Probiotic Characterization of Lactiplantibacillus paraplantarum SDN1.2 and Its Anti-Inflammatory Effect on Klebsiella pneumoniae-Infected Mammary Glands
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
2.2. DNA Extraction and Whole-Genome Sequencing
2.3. Hemolytic Activity of L. paraplantarum SDN1.2
2.4. Cytotoxicity Test
2.5. Antibacterial Potential of L. paraplantarum SDN 1.2
2.6. Growth Curve of L. paraplantarum SDN1.2 in Different pH Levels
2.7. Antibacterial Activity Under Different pH Conditions
2.8. Animal Experiments
2.9. Histopathological Observations
2.10. Bacterial Load in the Mammary Glands
2.11. Myeloperoxidase Evaluation
2.12. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.13. Hematoxylin and Eosin Staining
2.14. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Release Assay LDH
2.15. L. paraplantarum SDN1.2 Pretreatment on K. pneumoniae Adhesion and Invasion bMEC Assay Test
2.16. RNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR QPCR
2.17. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.18. Data Analysis
3. Results
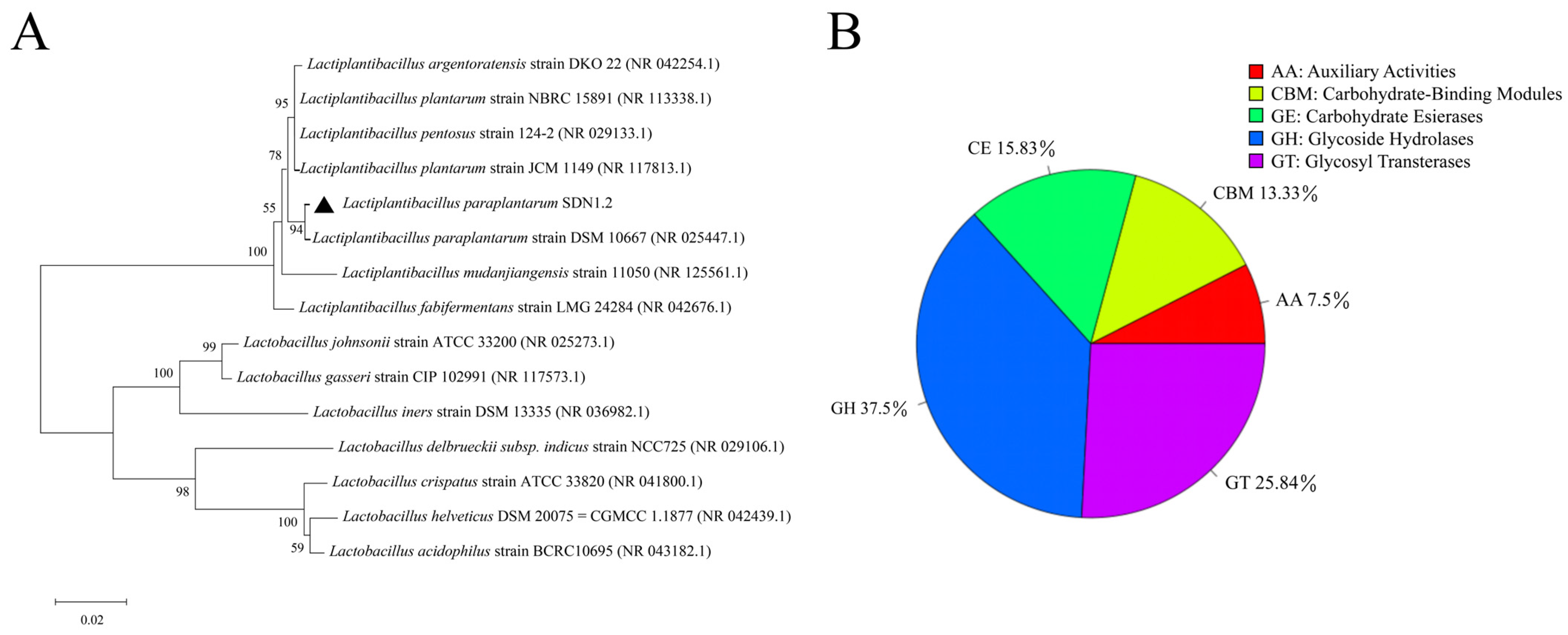
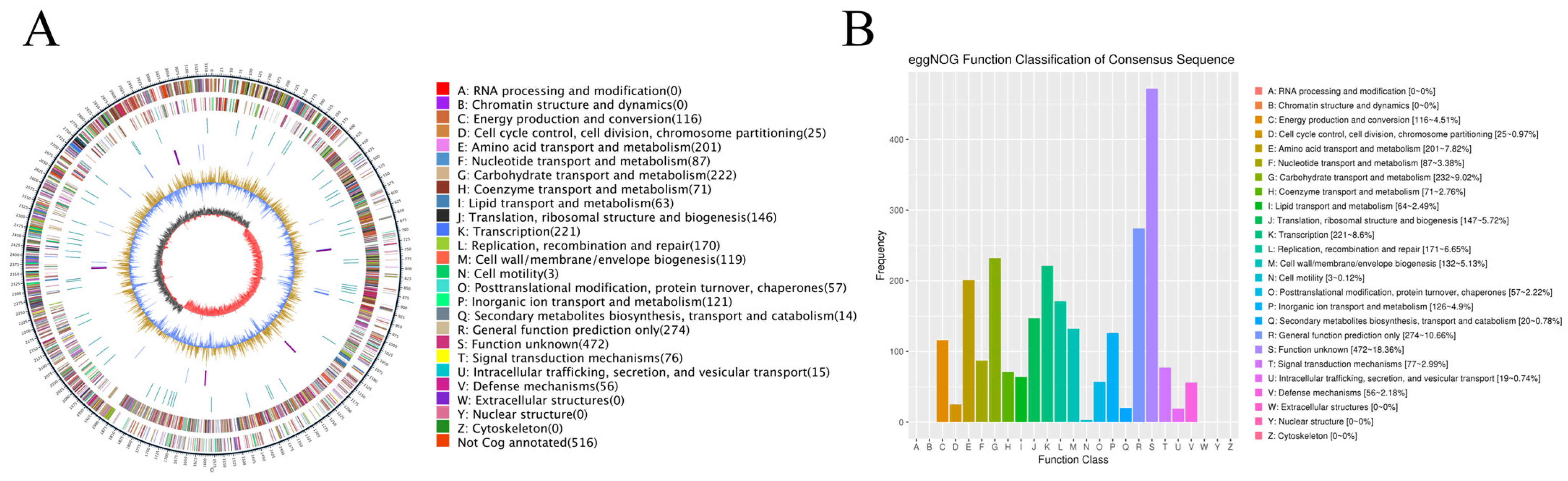
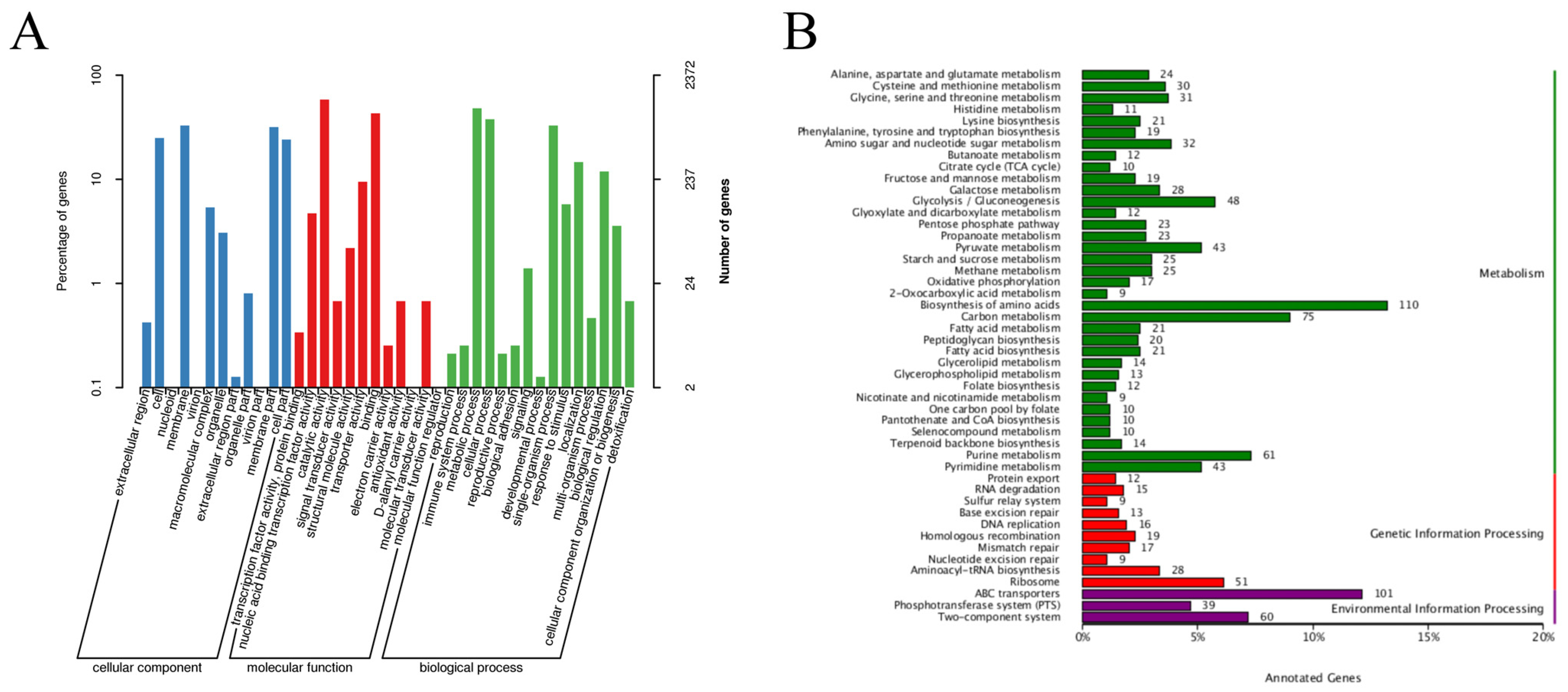
3.1. Whole-Genome Analysis of L. paraplantarum SDN1.2
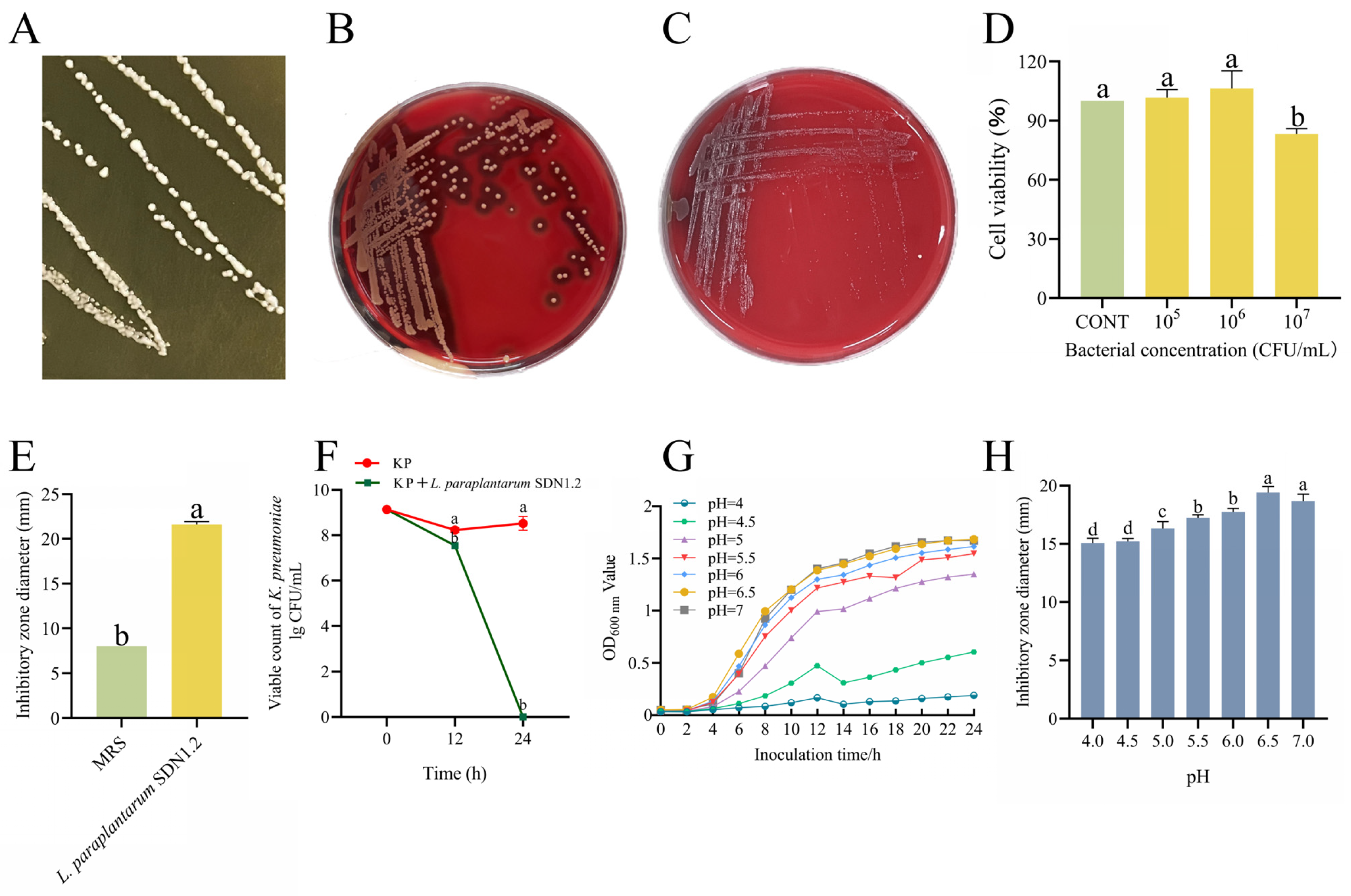
3.2. The Antibacterial Activity and Safety of L. paraplantarum SDN1.2
3.3. L. paraplantarum SDN1.2 Ameliorates K. pneumoniae-Induced Injury to Mouse Mastitis
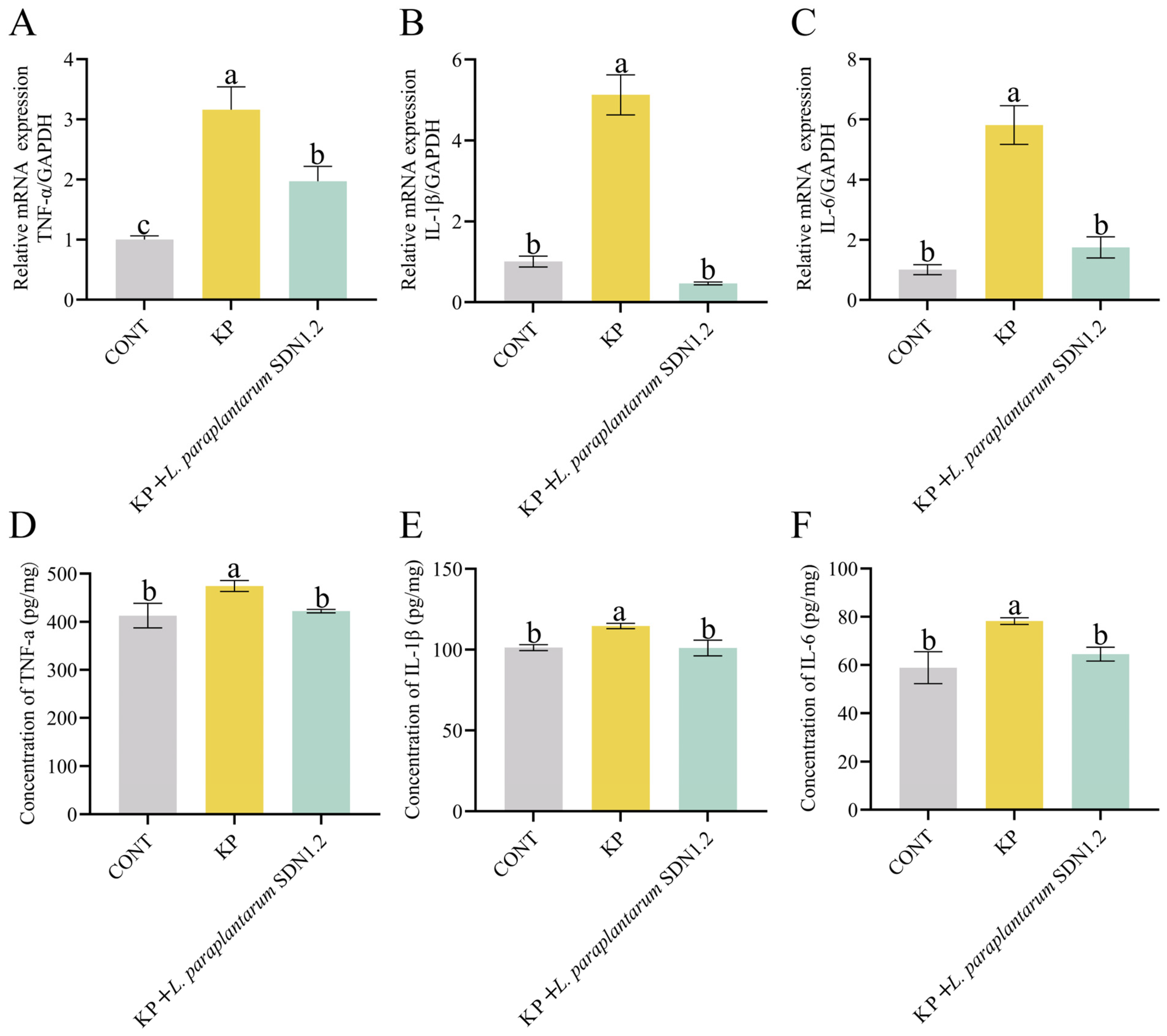
3.4. L. paraplantarum SDN1.2 Attenuates K. pneumoniae-Induced Inflammation in Mouse Mastitis
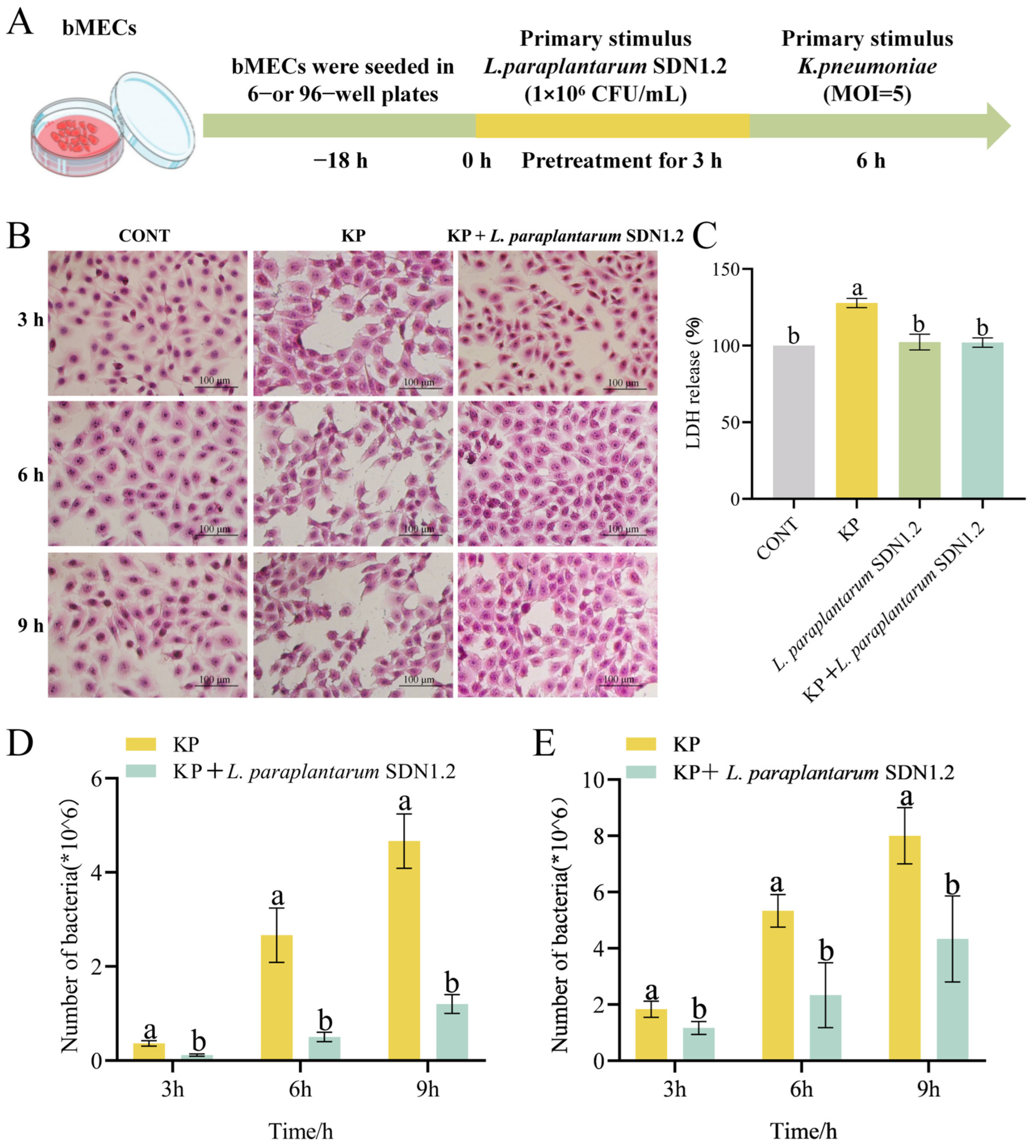
3.5. L. paraplantarum SDN1.2 Reduces the Cytotoxic Effects of bMECs in K. pneumoniae Infection
3.6. L. paraplantarum SDN 1.2 Reduce Adhesion and Invasion of K. pneumoniae to bMECs
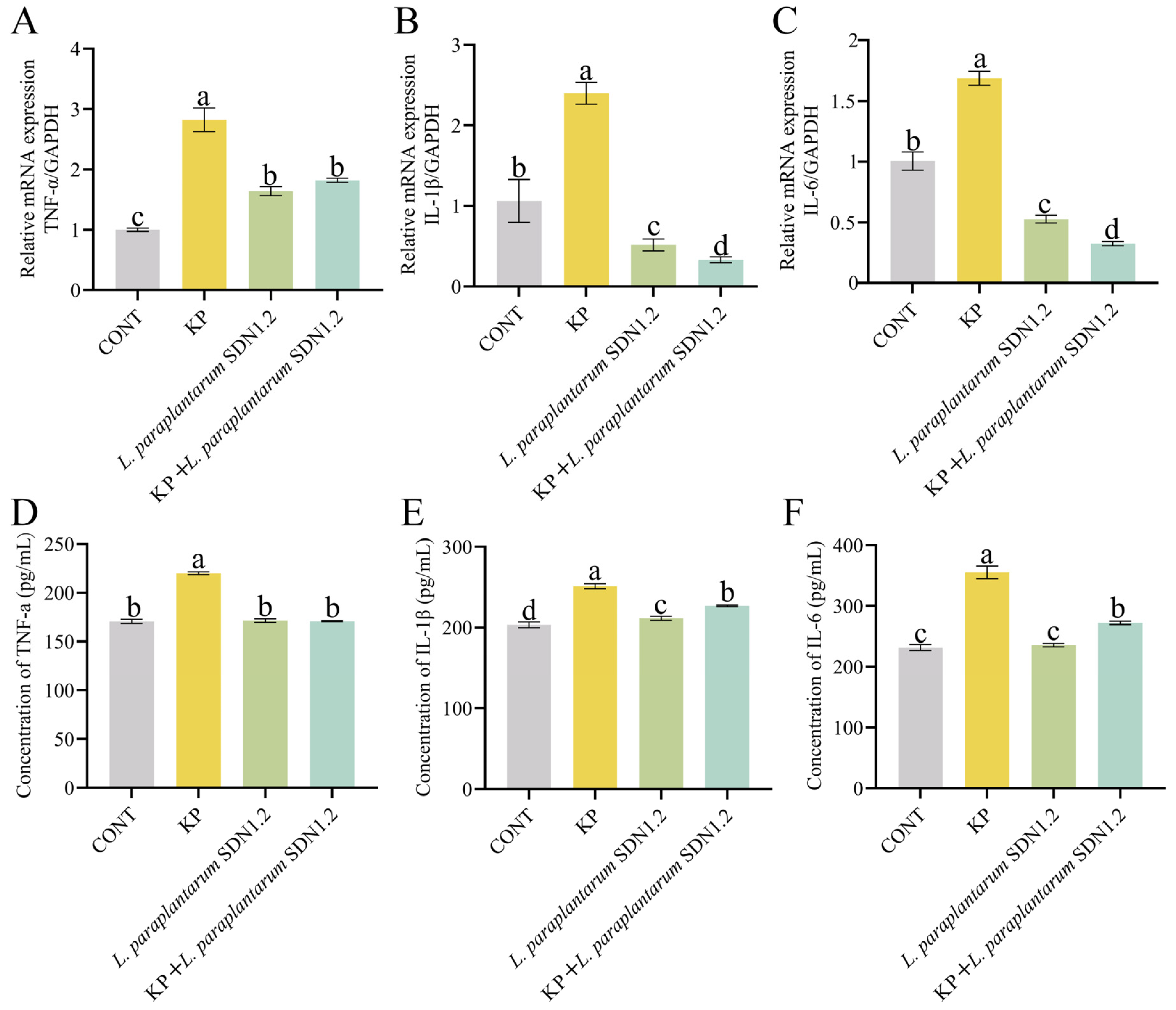
3.7. L. paraplantarum SDN1.2 Inhibits the Inflammatory Response of bMECs Infected with K. pneumoniae
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ashraf, A.; Imran, M. Causes, types, etiological agents, prevalence, diagnosis, treatment, prevention, effects on human health and future aspects of bovine mastitis. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2020, 21, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schukken, Y.; Chuff, M.; Moroni, P.; Gurjar, A.; Santisteban, C.; Welcome, F.; Zadoks, R. The “other” gram-negative bacteria in mastitis: Klebsiella, Serratia, and more. Vet. Clin. N. Am. Food Anim. Pract. 2020, 28, 239–256. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Anes, J.; Devineau, S.; Fanning, S. Klebsiella pneumoniae: Prevalence, Reservoirs, Antimicrobial Resistance, Pathogenicity, and Infection: A Hitherto Unrecognized Zoonotic Bacterium. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2021, 18, 63–84. [Google Scholar]
- Fuenzalida, M.J.; Ruegg, P.L. Negatively-controlled, randomized clinical trial to evaluate intramammary treatment of nonsevere, gramnegative clinical mastitis. J. Dairy Sci. 2019, 102, 5438–5457. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Xiong, Y.; Barkema, H.W.; Tong, X.; Lin, Y.; Deng, Z.; Kastelic, J.P.; Nobrega, D.B.; Wang, Y.; Han, B.; et al. Comparative genomic analyses of Klebsiella pneumoniae K57 capsule serotypes isolated from bovine mastitis in China. J. Dairy Sci. 2024, 107, 3114–3126. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, J.; Zhang, J.; Han, B.; Barkema, H.W.; Cobo, E.R.; Kastelic, J.P.; Zhou, M.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, R.; et al. Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from bovine mastitis is cytopathogenic for bovine mammary epithelial cells. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3493–3504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelopoulou, A.; Warda, A.K.; Hill, C.; Ross, R.P. Non-antibiotic microbial solutions for bovine mastitis—Live biotherapeutics, bacteriophage, and phage lysins. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 45, 564–580. [Google Scholar]
- Pal, C.; Bengtsson-Palme, J.; Kristiansson, E.; Larsson, D.G. The structure and diversity of human, animal and environmental resistomes. Microbiome 2016, 4, 54. [Google Scholar]
- Leite de Campos, J.; Gonçalves, J.L.; Kates, A.; Steinberger, A.; Sethi, A.; Suen, G.; Shutske, J.; Safdar, N.; Goldberg, T.; Ruegg, P.L. Variation in partial direct costs of treating clinical mastitis among 37 Wisconsin dairy farms. J. Dairy Sci. 2023, 106, 9276–9286. [Google Scholar]
- Ziesch, M.; Wente, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zaremba, W.; Engl, S.; Kromker, V. Noninferiority Trial Investigating the Efficacy of a Nonantibiotic Intramammary Therapy in the Treatment of Mild-to-Moderate Clinical Mastitis in Dairy Cows With Longer Lasting Udder Diseases. J. Vet. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 41, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque, M.N.; Moyna, Z.; Faisal, G.M.; Das, Z.C.; Islam, T.; Newton, I.L.G. Whole-genome sequence of multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae MNH_G2C5, isolated from bovine clinical mastitis milk. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2023, 12, e0007923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pineiro, M.; Stanton, C. Probiotic bacteria: Legislative framework—Requirements to evidence basis. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 850S–853S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burkholder, K.M.; Fletcher, D.H.; Gileau, L.; Kandolo, A. Lactic acid bacteria decrease Salmonella enterica Javiana virulence and modulate host inflammation during infection of an intestinal epithelial cell line. Pathog. Dis. 2019, 77, ftz025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Wang, S.; Guo, J.; Xie, Q.; Evivie, S.E.; Song, Y.; Li, B.; Huo, G. The Protective Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum KLDS 1.0344 on LPS-Induced Mastitis In Vitro and In Vivo. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 770822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; He, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Yang, B.; Chen, W. Lactobacillus plantarum relieves diarrhea caused by enterotoxin-producing Escherichia coli through inflammation modulation and gut microbiota regulation. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 10362–10374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; HuangFu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, S.; Liu, Y.; Lv, H.; Qin, G.; Tan, Z. Activity of Lactic Acid Producing Leuconostoc mesenteroides QZ1178 Against Pathogenic Gallibacterium anatis. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 630294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.C.; Lai, T.M.; Hsieh, Y.M. Evaluation of Lactobacilli for Antagonistic Activity Against the Growth, Adhesion and Invasion of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Gardnerella vaginalis. Indian J. Microbiol. 2019, 59, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Liu, B.; Hu, G.; Kan, X.; Li, Y.; Gong, Q.; Xu, D.; Ma, H.; Cao, Y.; Huang, B.; et al. Vanillin protects the blood-milk barrier and inhibits the inflammatory response in LPS-induced mastitis in mice. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 365, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.S.; Lee, J.O. Recognition of lipopolysaccharide pattern by TLR4 complexes. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 250, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Zheng, F.; Yu, H.; Wei, K. Xanthatin Alleviates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response in RAW264.7 Macrophages by Inhibiting NF-κB, MAPK and STATs Activation. Molecules 2022, 27, 4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burvenich, C.; Van Merris, V.; Mehrzad, J.; Diez-Fraile, A.; Duchateau, L. Severity of E. coli mastitis is mainly determined by cow factors. Vet. Res. 2003, 34, 521–564. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Wilksch, J.J.; Dunstan, R.A.; Mularski, A.; Wang, N.; Hocking, D.; Jebeli, L.; Cao, H.; Clements, A.; Jenney, A.W.J.; et al. LPS O Antigen Plays a Key Role in Klebsiella pneumoniae Capsule Retention. Microbiol. Spectr. 2022, 10, e0151721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Yang, M.; Tian, M.; Jia, L.; Du, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Yuan, L.; Ma, Y. Lactobacillus plantarum 17-5 attenuates Escherichia coli-induced inflammatory responses via inhibiting the activation of the NF-κB and MAPK signalling pathways in bovine mammary epithelial cells. BMC Vet. Res. 2022, 18, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; Jin, J.; Bai, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liao, Z.; Chen, Q. Isolation, identification, and whole genome sequence analysis of the alginate-degrading bacterium Cobetia sp. cqz5-12. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 10920. [Google Scholar]
- Holzapfel, W.; Arini, A.; Aeschbacher, M.; Coppolecchia, R.; Pot, B. Enterococcus faecium SF68 as a model for efficacy and safety evaluation of pharmaceutical probiotics. Benef. Microbes. 2018, 9, 375–388. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, T.; Feng, M.; Liang, H.; Liu, K.; Tong, J.; Ren, M.; Jiang, G.; Gao, J.; Liu, M.; Cheng, J. Isolation and Identification of 3 Lactic Acid Bacteria and Their Antibacterial Activity against Klebsiella pneumoniae Isolated from Bovine Mastitis. Chin. J. Vet. Med. 2025, 01, 013. [Google Scholar]
- Cuyvers, S.; Dornez, E.; Delcour, J.A.; Courtin, C.M. Occurrence and functional significance of secondary carbohydrate binding sites in glycoside hydrolases. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2012, 2, 93–107. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.W.; Liong, M.T.; Tsai, Y.C. New perspectives of Lactobacillus plantarum as a probiotic: The gut-heart-brain axis. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 601–613. [Google Scholar]
- Kalhoro, M.S.; Anal, A.K.; Kalhoro, D.H.; Hussain, T.; Murtaza, G.; Mangi, M.H. Antimicrobial Activities and Biopreservation Potential of Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) from Raw Buffalo (Bubalus bubalis) Milk. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2023, 2023, 8475995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilova, T.A.; Adzhieva, A.A.; Mezentseva, M.V.; Suetina, I.A.; Danilina, G.A.; Minko, A.G.; Dmitrieva, M.L.; Zhukhovitsky, V.G. The inhibitory activity of Lactobacillus plantarum supernatant against Enterobacteria, Campylobacter, and tumor cells. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2023, 176, 64–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punia, B.S.; Suri, S.; Trif, M.; Ozogul, F. Organic acids production from lactic acid bacteria: A preservation approach. Food Biosci. 2022, 46, 101615. [Google Scholar]
- Pino, A.; Vaccalluzzo, A.; Caggia, C.; Balzaretti, S.; Vanella, L.; Sorrenti, V.; Ronkainen, A.; Satokari, R.; Randazzo, C.L. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus CA15 (DSM 33960) as a Candidate Probiotic Strain for Human Health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyatina, A.A.; Low, H.H. Core architecture of a bacterial type II secretion system. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qiu, M.; Feng, L.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, C.; Gao, S.; Bao, L.; Zhang, N.; Fu, Y.; Hu, X. Probiotic Enterococcus mundtii H81 inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway to ameliorate Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis in mice. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 164, 105414. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Guo, C. The Roles of Neutrophil-Derived Myeloperoxidase (MPO) in Diseases: The New Progress. Antioxidants 2024, 13, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumaiya, K.; Langford, D.; Natarajaseenivasan, K.; Shanmughapriya, S. Macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF): A multifaceted cytokine regulated by genetic and physiological strategies. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 233, 108024. [Google Scholar]
- Bhol, N.K.; Bhanjadeo, M.M.; Singh, A.K.; Dash, U.C.; Ojha, R.R.; Majhi, S.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Jena, A.B. The interplay between cytokines, inflammation, and antioxidants: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic potentials of various antioxidants and anti-cytokine compounds. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117177. [Google Scholar]
- Isas, A.S.; Balcells, M.F.; Maldonado Galdeano, C.; Palomo, I.; Rodriguez, L.; Fuentes, E.; Luna Pizarro, P.; Mateos Briz, R.; Mozzi, F.; Van Nieuwenhove, C. Fermented pomegranate juice enriched with pomegranate seed oil ameliorates metabolic disorders associated with a high-fat diet in C57BL/6 mice. Food Chem. 2025, 463, 141434. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; Han, Z.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, N. Effects of neutrophil extracellular traps on bovine mammary epithelial cells in vitro. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, B.; Wang, Q.; Tang, L.; Zou, P.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Gong, L.; Li, W. Protective Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum Lac16 on Clostridium perfringens Infection-Associated Injury in IPEC-J2 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainard, P.; Foucrasm, G. A Critical Appraisal of Probiotics for Mastitis Control. Front. Vet. Sci. 2018, 5, 251. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.; Xu, C.; Wang, M.; Zhu, J.; Yu, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, S.; Gao, X. The preventive and therapeutic effects of probiotics on mastitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0274467. [Google Scholar]
- Petzl, W.; Zerbe, H.; Günther, J.; Seyfert, H.M.; Hussen, J.; Schuberth, H.J. Pathogen-specific responses in the bovine udder. Models and immunoprophylactic concepts. Res. Vet. Sci. 2018, 116, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M..; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | Product Length (bp) | Annealing Temperature (°C) | Accession Number | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bos | |||||
| IL-6 | Forward | GCTGAATCTTCCAAAAATGGAGG | 215 | 60 | NM_173923.2 |
| Reverse | GCTTCAGGATCTGGATCAGTG | ||||
| IL-1β | Forward | CCTCGGTTCCATGGGAGATG | 119 | 60 | NM_174093.1 |
| Reverse | AGGCACTGTTCCTCAGCTTC | ||||
| TNF-α | Forward | TCCAGAAGTTGCTTGTGCCT | 144 | 60 | NM_173966.3 |
| Reverse | CAGAGGGCTGTTGATGGAGG | ||||
| GAPDH | Forward | GTCTTCACTACCATGGAGAAGG | 201 | 60 | NM_001034034.2 |
| Reverse | TCATGGATGACCTTGGCCAG | ||||
| Mice | |||||
| IL-1β | Forward | CCTGGGCTGTCCTGATGAGAG | 188 | 60 | NM_008361.4 |
| Reverse | TCCACGGGAAAGACACAGGTA | ||||
| IL-6 | Forward | TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC | 142 | 60 | NM_001314054.1 |
| Reverse | TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC | ||||
| TNF-α | Forward | CAGGCGGTGCCTATGTCTC | 155 | 60 | NM_001278601.1 |
| Reverse | CGATCACCCCGAAGTTCAGTAG | ||||
| GAPDH | Forward | AGGTCGGTGTGAACGGATTTG | 139 | 60 | NM_001289726.2 |
| Reverse | TGTAGACCATGTAGTTGAGGTCA | ||||
| Features | Results | Features | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genome size | 3,246,458 | 5S rRNA | 6 |
| GC content | 43.74 | 16S rRNA | 5 |
| Number of genes | 3045 | 23S rRNA | 5 |
| Total gene length | 2,699,214 | tRNA | 69 |
| Proportion of coding genes | 83.14 | eggNOG | 2529 |
| Mean gene length | 886 | GO | 2372 |
| Repeat sequence length | 2813 | KEGG | 1484 |
| Repeat sequence content | 0.09 | VFDB | 0 |
| No | Pathway ID | Description | Gene Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ko00261 | Monobactam biosynthesis | 7 |
| 2 | ko00521 | Streptomycin biosynthesis | 4 |
| 3 | ko00550 | Peptidoglycan biosynthesis | 20 |
| 4 | ko00130 | Ubiquinone and other terpenoid-quinone biosynthesis | 6 |
| 5 | ko00590 | Arachidonic acid metabolism | 1 |
| 6 | ko00121 | GOSecondary bile acid biosynthesis | 2 |
| 7 | ko00480 | Glutathione metabolism | 9 |
| 8 | ko00430 | Taurine and hypotaurine metabolism | 5 |
| 9 | ko00230 | Purine metabolism | 61 |
| 10 | ko00330 | Arginine and proline metabolism | 6 |
| 11 | ko00970 | Aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis | 28 |
| 12 | ko00750 | Vitamin B6 metabolism | 3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, J.; Tong, J.; Li, C.; Wang, Z.; Li, H.; Ren, M.; Song, J.; Song, D.; Xie, Q.; Liu, M. Probiotic Characterization of Lactiplantibacillus paraplantarum SDN1.2 and Its Anti-Inflammatory Effect on Klebsiella pneumoniae-Infected Mammary Glands. Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040323
Cheng J, Tong J, Li C, Wang Z, Li H, Ren M, Song J, Song D, Xie Q, Liu M. Probiotic Characterization of Lactiplantibacillus paraplantarum SDN1.2 and Its Anti-Inflammatory Effect on Klebsiella pneumoniae-Infected Mammary Glands. Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(4):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040323
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Jia, Jingdi Tong, Can Li, Ziyan Wang, Hao Li, Meiyi Ren, Jinshang Song, Deyuan Song, Qinna Xie, and Mingchao Liu. 2025. "Probiotic Characterization of Lactiplantibacillus paraplantarum SDN1.2 and Its Anti-Inflammatory Effect on Klebsiella pneumoniae-Infected Mammary Glands" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 4: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040323
APA StyleCheng, J., Tong, J., Li, C., Wang, Z., Li, H., Ren, M., Song, J., Song, D., Xie, Q., & Liu, M. (2025). Probiotic Characterization of Lactiplantibacillus paraplantarum SDN1.2 and Its Anti-Inflammatory Effect on Klebsiella pneumoniae-Infected Mammary Glands. Veterinary Sciences, 12(4), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12040323





