Effect of Nanoemulsions of Betulinic Acid on the Development of Canine Mammary Tumors
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
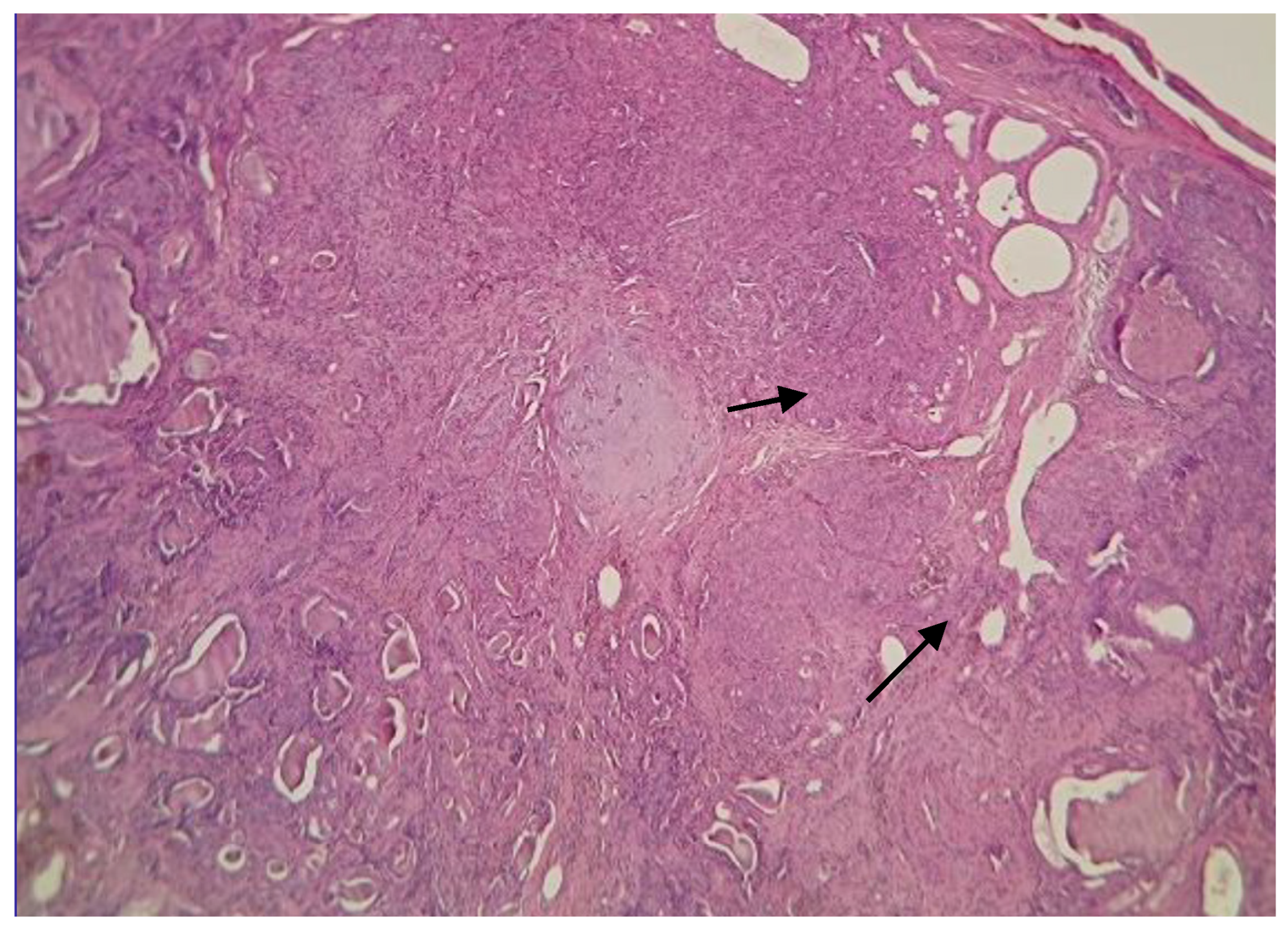
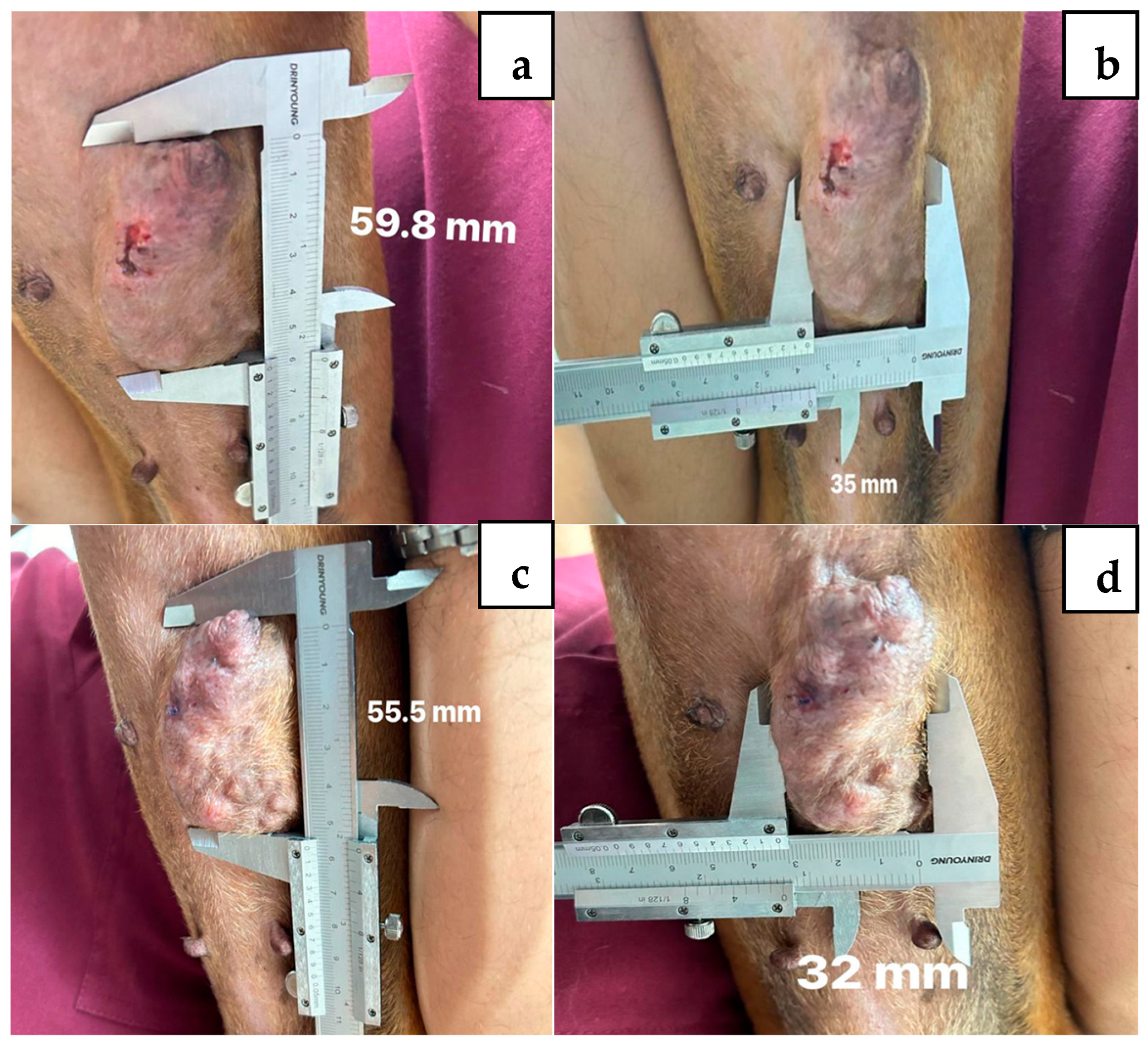
2. Case Description
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaszak, I.; Ruszczak, A.; Kanafa, S.; Kacprzak, K.; Król, M.; Jurka, P. Current biomarkers of canine mammary tumors. Acta Vet. Scand. 2018, 60, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, S.G.; Araujo, V.H.S.; Dos Santos, A.M.; Duarte, J.L.; Silvestre, A.L.P.; Fonseca-Santos, B.; Villanova, J.C.O.; Gremião, M.P.D.; Chorilli, M. Advances and challenges in nanocarriers and nanomedicines for veterinary application. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 580, 119214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Fan, K.; Jin, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, Q.; Tang, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, Z.; Wang, S.; Lin, J.; et al. PEGylated lipid bilayer coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles co-delivery of paclitaxel and curcumin leads to increased tumor site drug accumulation and reduced tumor burden. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 140, 105070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.H.; Inbaraj, B.S. Nanoemulsion and Nanoliposome Based Strategies for Improving Anthocyanin Stability and Bioavailability. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aswathy, M.; Vijayan, A.; Daimary, U.D.; Girisa, S.; Radhakrishnan, K.V.; Kunnumakkara, A.B. Betulinic acid: A natural promising anticancer drug, current situation, and future perspectives. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2022, 36, e23206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, S.; Vieira, M.; Prudêncio, C.; Ferraz, R. Betulinic Acid for Glioblastoma Treatment: Reality, Challenges and Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buya, A.B.; Beloqui, A.; Memvanga, P.B.; Préat, V. Self-Nano-Emulsifying Drug-Delivery Systems: From the Development to the Current Applications and Challenges in Oral Drug Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agame-Lagunes, B.; Alegria–Rivadeneyra, M.; Alexander-Aguilera, A.; Quintana-Castro, R.; Torres-Palacios, C.; Grube-Pagola, P.; Cano-Sarmiento, C.; García-Varela, R.; García, H.S. Bioactivity of betulinic acid nanoemulsions on skin Carcinogenesis in transgenic mice K14E6. Grasas Y Aceites 2021, 72, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudu-Lange, C.; Lange, E. Intensive Multimodal Chemotherapy in a Dog Suffering from Grade III/Stage IV Solid Mammary Carcinoma. Animals 2024, 14, 2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willmann, M.; Wacheck, V.; Buckley, J.; Nagy, K.; Thalhammer, J.; Paschke, R.; Triche, T.; Jansen, B.; Selzer, E. Characterization of NVX-207, a novel betulinic acid-derived anti-cancer compound. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 39, 384–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisha, E.; Chai, H.; Lee, I.S.; Chagwedera, T.E.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Cordell, G.A.; Beecher, C.W.; Fong, H.H.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Brown, D.M. Discovery of betulinic acid as a selective inhibitor of human melanoma that functions by induction of apoptosis. Nat. Med. 1995, 1, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Li, R.; Pawlak, A.; Henklewska, M.; Sysak, A.; Wen, L.; Yi, J.E.; Obmińska-Mrukowicz, B. Antitumor Activity of Betulinic Acid and Betulin in Canine Cancer Cell Lines. In Vivo 2018, 32, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Cichewicz, R.H.; Kouzi, S.A. Chemistry, biological activity, and chemotherapeutic potential of betulinic acid for the prevention and treatment of cancer and HIV infection. Med. Res. Rev. 2004, 24, 90–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Dog | Breed | Age (Years) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chihuahua | 8 |
| 2 | Chihuahua | 10 |
| 3 | Dachshund | 6 |
| 4 | Dachshund | 10 |
| 5 | Mixed | 12 |
| Females | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RV * | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Red blood cells, 103/mm3 | 3.3–7.8 | 7.6 | 5.3 | 5.9 | 6.4 | 5.3 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 14.7–21.2 | 19.6 | 12.3 | 13.2 | 15.9 | 11.9 |
| Hematocrit, % | 44.2–62.8 | 58.2 | 36.4 | 40.1 | 47.2 | 36.2 |
| GMT, fl | 60–77 | 76.2 | 68.5 | 67.9 | 74.2 | 68.2 |
| MHC, pg | 19.0–25.9 | 25.7 | 23.1 | 22.3 | 25.0 | 22.5 |
| MHCG, g/dL | 31–36 | 33.6 | 33.8 | 32.9 | 33.7 | 32.9 |
| Platelets, ×103/mm3 | 200–500 | 223 | 233 | 141 | 226 | 411 |
| WBC, ×103/mm3 | 7.9–17.5 | 7.3 | 7.9 | 10.7 | 8.6 | 1.4 |
| Glucose, mg/dL | 77–120 | 78.1 | 74.2 | 52.0 | 61.0 | 61.2 |
| Urea, mg/dL | 17.6–51.8 | 32.8 | 24.7 | 33.9 | 41.6 | 35.3 |
| BUN, mg/dL | 7–23 | 15.3 | 11.5 | 15.8 | 19.4 | 16.5 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.6–1.2 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 0.9 |
| Urea/Creatinine, % | >20–<10 | 18.9 | 19.5 | 22.9 | 16.2 | 18.9 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 129–331 | 177 | 265 | 158 | 169 | 236 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 36–135 | 71.5 | 86.3 | 67.6 | 78.6 | 66.2 |
| Uric acid, mg/dL | 0.5–1.4 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| Direct bilirubin mg/dL | 0.1–0.19 | 0.21 | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.16 |
| Indirect bilirubin, mg/dL | 0–0.8 | 0.38 | 0.28 | 0.42 | 0.38 | 0.32 |
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL | 0.2–0.8 | 0.62 | 0.43 | 0.70 | 0.62 | 0.48 |
| TGO, U/L | 14–42 | 36.7 | 33.2 | 40.2 | 43.5 | 38.4 |
| TGP, U/L | 15–52 | 52.3 | 47.1 | 41.4 | 41.9 | 73.3 |
| Alkaline phosphatase, U/L | 20–70 | 90.9 | 141.7 | 44.6 | 56.2 | 131.3 |
| γ-glutamyltranspeptidase, U/L | 1.0–9.7 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 3.1 | 4.1 | 2.8 |
| Total protein, g/dL | 5.4–7.2 | 8.4 | 9.2 | 8.6 | 8.0 | 8.3 |
| Serum albumin, g/dL | 2.6–3.6 | 4.4 | 4.1 | 3.5 | 4.3 | 3.1 |
| Globulin, g/dL | 2.3–4.4 | 4.0 | 5.0 | 5.1 | 3.7 | 5.2 |
| Female | Tumor Classification |
|---|---|
| 1 | Complex mammary adenoma 1 (CMA) |
| 2 | Tubular mammary carcinoma 2 grade II (TBC II) |
| 3 | Complex mammary adenoma (CMA) |
| 4 | Complex mammary adenoma (CMA) |
| 5 | Tubular mammary carcinoma (TBC I) |
| Week of Treatment | Percentage Change | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | mm | % | |
| Female 1 (CMA) | |||||||
| Length, mm | 8.6 | 8.0 | 6.9 | 6.6 | 6.6 | −2.0 | −23.0 |
| Width, mm | 10.8 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 8.8 | 8.6 | −2.2 | −20.3 |
| Female 2 (TBC II) | |||||||
| Length, mm | 24.0 | 24.0 | 21.2 | 20.0 | 19.5 | −4.5 | −18.7 |
| Width, mm | 24.3 | 23.7 | 22.0 | 21.1 | 19.5 | −4.8 | −20.0 |
| Female 3 (CMA) | |||||||
| Length, mm | 12.5 | 10.4 | 9.5 | 8.0 | 7.0 | −5.5 | −44.0 |
| Width, mm | 17.0 | 13.9 | 10.9 | 8.4 | 7.9 | −9.1 | −53.5 |
| Female 4 (CMA) | |||||||
| Length, mm | 35.0 | 32.0 | 31.2 | 30.4 | 29.8 | −5.2 | −14.8 |
| Width, mm | 59.8 | 55.5 | 55.7 | 54.4 | 50.9 | −8.9 | −14.8 |
| Female 5 (TBC I) | |||||||
| Length, mm | 24.4 | 22.2 | 19.9 | 18.2 | 15.0 | −9.4 | −38.5 |
| Width, mm | 51.7 | 50.1 | 49.9 | 49.7 | 48.7 | −3.0 | −5.8 |
| Average | |||||||
| Length, mm | 20.9 | 19.3 | 17.7 | 16.6 | 15.5 | −5.3 | −27.8 |
| Width, mm | 32.7 | 30.4 | 29.5 | 28.4 | 27.1 | −5.6 | −22.8 |
| Average, mm | 26.8 | 24.8 | 23.6 | 22.5 | 21.3 | −5.4 | −25.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Amoros-Cerón, Z.Y.; Pinos-Rodríguez, J.M.; García, H.S.; Olivares-Muñoz, A.; De Gasperin-López, I.; Flores-Primo, A. Effect of Nanoemulsions of Betulinic Acid on the Development of Canine Mammary Tumors. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060522
Amoros-Cerón ZY, Pinos-Rodríguez JM, García HS, Olivares-Muñoz A, De Gasperin-López I, Flores-Primo A. Effect of Nanoemulsions of Betulinic Acid on the Development of Canine Mammary Tumors. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(6):522. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060522
Chicago/Turabian StyleAmoros-Cerón, Zayra Yeretzi, Juan Manuel Pinos-Rodríguez, Hugo Sergio García, Angélica Olivares-Muñoz, Isaac De Gasperin-López, and Argel Flores-Primo. 2025. "Effect of Nanoemulsions of Betulinic Acid on the Development of Canine Mammary Tumors" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 6: 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060522
APA StyleAmoros-Cerón, Z. Y., Pinos-Rodríguez, J. M., García, H. S., Olivares-Muñoz, A., De Gasperin-López, I., & Flores-Primo, A. (2025). Effect of Nanoemulsions of Betulinic Acid on the Development of Canine Mammary Tumors. Veterinary Sciences, 12(6), 522. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060522






