Fecal Microbiota and Performance of Dairy Cattle from a West Mexican Family Dairy Farm Supplemented with a Fiber-Degrading Enzymatic Complex
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals and Groups
2.2. Cattle Feeding and Supplementation
2.3. Sample Collection
2.3.1. Milk
2.3.2. Feces
2.4. Analysis Procedures
2.4.1. Milk Composition
2.4.2. Milk Fatty Acid Profile
2.4.3. Fecal Bacterial Communities Study
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Dry Matter Intake
3.2. Milk Yield
3.3. Milk Composition Profile
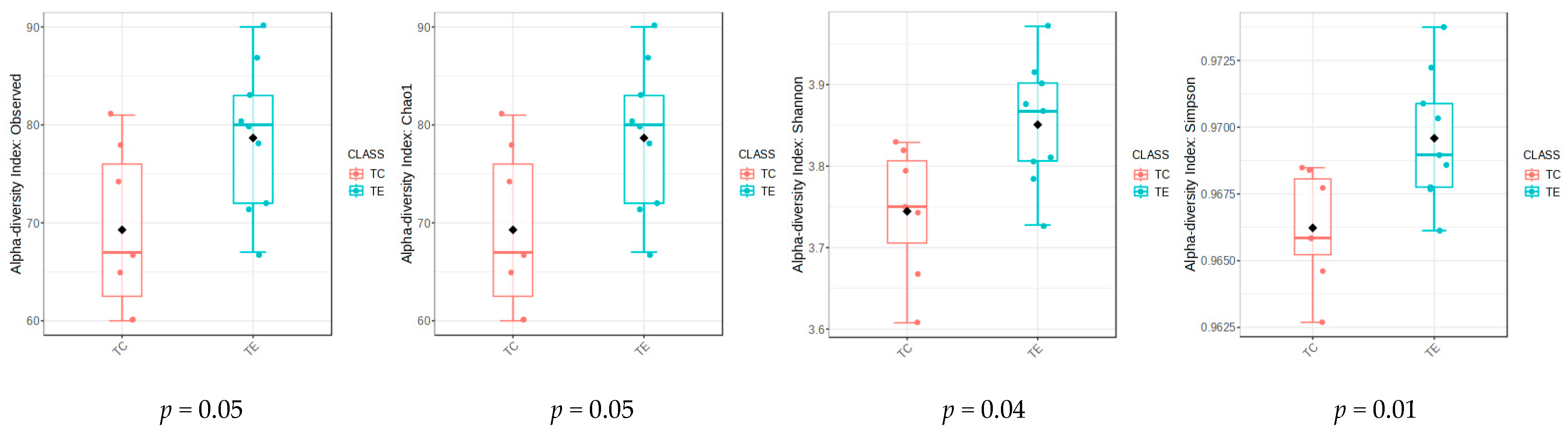
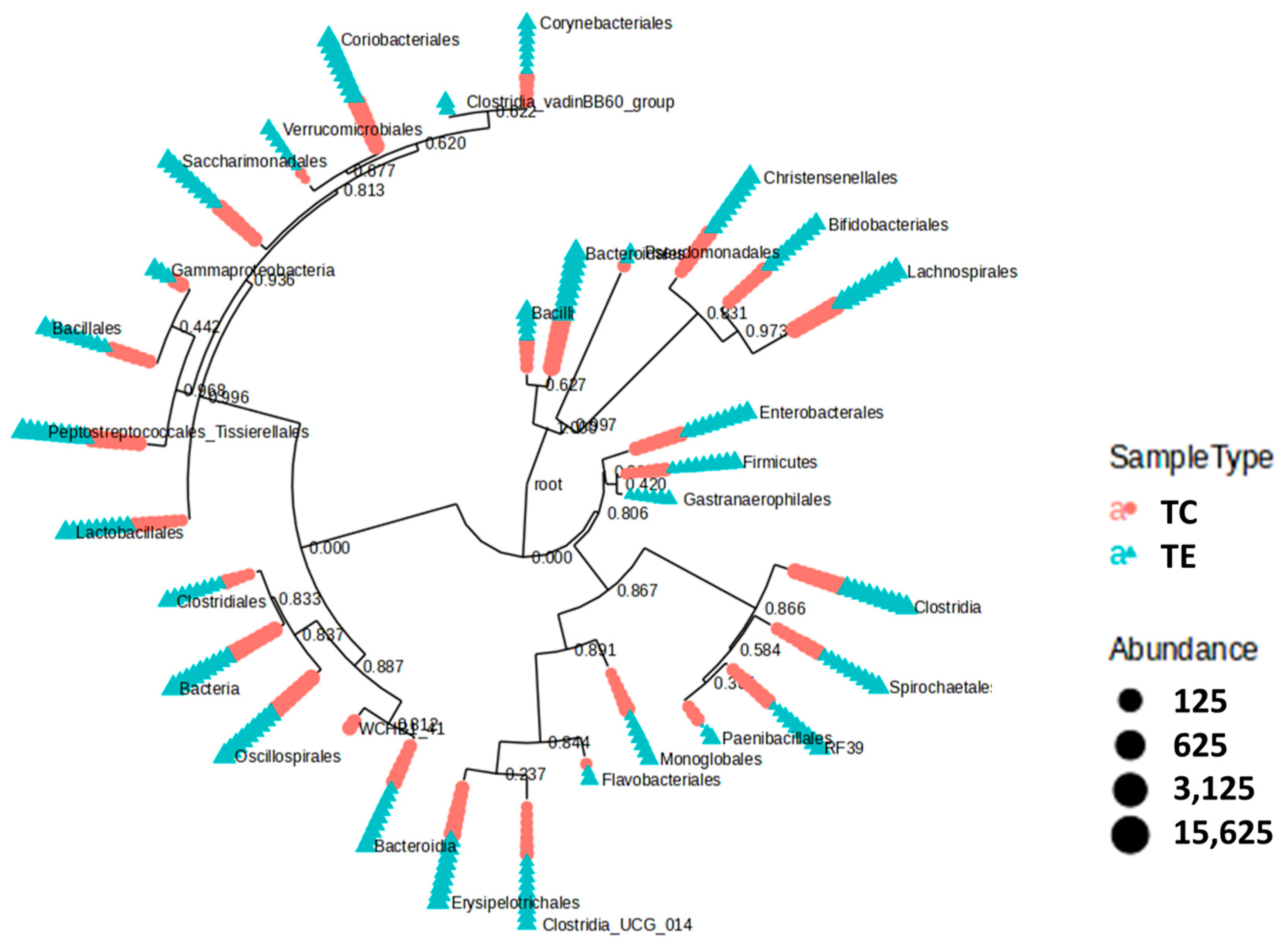
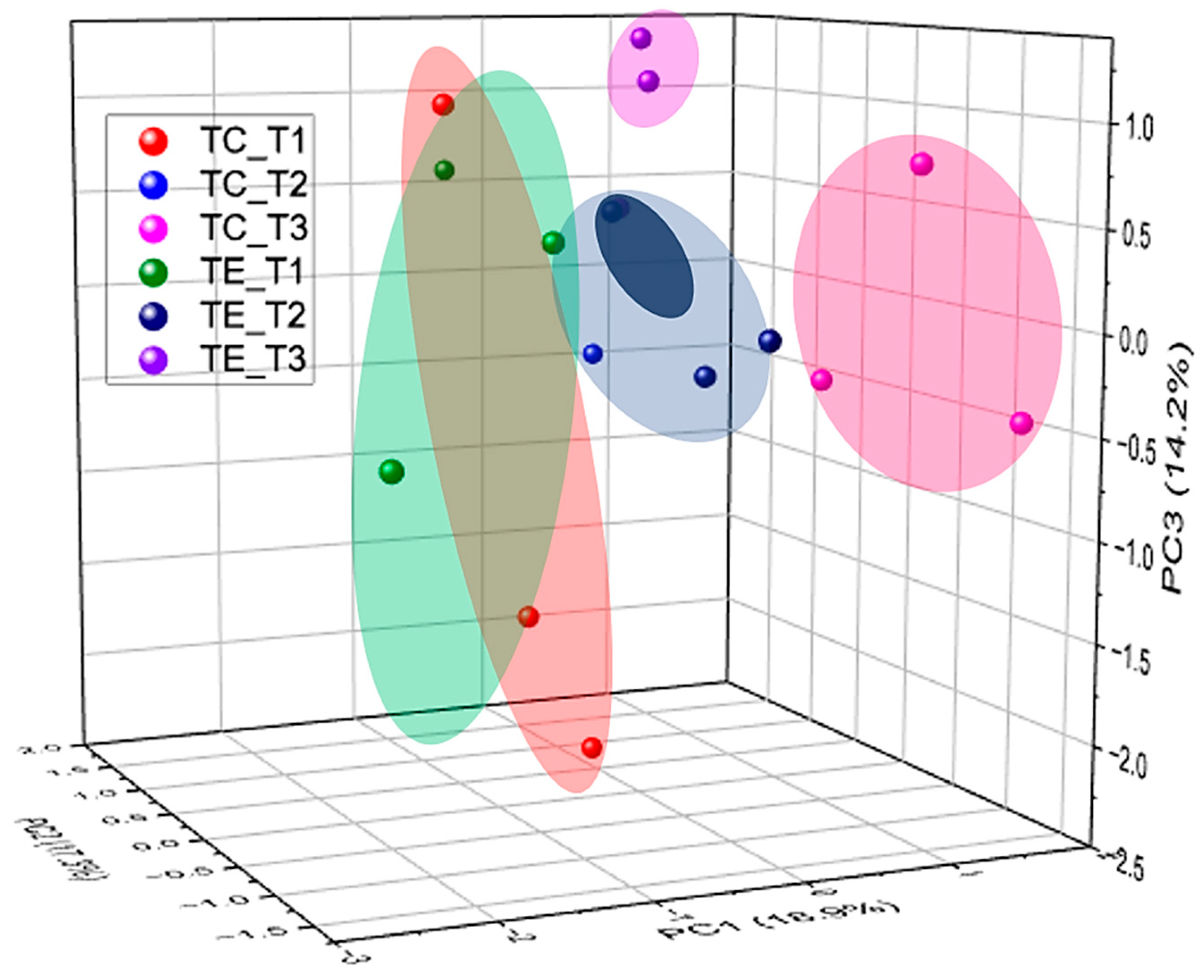
3.4. Fecal Microbiota
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Habte-Tsion, H.M.; Kumar, V. Nonstarch Polysaccharide Enzymes-General Aspects. In Enzymes in Human and Animal Nutrition: Principles and Perspectives; Nunes, S., Kumar, V., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018; pp. 183–209. [Google Scholar]
- Davidson, M.H.; McDonald, A. Fiber forms and functions. Nutr. Res. 1998, 18, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, C.H.M.; Annison, G. Non-Starch Plant Polysaccharides in Broiler Nutrition-towards a Physiologically Valid Approach to Their Determination. J. World Poult. Sci. 1996, 52, 203–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkovich, V.; Brydl, E.; Rafai, P. Effects of a Non-Starch Polysaccharidase Enzyme Preparation from Thermomyces lanuginosus on Energy and Protein Metabolism and Milk Yield of Dairy Cattle. Acta Vet. Hung. 2002, 50, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Sinha, A.K.; Makkar, H.P.S.; de Boeck, G.; Becker, K. Dietary Roles of Non-Starch Polysachharides in Human Nutrition: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 899–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, K.P.; Duncan, S.H.; Flint, H.J. Dietary Fibre and the Gut Microbiota. Nutr. Bull. 2008, 33, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontà, V.; Battelli, M.; Rama, E.; Casanova, M.; Pasotti, L.; Galassi, G.; Colombini, S.; Calvio, C. An In Vitro Study on the Role of Cellulases and Xylanases of Bacillus subtilis in Dairy Cattle Nutrition. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchemin, K.A.; Rode, L.M.; Maekawa, M.; Morgavi, D.P.; Kampen, R. Evaluation of a Nonstarch Polysaccharidase Feed Enzyme in Dairy Cow Diets. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 543–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.; Cohen, M.A.; Rode, L.M.; Treacher, R.J. The Effect of Fibrolytic Enzymes Sprayed onto Forages and Fed in a Total Mixed Ratio to Lactating Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2002, 85, 2396–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arriola, K.G.; Kim, S.C.; Staples, C.R.; Adesogan, A.T. Effect of Fibrolytic Enzyme Application to Low- and High-Concentrate Diets on the Performance of Lactating Dairy Cattle. J. Dairy Sci. 2011, 94, 832–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Ferreira, G.; Corl, B.A.; Campbell, B.T. Production Performance, Nutrient Digestibility, and Milk Fatty Acid Profile of Lactating Dairy Cows Fed Corn Silage- or Sorghum Silage-Based Diets with and without Xylanase Supplementation. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 2266–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.K.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C.C.; Liu, Z.J.; Wang, L.M.; Li, X.Y.; Pellikaan, W.F.; Yao, J.H.; Cao, Y.C. Effects of a Combination of Fibrolytic and Amylolytic Enzymes on Ruminal Enzyme Activities, Bacterial Diversity, Blood Profile and Milk Production in Dairy Cows. Animal 2022, 16, 100595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D.O.F. NMX-Y-098-SCFI-2018. Alimentos Para Animales-Determinación de Humedad en Alimentos Balanceados e Ingredientes Mayores. 2018. Available online: https://platiica.economia.gob.mx/normalizacion/nmx-y-098-scfi-2018/ (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- AOAC. Official Method of Analysis, 18th ed.; Association of Officiating Analytical Chemists: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vogel, K.P.; Pedersen, J.F.; Masterson, S.D.; Toy, J.J. Evaluation of a Filter Bag System for NDF, ADF, and IVDMD Forage Analysis. Crop Sci. 1999, 39, 276–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Serrenho, R.C.; Puga, S.O.; Torres, J.M.; Puga, S.O.; Stangaferro, M. Effect of Feeding a Saccharomyces cerevisiae Fermentation Product to Holstein Cows Exposed to High Temperature and Humidity Conditions on Milk Production Performance and Efficiency—A Pen-Level Trial. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 4650–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, E.A.; Cooke, R.F.; Brandão, A.P.; Wiegand, J.B.; Schubach, K.M.; Sowers, C.A.; Duff, G.C.; Block, E.; Gouvêa, V.N. Performance, Health, and Physiological Responses of Newly Received Feedlot Cattle Supplemented with Pre- and Probiotic Ingredients. Animal 2021, 15, 100214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamizad, M.; Dehghan-Banadaky, M.; Rezayazdi, K.; Moradi-Shahrbabak, M. Effects of 6 Times Daily Milking during Early versus Full Lactation of Holstein Cows on Milk Production and Blood Metabolites. J. Dairy Sci. 2010, 93, 4054–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehy, M.R.; Mulligan, F.J.; Taylor, S.T.; Fahey, A.G. Effects of a Novel Heat-Treated Protein and Carbohydrate Supplement on Feed Consumption, Milk Production, and Cheese Yield in Early-Lactation Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 4315–4326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Universidad del Valle de Bolivia. Manual de Recolección, Conservación y Envío de Muestras al Laboratorio Para Diagnóstico de Enfermedades Comunes de Los Animales. 2016. Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/esp/Animal_Health_in_the_World/docs/pdf/Self-declarations/Archives/Anexo_4._Manual_de_toma_y_remision_de_muestras.pdf (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Villaseñor, G.F.; Ruvalcaba, G.J.M.; Espinosa, M.M.A.; Arteaga, G.R.I.; Ruvalcaba, A.M.J.; Montes, O.L.R.; Hernández, J.A.L.; Érica, A.L. Comparación de Dos Métodos Automatizados Para Análisis de Leche Bovina. In Proceedings of the XVII Congreso Internacional de MVZ Especialistas en Bovinos, Torreón, Coahulia, México, 8–10 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- D.O.F. NMX-F-490-1999-NORMEX. Alimentos—Aceites y Grasas—Determinación de La Composición de Ácidos Grasos a Partir de C6 Por Cromatografía de Gases, 1999. 1999. Available online: https://platiica.economia.gob.mx/normalizacion/nmx-f-490-1999-normex/ (accessed on 21 May 2025).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewels, P.A.; Peltzer, A.; Fillinger, S.; Patel, H.; Alneberg, J.; Wilm, A.; Garcia, M.U.; Di Tommaso, P.; Nahnsen, S. The Nf-Core Framework for Community-Curated Bioinformatics Pipelines. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straub, D.; Blackwell, N.; Langarica-Fuentes, A.; Peltzer, A.; Nahnsen, S.; Kleindienst, S. Interpretations of Environmental Microbial Community Studies Are Biased by the Selected 16S RRNA (Gene) Amplicon Sequencing Pipeline. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 550420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-Resolution Sample Inference from Illumina Amplicon Data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewels, P.; Magnusson, M.; Lundin, S.; Käller, M. MultiQC: Summarize Analysis Results for Multiple Tools and Samples in a Single Report. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3047–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA Ribosomal RNA Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Kuczynski, J.; Stombaugh, J.; Bittinger, K.; Bushman, F.D.; Costello, E.K.; Fierer, N.; Peña, A.G.; Goodrich, J.K.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. QIIME Allows Analysis of High-Throughput Community Sequencing Data. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 335–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, G.M.; Maffei, V.J.; Zaneveld, J.R.; Yurgel, S.N.; Brown, J.R.; Taylor, C.M.; Huttenhower, C.; Langille, M.G.I. PICRUSt2 for Prediction of Metagenome Functions. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 685–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Ewald, J.; Pang, Z.; Shiri, T.; Xia, J. MicrobiomeAnalyst 2.0: Comprehensive Statistical, Functional and Integrative Analysis of Microbiome Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W310–W318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.H.; Takiya, C.S.; Vendramini, T.H.A.; de Jesus, E.F.; Zanferari, F.; Rennó, F.P. Effects of Dietary Fibrolytic Enzymes on Chewing Time, Ruminal Fermentation, and Performance of Mid-Lactating Dairy Cows. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 2016, 221, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilio, E.M.C.; Del Valle, T.A.; Ghizzi, L.G.; Takiya, C.S.; Dias, M.S.S.; Nunes, A.T.; Silva, G.G.; Rennó, F.P. Effects of Exogenous Fibrolytic and Amylolytic Enzymes on Ruminal Fermentation and Performance of Mid-Lactation Dairy Cows. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 4179–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Refat, B.; Guevara-Oquendo, V.H.; Yu, P. Lactational Performance, Feeding Behavior, Ruminal Fermentation and Nutrient Digestibility in Dairy Cows Fed Whole-Plant Faba Bean Silage-Based Diet with Fibrolytic Enzyme. Animal 2022, 16, 100606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savela, M.F.B.; Noschang, J.P.; Barbosa, A.A.; Feijó, J.d.O.; Rabassa, V.R.; Schmitt, E.; Pino, F.A.B.D.; Corrêa, M.N.; Brauner, C.C. Supplementation of a Dried, Fungal Fermentation Product with Fibrolytic Enzymatic Activity in the Diet of Dairy Cows on Feeding Behavior, Metabolic Profile, Milk Yield, and Milk Composition. Livest. Sci. 2022, 260, 104945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Meyer, U.; Dänicke, S. Effect of Exogenous Fibrolytic Enzymes on Performance and Blood Profile in Early and Mid-Lactation Holstein Cows. Anim. Nutr. 2015, 1, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliem, K.E.; Shingfield, K.J. Manipulation of Milk Fatty Acid Composition in Lactating Cows: Opportunities and Challenges. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 1661–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lock, A.L.; Bauman, D.E. Modifying Milk Fat Composition of Dairy Cows to Enhance Fatty Acids Beneficial to Human Health. Lipids 2004, 39, 1197–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markiewicz-Keszycka, M.; Czyzak-Runowska, G.; Lipinska, P.; Wójtowski, J. Fatty Acid Profile of Milk—A Review. Bull. Vet. Inst. Puławy 2013, 57, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo, R.; Kholif, A.E.; Salem, A.Z.M.; Elghandour, M.M.Y.; Odongo, N.E.; Montes De Oca, R.; Rivero, N.; Alonso, M.U. Influence of Cellulase Addition to Dairy Goat Diets on Digestion and Fermentation, Milk Production and Fatty Acid Content. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 153, 1514–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanks, O.C.; Kelty, C.A.; Archibeque, S.; Jenkins, M.; Newton, R.J.; McLellan, S.L.; Huse, S.M.; Sogin, M.L. Community Structures of Fecal Bacteria in Cattle from Different Animal Feeding Operations. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 2992–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Sun, H.; Guo, H.; Nie, C.; Nan, S.; Lu, Q.; Chen, C.; Zhang, W. Effect of the Supplementation of Exogenous Complex Non-Starch Polysaccharidases on the Growth Performance, Rumen Fermentation and Microflora of Fattening Sheep. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1396993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Li, G.; Tang, W.; Zhu, Q.; Li, X.; Du, C.; Li, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, L. Role of Sedum Alfredii and Soil Microbes in the Remediation of Ultra-High Content Heavy Metals Contaminated Soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 339, 108090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.R.; Callaway, T.R.; Lourenco, J.M.; Ryman, V.E. Characterization of Rumen, Fecal, and Milk Microbiota in Lactating Dairy Cows. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 984119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Yu, Z.; Wang, B. Perilla frutescens Leaf Alters the Rumen Microbial Community of Lactating Dairy Cows. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Jiang, W.; Tian, Z.; Wu, H.; Ning, H.; Yan, G.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Dong, F.; Sun, Y.; et al. Fecal g. Streptococcus and g. Eubacterium_coprostanoligenes_group Combined with Sphingosine to Modulate the Serum Dyslipidemia in High-Fat Diet Mice. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 4234–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Fernandez, G.; Denman, S.E.; Walker, N.; Kindermann, M.; McSweeney, C.S. Programming Rumen Microbiome Development in Calves with the Anti-Methanogenic Compound 3-NOP. Anim. Microbiome 2024, 6, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adeyemi, J.A.; Peters, S.O.; De Donato, M.; Cervantes, A.P.; Ogunade, I.M. Effects of a Blend of Saccharomyces cerevisiae-Based Direct-Fed Microbial and Fermentation Products on Plasma Carbonyl-Metabolome and Fecal Bacterial Community of Beef Steers. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 11, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabel, M.A.; Yeoman, C.J.; Han, Y.; Dodd, D.; Abbas, C.A.; de Bont, J.A.M.; Morrison, M.; Cann, I.K.O.; Mackie, R.I. Biochemical Characterization and Relative Expression Levels of Multiple Carbohydrate Esterases of the Xylanolytic Rumen Bacterium Prevotella ruminicola 23 Grown on an Ester-Enriched Substrate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 5671–5681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.N.; Méndez–García, C.; Geier, R.R.; Iakiviak, M.; Chang, J.; Cann, I.; Mackie, R.I. Metabolic Networks for Nitrogen Utilization in Prevotella ruminicola 23. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, W.; Mao, S. Comparative studies of the composition of bacterial microbiota associated with the ruminal content, ruminal epithelium and in the faeces of lactating dairy cows. Microb. Biotechnol. 2016, 9, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Ramos, J.J.; Solís-Oba, A.; Solís-Oba, M.; Calderón-Vázquez, C.L.; Higuera-Rubio, J.M.; Castro-Rivera, R. Effect of the Initial PH on the Anaerobic Digestion Process of Dairy Cattle Manure. AMB Express 2022, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brulin, L.; Ducrocq, S.; Estellé, J.; Even, G.; Martel, S.; Merlin, S.; Audebert, C.; Croiseau, P.; Sanchez, M.P. The Fecal Microbiota of Holstein Cows Is Heritable and Genetically Correlated to Dairy Performances. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 11254–11268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.B.; Gonzalez, E.L.; Choy, K.; Faull, K.F.; Jewell, T.; Arellano, A.; Liang, J.; Yu, K.B.; Paramo, J.; Hsiao, E.Y. Gut Microbiota Turicibacter Strains Differentially Modify Bile Acids and Host Lipids. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, P.; Li, L.; Bionaz, M.; Lin, P.; Yao, J. Altered Bile Acid and Correlations with Gut Microbiome in Transition Dairy Cows with Different Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Status. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 9915–9933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kong, F.; Liu, J.; Xia, J.; Du, W.; Li, S.; Wang, W. Comparative Analysis of Rumen Microbiota Composition in Dairy Cows with Simple Indigestion and Healthy Cows. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Lai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, J.; Jin, W.; Lin, L.; Mao, S. Host Genetic Regulation of Specific Functional Groups in the Rumen Microbiome of Dairy Cows: Implications for Lactation Trait. J. Adv. Res. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Liu, B.; Maimai, T.; Zhao, C.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, N.; Hu, X.; Fu, Y. Characterization of Bacterial Community in the Rumen of Bovine with Laminitis Using High-Throughput Sequencing. Genes 2021, 12, 1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarsella, E.; Zecconi, A.; Cintio, M.; Stefanon, B. Characterization of Microbiome on Feces, Blood and Milk in Dairy Cows with Different Milk Leucocyte Pattern. Animals 2021, 11, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duthoit, F.; Godon, J.J.; Montel, M.C. Bacterial Community Dynamics during Production of Registered Designation of Origin Salers Cheese as Evaluated by 16S RRNA Gene Single-Strand Conformation Polymorphism Analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3840–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Castilho, N.P.A.; Todorov, S.D.; Nero, L.A. Beneficial and Safety Properties of a Corynebacterium vitaeruminis Strain Isolated from the Cow Rumen. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2017, 9, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Ji, S.; Yan, H.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Li, S. The Day-to-Day Stability of the Ruminal and Fecal Microbiota in Lactating Dairy Cows. MicrobiologyOpen 2020, 9, e990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Y.; Lin, X.; Wang, Z.; Hou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Z. High-Production Dairy Cattle Exhibit Different Rumen and Fecal Bacterial Community and Rumen Metabolite Profile than Low-Production Cattle. MicrobiologyOpen 2019, 8, e00673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Fitamo, T.M.; Nesbø, C.L.; Guilford, N.G.H.; Kanger, K.; Yang, M.I.; Edwards, E.A. Microbial Community Dynamics of a Sequentially Fed Anaerobic Digester Treating Solid Organic Waste. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2023, 99, fiad017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.T.; Han, H.; Yu, Z.; Tsuruta, T.; Nishino, N. Variability, Stability, and Resilience of Fecal Microbiota in Dairy Cows Fed Whole Crop Corn Silage. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 6355–6364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brulin, L.; Ducrocq, S.; Even, G.; Sanchez, M.P.; Martel, S.; Merlin, S.; Audebert, C.; Croiseau, P.; Estellé, J. Short Communication: Bifidobacterium Abundance in the Faecal Microbiota Is Strongly Associated with Milk Traits in Dairy Cattle. Animal 2024, 18, 101243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, D.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Xu, D.; et al. Relationship between Sheep Feces Scores and Gastrointestinal Microorganisms and Their Effects on Growth Traits and Blood Indicators. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1348873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, L.; Suleiman, K.; Shamdas, M.; Bassilious, K.; Poonit, N.; Rossiter, A.E.; Acharjee, A.; Loman, N.; Murray, P.I.; Wallace, G.R.; et al. Gut Dysbiosis in Ocular Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 780354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Piao, X. Different Dietary Protein Sources Influence Growth Performance, Antioxidant Capacity, Immunity, Fecal Microbiota and Metabolites in Weaned Piglets. Anim. Nutr. 2022, 8, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, J.; Yang, Z.; Wang, E.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, S. Possibility of Using By-Products with High NDF Content to Alter the Fecal Short Chain Fatty Acid Profiles, Bacterial Community, and Digestibility of Lactating Dairy Cows. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Lopez, E.; Haselmann, A.; Petri, R.M.; Knaus, W.; Zebeli, Q. Evaluation of Fecal Fermentation Profile and Bacterial Community in Organically Fed Dairy Cows Consuming Forage-Rich Diets with Different Particle Sizes. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 8020–8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falalyeyeva, T.; Chornenka, N.; Cherkasova, L.; Tsyryuk, O.; Molchek, N.; Kovalchuk, O.; Kyriachenko, Y.; Ostapchenko, L.; Kobyliak, N. Gut Microbiota Interactions With Obesity. In Comprehensive Gut Microbiota; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 201–219. [Google Scholar]
- Bajpai, P. Xylanases. In Encyclopedia of Microbiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 600–612. [Google Scholar]
- Berrin, J.-G.; Juge, N. Factors Affecting Xylanase Functionality in the Degradation of Arabinoxylans. Biotechnol. Lett. 2008, 30, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, J.J.; Macias, E.G.; Ma, Z.X.; Martins, R.M.; Staples, C.R.; Beauchemin, K.A.; Adesogan, A.T. Improving the Performance of Dairy Cattle with a Xylanase-Rich Exogenous Enzyme Preparation. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 3486–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pech-Cervantes, A.A.; Ogunade, I.M.; Jiang, Y.; Estrada-Reyes, Z.M.; Arriola, K.G.; Amaro, F.X.; Staples, C.R.; Vyas, D.; Adesogan, A.T. Effects of a Xylanase-Rich Enzyme on Intake, Milk Production, and Digestibility of Dairy Cows Fed a Diet Containing a High Proportion of Bermudagrass Silage. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 7671–7681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchemin, K.A.; Holtshausen, L. Developments in Enzyme Usage in Ruminants. In Enzymes in Farm Animal Nutrition; CABI: London, UK, 2010; pp. 206–230. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.Z.; Beauchemin, K.A.; Rode, L.M. A Comparison of Methods of Adding Fibrolytic Enzymes to Lactating Cow Diets. J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 2512–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatment (Group) | ||
|---|---|---|
| TC (Control) | TE (ECS) | |
| Trait (%, DB) | ||
| Corn silage | 31.7 | 31.7 |
| Alfalfa hay | 7.9 | 7.9 |
| Corn stover | 11.9 | 11.9 |
| Concentrate 1 | 48.6 | 48.6 |
| Enzyme complex (g/cow) | 0 | 25 |
| Composition (g/Kg) | ||
| Dry matter | 567.2 | 565.5 |
| Organic matter | 915.0 | 916.4 |
| Crude protein | 158.7 | 161.7 |
| Ether extract | 36.1 | 35.9 |
| Neutral detergent fiber | 350.7 | 346.5 |
| Acid detergent fiber | 245.3 | 241.2 |
| Group (Treatment) | Significance (p-Value) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Item | TC (Control) | TE (ECS 1) | SEM | Treatment | Week | Treat × Week |
| DMI, KgDM/cow/d * | 26.59 | 27.20 | 0.092 | <0.0001 | 0.0008 | 0.0003 |
| Milk yield, kg/d | 36.70 | 39.01 | 0.605 | 0.007 | 0.306 | 0.981 |
| 4%FCM, kg/d | 32.54 | 34.11 | 0.533 | 0.039 | 0.519 | 0.975 |
| Milk fat, % | 3.25 | 3.16 | 0.050 | 0.226 | 0.981 | 0.670 |
| Milk fat yield, kg/cow/d | 1.19 | 1.23 | 0.019 | 0.112 | 0.739 | 0.781 |
| Milk protein, % | 3.08 | 3.03 | 0.004 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Milk protein yield, kg/cow/d | 1.13 | 1.18 | 0.001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Milk lactose, % | 4.78 | 4.70 | 0.006 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Milk lactose yield, kg/cow/d | 1.75 | 1.83 | 0.002 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Milk NFS, % | 8.65 | 8.50 | 0.009 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Milk NFS yield, kg/cow/d | 3.17 | 3.31 | 0.004 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Milk density, kg/L | 1.0288 | 1.0286 | 0.399 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 |
| Group (Treatment) | Significance (p-Value) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Component, g/L | TC (Control) | TE (ECS) | SEM | Treatment | Week | Treat × Week |
| Palmitic acid | 11.984 | 12.567 | 0.171 | 0.029 | 0.475 | 0.336 |
| Estearic acid | 3.550 | 3.326 | 0.197 | 0.437 | 0.491 | 0.481 |
| Oleic acid | 8.137 | 8.491 | 0.124 | 0.066 | 0.145 | 0.015 |
| Linoleic acid | 0.921 | 0.923 | 0.018 | 0.950 | 0.722 | 0.610 |
| Linolenic acid | 0.161 | 0.159 | 0.003 | 0.721 | 0.024 | 0.451 |
| Saturated fat | 14.615 | 15.891 | 0.654 | 0.193 | 0.383 | 0.251 |
| Monounsaturated fat | 8.137 | 8.491 | 0.124 | 0.066 | 0.145 | 0.015 |
| Polyunsaturated fat | 1.082 | 1.081 | 0.021 | 0.978 | 0.530 | 0.567 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruvalcaba-Gómez, J.M.; Arteaga-Garibay, R.I.; Anaya-Esparza, L.M.; Gómez-Godínez, L.J.; Martínez-Sotelo, J.G.; Hernández-Cruz, E.; Arias-Chávez, L.E. Fecal Microbiota and Performance of Dairy Cattle from a West Mexican Family Dairy Farm Supplemented with a Fiber-Degrading Enzymatic Complex. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060518
Ruvalcaba-Gómez JM, Arteaga-Garibay RI, Anaya-Esparza LM, Gómez-Godínez LJ, Martínez-Sotelo JG, Hernández-Cruz E, Arias-Chávez LE. Fecal Microbiota and Performance of Dairy Cattle from a West Mexican Family Dairy Farm Supplemented with a Fiber-Degrading Enzymatic Complex. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(6):518. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060518
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuvalcaba-Gómez, José Martín, Ramón Ignacio Arteaga-Garibay, Luis Miguel Anaya-Esparza, Lorena Jacqueline Gómez-Godínez, Jazmín Guadalupe Martínez-Sotelo, Elías Hernández-Cruz, and Luis Eduardo Arias-Chávez. 2025. "Fecal Microbiota and Performance of Dairy Cattle from a West Mexican Family Dairy Farm Supplemented with a Fiber-Degrading Enzymatic Complex" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 6: 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060518
APA StyleRuvalcaba-Gómez, J. M., Arteaga-Garibay, R. I., Anaya-Esparza, L. M., Gómez-Godínez, L. J., Martínez-Sotelo, J. G., Hernández-Cruz, E., & Arias-Chávez, L. E. (2025). Fecal Microbiota and Performance of Dairy Cattle from a West Mexican Family Dairy Farm Supplemented with a Fiber-Degrading Enzymatic Complex. Veterinary Sciences, 12(6), 518. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060518







