Synergistic Efficacy of Doxycycline and Florfenicol Against Aeromonas hydrophilia and Morganella morganii Infections in Pelodiscus sinensis with Skin Ulcer Disease
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Identification of Bacteria
2.2. Antimicrobial Resistance Testing
2.3. Ethical Statement
2.4. In Vivo Infection
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Isolation and Identification of Bacteria
3.2. Molecular Identification and Hemolysis Analysis
3.3. Antibiotic Resistance Analysis
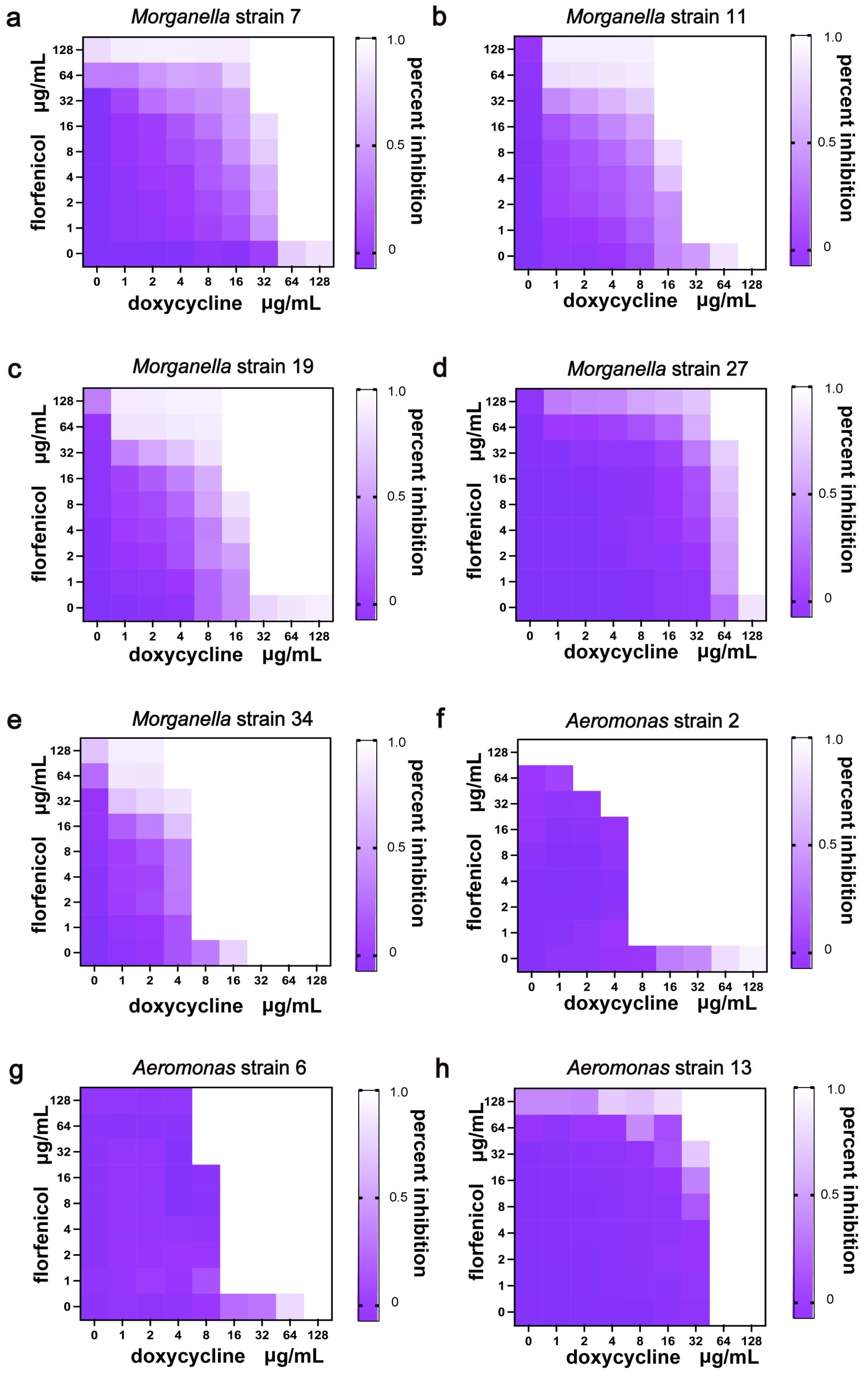
3.4. Combination Therapy
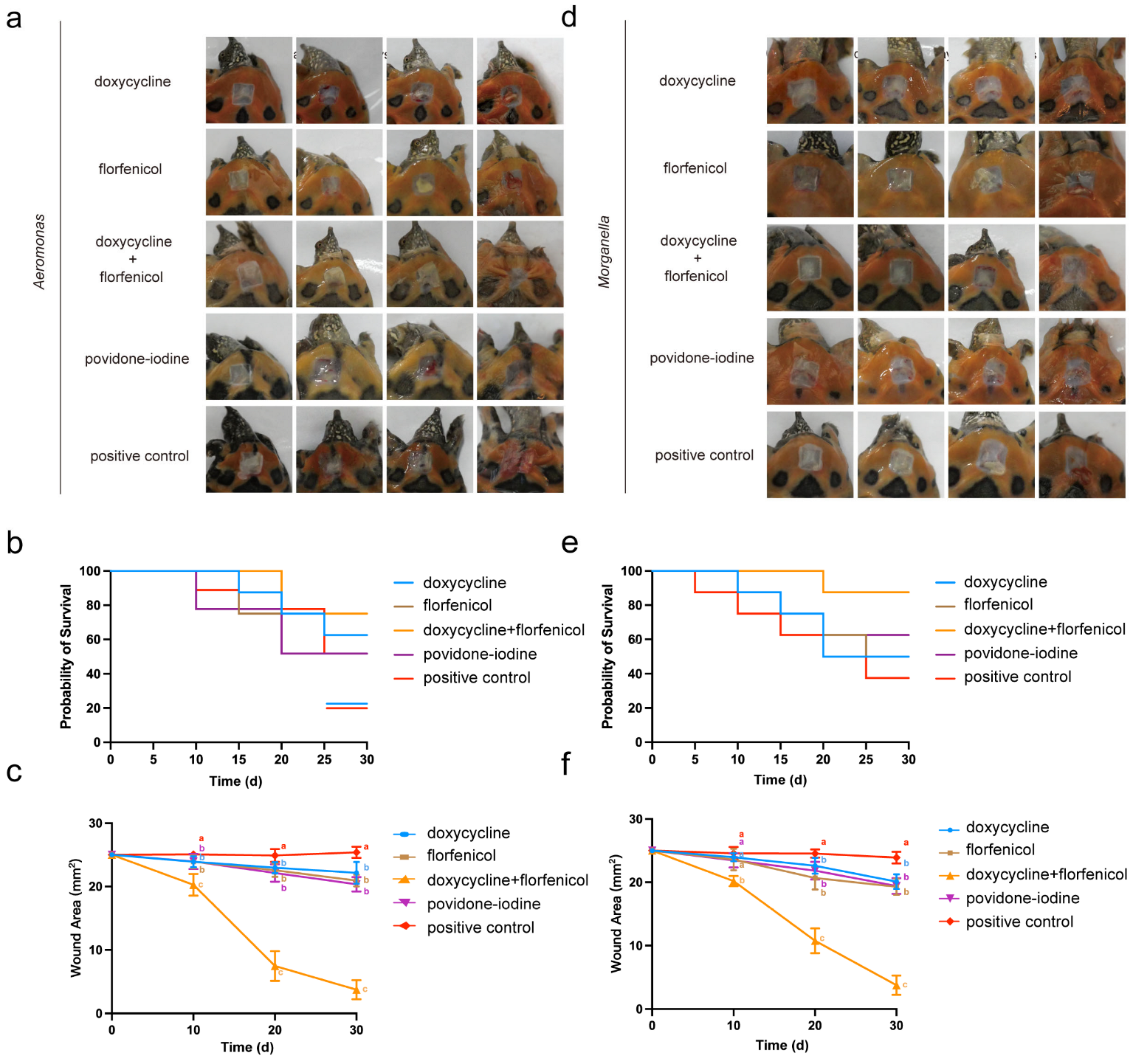
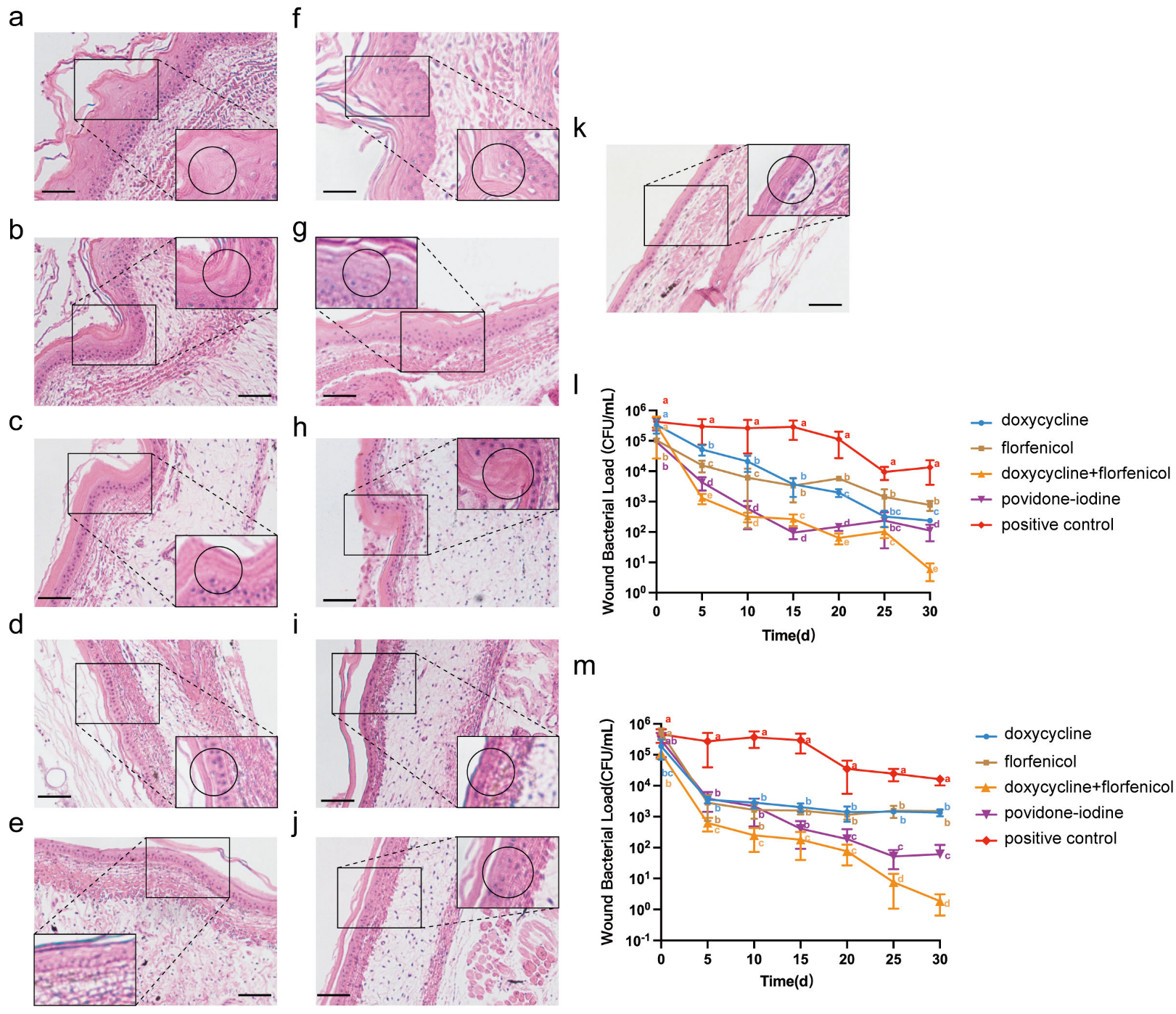
3.5. Combination Therapy on Infection Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Song, D.; He, X.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shuai, J.; Wang, H.; Li, Q.; Du, M. Cytotoxicity and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella enterica subspecies isolated from raised reptiles in Beijing, China. Animals 2023, 13, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Cheng, C.; Chen, J.; Xu, X.; Ding, C.; Gu, B. Interactions of commensal and pathogenic microorganisms with the mucus layer in the colon. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 680–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kuang, D.; Wang, F.; Meng, J.; Jin, H.; Yang, X.; Liao, M.; Klena, J.D.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Turtles as a possible reservoir of nontyphoidal Salmonella in Shanghai, China. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2016, 13, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Lei, J.; Zhai, X.; Lu, N.; Shi, H.; Wang, J. Diversity of underwater vocalizations in Chinese soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Animals 2023, 13, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuser, W.; Lierz, M.; Kraut, S.; Fischer, D. Laser therapy in a soft-shelled turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis) for the treatment of skin and shell ulceration: A case report. Tierärztliche Prax. Ausg. K Kleintiere/Heimtiere 2013, 41, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Cheng, M.; Hu, X.; Xue, M.; Jiang, N.; Liu, W.; Fan, Y.; Meng, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhou, Y. Pathological changes of highly pathogenic Bacillus cereus on Pelodiscus sinensis. Vet. Quart. 2023, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.; Liu, N.; Wang, C.; Luo, Y.; Liu, J. Lonicera japonica protects Pelodiscus sinensis by inhibiting the biofilm formation of Aeromonas hydrophila. Appl. Microbiol. Biot. 2024, 108, 12910–12919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Jin, F.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, D.; Hu, B.; Hong, Y. The impact of aquaculture system on the microbiome and gut metabolome of juvenile Chinese softshell turtle (Pelodiscus sinensis). Imeta 2022, 1, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, K. Neutrophils and aquatic pathogens. Parasite Immunol. 2022, 44, 12915–12924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunderkötter, C.; Wohlrab, J.; Hamm, H. Scabies: Epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Dtsch. Ärzteblatt Int. 2021, 118, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, D.; Santi, C.G.; Aoki, V.; Maruta, C.W. Bullous pemphigoid. An. Bras. Dermatol. 2019, 94, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sy, A.; Srinivasan, M.; Mascarenhas, J.; Lalitha, P.; Rajaraman, R.; Ravindran, M.; Oldenburg, C.E.; Ray, K.J.; Glidden, D.; Zegans, M.E.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa keratitis: Outcomes and response to corticosteroid treatment. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.X.; Zheng, J.C.; Jiang, Y.L. A new iridovirus isolated from soft-shelled turtle. Virus Res. 1999, 63, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lensink, M.J.; Li, Y.; Lequime, S. Aquatic Flaviviruses. J. Virol. 2022, 96, 43922–43932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.A.; Harbottle, H. Antimicrobial drug resistance in fish pathogens. Microbiol. Spectr. 2018, 6, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sures, B.; Nachev, M.; Schwelm, J.; Grabner, D.; Selbach, C. Environmental parasitology: Stressor effects on aquatic parasites. Trends Parasitol. 2023, 39, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, K.J.; Umair, M.; Altaf, M.; Hussain, T.; Ahmad, R.M.; Abdeen, S.M.Z.U.; Pieroni, A.; Abbasi, A.M.; Ali, S.; Ashraf, S.; et al. Cross-cultural diversity analysis: Traditional knowledge and uses of freshwater fish species by indigenous peoples of southern Punjab, Pakistan. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed. 2023, 19, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, K.; Chen, M.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Z.; Deng, L.; Li, T.; Feng, Y.; Ouyang, P.; Huang, X.; Chen, D.; et al. Genotype diversity and antibiotic resistance risk in Aeromonas hydrophila in Sichuan, China. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2023, 55, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Shama, U.H.; El Raheem, A.A.A.; Alsaadawy, R.M.; Sayed, H.H. Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Aeromonas hydrophila isolated from freshwater fishes at Middle Upper Egypt. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5920–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, M.M.; Sellera, F.P.; Furlan, J.P.R.; Aravena-Ramirez, V.; Fuentes-Castillo, D.; Fuga, B.; Dos Santos Froes, A.J.; de Sousa, A.L.; Garino Junior, F.; Lincopan, N. Gut colonization of semi-aquatic turtles inhabiting the Brazilian Amazon by international clones of CTX-M-8-producing Escherichia coli. Vet. Microbiol. 2025, 301, 110344–110352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percipalle, M.; Giardina, G.; Lipari, L.; Piraino, C.; Macrì, D.; Ferrantelli, V. Salmonella Infection in illegally imported Spur-Thighed Tortoises (Testudo graeca). Zoonoses Public Health 2011, 58, 262–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Luo, J.; Deng, F.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, H. Antibiotic combination therapy: A strategy to overcome bacterial resistance to aminoglycoside antibiotics. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worthington, R.J.; Melander, C. Combination approaches to combat multidrug-resistant bacteria. Trends Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, A.R.M.; Hu, Y.; Holt, J.; Yeh, P. Antibiotic combination therapy against resistant bacterial infections: Synergy, rejuvenation and resistance reduction. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangden, T. Combination antibiotic therapy for multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. Upsala J. Med. Sci. 2014, 119, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaf, M.; Ijaz, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Rehman, A.; Avais, M. Antibiotic susceptibility profile and synergistic effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on antibacterial activity of resistant antibiotics (Oxytetracycline and Gentamicin) against methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Microb. Pathog. 2019, 137, 103755–103762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, W.; Roessler, C.; Francis, P.J.; Noel, D.; Loukas, M. Post-surgical gangrene with Pseudomonas luteola resulting in Limb Amputation: A Case Review. Cureus J. Med. Sci. 2018, 10, 3441–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayers, E.W.; Beck, J.; Bolton, E.E.; Brister, J.R.; Chan, J.; Comeau, D.C.; Connor, R.; DiCuccio, M.; Farrell, C.M.; Feldgarden, M.; et al. Database resources of the national center for biotechnology information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 52, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Venkatachalam, P.; Shanmugam, S.R.; Paramasivam, N. Fractional inhibitory concentration of bio-actives from agricultural waste disassembles biofilms and quenches virulence of nosocomial pathogens. J. Med. Microbiol. 2025, 74, 1980–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Liu, X.; Xu, J.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J. Antimicrobial Effect of Zophobas morio hemolymph against bovine mastitis pathogens. Microorganisms. 2020, 8, 1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, L.; Wendy, U.; Raymond, A.; Cartner, S.; Grandin, T.; Greenacre, C.; Gwaltney-Brant, S.; McCrackin, M.A.; Meyer, R.; Miller, D.; et al. AVMA Guidelines for the Euthanasia of Animals: 2020 Edition; American Veterinary Medical Association: Schaumburg, IL, USA, 2020; pp. 40–64. [Google Scholar]
- Pace, A.; Meomartino, L.; Affuso, A.; Mennonna, G.; Hochscheid, S.; Dipineto, L. Aeromonas induced polyostotic osteomyelitis in a juvenile loggerhead sea turtle Caretta caretta. Dis. Aquat. Organ. 2018, 132, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, D.G.J.; Flach, C. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 20, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wencewicz, T.A. Crossroads of Antibiotic Resistance and Biosynthesis. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3370–3399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosikowska, U.; Stec, J.; Andrzejczuk, S.; Mendrycka, M.; Pietras-Ozga, D.; Stępien-Pysniak, D. Plasmid-mediated fluoroquinolone resistance genes in quinolone-susceptible Aeromonas spp. phenotypes isolated from recreational surface freshwater reservoir. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 885360–885371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odeyemi, O.A.; Ahmad, A. Antibiotic resistance profiling and phenotyping of Aeromonas species isolated from aquatic sources. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbandi, A.; Abdi, M.; Dashtbin, S.; Yaghoubi, S.; Sholeh, M.; Kouhsari, E.; Darbandi, T.; Ghanavati, R.; Taheri, B. Antibody-antibiotic conjugates: A comprehensive review on their therapeutic potentials against bacterial infections. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2024, 38, 25071–25083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Peng, K.; Yip, B.; Chih, Y.; Cheng, J. Boosting synergistic effects of short antimicrobial peptides with conventional antibiotics against resistant bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 747760–747773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Fágáin, C.Ó.; Kennedy, R.O. Antibody stability: A key to performance-Analysis, influences and improvement. Biochimie 2020, 177, 213–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, N.; Du, M.; Zhu, Y. Therapeutic effect of darkling beetle (Zophobas morio) hemolymph on skin thermal injury in mice infected by Staphylococcus haemolyticus. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Qin, T.; Chen, K.; Pan, L.; Xie, J.; Xi, B. Antimicrobial and antivirulence activities of carvacrol against pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Shuai, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Du, M.; Wang, H. Exploring the pathogenic role of Aeromonas hydrophilia in skin ulcer disease in turtles: Insights into treatment with longan leaf polysaccharides. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 316, 144674–144690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, S.; Du, M.; Liu, N.; Shan, Q.; Zou, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y. A Novel β-Hairpin Peptide Z-d14CFR Enhances Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Clearance in a Murine Model of Mastitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
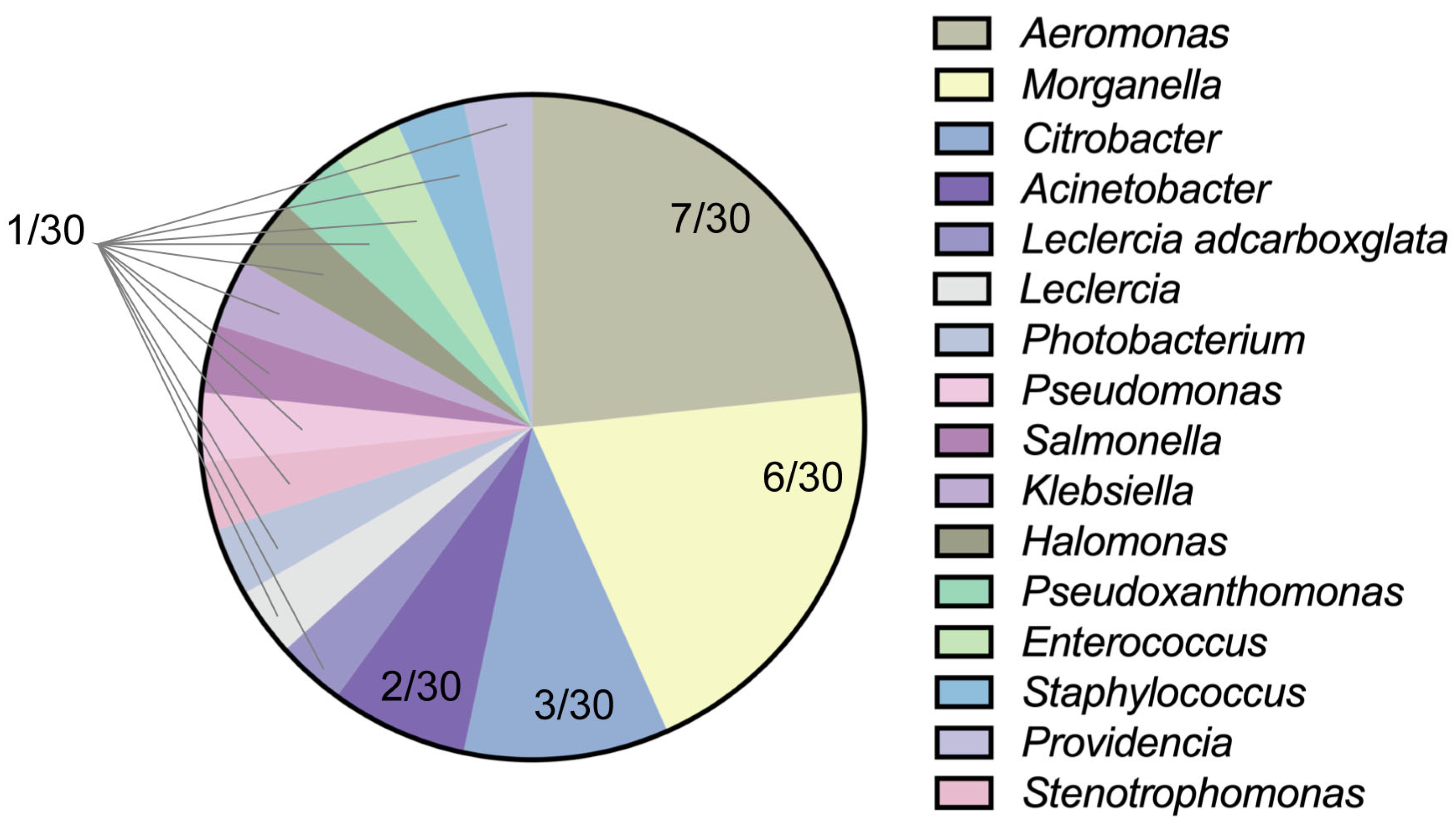
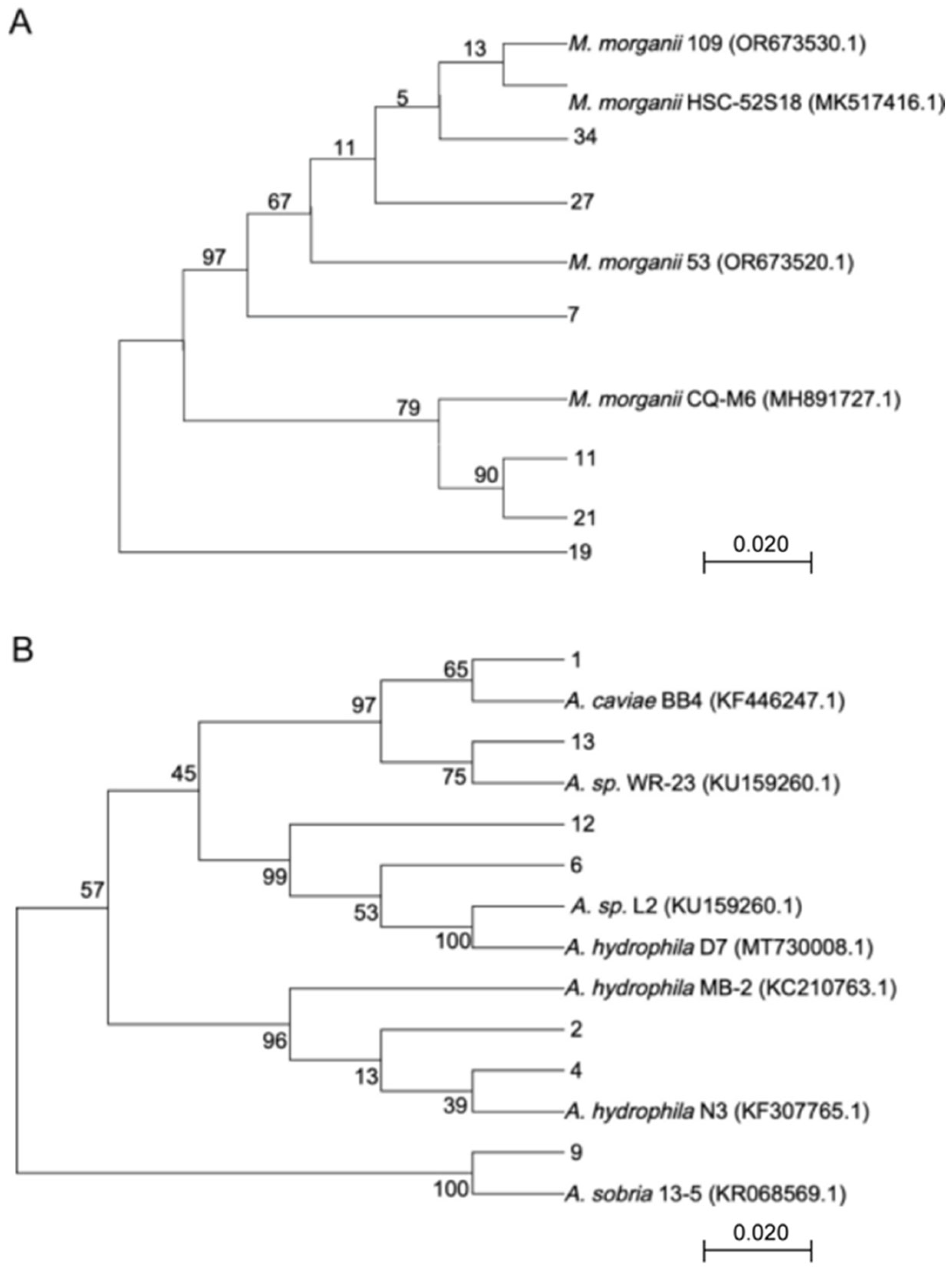
| Code | Reference Strain | Similarity |
|---|---|---|
| 7 | P. morganii (MK517416.1) | 99.30% |
| 11 | P. morganii (MH891727.1) | 89.64% |
| 19 | P. morganii (OR673530.1) | 99.70% |
| 21 | P. morganii (MH891727.1) | 99.40% |
| 27 | P. morganii (OR673520.1) | 99.40% |
| 34 | P. morganii (OR673520.1) | 99.70% |
| 1 | A. caviae (KF446247.1) | 95.39% |
| 2 | A. hydrophila (KC210763.1) | 99.12% |
| 4 | A. hydrophila (KF307765.1) | 97.31% |
| 6 | A. hydrophila (MT730008.1) | 97.21% |
| 9 | A. sobria (KR068569.1) | 86.67% |
| 12 | A. sp (HQ292718.2) | 97.21% |
| 13 | A. sp (KU159260.1) | 98.45% |
| Category | Antibacterial Agents | Rate (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | I | S | ||
| Chloramphenicols | Florfenicol | 100.0 | 0 | 0 |
| Cephalosporins | Ceftiofur | 100.0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tetracyclines | Doxycycline | 100.0 | 0 | 0 |
| β-lactams | Ampicillin | 100.0 | 0 | 0 |
| Carbapenem | Meropenem | 100.0 | 0 | 0 |
| Fluoroquinolones | Enrofloxacin | 53.5 | 46.15 | 0 |
| Drug Name | MIC (μg/mL) | Drug Name | MIC (μg/mL) | FIC | Combined Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single | Combined | Single | Combined | ||||
| Ceftiofur | >128 | 128 | Meropenem | >128 | 128 | 2 | Synergistic |
| >128 | Enrofloxacin | 128 | 128 | 2 | Synergistic | ||
| >128 | Ampicillin | >128 | >128 | 2 | Synergistic | ||
| 1 | Doxycycline | 128 | 128 | 1.008 | Synergistic | ||
| Florfenicol | >128 | 64 | Enrofloxacin | 128 | 64 | 0.75 | Additive |
| 16 | Doxycycline | 128 | 32 | 0.375 | Synergy | ||
| 128 | Ceftiofur | >128 | 4 | 0.516 | Additive | ||
| >128 | Ampicillin | >128 | >128 | 2 | Synergistic | ||
| 128 | Meropenem | >128 | 1 | 0.516 | Additive | ||
| Ampicillin | >128 | 128 | Enrofloxacin | 128 | 32 | 0.75 | Additive |
| 128 | Doxycycline | 128 | 128 | 1.5 | Synergistic | ||
| 128 | Meropenem | >128 | 128 | 1 | Additive | ||
| Meropenem | >128 | 32 | Doxycycline | 128 | 64 | 0.625 | Additive |
| Enrofloxacin | 128 | 64 | Meropenem | >128 | 1 | 0.504 | Additive |
| 64 | Doxycycline | 128 | 2 | 0.516 | Additive | ||
| Strain | Doxycycline MIC (μg/mL) | Florfenicol MIC (μg/mL) | FICI | Combined Results | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single | Combined | Single | Combined | |||
| 7 | 128 | 32 | 16 | >128 | 0.375 | Synergistic |
| 11 | 128 | 16 | >128 | 16 | 0.1875 | Synergistic |
| 19 | 128 | 16 | >128 | 16 | 0.1875 | Synergistic |
| 27 | 128 | 64 | >128 | 64 | 0.75 | Additive |
| 34 | 32 | 8 | >128 | 32 | 0.375 | Synergistic |
| 2 | >128 | 4 | 128 | 32 | 0.2656 | Synergistic |
| 6 | 128 | 8 | >128 | 32 | 0.1875 | Synergistic |
| 13 | >128 | 32 | >128 | 32 | 0.25 | Synergistic |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Lei, X.; Shi, X.; Du, M.; Liu, X. Synergistic Efficacy of Doxycycline and Florfenicol Against Aeromonas hydrophilia and Morganella morganii Infections in Pelodiscus sinensis with Skin Ulcer Disease. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070611
Cai Z, Zhang W, Wang Y, Yang Z, Lei X, Shi X, Du M, Liu X. Synergistic Efficacy of Doxycycline and Florfenicol Against Aeromonas hydrophilia and Morganella morganii Infections in Pelodiscus sinensis with Skin Ulcer Disease. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(7):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070611
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Ziwen, Wenjing Zhang, Yun Wang, Zhaoying Yang, Xiaolei Lei, Xiaomin Shi, Mengze Du, and Xiaoye Liu. 2025. "Synergistic Efficacy of Doxycycline and Florfenicol Against Aeromonas hydrophilia and Morganella morganii Infections in Pelodiscus sinensis with Skin Ulcer Disease" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 7: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070611
APA StyleCai, Z., Zhang, W., Wang, Y., Yang, Z., Lei, X., Shi, X., Du, M., & Liu, X. (2025). Synergistic Efficacy of Doxycycline and Florfenicol Against Aeromonas hydrophilia and Morganella morganii Infections in Pelodiscus sinensis with Skin Ulcer Disease. Veterinary Sciences, 12(7), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12070611






