Bacillus subtilis Fed to Sows Promotes Intestinal Development and Regulates Mucosal Immunity in Offspring
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Experimental Design and Sample Collection
2.3. Histological and Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.4. Immunofluorescence
2.5. ELISA
2.6. Real-Time PCR Quantification
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Feeding B.S-Dia to Sows on the Weight and Intestinal Morphology of Piglets
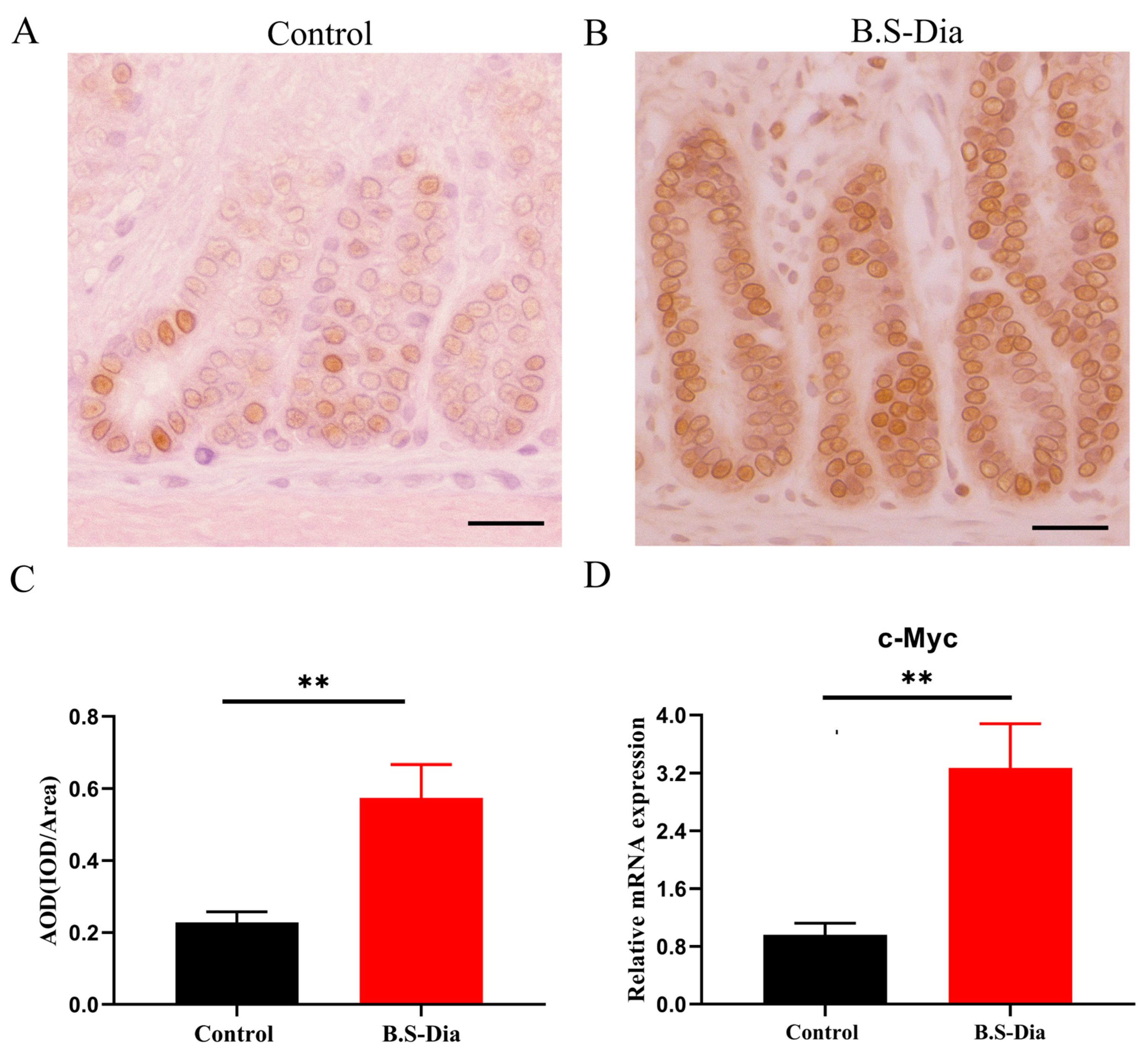
3.2. Difference in the Proliferation Status of the Jejunum After B.S-Dia Administration
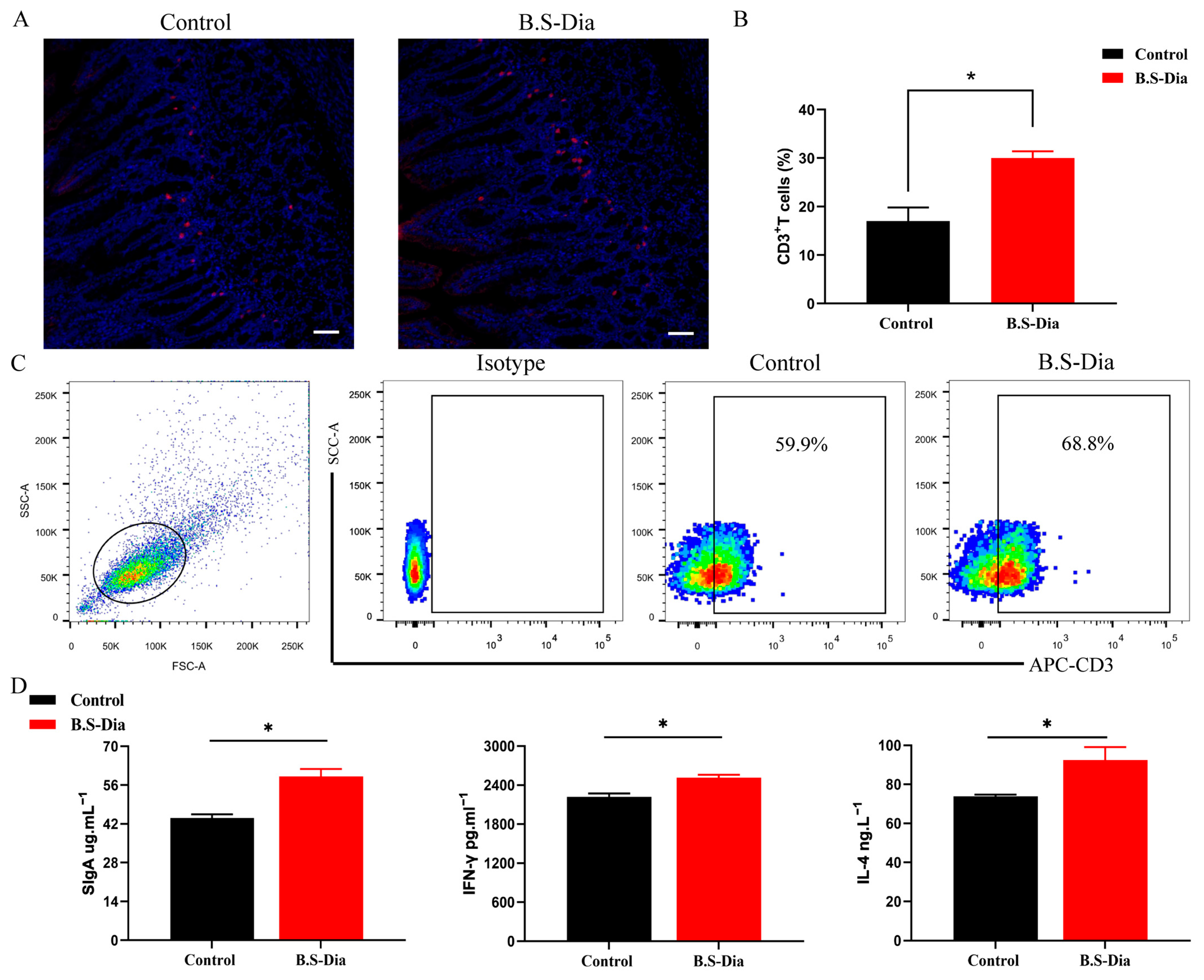
3.3. B.S-Dia Fed to Sows Improved Innate Immunity in Piglets
3.4. Activation of Mucosal Immunity in Piglets in the B.S-Dia Administration Group
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Karlsson, O.E.; Larsson, J.; Hayer, J.; Berg, M.; Jacobson, M. The Intestinal Eukaryotic Virome in Healthy and Diarrhoeic Neonatal Piglets. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Q.; Yang, H.S.; Yin, Y.L.; Huang, P.F. Amino Acids Influencing Intestinal Development and Health of the Piglets. Animals 2019, 9, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donald, K.; Petersen, C.; Turvey, S.E.; Finlay, B.B.; Azad, M.B. Secretory IgA: Linking microbes, maternal health, and infant health through human milk. Cell Host Microbe 2022, 30, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wu, Q.; Huang, L.; Yuan, C.; Wang, J.; Yang, Q. An alternative pathway of enteric PEDV dissemination from nasal cavity to intestinal mucosa in swine. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Yang, Q. Surfactin Inhibits Membrane Fusion during Invasion of Epithelial Cells by Enveloped Viruses. J. Virol. 2018, 92, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluske, J.R.; Turpin, D.L.; Kim, J.C. Gastrointestinal tract (gut) health in the young pig. Anim. Nutr. (Zhongguo Xu Mu Shou Yi xue hui) 2018, 4, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.R. Intestinal mucosal barrier function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 799–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vindigni, S.M.; Zisman, T.L.; Suskind, D.L.; Damman, C.J. The intestinal microbiome, barrier function, and immune system in inflammatory bowel disease: A tripartite pathophysiological circuit with implications for new therapeutic directions. Ther. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2016, 9, 606–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickert, G.; Neufert, C.; Leppkes, M.; Zheng, Y.; Wittkopf, N.; Warntjen, M.; Lehr, H.A.; Hirth, S.; Weigmann, B.; Wirtz, S.; et al. STAT3 links IL-22 signaling in intestinal epithelial cells to mucosal wound healing. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1465–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagarolli, R.A.; Tobar, N.; Oliveira, A.G.; Araújo, T.G.; Carvalho, B.M.; Rocha, G.Z.; Vecina, J.F.; Calisto, K.; Guadagnini, D.; Prada, P.O.; et al. Probiotics modulate gut microbiota and improve insulin sensitivity in DIO mice. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 50, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevins, C.L.; Salzman, N.H. Paneth cells, antimicrobial peptides and maintenance of intestinal homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, L.V.; Macpherson, A.J. Immune adaptations that maintain homeostasis with the intestinal microbiota. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Q.; Jia, J.; Lin, J.; Zhu, L.; Xie, S.; Yu, Q.; Li, Y. Bacillus subtilis programs the differentiation of intestinal secretory lineages to inhibit Salmonella infection. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, M.; Feng, L.; Zhao, C.; Gao, S.; Bao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Fu, Y.; Hu, X. Commensal Bacillus subtilis from cow milk inhibits Staphylococcus aureus biofilm formation and mastitis in mice. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2022, 98, fiac065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagliero, J.; Vernel-Pauillac, F.; Murray, G.; Adler, B.; Matsui, M.; Werts, C. Pathogenic Leptospires Limit Dendritic Cell Activation Through Avoidance of TLR4 and TRIF Signaling. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 911778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bampidis, V.; Azimonti, G.; Bastos, M.L.; Christensen, H.; Dusemund, B.; Fašmon Durjava, M.; Kouba, M.; López-Alonso, M.; López Puente, S.; Marcon, F.; et al. Safety and efficacy of a feed additive consisting of Bacillus velezensis ATCC PTA-6737 (Bacillus velezensis PB6) for turkeys for fattening, turkeys reared for breeding, laying hens, minor poultry species for laying, piglets (weaned), weaned minor porcine species and sows (Kemin Europe N.V.). EFSA J. Eur. Food Saf. Auth. 2022, 20, e07244. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, W.; Liu, X.; Zou, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Han, D.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J. Joint Application of Lactobacillus plantarum and Bacillus subtilis Improves Growth Performance, Immune Function and Intestinal Integrity in Weaned Piglets. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Wang, X.; Duan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Azad, M.A.K.; Wang, Z.; Blachier, F.; Kong, X. Dietary Supplementation with Bacillus subtilis Promotes Growth and Gut Health of Weaned Piglets. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 7, 600772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saladrigas-García, M.; Solà-Oriol, D.; López-Vergé, S.; D’Angelo, M.; Collado, M.C.; Nielsen, B.; Faldyna, M.; Pérez, J.F.; Martín-Orúe, S.M. Potential effect of two Bacillus probiotic strains on performance and fecal microbiota of breeding sows and their piglets. J. Anim. Sci. 2022, 100, skac163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Song, Z.; Chang, L.; He, X.; Fan, Z. Isomaltooligosaccharide and Bacillus regulate the duration of farrowing and weaning-estrous interval in sows during the perinatal period by changing the gut microbiota of sows. Anim. Nutr. (Zhongguo Xu Mu Shou Yi xue hui) 2021, 7, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Cao, M.; Li, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Fang, Z.; Che, L.; Xu, S.; Feng, B.; Lin, Y.; et al. Dietary supplementation of Bacillus subtilis PB6 improves sow reproductive performance and reduces piglet birth intervals. Anim. Nutr. (Zhongguo Xu Mu Shou Yi Xue Hui) 2020, 6, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NRC. Nutrient Requirements of Swine. In Nutrient Requirements of Domestic Animals; No. 2; National Academy of Science: Washington, DC, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, P.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, C.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Q. Feeding with 4,4′-diaponeurosporene-producing Bacillus subtilis enhances the lactogenic immunity of sow. BMC Vet. Res. 2023, 19, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junttila, I.S. Tuning the Cytokine Responses: An Update on Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 Receptor Complexes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Cross-regulation of signaling pathways by interferon-gamma: Implications for immune responses and autoimmune diseases. Immunity 2009, 31, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Zhang, P.; Jin, Y.; Ullah Shah, A.; Zhang, E.; Yang, Q. Single-Blinded Study Highlighting the Differences between the Small Intestines of Neonatal and Weaned Piglets. Animals 2021, 11, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachsel, C.; Küker, S.; Nathues, H.; Grahofer, A. Influence of different sow traits on the expulsion and characteristics of the placenta in a free farrowing system. Theriogenology 2021, 161, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura, M.; Martínez-Miró, S.; López, M.J.; Madrid, J.; Hernández, F. Effect of Parity on Reproductive Performance and Composition of Sow Colostrum during First 24 h Postpartum. Animals 2020, 10, 1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.V.; Yuan, L.; Azevedo, M.S.; Jeong, K.I.; Gonzalez, A.M.; Saif, L.J. Transfer of maternal cytokines to suckling piglets: In vivo and in vitro models with implications for immunomodulation of neonatal immunity. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2007, 117, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langel, S.N.; Paim, F.C.; Alhamo, M.A.; Buckley, A.; Van Geelen, A.; Lager, K.M.; Vlasova, A.N.; Saif, L.J. Stage of Gestation at Porcine Epidemic Diarrhea Virus Infection of Pregnant Swine Impacts Maternal Immunity and Lactogenic Immune Protection of Neonatal Suckling Piglets. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, S.M.; Schwartz, K.J.; Yoon, K.J.; Gabler, N.K.; Burrough, E.R. Effects of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus infection on nursery pig intestinal function and barrier integrity. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 211, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Kim, S.W. Intestinal challenge with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in pigs, and nutritional intervention to prevent postweaning diarrhea. Anim. Nutr. (Zhongguo Xu Mu Shou Yi xue hui) 2017, 3, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, L.W.; Artis, D. Intestinal epithelial cells: Regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, N. Adult intestinal stem cells: Critical drivers of epithelial homeostasis and regeneration. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elia, P.P.; Tolentino, Y.F.; Bernardazzi, C.; de Souza, H.S. The role of innate immunity receptors in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 936193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaolalla, R.; Abreu, M.T. Innate immunity in the small intestine. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2012, 28, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stadtmueller, B.M.; Huey-Tubman, K.E.; López, C.J.; Yang, Z.; Hubbell, W.L.; Bjorkman, P.J. The structure and dynamics of secretory component and its interactions with polymeric immunoglobulins. eLife 2016, 5, e10640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wang, J.Y. Role of Polymeric Immunoglobulin Receptor in IgA and IgM Transcytosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Zuo, J.; Lu, H.; Zhang, B.; Wu, C. Bacillus subtilis Fed to Sows Promotes Intestinal Development and Regulates Mucosal Immunity in Offspring. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050489
Liu P, Zuo J, Lu H, Zhang B, Wu C. Bacillus subtilis Fed to Sows Promotes Intestinal Development and Regulates Mucosal Immunity in Offspring. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(5):489. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050489
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Peng, Jinjiao Zuo, Hui Lu, Bin Zhang, and Caihong Wu. 2025. "Bacillus subtilis Fed to Sows Promotes Intestinal Development and Regulates Mucosal Immunity in Offspring" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 5: 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050489
APA StyleLiu, P., Zuo, J., Lu, H., Zhang, B., & Wu, C. (2025). Bacillus subtilis Fed to Sows Promotes Intestinal Development and Regulates Mucosal Immunity in Offspring. Veterinary Sciences, 12(5), 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050489




