Clinical Relevance of Distinguishing Between Three Endoscopy-Based Conditions, Bronchiectasis, Bronchomalacia, and Their Combination in Dogs: A Retrospective Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Case Selection and Data Collection
2.2. Bronchoscopy
2.3. Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Analysis
2.4. Diagnostic Imaging
2.5. Final Aetiology
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Description of the Clinicopathological Findings
3.1.1. Group Allocation Based on Bronchoscopy
3.1.2. Study Population
3.1.3. Clinical Signs
3.1.4. Blood and Fecal Analysis
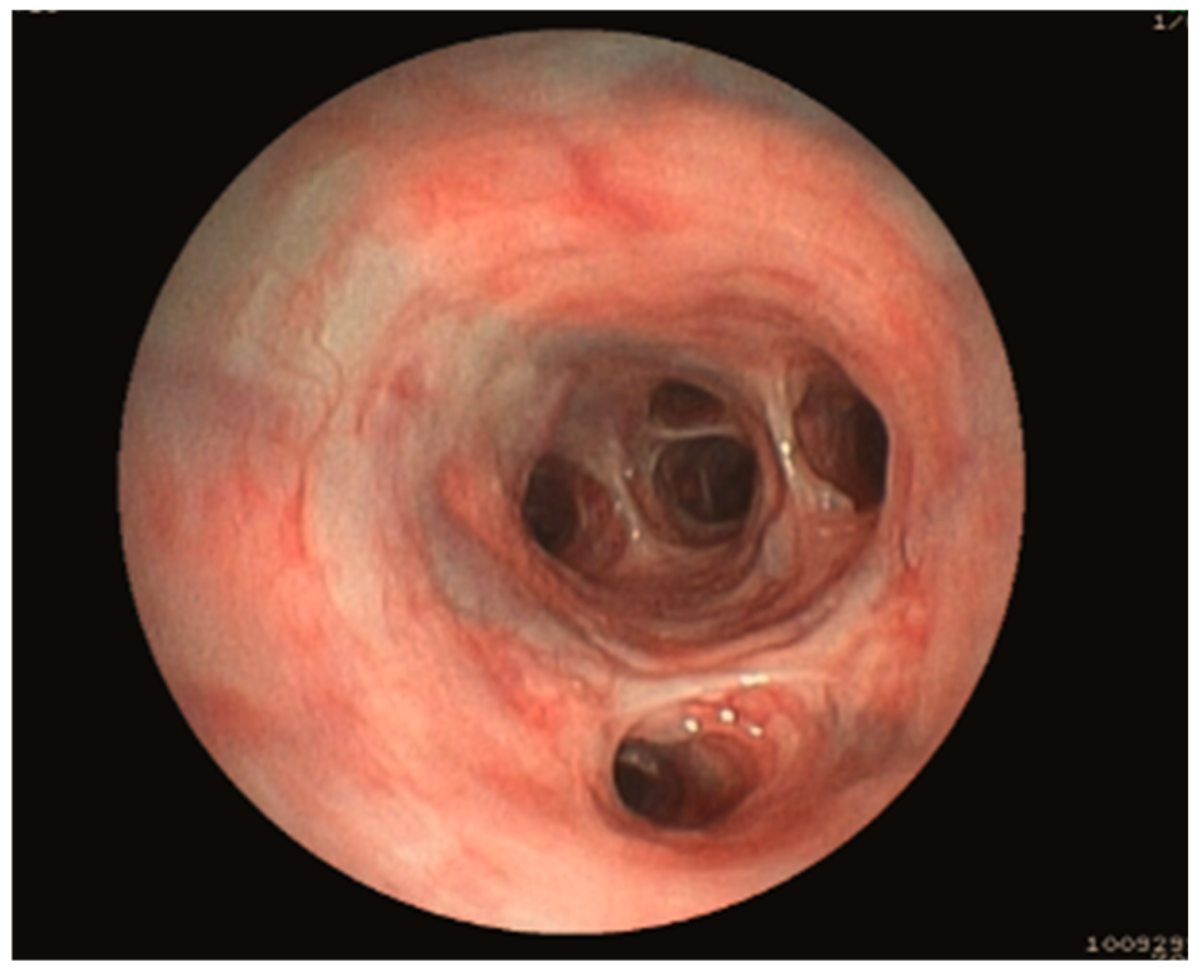
3.1.5. Bronchoscopy Findings
3.1.6. BALF Cytological and Microbiological Analysis
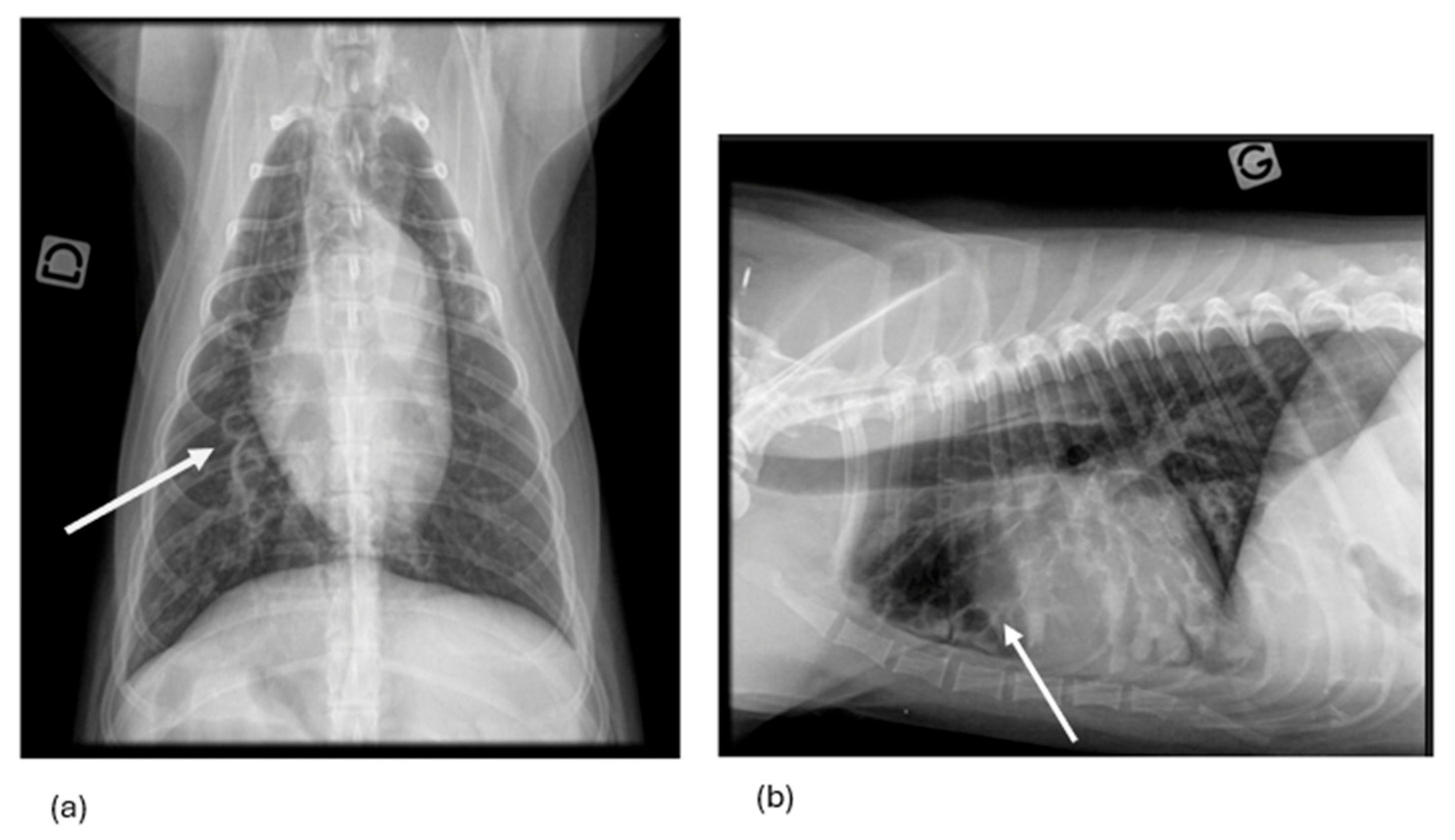
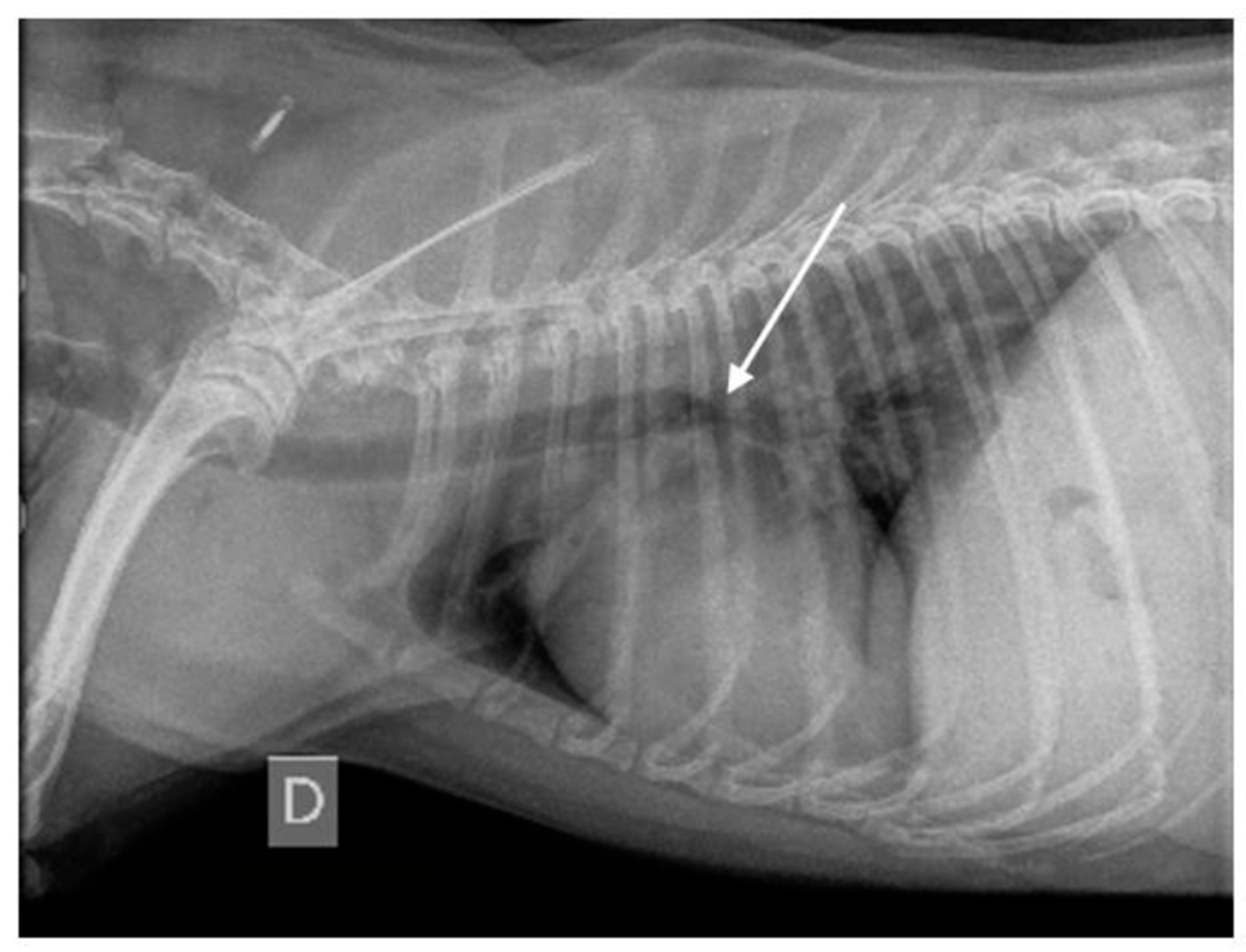
3.1.7. Thoracic Radiography Findings
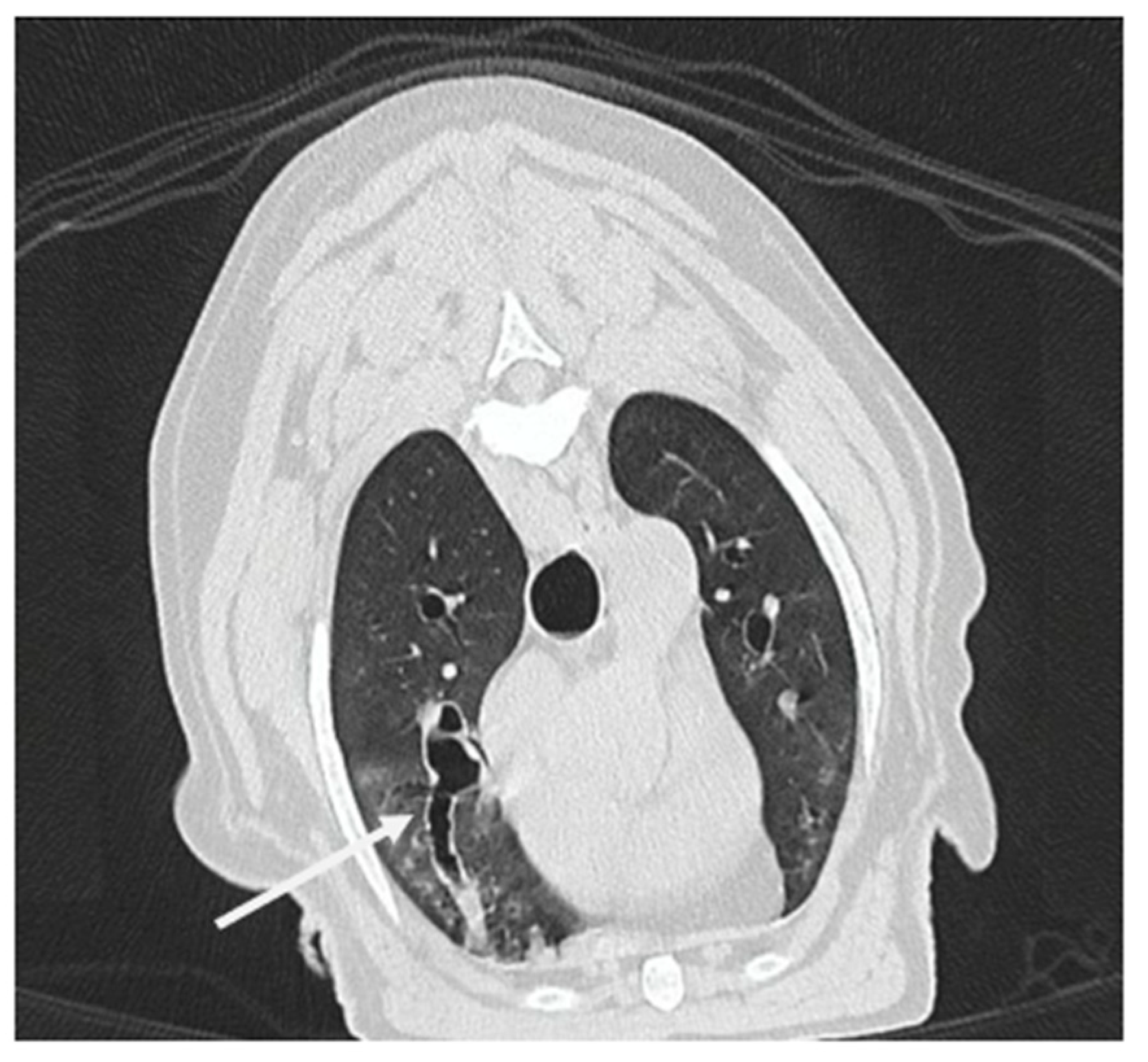
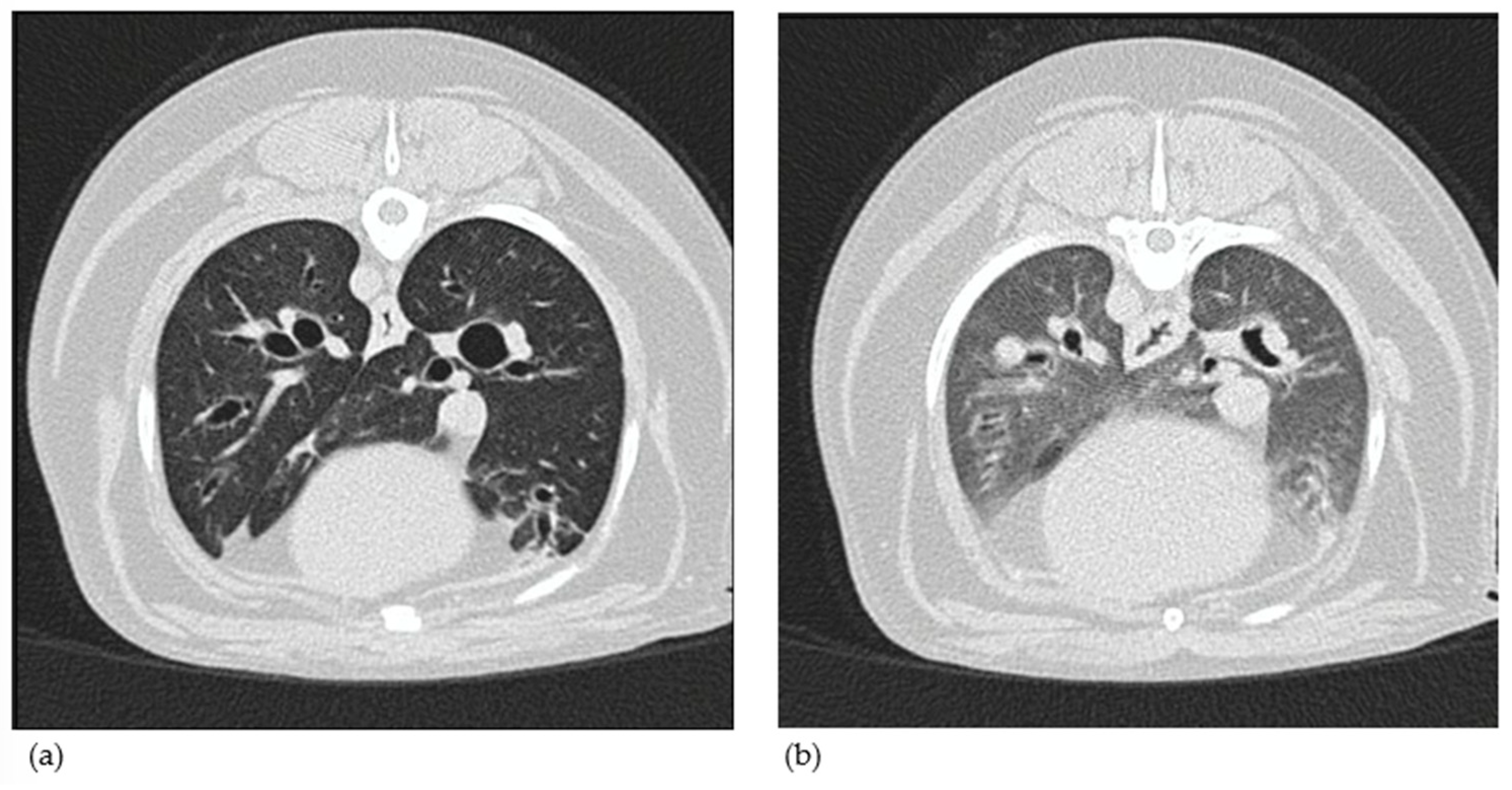
3.1.8. Computed Tomography Findings
3.1.9. Final Etiology
3.2. Comparison of the Imaging-Based Diagnosis with the Endoscopy-Based Diagnosis
3.2.1. Thoracic Radiography Versus Endoscopy
3.2.2. Thoracic CT Versus Endoscopy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BALF | Bronchoalveolar fluid analysis |
| BAR | Bronchial to arterial ratio |
| BE | Bronchiectasis |
| BEBM | Bronchiectasis and bronchomalacia |
| BM | Bronchomalacia |
| CFU | Colony-forming units |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| CT-BE | Computed-tomography-based diagnosis of bronchiectasis |
| CT-BEBM | Computed-tomography-based diagnosis of bronchiectasis and bronchomalacia |
| CT-BM | Computed-tomography-based diagnosis of bronchomalacia |
| DCC | Differentiated cellular count |
| E-BE | Endoscopy-based diagnosis of bronchiectasis |
| E-BEBM | Endoscopy-based diagnosis of bronchiectasis and bronchomalacia |
| E-BM | Endoscopy-based diagnosis of bronchomalacia |
| PH | Pulmonary hypertension |
| qPCR | Quantitative polymerase chain reaction |
| R-BE | Radiography-based diagnosis of bronchiectasis |
| R-BEBM | Radiography-based diagnosis of bronchiectasis and bronchomalacia |
| R-BM | Radiography-based diagnosis of bronchomalacia |
| RX | Thoracic radiography |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| TCC | Total cellular count |
References
- Hawkins, E.C.; Basseches, J.; Berry, C.R.; Stebbins, M.E.; Ferris, K.K. Demographic, clinical, and radiographic features of bronchiectasis in dogs: 316 cases (1988–2000). J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 2003, 223, 1628–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marolf, A.; Blaik, M.; Specht, A. A retrospective study of the relationship between tracheal collapse and bronchiectasis in dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound. 2007, 48, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyton, R.J.; Altmann, D.M. Bronchiectasis: Current concepts in pathogenesis, immunology and microbiology. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2016, 11, 523–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, A.; Floto, R.A. Pathophysiology, causes and genetics of paediatric and adult bronchiectasis. Respirology 2019, 24, 1053–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.R.; Johnson, E.G.; Vernau, W.; Kass, P.H.; Byrne, B.A. Bronchoscopy, imaging, and concurrent diseases in dogs with bronchiectasis. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2016, 30, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, R.; Aogain, M.M.; Chalmers, J.D.; Elborn, S.J.; Chotirmall, S.H. Geographic variation in the aetiology, epidemiology and microbiology of bronchiectasis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinero, C.R.; Masseau, I. Lower airway collapse: Revisiting the definition and clinicopathological features of canine bronchomalacia. Vet. J. 2021, 273, 105682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Della Maggiore, A. An update on tracheal and airway collapse in dogs. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2020, 50, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.B.; Boyce, N.C.; Masters, I.B.; Torzillo, P.J.; Masel, J.P. Bronchoscopic findings in children with non-cystic fibrosis chronic suppurative lung disease. Thorax 2002, 57, 935–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishino, M.; Siewert, B.; Roberts, D.H.; Gautam, S.; Boiselle, P.M.; Raptopoulos, V.; Hatabu, H. Excessive collapsibility of bronchi in bronchiectasis: Evaluation of volumetric expiratory high-resolution CT. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2006, 30, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, M.S.; Wisner, E.R.; Johnson, L.R.; Kass, P.H. Computed tomography bronchial lumen to pulmonary artery diameter ratio in dogs without clinical pulmonary disease. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound. 2009, 50, 622–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercier, E.; Bolognin, M.; Hoffmann, A.C.; Tual, C.; Day, M.J.; Clercx, C. Influence of age on bronchoscopic findings in healthy Beagle dogs. Vet. J. 2011, 187, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottero, E.; Bellino, C.; De Lorenzi, D.; Ruggiero, P.; Tarducci, A.; D’Angelo, A.; Gianella, P. Clinical evaluation and endoscopic classification of bronchomalacia in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2013, 27, 840–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flume, P.A.; Chalmers, J.D.; Olivier, K.N. Advances in bronchiectasis: Endotyping, genetics, microbiome and disease heterogenicity. Lancet 2018, 392, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henkle, E.; Daley, C.L.; Curtis, J.R.; Chan, B.; Aksamit, T.R.; Winthrop, K.L. Comparative safety of inhaled corticosteroids and macrolides in Medicare enrollees with bronchiectasis. ERJ Open Res. 2022, 8, 00786–02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canonne, A.M.; Roels, E.; Menard, M.; Desquilbet, L.; Billen, F.; Clercx, C. Clinical response to 2 protocols of aerosolized gentamicin in 46 dogs with Bordetella bronchiseptica infection (2012–2018). J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2020, 34, 2078–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, D.E.; McKiernan, B.C.; Weisiger, R.M.; Schaeffer, D.J.; Clercx, C. Quantitative bacterial cultures and cytological examination of bronchoalveolar lavage specimens in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2000, 14, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.R.; Singh, M.K.; Pollard, R.E. Agreement among radiographs, fluoroscopy and bronchoscopy in documentation of airway collapse in dogs. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2015, 29, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, M.S.; Johnson, L.R.; Pesavento, P.A.; Kass, P.H.; Wisner, E.R. Quantitative and qualitative computed tomographic characteristics of bronchiectasis in dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound. 2013, 54, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, D.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Choen, S.; Choi, M.; Yoon, J. Computed tomographic bronchial collapsibility values over 50% may be detected in healthy dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound. 2019, 60, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.R.; Johnson, E.G.; Hulsebosch, S.E.; Dear, J.D.; Vernau, W. Eosinophilic bronchitis, eosinophilic granuloma, and eosinophilic bronchopneumopathy in 75 dogs (2006–2016). J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2019, 33, 2217–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clercx, C.; Fastrès, A.; Roels, E. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in West Highland White Terriers: An update. Vet. J. 2018, 242, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozanski, E. Canine chronic bronchitis: An update. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2020, 50, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamama-Moraitou, K.K.; Pardali, D.; Day, M.J.; Prassinos, N.N.; Kritepsi-Konstantinou, M.; Patsikas, M.N.; Rallis, T.S. Canine bronchomalacia: A clinicopathological study of 18 cases diagnosed by endoscopy. Vet. J. 2012, 191, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nate, A.R.; Chapel, L.H. Lung crackles in bronchiectasis. Thorax 1980, 35, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, M.; Madabhavi, I.; Niranjan, N.; Dogra, M. Auscultation of the respiratory system. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2015, 10, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallis, C.; Alexopoulou, E.; Anton-Pacheco, J.L.; Bhatt, J.M.; Bush, A.; Chang, A.B.; Charatsi, A.M.; Coleman, C.; Depiazzi, J.; Douros, K.; et al. ERS statement on tracheomalacia and bronchomalacia in children. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 54, 1900382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.R.; Pollard, R.E. Tracheal collapse and bronchomalacia in dogs: 58 cases. J. Vet Intern. Med. 2010, 24, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, G.B.; van der Gast, C.J.; Cuthbertson, L.; Thomson, S.K.; Bruce, K.D.; Martin, M.L.; Serisier, D.J. Clinical measures of disease in adult non-CF bronchiectasis correlate with airway microbiota composition. Thorax 2013, 68, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, G.B.; Zain, N.M.N.; Bruce, K.D.; Burr, L.D.; Chen, A.C.; Rivett, D.W.; McGuckin, M.A.; Serisier, D.J. A novel microbiota stratification system predicts future exacerbations in bronchiectasis. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2014, 11, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Yu, J.; Gayeon, A.; Bang, S.; Kwon, D.; Kim, H.; Lee, H.; Chang, J.; Chang, D. CT and radiographic evaluation of bronchial collapsibility at forced expiration in asymptomatic brachycephalic dogs. Vet. Radiol. Ultrasound. 2020, 61, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Endoscopy Diagnosis | Dog | Age (year) | Sex | Breed | RX Findings | CT Findings | RX Diagnosis/CT Diagnosis | Final Etiology |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E-BE | 1 | 7 | FN | Beagle | NTA+, S+ C+, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BE | PB |
| 2 | 5 | FN | Bouvier des Flandres | NTA+, S+ C+, CMB+, PC+, BWTh+, BWO+ | N/A | R-BEBM | CB | |
| 3 | 12 | MN | Crossbreed | N/A | N/A | / | EBP | |
| 4 | 13 | MN | Crossbreed | NTA+, S− C+, CMB+, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BEBM | CB | |
| 5 | 11 | MN | Crossbreed | N/A | N/A | / | CB | |
| 6 $ | 10 | FN | Crossbreed | NTA+, S+ C−, CMB+, PC+, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BEBM | CB | |
| 7 | 12 | FN | Dachshund | NTA−, S− C−, CMB+, PC−, BWTh+, BWO+ | N/A | R-BM | CB | |
| 8 | 6 | FN | Dachshund | N/A | N/A | / | CB | |
| 9 | 5 | ME | Fox Terrier | N/A | N/A | / | CB | |
| 10 | 15 | FN | Jack Russel Terrier | NTA+, S− C+, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BE | EBP | |
| 11 | 10 | MN | Malinois | NTA+, S+ C+, CMB+, PC+, BWTh+, BWO− | NTA+, S+ C−, CMB−, PC+, BWTh+, BWO+, GGO+ | R-BEBM/CT-BE | CB | |
| 12 | 9 | FN | Maltese | NTA−, S− C−, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | -/- | CB | |
| 13 | 8 | ME | West Highland White Terrier | N/A | NTA+, S− C+, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO+, GGO+ | CT-BE | CB | |
| 14 $ | 3 | ME | Whippet | NTA−, S− C−, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | -/- | EBP | |
| 15 | 4 | MN | Whippet | NTA−, S− C−, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | -/- | EBP | |
| 16 | 9 | FN | Yorkshire Terrier | NTA+, S− C+, CMB+, PC−, BWTh−, BWO− | N/A | R-BEBM | CB | |
| E-BM 25–50% | 17 | 8 | FN | Cavalier King Charles Spaniel | NTA−, S− C−, CMB−, PC−, BWTh−, BWO− | N/A | -/- | CB |
| 18 | 12 | FE | Crossbreed | NTA−, S− C−, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | -/- | CB | |
| 19 | 12 | ME | Crossbreed | NTA+, S− C+, CMB−, PC+, BWTh+, BWO+ | N/A | R-BE | CB | |
| 20 | 13 | MN | Crossbreed | NTA+, S+ C+, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BE | CB | |
| 21 * | 11 | FN | Griffon Bruxellois | NTA+, S+ C+, CMB+, PC+, BWTh+, BWO− | NTA+, S+ C−, CMB+, PC−, BWTh+, BWO+, GGO+ | R-BEBM/CT-BEBM | CB | |
| 22 | 4 | FN | Pomerian | NTA−, S− C−, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | -/- | CB | |
| 23 | 9 | FN | Sheltie | NTA+, S− C+, CMB+,PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BEBM | CB | |
| 24 | 7 | MN | Shih Tzu | NTA+, S− C+, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | NTA−, S− C−, CMB+, PC−, BWTh−, BWO−, GGO− | R-BE/CT-BM | CB | |
| 25 | 7 | FN | Whippet | NTA+, S− C+, CMB+, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BEBM | CB | |
| 26 | 7 | MN | Yorkshire Terrier | NTA−, S− C−, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | -/- | CB | |
| E-BM 50–75% | 27 | 8 | FN | Crossbreed | NTA−, S− C−, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | -/- | CB |
| 28 | 13 | MN | Labrador Retriever | N/A | N/A | -/- | CB | |
| 29 | 13 | MN | Maltese | N/A | N/A | -/- | CB | |
| 30 | 11 | MN | Poodle | NTA−, S− C−, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO+ | N/A | -/- | CB | |
| 31 | 12 | ME | Poodle | NTA+, S+ C+, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BE | CB | |
| 32 $ | 8 | FN | Sheltie | NTA+, S+ C−, CMB−, PC+, BWTh+, BWO− | NTA−, S− C−, CMB+, PC+, BWTh+, BWO−, GGO+ | R-BE/CT-BM | CB | |
| 33 | 8 | FN | West Highland White Terrier | N/A | N/A | / | IPF | |
| 34 $ | 13 | FN | Yorkshire Terrier | N/A | N/A | / | CB | |
| 35 $ | 7 | MN | Yorkshire Terrier | N/A | N/A | / | CB | |
| 36 | 11 | MN | Yorkshire Terrier | NTA−, S− C−, CMB+, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BM | CB | |
| 37 | 13 | ME | Yorkshire Terrier | N/A | N/A | / | CB | |
| E-BM > 75% | 38 | 2 | FN | Cavalier King Charles Spaniel) | NTA−, S− C−, CMB+, PC+, BWTh−, BWO− | NTA−, S− C−, CMB+, PC+, BWTh+, BWO−, GGO+ | R-BM/CT-BM | CB |
| 39 $ | 8 | FN | Crossbreed | N/A | NTA+, S+ C−, CMB+, PC−, BWTh+, BWO−, GGO+ | CT-BEBM | CB | |
| 40 $ | 10 | FN | Jack Russel Terrier | N/A | N/A | / | CB | |
| 41 $ | 10 | FN | Jack Russel Terrier | NTA+, S− C+, CMB+, PC+, BWTh+, BWO− | NTA−, S− C−, CMB+, PC−, BWTh+, BWO−, GGO+ | R-BEBM/CT-BM | CB | |
| 42 | 12 | FN | Maltese | N/A | N/A | / | CB | |
| 43 | 17 | ME | Maltese | N/A | N/A | / | CB | |
| 44 $ | 7 | ME | Pomerian | NTA+, S+ C−, CMB+, PC+, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BEBM | CB | |
| 45 $ | 9 | MN | Shih Tzu | NTA+, S+ C−, CMB+, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BEBM | CB | |
| 46 | 11 | FN | Yorkshire Terrier | N/A | N/A | / | CB | |
| 47 | 14 | MN | Yorkshire Terrier | N/A | N/A | / | CB | |
| E-BEBM 25–50% | 48 | 7 | ME | Leonberger | NTA+, S+ C+, CMB−, PC+, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BE | CB |
| 49 | 9 | FE | Münsterländer | NTA+, S+ C+, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BE | CB | |
| 50 | 8 | FN | Samoyed | NTA+, S− C+, CMB+, PC+, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BEBM | EBP | |
| 51 | 11 | ME | West Highland White Terrier | N/A | NTA−, S− C−, CMB+, PC+, BWTh+, BWO−, GGO+ | CT-BM | IPF | |
| 52 | 7 | ME | Whippet | N/A | N/A | / | CB | |
| E-BEBM 50–75% | 53 $ | 11 | FN | Basset Fauve de Bretagne | NTA-, S− C−, CMB+, PC+, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BM | CB |
| 54 | 13 | ME | Beagle | NTA+, S− C+, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BE | CB | |
| 55 | 8 | MN | Chihuahua | NTA−, S− C−, CMB−, PC−, BWTh−, BWO− | N/A | -/- | CB | |
| 56 | 13 | MN | Crossbreed | NTA+, S+ C−, CMB+, PC+, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BEBM | CB | |
| 57 | 6 | FN | Crossbreed | NTA+, S+ C+, CMB−, PC+, BWTh+, BWO+ | N/A | R-BEBM | CB | |
| 58 | 9 | ME | Sheltie | N/A | NTA−, S− C−, CMB+, PC−, BWTh+, BWO−, GGO+ | CT-BM | CB | |
| 59 $ | 13 | MN | Shih Tzu | NTA+, S− C+, CMB+, PC+, BWTh+, BWO+ | N/A | R-BEBM | CB | |
| 60 | 10 | FN | Shih Tzu | NTA−, S− C−, CMB+, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | N/A | R-BM | CB | |
| 61 | 14 | MN | Tibetan Terrier | NTA+, S+ C−, CMB−, PC−, BWTh+, BWO− | NTA+, S+ C+, CMB+, PC+, BWTh+, BWO−, GGO+ | R-BE/CT-BEBM | CB | |
| 62 | 13 | FN | West Highland White Terrier | N/A | NTA−, S− C−, CMB+, PC−, BWTh+, BWO−, GGO+ | CT-BM | IPF | |
| 63 | 10 | FN | West Highland White Terrier | N/A | NTA+, S+ C−, CMB+, PC+, BWTh+, BWO−, GGO+ | CT-BEBM | IPF | |
| E-BEBM > 75% | 64 | 10 | ME | Shih Tzu | NTA−, S− C−, CMB+, PC−, BWTh−, BWO− | N/A | R-BM | CB |
| 65 $ | 8 | MN | Yorkshire Terrier | NTA+, S− C+, CMB+, PC−, BWTh+, BWO+ | N/A | R-BEBM | CB |
| Clinical Sign | E-BE (n = 16) n (%) | E-BM (n = 31) n (%) | E-BEBM (n = 18) n (%) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cough | 0.57 | |||
| Mild to moderate | 9 (13.85%) | 16 (24.62%) | 7 (10.77%) | |
| Severe | 7 (10.77%) | 15 (23.08%) | 11 (16.92%) | |
| Exercise intolerance | 4 (25%) | 16 (51.6%) | 11 (61.1%) | 0.091 |
| Dyspnea | 2 (12.5%) | 10 (32.3%) | 8 (44.4%) | 0.13 |
| Increased lung sounds | / | 7 (22.6%) | 2 (11.1%) | 0.097 |
| Lung crackles | 1 (6.3%) | 8 (25.8%) | 9 (50%) | 0.017 * |
| Bacteria | E-BE (n = 16) | E-BM (n = 31) | E-BEBM (n = 18) | Total (n = 65) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Escherichia sp. | 2 (dogs 7 & 9) | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Pseudomonas sp. | 2 (dogs 2 & 16) | 0 | 1 (dog 60) | 3 |
| Serratia sp. | 0 | 2 (dogs 19 and 26) | 0 | 2 |
| Streptococcus sp. | 0 | 0 | 1 (dog 48) | 1 |
| Bordetella bronchiseptica (qPCR) | 0 | 0 | 1 (dog 64) | 1 |
| Mycoplasma cynos (qPCR) | 1 (dog 14) | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Total number of dogs | 5 | 2 | 3 | 10 |
| Location | Median BAR [Interquartile Range Q1; Q3] (Inspiratory) | Median BAR [Interquartile Range Q1; Q3] (Expiratory) |
|---|---|---|
| R cranial lobe 4th rib | ||
| CT-BE | 2.4 [2.3; 2.6] | 2.2 [1.9; 2.5] |
| CT-BEBM | 2.1 [1.8; 2.3] | 1.5 [1.0; 1.6] |
| p-value | 0.56 | 0.081 |
| L cranial lobe 4th rib | ||
| CT-BE | 2.4 [2.3; 2.5] | 2.0 [1.8; 2.2] |
| CT-BEBM | 1.6 [1.1; 1.65] | 0.8 [0.7; 0.8] |
| p-value | 0.081 | 0.081 |
| R middle lobe | ||
| CT-BE | 2.2 [1.4; 2.9] | 1.9 [1.4; 2.3] |
| CT-BEBM | 1.6 [1.4; 2.5] | 1.3 [1.2; 1.5] |
| p-value | 0.85 | 0.33 |
| L cranial (caudal part) | ||
| CT-BE | 1.2 [1.2; 1.3] | 1.5 [1.4; 1.7] |
| CT-BEBM | 1.0 [1.0; 1.0] | 0.8 [0.8; 1.1] |
| p-value | 0.18 | 0.081 |
| R accessory lobe | ||
| CT-BE | 1.5 [1.3; 1.7] | 1.4 [1.3; 1.5] |
| CT-BEBM | 1.4 [0.9; 1.5] | 1.2 [1.1; 1.2] |
| p-value | 0.85 | 0.081 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lyssens, A.; Bolen, G.; Fastrès, A.; Clercx, C.; Billen, F. Clinical Relevance of Distinguishing Between Three Endoscopy-Based Conditions, Bronchiectasis, Bronchomalacia, and Their Combination in Dogs: A Retrospective Study. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050487
Lyssens A, Bolen G, Fastrès A, Clercx C, Billen F. Clinical Relevance of Distinguishing Between Three Endoscopy-Based Conditions, Bronchiectasis, Bronchomalacia, and Their Combination in Dogs: A Retrospective Study. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(5):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050487
Chicago/Turabian StyleLyssens, Aurélie, Géraldine Bolen, Aline Fastrès, Cécile Clercx, and Frédéric Billen. 2025. "Clinical Relevance of Distinguishing Between Three Endoscopy-Based Conditions, Bronchiectasis, Bronchomalacia, and Their Combination in Dogs: A Retrospective Study" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 5: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050487
APA StyleLyssens, A., Bolen, G., Fastrès, A., Clercx, C., & Billen, F. (2025). Clinical Relevance of Distinguishing Between Three Endoscopy-Based Conditions, Bronchiectasis, Bronchomalacia, and Their Combination in Dogs: A Retrospective Study. Veterinary Sciences, 12(5), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050487





