Occurrence of Aspergillus spp. in Parrot Feeds on the Polish Market: The Potential Health Threat of Aspergillosis and Mycotoxicosis for Exotic Pet Birds, a Pilot Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Amo, L.; Visser, M.E.; Van Oers, K. Smelling out predators is innate in birds. Ardea 2011, 99, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderfoot, O.V.; Holloway, T. Air pollution impacts on avian species via inhalation exposure and associated outcomes. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 083002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, A. Aspergillosis. In Current Therapy in Avian Medicine and Surgery; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Arné, P.; Risco-Castillo, V.; Jouvion, G.; Le Barzic, C.; Guillot, J. Aspergillosis in Wild Birds. J. Fungi 2021, 7, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arné, P.; Lee, M.D. Fungal Infections. In Diseases of Poultry; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1111–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Barton, J.T.; Daft, B.M.; Read, D.H.; Kinde, H.; Bickford, A.A. Tracheal aspergillosis in 6 1/2-week-old chickens caused by Aspergillus flavus. Avian Dis. 1992, 36, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perelman, B.; Kuttin, E.S. Aspergillosis in ostriches. Avian Pathol. 1992, 21, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.P.; Orosz, S.E. The Diagnosis of Aspergillosis in Birds. Semin. Avian Exot. Pet Med. 2000, 9, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagneau, P.E.; Houtain, J.Y. Cas d’aspergillose chez des perroquets en Belgique. J. De Mycol. Médicale 2001, 11, 171–172. [Google Scholar]
- Churria, C.D.G.; Reynaldi, F.; Origlia, J.; Marcantoni, H.; Píscopo, M.V.; Loyola, M.; Reinoso, E.H.; Petruccelli, M. Pulmonary Aspergillosis Due to Aspergillus flavus Infection in a Captive Eclectus Parrot (Eclectus roratus). Braz. J. Vet. Pathol. 2012, 5, 4–6. [Google Scholar]
- Kiser, P.K.; Meritet, D.M.; Bildfell, R.J. Aspergillus Section Nigri-Associated Calcium Oxalate Crystals in an Eurasian Eagle Owl (Bubo bubo). Case Rep. Vet. Med. 2018, 2018, 3807059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, J.L.; Thurston, J.R. Rapid hematogenous dissemination of Aspergillus fumigatus and A. flavus spores in turkey poults following aerosol exposure. Avian Dis. 1983, 27, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tell, L.A. Aspergillosis in Mammals and Birds: Impact on Veterinary Medicine. Med. Mycol. 2005, 43, S71–S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blount, W.P. Turkey “X” disease. J. Br. Turk. Fed. 1961, 9, 52. [Google Scholar]
- Bullerman, L.B.; Schroeder, L.L.; Park, K.Y. Formation and Control of Mycotoxins in Food. J. Food Prot. 1984, 47, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mislivec, P.B.; Dieter, C.T.; Bruce, V.R. Mycotoxin-producing potential of mold flora of dried beans. Appl. Microbiol. 1975, 29, 522–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweeney, M.J.; Dobson, A.D. Mycotoxin production by Aspergillus, Fusarium and Penicillium species. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 43, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boeuvre, M.; Mavungu, J.D.; Landshchoot, S.; Audenaert, K.; Eeckhout, M.; Maene, P. Natural occurrence of mycotoxins and their masked forms in food and feed products. World Mycotoxin J. 2012, 5, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin, S.; Ramos, A.J.; Cano-Sancho, G.; Sanchis, V. Mycotoxins: Occurrence, toxicology, and exposure assessment. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 60, 218–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshannaq, A.; Yu, J.H. Occurrence, Toxicity, and Analysis of Major Mycotoxins in Food. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchese, S.; Polo, A.; Ariano, A.; Velotto, S.; Costantini, S.; Severino, L. Aflatoxin B1 and M1: Biological Properties and Their Involvement in Cancer Development. Toxins 2018, 10, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gab-Allah, M.A.; Choi, K.; Kim, B. Type B Trichothecenes in Cereal Grains and Their Products: Recent Advances on Occurrence, Toxicology, Analysis and Post-Harvest Decontamination Strategies. Toxins 2023, 15, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitt, J.I. Toxigenic fungi: Which are important? Med. Mycol. 2000, 38, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wannop, C.C. The Histopathology of Turkey “X” Disease in Great Britain. Avian Dis. 1961, 5, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asplin, F.D.; Carnaghan, R.B.A. The Toxicity of Certain Groundnut Meals for Poultry with Special Reference to Their Effect on Ducklings and Chickens. Vet. Rec. 1961, 73, 1215–1219. [Google Scholar]
- Richard, J.L. Some major mycotoxins and their mycotoxicoses—An overview. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumagalli, F.; Ottoboni, M.; Pinotti, L.; Cheli, F. Integrated Mycotoxin Management System in the Feed Supply Chain: Innovative Approaches. Toxins 2021, 13, 572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieu, S.; Guillot, J.; Beaudeau, F. Antemortem diagnostic tests for the detection of Aspergillus infection in birds: A systematic review. Med. Mycol. 2024, 62, myae112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Baba, F.; Watza, D.; Soubani, A.O. Is Aspergillus isolated from respiratory cultures clinically significant? Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2021, 88, 543–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Silvanose, C.; Agrawal, S.K.; Agrawal, Y.K. The Synergistic Role of Endoscopy and Cytology in the Diagnosis of Aspergillosis: A Comprehensive Review of Human and Avian Medicine. J. Eur. Intern. Med. Prof. 2023, 1, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, I.D.; Richardson, M.; Denning, D.W. Antibody testing in aspergillosis—Quo vadis? Med. Mycol. 2015, 53, 417–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; He, J.; Xing, B.; Zhang, X.; Sun, G.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y. Potential value of serum Aspergillus IgG antibody detection in the diagnosis of invasive and chronic pulmonary aspergillosis in non-agranulocytic patients. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klich, M.A. Aspergillus flavus: The major producer of aflatoxin. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2007, 8, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awuchi, C.G.; Ondari, E.N.; Ogbonna, C.U.; Upadhyay, A.K.; Baran, K.; Okpala, C.O.R.; Korzeniowska, M.; Guiné, R.P.F. Mycotoxins Affecting Animals, Foods, Humans, and Plants: Types, Occurrence, Toxicities, Action Mechanisms, Prevention, and Detoxification Strategies—A Revisit. Foods 2021, 10, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazareth, T.M.; Soriano Pérez, E.; Luz, C.; Meca, G.; Quiles, J.M. Comprehensive Review of Aflatoxin and Ochratoxin A Dynamics: Emergence, Toxicological Impact, and Advanced Control Strategies. Foods 2024, 13, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuckey, R.E.; Lane, G.T.; Loewer, O.J.; Miller, C.E.; Bitzer, M.J. Aflatoxins in Corn; University of Kentucky, College of Agriculture: Lexington, KY, USA, 1984; p. 59. [Google Scholar]
- McMillan, M.C.; Petrak, M.L. Retrospective Study of Aspergillosis in Pet Birds. J. Assoc. Avian Vet. 1989, 3, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Herdt, P. Aspergillose bij papegaaien. Vlaams Diergeneeskd. Tijdschr. 1996, 65, 343–344. [Google Scholar]
- PN-ISO 21527-2:2009; Microbiology of Food and Feeding Stuffs—Horizontal Method for the Enumeration of Yeasts and Moulds—Part 2: Colony Count Technique in Products with Water Activity Less Than or Equal to 0.95. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2009.
- D’aoust, J.Y. Salmonella in Commercial Pet Foods. Can. Vet. J. 1978, 19, 99–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behravesh, C.B.; Ferraro, A.; Deasy, I.I.I.M.; Dato, V.; Moll, M.; Sandt, C.; Rea, N.K.; Rickert, R.; Marriott, C.; Warren, K.; et al. Human Salmonella Infections Linked to Contaminated Dry Dog and Cat Food, 2006–2008. Pediatrics 2010, 126, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemser, S.M.; Doran, T.; Grabenstein, M.; McConnell, T.; McGrath, T.; Pamboukian, R.; Smith, A.C.; Achen, M.; Danzeisen, G.; Kim, S.; et al. Investigation of Listeria, Salmonella, and Toxigenic Escherichia coli in Various Pet Foods. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2014, 11, 706–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hołda, K.; Głogowski, R.; Hac-Szymańczuk, E.; Wiczuk, W.A. Comprehensive Microbiological Evaluation of Dry Foods for Growing Dogs Marketed in Poland. Ann. Wars. Univ. Life Sci. 2017, 56, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Błajet-Kosicka, A.; Kosicki, R.; Twaruzek, M.; Grajewski, J. Determination of Moulds and Mycotoxins in Dry Dog and Cat Food Using Liquid Chromatography with Mass Spectrometry and Fluorescence Detection. Food Addit. Contam. Part B 2014, 7, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukier, E.; Goldsztejn, M.; Grenda, T.; Kwiatek, K.; Wasyl, D.; Hoszowski, A. Microbiological Quality of Compound Feed Used in Poland. Bull. Vet. Inst. Pulawy 2012, 56, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nešić, K.; Mitrović, R.; Marković, R. Categorization of Animal Feed According to Microbiological Quality—Preferable Improvement in the Food Chain. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 854, 012065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasconi, L.; Dazuk, V.; Molosse, V.L.; Cécere, B.G.O.; Deolindo, G.L.; Mendes, R.E.; Gloria, E.M.; Ternus, E.M.; Galli, G.M.; Paiano, D.; et al. Nursery Pigs Fed with Feed Contaminated by Aflatoxin B1 (Aspergillus flavus) and Anti-Mycotoxin Blend: Pathogenesis and Negative Impact on Animal Health and Weight Gain. Microb. Pathog. 2024, 186, 106474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunus, A.W.; Razzazi-Fazeli, E.; Bohm, J. Aflatoxin B1 in Affecting Broiler’s Performance, Immunity, and Gastrointestinal Tract: A Review of History and Contemporary Issues. Toxins 2011, 3, 566–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrinelli, V.; Teixeira, F.A.; Queiroz, M.R.; Brunetto, M.A. Environmental Impact of Diets for Dogs and Cats. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 18510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullerman, L.B.; Bianchini, A. Stability of Mycotoxins During Food Processing. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2007, 119, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Liu, X.; Zhao, M.; Guo, W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, W.; Liu, Z.; Deng, M.; et al. Occurrence and Diversity of Fungi and Their Mycotoxin Production in Common Edible and Medicinal Substances from China. J. Fungi 2025, 11, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lach, M.; Kotarska, K. Negative Effects of Occurrence of Mycotoxins in Animal Feed and Biological Methods of Their Detoxification: A Review. Molecules 2024, 29, 4563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witaszak, N.; Waśkiewicz, A.; Bocianowski, J.; Stępień, Ł. Contamination of Pet Food with Mycobiota and Fusarium Mycotoxins—Focus on Dogs and Cats. Toxins 2020, 12, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziętara-Wysocka, J.; Sierawska, O.; Taskin, C.; Poniewierska-Baran, A.; Bębnowska, D.; Hrynkiewicz, R.; Lewandowski, F.; Niedźwiedzka-Rystwej, P. Investigation of Microbiological Safety of Dry Cat Foods Marketed in Poland. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2023, 70, 971–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaemmaghami, S.S.; Pashootan, N.; Razzaghi-Abyaneh, M. Toxigenicity and Phylogeny of Aspergillus Section Flavi in Poultry Feed in Iran. Curr. Med. Mycol. 2020, 6, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bintvihok, A.; Thiengnin, S.; Doi, K.; Kumagai, S. Residues of Aflatoxins in the Liver, Muscle, and Eggs of Domestic Fowls. J. Vet. Sci. Med. Diagn. 2002, 64, 1037–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, M.A.; Brake, J.; Hamilton, P.B.; Hagler, W.M.; Nesheim, S. Dietary Exposure of Breeders to Aflatoxin Results in Immune Dysfunction in Progeny Chicks. Poult. Sci. 1998, 77, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, C.A.F.; Kobashigawa, E.; Reis, T.A.; Mestieri, L.; Albuquerque, R.; Correa, L.M.B. Aflatoxin B1 Residues in Eggs of Laying Hens Fed a Diet Containing Different Levels of the Mycotoxin. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2000, 17, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzo, G.; Pugliese, N.; Samarelli, R.; Schiavone, A.; Dimuccio, M.M.; Circella, E.; Bonerba, E.; Ceci, E.; Camarda, A. Ochratoxin A and Aflatoxin B1 Detection in Laying Hens for Omega 3-Enriched Eggs Production. Agriculture 2023, 13, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Balachandran, C. Haematological and biochemical alterations in broiler chicken fed aflatoxin and cyclopiazonic acid. Indian Vet. J. 2005, 82, 1255–1257. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, R.J.; Raval, P.J. Cytotoxicity of aflatoxin on red blood corpuscles. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 1991, 47, 428–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liggett, A.D.; Colvin, B.M.; Beaver, R.W.; Wilson, D.M. Canine aflatoxicosis: A continuing problem. Vet. Hum. Toxicol. 1986, 28, 428–430. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, L.E.; Prendergast, A.J.; Turner, P.C.; Humphrey, J.H.; Stoltzfus, R.J. Aflatoxin Exposure During Pregnancy, Maternal Anemia, and Adverse Birth Outcomes. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 96, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wangikar, P.B.; Dwivedi, P.; Sinha, N.; Sharma, A.K.; Telang, A.G. Effects of aflatoxin B1 on embryo fetal development in rabbits. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2005, 43, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shivasharanappa, G.Y.; Mundas, S.; Rao, D.G.K.; Tikare, V.; Shridhar, N.B. Histopathological changes in pigs exposed to aflatoxin B1 during pregnancy. Indian J. Anim. Res. 2013, 47, 386–391. [Google Scholar]
- Lawson, B.; Robinson, R.A.; Toms, M.P.; Risely, K.; MacDonald, S.; Cunningham, A.A. Health Hazards to Wild Birds and Risk Factors Associated with Anthropogenic Food Provisioning. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2018, 373, 20170091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.J.; Junaidu, K.; Kwanashie, C.N.; Salawudeen, M.T. Identification of Aspergillus Species in Feed Fed to Caged Birds Using Morphological Characteristics in Zaria, Nigeria. Microbiol. Res. Int. 2017, 5, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perpiñán, D. Problems of excess nutrients in psittacine diets. Companion Anim. 2015, 20, 532–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpsoy, L.; Yalvac, M.E. Key roles of vitamins A, C, and E in aflatoxin B1-induced oxidative stress. Vitam. Horm. 2011, 86, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atroshi, F.; Rizzo, A.; Sankari, S.; Biese, I.; Westermarck, T.; Veijalainen, P. Liver enzyme activities of rats exposed to ochratoxin A and T-2 toxin with antioxidants. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2000, 64, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, G.J.; Harrison, L.R.; Ritchie, B.W. Nutrition. In Avian Medicine: Principles and Application; Harrison, G.J., Harrison, L.R., Ritchie, B.W., Eds.; Spix Publishing Inc.: Palm Beach, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 85–140. [Google Scholar]
- Péron, F.; Grosset, C. The diet of adult psittacids: Veterinarian and ethological approaches. J. Anim. Physiol. Anim. Nutr. 2014, 98, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bintvihok, A.; Treebonmuang, S.; Srisakwattana, K.; Nuanchun, W.; Patthanachai, K.; Usawang, S. A Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Aflatoxin-producing Fungus Using an Optimized Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). Toxicol. Res. 2016, 32, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
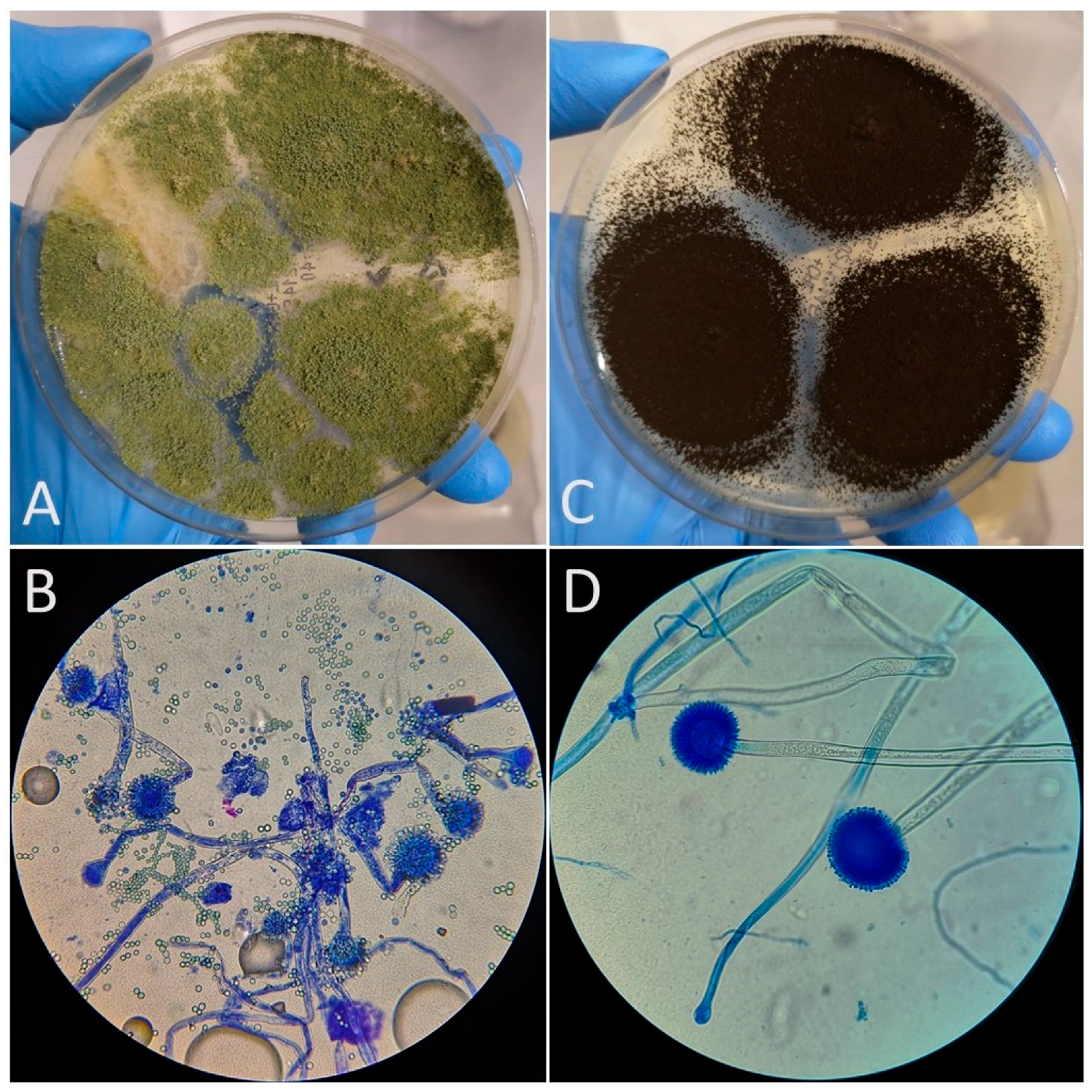

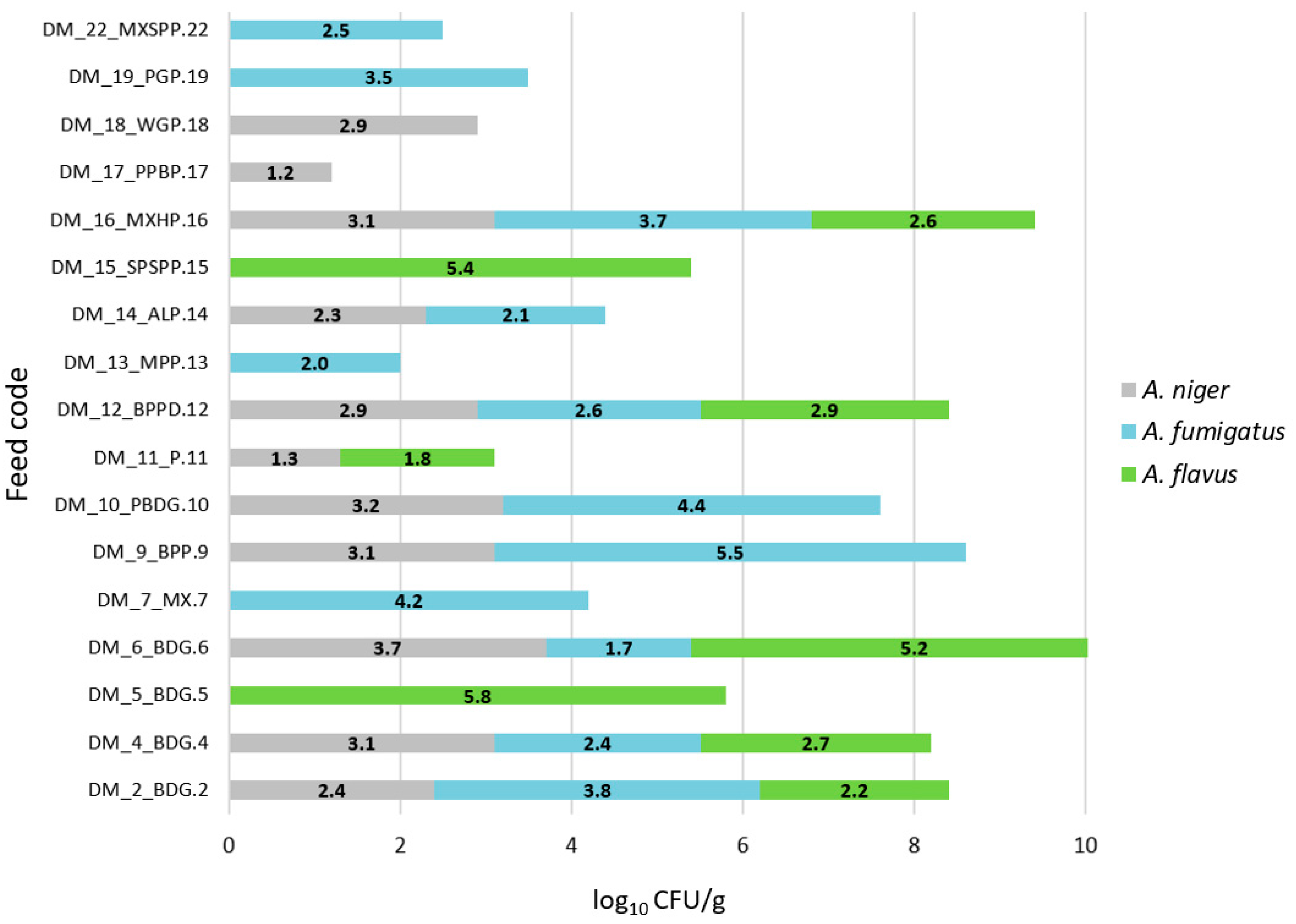
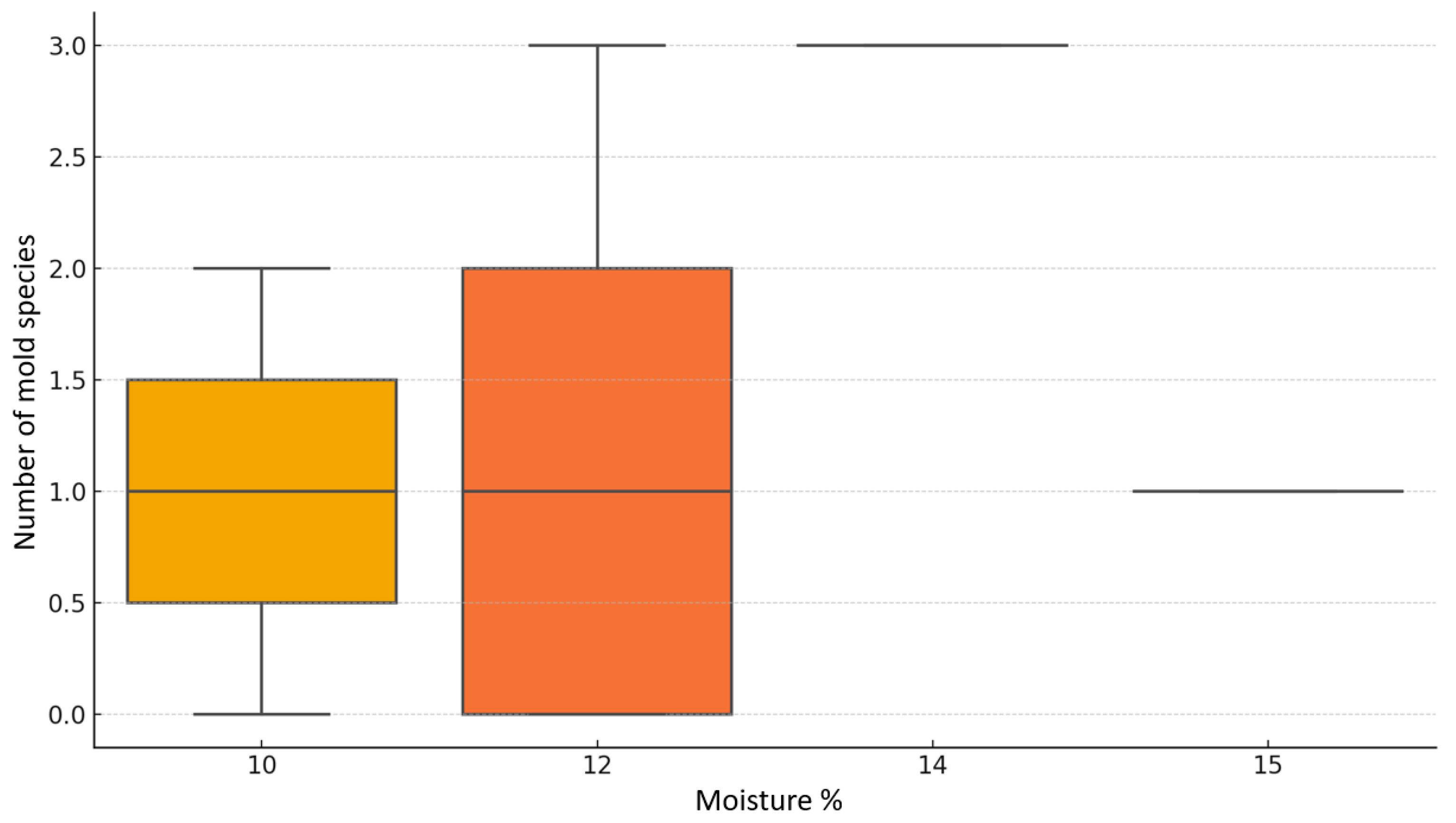
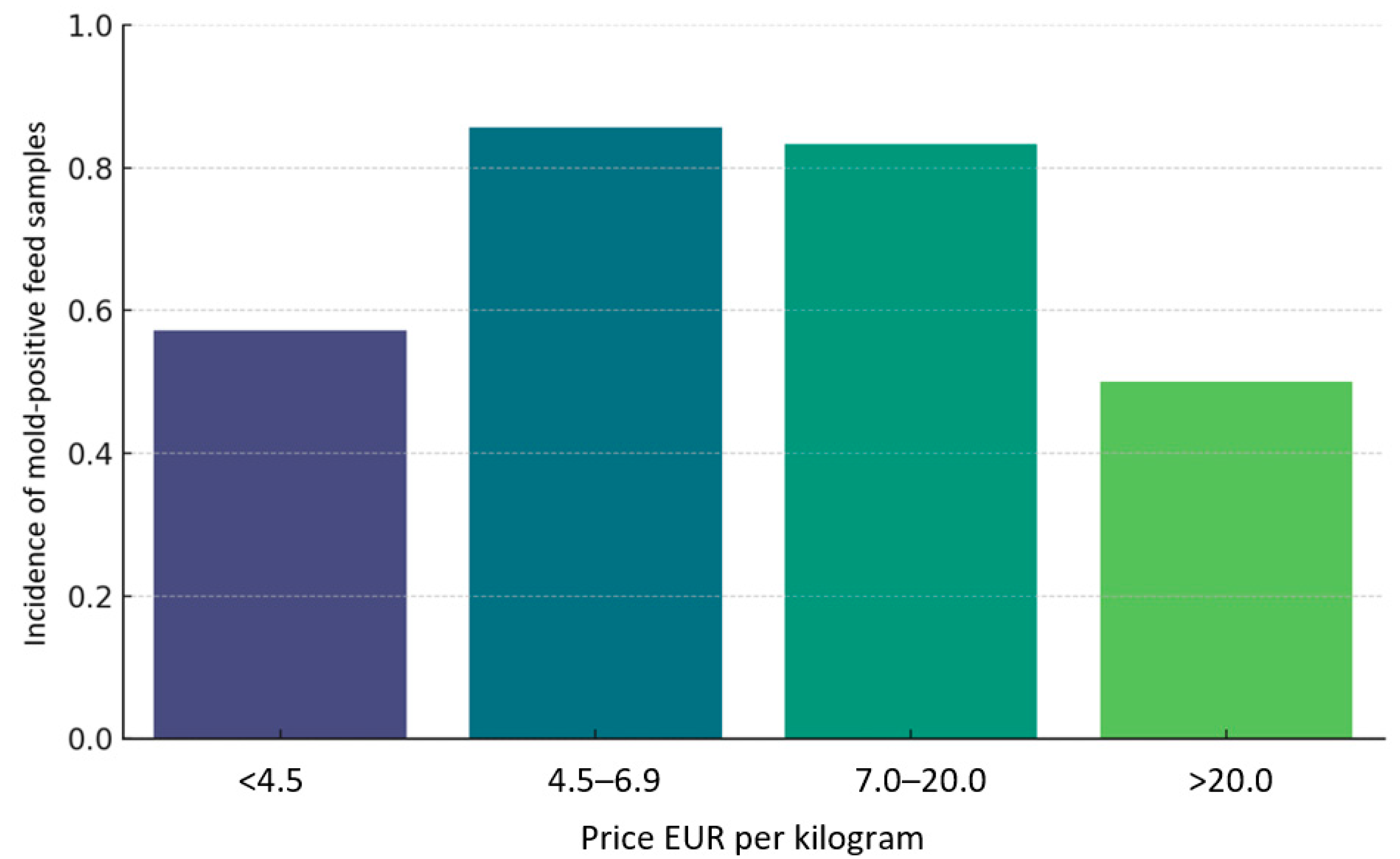
| Feed Code | Price Per Kilogram [EUR] | Moisture [%] | Crude Protein [%] | Fat [%] | Fiber [%] | Ash [%] | A. niger | A. fumigatus | A. flavus | Other Molds | Number of Cultured Molds |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DM_1_BDG.1 | 3.0 | 12.0 | 15.0 | 3.5 | 12.0 | 7.0 | - | - | - | Mucor sp. | 1 |
| DM_2_BDG.2 | 3.4 | 12.0 | 11.2 | 6.0 | 8.9 | 5.0 | + | + | + | - | 3 |
| DM_3_BDG.3 | 3.4 | 10.0 | 12.3 | 6.3 | 6.7 | 3.0 | - | - | - | - | 0 |
| DM_4_BDG.4 | 3.8 | 12.0 | 9.7 | 5.8 | 11.3 | 5.6 | + | + | + | - | 3 |
| DM_5_BDG.5 | 4.2 | 12.0 | 12.5 | 8.0 | 11.2 | 6.5 | - | - | - | - | 0 |
| DM_6_BDG.6 | 4.2 | 12.0 | 11.2 | 6.0 | 8.9 | 4.5 | + | + | + | - | 3 |
| DM_7_MX.7 | 4.7 | 12.0 | 15.0 | 13.2 | 8.0 | 6.0 | - | + | - | - | 1 |
| DM_8_NT.8 | 4.9 | 12.0 | 24.2 | 49.0 | 8.5 | 3.0 | - | - | - | - | 0 |
| DM_9_BPP.9 | 4.9 | 10.0 | 13.0 | 16.0 | 15.0 | 3.0 | + | + | - | - | 2 |
| DM_10_PBDG.10 | 4.9 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 5.0 | 7.5 | 3.5 | + | + | - | - | 2 |
| DM_11_P.11 | 5.1 | 12.0 | 12.5 | 7.0 | 8.0 | 6.0 | + | - | + | - | 2 |
| DM_12_BPPD.12 | 5.1 | 12.0 | 13.0 | 15.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | + | + | + | - | 3 |
| DM_13_MPP.13 | 5.6 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 7.5 | 11.2 | 6.2 | - | + | - | - | 1 |
| DM_14_ALP.14 | 6.5 | 12.0 | 13.8 | 13.0 | 13.6 | 2.5 | + | + | - | - | 2 |
| DM_15_SPSPP.15 | 7.0 | 12.0 | 12.6 | 7.0 | 8.5 | 4.9 | - | - | + | - | 1 |
| DM_16_MXHP.16 | 7.7 | 14.0 | 16.6 | 31.0 | 16.0 | 3.6 | + | + | + | - | 3 |
| DM_17_PPBP.17 | 7.7 | 12.0 | 13.2 | 14.7 | 14.0 | 3.5 | + | - | - | - | 1 |
| DM_18_WGP.18 | 7.7 | 15.0 | 11.0 | 4.0 | 10.0 | 5.8 | + | - | - | - | 1 |
| DM_19_PGP.19 | 9.8 | 15.0 | 12.5 | 4.5 | 9.7 | 3.0 | - | + | - | - | 1 |
| DM_20_PRMB.20 | 10.5 | 12.0 | 13.0 | 18.0 | 20.0 | 3.3 | - | - | - | - | 0 |
| DM_21_BPPT.21 | 23.4 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 6.0 | 2.0 | 3.1 | - | - | - | - | 0 |
| DM_22_MXSPP.22 | 105.0 | 12.0 | 11.0 | 19.0 | 13.0 | 3.0 | - | + | - | - | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maj, A.K.; Górecki, P.; Szaluś-Jordanow, O.; Jańczak, D. Occurrence of Aspergillus spp. in Parrot Feeds on the Polish Market: The Potential Health Threat of Aspergillosis and Mycotoxicosis for Exotic Pet Birds, a Pilot Study. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060597
Maj AK, Górecki P, Szaluś-Jordanow O, Jańczak D. Occurrence of Aspergillus spp. in Parrot Feeds on the Polish Market: The Potential Health Threat of Aspergillosis and Mycotoxicosis for Exotic Pet Birds, a Pilot Study. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(6):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060597
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaj, Aleksandra Kornelia, Piotr Górecki, Olga Szaluś-Jordanow, and Dawid Jańczak. 2025. "Occurrence of Aspergillus spp. in Parrot Feeds on the Polish Market: The Potential Health Threat of Aspergillosis and Mycotoxicosis for Exotic Pet Birds, a Pilot Study" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 6: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060597
APA StyleMaj, A. K., Górecki, P., Szaluś-Jordanow, O., & Jańczak, D. (2025). Occurrence of Aspergillus spp. in Parrot Feeds on the Polish Market: The Potential Health Threat of Aspergillosis and Mycotoxicosis for Exotic Pet Birds, a Pilot Study. Veterinary Sciences, 12(6), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060597







