Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Modeling of Enrofloxacin and Its Metabolite Ciprofloxacin in Pregnant Goats
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Analytical Method
2.4. Enrofloxacin and Ciprofloxacin Transplacental Passage
2.5. MIC and Tentative Epidemiological Cutoff Determination
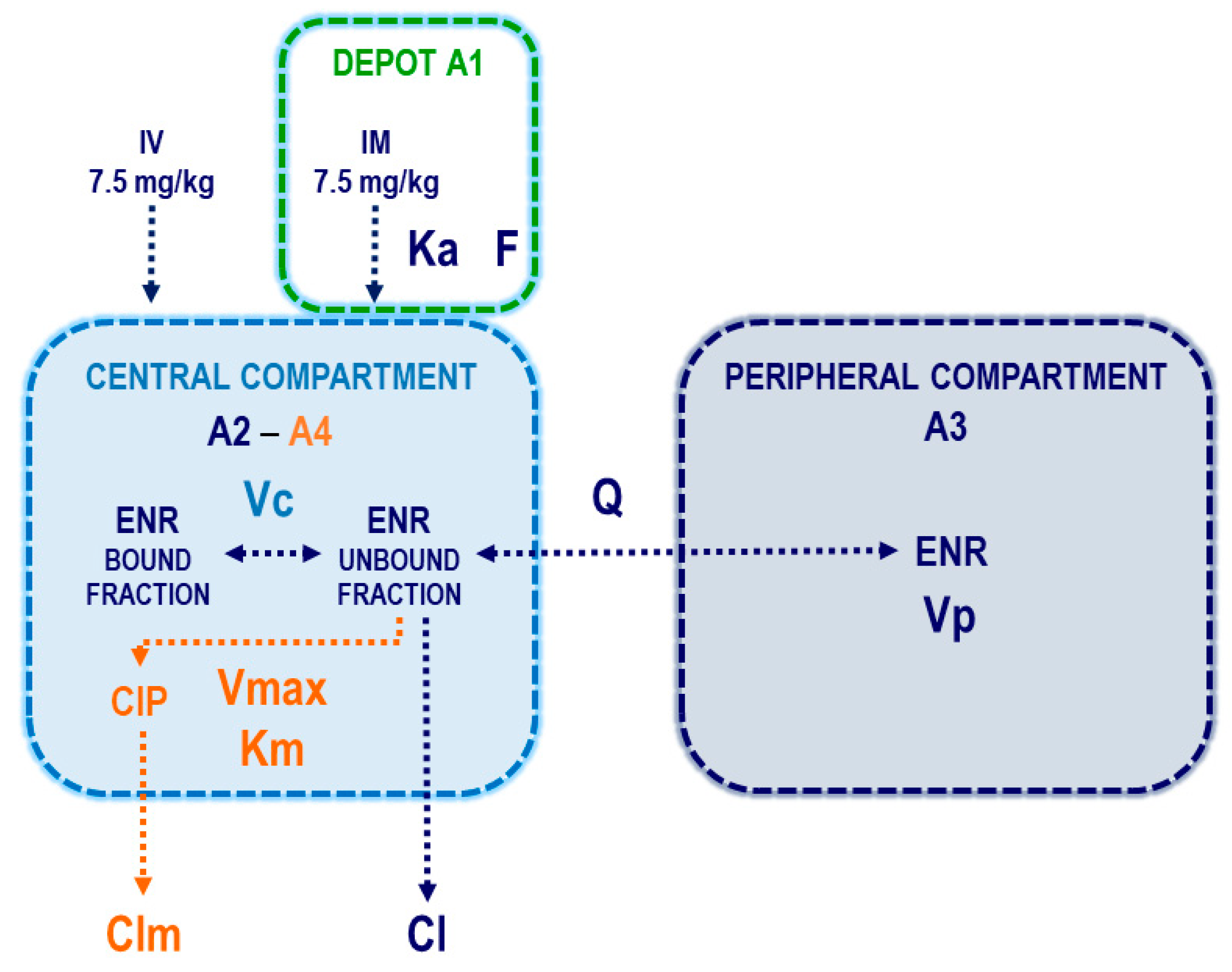
2.6. Pharmacokinetic Modeling
2.7. Pharmacokinetic Simulations and PK/PD Analysis
3. Results
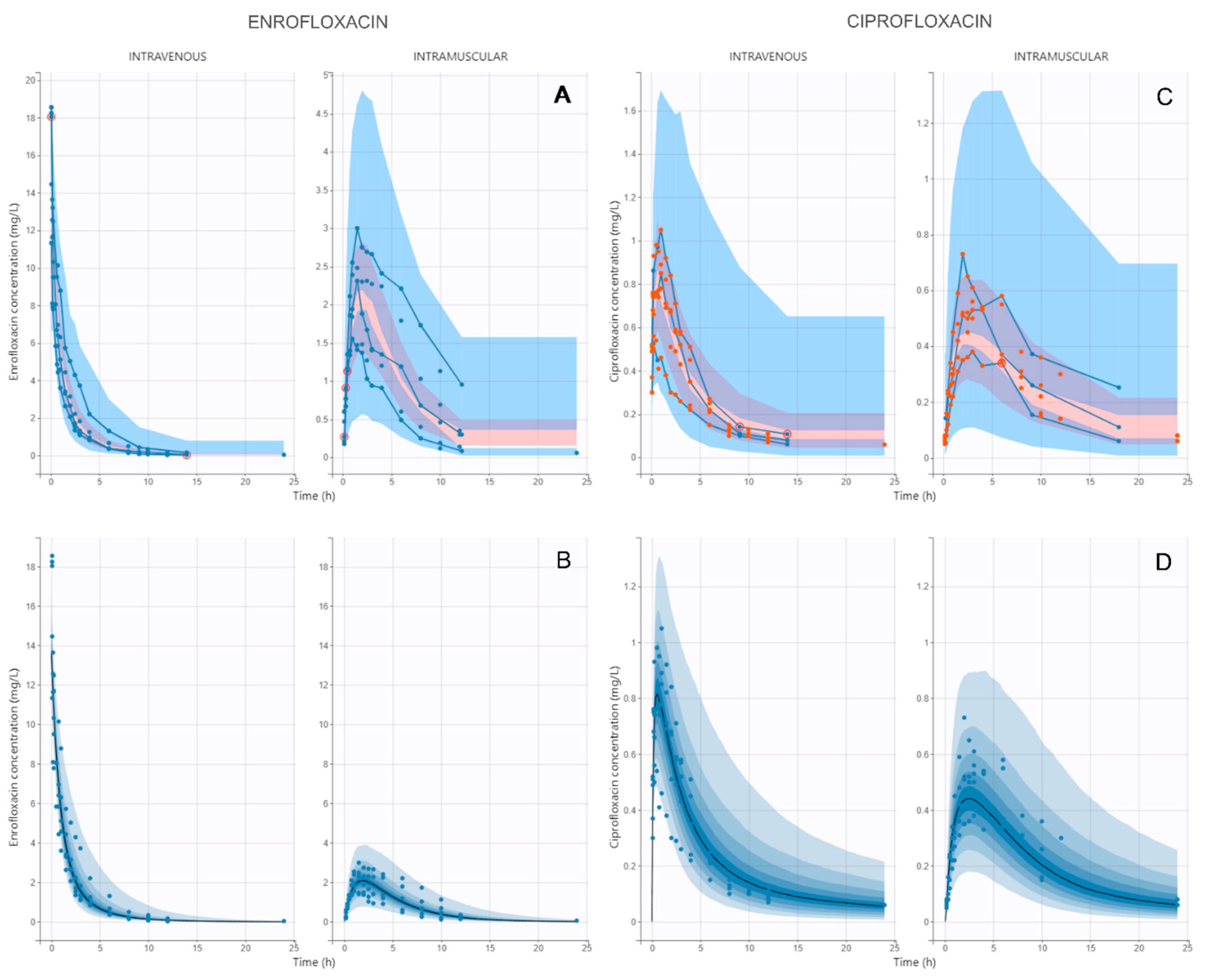
3.1. Pharmacokinetic Modeling
3.2. Enrofloxacin and Ciprofloxacin Transplacental Passage
3.3. MIC and Tentative Epidemiological Cutoff Determination
3.4. Pharmacokinetic Simulations and PK/PD Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Pharmacokinetic Modeling
4.2. Enrofloxacin and Ciprofloxacin Trasnplacental Passage
4.3. Pharmacokinetic Simulations and PK/PD Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martinez, M.; Modric, S. Patient variation in veterinary medicine: Part I. Influence of altered physiological states. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 33, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costantine, M.M. Physiologic and pharmacokinetic changes in pregnancy. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feghali, M.; Venkataramanan, R.; Caritis, S. Pharmacokinetics of drugs in pregnancy. Semin. Perinatol. 2015, 39, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, J.; Carvalho, B.; Shafer, S.L.; Flood, P. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of drugs commonly used in pregnancy and parturition. Anesth. Analg. 2016, 122, 786–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattison, D.; Halbert, L.A. (Eds.) Clinical Pharmacology During Pregnancy, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 2021; pp. 1–457. [Google Scholar]
- Ganapathy, V.; Prasad, P.D.; Ganapathy, M.E.; Leibach, F.H. Placental Transporters Relevant to Drug Distribution across the Maternal-Fetal Interface. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 294, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holcberg, G.; Tsadkin-Tamir, M.; Sapir, O.; Huleihel, M.; Mazor, M.; Zvi, Z.B. New aspects in placental drug transfer. IMAJ 2003, 5, 873–876. [Google Scholar]
- Papich, M.G. Fluoroquinolone antimicrobials drugs. In Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics, 10th ed.; Riviere, J.E., Papich, M.G., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Ames, IA, USA, 2018; pp. 953–987. [Google Scholar]
- World Organisation for Animal Health. OIE List of Antimicrobial Agents of Veterinary Importance. 2021. Available online: https://www.woah.org/app/uploads/2021/06/a-oie-list-antimicrobials-june2021.pdf (accessed on 20 February 2025).
- European Medicines Agency. Committee for Medicinal Products for Veterinary Use (CVMP). EMA/CVMP/CHMP/682198/2017. Categorisation of Antibiotics in the European Union. 2020. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/categorisation-antibiotics-european-union-answer-request-european-commission-updating-scientific_en.pdf (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Ellerbrock, R.E.; Canisso, I.F.; Roady, P.J.; Rothrock, L.T.; Zhong, L.; Wilkins, P.; Dirikolu, L.; Lima, F.S.; Honoroto, J. Diffusion of enrofloxacin to pregnancy fluids and effects on fetal cartilage after intravenous administration to late pregnant mares. Equine Vet. J. 2019, 51, 544–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papini, O.; da Cunha, S.P.; da Silva Mathes, Â.D.; Bertucci, C.; Moisés, E.C.; de Barros Duarte, L.; de Carvalho Cavalli, R.; Lanchote, V.L. Kinetic disposition of lorazepam with focus on the glucuronidation capacity, transplacental transfer in parturients and racemization in biological samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2006, 40, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A.E.; Mouton, J.W.; Oostvogel, P.M.; Dörr, P.J.; Voskuyl, R.A.; DeJongh, J.; Steegers, E.A.; Danhof, M. Pharmacokinetics of clindamycin in pregnant women in the peripartum period. AAC 2010, 54, 2175–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozyuncu, O.; Nemutlu, E.; Katlan, D.; Kir, S.; Beksac, M.S. Maternal and fetal blood levels of moxifloxacin, levofloxacin, cefepime and cefoperazone. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 36, 175–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polachek, H.; Holcberg, G.; Sapir, G.; Tsadkin-Tamir, M.; Polachek, J.; Katz, M.; Ben-Zvi, Z. Transfer of ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin and levofloxacin across the perfused human placenta in vitro. OGS 2006, 61, 77–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmas, M.; Tras, B.; Kaya, S.; Bas, A.L.; Yazar, E.; Yarsan, E. Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin after intravenous and intramuscular administration in Angora goats. Can. J. Vet. Res. 2001, 65, 64. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, G.S.; Ramesh, S.; Ahmad, A.H.; Tripathi, H.C.; Sharma, L.D.; Malik, J.K. Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin and its metabolite ciprofloxacin after intramuscular administration of enrofloxacin in goats. Vet. Res. Commun. 2001, 25, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.S.; Ramesh, S.; Ahmad, A.H.; Tripathi, H.C.; Sharma, L.D.; Malik, J.K. Disposition kinetics of enrofloxacin and ciprofloxacin following intravenous administration of enrofloxacin in goats. Small Rumin. Res. 2002, 44, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, G.S.; Ramesh, S.; Ahmad, A.H.; Tripathi, H.C.; Sharma, L.D.; Malik, J.K. Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin and its metabolite ciprofloxacin in goats given enrofloxacin alone and in combination with probenecid. Vet. J. 2002, 163, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboubakr, M.H. Evaluation of bioequivalence of two enrofloxacin formulations after intramuscular administration in goats. Korean J. Vet. Res. 2013, 53, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, T.; Javed, I.; Muhammad, F. Disposition Kinetics of Enrofloxacin Following Intramuscular Administration in Goats. Pak. Vet. J. 2014, 34, 293. [Google Scholar]
- Aktaş, İ.; Altintaş, L.; Çakir, E.O.; Demir, O.; Yarsan, E. Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin following intravenous and intramuscular administration in Kilis goats. IJVAR 2019, 2, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Mould, D.R.; Upton, R.N. Basic concepts in population modeling, simulation, and model-based drug development. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2012, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mould, D.R.; Upton, R.N. Basic concepts in population modeling, simulation, and model-based drug development—Part 2: Introduction to pharmacokinetic modeling methods. CPT Pharmacomet. Syst. Pharmacol. 2013, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lucas, J.J.; Rodriguez, C.; Waxman, S.; Gonzalez, F.; De Vicente, M.L.; San Andres, M.I. Pharmacokinetics of enrofloxacin after single intravenous and intramuscular administration in young domestic ostrich (Struthio camelus). JVPT 2004, 27, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CLSI Standard M07; Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically, 11th ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standars Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2018.
- Turnidge, J.; Kahlmeter, G.; Kronvall, G. Statistical characterisation of bacterial wild-type MIC value distributions and the determination of epidemiological cut-off values. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisskopf, E.; Guidi, M.; Fischer, C.J.; Bickle Graz, M.; Beaufils, E.; Nguyen, K.A.; Morisod Harari, M.; Rouiller, S.; Rothenburger, S.; Gaucherand, P.; et al. A population pharmacokinetic model for escitalopram and its major metabolite in depressive patients during the perinatal period: Prediction of infant drug exposure through breast milk. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2020, 86, 1642–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulin, A.; Schneider, M.; Dron, F.; Woehrle, F. Pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic evaluation of marbofloxacin as a single injection for Pasteurellaceae respiratory infections in cattle using population pharmacokinetics and Monte Carlo simulations. JVPT 2018, 41, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet-Mélou, A.; Schneider, M.; El Garch, F.; Broussou, D.C.; Ferran, A.A.; Lallemand, E.A.; Triboulloy, C.; Damborg, P.; Toutain, P.L. Determination of the pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic cut-off values of marbofloxacin in horses to support the establishment of a clinical breakpoint for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. Equine Vet. J. 2021, 53, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bon, C.; Toutain, P.L.; Concordet, D.; Gehring, R.; Martin-Jimenez, T.; Smith, J.; Pelligand, L.; Martinez, M.; Whittem, T.; Riviere, J.E.; et al. Mathematical modeling and simulation in animal health. Part III: Using nonlinear mixed-effects to characterize and quantify variability in drug pharmacokinetics. JVPT. 2018, 41, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García Ovando, H.G.; Gorla, N.; Poloni, G.; Trotti, N.; Prieto, G.; Errecalde, C. Intravenous pharmacokinetics of ciprofloxacin in goats. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2000, 15, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toutain, P.L.; Bousquet-mélou, A. Plasma clearance. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2004, 27, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, R.; Prawez, S.; Dimitrova, D.J.; Pankaj, N.K.; Verma, P.K. Disposition kinetics and urinary excretion of ciprofloxacin in goats following single intravenous administration. J. Vet. Sci. 2008, 9, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noergaard, M.; Jensen, P.B.; Gotfredsen, D.R.; Bergholt, T.; Andersen, J.T.; Mathiesen, L. Therapeutic concentration of ciprofloxacin and transfer across the human term placenta. AJOG 2021, 225, 670.e1–670.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Tamai, I.; Kato, H.; Nagata, O.; Kato, H.; Tsuji, A. Efflux transport of a new quinolone antibacterial agent, HSR-903, across the blood-brain barrier. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 290, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Yang, Y.; Ying, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, M.; Hong, M.; Wang, H.; Xie, S.; Chen, D. ABC transporters and CYP3A4 mediate drug interactions between enrofloxacin and salinomycin leading to increased risk of drug residues and resistance. ABX 2023, 12, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceckova-Novotna, M.; Pavek, P.; Staud, F. P-glycoprotein in the placenta: Expression, localization, regulation and function. Reprod. Toxicol. 2006, 22, 400–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fresno, L.; Andaluz, A.; Moll, X.; Cristofol, C.; Arboix, M.; García, F. Placental transfer of etomidate in pregnant ewes after an intravenous bolus dose and continuous infusion. Vet. J. 2008, 175, 395–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Q. BCRP/ABCG2 in the placenta: Expression, function and regulation. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 1244–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papich, M.G. Pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic (PK–PD) modeling and the rational selection of dosage regimes for the prudent use of antimicrobial drugs. Vet. Microbiol. 2014, 171, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CLSI Document VET01-S2; Performances Standards for Antimicrobial Disk and Dilution Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria Isolated from Animals; Second Informational Supplement. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2013.
| Fixed Effects | Estimate | IIV (CV %) | Bootstrap Estimate (95% CI) | Schrinkage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Enrofloxacin (parent) | ||||
| F | 0.80 | 9.97 | 0.59–0.92 | 0.20 |
| Ka (1/h) | 0.25 | 25.81 | 0.19–0.33 | 0.20 |
| fu | 0.39 | 11.67 | 0.30–0.84 | 4.65 |
| Cl (L/h/kg) | 0.81 | 16.28 | 0.43–1.52 | −4.42 |
| Vc (L/kg) | 0.65 | - | 0.56–0.75 | - |
| Q (L/h/kg) | 0.28 | - | 0.15–0.54 | - |
| Vp (L/kg) | 2.83 | 45.79 | 1.27–6.3 | 8.05 |
| Ciprofloxacin (metabolite) | ||||
| Clm (L/h/kg) | 4.56 | 25.18 | 3.45–6.04 | −1.21 |
| Vmax (mg/L/h) | 4.61 | 1.65 | 3.62–5.86 | −17.2 |
| Km (mg/L) | 0.86 | 13.06 | 0.45–1.63 | 6.34 |
| Residual error model | ||||
| Enrofloxacin | 0.37 | - | 0.366–0.367 | |
| Ciprofloxacin | 0.18 | - | 0.177–0.186 | |
| Secondary parameters | ||||
| Enrofloxacin (parent) | ||||
| Intravenous | Intramuscular | |||
| Estimate | CV (%) | Estimate | CV (%) | |
| AUC (mg/L/h) | 21.02 | 37.12 | 14.10 | 40.34 |
| Vss (L/kg) | 3.65 | 21.90 | 4.45 | 33.83 |
| t1/2e (h) | 3.15 | 26.89 | 3.07 | 32.60 |
| Ciprofloxacin (metabolite) | ||||
| Intravenous | Intramuscular | |||
| Estimate | CV (%) | Estimate | CV (%) | |
| AUC (mg/L/h) | 3.95 | 25.28 | 5.80 | 25.94 |
| MR | 0.20 | 33.08 | 0.47 | 64.43 |
| Enrofloxacin | Enrofloxacin + Ciprofloxacin | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P05 | Median | P95 | P05 | Median | P95 | |
| 7.5 mg/kg/day IV | 14.22 | 19.11 | 34.84 | 17.71 | 24.74 | 42.84 |
| 7.5 mg/kg/day IM | 6.52 | 13.98 | 25.91 | 9.37 | 19.74 | 35.95 |
| 10 mg/kg/day IV | 18.97 | 25.48 | 46.45 | 23.1 | 32.15 | 55.79 |
| 10 mg/kg/day IM | 8.69 | 18.64 | 34.54 | 12.31 | 25.72 | 46.38 |
| PDT (h) | Dose Regimen | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.5 mg/kg/day IV | 7.5 mg/kg/day IM | 10 mg/kg/day IV | 10 mg/kg/day IM | |
| Enrofloxacin | ||||
| 24 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.25 |
| 48 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.125 |
| 72 | 0.125 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 |
| 96 | 0.125 | 0.06 | 0.125 | 0.06 |
| Enrofloxacin + ciprofloxacin | ||||
| 24 | 0.5 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.5 |
| 48 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.5 | 0.25 |
| 72 | 0.25 | 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.125 |
| 96 | 0.125 | 0.06 | 0.25 | 0.125 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ambros, L.A.; Kreil, V.; de Lucas Burneo, J.J.; Tinti, M.G.; San Andrés Larrea, M.I.; Lorenzutti, A.M. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Modeling of Enrofloxacin and Its Metabolite Ciprofloxacin in Pregnant Goats. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060588
Ambros LA, Kreil V, de Lucas Burneo JJ, Tinti MG, San Andrés Larrea MI, Lorenzutti AM. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Modeling of Enrofloxacin and Its Metabolite Ciprofloxacin in Pregnant Goats. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(6):588. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060588
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmbros, Luis Adrian, Verónica Kreil, José Julio de Lucas Burneo, Mariano Guillermo Tinti, Manuel Ignacio San Andrés Larrea, and Augusto Matías Lorenzutti. 2025. "Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Modeling of Enrofloxacin and Its Metabolite Ciprofloxacin in Pregnant Goats" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 6: 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060588
APA StyleAmbros, L. A., Kreil, V., de Lucas Burneo, J. J., Tinti, M. G., San Andrés Larrea, M. I., & Lorenzutti, A. M. (2025). Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Modeling of Enrofloxacin and Its Metabolite Ciprofloxacin in Pregnant Goats. Veterinary Sciences, 12(6), 588. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060588







