chuang, Y.C.; Chen, C.C.; Lee, M.F.; Yang, Y.C.; Tang, H.J.; Yu, W.L. Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolates from Meningitis: Epidemiology, Virulence and Antibiotic Resistance. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochan, T.J.; Nozick, S.H.; Valdes, A.; Mitra, S.D.; Cheung, B.H.; Lebrun-Corbin, M.; Medernach, R.L.; Vessely, M.B.; Mills, J.O.; Axline, C.M.R.; et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae clinical isolates with features of both multidrug-resistance and hypervirulence have unexpectedly low virulence. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizgerd, J.P. Respiratory infection and the impact of pulmonary immunity on lung health and disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 824–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenne, C.N.; Kubes, P. Immune surveillance by the liver. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 996–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, A.A.; VanAllen, M.E.; Ahmed, H.; Whitehead-Tillery, C.; Rafique, S.; Bell, J.A.; Zhang, L.; Mansfield, L.S. Conjugative RP4 Plasmid-Mediated Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance Genes to Commensal and Multidrug-Resistant Enteric Bacteria In Vitro. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintelas, M.; Silva, V.; Araújo, S.; Tejedor-Junco, M.T.; Pereira, J.E.; Igrejas, G.; Poeta, P. Klebsiella in Wildlife: Clonal Dynamics and Antibiotic Resistance Profiles, a Systematic Review. Pathogens 2024, 13, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, K. Bench-to-bedside review: The role of beta-lactamases in antibiotic-resistant Gram-negative infections. Crit. Care 2010, 14, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).