Identification, Pathogenicity, and Reverse Genetics System Construction of a Pseudorabies Virus Isolate from Pigs in China
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Virus Strain and Cell Culture
2.3. Isolation of the Virus
2.4. PCR Identification of the Virus
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
2.6. Pathogenicity Analysis of PRV-HL-2021 in Mice
2.7. Establishment of a Reverse Genetics Platform for the PRV-HL-2021 Strain
2.8. IFA Test
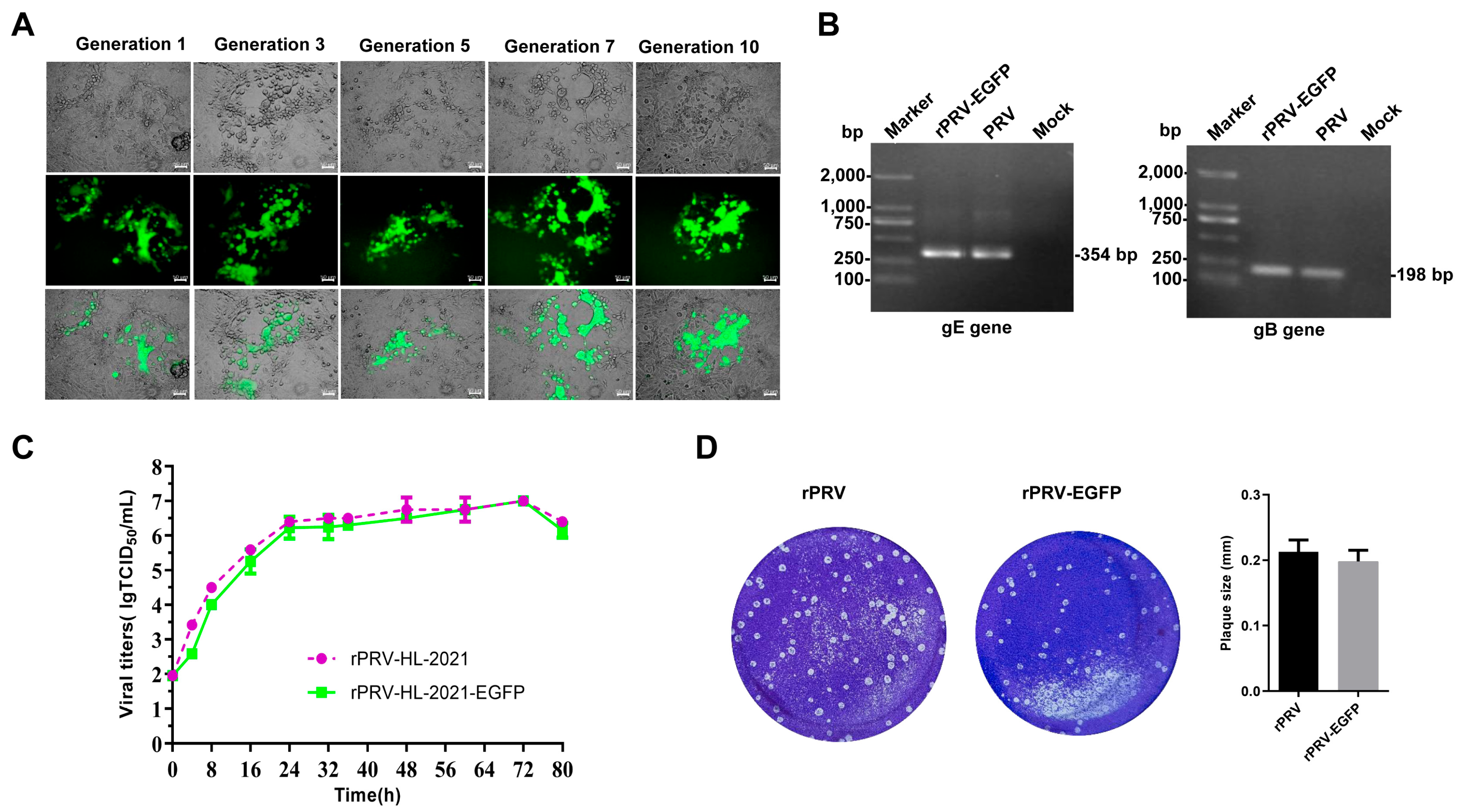
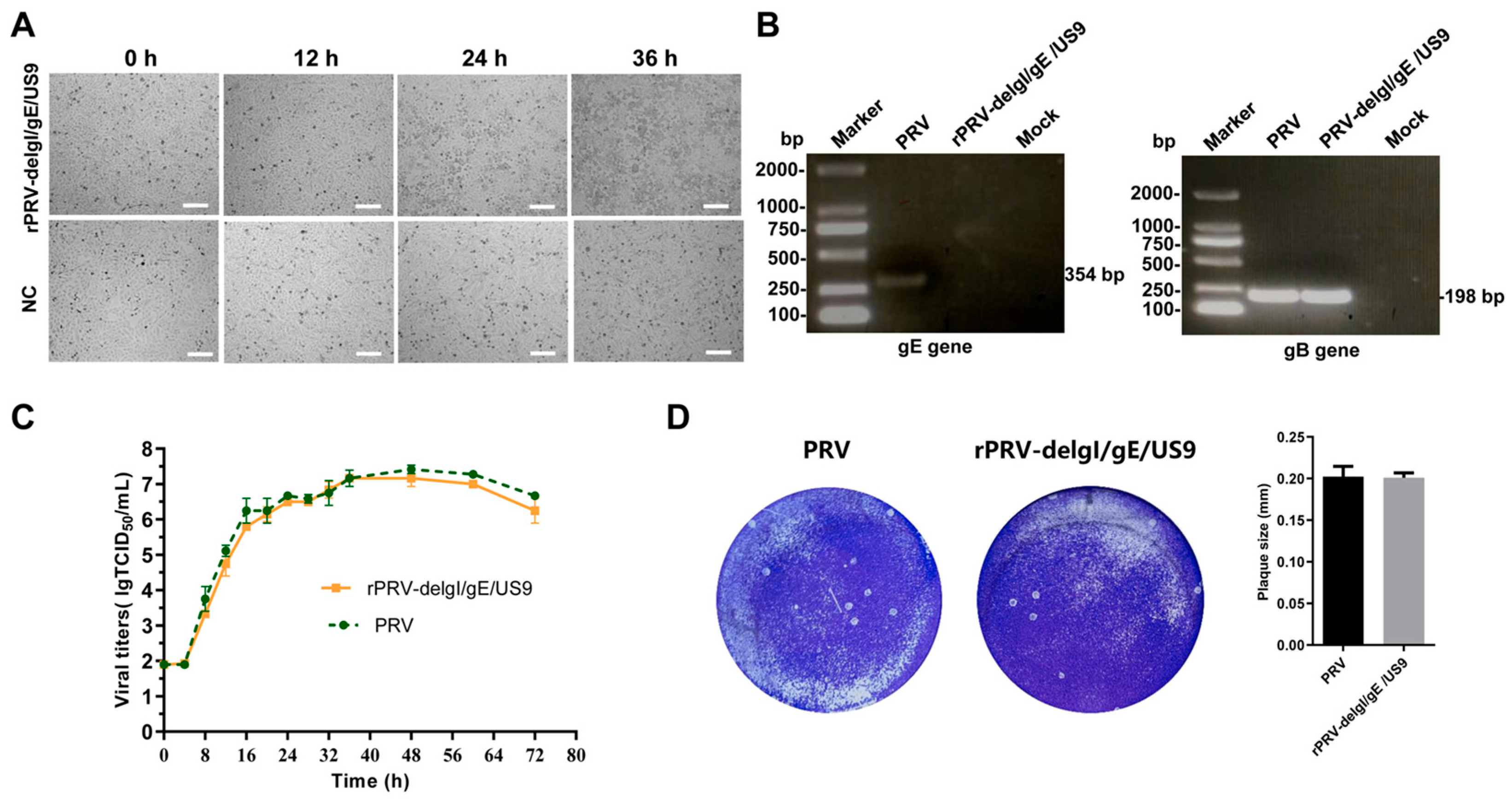
2.9. Examination of the Replication Kinetics of rPRV-HL-2021
2.10. Plaque Assays
2.11. Generation of a Recombinant PRV Expressing EGFP
2.12. Generation of a Recombinant PRV with Three Gene Knockouts
3. Results
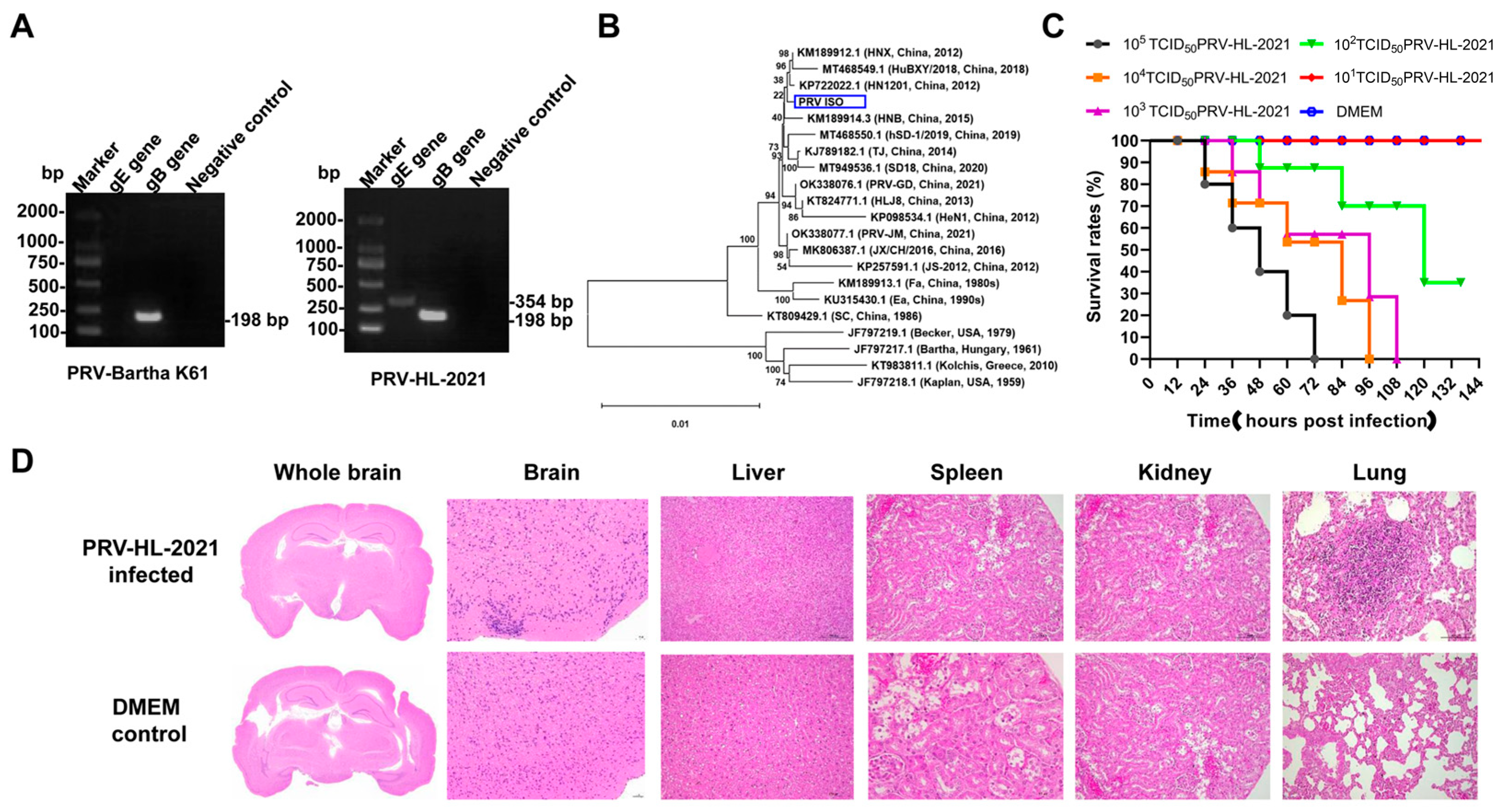
3.1. Isolation and Identification of PRV Epidemic Strain
3.2. The Pathogenicity of PRV-HL-2021
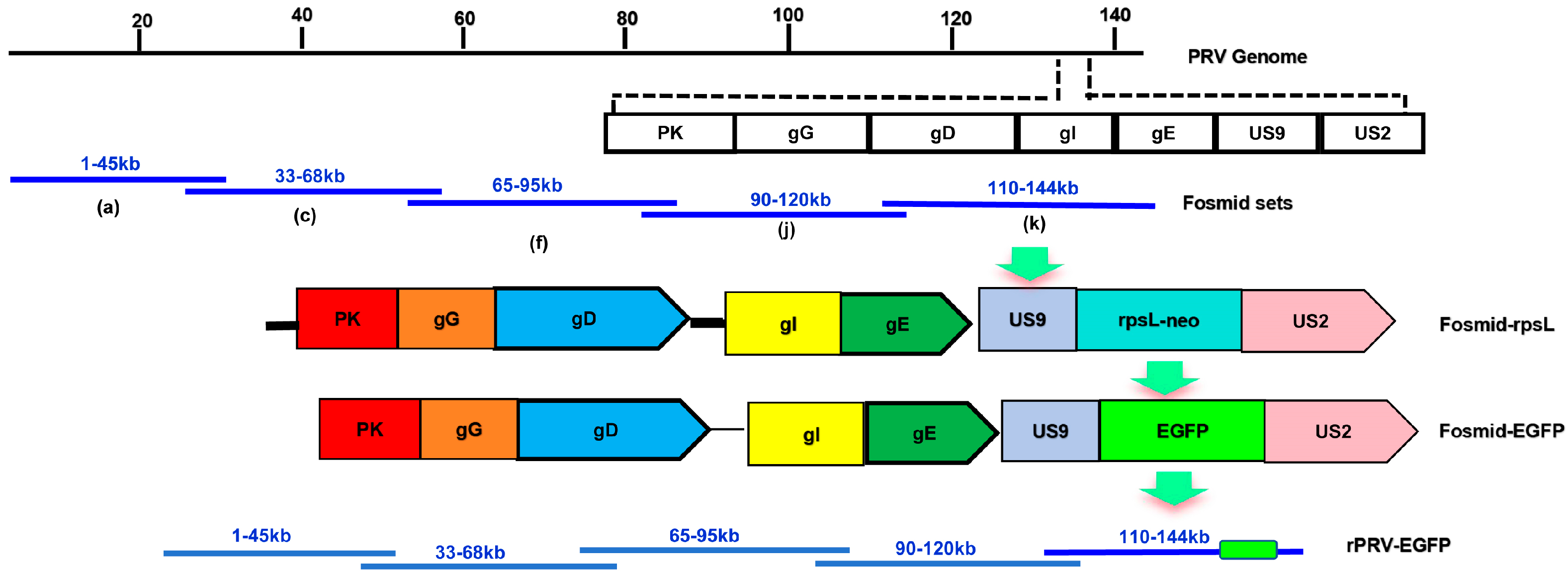
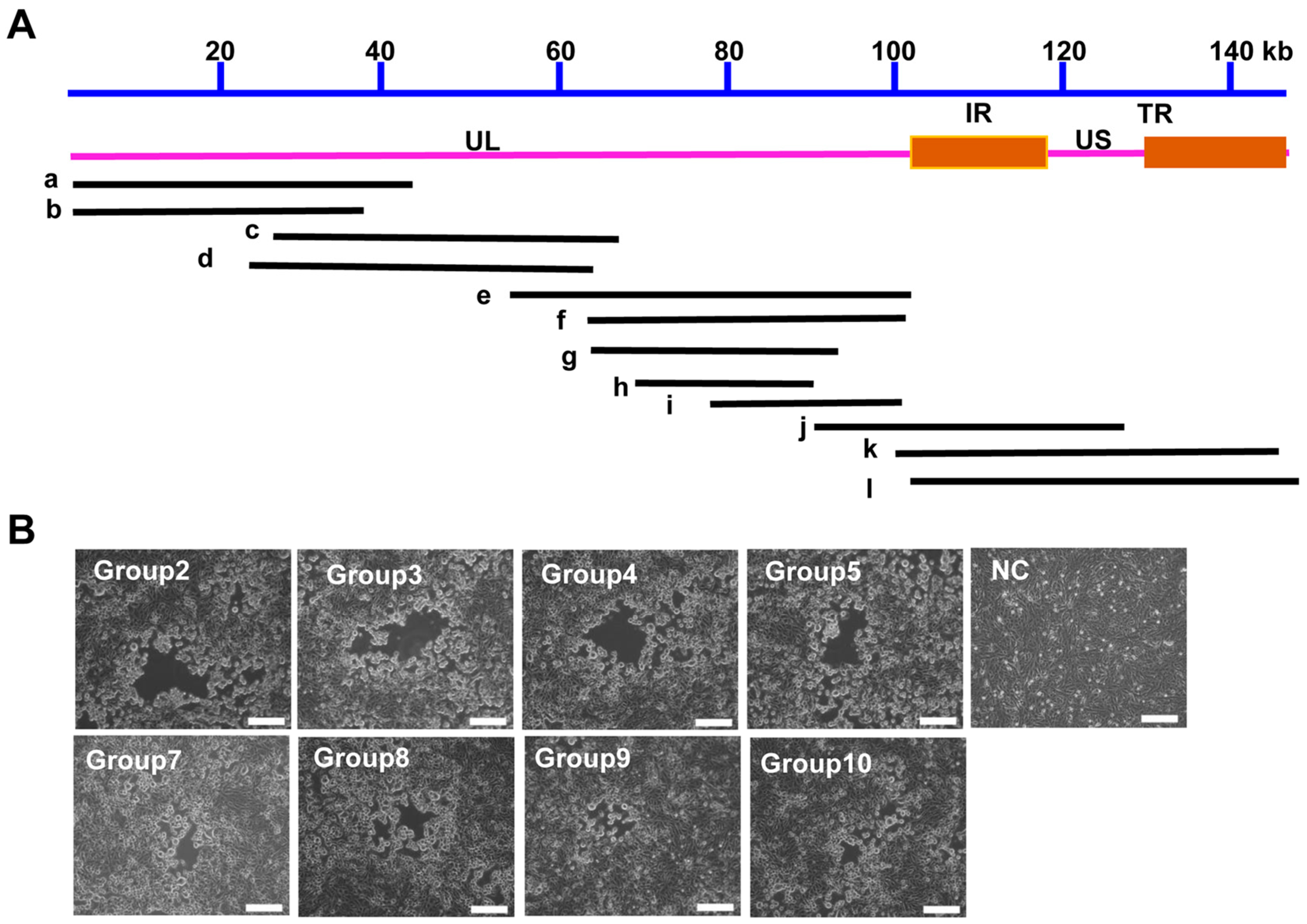
3.3. Construction of a PRV Reverse Genetics Platform Based on the Fosmid Library
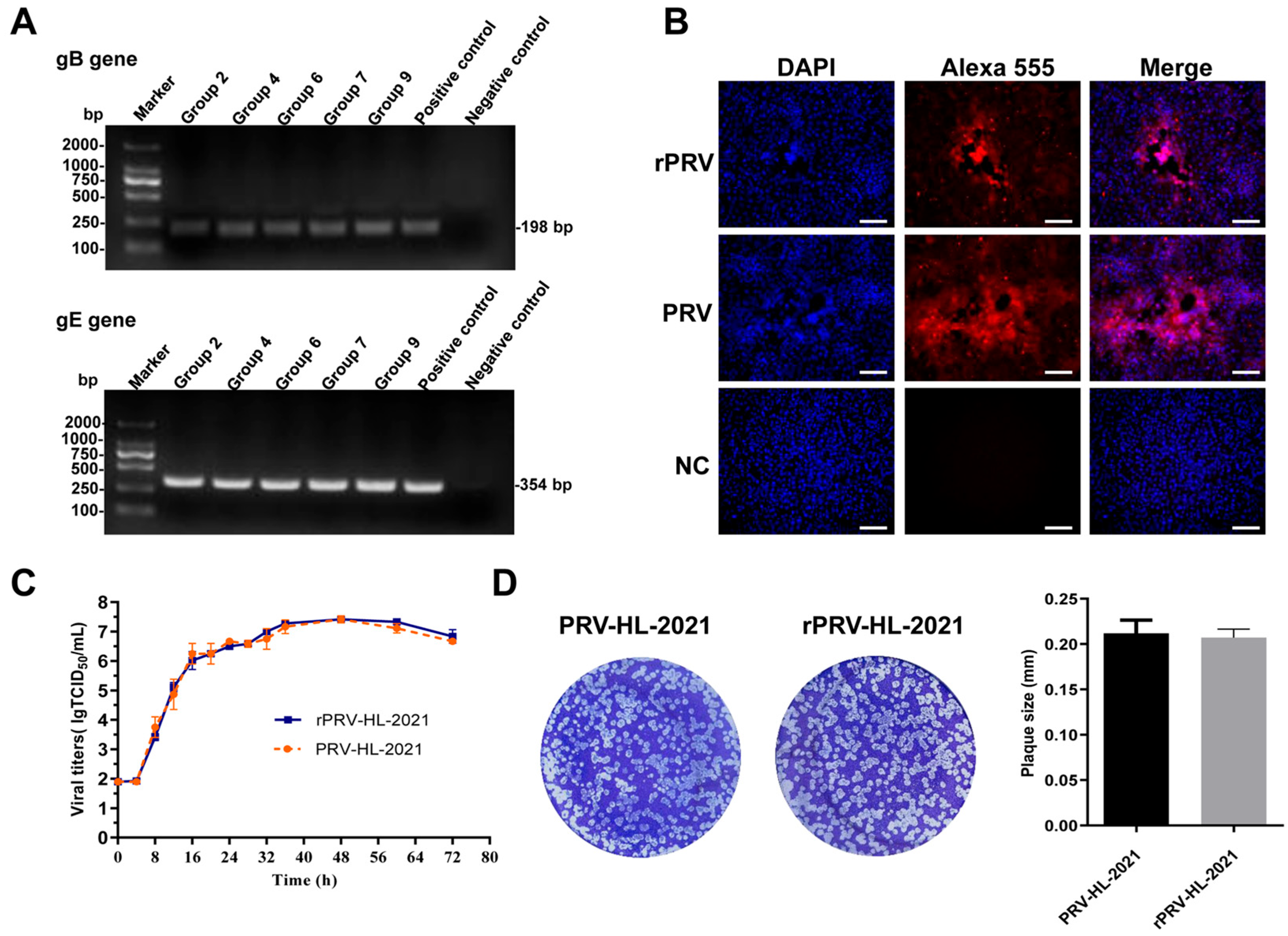
3.4. Rescue and Characterization of Recombinant Virus Expressing EGFP
3.5. Rescue of the Recombinant Virus Deleting gI/gE/US9 Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nie, Z.; Zhu, S.; Wu, L.; Sun, R.; Shu, J.; He, Y.; Feng, H. Progress on innate immune evasion and live attenuated vaccine of pseudorabies virus. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1138016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mettenleiter, T.C. Aujeszky’s disease (pseudorabies) virus: The virus and molecular pathogenesis—State of the art, June 1999. Vet. Res. 2000, 31, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.H.; Fu, P.F.; Chen, H.Y.; Wang, Z.Y. Pseudorabies Virus: From Pathogenesis to Prevention Strategies. Viruses 2022, 14, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, G.; Yin, J.; Li, L.; Huang, K.; Du, Q.; Tong, D.; Huang, Y. Pseudorabies virus infection activates the NLRP3 and IFI16 inflammasomes to trigger pyroptosis. Vet. Microbiol. 2023, 284, 109826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ding, C.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, W.; Wen, W.; Favoreel, H.W.; Li, X. Pseudorabies virus infection triggers mitophagy to dampen the interferon response and promote viral replication. J. Virol. 2024, 98, e0104824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombácz, D.; Tóth, J.S.; Petrovszki, P.; Boldogkoi, Z. Whole-genome analysis of pseudorabies virus gene expression by real-time quantitative RT-PCR assay. BMC Genomics 2009, 10, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engel, E.A.; Card, J.P.; Enquist, L.W. Transneuronal Circuit Analysis with Pseudorabies Viruses. Curr. Protoc. 2023, 3, e841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Shi, D.; Tang, Y.D.; Zhang, L.; Hu, B.; Zheng, C.; Huang, L.; Weng, C. Pseudorabies virus gM and its homologous proteins in herpesviruses induce mitochondria-related apoptosis involved in viral pathogenicity. PLoS Pathog. 2024, 20, e1012146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Han, T.; Li, X.; Gu, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; et al. Pathogenic pseudorabies virus, China, 2012. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2014, 20, 102–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Z.; Li, X. A Review of Pseudorabies Virus Variants: Genomics, Vaccination, Transmission, and Zoonotic Potential. Viruses 2022, 14, 1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Kuang, Y.; Li, Y.; Guo, H.; Zhou, C.; Guo, S.; Tan, C.; Wu, B.; Chen, H.; Wang, X. The Epidemiology and Variation in Pseudorabies Virus: A Continuing Challenge to Pigs and Humans. Viruses 2022, 14, 1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Gao, J.; Hua, R.; Zhang, G. Pseudorabies virus as a zoonosis: Scientific and public health implications. Virus Genes 2025, 61, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Abid, M.; Cao, S.; Zhu, S. Recombinant Pseudorabies Virus Usage in Vaccine Development against Swine Infectious Disease. Viruses 2023, 15, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zha, Z.; Huang, P.; Sun, H.; Huang, Y.; He, M.; Chen, T.; Lin, L.; Chen, Z.; Kong, Z.; et al. Structures of pseudorabies virus capsids. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klupp, B.G.; Hengartner, C.J.; Mettenleiter, T.C.; Enquist, L.W. Complete, annotated sequence of the pseudorabies virus genome. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 424–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Porat, T.; Rixon, F.J.; Blankenship, M.L. Analysis of the structure of the genome of pseudorabies virus. Virology 1979, 95, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Zhao, W.; Li, K.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Su, S.; Zhou, J.; Lei, J.; Xing, G.; Sun, H.; et al. Genome Characteristics and Evolution of Pseudorabies Virus Strains in Eastern China from 2017 to 2019. Virol. Sin. 2019, 34, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomniczi, B.; Kaplan, A.S.; Ben-Porat, T. Multiple defects in the genome of pseudorabies virus can affect virulence without detectably affecting replication in cell culture. Virology 1987, 161, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.Y.; Liu, K.S.; Zhang, C.; Ni, Z.; Zhu, Y.C.; Bao, H.L.; Chen, L.; Ye, W.C.; Hua, J.G.; Huo, S.X.; et al. Recombinant pseudorabies virus (PRV) expressing stabilized E2 of classical swine fever virus (CSFV) protects against both PRV and CSFV. Antivir. Res. 2023, 211, 105548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Liu, C.; He, X.; Abbas, B.; Chen, Q.; Li, Z.; Feng, Z. Generation and Characterization of Recombinant Pseudorabies Virus Delivering African Swine Fever Virus CD2v and p54. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 25, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Forlenza, M.; Chen, H. Application of CRISPR/Cas9 for Rapid Genome Editing of Pseudorabies Virus and Bovine Herpesvirus-1. Viruses 2024, 16, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cleemput, J.; Koyuncu, O.O.; Laval, K.; Engel, E.A.; Enquist, L.W. CRISPR/Cas9-Constructed Pseudorabies Virus Mutants Reveal the Importance of UL13 in Alphaherpesvirus Escape from Genome Silencing. J. Virol. 2021, 95, e02286-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, A.; Qin, C.; Lang, Y.; Wang, M.; Lin, M.; Li, C.; Zhang, R.; Tang, J. A simple and rapid approach to manipulate pseudorabies virus genome by CRISPR/Cas9 system. Biotechnol. Lett. 2015, 37, 1265–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Abid, M.; Yin, H.; Wu, H.; Teklue, T.; Qiu, H.J.; Sun, Y. Establishment of an Efficient and Flexible Genetic Manipulation Platform Based on a Fosmid Library for Rapid Generation of Recombinant Pseudorabies Virus. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, I.C.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Wheeler, M.A.; Li, Z.; Rothhammer, V.; Linnerbauer, M.; Sanmarco, L.M.; Guo, L.; Blain, M.; Zandee, S.; et al. Barcoded viral tracing of single-cell interactions in central nervous system inflammation. Science 2021, 372, eabf1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laval, K.; Enquist, L.W. The Neuropathic Itch Caused by Pseudorabies Virus. Pathogens 2020, 9, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, X.; Xie, C.; Ding, S.; Yang, H.; Guo, S.; Li, J.; Qin, L.; Ban, F.; Wang, D.; et al. A Novel Human Acute Encephalitis Caused by Pseudorabies Virus Variant Strain. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e3690–e3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Wu, H.; Abid, M.; Qiu, H.J.; Sun, Y. Establishment of a Fosmid Library for Pseudorabies Virus SC Strain and Application in Viral Neuronal Tracing. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.D.; Liu, J.T.; Wang, T.Y.; Sun, M.X.; Tian, Z.J.; Cai, X.H. Comparison of Pathogenicity-Related Genes in the Current Pseudorabies Virus Outbreak in China. Sci Rep. 2017, 7, 7783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Y.; Chen, P.; Shi, L.; Yuan, C.; Cao, L.; Sun, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. A rapid and versatile reverse genetic approach and visualization animal models for emerging zoonotic pseudorabies virus. Antivir. Res. 2024, 232, 106036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, M.; Teklue, T.; Li, Y.; Wu, H.; Wang, T.; Qiu, H.J.; Sun, Y. Generation and Immunogenicity of a Recombinant Pseudorabies Virus Co-Expressing Classical Swine Fever Virus E2 Protein and Porcine Circovirus Type 2 Capsid Protein Based on Fosmid Library Platform. Pathogens 2019, 8, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, L.Q.; Zheng, H.H.; Yang, Y.R.; Liu, F.; Zheng, L.L.; Jin, Y.; Chen, H.Y. Construction and immunogenicity of a gE/gI/TK-deleted PRV based on porcine pseudorabies virus variant. Mol. Cell Probes. 2020, 53, 101605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cong, X.; Lei, J.L.; Xia, S.L.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Luo, Y.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, H.J. Pathogenicity and immunogenicity of a gE/gI/TK gene-deleted pseudorabies virus variant in susceptible animals. Vet. Microbiol. 2016, 182, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| No. | Name of the Primer | Sequences of the Primers | Target Genes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | F-identify-gE | TGGCTCTGCGTGCTGTGCTC | gE |
| R-identify-gE | CATTCGTCACTTCCGGTTTC | ||
| 2 | F-identify- gB | GGGGTTGGACAGGAAGGACACCA | gB |
| R-identify- gB | AACCAGCTGCACGCGCTCAA | ||
| 3 | F-US9-rpsL | TCTGCTCGCTGTCCGCGCTACTCGGGGGCATCGTCGCCAGGCACGTGTAGGCTCCCCGCGGGGCTCCTCC | rpsL |
| R-US9-rpsL | GGGCGCGGCGGATGGGGGCGGGCCCCCGCTCCCGTTCGCTCGCTCGCTCGCCTCGGCGCCGGCGCACGTC | ||
| 4 | F-replace rpsL-insert-EGFP | TCTGCTCGCTGTCCGCGCTACTCGGGGGCATCGTCGCCAGGCACGTGTAGTAGTTATTAATAGTAATC | EGFP |
| R-replace rpsL-insert-EGFP | GGGCGCGGCGGATGGGGGCGGGCCCCCGCTCCCGTTCGCTCGCTCGCTCGGCAGTGAAAAAAATGCTT | ||
| 5 | F-delgE/gI/US9-rpsL | GCCTCCGCAGTACCGGCGTCGATGATGATGGTGGCGCGCGACGTGACCCGGCAGTGAAAAAAATGCTT | rpsL |
| R-delgE/gI/US9-rpsL | TCTAGGAGATGGTACATCGCGGGGCGCGCTCGCGTCCGTTGCCGCGCCCGTCAGAAGAACTCGTCAAGAAGGCG | ||
| 6 | F-replace rpsL-delgE/gI/US9 | TCTAGGAGATGGTACATCGCGGGGCGCGCTCGCGTCCGTTGCCGCGCCCGCCTCGGCGCCGGCGCACGTC | Parts of US2 and US7 |
| PRV Strain | Country | Year of Isolating | GenBank No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| HNX | China | 2012 | KM189912.1 |
| HuBXY/2018 | China | 2018 | MT468549.1 |
| HN1201 | China | 2012 | KP722022.1 |
| HNB | China | 2015 | KM189914.1 |
| hSD-1/2019 | China | 2019 | MT468550.1 |
| TJ | China | 2014 | KJ789182.1 |
| SD18 | China | 2020 | MT949536.1 |
| PRV-GD | China | 2021 | OK338076.1 |
| HLJ8 | China | 2013 | KT824771.1 |
| HeN1 | China | 2012 | KP098534.1 |
| PRV-JM | China | 2021 | OK338077.1 |
| JX/CH/2016 | China | 2016 | MK806387.1 |
| JS-2012 | China | 2012 | KP257591.1 |
| Fa | China | 1980s | KM189913.1 |
| Ea | China | 1990s | KU315430.1 |
| SC | China | 1986 | KT809429.1 |
| Becker | USA | 1979 | JF797219.1 |
| Bartha | Hungary | 1961 | JF797217.1 |
| Kolchis | Greece | 2010 | KT983811.1 |
| Kaplan | USA | 1959 | JF797218.1 |
| The Number of Animals That Can Detect PRV | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strain | Dose (TICD50) | Route | Brain | Heart | Liver | Spleen | Lung | Kidney |
| PRV-HL-2021 | 105 | i.p. | 4/5 | 1/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 |
| 104 | i.p. | 2/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | |
| 103 | i.p. | 2/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | |
| 102 | i.p. | 2/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | |
| DMEM | 0.1 mL | i.p. | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 | 0/5 |
| Fosmid | Relative Position in the Genome (nt) | The Size of the Fragment (bp) | Fosmid | Relative Position in the Genome (nt) | The Size of the Fragment (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRV-IF-a | 1–44102 | 44,101 | PRV-IF-g | 50226–89728 | 39,502 |
| PRV-IF-b | 1–39716 | 39,515 | PRV-IF-h | 51898–85801 | 33,903 |
| PRV-IF-c | 33891–68519 | 34,628 | PRV-IF-i | 67889–102713 | 34,824 |
| PRV-IF-d | 28749–61624 | 32,875 | PRV-IF-j | 91337–122601 | 25,883 |
| PRV-IF-e | 47680–10987 | 35,793 | PRV-IF-k | 100865–end | 26,640 |
| PRV-IF-f | 61229–101922 | 40,693 | PRV-IF-l | 101794–end | 25,711 |
| Group | Fosmid Combination | CPE Occurrence Time (hpt) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | a + c + e + j + k | no CPE occurrence |
| 2 | a + c + f + j + k | 24 |
| 3 | b + d + f + g + h + i | 48 |
| 4 | b + d + h + i + k | 36 |
| 5 | b + d + h + i + j + k | 54 |
| 6 | a + c + e + j + l | no CPE occurrence |
| 7 | a + c + f + j + l | 36 |
| 8 | b + d + f + g + h + l | 54 |
| 9 | b + d + h + i + l | 36 |
| 10 | b + d + h + i + j + l | 36 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, M.; Liang, H.; Nie, N.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, R.; Cao, S.; Zhu, S. Identification, Pathogenicity, and Reverse Genetics System Construction of a Pseudorabies Virus Isolate from Pigs in China. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060519
Zhou M, Liang H, Nie N, Zhang L, Zhu R, Cao S, Zhu S. Identification, Pathogenicity, and Reverse Genetics System Construction of a Pseudorabies Virus Isolate from Pigs in China. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(6):519. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060519
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Mo, Haiyang Liang, Nannan Nie, Li Zhang, Rui Zhu, Shinuo Cao, and Shanyuan Zhu. 2025. "Identification, Pathogenicity, and Reverse Genetics System Construction of a Pseudorabies Virus Isolate from Pigs in China" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 6: 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060519
APA StyleZhou, M., Liang, H., Nie, N., Zhang, L., Zhu, R., Cao, S., & Zhu, S. (2025). Identification, Pathogenicity, and Reverse Genetics System Construction of a Pseudorabies Virus Isolate from Pigs in China. Veterinary Sciences, 12(6), 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12060519






