Establishment of a TaqMan Quantitative Real-Time PCR for Detecting Lawsonia intracellularis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Primers and Probes
2.2. Standard Plasmids
2.3. Optimization of Reaction Conditions
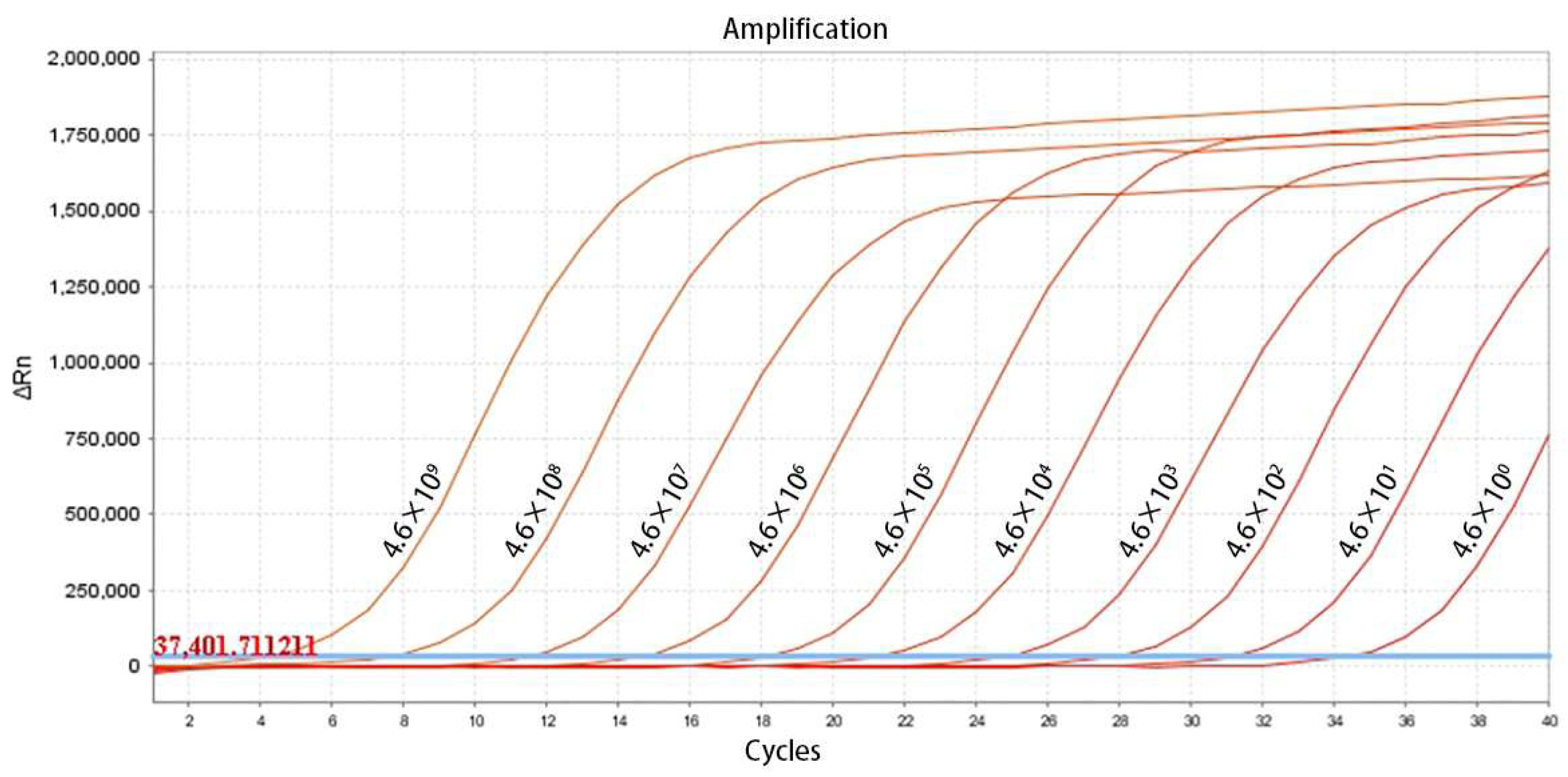
2.4. Evaluation of Sensitivity and Construction of Standard Curves
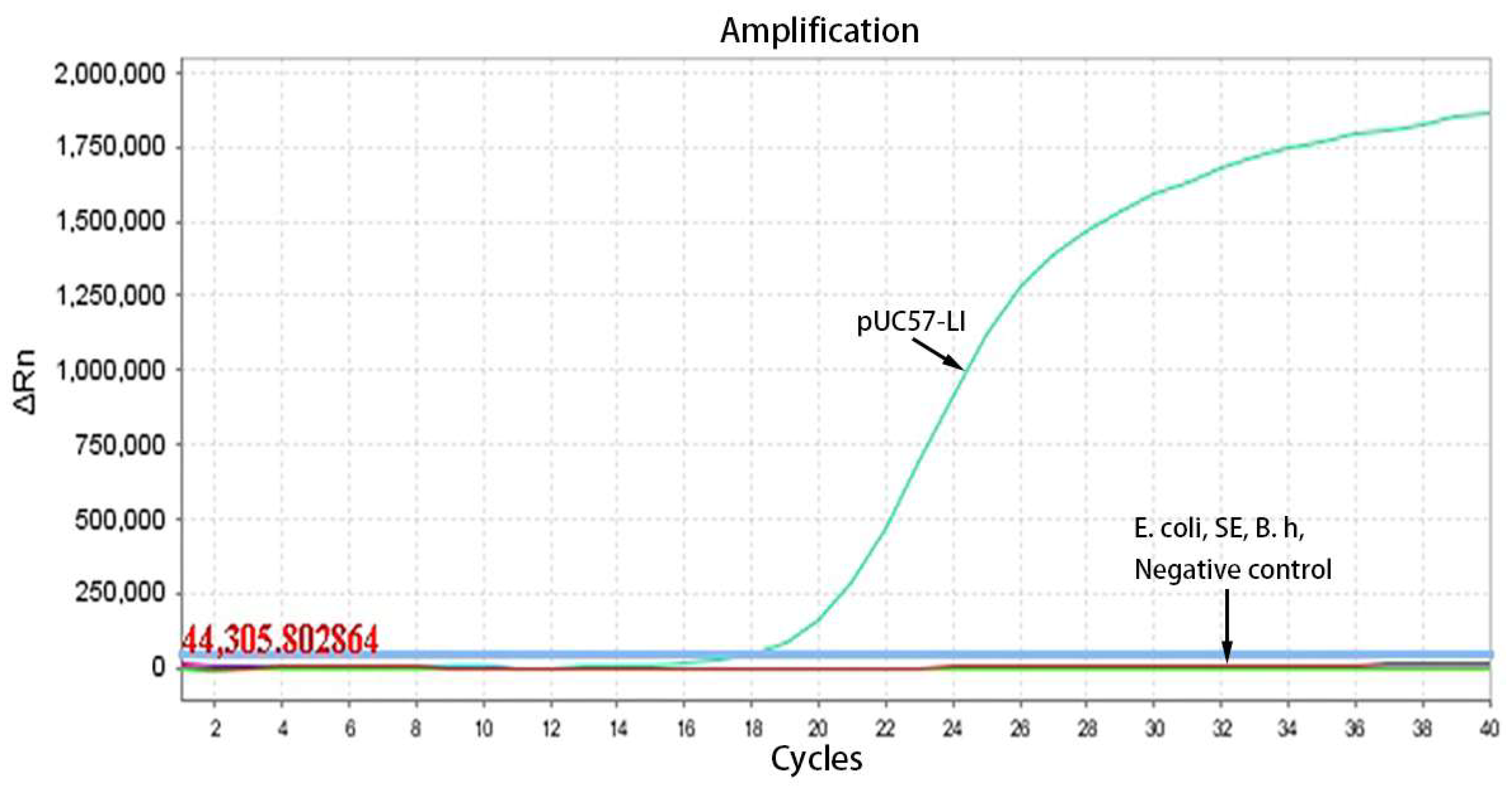
2.5. Evaluation of Specificity
2.6. Evaluation of Reproducibility
2.7. Comparison Between TapMan-qPCR and Conventional PCR with Clinical Samples
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of Reaction Conditions
3.2. Establishment of the Standard Curve
3.3. Specificity Testing
3.4. Repeatability Testing
3.5. Comparison Between the TaqMan-RT-PCR Method and the Conventional PCR Method with Clinical Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PPE | porcine proliferative enteropathy |
| LI | Lawsonia intracellularis |
| IFA | indirect immunofluorescence assay |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| IPMA | immunoperoxidase monolayer assay |
| Cq | quantification cycle |
| CV | coefficients of variation |
References
- Bengtsson, R.J.; Wee, B.A.; Yebra, G.; Bacigalupe, R.; Watson, E.; Guedes, R.M.C.; Jacobson, M.; Stadejek, T.; Archibald, A.L.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; et al. Metagenomic sequencing of clinical samples reveals a single widespread clone of Lawsonia intracellularis responsible for porcine proliferative enteropathy. Microb. Genom. 2020, 6, e000358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obradovic, M.; Pasternak, J.A.; Hon Ng, S.; Allan, B.; Brownlie, R.; Wilson, H.L. Immunoproteomic analysis of Lawsonia intracellularis identifies candidate neutralizing antibody targets for use in subunit vaccine development. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 235, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campillo, M.; Smith, S.H.; Gally, D.L.; Opriessnig, T. Review of methods for the detection of Lawsonia intracellularis infection in pigs. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2021, 33, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroll, J.J.; Roof, M.B.; Hoffman, L.J.; Dickson, J.S.; Harris, D.L. Proliferative enteropathy: A global enteric disease of pigs caused by Lawsonia intracellularis. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2005, 6, 173–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holyoake, P.K.; Cutler, R.S.; Caple, I.W. A diagnostic dilemma: Detecting proliferative enteritis in pigs at slaughter. Aust. Vet. J. 1994, 71, 308–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, G.; Hillen, S.; von Berg, S.; Kixmöller, M.; Willems, H. Analysis of bacterial load and prevalence of mixed infections with Lawsonia intracellularis, Brachyspira hyodysenteriae and/or Brachyspira pilosicoli in German pigs with diarrhoea. Berl. Munch. Tierarztl. Wochenschr. 2011, 124, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Crienen, A.; Swam, H.; von Berg, S.; Jolie, R.; Nathues, H. Prevalence of Lawsonia intracellularis in pig herds in different European countries. Porc. Health Manag. 2019, 5, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McOrist, S. Defining the full costs of endemic porcine proliferative enteropathy. Vet. J. 2005, 170, 8–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, G.; Chi, N.K.; Park, Y. The Effectiveness of Commercial Vaccination against Lawsonia intracellularis in Mitigating the Reduction in ADWG, the Increased Mortality and Fecal Shedding of the Vaccinated Pigs: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberton, E.; Cruz, R.A.S.; Caldeira, F.H.B.; Pescador, C.A.; Souza, M.; Colodel, E.M. Prevalence of porcine proliferative enteropathy associated to Lawsonia intracellularis in pigs slaughtered in Mato Grosso State, Brazil. Acta Sci. Vet. 2011, 39, 943. [Google Scholar]
- Chouet, S.; Prieto, C.; Mieli, L.; Veenhuizen, M.F.; McOrist, S. Patterns of exposure to Lawsonia intracellularis infection on European pig farms. Vet. Rec. 2003, 152, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, S.; Ogawa, Y.; Eguchi, M.; Rambukkana, A.; Shimoji, Y. Draft Genome Sequences of Lawsonia intracellularis Swine Strains Causing Proliferative Enteropathy in Japan. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2018, 7, e01021-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wu, W.; Zhao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Yao, X.; Fan, J.; Chen, H.; Song, W.; Huang, X.; Hua, L.; et al. Fecal PCR survey and genome analysis of Lawsonia intracellularis in China. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1324768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, G.H.; McOrist, S.; Rowland, A.C.; McCartney, E.; Roberts, L. Serological diagnosis of the porcine proliferative enteropathies: Implications for aetiology and epidemiology. Vet. Rec. 1988, 122, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, A.A.C.; Harks, F.; Hazenberg, L.; Hoeijmakers, M.J.H.; Nell, T.; Pel, S.; Segers, R. Efficacy of a novel inactivated Lawsonia intracellularis vaccine in pigs against experimental infection and under field conditions. Vaccine 2019, 37, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabardo, M.P.; Sato, J.P.H.; Resende, T.P.; Otoni, L.V.A.; Rezende, L.A.; Daniel, A.G.S.; Pereira, C.E.R.; Guedes, R.M.C. Use of oral fluids to detect anti Lawsonia intracellularis antibodies in experimentally infected pigs. Pesqui. Veterinária Bras. 2020, 40, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzone, C.J.; Karsten, W.E.; Conley, J.D.; Viola, R.E. L-aspartase from Escherichia coli: Substrate specificity and role of divalent metal ions. Biochemistry 1988, 27, 9089–9093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.S.; Mandyoli, L.; Hughes, R.; Wakabayashi, S.; Pinkham, J.T.; Selbach, B.; Guinn, K.M.; Rubin, E.J.; Sacchettini, J.C.; Rhee, K.Y. Aspartate aminotransferase Rv3722c governs aspartate-dependent nitrogen metabolism in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, P.; Wang, C.; Lu, Q.; Liu, L.; Wang, X.; Luo, Q.; Shao, H. Role of aspartate ammonia-lyase in Pasteurella multocida. BMC Microbiol. 2020, 20, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Lu, J.; Wang, N.; He, W.T.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, W.; Su, S. Development of a TaqMan-probe-based multiplex real-time PCR for the simultaneous detection of emerging and reemerging swine coronaviruses. Virulence 2020, 11, 707–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, K.; Zhu, M.; Yuan, Q.; Deng, Z.; Feng, S.; Liu, D.; Yuan, X. Development of an Indirect ELISA to Detect African Swine Fever Virus pp62 Protein-Specific Antibodies. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 8, 798559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindecrona, R.H.; Jensen, T.K.; Andersen, P.H.; Møller, K. Application of a 5’ nuclease assay for detection of Lawsonia intracellularis in fecal samples from pigs. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2002, 40, 984–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nathues, H.; Holthaus, K.; Grosse Beilage, E. Quantification of Lawsonia intracellularis in porcine faeces by real-time PCR. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczotka, A.; Stadejek, T.; Zmudzki, J.; Nowak, A.; Osiński, Z.; Pejsak, Z. Immunohistochemical detection of Lawsonia intracellularis in tissue sections from pigs. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2011, 14, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, M.; Crienen, A.; Swam, H.; Berg, S.V.; Jolie, R.; Nathues, H. Correlation of Lawsonia intracellularis positivity in quantitative PCR and herd factors in European pig herds. Porc. Health Manag. 2021, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.M.; Seo, M.J.; Yeh, J.Y. Lawsonia intracellularis in the feces of wild rodents and stray cats captured around equine farms. BMC Vet. Res. 2017, 13, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Li, F.; Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Sha, Y.; Li, X. Development of a TaqMan-based multiplex real-time PCR for simultaneous detection of porcine epidemic diarrhea virus, Brachyspira hyodysenteriae, and Lawsonia intracellularis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2024, 11, 1450066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, K.S.; Stege, H.; Jensen, T.K.; Guedes, R.; Ståhl, M.; Nielsen, J.P.; Hjulsager, C.; Larsen, L.E.; Angen, Ø. Diagnostic performance of fecal quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction for detection of Lawsonia intracellularis-associated proliferative enteropathy in nursery pigs. J. Vet. Diagn. Investig. 2013, 25, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Primer or Probe | Sequence (5′ to 3′) |
|---|---|
| F | GGTATTGGTATTCTCCTTTCTCA |
| R | CTGCATGTAATGAAATCATAAATG |
| Probe | FAM-TGTTGTGGATTGTATTCAAGGAGGTG-BHQ1 |
| Concentration of Standard Plasmids (Copies/μL) | Intra-Coefficient of Variation | Inter-Coefficient of Variation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | ± SD | CV% | n | ± SD | CV% | |
| 4.6 × 105 | 3 | 18.34 ± 0.04 | 0.48% | 3 | 18.24 ± 0.09 | 0.52% |
| 4.6 × 103 | 3 | 24.75 ± 0.06 | 0.24% | 3 | 24.84 ± 0.09 | 0.37% |
| 4.6 × 101 | 3 | 31.49 ± 0.20 | 0.74% | 3 | 31.63 ± 0.22 | 0.69% |
| Conventional PCR | Total | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| + | − | |||
| TaqMan-RT-PCR | + | 34 | 3 | 37 |
| − | 0 | 3 | 3 | |
| Total | 34 | 6 | 40 | |
| Relative sensitivity = 34/34 = 100% | ||||
| Relative specificity = 3/6 = 50.00% | ||||
| Compliance rate = 37/40 = 92.50% | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Z.; Lai, R.; Xu, W.; Guan, R.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, G.; Hao, G. Establishment of a TaqMan Quantitative Real-Time PCR for Detecting Lawsonia intracellularis. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050450
Hu Z, Lai R, Xu W, Guan R, Zhang Z, Yan G, Hao G. Establishment of a TaqMan Quantitative Real-Time PCR for Detecting Lawsonia intracellularis. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(5):450. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050450
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Zhiqiang, Ranran Lai, Wei Xu, Ran Guan, Zhimin Zhang, Guangwen Yan, and Guiying Hao. 2025. "Establishment of a TaqMan Quantitative Real-Time PCR for Detecting Lawsonia intracellularis" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 5: 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050450
APA StyleHu, Z., Lai, R., Xu, W., Guan, R., Zhang, Z., Yan, G., & Hao, G. (2025). Establishment of a TaqMan Quantitative Real-Time PCR for Detecting Lawsonia intracellularis. Veterinary Sciences, 12(5), 450. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12050450






