Antiviral Efficacy of Lignan Derivatives (-)-Asarinin and Sesamin Against Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus by Targeting RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (3Dpol)
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
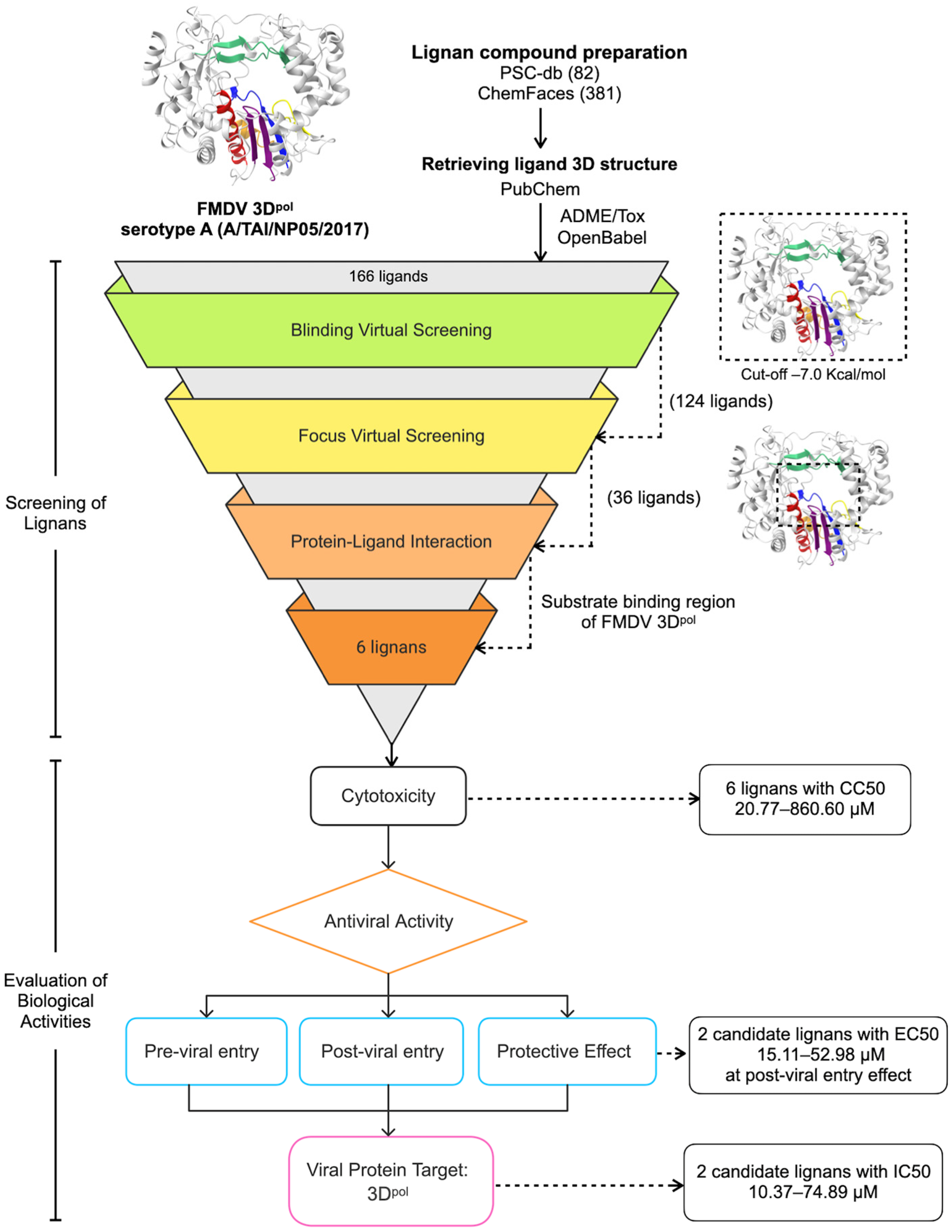
2.1. Virtual Screening of Lignan Compounds and Molecular Docking
2.2. Cells, Viruses, and Lignans
2.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
2.4. Antiviral Activity Assay
2.5. Immunoperoxidase Monolayer Assay (IPMA)
2.6. Viral Copy Number Quantification Using RT-qPCR
2.7. Evaluation of 3Dpol Inhibition Activity Using a Cell-Based FMDV Minigenome Assay
2.8. Intracellular FMDV 3Cpro Inhibition Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Virtual Screening
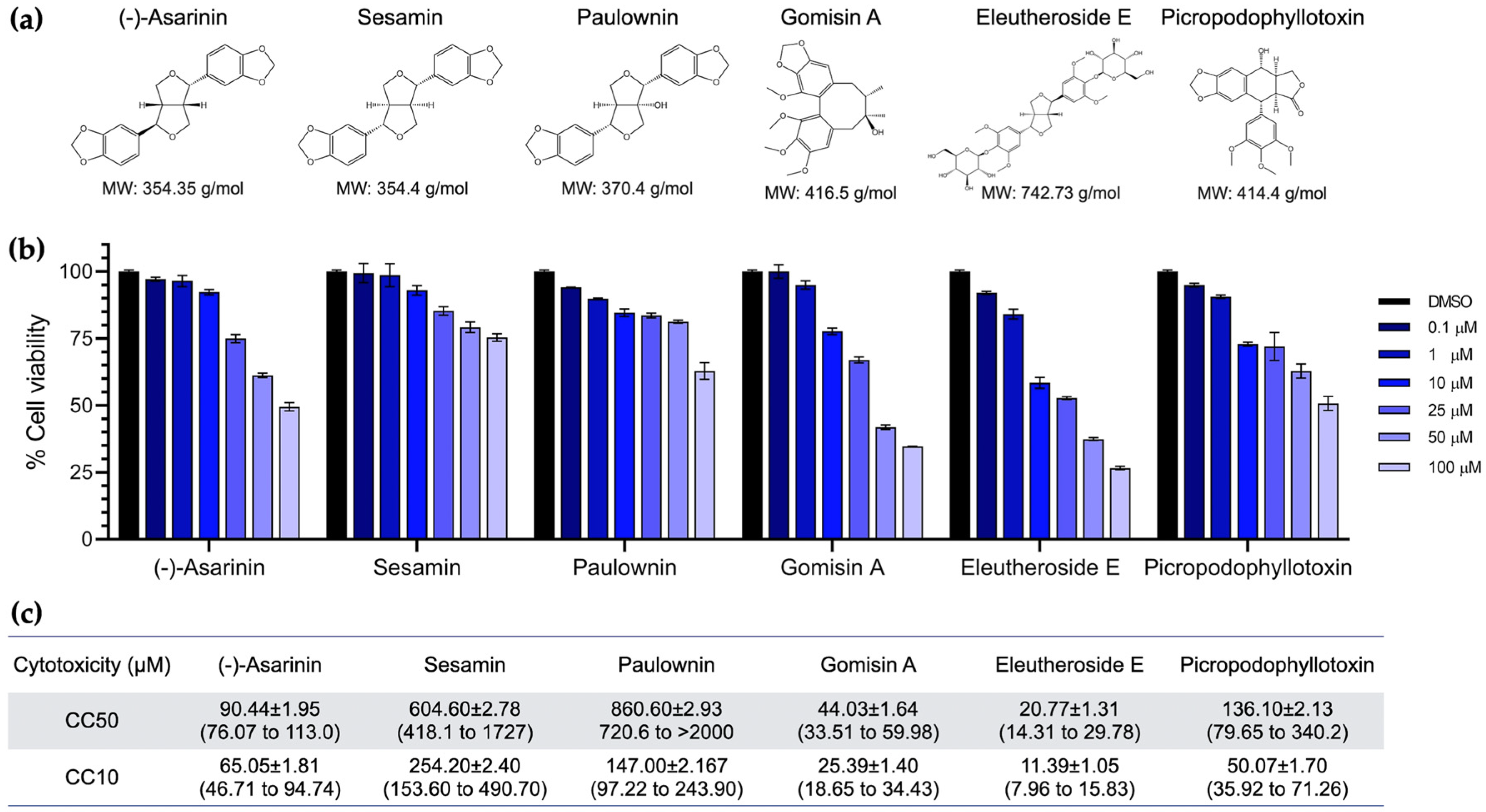
3.2. Cytotoxicity of Lignans on BHK-21 Cells
3.3. (-)-Asarinin and Sesamin Inhibit Cytopathic Effects After FMDV Infection in BHK-21 Cells
3.4. (-)-Asarinin and Sesamin Reduce FMDV Protein Expression and Replication in a Dose-Dependent Manner
3.5. (-)-Asarinin and Sesamin Potentially Affect FMDV 3Dpol Activity in Transfected BHK-21 Cells
3.6. Molecular Docking Confirms Specific Binding Interactions Between Lignans and FMDV 3Dpol Catalytic Domains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3Dpol | RNA-dependent RNA polymerase |
| BHK-21 cells | Baby Hamster Kidney-21 cell |
| CCK-8 | Cell Counting Kit-8 |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| FMD | Foot-and-Mouth Disease |
| FMDV | Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus |
| GFP | Green Fluorescent Protein |
| HEK-293 cells | Human Embryonic Kidney-293 cell |
| MOI | Multiplicity Of Infection |
| scFv-Fc | Single-Chain Variable Fragment fused to the Fc region |
| TCID50 | Half Tissue Culture Infective Dose |
References
- Grubman, M.J.; Baxt, B. Foot-and-Mouth Disease. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2004, 17, 465–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brito, B.P.; Rodriguez, L.L.; Hammond, J.M.; Pinto, J.; Perez, A.M. Review of the global distribution of foot-and-mouth disease virus from 2007 to 2014. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2017, 64, 316–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zell, R.; Delwart, E.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Hovi, T.; King, A.M.Q.; Knowles, N.J.; Lindberg, A.M.; Pallansch, M.A.; Palmenberg, A.C.; Reuter, G.; et al. ICTV virus taxonomy profile: Picornaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 2017, 98, 2421–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH). Infection with Foot and Mouth Disease Virus. Terrestrial Animal Health Code. Volume 2: Recommendations Applicable to WOAH Listed Diseases and Other Diseases of Importance to International Trade, Section 8. Chapter 8. Available online: https://www.woah.org/fileadmin/Home/eng/Health_standards/tahc/2024/en_sommaire.htm (accessed on 7 October 2025).
- Paton, D.J.; Di Nardo, A.; Knowles, N.J.; Wadsworth, J.; Pituco, E.M.; Cosivi, O.; Rivera, A.M.; Kassimi, L.B.; Brocchi, E.; de Clercq, K.; et al. The history of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype C: The first known extinct serotype? Virus Evol. 2021, 7, veab009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goris, N.; Vandenbussche, F.; De Clercq, K. Potential of antiviral therapy and prophylaxis for controlling RNA viral infections of livestock. Antivir. Res. 2008, 78, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, L.; Knight-Jones, T.J.D.; Charleston, B.; Rodriguez, L.L.; Gay, C.G.; Sumption, K.J.; Vosloo, W. Global foot-and-mouth disease research update and gap analysis: 7—Pathogenesis and molecular biology. Transbound. Emerg. Dis. 2016, 63, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Z.; Zhai, F.; Zhang, H.; Zheng, H.; Pei, J. The multiple roles of viral 3Dpol protein in picornavirus infections. Virulence 2024, 15, 2333562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Orta, C.; Arias, A.; Perez-Luque, R.; Escarmís, C.; Domingo, E.; Verdaguer, N. Structure of foot-and-mouth disease virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and its complex with a template-primer RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 47212–47221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Orta, C.; Ferrero, D.; Verdaguer, N. RNA-dependent RNA polymerases of picornaviruses: From the structure to regulatory mechanisms. Viruses 2015, 7, 4438–4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Orta, C.; Arias, A.; Agudo, R.; Pérez-Luque, R.; Escarmís, C.; Domingo, E.; Verdaguer, N. The structure of a protein primer-polymerase complex in the initiation of genome replication. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.-Y.; Wang, D.-Y.; Li, Y.-P.; Deyrup, S.T.; Zhang, H.-J. Plant-derived lignans as potential antiviral agents: A systematic review. Phytochem. Rev. 2022, 21, 239–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Du, R.; Liu, M.; Rong, L. Lignans and their derivatives from plants as antivirals. Molecules 2020, 25, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theerawatanasirikul, S.; Semkum, P.; Lueangaramkul, V.; Chankeeree, P.; Thangthamniyom, N.; Lekcharoensuk, P. Non-nucleoside inhibitors decrease foot-and-mouth disease virus replication by blocking the viral 3Dpol. Viruses 2023, 15, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semkum, P.; Kaewborisuth, C.; Thangthamniyom, N.; Theerawatanasirikul, S.; Lekcharoensuk, C.; Hansoongnern, P.; Ramasoota, P.; Lekcharoensuk, P. A Novel plasmid DNA-based foot and mouth disease virus minigenome for intracytoplasmic mRNA production. Viruses 2021, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Jiménez, A.; Peña-Varas, C.; Borrego-Muñoz, P.; Arrue, L.; Alegría-Arcos, M.; Nour-Eldin, H.; Dreyer, I.; Nuñez-Vivanco, G.; Ramírez, D. PSC-db: A structured and searchable 3D-database for plant secondary compounds. Molecules 2021, 26, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daina, A.; Michielin, O.; Zoete, V. SwissADME: A free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2009, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallakyan, S.; Olson, A.J. Small-molecule library screening by docking with PyRx. In Chemical Biology: Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology; Hempel, J.E., Williams, C.H., Hong, C.C., Eds.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1263, pp. 243–250. ISBN 978-1-4939-2268-0. [Google Scholar]
- Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Meeting modern challenges in visualization and analysis. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semkum, P.; Thangthamniyom, N.; Chankeeree, P.; Keawborisuth, C.; Theerawatanasirikul, S.; Lekcharoensuk, P. The application of the gibson assembly method in the production of two pKLS3 vector-derived infectious clones of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Vaccines 2023, 11, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, L.J.; Muench, H. A Simple method of estimating fifty per cent endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1938, 27, 493–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mana, N.; Theerawatanasirikul, S.; Semkum, P.; Lekcharoensuk, P. Naturally derived terpenoids targeting the 3Dpol of foot-and-mouth disease virus: An integrated in silico and in vitro investigation. Viruses 2024, 16, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekcharoensuk, P.; Nanakorn, J.; Wajjwalku, W.; Webby, R.; Chumsing, W. First whole genome characterization of swine influenza virus subtype H3N2 in Thailand. Vet. Microbiol. 2010, 145, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sariya, L.; Thangthumniyom, N.; Wajjwalku, W.; Chumsing, W.; Ramasoota, P.; Lekcharoensuk, P. Expression of foot and mouth disease virus nonstructural polyprotein 3ABC with inactive 3Cpro in Escherichia coli. Protein Expr. Purif. 2011, 80, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theerawatanasirikul, S.; Thangthamniyom, N.; Kuo, C.-J.; Semkum, P.; Phecharat, N.; Chankeeree, P.; Lekcharoensuk, P. Natural Phytochemicals, Luteolin and isoginkgetin, inhibit 3C protease and infection of FMDV, in silico and in vitro. Viruses 2021, 13, 2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theerawatanasirikul, S.; Lueangaramkul, V.; Pantanam, A.; Mana, N.; Semkum, P.; Lekcharoensuk, P. Small molecules targeting 3C protease inhibit FMDV replication and exhibit virucidal effect in cell-based assays. Viruses 2023, 15, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, M.; Kim, H.M.; Lee, J.S.; Choi, J.-H.; Jang, D.S. (−)-Asarinin from the roots of asarum sieboldii induces apoptotic cell death via caspase activation in human ovarian cancer cells. Molecules 2018, 23, 1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, G.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, G. Comparative Biochemical and Pharmacodynamic Analyses of Asarum heterotropoides fr. schmidt var. mandshuricum (maxim) kitag and Asarum sieboldii miq var. seoulense nakai roots. Pharmaceuticals 2024, 17, 1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Ando, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Kajiwara, K.; Honda, Y.; Kobayashi, T. Synergistic effect of ribavirin and vaccine for protection during early infection stage of foot-and-mouth disease. J. Vet. Sci. 2018, 17, 296–301. [Google Scholar]
- Fanhchaksai, K.; Kodchakorn, K.; Pothacharoen, P.; Kongtawelert, P. Effect of sesamin against cytokine production from influenza type A H1N1-induced peripheral blood mononuclear cells: Computational and experimental studies. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol.—Anim. 2016, 52, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanisamy, K.; Maiyelvaganan, K.R.; Kamalakannan, S.; Thilagavathi, R.; Selvam, C.; Prakash, M. In silico screening of potential antiviral inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Mol. Simul. 2023, 49, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed–Belkacem, A.; Ahnou, N.; Barbotte, L.; Wychowski, C.; Pallier, C.; Brillet, R.; Pohl, R.; Pawlotsky, J. Silibinin and related compounds are direct inhibitors of hepatitis C virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byler, K.G.; Ogungbe, I.V.; Setzer, W.N. In-silico screening for anti-Zika virus phytochemicals. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2016, 69, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Famiglini, V.; Silvestri, R. Focus on chirality of HIV-1 Non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors. Molecules 2016, 21, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrer-Orta, C.; Arias, A.; Pérez-Luque, R.; Escarmís, C.; Domingo, E.; Verdaguer, N. Sequential structures provide insights into the fidelity of RNA replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 9463–9468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durk, R.C.; Singh, K.; Cornelison, C.A.; Rai, D.K.; Matzek, K.B.; Leslie, M.D.; Schafer, E.; Marchand, B.; Adedeji, A.; Michailidis, E.; et al. Inhibitors of foot and mouth disease virus targeting a novel pocket of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharbi-Ayachi, A.; Santhanakrishnan, S.; Wong, Y.H.; Chan, K.W.K.; Tan, S.T.; Bates, R.W.; Vasudevan, S.G.; El Sahili, A.; Lescar, J. Non-nucleoside Inhibitors of Zika Virus RNA-Dependent RNA polymerase. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00794-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Gong, M.; Sun, Y.; Shao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, H. Antiviral activity of brequinar against foot-and-mouth disease virus infection in vitro and in vivo. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 116, 108982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, M.; Airaksinen, A.; González-López, C.; Agudo, R.; Arias, A.; Domingo, E. Foot-and-mouth disease virus mutant with decreased sensitivity to ribavirin: Implications for Error Catastrophe. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 2012–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudo, R.; Ferrer-Orta, C.; Arias, A.; de la Higuera, I.; Perales, C.; Pérez-Luque, R.; Verdaguer, N.; Domingo, E. A Multi-step process of viral adaptation to a mutagenic nucleoside analogue by modulation of transition types leads to extinction-escape. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6, e1001072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compounds | Antiviral Activity (EC50 a, µM) | Inhibitory Activity (IC50 b, µM) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FMDV Specific-Positive Cell (IPMA) | Viral Copy Number (RT-qPCR) | Normalized Delta Ct (RT-qPCR) | GFP Signal (FMDV Minigenome) | |
| (-)-Asarinin | 15.11 ± 1.18 (13.72 to 16.49) SI c = 5.99 | 36.70 ± 1.57 (36.06 to 37.34) SI = 2.46 | 31.67 ± 1.50 (30.47 to 32.87) SI = 2.86 | 10.37 ± 1.01 (9.56 to 11.18) SI = 8.72 |
| Sesamin | 52.98 ± 1.72 (51.60 to 54.36) SI = 11.41 | 82.43 ± 1.92 (81.65 to 83.21) SI = 7.33 | 60.94 ± 1.79 (60.21 to 61.67) SI = 9.92 | 74.89 ± 1.87 (73.39 to 76.39) SI = 8.07 |
| Ribavirin (drug control) | 39.62 ± 1.60 (38.34 to 40.90) SI = 12.62 | 32.81 ± 1.52 (31.53 to 34.10) SI = 15.24 | 29.43 ± 1.47 (28.25 to 30.61) SI = 16.99 | 1.49 ± 0.17 (1.35 to 1.63) SI = 335.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Semkum, P.; Mana, N.; Lueangaramkul, V.; Phetcharat, N.; Lekcharoensuk, P.; Theerawatanasirikul, S. Antiviral Efficacy of Lignan Derivatives (-)-Asarinin and Sesamin Against Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus by Targeting RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (3Dpol). Vet. Sci. 2025, 12, 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12100971
Semkum P, Mana N, Lueangaramkul V, Phetcharat N, Lekcharoensuk P, Theerawatanasirikul S. Antiviral Efficacy of Lignan Derivatives (-)-Asarinin and Sesamin Against Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus by Targeting RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (3Dpol). Veterinary Sciences. 2025; 12(10):971. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12100971
Chicago/Turabian StyleSemkum, Ploypailin, Natjira Mana, Varanya Lueangaramkul, Nantawan Phetcharat, Porntippa Lekcharoensuk, and Sirin Theerawatanasirikul. 2025. "Antiviral Efficacy of Lignan Derivatives (-)-Asarinin and Sesamin Against Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus by Targeting RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (3Dpol)" Veterinary Sciences 12, no. 10: 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12100971
APA StyleSemkum, P., Mana, N., Lueangaramkul, V., Phetcharat, N., Lekcharoensuk, P., & Theerawatanasirikul, S. (2025). Antiviral Efficacy of Lignan Derivatives (-)-Asarinin and Sesamin Against Foot-and-Mouth Disease Virus by Targeting RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (3Dpol). Veterinary Sciences, 12(10), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/vetsci12100971






